c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor IQ-1S as a Suppressor of Tumor Spheroid Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
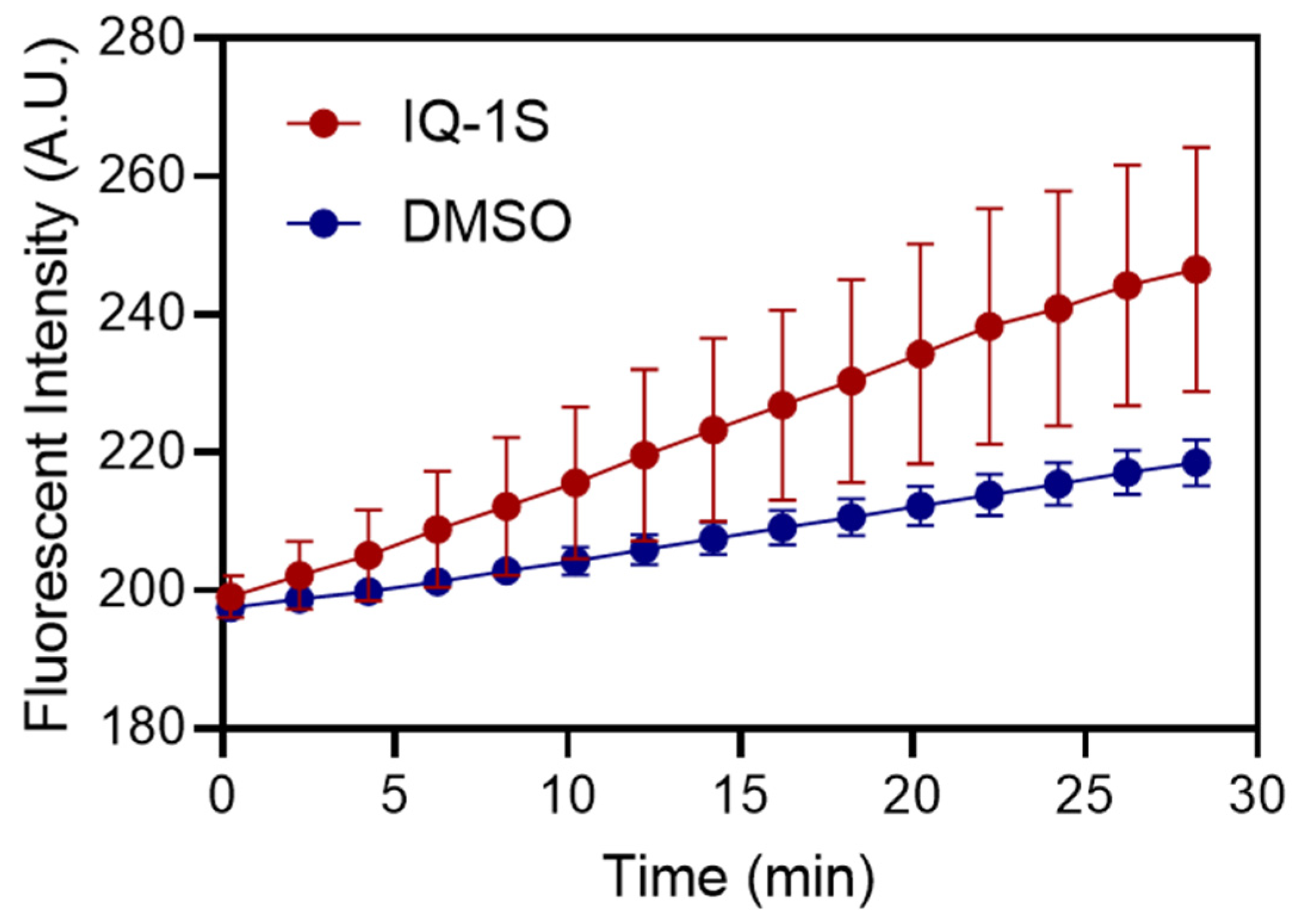
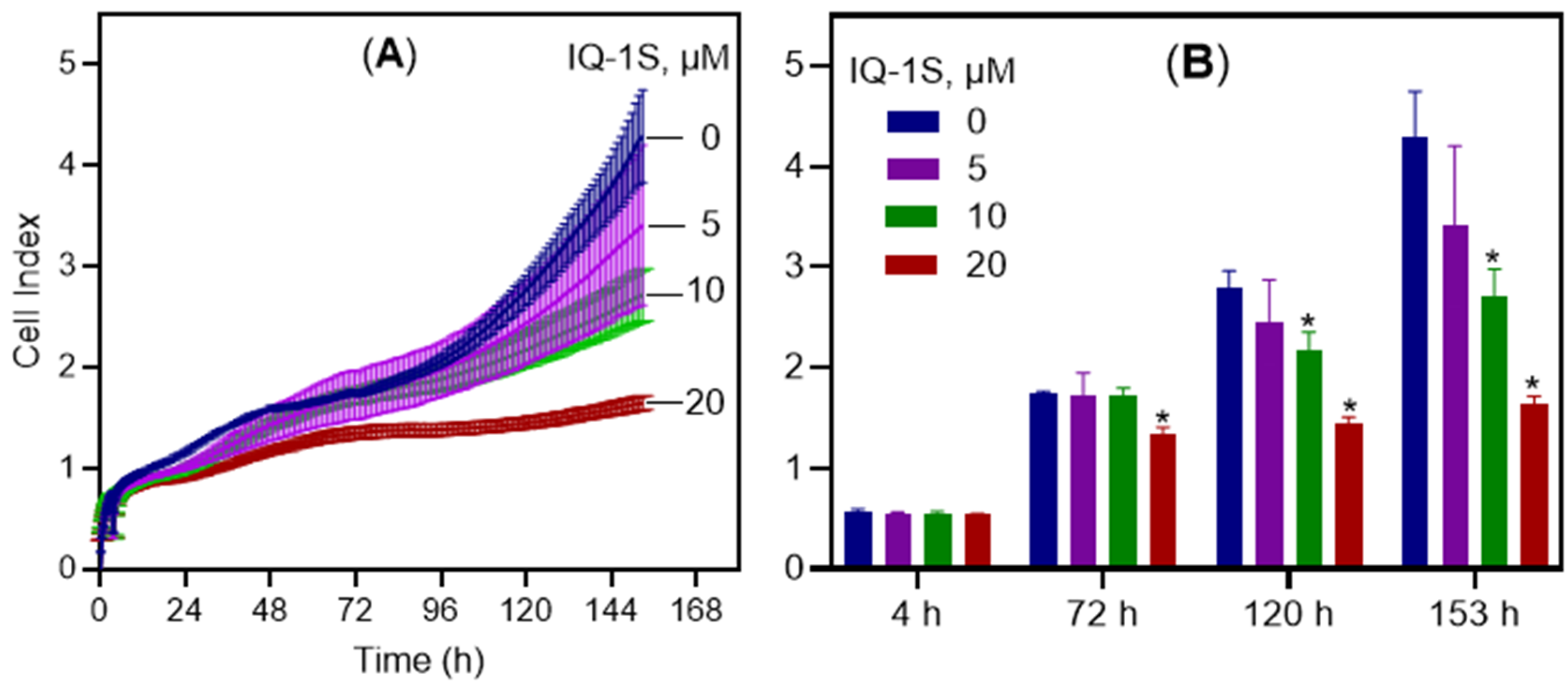
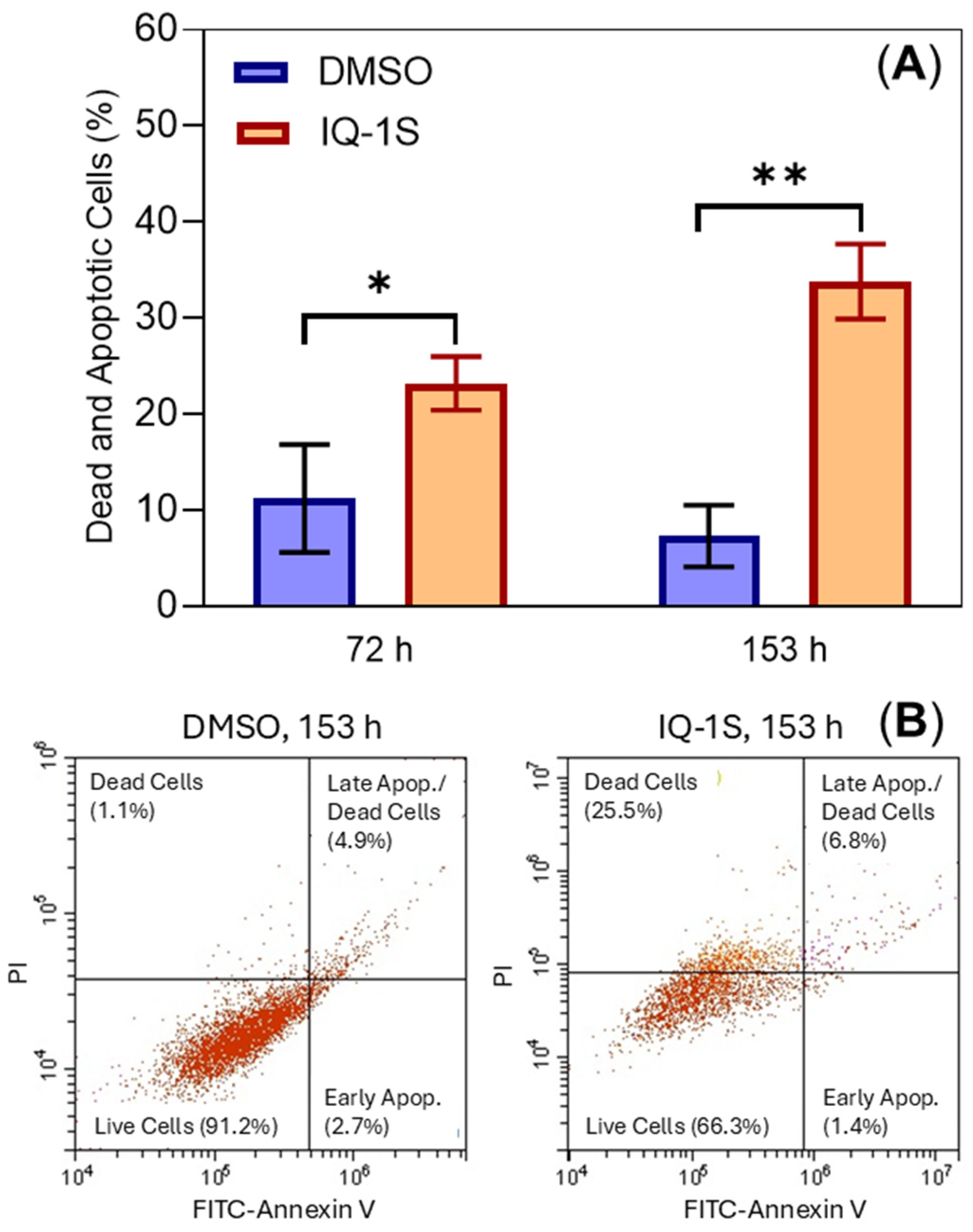
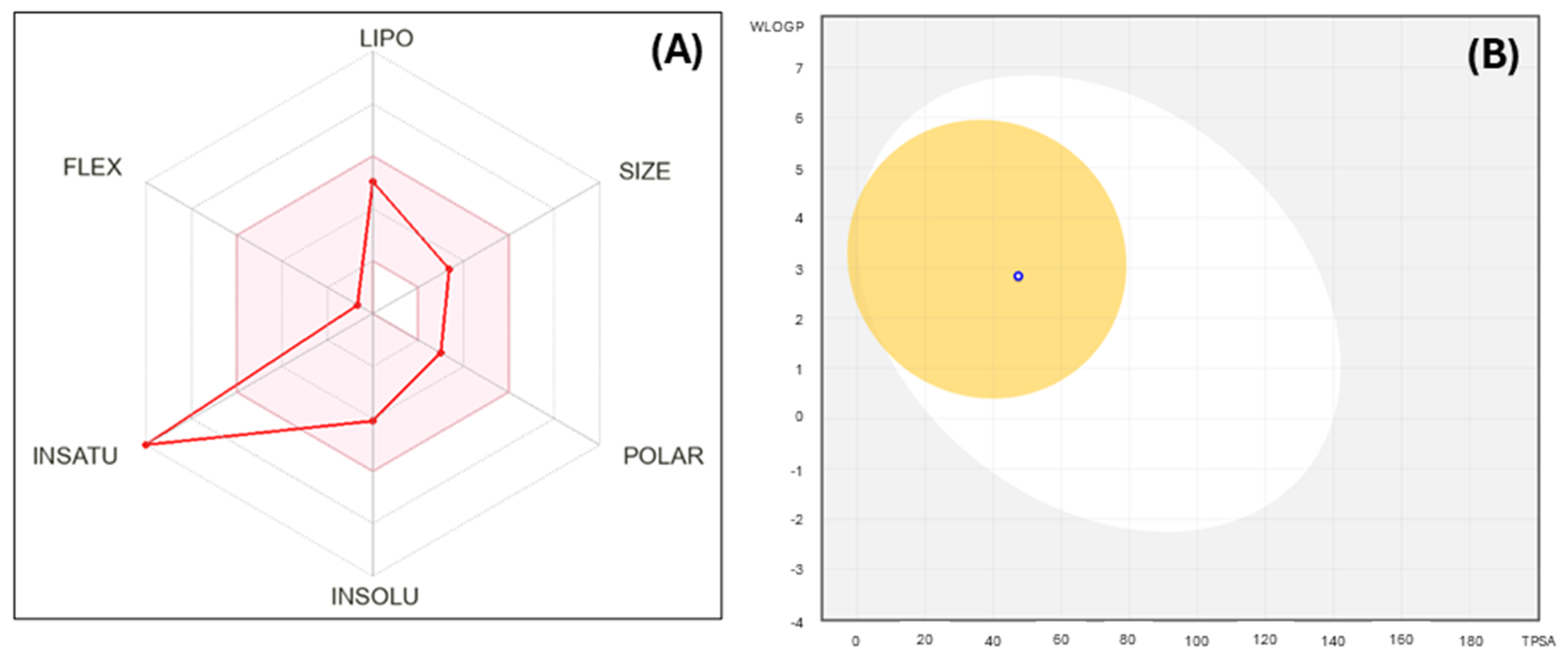
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials, Reagents, and Studied Compound
3.2. Hydrogel Microchamber Array (hMCA)
3.3. Cell Culture and Microtissue Formation
3.4. Cellular Object Staining
3.5. Imaging System and Operating Software
3.6. Image Analysis
3.7. Real-Time Cell Analysis Using the iCELLigence System
3.8. Apoptosis Detection with Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide
3.9. Statistical Analysis
3.10. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebelt, N.D.; Kaoud, T.S.; Edupuganti, R.; Van Ravenstein, S.; Dalby, K.N.; Van den Berg, C.L. A c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor, JNK-IN-8, sensitizes triple negative breast cancer cells to lapatinib. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 104894–104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, V.T.; Gonçalves, B.S.; Linden, R.; Chiarini, L.B. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) during mitosis in retinal progenitor cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, M.; Okada, M.; Shibuya, K.; Seino, S.; Suzuki, S.; Ohta, T.; Kurachi, H.; Kitanaka, C. Requirement of JNK signaling for self-renewal and tumor-initiating capacity of ovarian cancer stem cells. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 4723–4731. [Google Scholar]
- Eckhoff, K.; Flurschutz, R.; Trillsch, F.; Mahner, S.; Janicke, F.; Milde-Langosch, K. The prognostic significance of Jun transcription factors in ovarian cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanaka, C.; Sato, A.; Okada, M. JNK Signaling in the Control of the Tumor-Initiating Capacity Associated with Cancer Stem Cells. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas-Mejia, P.; Benito, J.M.; Fernandez, A.; Han, H.D.; Mangala, L.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Lin, Y.G.; Carey, M.S.; Nick, A.M.; et al. c-Jun-NH2-kinase-1 inhibition leads to antitumor activity in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuiki, H.; Tnani, M.; Okamoto, I.; Kenyon, L.C.; Emlet, D.R.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Lanham, I.S.; Joynes, C.J.; Vo, K.T.; Wong, A.J. Constitutively active forms of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase are expressed in primary glial tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, H.; May, S.; Song, X.; Fueyo, J.; Fuller, G.N.; Wang, H. Constitutive activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase correlates with histologic grade and EGFR expression in diffuse gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 88, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonyak, M.A.; Kenyon, L.C.; Godwin, A.K.; James, D.C.; Emlet, D.R.; Okamoto, I.; Tnani, M.