Almond Shell-Derived Biochar for Lead Adsorption: Comparative Study of Pyrolysis Techniques and Sorption Capacities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Almond Shell-Derived Biochars
2.1.1. Proximate and Elemental Analysis
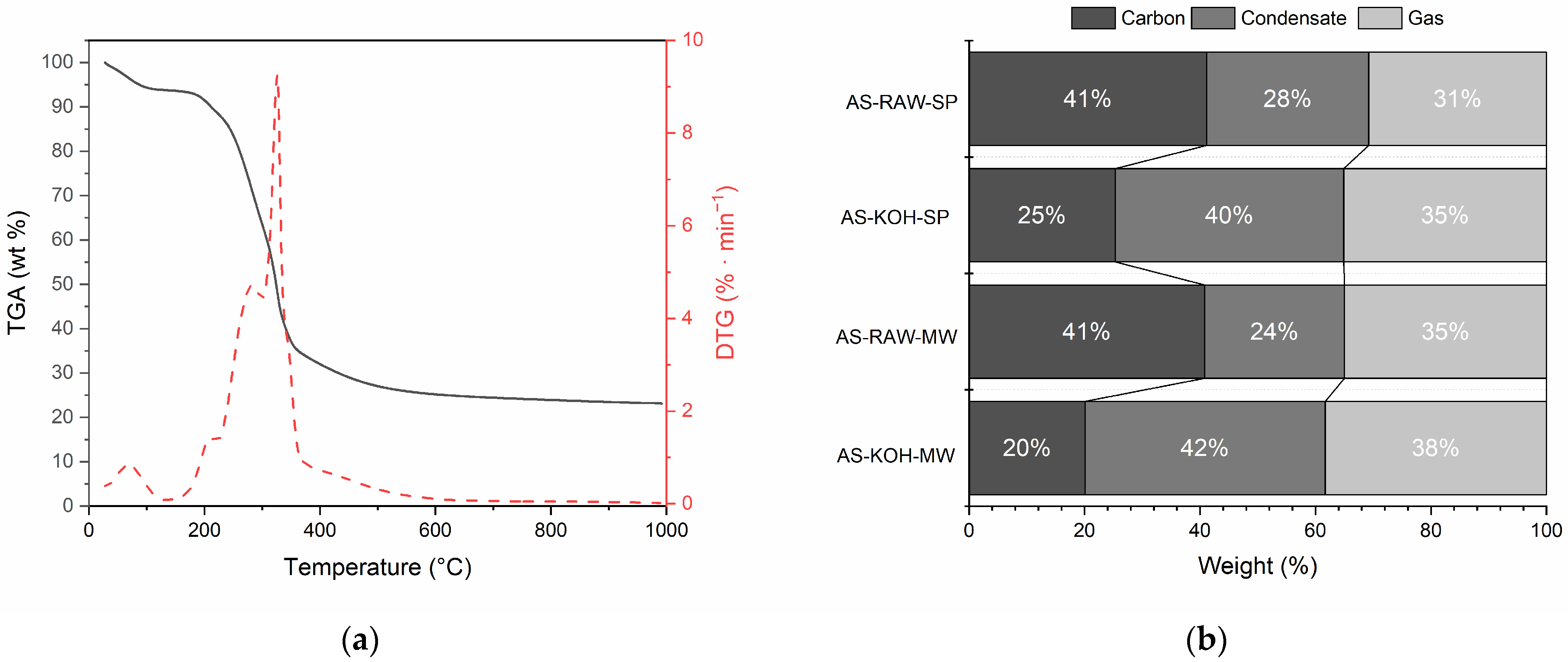
2.1.2. Thermal Decomposition and Product Distribution
2.1.3. Textural Properties
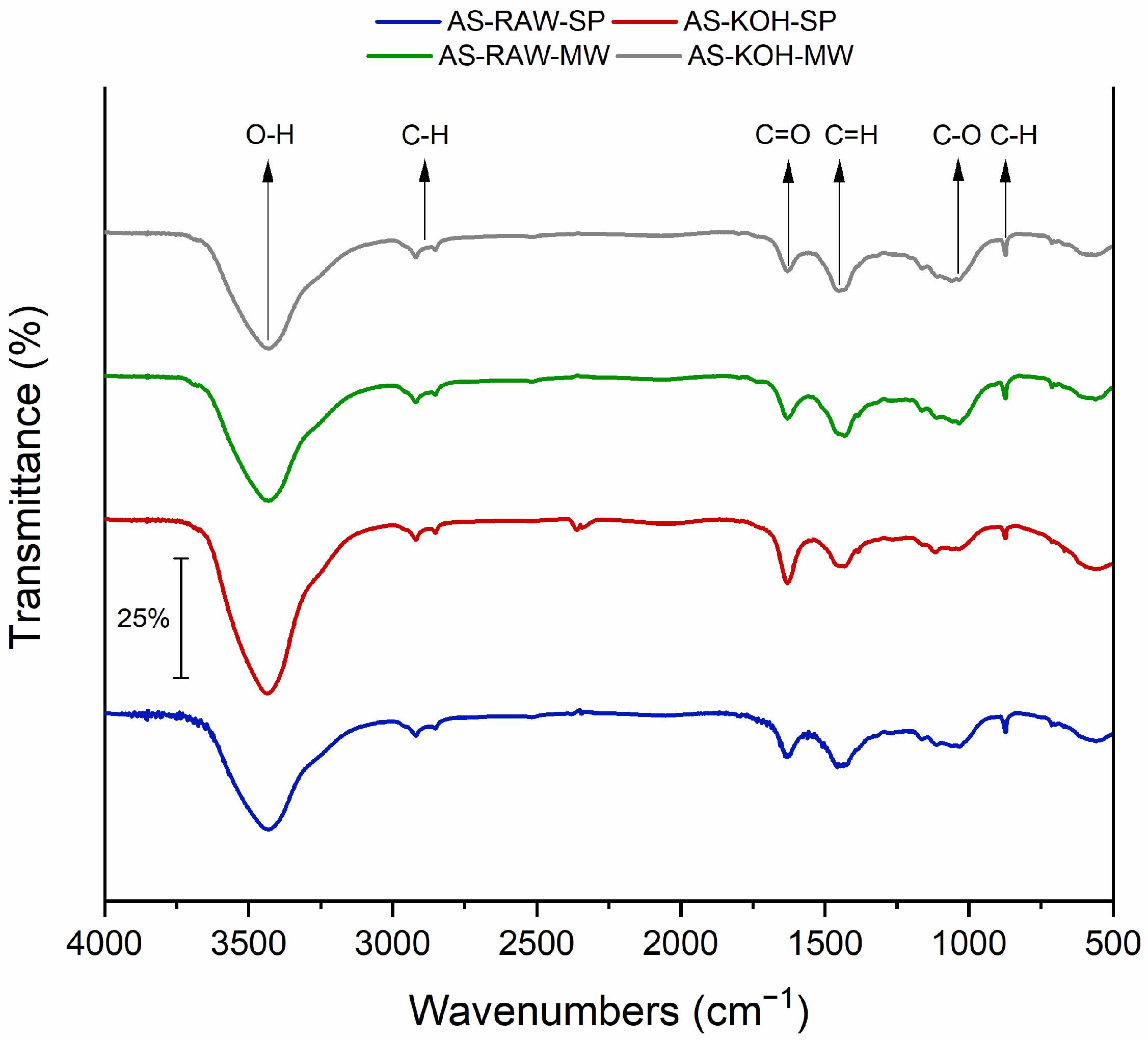
2.1.4. FTIR Spectral Analysis
2.1.5. Physico-Chemical Differences and Implications
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
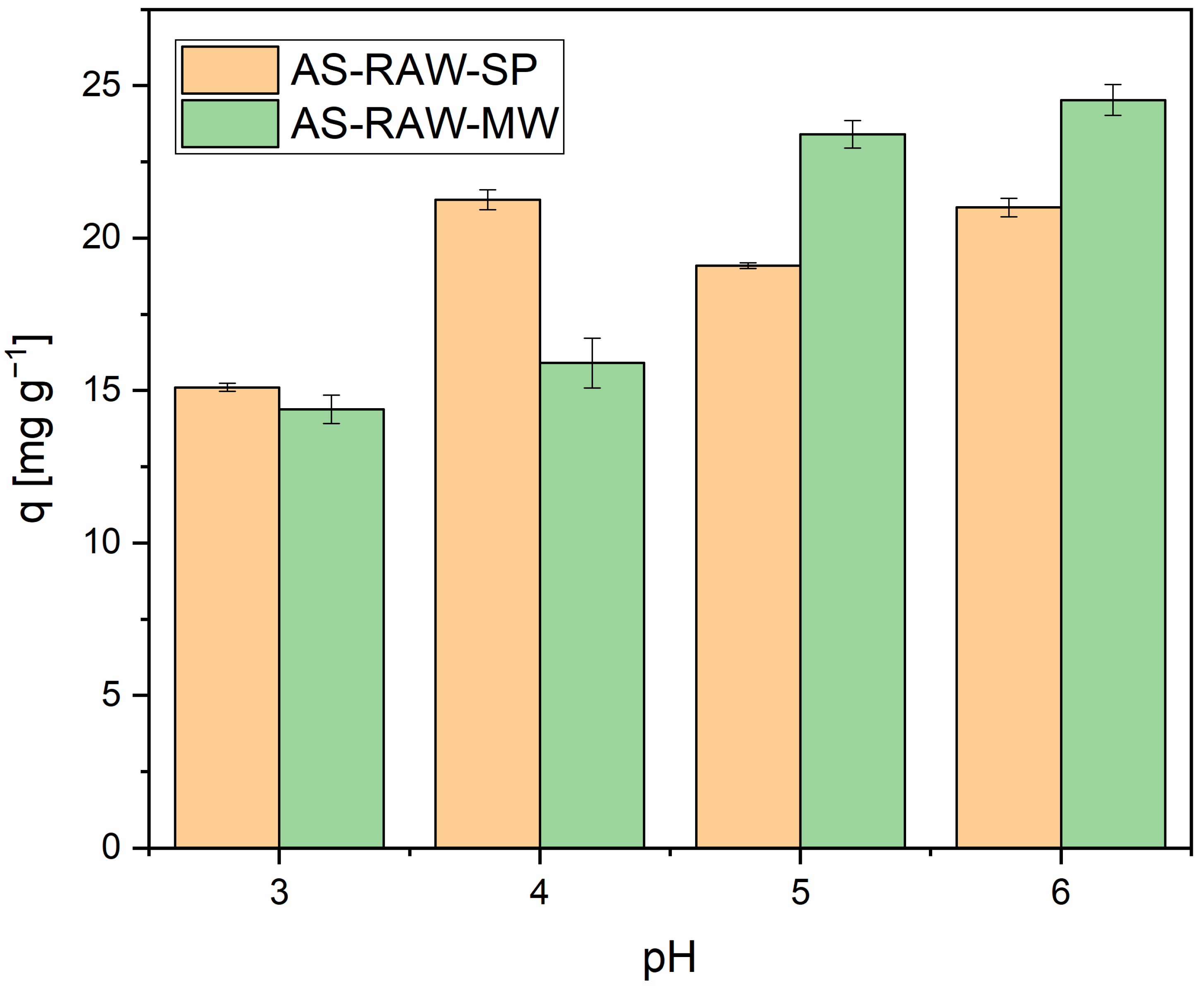
2.3. Effect of pH
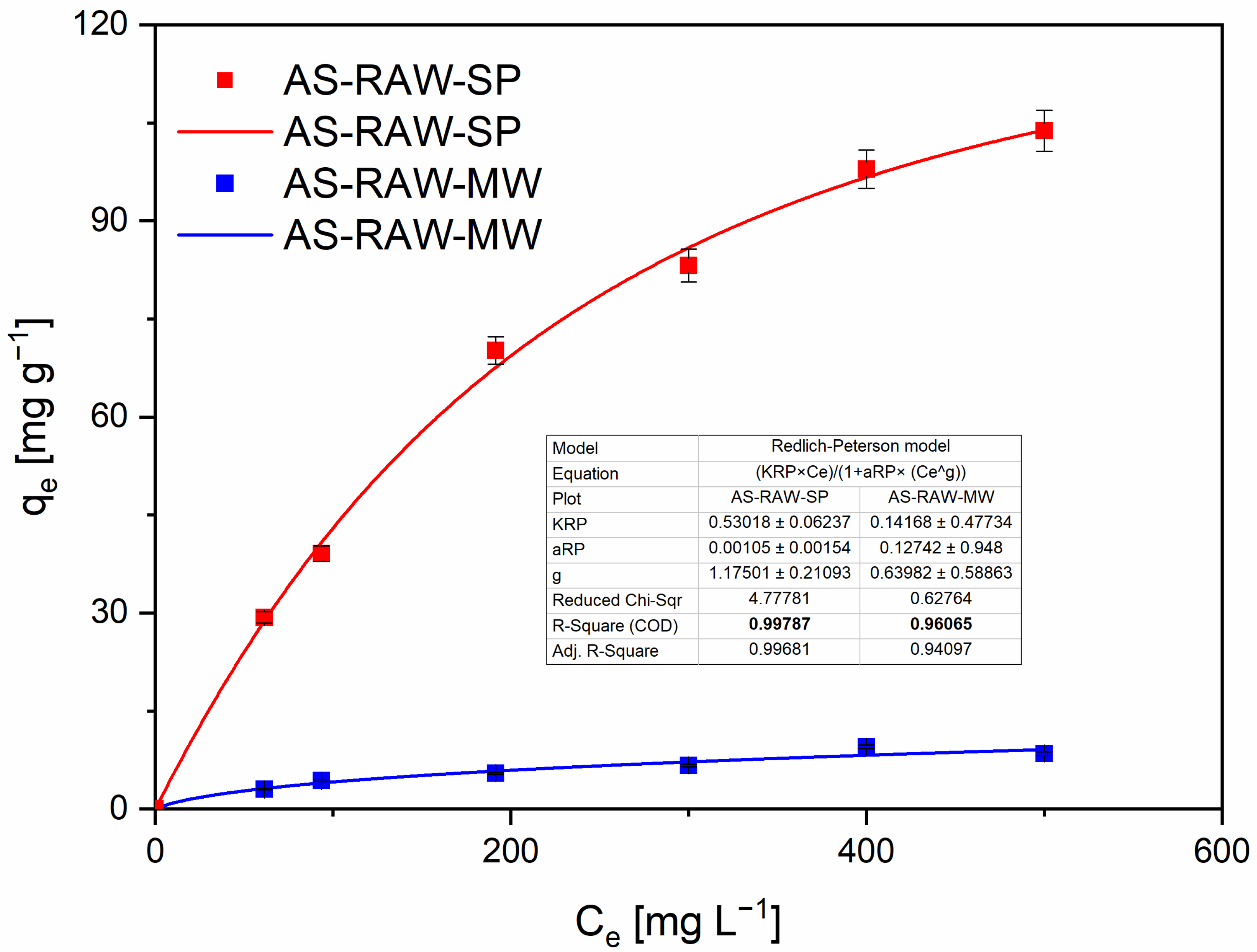
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Linking Biochar Properties to Adsorption Behavior
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biomass Preparation
3.2. Chemical Activation of Biomass
3.3. Pyrolysis Processes
Post-Pyrolysis Biochar Treatment
3.4. Biochar Characterization
3.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
Kinetic and Equilibrium Models
3.6. Methodology for the Determination of Pb
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Swizerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.A. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a Sorbent for Contaminant Management in Soil and Water: A Review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, G.; Kuang, C.; Li, X.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y. A Novel Almond Shell Biochar Modified with FeS and Chitosan as Adsorbents for Mitigation of Heavy Metals from Water and Soil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkolu, M.; Gundekari, S.; Omvesh; Palla, V.C.S.; Kumar, P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Vinodkumar, T. Recent Advances in Biochar Production, Characterization, and Environmental Applications. Catalysts 2025, 15, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Cheng, W.Y.; Liew, R.K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M. Chapter 25—Production of Biochar Using Sustainable Microwave Pyrolysis Approach. In Biochar in Agriculture for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals; Tsang, D.C.W., Ok, Y.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 323–332. ISBN 978-0-323-85343-9. [Google Scholar]
