Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression: Carbohydrate-, Fat- and Amino Acid-Dependent Modulation of Transcriptional Activity
Abstract
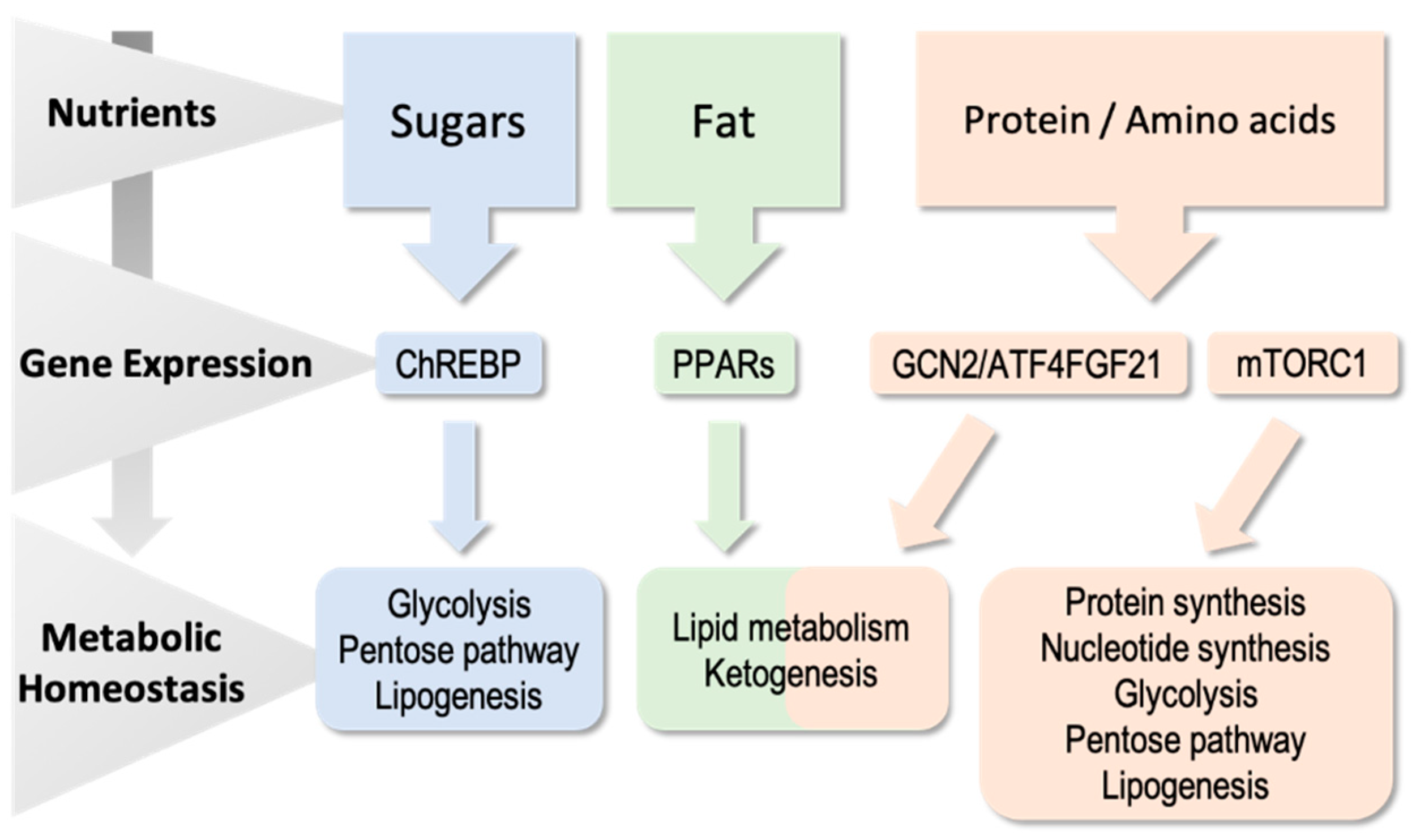
1. Introduction
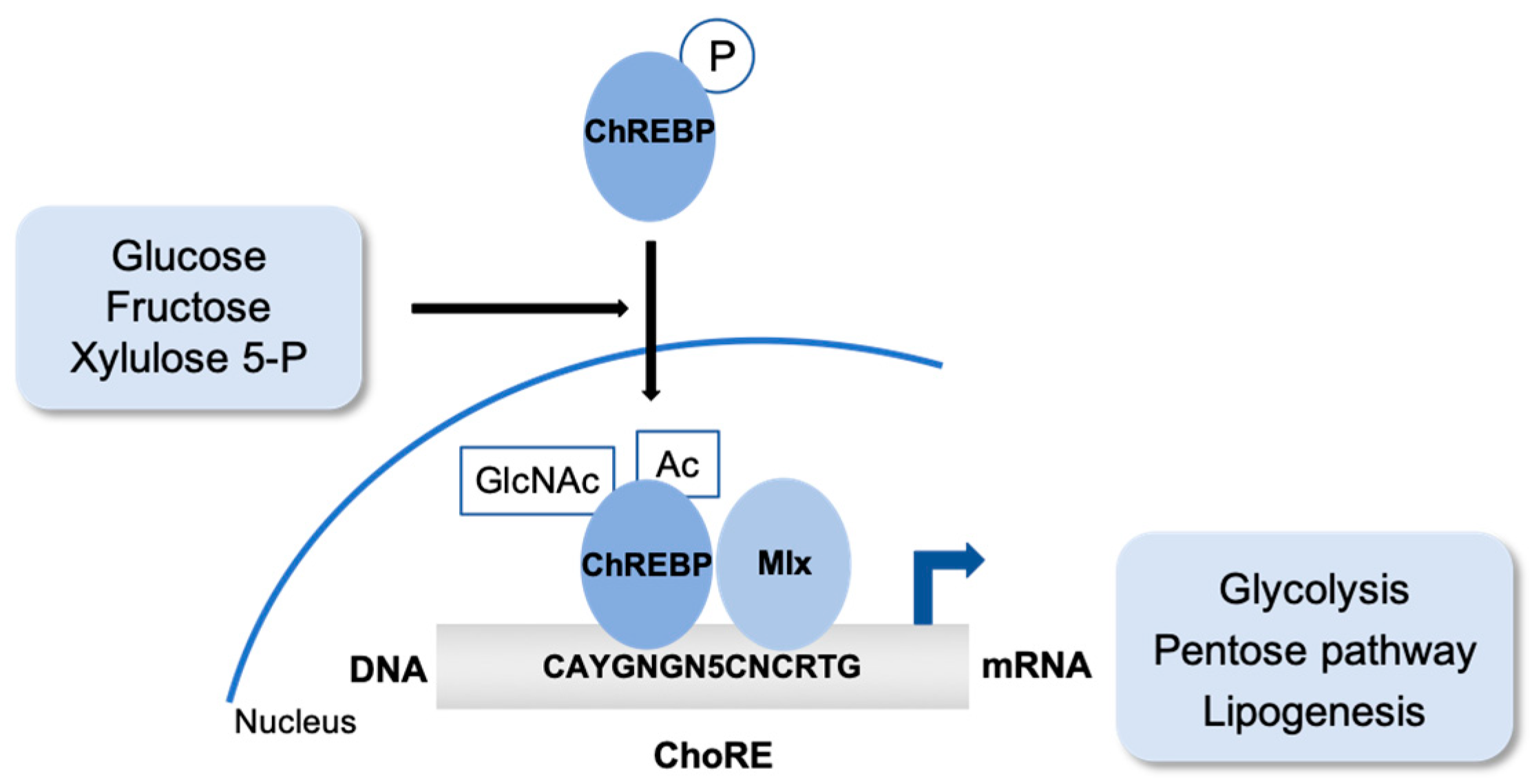
2. Sugar. The Carbohydrate-Responsive Element Binding Protein (ChREBP)
2.1. ChREBP Post-Translational Modifications
2.2. ChREBP Partners to Regulate Gene Expression and Metabolism
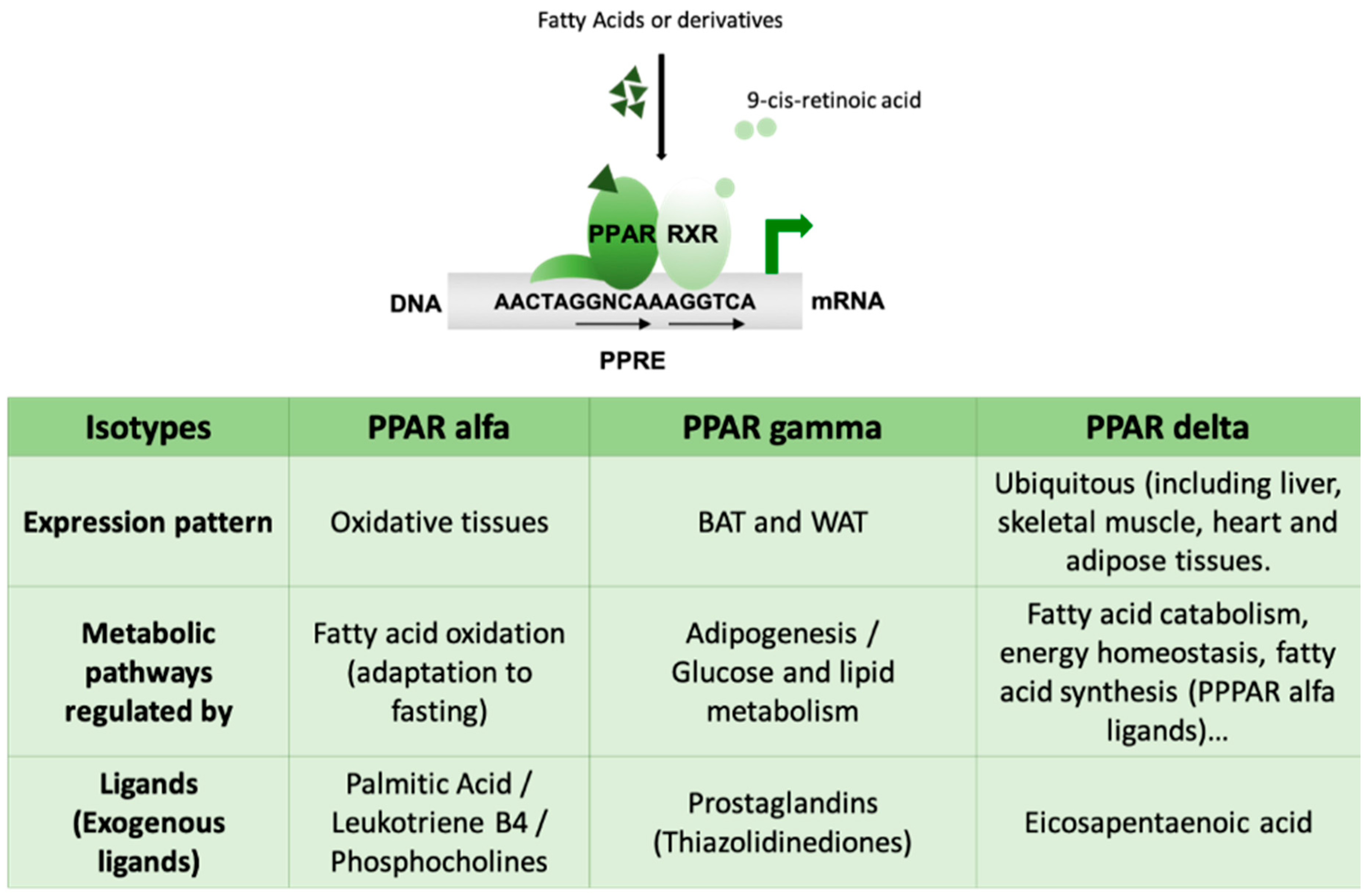
3. Fat. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs)
3.1. PPAR Isotypes and Metabolic Integration
3.2. New Fats are the PPARα Endogenous Ligands
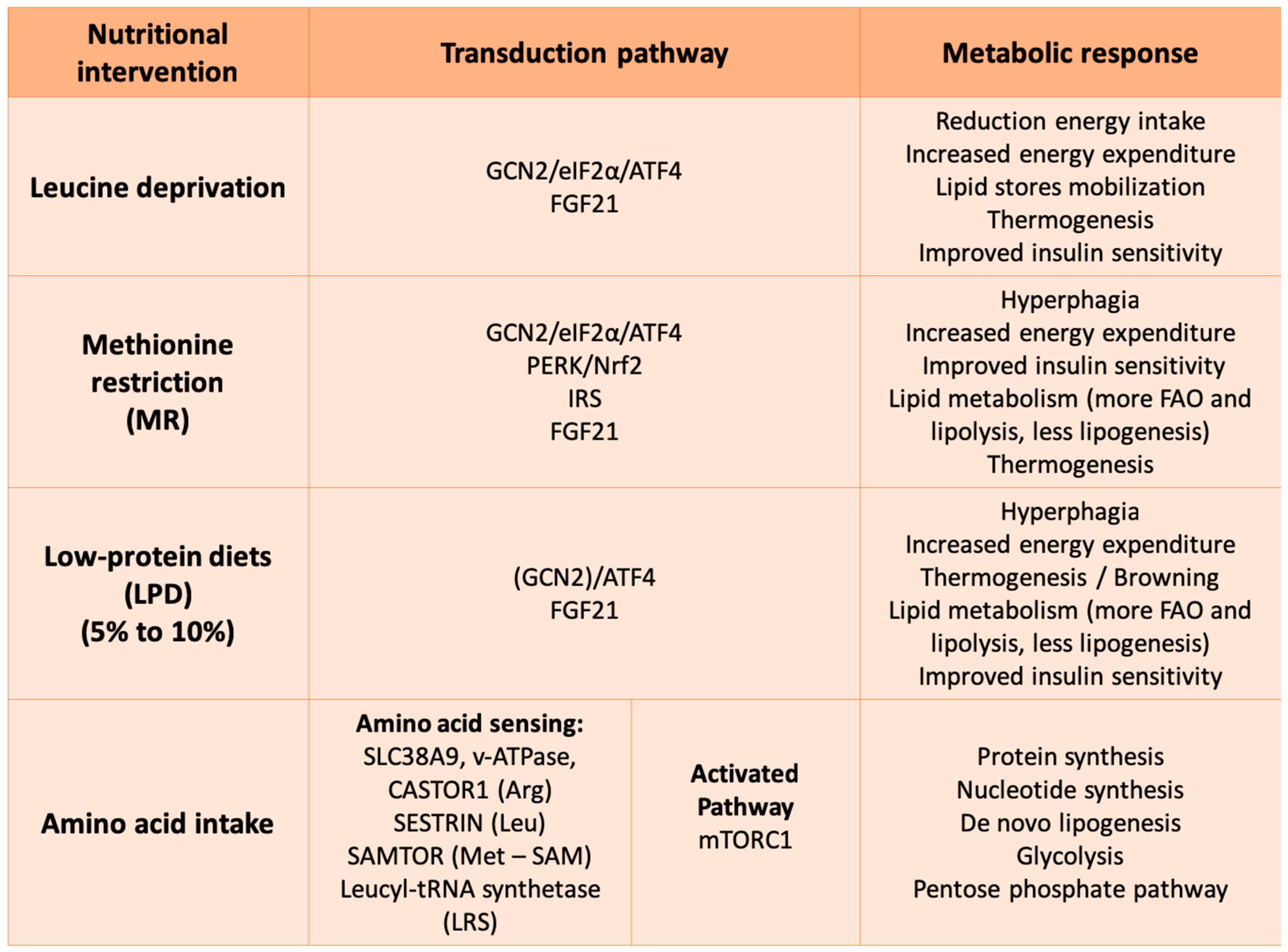
4. Amino Acids as Signaling Molecules from Restriction/Deficiency to Protein
4.1. Amino Acid Response (AAR): The GCN2/ATF4 Pathway to Sense Low Amino Acid Levels
4.2. Metabolic Impact of Amino Acid Restricted/Deprived Diets
4.3. mTOR Signaling Pathway to Sense Amino Acid Availability
4.4. Metabolic Impact of TORC1 Activation: Protein Synthesis, de novo Lipogenesis, Glycolysis and Pentose Phosphate Pathway
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAR | Amino acid response |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| ChoRE | Carbohydrate response element |
| ChREBP | Carbohydrate responsive element binding protein |
| DBD | DNA binding domain |
| Dio2 | Type 2 deiodinase |
| EAA | Essential amino acids |
| EE | Energy expenditure |
| eIF2α | Eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha |
| eIF4B | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4B |
| FAO | Fatty acid oxidation |
| FASN | Fatty acid synthase |
| FGF21 | Fibroblast growth factor 21 |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
| G6P | Glucose 6-phosphate |
| GAP | GTPase activating protein |
| GCN2 | general control nonderepressible 2 |
| GK | Glucokinase |
| HBP | Hexosamine biosynthetic pathway |
| ISR | Integrated stress response |
| LBD | Ligand binding domain |
| LPD | Low protein diet |
| LRS | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase |
| LXR | Liver X Receptor |
| MR | Methionine-restricted |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NR | Nuclear receptors |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor-like 2 |
| NRRE | Nuclear receptors responsive element |
| O-GlcNAc | O-linked N acetylglucosamine |
| PERK | protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor |
| PPRE | PPAR responsive element |
| RHEB | Ras homolog enriched in the brain |
| S6K1 | S6 kinase 1 |
| SAM | S-adenosylmethionine |
| SCD1 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase |
| SREBP | Sterol regulatory element binding protein |
| TZD | Thiazolidinediones |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
| X5P | Xylulose 5-phosphate |
References
- Jacob, F.; Monod, J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1961, 3, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, L. Hormonal and Metabolite Regulation of Hepatic Glucokinase. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 389–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaulont, S.; Munnich, A.; Decaux, J.F.; Kahn, A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 7621–7625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eckert, D.T.; Zhang, P.; Collier, J.J.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Scott, D.K. Detailed molecular analysis of the induction of the L-PK gene by glucose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Park, S.W.; Kim, Y.S. Regulation of ATP-citrate lyase at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels in rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 189, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsurada, A.; Iritani, N.; Fukuda, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Nishimoto, N.; Noguchi, T.; Tanaka, T. Effects of nutrients and hormones on transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 190, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, H.S.; Wang, D. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of enzymes in fat synthesis: Studies of fatty acid synthase and mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gene transcription. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1998, 18, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvoisin, D.; Mounier, C. Hormonal and nutritional regulation of SCD1 gene expression. Biochimie 2011, 93, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salati, L.M.; Amir-Ahmady, B. Dietary regulation of expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Takenoshita, M.; Sakurai, M.; Bruick, R.K.; Henzel, W.J.; Shillinglaw, W.; Arnot, D.; Uyeda, K. A glucose-responsive transcription factor that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9116–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havula, E.; Hietakangas, V. Sugar sensing by ChREBP/Mondo-Mlx-new insight into downstream regulatory networks and integration of nutrient-derived signals. