Improved General and Oral Health in Diabetic Patients by an Okinawan-Based Nordic Diet: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
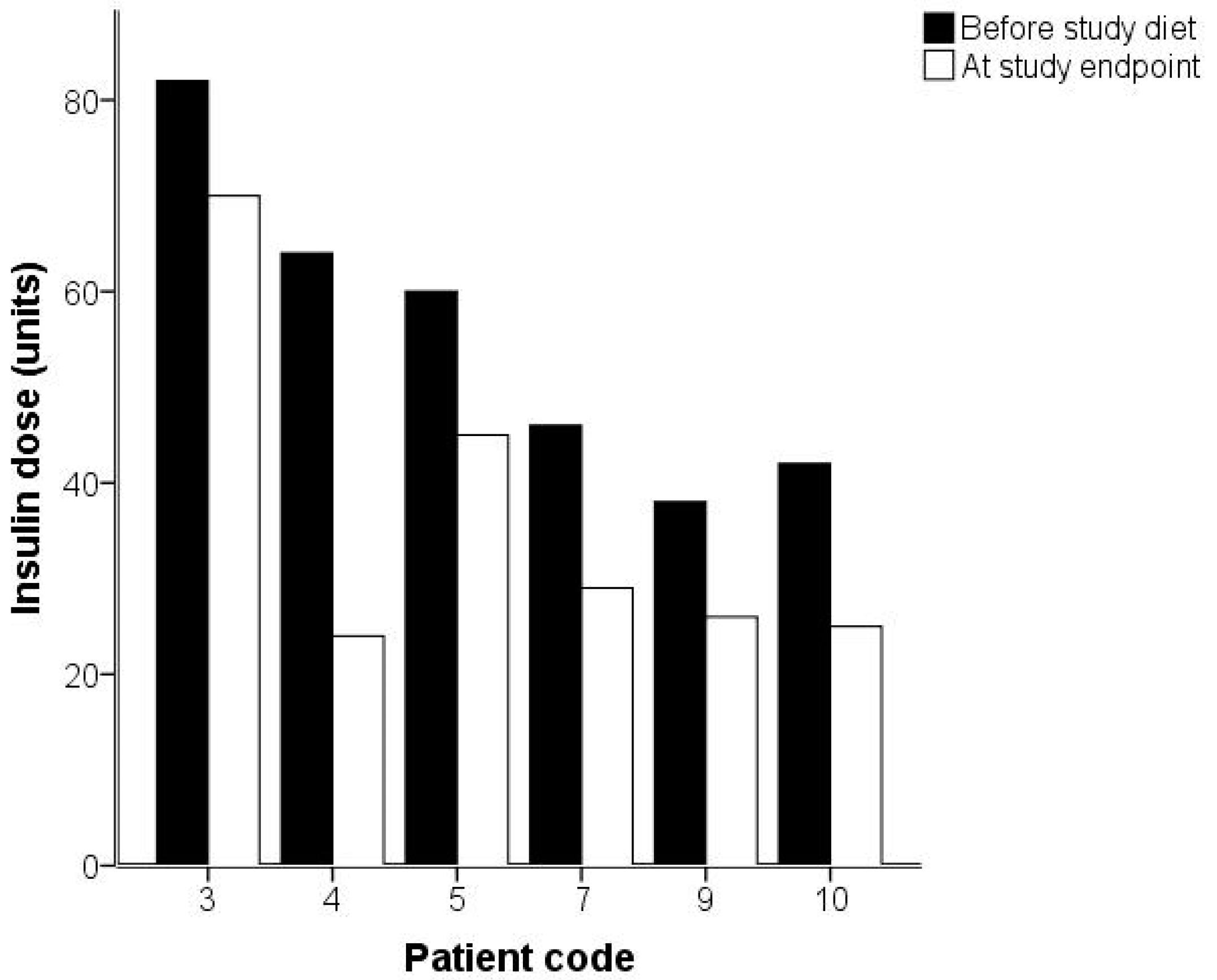
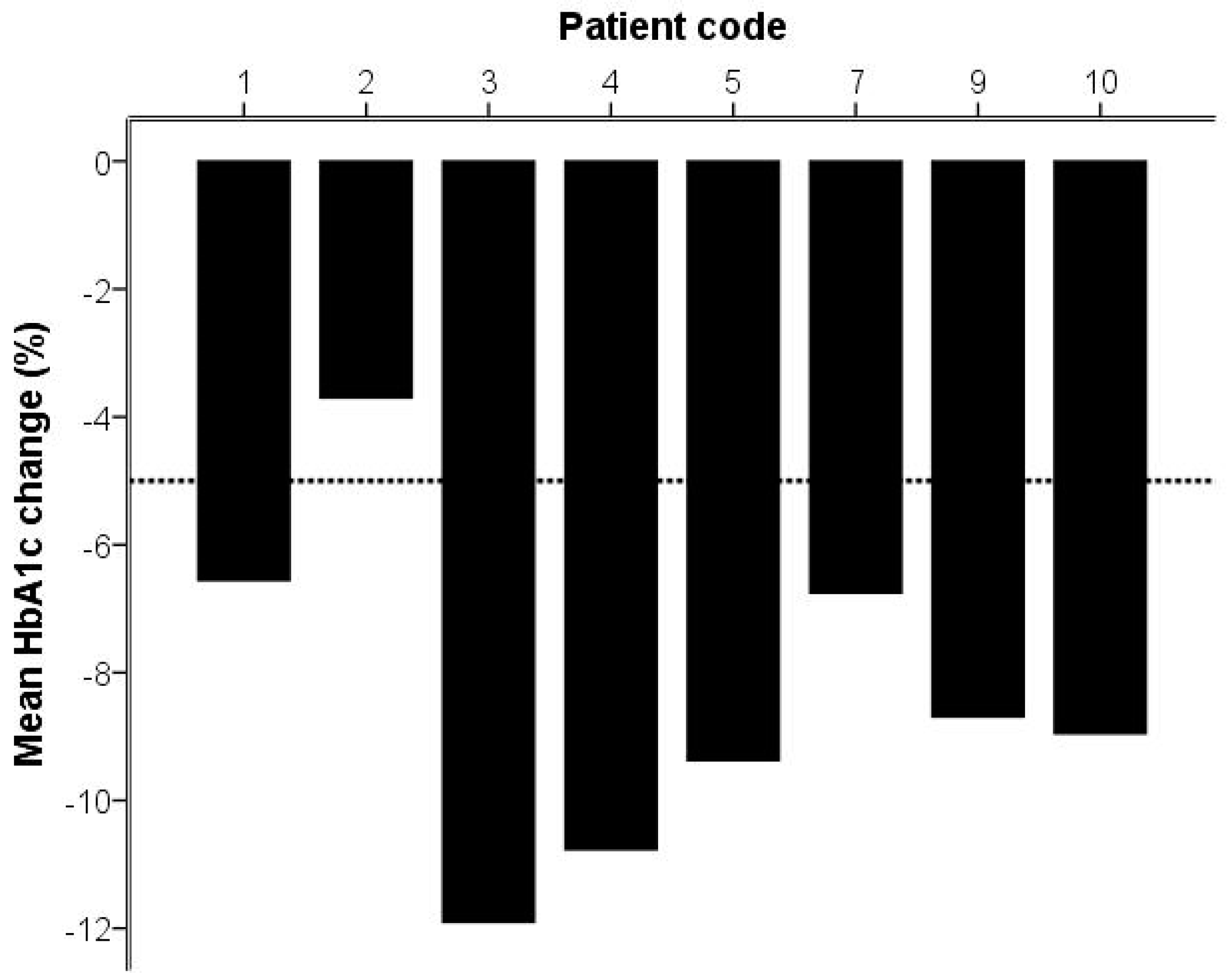
2. Results
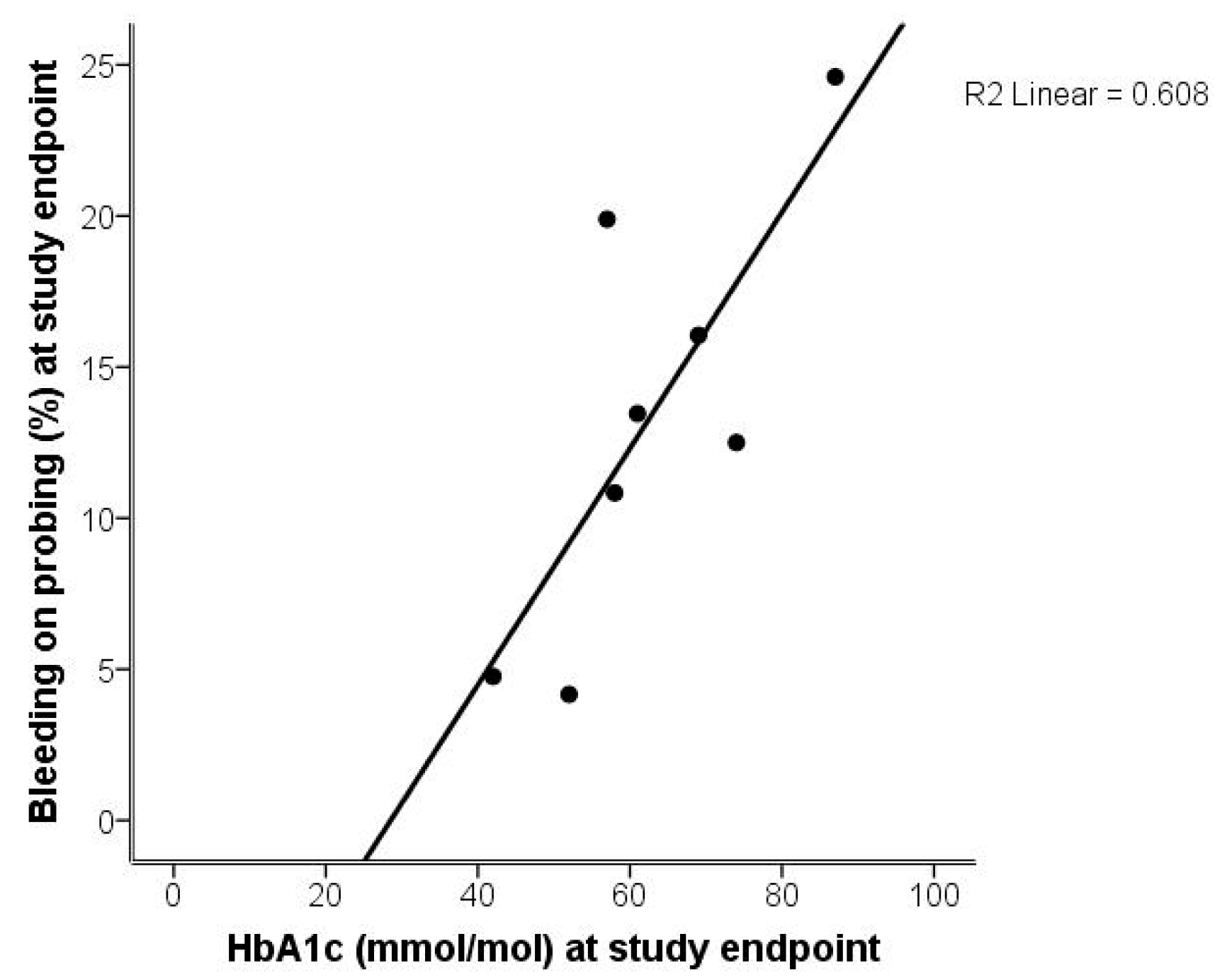
2.1. Analysis of Gingivitis and Periodontitis
2.2. Analysis of Gingivitis and Diabetes
2.3. Analysis of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Serum Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Study Diet
4.2. Medical Examination
4.3. Periodontal Examination
4.4. Cytokine Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Overweight and Obesity; Fact Sheet n 311; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sweden Statistics. Statistics Sweden, Living Conditions Surveys, Physical and Mental Health. Proportion of Persons in Percent by Indicator, Foreign/Swedish Background, Sex and Period; Sweden Statistics: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014.
