The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release
Abstract
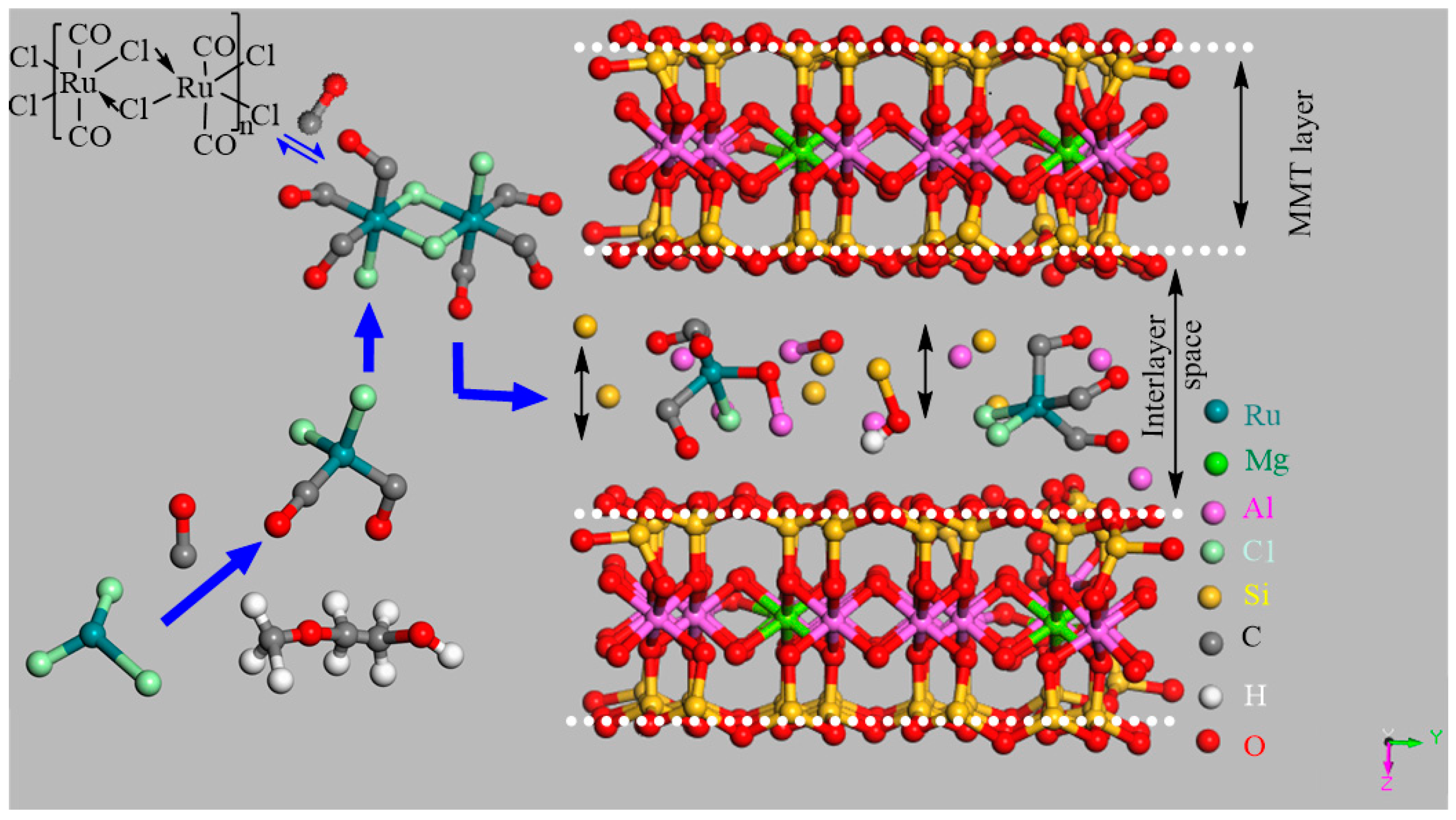
1. Introduction
2. Characterization Techniques
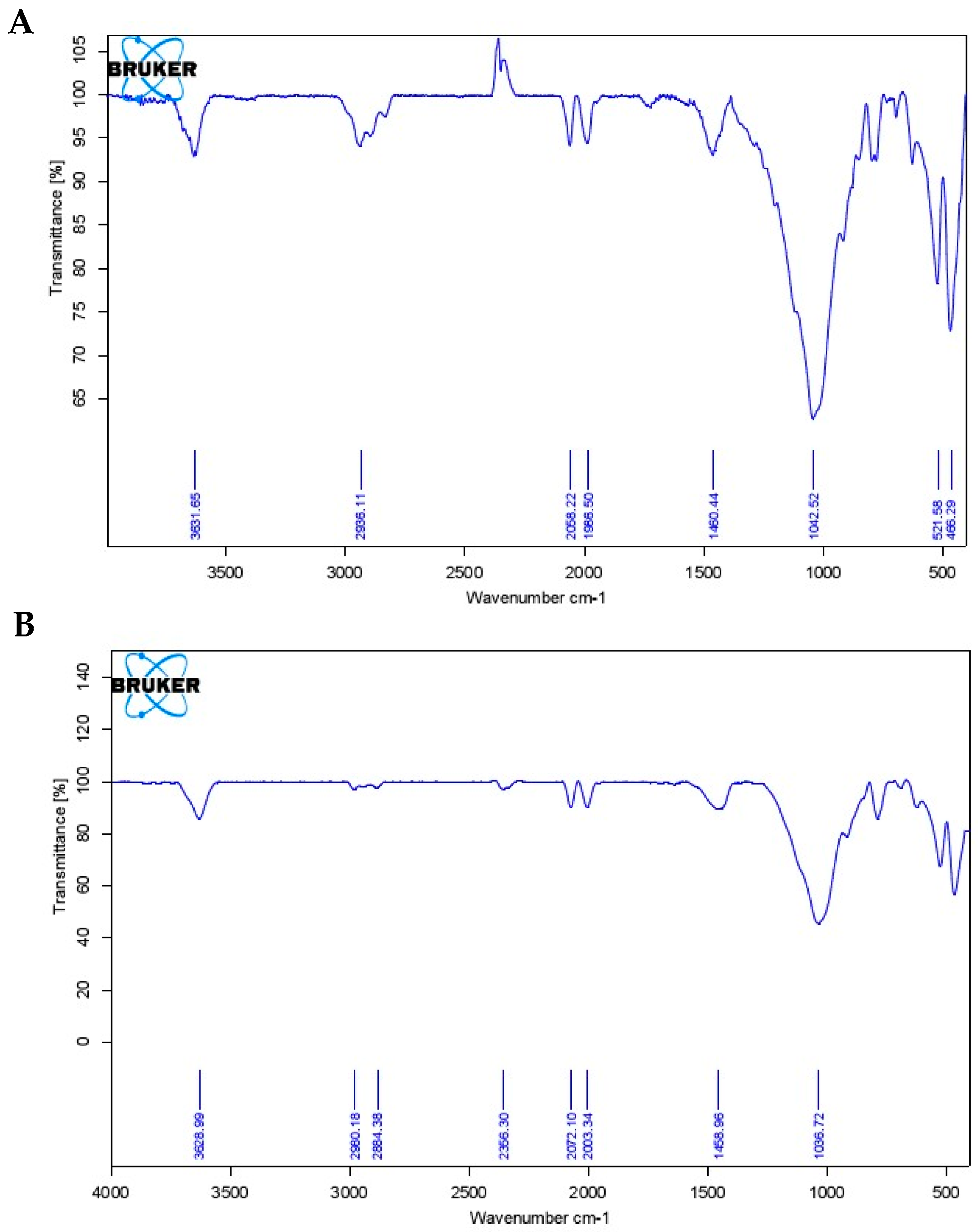
2.1. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
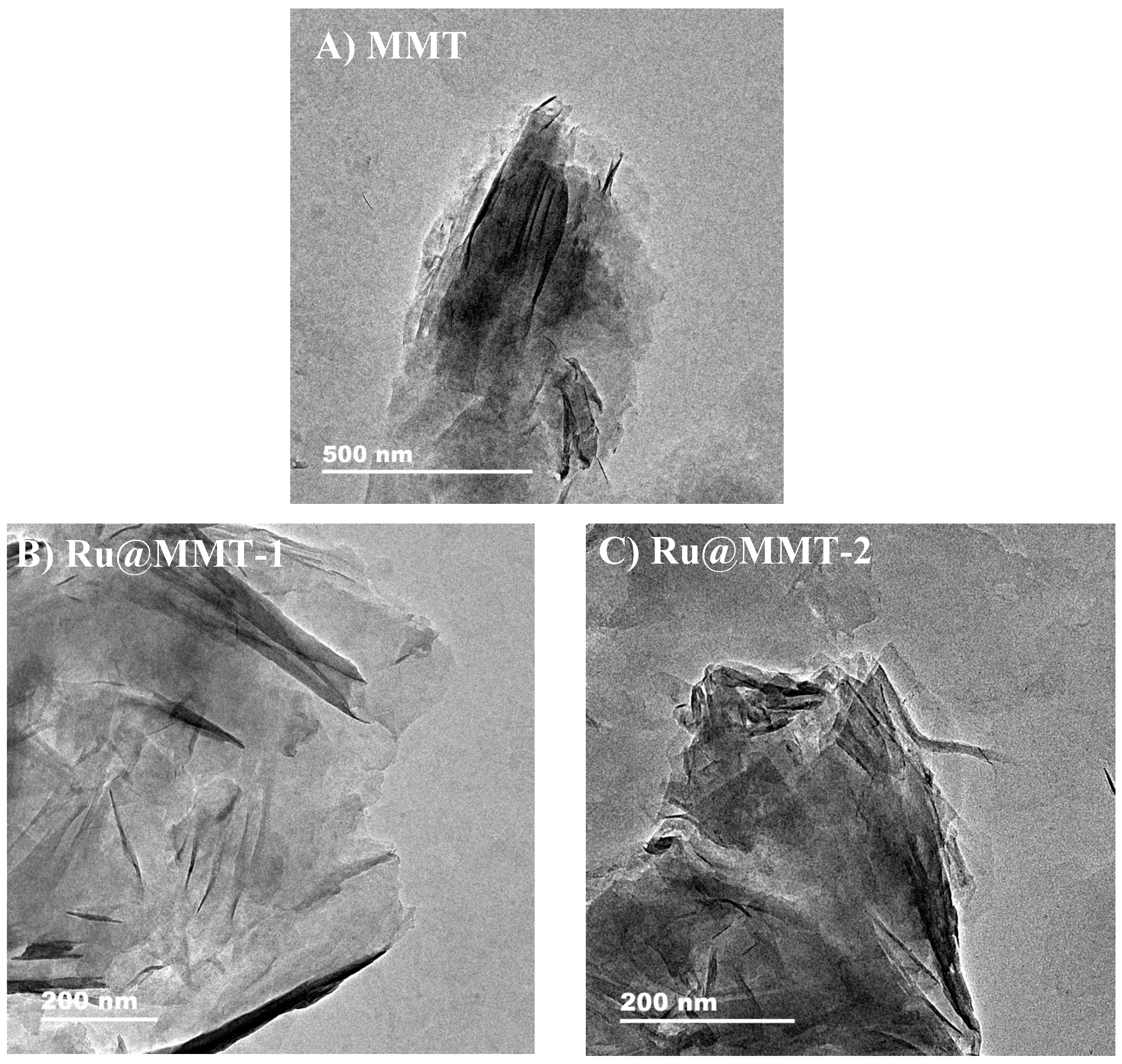
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.4. X-Ray Diffraction (X-ray)
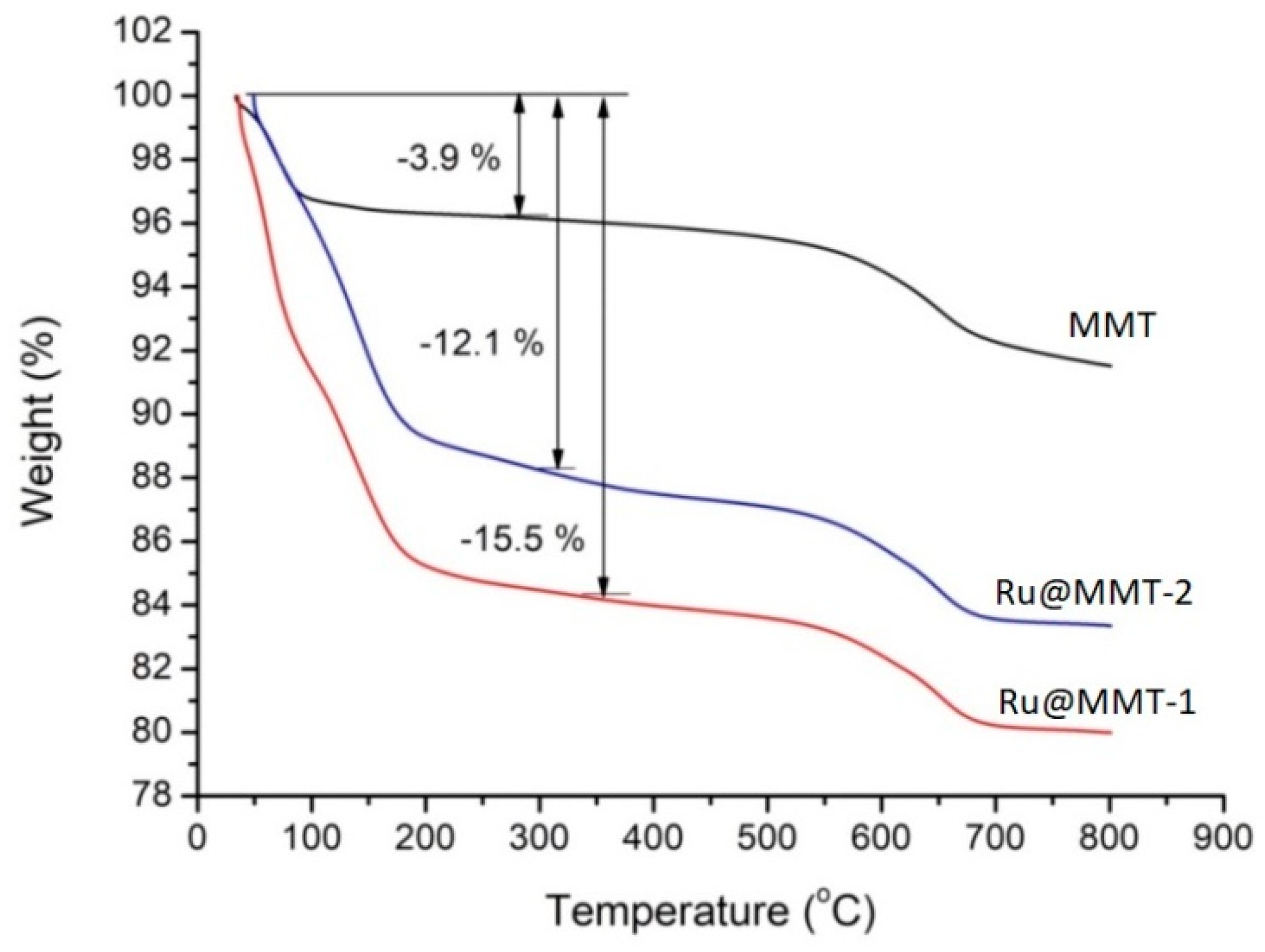
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
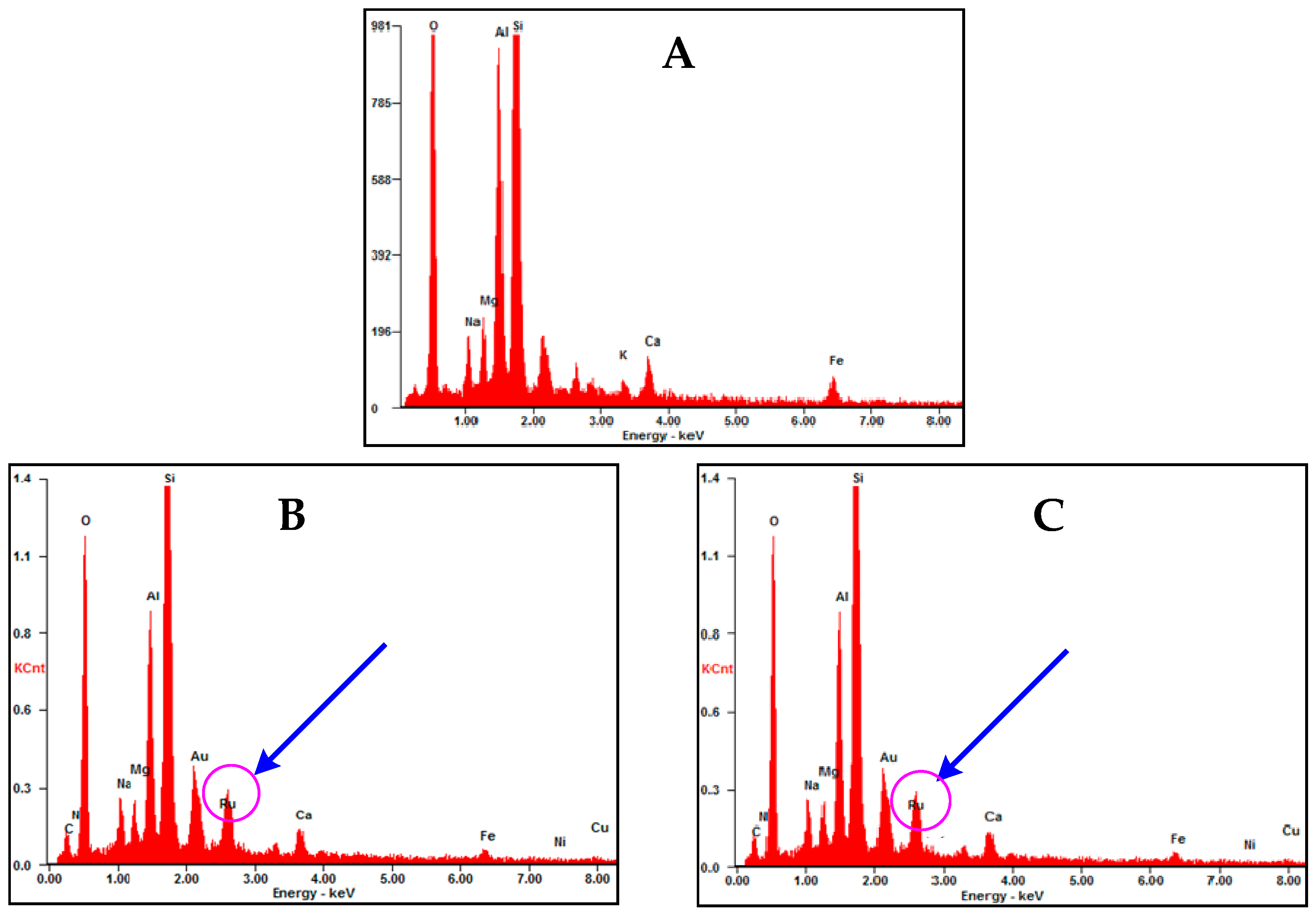
2.6. Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
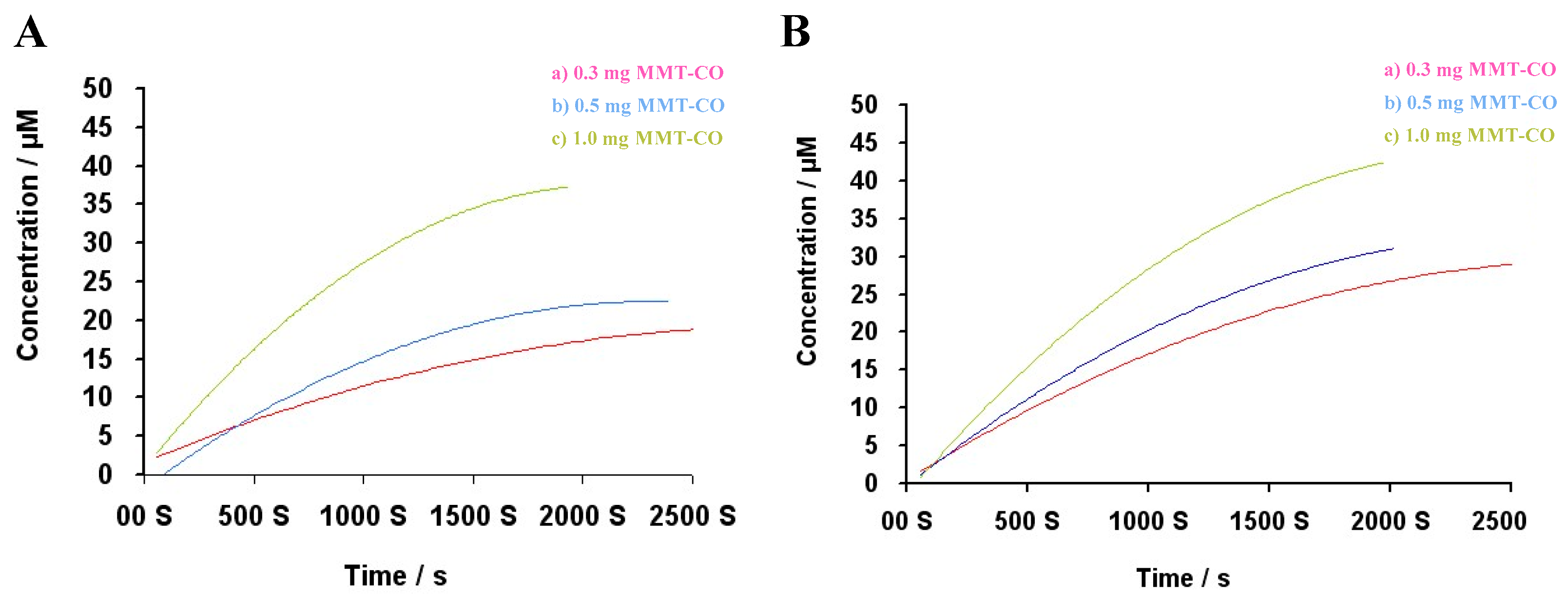
2.7. Myoglobin Assay (Mb)
3. Discussion
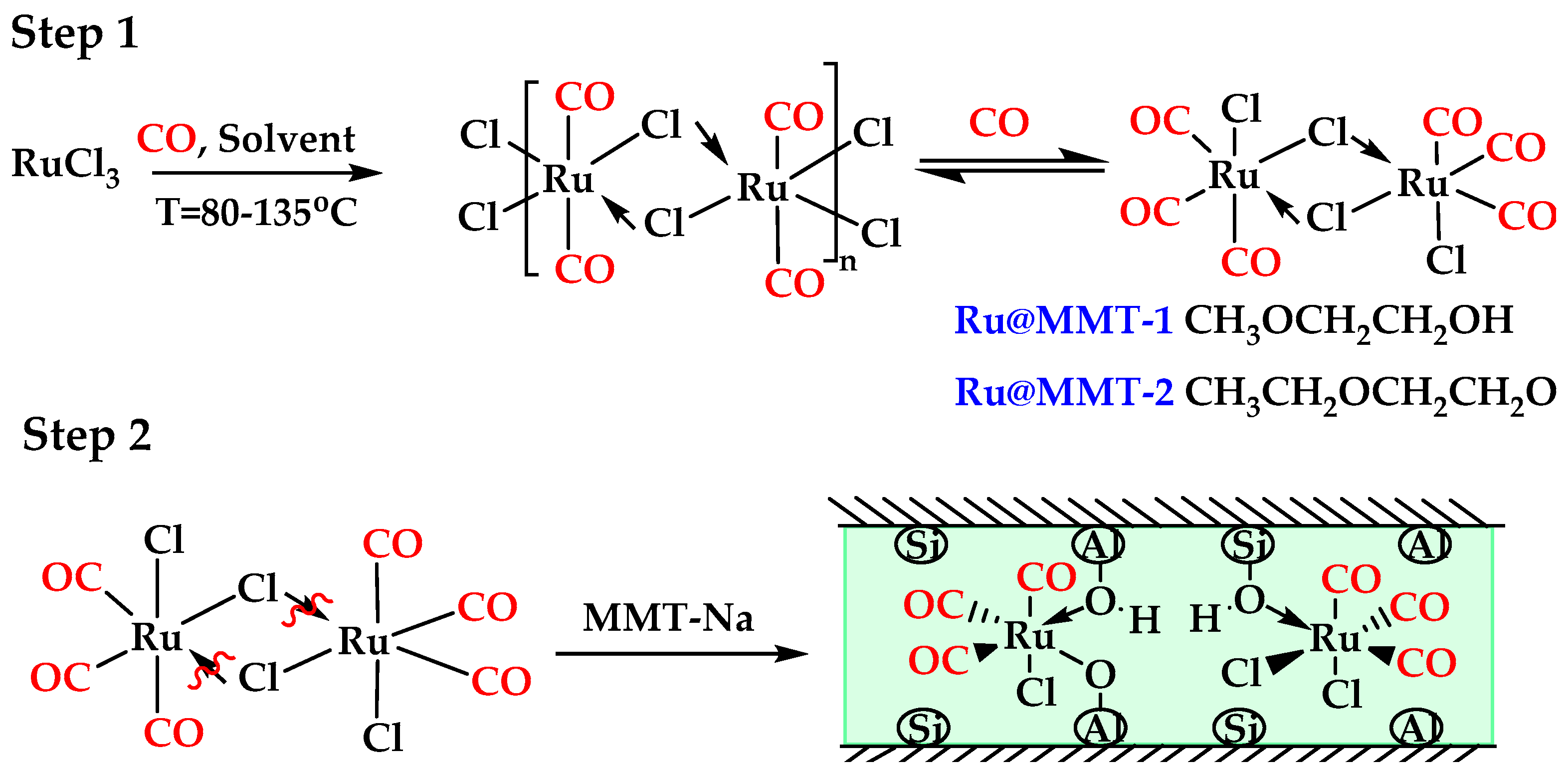
4. Materials and Synthesis Procedure
4.1. Materials
4.2. Characterization
4.2.1. General Remarks
4.2.2. Preparation Ru@MMT-1
4.2.3. Preparation Ru@MMT-2
4.3. Myoglobin Assay for CO Kinetics Profile
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning—a public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldane, J.B.S. Carbon monoxide as a tissue poison. Biochem. J. 1927, 21, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, C.G.; Haldane, J.S.; Haldane, J.B.S. The laws of combination of haemoglobin with carbon monoxide and oxygen. J. Physiol. (Oxford, Oxf. UK) 1912, 44, 275–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.h. Relationship between endogenous carbon monoxide production and disease. J. Mod. Lab. Med. 2013, 28, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, C.W.; Parfenova, H.; Jaggar, J.H. Carbon monoxide as an endogenous vascular modulator. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1–H11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-H.; Choi, S. Therapeutic Aspects of Carbon Monoxide in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Quantification of Nanomaterial/Nanomedicine Trafficking in Vivo. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 589–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palao, E.; Slanina, T.; Muchová, L.; Šolomek, T.; Vítek, L.; Klán, P. Transition-Metal-Free CO-Releasing BODIPY Derivatives Activatable by Visible to NIR Light as Promising Bioactive Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Men, F.; Wang, W.-C.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Zhang, H.-W.; Ye, D.-W. Carbon Monoxide and Its Controlled Release: Therapeutic Application, Detection, and Development of Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecules (CORMs). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2611–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresti, R.; Bani-Hani, M.G.; Motterlini, R. Use of carbon monoxide as a therapeutic agent: Promises and challenges. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.J.; Rotella, D.P. Medicinal Chemistry and Therapeutic Applications of the Gasotransmitters NO, CO, and H2S and their Prodrugs. In Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry, Drug Discovery, and Development, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, C. Gaseotransmitters: New frontiers for translational science. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 59ps54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Chen, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, W. Photo-activated CO-releasing molecules (PhotoCORMs) of robust sawhorse scaffolds [μ2-OOCR1, η1-NH2CHR2(C=O] OCH3, Ru(I)2CO4]. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 3727–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Qu, Y.; Fu, X.; Fan, J.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Z.; et al. NIR-Responsive On-Demand Release of CO from Metal Carbonyl-Caged Graphene Oxide Nanomedicine. Adv. Mater. (Deerfield Beach Fla.) 2015, 27, 6741–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Fang, J.; Liao, L.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. Styrene-maleic acid copolymer-encapsulated CORM2, a water-soluble carbon monoxide (CO) donor with a constant CO-releasing property, exhibits therapeutic potential for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Controll. Release Off. J. Controll. Release Soc. 2014, 187, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Johns, V.K.; Ma, L.; Oyer, J.; Copik, A.; Igarashi, R.; Liao, Y. Visible-light activatable organic CO-releasing molecules (PhotoCORMs) that simultaneously generate fluorophores. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 6671–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, U.; van der Vlies, A.J.; Simeoni, E.; Wandrey, C.; Hubbell, J.A. Carbon monoxide-releasing micelles for immunotherapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18273–18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Radacki, K.; Schatzschneider, U. Sonogashira, CuAAC, and Oxime Ligations for the Synthesis of MnI Tricarbonyl PhotoCORM Peptide Conjugates. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, H.; Rojas, A.; Niesel, J.; Schatzschneider, U. Sonogashira and “Click” reactions for the N-terminal and side-chain functionalization of peptides with [Mn(CO)3(tpm)]+-based CO releasing molecules (tpm = tris(pyrazolyl)methane). Dalton Trans. (Camb. Engl. 2003) 2009, 4292–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.S.; Schmitt, S.; Dou, Q.P.; Kodanko, J.J. Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity of the stable iron carbonyl complex [Fe(CO)(N4Py)](ClO4)2: Photoactivated carbon monoxide release, growth inhibitory activity, and peptide ligation. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 5336–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, J.B.; Webber, M.J.; Tamboli, V.K.; Weber, B.; Stupp, S.I. A peptide-based material for therapeutic carbon monoxide delivery. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6689–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, C.; Joshi, T.; Dimri, A.; Spiccia, L.; Schatzschneider, U. Synthesis, spectroscopic properties, and photoinduced CO-release studies of functionalized ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes: Versatile building blocks for development of CORM-peptide nucleic acid bioconjugates. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9297–9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, H.; Sowik, T.; Schatzschneider, U. Bioorthogonal oxime ligation of a Mo(CO)4(N–N) CO-releasing molecule (CORM) to a TGF β-binding peptide. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 734, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobi, F.; Blacque, O.; Jacobs, R.A.; Schaub, M.C.; Bogdanova, A.Y. 17 e−rhenium dicarbonyl CO-releasing molecules on a cobalamin scaffold for biological application. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.L.; Fayad Kobeissi, S.; Oudir, S.; Haas, B.; Michel, B.; Dubois Rande, J.L.; Ollivier, A.; Martens, T.; Rivard, M.; Motterlini, R.; et al. Design and synthesis of new hybrid molecules that activate the transcription factor Nrf2 and simultaneously release carbon monoxide. Chemistry (Weinh. der Bergstr. Ger.) 2014, 20, 14698–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, A.C.; Penacho, N.; Mancio-Silva, L.; Neres, R.; Seixas, J.D.; Fernandes, A.C.; Romao, C.C.; Mota, M.M.; Bernardes, G.J.; Pamplona, A. A novel carbon monoxide-releasing molecule fully protects mice from severe malaria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Kromer, L.; Gallo, D.J.; Penacho, N.; Rodrigues, S.S.; Seixas, J.D.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Reis, P.M.; Otterbein, S.L.; Ruggieri, R.A.; et al. Generation of Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecules (CO-RMs) as Drug Candidates for the Treatment of Acute Liver Injury: Targeting of CO-RMs to the Liver. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5810–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, P.C.; Brückmann, N.E.; Spingler, B. Towards Polymer Diagnostic Agents—Copolymers of N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide and Bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-4-vinylbenzylamine: Synthesis, Characterisation and Re(CO)3-Labelling. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückmann, N.E.; Wahl, M.; Reiß, G.J.; Kohns, M.; Wätjen, W.; Kunz, P.C. Polymer Conjugates of Photoinducible CO-Releasing Molecules. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 4571–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabe, H.; Fujita, K.; Abe, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Kuchimaru, T.; Kizaka-Kondoh, S.; Takano, M.; Kitagawa, S.; Ueno, T. Preparation of a Cross-Linked Porous Protein Crystal Containing Ru Carbonyl Complexes as a CO-Releasing Extracellular Scaffold. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabe, H.; Shimoi, T.; Fujita, K.; Abe, S.; Ijiri, H.; Tsujimoto, M.; Kuchimaru, T.; Kizaka-Kondo, S.; Mori, H.; Kitagawa, S.; et al. Design of a CO-releasing Extracellular Scaffold Using in Vivo Protein Crystals. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Ferreira, M.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Matak-Vinkovic, D.; Coelho, A.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; Saraiva, L.M.; Romao, C.C.; Bernardes, G.J. Spontaneous CO release from RuII(CO)2-protein complexes in aqueous solution, cells, and mice. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2015, 54, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, I.S.; Jeremias, H.F.; Chaves-Ferreira, M.; Matak-Vinkovic, D.; Boutureira, O.; Romão, C.C.; Bernardes, G.J.L. An artificial CO-releasing metalloprotein built by histidine-selective metallation. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3993–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Sho, T.; Ozeki, S.; Abe, S.; Hikage, T.; Kuchimaru, T.; Kizaka-Kondoh, S.; Ueno, T. Intracellular CO release from composite of ferritin and ruthenium carbonyl complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16902–16908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diring, S.; Carné-Sánchez, A.; Zhang, J.; Ikemura, S.; Kim, C.; Inaba, H.; Kitagawa, S.; Furukawa, S. Light responsive metal–organic frameworks as controllable CO-releasing cell culture substrates. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dördelmann, G.; Pfeiffer, H.; Birkner, A.; Schatzschneider, U. Silicium Dioxide Nanoparticles As Carriers for Photoactivatable CO-Releasing Molecules (PhotoCORMs). Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4362–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, M.A.; Han, H.; Moyes, A.; Radinos, A.; Hobbs, A.J.; Coombs, N.; Oliver, S.R.J.; Mascharak, P.K. Light-triggered carbon monoxide delivery with Al-MCM-41-based nanoparticles bearing a designed manganese carbonyl complex. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordelmann, G.; Meinhardt, T.; Sowik, T.; Krueger, A.; Schatzschneider, U. CuAAC click functionalization of azide-modified nanodiamond with a photoactivatable CO-releasing molecule (PhotoCORM) based on [Mn(CO)3(tpm)]+. Chem. Commun. (Camb. Engl.) 2012, 48, 11528–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, P.C.; Meyer, H.; Barthel, J.; Sollazzo, S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Janiak, C. Metal carbonyls supported on iron oxide nanoparticles to trigger the CO-gasotransmitter release by magnetic heating. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4896–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, P.; Pai, S.; Schatzschneider, U.; Smith, G.S. Next generation PhotoCORMs: Polynuclear tricarbonylmanganese(I)-functionalized polypyridyl metallodendrimers. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 5470–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupskaya, V.V.; Zakusin, S.V.; Tyupina, E.A.; Dorzhieva, O.V.; Zhukhlistov, A.P.; Belousov, P.E.; Timofeeva, M.N. Experimental Study of Montmorillonite Structure and Transformation of Its Properties under Treatment with Inorganic Acid Solutions. Minerals 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, S.; Duman, O. The effect of different molecular weight of poly(ethylene glycol) on the electrokinetic and rheological properties of Na-bentonite suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-R.C.; Skipper, N.T.; Sposito, G. Computer Simulation of Interlayer Molecular Structure in Sodium Montmorillonite Hydrates. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2734–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jia, F.; Peng, C. Study On Decomposition of Goethite/Siderite in Thermal Modification Through Xrd, Sem and Tga Measurements. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2014, 21, 1450019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, S.; Dong, X.; Min, F.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, C.; Nahmad, Y. Molecular Dynamics Study of Crystalline Swelling of Montmorillonite as Affected by Interlayer Cation Hydration. JOM 2018, 70, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Muhammad, N.; Niazi, K.U.K.