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 51, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Cha, J.Y. Recent insights into the role of ChREBP in intestinal fructose absorption and metabolism. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Samuel, V.T. The Sweet Path to Metabolic Demise: Fructose and Lipid Synthesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Kim, M.; Doridot, L.; Cunniff, J.C.; Parker, T.S.; Levine, D.M.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Hudgins, L.C.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Herman, M.A. A critical role for ChREBP-mediated FGF21 secretion in hepatic fructose metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, K. The Role of Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein in Intestinal and Hepatic Fructose Metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Peroni, O.D.; Villoria, J.; Schön, M.R.; Abumrad, N.A.; Blüher, M.; Klein, S.; Kahn, B.B. A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism. Nature 2012, 484, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, G.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Shalev, A. Islet ChREBP-β is increased in diabetes and controls ChREBP-α and glucose-induced gene expression via a negative feedback loop. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filhoulaud, G.; Guilmeau, S.; Dentin, R.; Girard, J.; Postic, C. Novel insights into ChREBP regulation and function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraille, F.; Planchais, J.; Dentin, R.; Guilmeau, S.; Postic, C. Integration of ChREBP-Mediated Glucose Sensing into Whole Body Metabolism. Physiology 2015, 30, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsos, N.G.; Davies, M.N.; O’Callaghan, B.L.; Towle, H.C. Identification and function of phosphorylation in the glucose-regulated transcription factor ChREBP. Biochem. J. 2008, 411, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Takenoshita, M.; Kabashima, T.; Uyeda, K. Glucose and cAMP regulate the L-type pyruvate kinase gene by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13710–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Osatomi, K.; Yamashita, H.; Kabashima, T.; Uyeda, K. Mechanism for fatty acid “sparing” effect on glucose-induced transcription: Regulation of carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein by AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3829–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merla, G.; Howald, C.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Reymond, A. The subcellular localization of the ChoRE-binding protein, encoded by the Williams-Beuren syndrome critical region gene 14, is regulated by 14-3-3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakiyama, H.; Wynn, R.M.; Lee, W.R.; Fukasawa, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Gardner, K.H.; Repa, J.J.; Uyeda, K. Regulation of nuclear import/export of carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP): Interaction of an alpha-helix of ChREBP with the 14-3-3 proteins and regulation by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24899–24908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashima, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Wadzinski, B.E.; Uyeda, K. Xylulose 5-phosphate mediates glucose-induced lipogenesis by xylulose 5-phosphate-activated protein phosphatase in rat liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5107–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentin, R.; Tomas-Cobos, L.; Foufelle, F.; Leopold, J.; Girard, J.; Postic, C.; Ferré, P. Glucose 6-phosphate, rather than xylulose 5-phosphate, is required for the activation of ChREBP in response to glucose in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, C.; Tudhope, S.J.; Petrie, J.L.; Al-Oanzi, Z.H.; Cullen, K.S.; Lange, A.J.; Towle, H.C.; Agius, L. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is essential for glucose-regulated gene transcription of glucose-6-phosphatase and other ChREBP target genes in hepatocytes. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinez, C.; Filhoulaud, G.; Rayah-Benhamed, F.; Marmier, S.; Dubuquoy, C.; Dentin, R.; Moldes, M.; Burnol, A.F.; Yang, X.; Lefebvre, T.; et al. O-GlcNAcylation increases ChREBP protein content and transcriptional activity in the liver. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricambert, J.; Miranda, J.; Benhamed, F.; Girard, J.; Postic, C.; Dentin, R. Salt-inducible kinase 2 links transcriptional coactivator p300 phosphorylation to the prevention of ChREBP-dependent hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4316–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.Q.; Li, D.; Chi, L.; Ye, X.S. Validation, Identification, and Biological Consequences of the Site-specific. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.R.; Hanover, J.A. O-GlcNAc cycling: A link between metabolism and chronic disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2013, 33, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Feng, M.; Dong, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Identification of HNF-4α as a key transcription factor to promote ChREBP expression in response to glucose. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poupeau, A.; Postic, C. Cross-regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism via ChREBP and nuclear receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, S.; Huaman Samanez, C.; Dehondt, H.; Ploton, M.; Briand, O.; Lien, F.; Dorchies, E.; Dumont, J.; Postic, C.; Cariou, B.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor inhibits the transcriptional activity of carbohydrate response element binding protein in human hepatocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamed, F.; Filhoulaud, G.; Caron, S.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B.; Postic, C. O-GlcNAcylation Links ChREBP and FXR to Glucose-Sensing. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Nørgaard, R.C.; Bindesbøll, C.; Lucas, C.; Dalen, K.T.; Babaie, E.; Itkonen, H.M.; Matthews, J.; Nebb, H.I.; Grønning-Wang, L.M. LXRα Regulates Hepatic ChREBPα Activity and Lipogenesis upon Glucose, but Not Fructose Feeding in Mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroz, A.; Montagner, A.; Benhamed, F.; Levavasseur, F.; Polizzi, A.; Anthony, E.; Régnier, M.; Fouché, E.; Lukowicz, C.; Cauzac, M.; et al. A Specific ChREBP and PPARα Cross-Talk Is Required for the Glucose-Mediated FGF21 Response. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tong, X.; VanDommelen, K.; Gupta, N.; Stamper, K.; Brady, G.F.; Meng, Z.; Lin, J.; Rui, L.; Omary, M.B.; et al. Lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP mediates fructose-induced metabolic adaptations to prevent hepatotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Astapova, I.I.; Flier, S.N.; Hannou, S.A.; Doridot, L.; Sargsyan, A.; Kou, H.H.; Fowler, A.J.; Liang, G.; Herman, M.A. Intestinal, but not hepatic, ChREBP is required for fructose tolerance. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.G.; Li, S.; Choi, H.Y.; Fang, F.; Fukasawa, M.; Uyeda, K.; Hammer, R.E.; Horton, J.D.; Engelking, L.J.; Liang, G. Interplay between ChREBP and SREBP-1c coordinates postprandial glycolysis and lipogenesis in livers of mice. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Aryal, P.; Wen, J.; Syed, I.; Vazirani, R.P.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Camporez, J.P.; Gallop, M.R.; Perry, R.J.; Peroni, O.D.; et al. Absence of Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein in Adipocytes Causes Systemic Insulin Resistance and Impairs Glucose Transport. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jois, T.; Chen, W.; Howard, V.; Harvey, R.; Youngs, K.; Thalmann, C.; Saha, P.; Chan, L.; Cowley, M.A.; Sleeman, M.W. Deletion of hepatic carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP) impairs glucose homeostasis and hepatic insulin sensitivity in mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Tang, Y.; Jespersen, N.Z.; Wallace, M.; Martinez Calejman, C.; Gujja, S.; Li, H.; Edwards, Y.J.K.; Wolfrum, C.; Metallo, C.M.; et al. Brown Fat AKT2 Is a Cold-Induced Kinase that Stimulates ChREBP-Mediated De Novo Lipogenesis to Optimize Fuel Storage and Thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 195–209.e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.N.; Gelman, L.; Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. From molecular action to physiological outputs: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 120–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, R.; Glass, C.K. Signaling by nuclear receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalve, F.A.; Pyarasani, R.D.; Delgado-Lopez, F.; Moore-Carrasco, R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 549627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvergne, B.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W. Transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 465–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napal, L.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D. An intronic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding sequence mediates fatty acid induction of the human carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 354, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.C.; Gil-Gómez, G.; Hegardt, F.G.; Haro, D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor mediates induction of the mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase gene by fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18767–18772. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.M.; Barish, G.D.; Wang, Y.X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Seydoux, J.; Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha mediates the adaptive response to fasting. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, M.A. Becoming fat. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.S.; Maeda, N. PPARgamma: A critical determinant of body fat distribution in humans and mice. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 15, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Rosen, E.D.; Brun, R.; Hauser, S.; Adelmant, G.; Troy, A.E.; McKeon, C.; Darlington, G.J.; Spiegelman, B.M. Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Song, J.; Park, K.W. The multifaceted factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in metabolism, immunity, and cancer. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Barrick, C.; Kim, K.A.; Lindner, J.; Blondeau, B.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shiota, M.; Kesterson, R.A.; Kahn, B.B.; Magnuson, M.A. Deletion of PPARgamma in adipose tissues of mice protects against high fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdtke, A.; Buettner, J.; Schmidt, H.H.; Worman, H.J. New PPARG mutation leads to lipodystrophy and loss of protein function that is partially restored by a synthetic ligand. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 44, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barish, G.D.; Narkar, V.A.; Evans, R.M. PPAR delta: A dagger in the heart of the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, C.L.; Yu, R.T.; Cho, H.K.; Nelson, M.C.; Bayuga-Ocampo, C.R.; Ham, J.; Kang, H.; Evans, R.M. Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARdelta. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hatano, B.; Zhao, M.; Yen, C.C.; Kang, K.; Reilly, S.M.; Gangl, M.R.; Gorgun, C.; Balschi, J.A.; Ntambi, J.M.; et al. Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor {delta}/{beta} in hepatic metabolic regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Olson, P.; Hevener, A.; Mehl, I.; Chong, L.W.; Olefsky, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, H.; Peters, J.M.; et al. PPARdelta regulates glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Brown, J.D.; Stanya, K.J.; Homan, E.; Leidl, M.; Inouye, K.; Bhargava, P.; Gangl, M.R.; Dai, L.; Hatano, B.; et al. A diurnal serum lipid integrates hepatic lipogenesis and peripheral fatty acid use. Nature 2013, 502, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarthy, M.V.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tordjman, K.; Schneider, J.G.; Coleman, T.; Turk, J.; Semenkovich, C.F. “New” hepatic fat activates PPARalpha to maintain glucose, lipid, and cholesterol homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, M.V.; Lodhi, I.J.; Yin, L.; Malapaka, R.R.; Xu, H.E.; Turk, J.; Semenkovich, C.F. Identification of a physiologically relevant endogenous ligand for PPARalpha in liver. Cell 2009, 138, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.J.; Affolter, M.; Kussmann, M. A nutrigenomics view of protein intake: Macronutrient, bioactive peptides, and protein turnover. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2012, 108, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Dong, J.; Hu, C.; Francklyn, C.S.; Hinnebusch, A.G. The tRNA-binding moiety in GCN2 contains a dimerization domain that interacts with the kinase domain and is required for tRNA binding and kinase activation. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, T.G.; McDaniel, B.J.; Byerley, R.L.; McGrath, B.C.; Cavener, D.R.; McNurlan, M.A.; Wek, R.C. Preservation of liver protein synthesis during dietary leucine deprivation occurs at the expense of skeletal muscle mass in mice deleted for eIF2 kinase GCN2. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36553–36561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Sharp, J.W.; Ross-Inta, C.M.; McDaniel, B.J.; Anthony, T.G.; Wek, R.C.; Cavener, D.R.; McGrath, B.C.; Rudell, J.B.; Koehnle, T.J.; et al. Uncharged tRNA and sensing of amino acid deficiency in mammalian piriform cortex. Science 2005, 307, 1776–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, H.P.; Novoa, I.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wek, R.; Schapira, M.; Ron, D. Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Qureshi, S.S.; Jennings, M.D.; Pavitt, G.D. Clues to the mechanism of action of eIF2B, the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor for translation initiation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilberg, M.S.; Shan, J.; Su, N. ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid limitation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2009, 20, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattem, K.M.; Wek, R.C. Reinitiation involving upstream ORFs regulates ATF4 mRNA translation in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11269–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Ord, D.; Ord, T.; Kilberg, M.S. Elevated ATF4 expression, in the absence of other signals, is sufficient for transcriptional induction via CCAAT enhancer-binding protein-activating transcription factor response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21241–21248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deval, C.; Chaveroux, C.; Maurin, A.C.; Cherasse, Y.; Parry, L.; Carraro, V.; Milenkovic, D.; Ferrara, M.; Bruhat, A.; Jousse, C.; et al. Amino acid limitation regulates the expression of genes involved in several specific biological processes through GCN2-dependent and GCN2-independent pathways. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanders, D.; Stone, K.P.; Forney, L.A.; Cortez, C.C.; Dille, K.N.; Simon, J.; Xu, M.; Hotard, E.C.; Nikonorova, I.A.; Pettit, A.P.; et al. Role of GCN2-Independent Signaling Through a Noncanonical PERK/NRF2 Pathway in the Physiological Responses to Dietary Methionine Restriction. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeger, T.; Albarado, D.C.; Burke, S.J.; Trosclair, L.; Hedgepeth, J.W.; Berthoud, H.R.; Gettys, T.W.; Collier, J.J.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Metabolic Responses to Dietary Protein Restriction Require an Increase in FGF21 that Is Delayed by the Absence of GCN2. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, A.P.; Jonsson, W.O.; Bargoud, A.R.; Mirek, E.T.; Peelor, F.F.; Wang, Y.; Gettys, T.W.; Kimball, S.R.; Miller, B.F.; Hamilton, K.L.; et al. Dietary Methionine Restriction Regulates Liver Protein Synthesis and Gene Expression Independently of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 Phosphorylation in Mice. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, T.G.; Morrison, C.D.; Gettys, T.W. Remodeling of lipid metabolism by dietary restriction of essential amino acids. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Borg, H.M.; Buffenstein, R. Cutting back on the essentials: Can manipulating intake of specific amino acids modulate health and lifespan? Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Cavener, D.R. The GCN2 eIF2alpha kinase regulates fatty-acid homeostasis in the liver during deprivation of an essential amino acid. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Xia, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Xiao, F.; Du, Y.; et al. Leucine Deprivation Stimulates Fat Loss via Increasing CRH Expression in The Hypothalamus and Activating The Sympathetic Nervous System. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S.; Xiao, F.; Guo, F. Leucine deprivation decreases fat mass by stimulation of lipolysis in white adipose tissue and upregulation of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in brown adipose tissue. Diabetes 2010, 59, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, J.R.; Berthiaume, L.G.; Thomas, P.D.; Kantor, P.F.; Barr, A.J.; Barr, R.; Singh, D.; Hopkins, T.A.; Voilley, N.; Prentki, M.; et al. Characterization of rat liver malonyl-CoA decarboxylase and the study of its role in regulating fatty acid metabolism. Biochem. J. 2000, 350 Pt 2, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Meng, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; et al. Leucine deprivation increases hepatic insulin sensitivity via GCN2/mTOR/S6K1 and AMPK pathways. Diabetes 2011, 60, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malloy, V.L.; Krajcik, R.A.; Bailey, S.J.; Hristopoulos, G.; Plummer, J.D.; Orentreich, N. Methionine restriction decreases visceral fat mass and preserves insulin action in aging male Fischer 344 rats independent of energy restriction. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, V.L.; Perrone, C.E.; Mattocks, D.A.; Ables, G.P.; Caliendo, N.S.; Orentreich, D.S.; Orentreich, N. Methionine restriction prevents the progression of hepatic steatosis in leptin-deficient obese mice. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasek, B.E.; Boudreau, A.; Shin, J.; Feng, D.; Hulver, M.; Van, N.T.; Laque, A.; Stewart, L.K.; Stone, K.P.; Wanders, D.; et al. Remodeling the integration of lipid metabolism between liver and adipose tissue by dietary methionine restriction in rats. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3362–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Buehner, G.; Chang, Y.; Harper, J.M.; Sigler, R.; Smith-Wheelock, M. Methionine-deficient diet extends mouse lifespan, slows immune and lens aging, alters glucose, T4, IGF-I and insulin levels, and increases hepatocyte MIF levels and stress resistance. Aging Cell 2005, 4, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, K.P.; Wanders, D.; Orgeron, M.; Cortez, C.C.; Gettys, T.W. Mechanisms of increased in vivo insulin sensitivity by dietary methionine restriction in mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasek, B.E.; Stewart, L.K.; Henagan, T.M.; Boudreau, A.; Lenard, N.R.; Black, C.; Shin, J.; Huypens, P.; Malloy, V.L.; Plaisance, E.P.; et al. Dietary methionine restriction enhances metabolic flexibility and increases uncoupled respiration in both fed and fasted states. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R728–R739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaisance, E.P.; Henagan, T.M.; Echlin, H.; Boudreau, A.; Hill, K.L.; Lenard, N.R.; Hasek, B.E.; Orentreich, N.; Gettys, T.W. Role of beta-adrenergic receptors in the hyperphagic and hypermetabolic responses to dietary methionine restriction. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R740–R750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jové, M.; Ayala, V.; Ramírez-Núñez, O.; Naudí, A.; Cabré, R.; Spickett, C.M.; Portero-Otín, M.; Pamplona, R. Specific lipidome signatures in central nervous system from methionine-restricted mice. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaisance, E.P.; Greenway, F.L.; Boudreau, A.; Hill, K.L.; Johnson, W.D.; Krajcik, R.A.; Perrone, C.E.; Orentreich, N.; Cefalu, W.T.; Gettys, T.W. Dietary methionine restriction increases fat oxidation in obese adults with metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E836–E840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, J.E.; Teh, P.S.; Wang, C.X.; Gietzen, D.W. Effects of amino acid deficiency on monoamines in the lateral hypothalamus (LH) in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Nagao, K.; Bannai, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakahara, K.; Kangawa, K.; Murakami, N. Anorexia in rats caused by a valine-deficient diet is not ameliorated by systemic ghrelin treatment. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, K.; Takata, S.; Ishii, A.; Nagao, K.; Bannai, M.; Takahashi, M.; Murakami, N. Somatostatin is involved in anorexia in mice fed a valine-deficient diet. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, T.; Huang, J.F.; Wang, S.B.; Zhou, L.L.; Yang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.D. The link between fibroblast growth factor 21 and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c during lipogenesis in hepatocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa-Coelho, A.L.; Relat, J.; Hondares, E.; Pérez-Martí, A.; Ribas, F.; Villarroya, F.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D. FGF21 mediates the lipid metabolism response to amino acid starvation. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Mart, A.; Garcia-Guasch, M.; Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Carrilho-Do-Rosario, A.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Angel Martinez-Gonzalez, M.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D.; et al. A low-protein diet induces body weight loss and browning of subcutaneous white adipose tissue through enhanced expression of hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domouzoglou, E.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is a metabolic regulator that plays a role in the adaptation to ketosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 901S–905S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.L.; Weston, J.Y.; Chadi, S.A.; Fazio, E.N.; Huff, M.W.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Köester, A.; Pin, C.L. Fibroblast growth factor 21 reduces the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa-Coelho, A.L.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D. Activating transcription factor 4-dependent induction of FGF21 during amino acid deprivation. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ables, G.P.; Perrone, C.E.; Orentreich, D.; Orentreich, N. Methionine-restricted C57BL/6J mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance but have low bone density. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, E.K.; Król, E.; Grant, L.; Shearer, K.; Wyse, C.; Moncur, E.; Bykowska, A.S.; Mody, N.; Gettys, T.W.; Delibegovic, M. Methionine restriction restores a younger metabolic phenotype in adult mice with alterations in fibroblast growth factor 21. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanders, D.; Forney, L.A.; Stone, K.P.; Burk, D.H.; Pierse, A.; Gettys, T.W. FGF21 Mediates the Thermogenic and Insulin-Sensitizing Effects of Dietary Methionine Restriction but not its Effects on Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Diabetes 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, A.K.; Valdivia-Garcia, M.; Mattocks, D.A.; Plummer, J.D.; Smith, A.D.; Drevon, C.A.; Refsum, H.; Perrone, C.E. Cysteine supplementation reverses methionine restriction effects on rat adiposity: Significance of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Gomez, J.; Lopez Torres, M.; Naudi, A.; Mota-Martorell, N.; Pamplona, R.; Barja, G. Cysteine dietary supplementation reverses the decrease in mitochondrial ROS production at complex I induced by methionine restriction. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, A.; Zapata, R.C.; Singh, A.; Yee, N.J.; Chelikani, P.K. Low protein diets produce divergent effects on energy balance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laeger, T.; Henagan, T.M.; Albarado, D.C.; Redman, L.M.; Bray, G.A.; Noland, R.C.; Münzberg, H.; Hutson, S.M.; Gettys, T.W.; Schwartz, M.W.; et al. FGF21 is an endocrine signal of protein restriction. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3913–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Saito, K.; Nakazawa, K.