Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
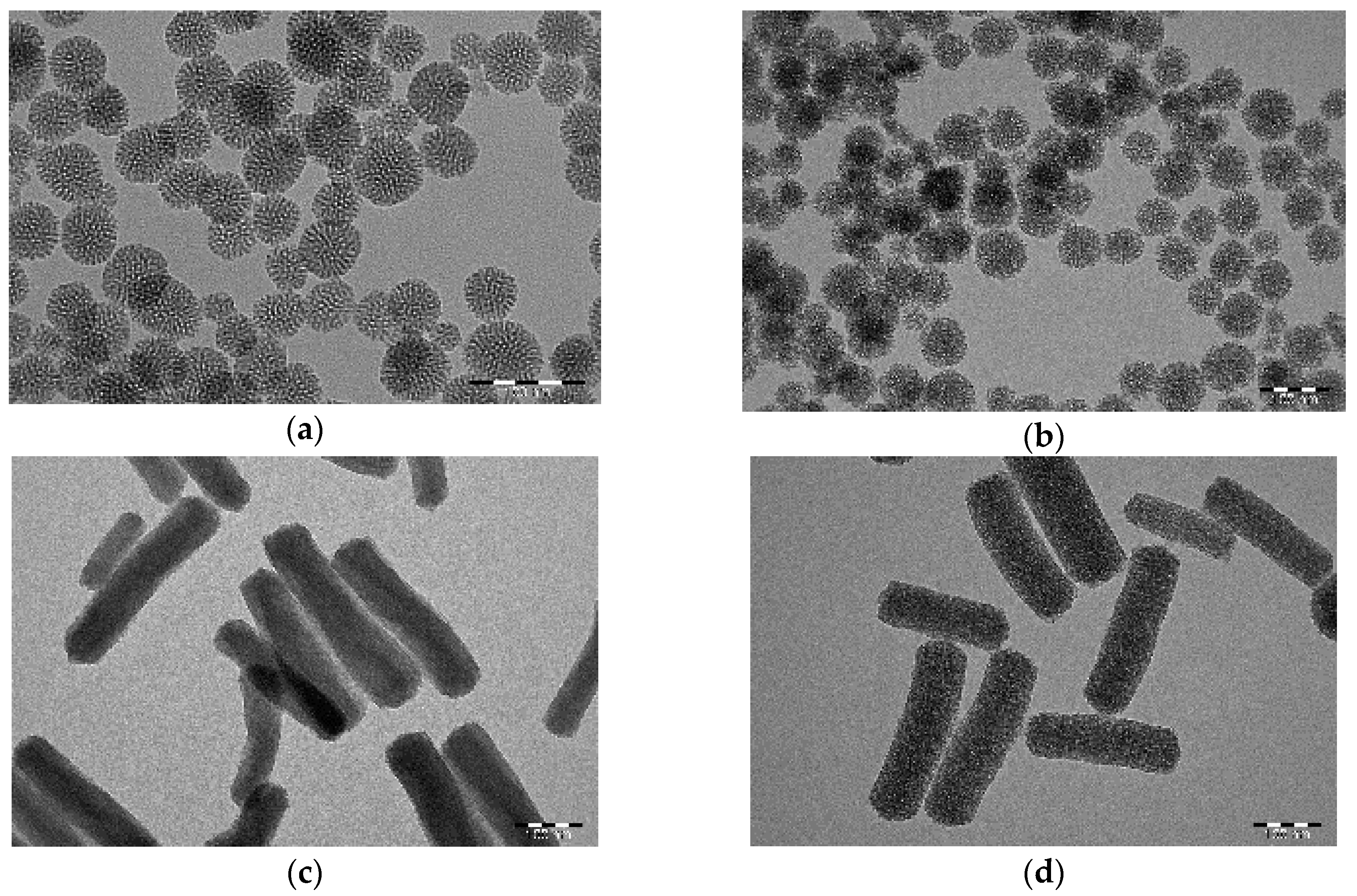
2.1. Characterization of the Nanoparticles
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation of MSN@PDA as a Drug Delivery System
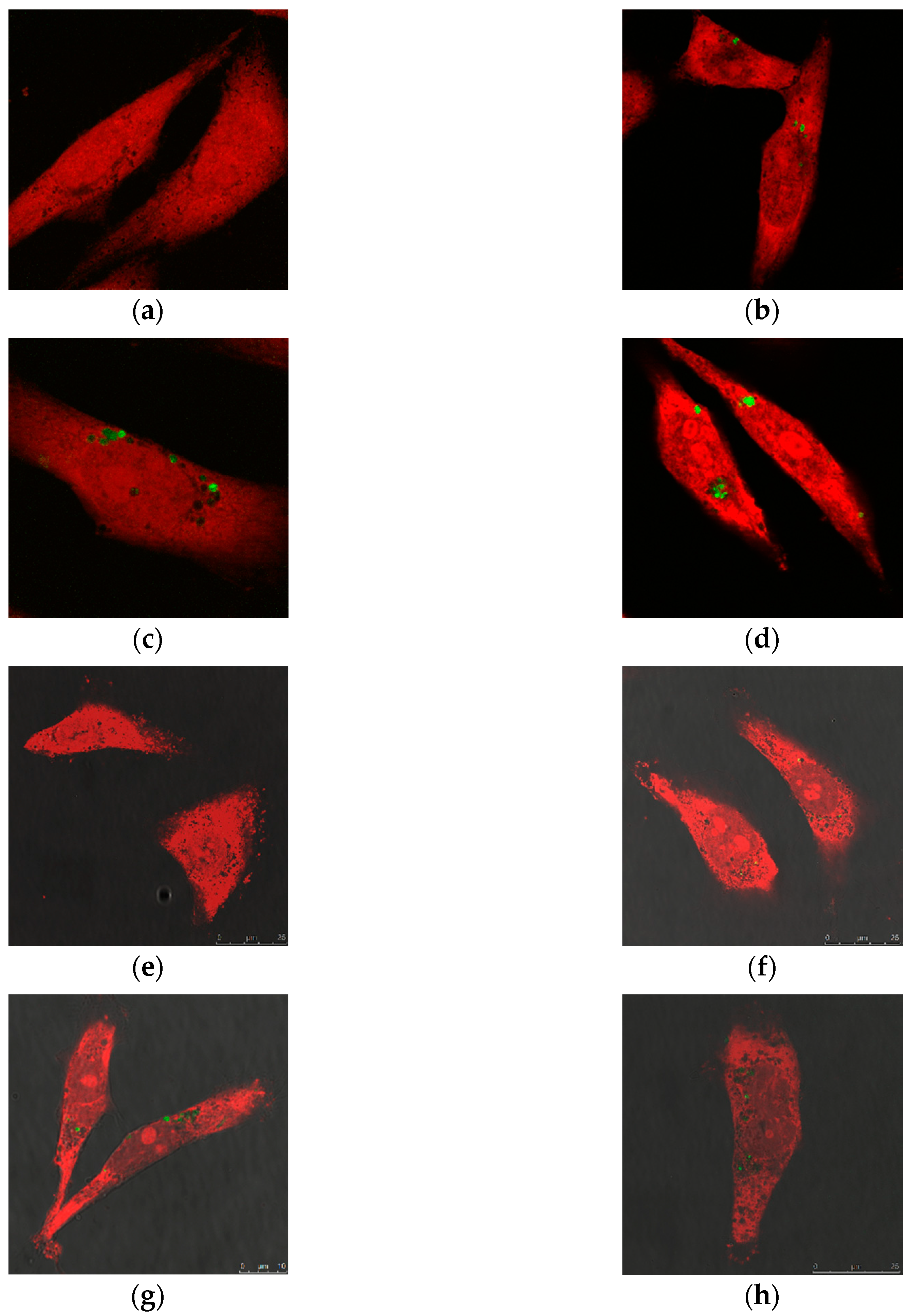
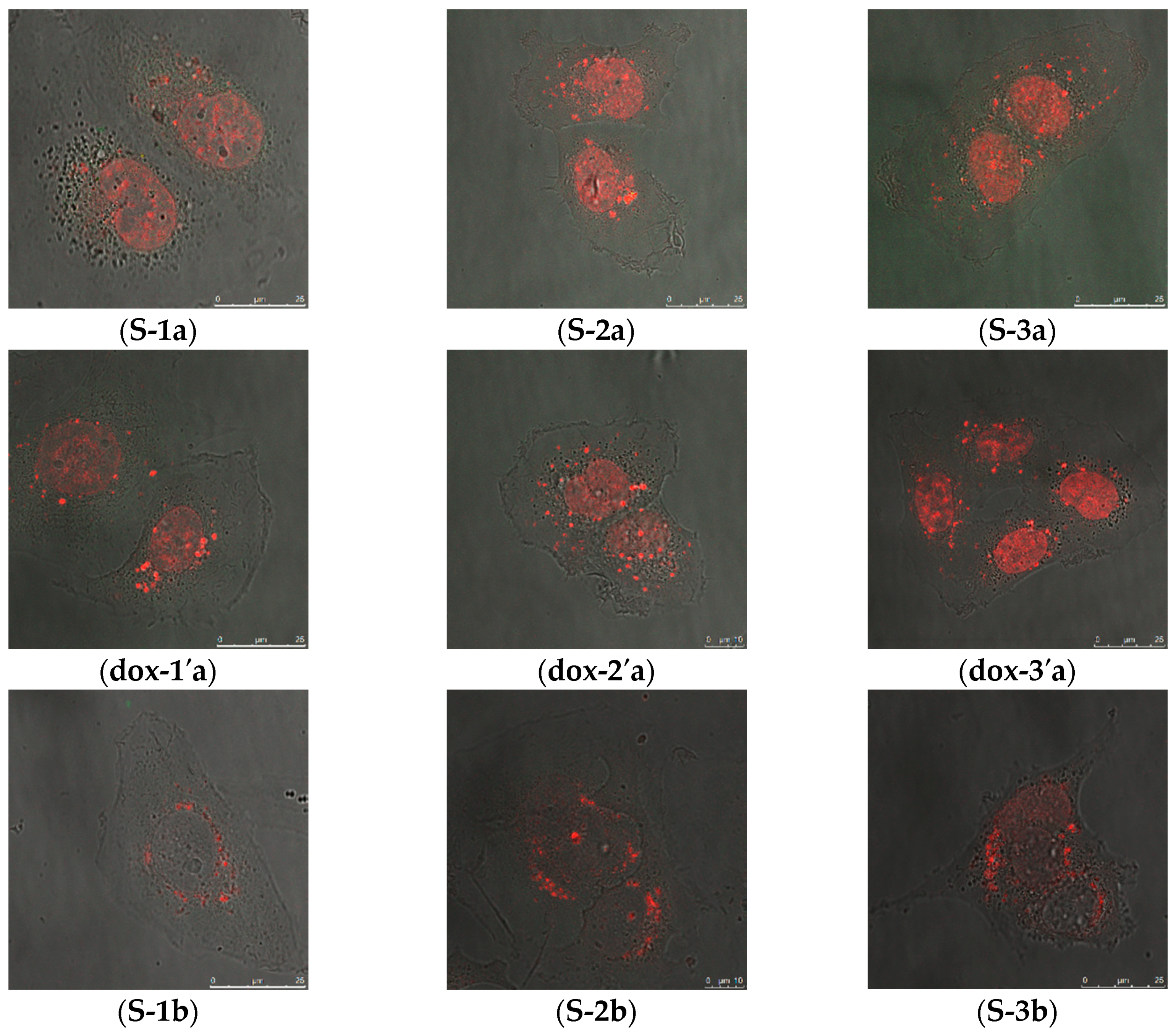
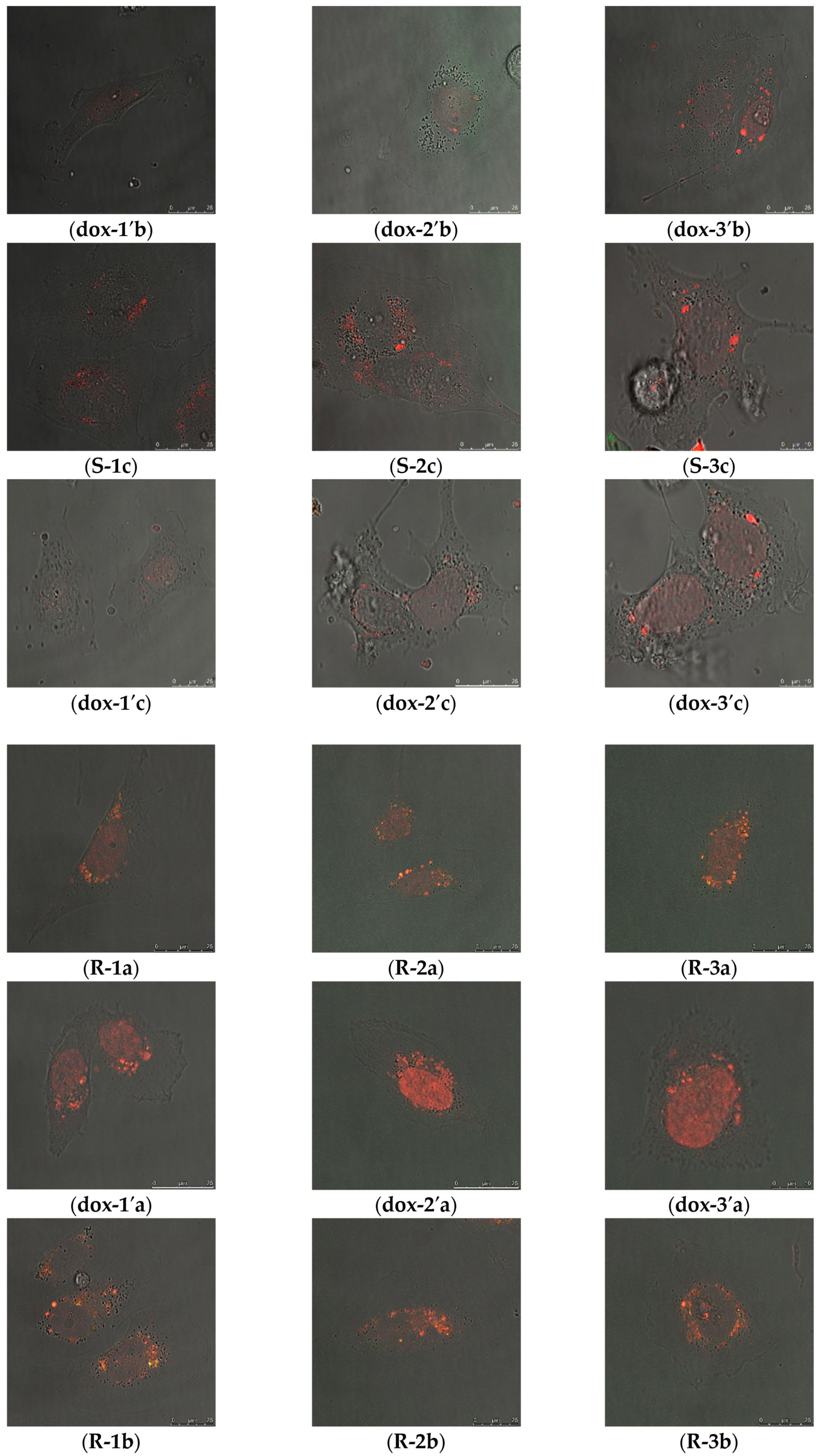
2.2.1. Cellular Uptake of MSN@PDA-COP Particles
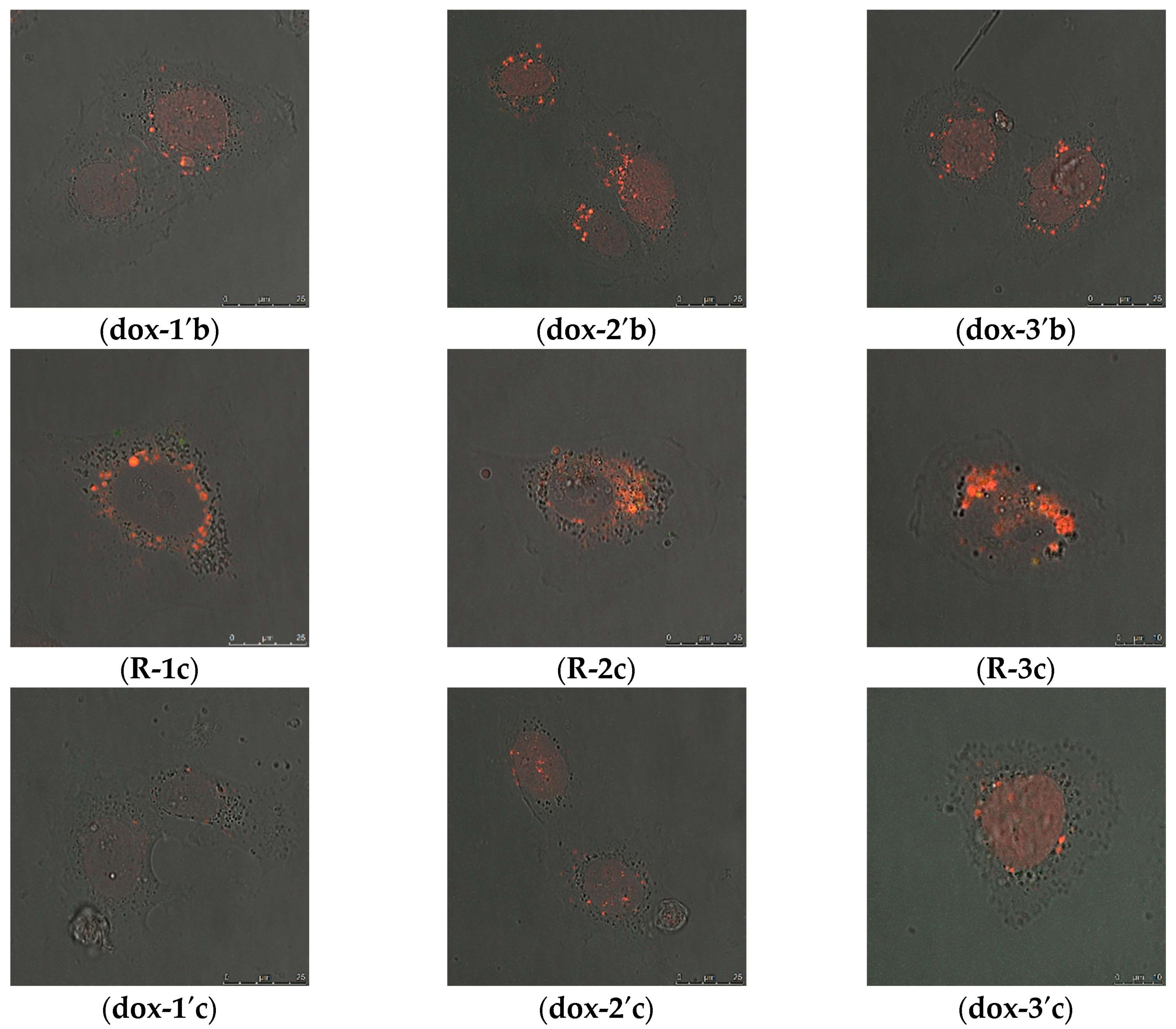
2.2.2. Intracellular Distribution of DOX Delivered by MSN@PDA-COP Particles
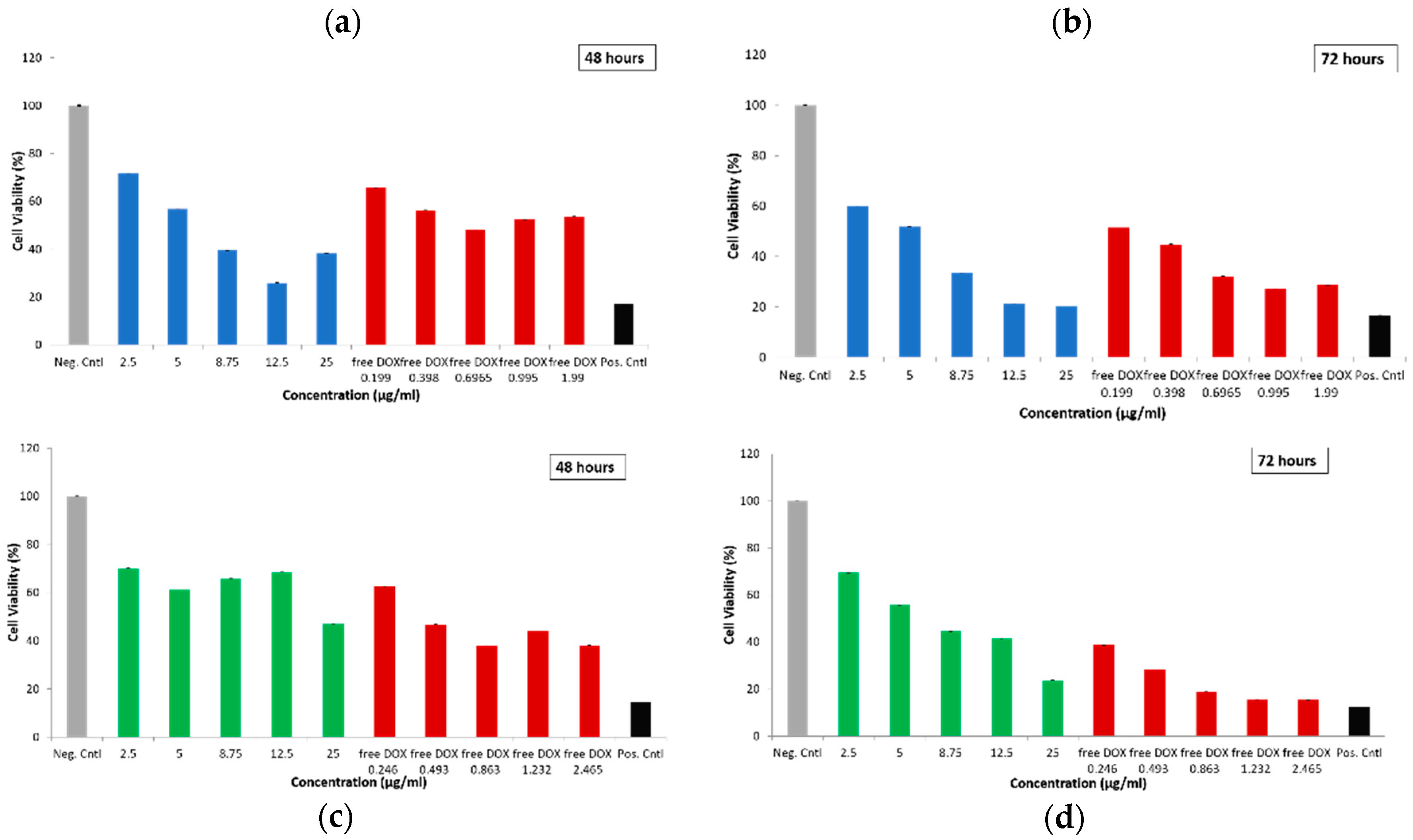
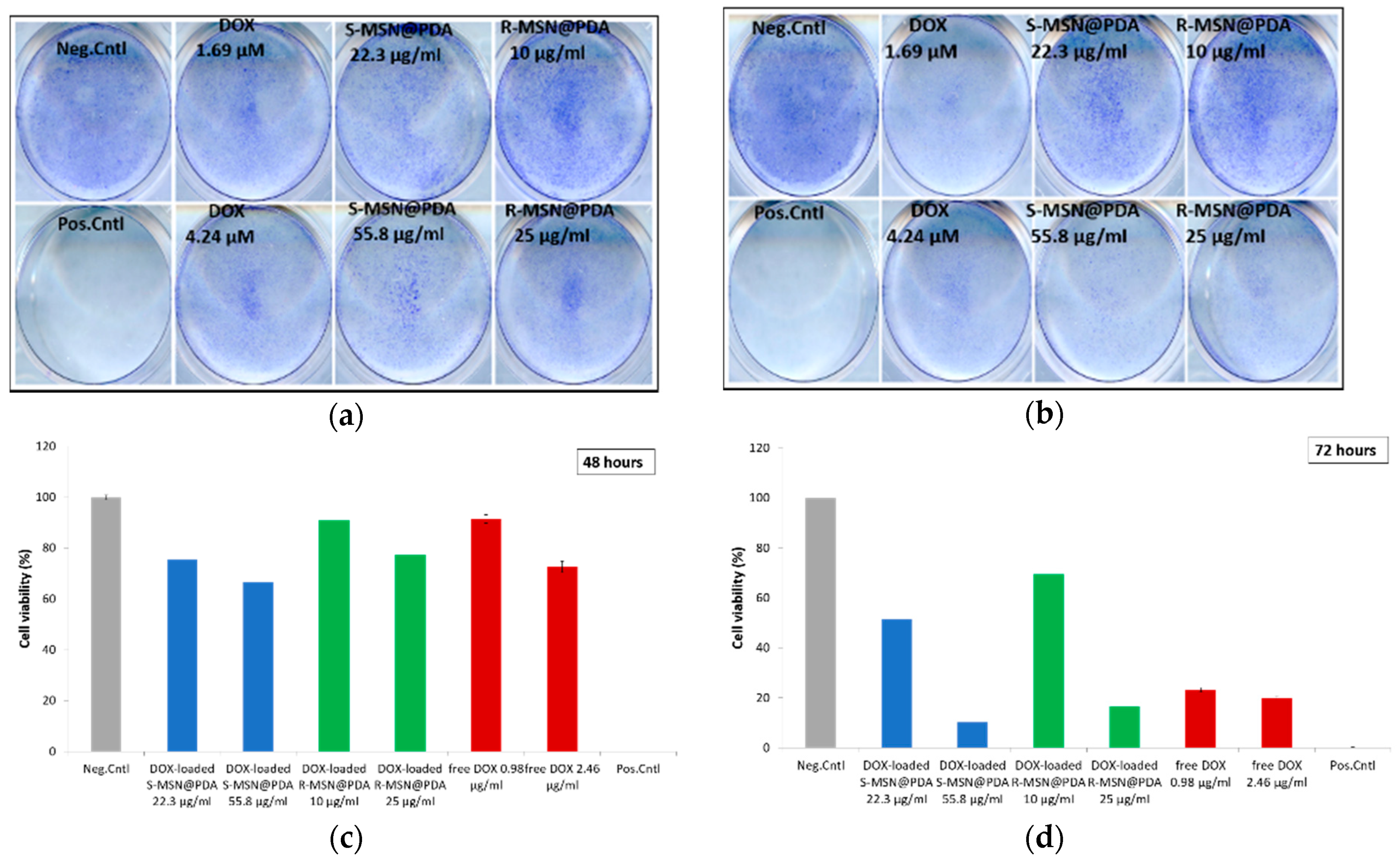
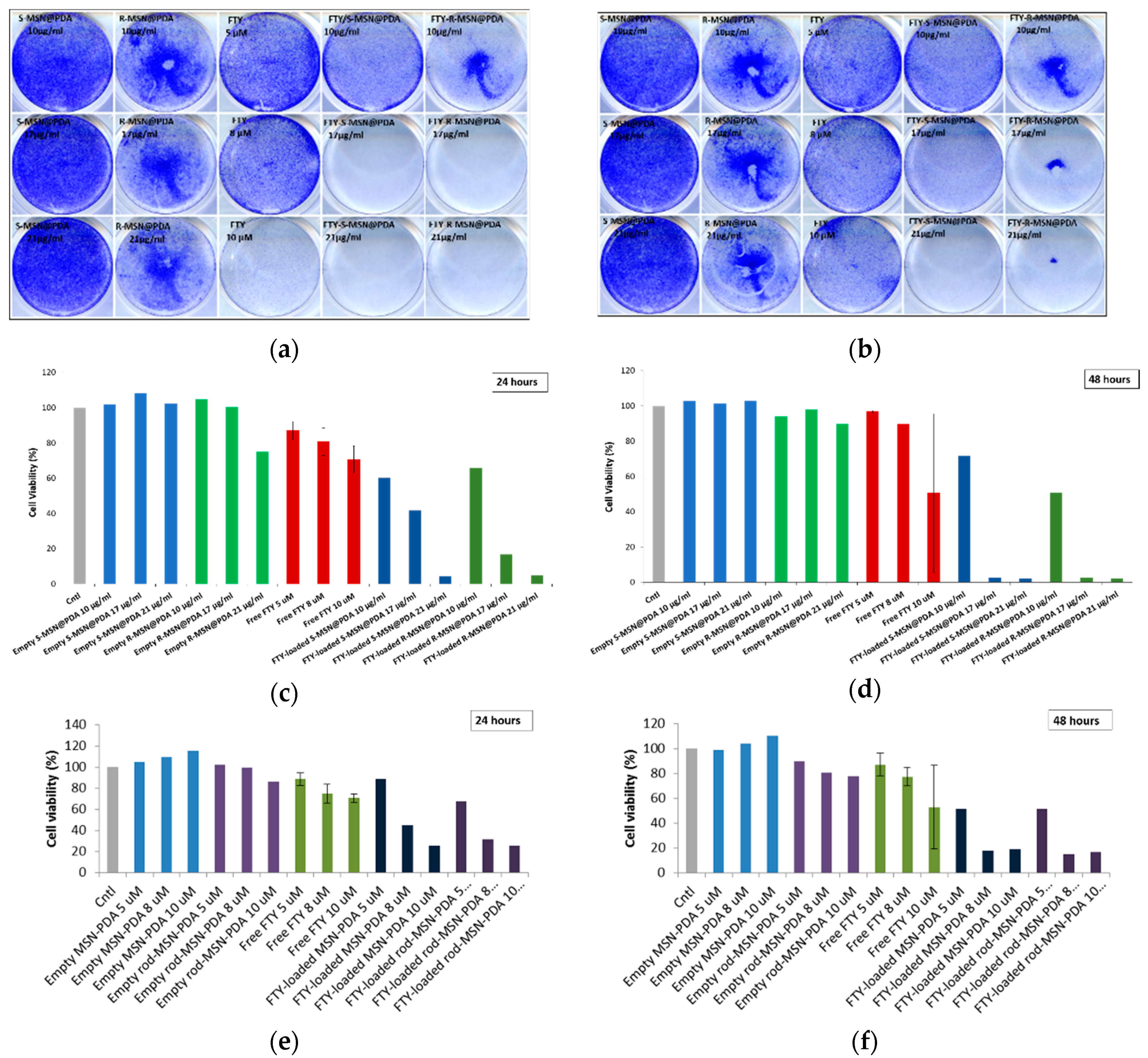
2.2.3. Cytotoxicity of Empty and Drug-Loaded MSN@PDA-COP Particles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Polydopamine Coating of MSN
3.2. Characterization of MSN@PDA Particles
3.3. Drug Loading and Loading Degree Determination
3.4. Cell Cultures
3.5. Cellular Uptake of MSN@PDA
3.5.1. Confocal Microscopy
3.5.2. Fluorescent Activated Cell Sorting
3.6. Intracellular Distribution of DOX-Loaded MSN@PDA Particles
3.7. Cytotoxicity
3.7.1. WST-1 for DOX-Loaded Particles
3.7.2. Crystal Violet for DOX-Loaded Particles
3.7.3. Crystal Violet for FTY720-Loaded Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSN | Mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| FTY720 | Fingolimod |
| MSN-NH2 | Amino-functionalized MSN |
| MDA-MB-231 | Human breast cancer cells |
| ML-1 | Human follicular thyroid cancer cells |