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, R.; Dong, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. CO-Releasing Materials: An Emphasis on Therapeutic Implications, as Release and Subsequent Cytotoxicity Are the Part of Therapy. Materials 2019, 12, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.-l.; Yu, M.-a.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.-l. Research progress of montmorillonite as pharmaceutical excipients and drug carriers. Guisuanyan Tongbao 2013, 32, 414–418. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K. Composite Adsorbent Containing Montmorillonite and Its Preparation Method and Its Application in Treating Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products. Patent CN108126672A, 8 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bekaroğlu, M.G.; Nurili, F.; İşçi, S. Montmorillonite as imaging and drug delivery agent for cancer therapy. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul Haque, S.; Nasar, A. Montmorillonite clay nanocomposites for drug delivery. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Inamuddin, Asiri, A.M., Mohammad, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Zeng, H.; Xiang, Y. Comparative study of organo-vermiculite, organo-montmorillonite and organo-silica nanosheets functionalized by an ether-spacer-containing Gemini surfactant: Congo red adsorption and wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraqué, F.; Montes, M.L.; Fernández, M.A.; Mercader, R.C.; Candal, R.J.; Torres Sánchez, R.M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic-montmorillonite and magnetic-organo-montmorillonite: Surface sites involved on cobalt sorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 466, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, B.H.; Pushpalatha, M.; Basavaprasad, V.M.; Huvanna, T.P. Modified nano-clay formulation and their application. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; Liang, T.; Chen, Y.; Tian, T.; Li, T.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; et al. Nano Clay and Desulfurization ash Solidified Emulsified Asphalt Mixture and Preparation Method Thereof. Patent CN106746933A, 31 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wypych, F. Chemical Modification of Clay Surfaces. In Interface Science and Technology; Wypych, F., Satyanarayana, K.