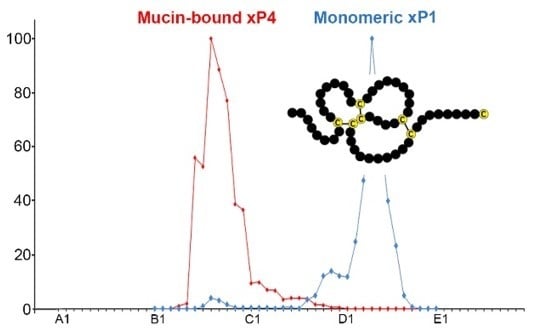
The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
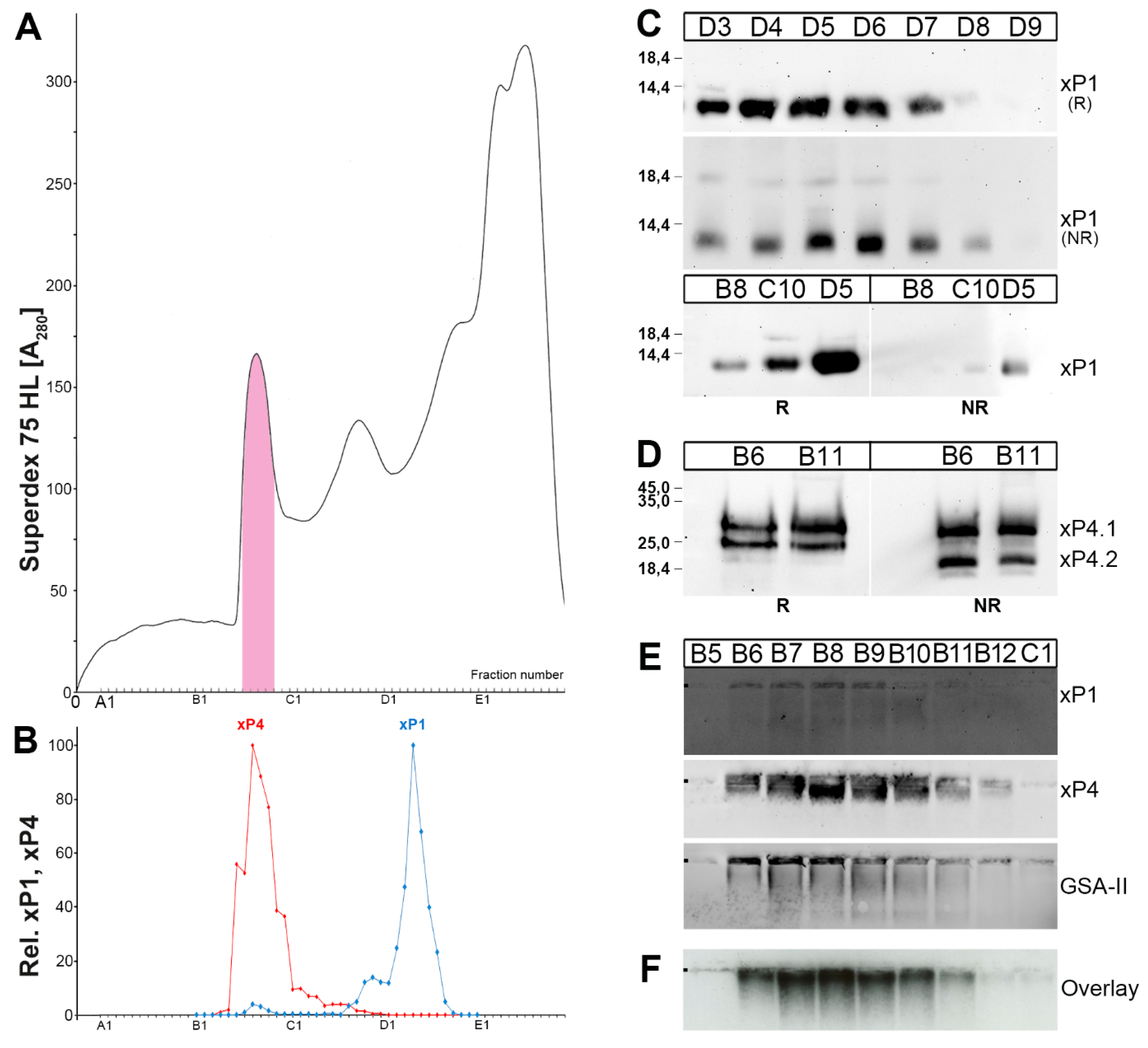
2.1. Characterzation of xP1 and xP4 in X. Laevis Gastric Extracts by SEC and Western Blot Analysis
2.2. Binding of 125I-Labeled Porcine TFF2 to X. Laevis Gastric Mucin In Vitro (Overlay Assay)
3. Discussion
3.1. xP1 Mainly Occurs in An Unusual Monomeric Form: Possible Functional Implications
3.2. xP4 is Mucin-Associated: Interaction with the Ortholog of MUC6
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction of Proteins and Purification by SEC
4.2. SDS-PAGE, Agarose Gel Electrophoresis, and Western Blot Analysis
4.3. TFF2 Binding Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgGE | Agarose gel electrophoresis |
| PAS | Periodic acid-Schiff |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| TFF | Trefoil factor family |
References
- Hauser, F.; Hoffmann, W. xP1 and xP4. P-domain peptides expressed in Xenopus laevis stomach mucosa. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21306–21309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W. Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: Colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 147–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides: Regulators of mucosal regeneration and repair, and more. Peptides 2004, 25, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W.; Hauser, F. The P-domain or trefoil motif: A role in renewal and pathology of mucous epithelia? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, W.; Wiede, A.; Kolle, S.; Hoffmann, W. Differential expression of the TFF-peptides xP1 and xP4 in the gastrointestinal tract of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res. 1998, 291, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Session, A.M.; Uno, Y.; Kwon, T.; Chapman, J.A.; Toyoda, A.; Takahashi, S.; Fukui, A.; Hikosaka, A.; Suzuki, A.; Kondo, M.; et al. Genome evolution in the allotetraploid frog Xenopus laevis. Nature 2016, 538, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzler, C.; Oertel, M.; Hinz, M.; Hoffmann, W. Structure of the Xenopus laevis TFF-gene xP4.1, differentially expressed to its duplicated homolog xP4.2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1489, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF Peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Kastin, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Ribieras, S.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. The pS2/TFF1 trefoil factor, from basic research to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1378, F61–F77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, B.R.; Griffin, S.M.; May, F.E. Interaction between TFF1, a gastric tumor suppressor trefoil protein, and TFIZ1, a brichos domain-containing protein with homology to SP-C. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Pleiotropic effects of Trefoil Factor 1 deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, O.; Chenard, M.P.; Masson, R.; Linares, J.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Wendling, C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P.; Rio, M.C. Gastric mucosa abnormalities and tumorigenesis in mice lacking the pS2 trefoil protein. Science 1996, 274, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutto, M.; Saleh, M.; Arredouani, M.S.; Piazuelo, B.; Belkhiri, A.; El-Rifai, W. Loss of Tff1 Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype with Increase in the Levels of RORγt+ T Lymphocytes and Il-17 in Mouse Gastric Neoplasia. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saukkonen, K.; Tomasetto, C.; Narko, K.; Rio, M.C.; Ristimaki, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and effect of celecoxib in gastric adenomas of trefoil factor 1-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3032–3036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Trefoil factor 1 is required for the commitment programme of mouse oxyntic epithelial progenitors. Gut 2004, 53, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Amplification and invasiveness of epithelial progenitors during gastric carcinogenesis in trefoil factor 1 knockout mice. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, E.P.; Ali, T.; Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R.; May, F.E.B.; Westley, B.R.; Josenhans, C.; Rust, M.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide interacts with TFF1 in a pH-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.; May, F.E.B. The Interaction of Helicobacter pylori with TFF1 and Its Role in Mediating the Tropism of the Bacteria Within the Stomach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: From structure to function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thim, L.; Madsen, F.; Poulsen, S.S. Effect of trefoil factors on the viscoelastic properties of mucus gels. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellev, S.; Nexo, E.; Thim, L.; Poulsen, S.S. Systemically administered trefoil factors are secreted into the gastric lumen and increase the viscosity of gastric contents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Hayama, M.; Momose, M.; El-Zimaity, H.M.; Matsuda, K.; Sano, K.; Maruta, F.; Okumura, N.; Katsuyama, T. Co-localization of TFF2 with gland mucous cell mucin in gastric mucous cells and in extracellular mucous gel adherent to normal and damaged gastric mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more. Int. J. Oncool. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.; Westley, B.; May, F. Dramatic diurnal variation in the concentration of the human trefoil peptide TFF2 in gastric juice. Gut 2001, 48, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, F.E.; Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.L.; Westley, B.R. The human two domain trefoil protein, TFF2, is glycosylated in vivo in the stomach. Gut 2000, 46, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Ragge, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Human gastric TFF2 peptide contains an N-linked fucosylated N,N’-diacetyllactosediamine (LacdiNAc) oligosaccharide. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Bonar, D.; Schloerer, N.; Schroten, H. Human trefoil factor 2 is a lectin that binds α-GlcNAc-capped mucin glycans with antibiotic activity against Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27363–27375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinuma, T.; Ide, S.; Kawano, J.; Suganuma, T. Purification and immunohistochemistry of Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin-II-binding mucus glycoprotein in rat stomach. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Kurihara, M.; Goso, Y.; Urata, T.; Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T.; Hotta, K. Peripheral α-linked N-acetylglucosamine on the carbohydrate moiety of mucin derived from mammalian gastric gland mucous cells: Epitope recognized by a newly characterized monoclonal antibody. Biochem. J. 1996, 318, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, M.; Ito, Y.; Okimura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakura, K.; Kasama, S.; Fukuda, M.N.; Fukuda, M.; Katsuyama, T.; Nakayama, J. Natural antibiotic function of a human gastric mucin against Helicobacter pylori infection. Science 2004, 305, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Ohtani, M.; Jones, E.K.; Wang, T.C. Accelerated progression of gastritis to dysplasia in the pyloric antrum of TFF2-/- C57BL6 x Sv129 Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human intestinal TFF3 forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemer, J.; Bulleid, N.; Herrmann, J.M. Disulfide formation in the ER and mitochondria: Two solutions to a common process. Science 2009, 324, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Sparvoli, A.; Fagioli, C.; Fassina, G.; Sitia, R. Formation of reversible disulfide bonds with the protein matrix of the endoplasmic reticulum correlates with the retention of unassembled Ig light chains. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuzawa, M.; Yasumasu, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Iuchi, I. Cloning and expression of xP1-L, a new marker gene for larval surface mucous cells of tadpole stomach in Xenopus laevis. Gene Expr. Patterns 2007, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.F. Molecular and cellular aspects of thiol-disulfide exchange. In Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology; Meister, A., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1963; Volume 63, pp. 69–172. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, L.B. The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Clavreul, N.; Sethuraman, M.; Adachi, T.; Cohen, R.A. Thiol oxidation in signaling and response to stress: Detection and quantification of physiological and pathophysiological thiol modifications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.F.; Karam, S.M.; Wendling, C.; Chenard, M.P.; Kershenobich, D.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Trefoil factor 1 (TFF1/pS2) deficiency activates the unfolded protein response. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasberger, H.; El-Zaatari, M.; Dang, D.T.; Merchant, J.L. Dual oxidases control release of hydrogen peroxide by the gastric epithelium to prevent Helicobacter felis infection and inflammation in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennett, E.C.; Chuang, C.Y.; Degendorfer, G.; Whitelock, J.M.; Davies, M.J. Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative damage to extracellular matrix. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Mogami, S.; Hibi, T. Roles of oxidative stress in stomach disorders. J. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 50, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.A.; Poulsom, R.; Stamp, G.W.H.; Hall, P.A.; Jeffery, R.E.; Longcroft, J.M.; Rio, M.-C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P. Epidermal growth factor (EGF/URO) induces expression of regulatory peptides in damaged human gastrointestinal tissues. J. Pathol. 1990, 162, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, M.-C.; Chenard, M.-P.; Wolf, C.; Marcellin, L.; Tomasetto, C.; Lathe, R.; Bellocq, J.-P.; Chambon, P. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.P.A.; Hoffmann, J.; Haeckel, C.; Rutkowski, K.; Schmid, R.M.; Wagner, M.; Adler, G.; Schulz, H.U.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Induction of TFF1 gene expression in pancreas overexpressing transforming growth factor α. Gut 1999, 45, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Bälder, R.; Hinz, M.; Braun, A.; Krug, N.; Hoffmann, W. Induced trefoil factor family 1 expression by trans-differentiating Clara cells in a murine asthma model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Guttek, K.; Händel, U.; Reinhold, D.; Hoffmann, W. Increased cerebral Tff1 expression in two murine models of neuroinflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Salm, F.; Händel, U.; Hoffmann, W. Transcriptional responses in the murine spleen after Toxoplasma gondii infection: Inflammasome und mucus-associated genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Wu, Z.; Nuding, S.; Groscurth, S.; Marcinowski, M.; Beisner, J.; Buchner, J.; Schaller, M.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human β-defensin 1. Nature 2011, 469, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Hoffmann, W. Porcine gastric TFF2 is a mucus constituent and differs from pancreatic TFF2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Hoffmann, W. Commercial Porcine Gastric Mucin Preparations, also Used as Artificial Saliva, are a Rich Source for the Lectin TFF2: In Vitro Binding Studies. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Klasson, S.; Larsson, E.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C.; Samuelsson, T. Searching the evolutionary origin of epithelial mucus protein components—mucins and FCGBP. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J. Dual roles of gastric gland mucin-specific O-glycans in prevention of gastric cancer. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jørgensen, K.H.; Thim, L.; Jacobsen, H.E. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Regul. Pept. 1982, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga Emidio, N.; Hoffmann, W.; Brierly, S.M.; Muttenthaler, M. Trefoil factor family: Unresolved questions and clinical perspectives. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
Stürmer R, Reising J, Hoffmann W. The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
Chicago/Turabian StyleStürmer, René, Jana Reising, and Werner Hoffmann. 2019. "The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
APA StyleStürmer, R., Reising, J., & Hoffmann, W. (2019). The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052