| FACS | Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting |
| S-MSN | Spherical shaped MSN |
| R-MSN | Rod shaped MSN |
| PEG-PEI | Polyethylene glycol-Polyethylenimine |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| WST | Water Soluble Tetrazolium salt |
| PI | Propidium Iodide |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid |
References
- Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Sugisaka, M. From Molecular Biology to Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine. Biosystems 2002, 65, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-E.; Kwak, J.-W.; Park, J.W. Nanotechnology for Early Cancer Detection. Sensors 2010, 10, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigneuric, R.; Markey, L.; Nuyten, D.S.A.; Dubernet, C.; Evelo, C.T.A.; Finot, E.; Garrido, C. From Nanotechnology to Nanomedicine: Applications to Cancer Research. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobmyer, S.R.; Iwakuma, N.; Sharma, P.; Moudgil, B.M. What Is Cancer Nanotechnology? In Methods in Molecular Biology; Clifton, N.J., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 624, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Montalti, M.; Petrizza, L.; Prodi, L.; Rampazzo, E.; Zaccheroni, N.; Marchiò, S. Luminescent Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Diagnosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.-T.; Cheng, S.-H.; Souris, J.S.; Chen, C.-T.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lo, L.-W. Theranostic Applications of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Their Organic/Inorganic Hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.P.; Lu, J.; Gothard, C.; Yanes, R.; Thomas, C.R.; Olsen, J.; Stoddart, J.F.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Synthesis of Biomolecule-modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Hydrophobic Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Small 2011, 7, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, D.; Ashley, C.E.; Xue, M.; Carnes, E.C.; Zink, J.I.; Brinker, C.J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Nanocarriers: Biofunctionality and Biocompatibility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Visible Light Responsive Controlled Release Delivery System. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2817–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Soeriyadi, A.H.; Sagnella, S.M.; Lu, X.; Scott, J.A.; Lowe, S.B.; Kavallaris, M.; Gooding, J.J. Stimuli-Responsive Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Release in Response to Various Biological Stimuli. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukappa, A.; Ultimo, A.; de la Torre, C.; Pardo, T.; Sancenón, F.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Polyglutamic Acid-Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enzyme-Controlled Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8507–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Drug Delivery: Advances, Challenges, and Outlook. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Qi, X.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Cai, K. Polydopamine Coatings in Confined Nanopore Space: Toward Improved Retention and Release of Hydrophilic Cargo. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24512–24521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghirov, H.; Karaman, D.; Viitala, T.; Duchanoy, A.; Lou, Y.R.; Mamaeva, V.; Pryazhnikov, E.; Khiroug, L.; De Lange Davies, C.; Sahlgren, C.; et al. Feasibility Study of the Permeability and Uptake of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles across the Blood-Brain Barrier. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwiler, A.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U. The Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Modulator Fingolimod as a Therapeutic Agent: Recent Findings and New Perspectives. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 185, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen Karaman, D.; Gulin-Sarfraz, T.; Hedström, G.; Duchanoy, A.; Eklund, P.; Rosenholm, J.M. Rational Evaluation of the Utilization of PEG-PEI Copolymers for the Facilitation of Silica Nanoparticulate Systems in Biomedical Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 418, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, M.; Aseyev, V.; von Haartman, E.; Karaman, D.Ş.; Mäkilä, E.; Tenhu, H.; Rosenholm, J.; Salonen, J. Size, Stability, and Porosity of Mesoporous Nanoparticles Characterized with Light Scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Rasband, W. ImageJ User Guide. In IJ 1.43r; Centre for Research in Neuroscience, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2010; pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Karukstis, K.K.; Thompson, E.H.Z.; Whiles, J.A.; Rosenfeld, R.J. Deciphering the Fluorescence Signature of Daunomycin and Doxorubicin. Biophys. Chem. 1998, 73, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin Pathways. Pharm. Genom. 2010, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, D.R.; Markowitz, C.E.; Reder, A.T.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Tobias, K. Fingolimod for the Treatment of Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingwersen, J.; Aktas, O.; Kuery, P.; Kieseier, B.; Boyko, A.; Hartung, H.P. Fingolimod in Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Efficacy. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 142, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzola, M.A.; Raheja, R.; Murugaiyan, G.; Rajabi, H.; Kumar, D.; Pertel, T.; Regev, K.; Griffin, R.; Aly, L.; Kivisakk, P.; et al. Identification of a Novel Mechanism of Action of Fingolimod (FTY720) on Human Effector T Cell Function through TCF-1 Upregulation. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalhori, V.; Magnusson, M.; Asghar, M.Y.; Pulli, I.; Törnquist, K. FTY720 (Fingolimod) Attenuates Basal and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Evoked Thyroid Cancer Cell Invasion. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Li, L.; Tang, F. Shape Matters When Engineering Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanomedicines. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, D.S.; Desai, D.; Senthilkumar, R.; Johansson, E.M.; Råtts, N.; Odén, M.; Eriksson, J.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Toivola, D.M.; Rosenholm, J.M. Shape Engineering vs. Organic Modification of Inorganic Nanoparticles as a Tool for Enhancing Cellular Internalization. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 2–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilova, O.N.; Shilov, E.S.; Deyev, S.M. The Effect of Trypan Blue Treatment on Autofluorescence of Fixed Cells. Cytom. Part. A 2017, 91, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Karaman, D.S.E.N.; Prabhakar, N.; Tadayon, S.; Duchanoy, A.; Toivola, D.M.; Rajput, S.; Näreoja, T.; Rosenholm, J.M. Design Considerations for Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticulate Systems in Facilitating Biomedical Applications. Open Mater. Sci. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Teng, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; He, J. The Effect of the Shape of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Cellular Uptake and Cell Function. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, S.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yan, Z.; Lu, G.Q. Hydrophobic Functional Group Initiated Helical Mesostructured Silica for Controlled Drug Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3834–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, C.; Vega, M.A.; Marcelo, G.; Martín Del Valle, E.M. Polydopamine Nanoparticles Kill Cancer Cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 36201–36208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin: An Update on Anticancer Molecular Action, Toxicity and Novel Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2013, 65, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Zhang, J.; Honbo, N.; Karliner, J.S. Doxorubicin Cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 2010, 115, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, M.; Russell, R. Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity: Prevalence, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 7, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octavia, Y.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Janssens, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Moens, A.L. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönberger, J.; Bauer, J.; Spruss, T.; Weber, G.; Chahoud, I.; Eilles, C.; Grimm, D. Establishment and characterization of the follicular thyroid carcinoma cell line ML-1. J. Mol. Med. (Heidelb. Ger.) 2000, 78, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Particle