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Qutubuddin, S. Polymer–clay nanocomposites: Exfoliation of organophilic montmorillonite nanolayers in polystyrene. Polymer 2001, 42, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced exfoliation of montmorillonite prepared by hydrothermal method. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, V.E.; Abate, G.; Grassi, M.T. Determination of labile species of As(V), Ba, Cd, Co, Cr(III), Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sr, V(V), and Zn in natural waters using diffusive gradients in thin-film (DGT) devices modified with montmorillonite. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prayongphan, S.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Suzuki, S.; Chae, B.-G. Diffusion with micro-sorption in bentonite: evaluation by molecular dynamics and homogenization analysis. Comput. Mech. 2006, 37, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrish, K. Crystalline Swelling of Montmorillonite: Manner of Swelling of Montmorillonite. Nature 1954, 173, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuki, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Kojima, Y.; Okada, A.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Swelling behavior of montmorillonite cation exchanged for ω-amino acids by ε-caprolactam. J. Mater. Res. 1993, 8, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, L.; Almeida, C.A.P.; Naidek, N.; Viante, M.F.; Lopes, M.C.; Debacher, N.A. Adsorption characteristics of montmorillonite clay modified with iron oxide with respect to methylene blue in aqueous media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, A.J.; Lynam, J.M.; Moulton, B.E.; Sawle, P.; Motterlini, R.; Boyle, N.M.; Pryce, M.T.; Fairlamb, I.J. Modification of the deoxy-myoglobin/carbonmonoxy-myoglobin UV-vis assay for reliable determination of CO-release rates from organometallic carbonyl complexes. Dalton Trans. (Camb. Engl. 2003) 2011, 40, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.; Mann, B.E.; Poole, R.K. Sulfite species enhance carbon monoxide release from CO-releasing molecules: implications for the deoxymyoglobin assay of activity. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 427, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, A.C.; Kunz, P.C.; Janiak, C. CO-releasing molecule (CORM) conjugate systems. Dalton Trans. (Camb. Engl. 2003) 2016, 45, 18045–18063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sr. No. | Strategic Advantages | CO | CORMs | CORMats (This Work) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Therapeutic ways | Direct insertion | Indirect insertion | Indirect insertion |
