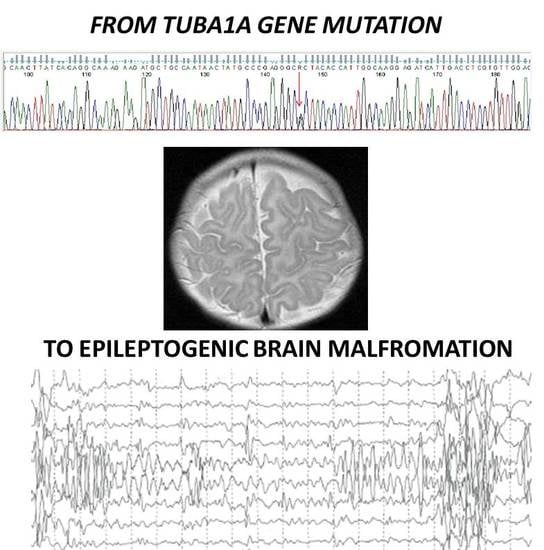
Epileptogenic Brain Malformations and Mutations in Tubulin Genes: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
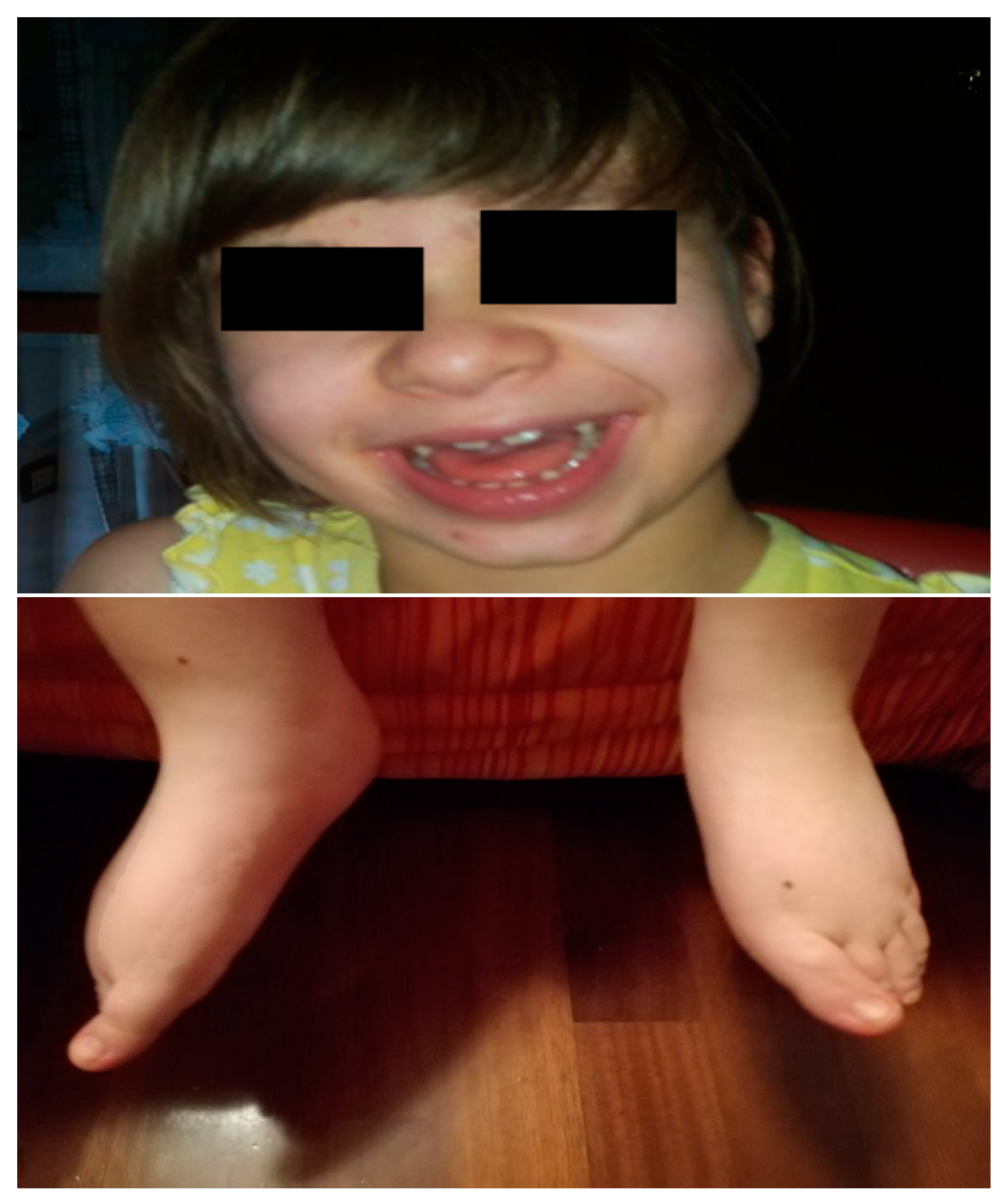
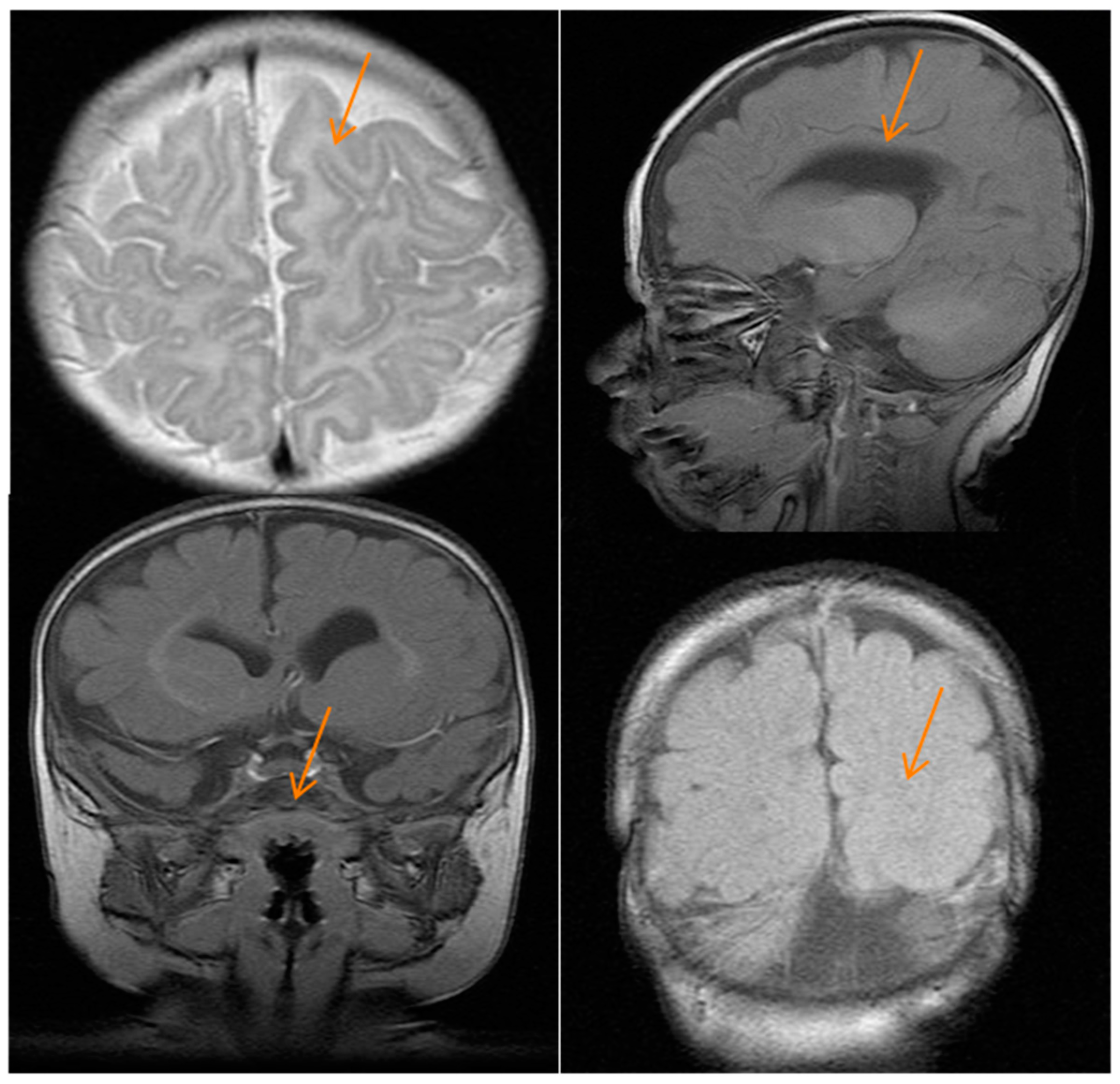
2.1. Case Report
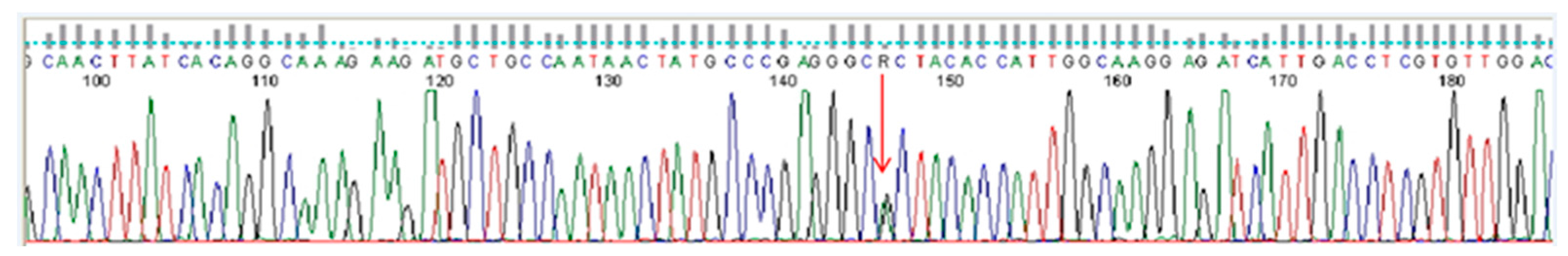
2.2. Genetic Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desikan, R.S.; Barkovich, A.J. Malformations of cortical development. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, K.; Saillour, Y.; Bahi-Buisson, N.; Jaglin, X.H.; Fallet-Bianco, C.; Nabbout, R.; Castelnau-Ptakhine, L.; Roubertie, A.; Attie-Bitach, T.; Desguerre, I.; et al. Mutations in the neuronal β-tubulin subunit TUBB3 result in malformation of cortical development and neuronal migration defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4462–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuss, M.W.; Hansen, A.H.; Landler, L.; Keays, D.A. Brain-specific knockin of the pathogenic Tubb5 E401K allele causes defects in motor coordination and prepulse inhibition. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 323, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, K.; Lebrun, N.; Broix, L.; Tian, G.; Saillour, Y.; Boscheron, C.; Parrini, E.; Valence, S.; Pierre, B.S.; Oger, M.; et al. Mutations in TUBG1, DYNC1H1, KIF5C and KIF2A cause malformations of cortical development and microcephaly. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahi-Buisson, N.; Poirier, K.; Fourniol, F.; Saillour, Y.; Valence, S.; Lebrun, N.; Hully, M.; Bianco, C.F.; Boddaert, N.; Elie, C.; et al. The wide spectrum of tubulinopathies: what are the key features for the diagnosis? Brain 2014, 137, 1676–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutch, C.A.; Poduri, A.; Sahin, M.; Barry, B.; Walsh, C.A.; Barkovich, A.J. Disorders of microtubule function in neurons: Imaging correlates. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuss, M.W.; Leca, I.; Gstrein, T.; Hansen, A.H.; Keays, D.A. Tubulins and brain development–The origins of functional specification. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Rosendahl, D.J.; Najm, J.; Lachmeijer, A.M.; Sztriha, L.; Martins, M.; Kuechler, A.; Haug, V.; Zeschnigk, C.; Martin, P.; Santos, M.; et al. Refining the phenotype of α-1a Tubulin (TUBA1A) mutation in patients with classical lissencephaly. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahi-Buisson, N.; Poirier, K.; Boddaert, N.; Saillour, Y.; Castelnau, L.; Philip, N.; Buyse, G.; Villard, L.; Joriot, S.; Marret, S.; et al. Refinement of cortical dysgeneses spectrum associated with TUBA1A mutations. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, K.; Saillour, Y.; Fourniol, F.; Francis, F.; Souville, I.; Valence, S.; Desguerre, I.; Marie Lepage, J.; Boddaert, N.; Line Jacquemont, M.; et al. Expanding the spectrum of TUBA1A-related cortical dysgenesis to Polymicrogyria. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 381–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrini, E.; Marini, C.; Mei, D.; Galuppi, A.; Cellini, E.; Pucatti, D.; Chiti, L.; Rutigliano, D.; Bianchini, C.; Virdò, S.; et al. Diagnostic Targeted Resequencing in 349 Patients with Drug-Resistant Pediatric Epilepsies Identifies Causative Mutations in 30 Different Genes. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, K. Genomic variant annotation and prioritization with ANNOVAR and Wannovar. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederquist, G.Y.; Luchniak, A.; Tischfield, M.A.; Peeva, M.; Song, Y.; Menezes, M.P.; Chan, W.M.; Andrews, C.; Chew, S.; Jamieson, R.V.; et al. An inherited TUBB2B mutation alters a kinesin binding site and causes polymicrogyria, CFEOM, and axon dysinnervation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 5484–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, V. The β-tubulin gene TUBB2B is involved in a large spectrum of neuronal migration disorders. Clin. Genet. 2010, 77, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuss, M.; Heng, J.I.; Poirier, K.; Tian, G.; Jaglin, X.H.; Qu, Z.; Braun, A.; Gstrein, T.; Ngo, L.; Haas, M.; et al. Mutations in the β-tubulin gene TUBB5 cause microcephaly with structural brain abnormalities. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1554–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, K.; Keays, D.A.; Francis, F.; Saillour, Y.; Bahi, N.; Manouvrier, S.; Fallet-Bianco, C.; Pasquier, L.; Toutain, A.; Tuy, F.P.; et al. Large spectrum of lissencephaly and pachygyria phenotypes resulting from de novo missense mutations in tubulin alpha 1A (TUBA1A). Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.A.; Pilz, D.T.; Babatz, T.D.; Cushion, T.D.; Harvey, K.; Topf, M.; Yates, L.; Robb, S.; Uyanik, G.; Mancini, G.M.; et al. TUBA1A mutations cause wide spectrum lissencephaly (smooth brain) and suggest that multiple neuronal migration pathways converge on alpha tubulins. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.C.; Oostra, A.; Desprechins, B.; De Vlaeminck, Y.; Verhelst, H.; Regal, L.; Verloo, P.; Bockaert, N.; Keymolen, K.; Seneca, S.; et al. TUBA1A mutations: From isolated lissencephaly to familial polymicrogyria. Neurology 2011, 76, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zillhardt, J.L.; Poirier, K.; Broix, L.; Lebrun, N.; Elmorjani, A.; Martinovic, J.; Saillour, Y.; Muraca, G.; Nectoux, J.; Bessieres, B.; et al. Mosaic parental germline mutations causing recurrent forms of malformations of cortical development. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 4, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamuar, S.S.; Walsh, C.A. Somatic mutations in cerebral cortical malformations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mencarelli, A.; Prontera, P.; Stangoni, G.; Mencaroni, E.; Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Epileptogenic Brain Malformations and Mutations in Tubulin Genes: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112273
Mencarelli A, Prontera P, Stangoni G, Mencaroni E, Principi N, Esposito S. Epileptogenic Brain Malformations and Mutations in Tubulin Genes: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112273
Chicago/Turabian StyleMencarelli, Annalisa, Paolo Prontera, Gabriela Stangoni, Elisabetta Mencaroni, Nicola Principi, and Susanna Esposito. 2017. "Epileptogenic Brain Malformations and Mutations in Tubulin Genes: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112273
APA StyleMencarelli, A., Prontera, P., Stangoni, G., Mencaroni, E., Principi, N., & Esposito, S. (2017). Epileptogenic Brain Malformations and Mutations in Tubulin Genes: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112273