- Amalina, F.; Razak, A.S.A.; Krishnan, S.; Zularisam, A.W.; Nasrullah, M. A Comprehensive Assessment of the Method for Producing Biochar, Its Characterization, Stability, and Potential Applications in Regenerative Economic Sustainability—A Review. Clean. Mater. 2022, 3, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Naz, M.Y.; Zhang, Y. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Biomass: Influence of Feedstock and Pyrolysis Parameters on Porous Biochar Properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 193, 107583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grycova, B.; Pryszcz, A.; Lestinsky, P.; Chamradova, K. Influence of Potassium Hydroxide and Method of Carbonization Treatment in Garden and Corn Waste Microwave Pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 118, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavan Kumar, V.; Panwar, N.L. Pyrolysis Technologies for Biochar Production in Waste Management: A Review. Clean Energy 2024, 8, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickler, C.A.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Anandhi, A.; Chen, G. Comparing Physicochemical Properties and Sorption Behaviors of Pyrolysis-Derived and Microwave-Mediated Biochar. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Shen, D.; Li, N. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste for Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Production with Different Types of Inoculum: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbaş, A. Biomass Resource Facilities and Biomass Conversion Processing for Fuels and Chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 1357–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Lehmann, J.; McBride, M.B.; Hay, A.G. Adsorption of Copper and Zinc by Biochars Produced from Pyrolysis of Hardwood and Corn Straw in Aqueous Solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lua, A.C.; Yang, T.; Guo, J. Effects of Pyrolysis Conditions on the Properties of Activated Carbons Prepared from Pistachio-Nut Shells. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 72, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhiya, A.K.; Anand, A.; Kaushal, P. Production, Activation, and Applications of Biochar in Recent Times. Biochar 2020, 2, 253–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Li, C.; Guang, M.; Zhang, Y. Porous Carbon Material Production from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Peanut Shell. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, N.L.; Pawar, A. Influence of Activation Conditions on the Physicochemical Properties of Activated Biochar: A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panczyk, T.; Rudzinski, W. Kinetics of Gas Adsorption on Strongly Heterogeneous Solid Surfaces: A Statistical Rate Theory Approach. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2004, 21, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Removal of Lead(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Date Seed-Derived Biochar: Batch and Column Studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkum, P.; Kumar, S. Evaluation of Lead (Pb(II)) Removal Potential of Biochar in a Fixed-Bed Continuous Flow Adsorption System. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 201210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Tao, J.; Yan, B.; Cui, X.; Chen, G. Adsorption of Lead from Aqueous Solution by Biochar: A Review. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireles, S.; Parsons, J.; Trad, T.; Cheng, C.-L.; Kang, J. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Biochars Derived from Corn Stover, Orange Peel, and Pistachio Shell. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Hashim, R.; Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Ahmad, A. Govind Adsorption of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Date Bead Carbon Activated with ZnCl2. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Deng, H.; Du, Z.; Tian, K.; Zhang, J. Design of Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Doped Biochar and Its Lead Adsorption Performance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 28984–28994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, J.; Ali, N.; Dong, Y.; Ahmad, U.; Anjum, M.M.; Khan, G.R.; Zaib, M.; Jalal, A.; Ali, R.; Ali, L. Biochar-Based Adsorption for Heavy Metal Removal in Water: A Sustainable and Cost-Effective Approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Huang, T.; Lu, H.; Wu, X.