| 2 | Constructability | Not recommended | Possible | Possible |
| 3 | Controllability | Proper arrangement required | Possible | Possible |
| 4 | Administration capability | Proper arrangement (In-need hospital) | Itinerant | Itinerant |
| 5 | Loading capability | High | Low | Controllable |
| 6 | Specific equipment | Yes | No special requirement (Just orally intake) | No special requirement (Just orally intake) |
| 7 | Targeting tissue facility | Nearly impossible | Feasible, moderate Control | Feasible, more Control |
| 8 | Tissue selectivity | Not prefer | Prefer | Confident |
| 9 | Toxicity of MMCs | Not present | Difficult to control | Reduced toxicity |
| 10 | Tissue receptor | Impossible | Need special arrangement | Easy to modified |
| Mass Percentage [Wt%] 1 | MMT 2 | Before Degradation | After Degradation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru@MMT-1 | Ru@MMT-2 | Ru@MMT-1 | Ru@MMT-2 | ||
| Mg | 2.26 | 1.81 | 1.41 | 1.99 | 1.87 |
| Al | 10.54 | 8.99 | 7.34 | 12.44 | 13.01 |
| Si | 34.40 | 29.72 | 25.76 | 40.15 | 38.04 |
| Ru | 0.00 | 5.38 | 4.18 | 3.81 | 2.71 |
| Elements 1 | Montmorillonite 2 | Ru@MMT-1 | Ru@MMT-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt [%] | At [%] | Wt [%] | At [%] | Wt [%] | At [%] | |
| O K | 43.20 | 58.07 | 35.55 | 55.33 | 33.20 | 46.29 |
| Na K | 02.41 | 02.25 | 02.97 | 03.21 | 02.40 | 02.33 |
| Mg K | 02.26 | 02.00 | 01.81 | 01.85 | 01.41 | 01.30 |
| Al K | 10.54 | 08.40 | 08.99 | 08.30 | 07.34 | 06.07 |
| Si K | 34.40 | 26.34 | 29.72 | 26.35 | 25.76 | 20.46 |
| Pd L | 01.35 | 00.27 | 00.63 | 00.15 | 00.15 | 00.03 |
| Ca K | 01.98 | 01.06 | 02.06 | 01.28 | 01.52 | 00.85 |
| Fe K | 03.15 | 01.21 | 01.53 | 00.68 | 01.27 | 00.51 |
| Ru L | 0.00 | 0.00 | 05.38 | 01.33 | 04.18 | 00.92 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faizan, M.; Niazi, K.U.K.; Muhammad, N.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Z. The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143453
Faizan M, Niazi KUK, Muhammad N, Hu Y, Wang Y, Lin D, Liu Y, Zhang W, Gao Z. The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143453
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaizan, Muhammad, Kifayat Ullah Khan Niazi, Niaz Muhammad, Yongxia Hu, Yanyan Wang, Dezhi Lin, Yuanyuan Liu, Weiqiang Zhang, and Ziwei Gao. 2019. "The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143453
APA StyleFaizan, M., Niazi, K. U. K., Muhammad, N., Hu, Y., Wang, Y., Lin, D., Liu, Y., Zhang, W., & Gao, Z. (2019). The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143453