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Moscatello, D.K.; Wong, A.J. Elevated JNK activation contributes to the pathogenesis of human brain tumors. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5038–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Han, S.Y.; Wang, C.; Su, W.; Harshyne, L.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Wong, A.J. c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2alpha2 promotes the tumorigenicity of human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10024–10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, R.K.; Lim, E.J.; Choi, K.S.; An, S.; Hwang, S.G.; Kang, S.G.; Suh, Y.; Park, M.J.; et al. c-Jun N-terminal kinase has a pivotal role in the maintenance of self-renewal and tumorigenicity in glioma stem-like cells. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.M.; Tong, J.L.; Xu, Q.; Nie, F.; Xu, X.T.; Xiao, S.D.; Ran, Z.H. Increased JNK1 signaling pathway is responsible for ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance in human colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.K.; Yadav, V.K.; Bajaj, S.; Datta, A.; Dutta, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Debnath, S.; Roy, S.; Boardman, L.A.; et al. DNA damage-induced ephrin-B2 reverse signaling promotes chemoresistance and drives EMT in colorectal carcinoma harboring mutant p53. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Sato, A.; Okada, M.; Shibuya, K.; Seino, S.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, E.; Narita, Y.; Shibui, S.; Kayama, T.; et al. Targeting JNK for therapeutic depletion of stem-like glioblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashenden, M.; van Weverwijk, A.; Murugaesu, N.; Fearns, A.; Campbell, J.; Gao, Q.; Iravani, M.; Isacke, C.M. An in vivo functional screen identifies JNK signaling as a modulator of chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, M.; Somma, A.; Kaoud, T.; Goyal, R.; Bustamante, J.; Wylie, D.C.; Holay, N.; Looney, A.; Giri, U.; Triplett, T.; et al. Covalent JNK Inhibitor, JNK-IN-8, Suppresses Tumor Growth in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Activating TFEB- and TFE3-Mediated Lysosome Biogenesis and Autophagy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ma, R.; Zhang, M. XRCC1 rs1799782 (C194T) polymorphism correlated with tumor metastasis and molecular subtypes in breast cancer. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 8435–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirello, V.; Vaira, V.; Grassi, E.S.; Vezzoli, V.; Ricca, D.; Colombo, C.; Bosari, S.; Vicentini, L.; Persani, L.; Ferrero, S.; et al. Multicellular spheroids from normal and neoplastic thyroid tissues as a suitable model to test the effects of multikinase inhibitors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9752–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, T.M.; McCalla, S.; Tripathi, A.; Morgan, J.R. Quantification of the Kinetics and Extent of Self-Sorting in Three Dimensional Spheroids. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2012, 18, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.; Giachi, A.; Spínola-Lasso, E.; Marra, F.; Raggi, C. Organoids and spheroids: Advanced in vitro models for liver cancer research. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 12, 1536854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Kundu, B.; Silva-Correia, J.; Kundu, S.C.; Oliveir, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M. Emerging tumor spheroids technologies for 3D in vitro cancer modeling. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2018, 184, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, P.C.D.W.; Van Tilborg, A.A.G.; Eijk, P.P.; Sminia, P.; Troost, D.; Van Noorden, C.J.F.; Ylstra, B.; Leenstra, S. The genomic profile of human malignant glioma is altered early in primary cell culture and preserved in spheroids. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.H.S.; Chia, S.S.; Toh, S.L.; Goh, J.C.H.; Nathan, S.S. Three-dimensional spatial configuration of tumour cells confers resistance to chemotherapy independent of drug delivery. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Martinez, E.; Suazo-Sanchez, I.; Celis-Romero, M.; Carnero, A. 3D and organoid culture in research: Physiology, hereditary genetic diseases and cancer. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, T.H. Recent Advances in Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Generation for Drug Screening. Biosensors 2021, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kwon, S.; Kim, K.S. Challenges of applying multicellular tumor spheroids in preclinical phase. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Forte, I.M.; Pentimalli, F.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Alfano, L.; Capone, F.; Camerlingo, R.; Calabrese, A.; von Arx, C.; Dominguez, R.B.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of CDK4/6 impairs diffuse pleural mesothelioma 3D spheroid growth and reduces viability of cisplatin-resistant cells. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1418951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Wu, W.J. Tumor extrinsic factors mediate primary T-DM1 resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.R.; Luo, J.; Liu, W.F.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Hu, S.K.; Shen, X.Z.; Du, X.J.; Xiang, W. Alisertib impairs the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting purine synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchard, A.; Laborie, H.; Rouillard, H.; Lozach, O.; Ferandin, Y.; Le Guével, R.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Meijer, L.; Besson, T.; Thiéry, V. Synthesis and kinase inhibitory activity of novel substituted indigoids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6257–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Plotnikov, M.B.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Plotnikova, T.M.; Quinn, M.T. Oximes: Novel therapeutics with anticancer and anti-inflammatory potential. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A. Synthesis and evaluation of new chalcones and oximes as anticancer agents. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 10307–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Potapov, A.S.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Matveevskaya, V.V.; Belyanin, M.L.; Atochin, D.N.; Zanoza, S.O.; Gaidarzhy, N.M.; Lyakhov, S.A.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of 11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one derivatives and tryptanthrin-6-oxime as c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Hanks, T.S.; Kochetkova, I.; Pascual, D.W.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Identification and characterization of a novel class of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakhov, S.A.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Karpenko, O.S.; Duma, H.I.; Haidarzhy, N.M.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Bagryanskaya, I.Y.; Quinn, M.T. Novel c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitors with an 11H-Indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one Scaffold. Molecules 2021, 26, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L.J. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüningk, S.C.; Rivens, I.; Box, C.; Oelfke, U.; ter Haar, G. 3D tumour spheroids for the prediction of the effects of radiation and hyperthermia treatments. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrimzon, E.; Botchkina, G.; Zurgil, N.; Shafran, Y.; Sobolev, M.; Moshkov, S.; Ravid-Hermesh, O.; Ojimac, I.; Deutsch, M. Hydrogel microstructure live-cell array for multiplexed analyses of cancer stem cells, tumor heterogeneity and differential drug response at single-element resolution. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, Y.; Zurgil, N.; Ravid-Hermesh, O.; Sobolev, M.; Afrimzon, E.; Hakuk, Y.; Shainberg, A.; Deutsch, M. Nitric oxide is cytoprotective to breast cancer spheroids vulnerable to estrogen-induced apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108890–108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neha; Ranjan, P.; Das, P. Calcimycin mediates apoptosis in breast and cervical cancer cell lines by inducing intracellular calcium levels in a P2RX4-dependent manner. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2024, 1868, 130535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrimzon, E.; Zurgil, N.; Shafran, Y.; Sandbank, J.; Orda, R.; Lalchuk, S.; Deutsch, M. Monitoring of intracellular enzyme kinetic characteristics of peripheral mononuclear cells in breast cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, M.; Zurgil, N.; Kaufman, M.; Berke, G. Fluorescence polarization as an early measure of T-lymphocyte stimulation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 134, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G.; Somlyai, I.; Kovács, B.Z.; Puskás, L.G.; Nagy, L.I.; Dux, L.; Farkas, G.; Somlyai, G. Deuterium depletion inhibits cell proliferation, RNA and nuclear membrane turnover to enhance survival in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Control 2021, 28, 1073274821999655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.G.; Silva, I.B.B.; Campos-Fernández, E.; Barcelos, L.S.; Souza, J.B.; Marangoni, K.; Goulart, L.R.; Alonso-Goulart, V. Comparative assay of 2D and 3D cell culture models: Proliferation, gene expression and anticancer drug response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Nguyen, H.T.; Zhuang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Flemington, E.K.; Guo, W.C.; Guenther, J.; Burow, M.E.; Morris, G.F.; Sullivan, D.; et al. Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of miR-21 by Type I Collagen. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, S.; McArdle, E.; Gilligan, E.; Napoletano, S.; Gajewska, M.; Bergin, O.; McCarthy, S.; Whyte, J.; Bianchi, A.; Stack, J.; et al. c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity supports multiple phases of 3D-mammary epithelial acinus formation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Sasaki, D.T.; Murray, B.W.; O’Leary, E.C.; Sakata, S.T.; Xu, W.M.; Leisten, J.C.; Motiwala, A.; Pierce, S.; Satoh, Y.; et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantore, M.; Leopoldo, M.