- Loe, H. Periodontal disease. The sixth complication of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, B.; Gautam, A.; Prasad, B.R.; Kumari, S. Evaluation of micronutrient (zinc, copper and iron) levels in periodontitis patients with and without diabetes mellitus type 2: A biochemical study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kocgozlu, L.; Elkaim, R.; Tenenbaum, H.; Werner, S. Variable cell responses to P. gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, P.I.; Dye, B.A.; Wei, L.; Thornton-Evans, G.O.; Genco, R.J.; CDC Periodontal Disease Surveillance Workgroup. Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabe, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of severe periodontitis in 1990–2010: A systematic review and meta-regression. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, Y.H.; Won, K.C.; Moon, J.S.; Merchant, A.T.; Lee, H.K. Association between diabetes-related factors and clinical periodontal parameters in type-2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2013, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Herrera, M.; Silvestre, F.J.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; Banuls, C.; Rocha, M.; Hernandez-Mijares, A. Involvement of insulin resistance in normoglycaemic obese patients with periodontitis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, C.M.; Munoz, F.; Andriankaja, O.M.; Ritchie, C.S.; Martinez, S.; Vergara, J.; Vivaldi, J.; Lopez, L.; Campos, M.; Joshipura, K.J. Cross-sectional associations of impaired glucose metabolism measures with bleeding on probing and periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, K.; Park, K.; Mima, A.; Katagiri, S.; King, G.L. Obesity-associated gingival vascular inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlstrom, B. Treatment of periodontitis: Key principles include removing subgingival bacterial deposits; providing a local environment and education to support good home care; providing regular professional maintenance. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Debiaggi, M.; Zara, F.; Brerra, R.; Comelli, M.; Bianchi, M.; Pollone, S.R.; Scribante, A. Influence of lingual bracket position on microbial and periodontal parameters in vivo. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. Periodontal health and quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodley, A.; Wood, N.H.; Shangase, S.L. The relationship between periodontitis and diabetes: A brief review. SADJ 2013, 68, 260, 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- Telgi, R.L.; Tandon, V.; Tangade, P.S.; Tirth, A.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, V. Efficacy of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on glycaemic control in type ii diabetic patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013, 43, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, I.L.; Genco, R. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: Consensus report of the joint EFP/AAP workshop on periodontitis and systemic diseases. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, S106–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, A.T.; Georgantopoulos, P.; Howe, C.J.; Virani, S.S.; Morales, D.A.; Haddock, K.S. Effect of long-term periodontal care on hemoglobin A1C in type 2 diabetes. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botero, J.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Agudelo-Suarez, A.A. Periodontal treatment and glycaemic control in patients with diabetes and periodontitis: An umbrella review. Aust. Dent. J. 2016, 61, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisinger, M.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Hou, W.; Schoenfeld, E.; Gelato, M.; Engebretson, S.P.; Reddy, M.S.; Hyman, L. Systemic inflammatory biomarkers and their association with periodontal and diabetes-related factors in the diabetes and periodontal therapy trial, a randomized controlled trial. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, T.C.; Weldon, J.C.; Worthington, H.V.; Needleman, I.; Wild, S.H.; Moles, D.R.; Stevenson, B.; Furness, S.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, Z. Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD004714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, P.M.; Bezerra, J.P.; Miranda, T.S.; Feres, M.; Chambrone, L.; Shaddox, L.M. Local levels of inflammatory mediators in uncontrolled type 2 diabetic subjects with chronic periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Al-Askar, M.; Al-Hezaimi, K. Cytokine profile in the gingival crevicular fluid of periodontitis patients with and without type 2 diabetes: A literature review. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, S.; Imfeld, T.; Schicht, O.; Rath, C.; Persson, R.E.; Persson, G.R. The impact of the stone age diet on gingival conditions in the absence of oral hygiene. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, B. Anti-inflammatory diets. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widén, C.; Coleman, M.; Criten, S.; Karlgren-Andersson, P.; Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R. Consumption of bilberries controls gingival inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10665–10673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woelber, J.P.; Bremer, K.; Vach, K.; Konig, D.; Hellwig, E.; Ratka-Kruger, P.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Tennert, C. An oral health optimized diet can reduce gingival and periodontal inflammation in humans—A randomized controlled pilot study. BMC Oral Health 2016, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, D.C.; Scapagnini, G.; Willcox, B.J. Healthy aging diets other than the mediterranean: A focus on the okinawan diet. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwiche, G.; Hoglund, P.; Roth, B.; Larsson, E.; Sjoberg, T.; Wohlfart, B.; Steen, S.; Ohlsson, B. An okinawan-based nordic diet improves anthropometry, metabolic control, and health-related quality of life in scandinavian patients with type 2 diabetes: A pilot trial. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 32594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, D.; Van Scoyoc, E.; Gerrald, K.; Wines, R.; Amick, H.; Triplette, M.; Runge, T. Drug Class Review: Newer Diabetes Medications, Tzds, and Combinations; Oregon Health & Science University: Portland, OR, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes Care; The Journal of Clinical and Applied Research and Education, 2017, Volume 40, Supplement 1, ISSN 0149-5992. Available online: www.diabetes.org/diabetescare (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Henson, J.; Dunstan, D.W.; Davies, M.J.; Yates, T. Sedentary behaviour as a new behavioural target in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Bazzano, L.A. The low-carbohydrate diet and cardiovascular risk factors: Evidence from epidemiologic studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, B.J.; Willcox, D.C.; Todoriki, H.; Fujiyoshi, A.; Yano, K.; He, Q.; Curb, J.D.; Suzuki, M. Caloric restriction, the traditional okinawan diet, and healthy aging: The diet of the world’s longest-lived people and its potential impact on morbidity and life span. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1114, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, S.; Iwama, N.; Kawabata, T.; Hasegawa, K. Longevity and diet in okinawa, japan: The past, present and future. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2003, 15, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamsson, V.; Reumark, A.; Cederholm, T.; Vessby, B.; Riserus, U.; Johansson, G. What is a healthy nordic diet? Foods and nutrients in the nordiet study. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Lim, L.P. Interrelationships of periodontitis and diabetes: A review of the current literature. J. Dent. Sci. 2012, 7, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, K.H.; Koch, G.; Norderyd, O.; Romao, C.; Wennstrom, J.L. Periodontal conditions in a swedish city population of adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Swed. Dent. J. 2006, 30, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapple, I.L.C.; Milward, M.R.; Ling-Mountford, N.; Weston, P.; Carter, K.; Askey, K.; Dallal, G.E.; De Spirt, S.; Sies, H.; Patel, D.; et al. Adjunctive daily supplementation with encapsulated fruit, vegetable and berry juice powder concentrates and clinical periodontal outcomes: A double-blind RCT. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalowicz, B.S.; Wolff, L.F.; Klump, D.; Hinrichs, J.E.; Aeppli, D.M.; Bouchard, T.J., Jr.; Pihlstrom, B.L. Periodontal bacteria in adult twins. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scribante, A.; Sfondrini, M.F.; Collesano, V.; Tovt, G.; Bernardinelli, L.; Gandini, P. Dental hygiene and orthodontics: Effect of ultrasonic instrumentation on bonding efficacy of different lingual orthodontic brackets. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3714651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, R.; Tolvanen, M.; Suhonen, R.; Lahti, S.; Narhi, T. Knowledge, perceived skills and activities of nursing staff to support oral home care among older domiciliary care clients. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and its role in insulin resistance. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2007, 18, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piemonti, L.; Calori, G.; Lattuada, G.; Mercalli, A.; Ragogna, F.; Garancini, M.P.; Ruotolo, G.; Luzi, L.; Perseghin, G. Association between plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentration and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Sacanella, E.; Arranz, S.; Corella, D.; Castaner, O.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Lapetra, J.; Portillo, M.P.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of the mediterranean diet in the early and late stages of atheroma plaque development. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3674390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordic Council of Ministers. Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012: Integrating Nutrition and Physical Activity; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes, A.; Bantle, J.P.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Albright, A.L.; Apovian, C.M.; Clark, N.G.; Franz, M.J.; Hoogwerf, B.J.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Mayer-Davis, E.; et al. Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: A position statement of the american diabetes association. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S61–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Task Force on Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); Ryden, L.; Grant, P.J.; Anker, S.D.; Berne, C.; Cosentino, F.; Danchin, N.; Deaton, C.; Escaned, J.; et al. Esc guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the easd-summary. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2014, 11, 133–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Patient Code | Age (Years) | Gender | Diabetes Duration (Years) | Tobacco | Complications | Medication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | male | 6 | Quit 2010 | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, myocardial infarction | Metformin |
| 2 | 72 | male | 30 | Never | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, retinopathy | Metformin, insulin, Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| 3 | 51 | female | 19 | Never | Hypertension, sleep apnea syndrome, acromegaly, hyperthyroidism | Levaxin, Genotropin, insulin |
