Diorganotin(IV) Complexes of Organoselenolato Ligands with Pyrazole Moieties—Synthesis, Structure and Properties †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
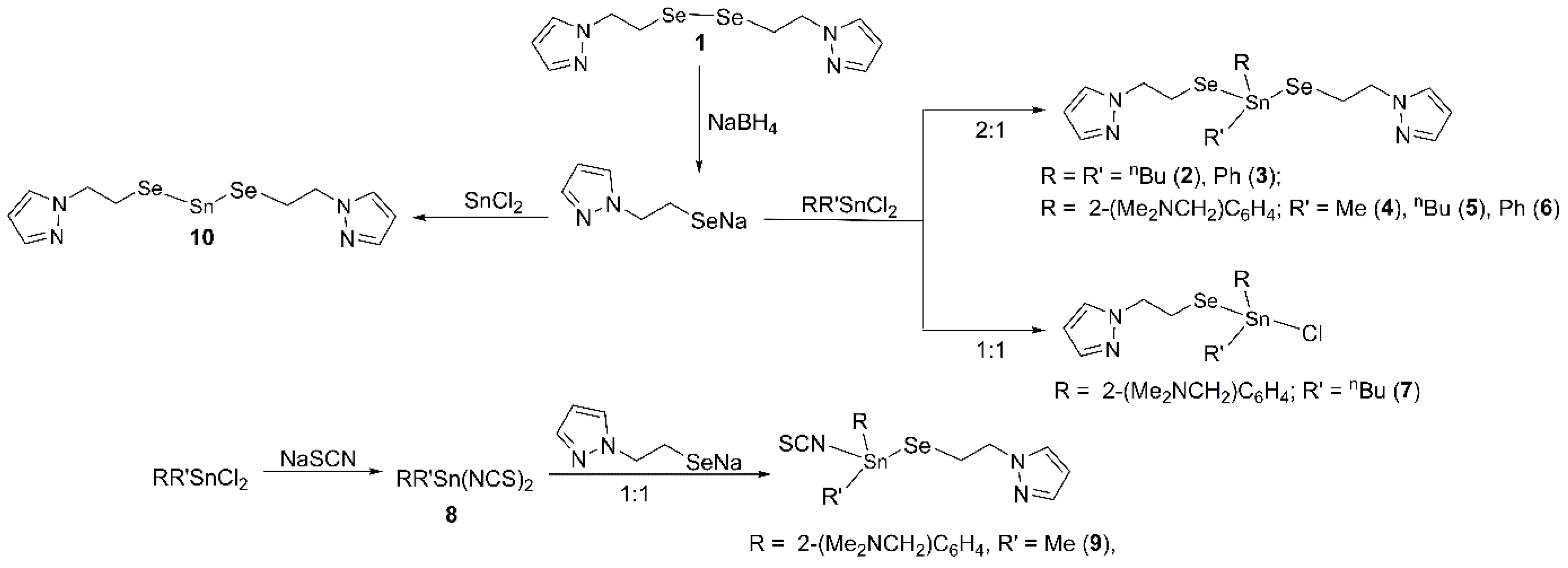
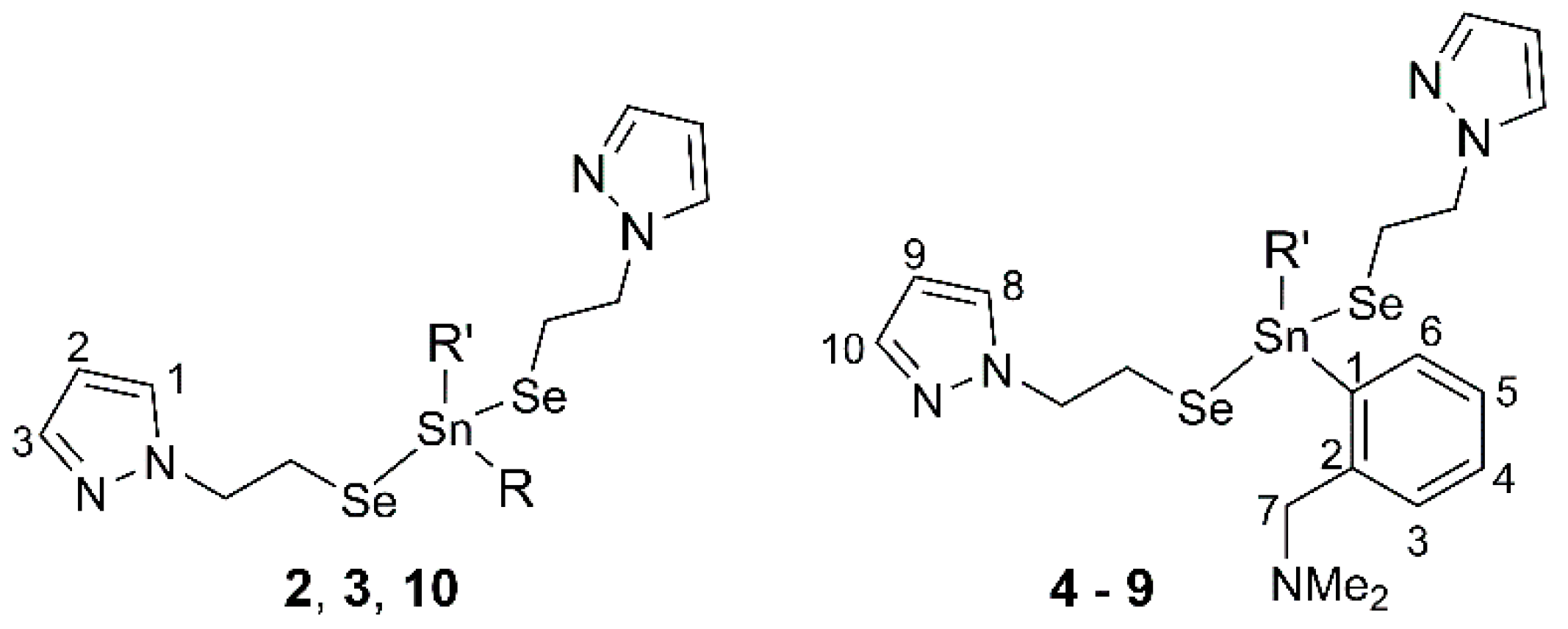
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Spectroscopic Characterization
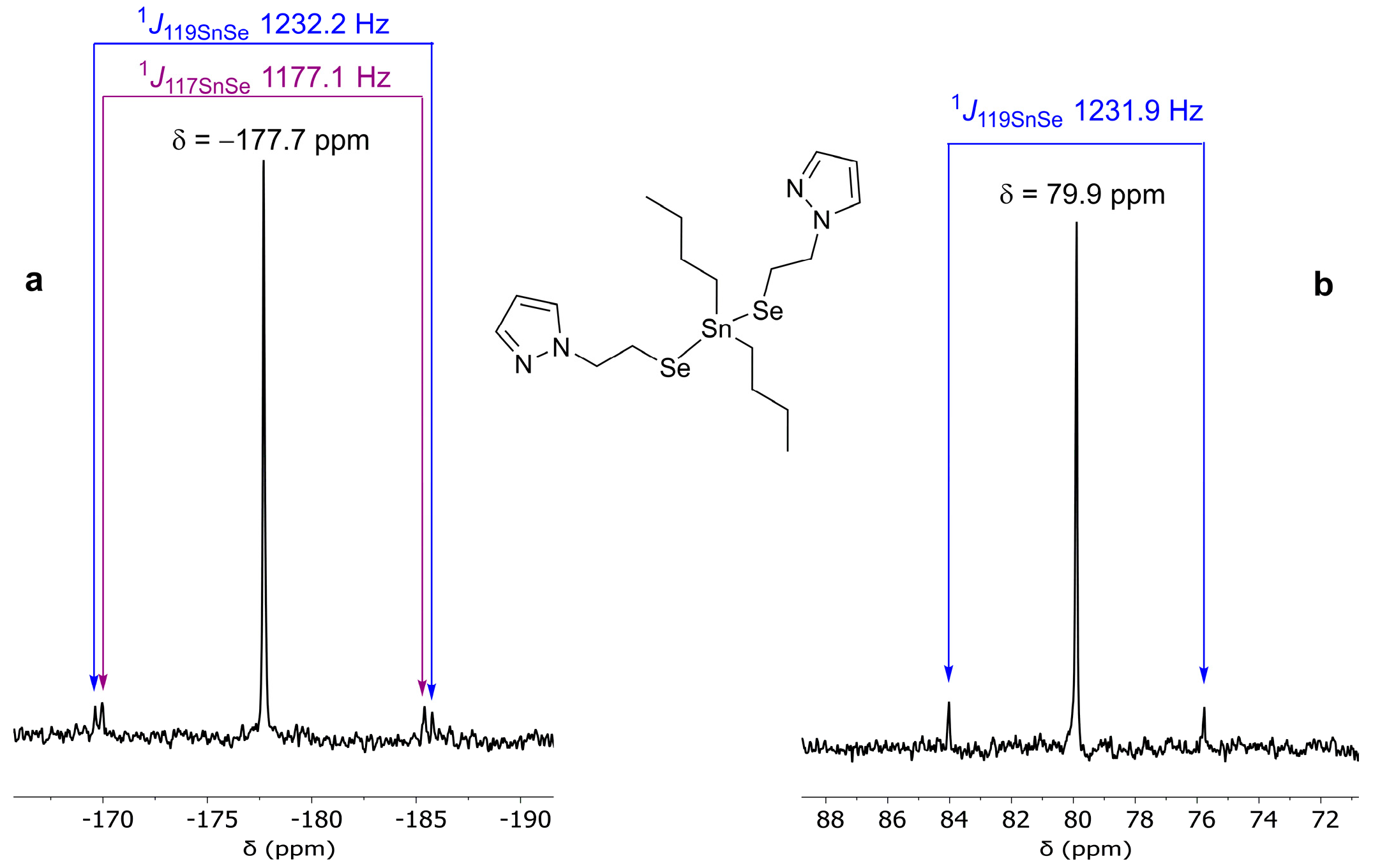
Solution Behaviour
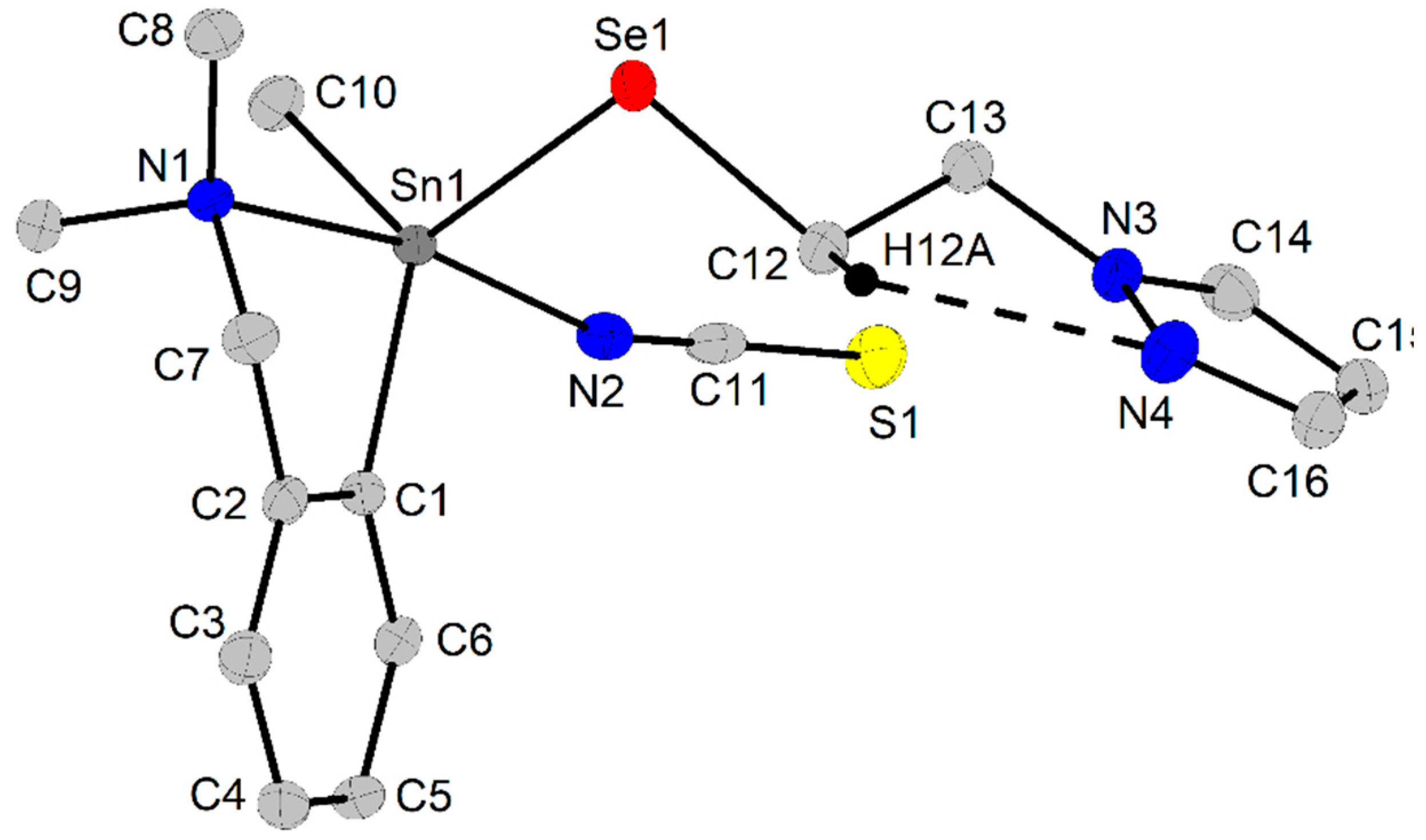
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction Studies
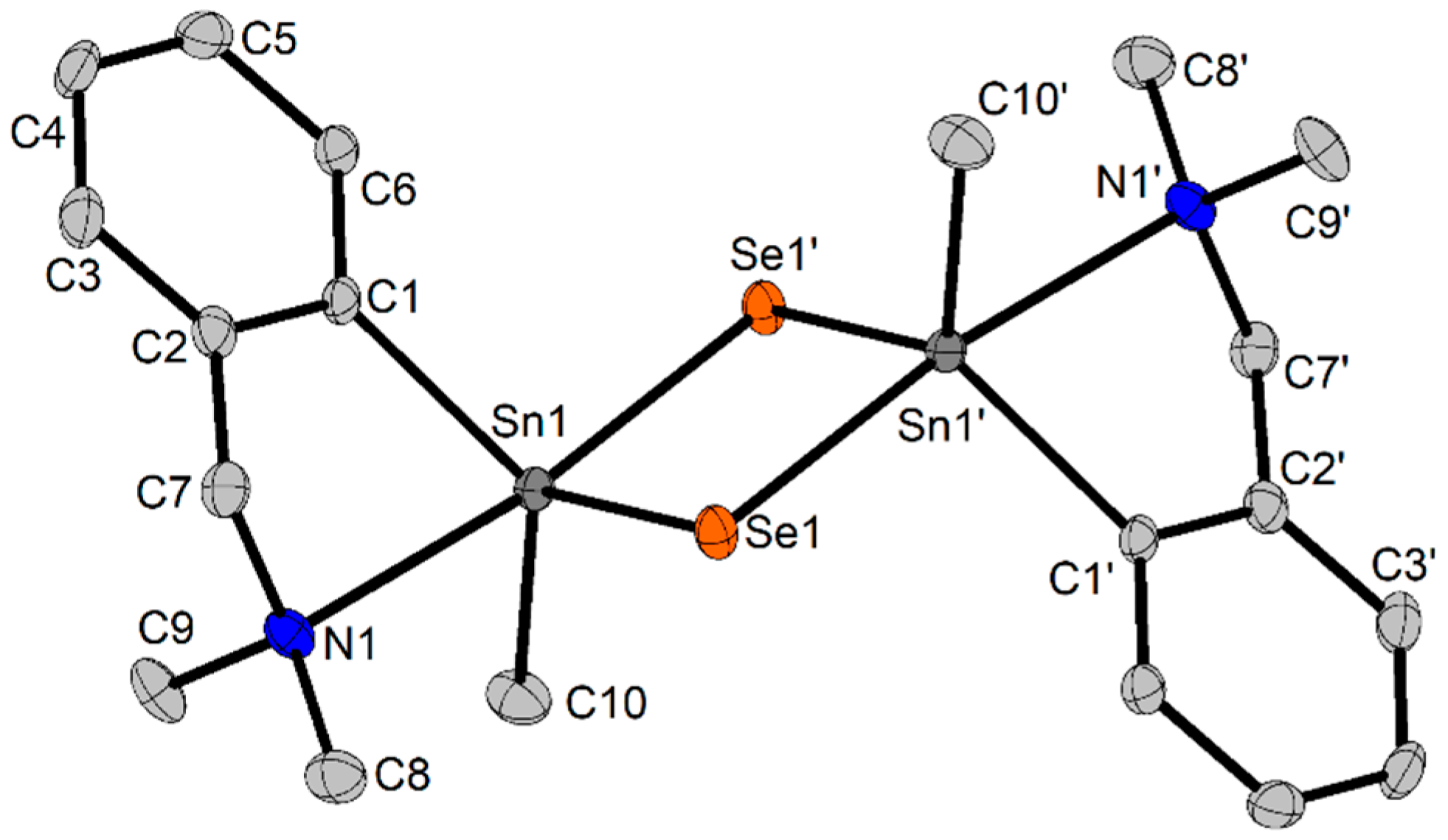
2.3.1. Crystal and Molecular Structure of {[2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)SnSe}2 (4-a) and {[2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](nBu)SnSe}2 (5-a)
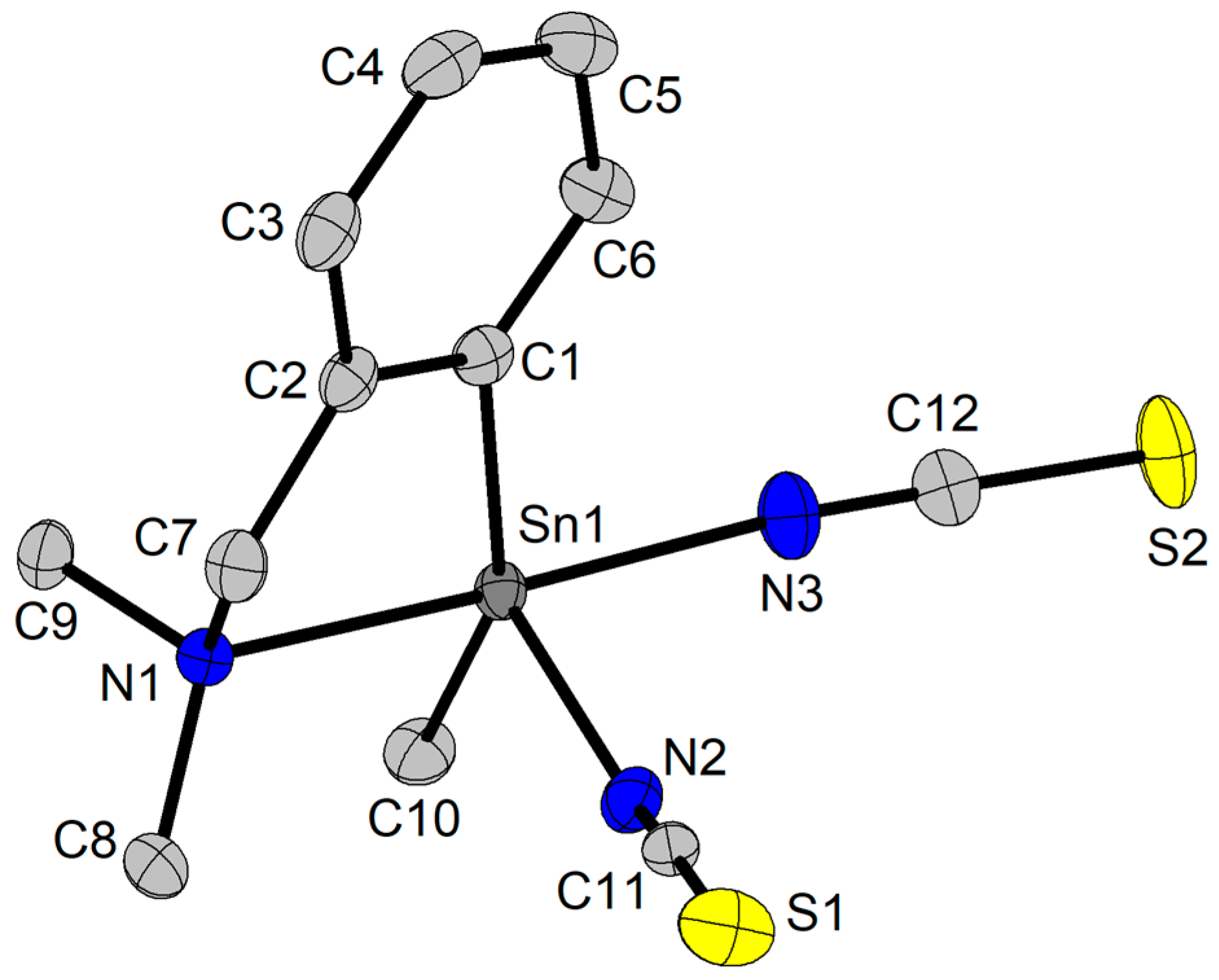
2.3.2. Crystal and Molecular Structure of [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)Sn(NCS)2 (8) and [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)Sn(NCS)(SeCH2CH2pz) (9)
2.4. Thermal Behaviour
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. nBu2Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (2)
3.2.2. Ph2Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (3)
3.2.3. [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (4)
3.2.4. [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](nBu)Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (5)
3.2.5. [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Ph)Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (6)
3.2.6. Synthesis of [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](nBu)SnCl(SeCH2CH2pz) (7)
3.2.7. Synthesis of [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)Sn(SCN)2 (8)
3.2.8. Synthesis of [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4](Me)Sn(SCN)(SeCH2CH2pz) (9)
3.2.9. Synthesis of Sn(SeCH2CH2pz)2 (10)
3.3. Crystal Structure Determination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mugesh, G.; Singh, H.B. Synthetic organoselenium compounds as antioxidants: Glutathione peroxidase activity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kedarnath, G.; Jain, V.K. Pyridyl and pyrimidyl chalcogen (Se and Te) compounds: A family of multi utility molecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1409–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.K.; Priyadarsini, K.I. (Eds.) Organoselenium Compounds in Biology and Medicine: Synthesis, Biological and Therapeutic Treatments; RSC Publishing: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, R.; Oilunkaniemi, R. (Eds.) Selenium and Tellurium Reagents. In Chemistry and Materials Science; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.J.; Zade, S.S.; Singh, H.B.; Sunoj, R.B. Organoselenium Chemistry: Role of Intramolecular Interactions. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4357–4416. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, V.K.; Chauhan, R.S. Chalcogen Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications; Lippolis, V., Santi, C., Lenardao, E.J., Braga, A.L., Eds.; RSC Publishing: London, UK, 2023; Chapter 3; pp. 58–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pellerito, L.; Nagy, L. Organotin(IV)n+ complexes formed with biologically active ligands: Equilibrium and structural studies, and some biological aspects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 224, 111–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikakou, S.K.; Hadjiliadis, N. Antiproliferative and anti-tumor activity of organotin compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gielen, M.; Tiekink, E.R.T. Metallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents: The Use of Metals in Medicine; Gielen, M., Tiekink, E.R.T., Eds.; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2005; p. 421. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.G. Organotin Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Otera, J.; Biesemans, M.; Pinoie, V.; Poelmans, K.; Willem, R. Tin Chemistry: Fundamentals, Frontiers, and Applications; Gielen, M., Davies, A., Pannell, K., Tiekink, E.R.T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter 6; p. 667. [Google Scholar]
- De Lima, G.M. Tin Chemistry: Fundamentals, Frontiers, and Applications; Gielen, M., Davies, A., Pannell, K., Tiekink, E.R.T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter 3; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, V.K.; Kedarnath, G. Applications of metal selenium/tellurium compounds in materials science. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2019, 4, 20170127. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, V.K. Synthesis and characterization of single-source molecular precursors for the preparation of metal chalcogenides. J. Chem. Sci. 2006, 118, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, J.J.; Ng, M.T. Chemistry of Metal Thio- and Selenocarboxylates: Precursors for Metal Sulfide/Selenide Materials, Thin Films, and Nanocrystals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 869–877. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmet, I.Y.; Hill, M.S.; Raithby, P.R.; Johnson, A.L. Tin guanidinato complexes: Oxidative control of Sn, SnS, SnSe and SnTe thin film deposition. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5031–5048. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, H.S.; Abdel Hady, D.A.; Abdel Rahman, K.F.; Youssef, S.B.; El-Shazly, A.A. Optical properties of tin-selenide films. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 1995, 216, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Domingo, G.; Itoga, R.S.; Kannewurf, C.R. Fundamental Optical Absorption in SnS2 and SnSe2. Phys. Rev. 1966, 143, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Hartl, F.; Brune, V.; Lϋggert, S.; Hegemann, C.; van Gerven, D.; Wilhelm, M.; Ji, S.; Choi, H.; Mathur, S. Direct Synthesis of Two-Dimensional SnSe and SnSe2 through Molecular Scale Preorganization. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 6274–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, V.; Raydan, N.; Sutorius, A.; Hartl, F.; Purohit, B.; Gahlot, S.; Bargiela, P.; Burel, L.; Wilhelm, M.; Hegemann, C.; et al. Single source precursor route to nanometric tin chalcogenides. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 17346–17360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seligson, A.L.; Arnold, J. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of homoleptic tin(II) and lead(II) chalcogenolates and conversion to metal chalcogenides. X-ray crystal structures of {Sn[TeSi(SiMe3)3]2}2 and (PMe3)Sn[TeSi(SiMe3)3]. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8214–8220. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Emge, T.J.; Brennan, J.G. Pyridineselenolate Complexes of Tin and Lead: Sn(2-SeNC5H4)2, Sn(2-SeNC5H4)4, Pb(2-SeNC5H4)2, and Pb(3-Me3Si-2-SeNC5H3)2. Volatile CVD Precursors to Group IV–Group VI Semiconductors. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht, S.; Budde, M.; Kienle, L. Nanocrystalline Tin as a Preparative Tool: Synthesis of Unprotected Nanoparticles of SnTe and SnSe and a New Route to (PhSe)4Sn. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 6001–6005. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, S.R.; Boudjouk, P.; McCarthy, G.J. Tin-sulfur and tin-selenium phenylated ring systems as organometallic precursors to tin sulfide and tin selenide. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjouk, P.; Seidler, D.J.; Bahr, S.R.; McCarthy, G.J. Bis(triphenyltin) Chalcogenides as Convenient Precursors to Phase-Pure Binary Semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 2108–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Chuprakov, I.S.; Dahmen, K.H.; Schneider, I.J.; Hagon, J. Bis(bis(trimethylsilyl) methyl)tin(IV) Chalcogenides as Possible Precursors for the Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition of Tin(II) Selenide and Tin(II) Telluride Films. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 3467–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, A.; Kedarnath, G.; Wadawale, A.; Shah, A.Y.; Jain, V.K.; Vishwanadh, B. Diorganotin(IV) 4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidyl selenolates: Synthesis, structures and their utility as molecular precursors for the preparation of SnSe2 nano-sheets and thin films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8367–8376. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.K.; Kedarnath, G.; Wadawale, A.; Betty, C.A.; Vishwanadh, B.; Jain, V.K. Diorganotin(IV) 2-pyridyl selenolates: Synthesis, structures and their utility as molecular precursors for the preparation of tin selenide nanocrystals and thin films. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 12129–12138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.; Karmakar, G.; Wadawale, A.; Shah, A.Y.; Kedarnath, G.; Srivastava, A.P.; Singh, V.; Jain, V.K. Facile one-pot synthesis of tin selenide nanostructures using diorganotin bis (5-methyl-2-pyridylselenolates). J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 873, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kevin, P.; Malik, S.J.; Malik, M.A.; O’Brien, P. The aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of SnSe and Cu2SnSe3 thin films from molecular precursors. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14328–14330. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.D.; Aamir, M.; Sohail, M.; Sher, M.; Baig, N.; Akhtar, J.; Malik, M.A.; Revaprasadu, N. Bis(selenobenzoato)dibutyltin(IV) as a single source precursor for the synthesis of SnSe nanosheets and their photo-electrochemical study for water splitting. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5465–5473. [Google Scholar]
- Mairychova, B.; Svoboda, T.; Erben, M.; Rûžička, A.; Dostál, L.; Jambor, R. Intramolecularly Coordinated Group 14 and 15 Chalcogenites. Organometallics 2013, 32, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Bouska, M.; Strizk, L.; Dostál, L.; Rûžička, A.; Lycka, A.; Benes, L.; Vlcek, M.; Prikryl, J.; Knotek, P.; Wagner, T.; et al. Mixed Organotin(IV) Chalcogenides: From Molecules to Sn-S-Se Semiconducting Thin Films Deposited by Spin-Coating. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Singh, H.B.; Butcher, R.J. Stable Selenenium Cations: Unusual Reactivity and Excellent Glutathione Peroxidase-Like Activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 637–647. [Google Scholar]
- Svec, P.; Rûžičkova, Z.; Vlasak, P.; Turek, J.; De Proft, F.; Rûžička, A. Expanding the family of C,N-chelated organotin(IV) pseudohalides: Synthesis and structural characterization. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 801, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairychova, B.; Svoboda, T.; Stepnicka, P.; Rûžička, A.; Havenith, R.W.A.; Alonso, M.; De Proft, F.; Jambor, R.; Dostál, L. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of Heteroboroxines with MB2O3 Core (M = Sb, Bi, Sn). Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, R.A.; Jurkschat, K.; Silvestru, C. Solid-State Structure and Behaviour in Solution of Hypervalent Organotin(IV) Derivatives Containing 2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4 Moieties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, R.A.; Rotar, A.; Schürmann, M.; Jurkschat, K.; Silvestru, C. Hypercoordinated Organotin(IV) Halides Containing 2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4 Groups: {2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4}2SnX2 (X = F, Cl, Br, I) and {2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4}R2SnX (R = Me, Ph; X = F, Cl, Br, I) and Their Solution Behaviour and Solid-State, Hydrogen-Bonding-Based Supramolecular Architecture. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, R.A.; David, M.; Licarete, E.; Banciu, M.; Silvestru, A. On the coordination behaviour of diorganoselenium ligands based on amino and azole functionalities: Silver(I) complexes with relevance for biological applications. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 23019–23029. [Google Scholar]