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R.; Colabufo, N.A. Design and synthesis of new selective P-gp substrates and inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5774–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakeev, A.P.; Frelikh, G.A.; Yanovskaya, E.A.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Udut, V.V. Quantification of a promising JNK inhibitor and nitrovasodilator IQ-1 and its major metabolite in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2022, 14, 1423–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelikh, G.A.; Yanovskaya, E.A.; Lakeev, A.P.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Smolyakova, V.I.; Kovrizhina, A.R. Dose proportionality and bioavailability of quinoxaline-based JNK inhibitor after single oral and intravenous administration in rats. Xenobiotica 2024, 54, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Hammaker, D.; Kochetkova, I.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Lyakhov, S.A.; Firestein, G.S.; Quinn, M.T. Anti-Inflammatory effects and joint protection in collagen-induced arthritis after treatment with IQ-1S, a selective c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Aliev, O.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Smol’yakova, V.; Osipenko, A.N.; Plotnikov, M.B.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Khlebnikov, A.; Plotnikov, E.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of the lithium salt of a novel JNK inhibitor in an animal model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochin, D.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Seledtsov, V.I.; Swanson, H.; Quinn, M.T.; Huang, P.L. A novel dual NO-donating oxime and c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 618, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Paik, Y.; Ryu, H.J.; Lee, J.; Shin, I.; Park, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Lim, Y.J.; Shin, H.; Kim, W.; et al. Dual inhibitors of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein for overcoming the blood-brain barrier: In silico discovery and preclinical evaluation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevich, K.S.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Goreninskii, S.I.; Lavrinenko, A.K.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Filimonov, V.D.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; et al. Poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds doped with c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors modulate phagocyte activation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5990–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, E.; Lavrinenko, A.; Kolesnik, I.; Stankevich, K.; Bolbasov, E.; Kudryavtseva, V.; Leonov, A.; Schepetkin, I.; Khlebnikov, A.; Quinn, M.T.; et al. Electrosprayed poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles as a promising drug delivery system for the novel JNK inhibitor IQ-1. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 127, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Smolyakova, V.I.; Aliev, O.I.; Trofimova, E.S.; Sherstoboev, E.Y.; Osipenko, A.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of a novel inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Cells 2020, 9, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.F.; Göransson, S.; Olofsson, H.; Vogiatzakis, C.; Acharekar, A.; Strömblad, S. Matrix stiffness-induced IKBKE and MAPK8 signaling drives a phenotypic switch from DCIS to invasive breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics of 3D Objects | IQ-1S | Vehicle | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell seeded (cells/3D object) | 9.0 ± 3.4 | 9.7 ± 3.5 | 0.66 |
| CSA of 3D objects at 24 h (mm2) | 0.0013 ± 0.0005 | 0.0015 ± 0.0006 | 0.44 |
| CSA of 3D objects at 168 h (mm2) | 0.0036 ± 0.0014 | 0.0076 ± 0.0037 | 0.003 |
| p-value (CSA at 24 vs. 168 h) | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Fluorescent Dye and Parameter | IQ-1S | Vehicle | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI (% of entire CSA) | 7.2 ± 4.4 | 2.5 ± 1.3 | 0.13 |
| TMRM FI as CV (%) | 123.4 ± 29.6 | 124.2 ± 33.7 | 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afrimzon, E.; Deutsch, M.; Sobolev, M.; Zurgil, N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Buldakov, M.A.; Schepetkin, I.A. c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor IQ-1S as a Suppressor of Tumor Spheroid Growth. Molecules 2025, 30, 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214278
Afrimzon E, Deutsch M, Sobolev M, Zurgil N, Khlebnikov AI, Buldakov MA, Schepetkin IA. c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor IQ-1S as a Suppressor of Tumor Spheroid Growth. Molecules. 2025; 30(21):4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214278
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfrimzon, Elena, Mordechai Deutsch, Maria Sobolev, Naomi Zurgil, Andrei I. Khlebnikov, Mikhail A. Buldakov, and Igor A. Schepetkin. 2025. "c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor IQ-1S as a Suppressor of Tumor Spheroid Growth" Molecules 30, no. 21: 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214278
APA StyleAfrimzon, E., Deutsch, M., Sobolev, M., Zurgil, N., Khlebnikov, A. I., Buldakov, M. A., & Schepetkin, I. A. (2025). c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor IQ-1S as a Suppressor of Tumor Spheroid Growth. Molecules, 30(21), 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214278