| 4 | 63 | male | 24 | Quit 1991 | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, retinopathy, nephropathy | Metformin, insulin, Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| 5 | 65 | male | 9 | Quit 2006 | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, cerebrovascular insult | Insulin |
| 7 | 63 | female | 16 | Quit 2015 | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension | Metformin, insulin, Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| 9 | 48 | male | 6 | Quit 1990 | Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, sleep apnea syndrome | Metformin, insulin |
| 10 | 54 | male | 10 | Quit 2009 | Hypertension, retinopathy, nephropathy, hepatitis C | Insulin |
| Medical Data | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Study Diet (Week 2; n = 8) | At Study Endpoint (Week 4; n = 8) | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 95.1 | 11.6 | 92.3 | 11.1 | p = 0.01 |
| Body mass index (BMI; kg/m2) | 31.8 | 3.4 | 30.8 | 3.4 | p = 0.01 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 110.6 | 5.9 | 107.6 | 6.6 | p = 0.01 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 143.5 | 11.6 | 138.3 | 14.9 | p = 0.26 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 79.8 | 8.8 | 77.8 | 6.3 | p = 0.61 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 10.4 | 2.7 | 6.8 | 2.2 | p = 0.05 |
| Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c; mmol/mol) | 68.4 | 16.1 | 62.5 | 13.9 | p = 0.01 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 2.8 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 0.8 | p = 0.05 |
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL; mmol/L) | 2.5 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 0.8 | p = 0.05 |
| Bleeding on probing (BOP; %) | 28.5 | 8.7 | 13.3 | 7.0 | p = 0.01 |
| Variable | Cases with Reduction | Before Study Diet (Week 2) | At Study Endpoint (Week 4) | Significance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 25% | 75% | Median | 25% | 75% | |||
| ≥10% reduction | ||||||||
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 7 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 2.1 | p = 0.05 |
| IL12 (pg/mL) | 2 | 54.8 | 27.1 | 64.0 | 37.7 | 27.4 | 61.1 | NS |
| IL13 (pg/mL) | 5 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 4.5 | 4.1 | 5.3 | NS |
| IP10 (pg/mL) | 3 | 482.3 | 327.2 | 776.0 | 372.6 | 279.6 | 915.0 | NS |
| MCP1 (pg/mL) | 5 | 8.2 | 2.6 | 10.3 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 9.0 | p = 0.05 |
| VEGF (pg/mL) | 3 | 182.4 | 92.8 | 230.9 | 157.9 | 106.3 | 174.0 | NS |
| ≥20% reduction | ||||||||
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 6 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 2.1 | p = 0.05 |
| IL12 (pg/mL) | 2 | 54.8 | 27.1 | 64.0 | 37.7 | 27.4 | 61.1 | NS |
| IP10 (pg/mL) | 2 | 482.3 | 327.2 | 776.0 | 372.6 | 279.6 | 915.0 | NS |
| MCP1 (pg/mL) | 5 | 8.2 | 2.6 | 10.3 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 9.0 | p = 0.05 |
| Breakfast | ||||||
| Porridge or sour milk with muesli, sandwich with cheese or ham, fruit | ||||||
| Morning Tea | ||||||
| Arranged individually | ||||||
| Lunch | ||||||
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 |
| French vegetable soup, basil pesto, wholegrains Apple compote, vanilla yoghurt, Igelösa wholegrain sprinkle | Salmon pudding, dill and mustard yoghurt sauce, cauliflower, cabbage salad with quinoa | Carrot and coconut soup, red lentils and prawns, wholegrains | Salmon with saffron sauce, wholegrains, ratatouille | Italian millet nuggets, basil and sundried tomato yoghurt sauce, grilled vegetables | Sesame fried salmon, black rice, sesame chili sauce, broccoli and carrots | Mush room soup, wholegrains, zucchini bread |
| Afternoon Tea | ||||||
| Orange and almonds | Pear and bean truffle with taste of orange | Apple and walnuts | Pear and bean truffle with brandy flavoring | Orange and almonds | Apple and a piece of dark chocolate | Pear and walnuts |
| Dinner | ||||||
| Sausage stroganoff, rice, green peas | Aubergine pizza, cabbage salad with lentils, basil pesto with yoghurt sauce | Grilled chicken, mustard sauce, grilled vegetables Chocolate cake, bilberry, whipped cream | Beef stew, mixed vegetables, wholegrains | Pasta with minced chicken-sauce | Potato burgers with feta cheese and sundried tomatoes, grilled vegetables, tomato cream sauce | Cabbage pudding, brown sauce, lingonberries, grilled vegetables |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holmer, H.; Widén, C.; Wallin Bengtsson, V.; Coleman, M.; Wohlfart, B.; Steen, S.; Persson, R.; Sjöberg, K. Improved General and Oral Health in Diabetic Patients by an Okinawan-Based Nordic Diet: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071949
Holmer H, Widén C, Wallin Bengtsson V, Coleman M, Wohlfart B, Steen S, Persson R, Sjöberg K. Improved General and Oral Health in Diabetic Patients by an Okinawan-Based Nordic Diet: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071949
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolmer, Helene, Cecilia Widén, Viveca Wallin Bengtsson, Michael Coleman, Björn Wohlfart, Stig Steen, Rutger Persson, and Klas Sjöberg. 2018. "Improved General and Oral Health in Diabetic Patients by an Okinawan-Based Nordic Diet: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071949
APA StyleHolmer, H., Widén, C., Wallin Bengtsson, V., Coleman, M., Wohlfart, B., Steen, S., Persson, R., & Sjöberg, K. (2018). Improved General and Oral Health in Diabetic Patients by an Okinawan-Based Nordic Diet: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071949