- Fourmigue, M.; Dhaka, A. Chalcogen bonding in crystalline diselenides and selenocyanates: From molecules of pharmaceutical interest to conducting materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 403, 213084. [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumar, K.; Singh, H.B. Adaptive responses of sterically confined intramolecular chalcogen bonds. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7027–7042. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, A.; Silvestru, A. Organoselenium compounds with N,C,N pincer groups. Synthesis, structure and reactivity. Polyhedron 2019, 160, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, A.; Wang, L.; Dorcet, V.; Roisnel, T.; Carpentier, J.-F.; Silvestru, A.; Sarazin, Y. On the coordination chemistry of organochalcogenolates RNMe2^E- and RNMe2^E^O- (E = S, Se) onto lead(II) and lighter divalent tetrel elements. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 16459–16474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coza, C.; Stegarescu, A.; Suteu, R.; Silvestru, A. Organotin(IV) hypervalent pseudohalides. Synthesis and structural characterization. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 777, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiorean, N.; Coza, C.; Pop, A.; Silvestru, A. New hypercoordinated diorganotin(IV) compounds with dithiocarbamato ligands. Synthesis and structural characterization. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 880, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, R.A.; Licarete, E.; Banciu, M.; Silvestru, A. Organoselenium compounds containing pyrazole or phenylthiazole groups:Synthesis, structure, tin(IV) complexes and antiproliferative activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4252. [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart, T.P.; Manders, W.F.; Zuckerman, J.J. Structural investigations by solid-state C-13 NMR. Dependence of [1J(119Sn,13C)] on the Me-Sn-Me angle in methyltin(IV)s. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 4546–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, J.; Lycka, A. Dependence of 1J(119Sn,13C) on the C―Sn―C Angle in n-Butyltin(IV) Compounds. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1986, 118, L15–L16. [Google Scholar]