Type | Z-Average Size (nm) (Measured in DI Water) | Polydispersity Index (PdI) | Zeta Potential (mV) (Measured in HEPES Buffer, 25mM, pH 7.4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S-MSN | 181.7 ± 1.45 | 0.191 | 15.3 |
| Rod-MSN | 248.73 ± 3.90 | 0.087 | −20.83 ± 1.05 |
| S-MSN@PDA | 191.77 ± 5.15 | 0.269 | −13.43 ± 0.31 |
| Rod-MSN@PDA | 1678.00 ± 159.45 | 0.313 | −22.93 ± 0.96 |
| S-MSN@PDA-COP | 158.80 ± 1.32 | 0.198 | 3.91 ± 0.49 |
| Rod-MSN@PDA-COP | 219.60 ± 4.92 | 0.097 | 5.74 ± 0.39 |
| Particle Type | Concentration (µg/mL) | Uptake by Cells (MFI) |
|---|---|---|
| S-MSN@PDA | 5 | 30 |
| 10 | 40 | |
| 25 | 70 | |
| 50 | 150 | |
| R-MSN@PDA | 5 | 40 |
| 10 | 60 | |
| 25 | 165 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pada, A.-K.; Desai, D.; Sun, K.; Prakirth Govardhanam, N.; Törnquist, K.; Zhang, J.; Rosenholm, J.M. Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143408
Pada A-K, Desai D, Sun K, Prakirth Govardhanam N, Törnquist K, Zhang J, Rosenholm JM. Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143408
Chicago/Turabian StylePada, Anna-Karin, Diti Desai, Kaiyao Sun, Narayana Prakirth Govardhanam, Kid Törnquist, Jixi Zhang, and Jessica M. Rosenholm. 2019. "Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143408
APA StylePada, A.-K., Desai, D., Sun, K., Prakirth Govardhanam, N., Törnquist, K., Zhang, J., & Rosenholm, J. M. (2019). Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143408