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N.; Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.; Kato, H.; Takenaka, A. Rapid increase in fibroblast growth factor 21 in protein malnutrition and its impact on growth and lipid metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Laeger, T. Protein-dependent regulation of feeding and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, P.; Bunpo, P.; Cundiff, J.K.; Wek, R.C.; Harris, R.A.; Anthony, T.G. General control nonderepressible 2 (GCN2) kinase protects oligodendrocytes and white matter during branched-chain amino acid deficiency in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31250–31260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Guan, K.L. mTOR as a central hub of nutrient signalling and cell growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutouja, F.; Stiehm, C.M.; Platta, H.W. mTOR: A Cellular Regulator Interface in Health and Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; Li, L.; Neufeld, T.P.; Guan, K.L. Regulation of TORC1 by Rag GTPases in nutrient response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Peterson, T.R.; Shaul, Y.D.; Lindquist, R.A.; Thoreen, C.C.; Bar-Peled, L.; Sabatini, D.M. The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science 2008, 320, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Peled, L.; Schweitzer, L.D.; Zoncu, R.; Sabatini, D.M. Ragulator is a GEF for the rag GTPases that signal amino acid levels to mTORC1. Cell 2012, 150, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Bar-Peled, L.; Zoncu, R.; Markhard, A.L.; Nada, S.; Sabatini, D.M. Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 2010, 141, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Guan, K.L. Rheb GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR signaling. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Lin, Y.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K.; Avruch, J. Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyant, G.A.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Wolfson, R.L.; Chen, W.W.; Freinkman, E.; Danai, L.V.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 Activator SLC38A9 Is Required to Efflux Essential Amino Acids from Lysosomes and Use Protein as a Nutrient. Cell 2017, 171, 642–654.e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Genau, H.M.; Behrends, C. Amino Acid-Dependent mTORC1 Regulation by the Lysosomal Membrane Protein SLC38A9. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 2479–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tsun, Z.Y.; Wolfson, R.L.; Shen, K.; Wyant, G.A.; Plovanich, M.E.; Yuan, E.D.; Jones, T.D.; Chantranupong, L.; Comb, W.; et al. Metabolism. Lysosomal amino acid transporter SLC38A9 signals arginine sufficiency to mTORC1. Science 2015, 347, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebsamen, M.; Pochini, L.; Stasyk, T.; de Araújo, M.E.; Galluccio, M.; Kandasamy, R.K.; Snijder, B.; Fauster, A.; Rudashevskaya, E.L.; Bruckner, M.; et al. SLC38A9 is a component of the lysosomal amino acid sensing machinery that controls mTORC1. Nature 2015, 519, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoncu, R.; Bar-Peled, L.; Efeyan, A.; Wang, S.; Sancak, Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 senses lysosomal amino acids through an inside-out mechanism that requires the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Science 2011, 334, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Peled, L.; Chantranupong, L.; Cherniack, A.D.; Chen, W.W.; Ottina, K.A.; Grabiner, B.C.; Spear, E.D.; Carter, S.L.; Meyerson, M.; Sabatini, D.M. A Tumor suppressor complex with GAP activity for the Rag GTPases that signal amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1. Science 2013, 340, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Yin, N.; Li, M.O. SZT2 dictates GATOR control of mTORC1 signalling. Nature 2017, 543, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, R.L.; Chantranupong, L.; Wyant, G.A.; Gu, X.; Orozco, J.M.; Shen, K.; Condon, K.J.; Petri, S.; Kedir, J.; Scaria, S.M.; et al. KICSTOR recruits GATOR1 to the lysosome and is necessary for nutrients to regulate mTORC1. Nature 2017, 543, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantranupong, L.; Scaria, S.M.; Saxton, R.A.; Gygi, M.P.; Shen, K.; Wyant, G.A.; Wang, T.; Harper, J.W.; Gygi, S.P.; Sabatini, D.M. The CASTOR Proteins Are Arginine Sensors for the mTORC1 Pathway. Cell 2016, 165, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Chantranupong, L.; Knockenhauer, K.E.; Schwartz, T.U.; Sabatini, D.M. Mechanism of arginine sensing by CASTOR1 upstream of mTORC1. Nature 2016, 536, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantranupong, L.; Wolfson, R.L.; Orozco, J.M.; Saxton, R.A.; Scaria, S.M.; Bar-Peled, L.; Spooner, E.; Isasa, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Sabatini, D.M. The Sestrins interact with GATOR2 to negatively regulate the amino-acid-sensing pathway upstream of mTORC1. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmigiani, A.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Ding, B.; Wang, W.; Kim, Y.C.; Akopiants, K.; Guan, K.L.; Karin, M.; Budanov, A.V. Sestrins inhibit mTORC1 kinase activation through the GATOR complex. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, R.L.; Chantranupong, L.; Saxton, R.A.; Shen, K.; Scaria, S.M.; Cantor, J.R.; Sabatini, D.M. Sestrin2 is a leucine sensor for the mTORC1 pathway. Science 2016, 351, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Orozco, J.M.; Saxton, R.A.; Condon, K.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Krawczyk, P.A.; Scaria, S.M.; Harper, J.W.; Gygi, S.P.; Sabatini, D.M. SAMTOR is an. Science 2017, 358, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J.L.; Kim, Y.C.; Russell, R.C.; Yu, F.X.; Park, H.W.; Plouffe, S.W.; Tagliabracci, V.S.; Guan, K.L. Metabolism. Differential regulation of mTORC1 by leucine and glutamine. Science 2015, 347, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsun, Z.Y.; Bar-Peled, L.; Chantranupong, L.; Zoncu, R.; Wang, T.; Kim, C.; Spooner, E.; Sabatini, D.M. The folliculin tumor suppressor is a GAP for the RagC/D GTPases that signal amino acid levels to mTORC1. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.S.; Roczniak-Ferguson, A.; Ferguson, S.M. Recruitment of folliculin to lysosomes supports the amino acid-dependent activation of Rag GTPases. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Jeong, S.J.; Park, M.C.; Kim, G.; Kwon, N.H.; Kim, H.K.; Ha, S.H.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, S. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is an intracellular leucine sensor for the mTORC1-signaling pathway. Cell 2012, 149, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.D.; Gong, W.; Zhang, J.N.; Nie, J.; Yao, C.F.; Guo, F.S.; Lin, Y.; Wu, X.H.; Li, F.; Li, J.; et al. Sensing and Transmitting Intracellular Amino Acid Signals through Reversible Lysine Aminoacylations. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 151–166.e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, M.K.; Ballif, B.A.; Gygi, S.P.; Blenis, J. mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 2005, 123, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrello, N.V.; Peschiaroli, A.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Colburn, N.H.; Sherman, N.E.; Pagano, M. S6K1—And betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 2006, 314, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, G.J.; Hudson, C.C.; Sekulić, A.; Williams, J.M.; Hosoi, H.; Houghton, P.J.; Lawrence, J.C.; Abraham, R.T. Phosphorylation of the translational repressor PHAS-I by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Science 1997, 277, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingras, A.C.; Gygi, S.P.; Raught, B.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Abraham, R.T.; Hoekstra, M.F.; Aebersold, R.; Sonenberg, N. Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: A novel two-step mechanism. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Düvel, K.; Yecies, J.L.; Menon, S.; Raman, P.; Lipovsky, A.I.; Souza, A.L.; Triantafellow, E.; Ma, Q.; Gorski, R.; Cleaver, S.; et al. Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1 required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of gluconeogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3441–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.T.; Li, J.N.; Ren, G.P.; Liu, M.Y.; Sun, G.P.; Wang, W.F.; Li, D.S. Cloning, expression and glucose regulation activity of human FGF-21. Yi Chuan Hered. 2010, 32, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.R.; Sengupta, S.S.; Harris, T.E.; Carmack, A.E.; Kang, S.A.; Balderas, E.; Guertin, D.A.; Madden, K.L.; Carpenter, A.E.; Finck, B.N.; et al. mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1 localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell 2011, 146, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haro, D.; Marrero, P.F.; Relat, J. Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression: Carbohydrate-, Fat- and Amino Acid-Dependent Modulation of Transcriptional Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061386
Haro D, Marrero PF, Relat J. Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression: Carbohydrate-, Fat- and Amino Acid-Dependent Modulation of Transcriptional Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061386
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaro, Diego, Pedro F. Marrero, and Joana Relat. 2019. "Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression: Carbohydrate-, Fat- and Amino Acid-Dependent Modulation of Transcriptional Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061386
APA StyleHaro, D., Marrero, P. F., & Relat, J. (2019). Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression: Carbohydrate-, Fat- and Amino Acid-Dependent Modulation of Transcriptional Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061386