- Wrackmeyer, B.; Maisel, H.E.; Milius, W.; Herberhold, M. 1,3,2-Diazastanna-[3]ferrocenophanes bearing alkyn-1-yl groups at tin and their 1,1-organoboration with triethylborane—Molecular structure of a novel spirotin compound. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 680, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Holeček, J.; Nádvorník, M.; Handlír, K.; Lycka, A. 13C and 119Sn NMR spectra of di-n-butyltin(IV) compounds. J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 315, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Holeček, J.; Lycka, A.; Handlír, K.; Nádvorník, M. 13C and 119Sn NMR spectra of diphenyl- and dibenzyltin(IV) compounds and their complexes. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1990, 55, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Van Koten, G.; Jastrzebski, J.T.B.H.; Noltes, J.G. Arylcopper compounds ArnCun as intermediates in organometallic synthesis. Single-step synthesis and dynamic NMR spectroscopy of diorganotin dihalides Ar2-nRnSnX2 (Ar = 2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4 or (S)-2-(Me2NCHMe)C6H4; n = 0 or 1). J. Organomet. Chem. 1979, 177, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Someșan, A.-A.; Varga, R.A.; Silvestru, C. [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4]SnMeCl2 and its hydrolysis product, [{2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4}SnMe(OH)(OH2)]22+·2Br−—Solution and solid state characterization. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2014, 59, 931–938. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, P.; Padělková, Z.; Kolářová, L.; Císařová, I.; Rûžička, A.; Holeček. Structure and properties of double-C,N-chelated tri and diorganotin(IV) halides. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 19, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Iwaoka, M.; Tomoda, S. Nature of the Intramolecular Se···N Nonbonded Interaction of 2-Selenobenzylamine Derivatives. An Experimental Evaluation by 1H, 77Se, and 15N NMR Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8077–8084. [Google Scholar]
- Otera, J. 119Sn Chemical Shifts in Five- and Six Coordinate Organotin Chelates. J. Organomet. Chem. 1981, 221, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, G.; Chaplin, T.; Hibbert, T.G.; Kana, A.T.; Mahon, M.F.; Molloy, K.C.; Worsley, I.D.; Parkin, I.P.; Price, L.S. Synthesis and thermal decomposition studies of homo- and heteroleptic tin(IV) thiolates and dithiocarbamates: Molecular precursors for tin sulfides. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 2002, 6, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S. A cartography of the van der Waals territories. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 8617–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, C.W.; Martin, J.C.; Arduengo, A.J., III; Lau, W.; Alegria, A.; Kochi, K. An electrically neutral. sigma.-sulfuranyl radical from the homolysis of a perester with neighboring sulfenyl sulfur: 9-S-3 species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7753–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, N.T.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, N.G.; Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R.M.; Hutton, A.T. (Eds.) . Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Cryst. 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Eichhöfer, A.; Jiang, J.-J.; Sommer, H.; Weigend, F.; Fuhr, O.; Fenske, D.; Su, C.Y.; Buth, G. 1-D-Tin(II) Phenylchalcogenolato Complexes ∞1[Sn(EPh)2] (E = S, Se, Te) – Synthesis, Structures, Quantum Chemical Studies and Thermal Behaviour. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Ahmet, I.Y.; Johnson, A.L.; Kociok-Köhn, G. Tin(IV) Chalcogenide Complexes: Single Source Precursors for SnS, SnSe and SnTe Nanoparticle Synthesis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4711–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, G.; Halankar, K.K.; Tyagi, A.; Mandal, B.P.; Wadawale, A.; Kedarnath, G.; Srivastava, A.P.; Singh, V. Dimethyltin(iv)-4,6-dimethyl-2-pyridylselenolate: An efficient single source precursor for the preparation of SnSe nanosheets as anode material for lithium ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 15730–15742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MestReC and MestReNova, Mestrelab Research S.L. Available online: https://mestrelab.com/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Qual Browser Thermo Xcalibur, Version 2.1.0 SP1.1160; Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011.
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, H.; Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND—Crystal and Molecular Structure Visualization. In Crystal Impact GbR; Kreuzherrenstr: Bonn, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | 13C{1H} NMR | |
|---|---|---|
| 1J(119Sn,13C) | C–Sn–C | |
| 2 | 341.4 | 106.7° a 108.8° b |
| Cpd. | δ77Se (ppm) | 1J117SnSe/1J119SnSe (Hz) | δ119Sn (ppm) | 1JSe119Sn (Hz) | RR′SnCl2 | δ119Sn (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 292.1 [25] | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | −177.7 | 1177.1 (117Sn) 1232.2 (119Sn) | 79.9 | 1231.9 | nBu2SnCl2 | 126.3 [50] |
| 3 | −182.3 | 1261.7 (117Sn) 1321.3 (119Sn) | −23.5 | 1320.3 | Ph2SnCl2 | −26.7 [51] |
| 4 | −163.6 | 1066.3 (117Sn) 1117.5 (119Sn) | −74.2 | 1116.4 | R′MeSnCl2 | −97.3 [52,53] |
| 5 | −161.0 | 1317.4 (117Sn) 1375.5 (119Sn) | −104.8 | 1380.5 | R′nBuSnCl2 | −103 [37] |
| 6 | −182.4 | 1121.7 (117Sn) 1173.4 (119Sn) | −107.2 | 1171.5 | R′PhSnCl2 | −170 [54] |
| 7 | −160.9 | 1317.4 (117Sn) 1374.9 (119Sn) | −104.6 | 1374.4 | R′nBuSnCl2 | −103 |
| 8 | −252.7 | R′MeSnCl2 | −97.3 | |||
| 9 | −167.1 | 1353.7 (117Sn) 1422.3 (119Sn) | −161.8 | 1427.1 | R′MeSn(SCN)2 | −252.7 |
| 10 | −11.5 | 1447.1 (117Sn) 1513.5 (119Sn) | −167.6 | 1511.4 |
| Bond/Angle | 4-a | 5-a | 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn1–Se1 | 2.5033(3) | 2.5317(2) | Sn1–Se1 | 2.5298(3) |
| Sn1–Se1′ | 2.6545(3) | 2.6475(4) | Sn1–N1 | 2.4110(3) |
| Sn1–N1 | 2.5633(3) | 2.6046(2) | Sn1–N2 | 2.2410(2) |
| Sn1–C1 | 2.1434(2) | 2.1528(1) | Sn1–C1 | 2.1231(2) |
| Sn1–C10 | 2.1365(2) | 2.1662(1) | Sn1–C10 | 2.1202(2) |
| Se1–Se1′ | 3.7960(4) | 3.8025(5) | N2–C11 | 1.1354(1) |
| Sn1–Sn1′ | 3.4952(4) | 3.5183(4) | S1–C11 | 1.6273(2) |
| Se1–Sn1–Se1′ | 94.73(1) | 94.45(1) | N1–Sn1–Se1 | 89.85(1) |
| N1–Sn1–Se1 | 88.60(1) | 87.11(1) | C1–Sn1–Se1 | 114.92(1) |
| N1–Sn1–Se1′ | 173.16(1) | 172.01(6) | C1–Sn1–C10 | 127.58(1) |
| N1–Sn1–C1 | 73.83(1) | 72.89(1) | C10–Sn1–Se1 | 116.46(1) |
| N1–Sn1–C10 | 85.76(1) | 84.82(1) | N2–Sn1–Se1 | 93.37(1) |
| C1–Sn1–Se1 | 114.27(1) | 111.92(1) | N2–Sn1–C1 | 92.91(1) |
| C1–Sn1–Se1′ | 99.35(1) | 99.30(7) | N2–Sn1–C10 | 93.86(1) |
| C1–Sn1–C10 | 124.23(1) | 123.22(1) | N2–Sn1–N1 | 169.64(1) |
| C10–Sn1–Se1 | 116.50(1) | 118.42(1) | N2–C11–S1 | 179.09(1) |
| C10–Sn1–Se1′ | 98.05(1) | 101.23(7) | ||
| Sn1–Se1–Sn1′ | 85.27(1) | 85.55(1) |
| Bond/Angle | 8a | 8b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sn1–N1 | 2.3926(1) | Sn2–N4 | 2.3804(1) |
| Sn1–N2 | 2.1183(1) | Sn2–N5 | 2.1567(1) |
| Sn1–N3 | 2.1874(1) | Sn2–N6 | 2.1848(1) |
| Sn1–C1 | 2.1082(1) | Sn2–C13 | 2.1178(1) |
| Sn1–C10 | 2.1075(1) | Sn2–C22 | 2.1051(1) |
| N2–C11 | 1.1460(1) | N5–C23 | 1.1615(1) |
| N3–C12 | 1.1605(1) | N6–C24 | 1.1229(1) |
| S1–C11 | 1.6094(1) | S3–C23 | 1.6159(1) |
| S2–C12 | 1.6241(1) | S4–C24 | 1.6229(1) |
| Sn1′–S3 | 3.2876(6) | Sn2–S2 | 3.1441(7) |
| N1–Sn1–N2 | 86.74(1) | N4–Sn2–N5 | 84.37(1) |
| N1–Sn1–N3 | 170.38(1) | N4–Sn2–N6 | 167.92(1) |
| N2–Sn1–N3 | 88.58(1) | N5–Sn2–N6 | 87.47(1) |
| N1–Sn1–C1 | 77.63(1) | N4–Sn2–C13 | 76.63(1) |
| N1–Sn1–C10 | 94.07(1) | N4–Sn2–C22 | 93.64(1) |
| C1–Sn1–C10 | 154.39(1) | C13–Sn2–C22 | 158.17(1) |
| N2–Sn1–C1 | 99.80(1) | N5–Sn2–C13 | 99.24(1) |
| N2–Sn1–C10 | 103.91(1) | N5–Sn2–C22 | 99.18(1) |
| N3–Sn1–C1 | 94.91(1) | N6–Sn2–C13 | 95.97(1) |
| N3–Sn1–C10 | 95.22(1) | N6–Sn2–C22 | 96.45(1) |
| N2–C11–S1 | 177.35(1) | N5–C23–S3 | 178.85(1) |
| N3–C12–S2 | 179.23(1) | N6–C24–S4 | 179.58(1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamas, M.; Butuza, R.A.; Dan, M.; Silvestru, A. Diorganotin(IV) Complexes of Organoselenolato Ligands with Pyrazole Moieties—Synthesis, Structure and Properties. Molecules 2025, 30, 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071648
Tamas M, Butuza RA, Dan M, Silvestru A. Diorganotin(IV) Complexes of Organoselenolato Ligands with Pyrazole Moieties—Synthesis, Structure and Properties. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071648
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamas, Melinda, Roxana A. Butuza, Monica Dan, and Anca Silvestru. 2025. "Diorganotin(IV) Complexes of Organoselenolato Ligands with Pyrazole Moieties—Synthesis, Structure and Properties" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071648
APA StyleTamas, M., Butuza, R. A., Dan, M., & Silvestru, A. (2025). Diorganotin(IV) Complexes of Organoselenolato Ligands with Pyrazole Moieties—Synthesis, Structure and Properties. Molecules, 30(7), 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071648