-L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, B.; et al. Biochar-Based Materials in Environmental Pollutant Elimination, H2 Production and CO2 Capture Applications. Biochar 2023, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Alagusundaram, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Christopher, F.C.; Balaji, B.; Viswanathan, V.; Sankar, S. Microwave Pyrolysis of Coal, Biomass and Plastic Waste: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3609–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, N.M.; Lahijani, P.; Mohammadi, M.; Mohamed, A.R. Modification of Biomass-Derived Biochar: A Practical Approach towards Development of Sustainable CO2 Adsorbent. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 7401–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedynak, K.; Charmas, B. Adsorption Properties of Biochars Obtained by KOH Activation. Adsorption 2024, 30, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, R.; Imran-Shaukat, M.; Ngaini, Z.; Zuhaidi, N.F.Q. Modifications of Surface Properties of Biochar by Different Treatment Methods. In Biochar: A Sustainable Approach; Bhawani, S.A., Bhat, A.H., Wahi, R., Ngaini, Z., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 19–36. ISBN 978-981-9742-52-3. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, B.; Balla, P.; Krishna, B.B.; Adhikari, S.; Bhaskar, T. Physiochemical Characteristics of Bio-Char Derived from Pyrolysis of Rice Straw under Different Temperatures. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 12775–12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Song, S. Enhanced Adsorption of Phenol Using EDTA-4Na- and KOH-Modified Almond Shell Biochar. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2025, 35, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.; Pirilä, M.; Huuhtanen, M.; Carrión, L.; Alvarenga, E.; Keiski, R. Production of Activated Carbon from Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) Pod Husk. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2012, 2012, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovská, Z.; Matějová, L.; Tokarský, J.; Peikertová, P.; Dopita, M.; Gorzolková, K.; Habermannová, D.; Vaštyl, M.; Bělík, J. Microporous Carbon Prepared by Microwave Pyrolysis of Scrap Tyres and the Effect of K+ in Its Structure on Xylene Adsorption. Carbon 2024, 216, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaštyl, M.; Jankovská, Z.; Cruz, G.J.F.; Matějová, L. A Case Study on Microwave Pyrolysis of Waste Tyres and Cocoa Pod Husk; Effect on Quantity and Quality of Utilizable Products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7582; Standard Test Methods for Proximate Analysis of Coal and Coke by Macro Thermogravimetric Analysis. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, M.D.; Aranovich, G.L. Classification of Gibbs Adsorption Isotherms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 76–77, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.H.; Singh, K.K.; Prakash, O.; Talat, M.; Ho, Y.S. Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solutions Using Agricultural Waste ‘Maize Bran’. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Bednárek, J.; Ritz, M.; Kormunda, M.; Zelenka, T.; Vaštyl, M.; Gavlová, A.; Kolská, Z.; Férová, M. Microporous Carbonaceous Adsorbent Prepared from a Pyrolyzed Polymer. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 6458–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. The Sorption of Lead(II) Ions on Peat. Water Res. 1999, 33, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Bao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Chen, A.; Long, F. Adsorption of Chromium (VI) by Ethylenediamine-Modified Cross-Linked Magnetic Chitosan Resin: Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, U.A.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Adsorption of Phosphates from Model Wastewater Using Recycled Brick Waste. Processes 2020, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hossain, M.F.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Islam, M.S.; Zhou, Y. Isotherm Models for Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Water—A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Isotherm Models: Classification, Physical Meaning, Application and Solving Method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwabanne, J.T.; Iheanacho, O.C.; Obi, C.C.; Onu, C.E. Linear and Nonlinear Kinetics Analysis and Adsorption Characteristics of Packed Bed Column for Phenol Removal Using Rice Husk-Activated Carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikhiev, I.G.; Kraysman, N.V.; Sverguzova, S.V. Review of Pistachio (Pistacia) Shell Use to Remove Pollutants from Aqua Media. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, K.; Zaharaki, D.; Pyliotis, I.; Vamvuka, D.; Bartzas, G. Assessment of Pistachio Shell Biochar Quality and Its Potential for Adsorption of Heavy Metals. Waste Biomass Valorization 2015, 6, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Parthasarathy, P.; Mackey, H.R.; Al-Ansari, T.; McKay, G. Effect of Pistachio Shell Biochar and Organic Cow Manure Application on Plant Growth, Water Retention Capacity and Nutrient Stress Mitigation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 16, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Koprivica, M.; Ercegović, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Vuković, N.S.; Fiol, N. Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium. Toxics 2025, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşar, Ş.; Özer, A. A Thermodynamic and Kinetic Evaluation of the Adsorption of Pb(II) Ions Using Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea) Shell-Based Biochar from Aqueous Media. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 29, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwiejuah, A.B.; Quainoo, A.K.; Abubakari, A.-H. Simultaneous Adsorption of Toxic Metals in Binary Systems Using Peanut and Sheanut Shells Biochars. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Moisture (wt.%) | Ash (wt.%) | Volatile Matter (wt.%) | Fixed Carbon (wt.%) | C (wt.%) | H (wt.%) | N (wt.%) | S (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS-RAW | 0 | 3.1 | 79.4 | 17.4 | 45.60 | 6.40 | 1.74 | 0.30 |
| AS-RAW-SP | 0 | 2.9 | 8.3 | 88.8 | 87.86 | 0.96 | 0.78 | n.a. |
| AS-KOH-SP | 0 | 5.2 | 13.4 | 81.4 | 76.56 | 1.42 | 0.41 | n.a. |
| AS-RAW-MW | 0 | 2.0 | 8.5 | 89.5 | 87.93 | 1.10 | 0.96 | n.a. |
| AS-KOH-MW | 0 | 4.9 | 13.9 | 81.2 | 76.13 | 1.34 | 0.41 | n.a. |
| Material | SBET (m2·g−1) | Vnet (cm3·g−1) | Vmic (cm3·g−1) | Vmeso (cm3·g−1) | Median Micropore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS-RAW-SP | 693 | 0.598 | 0.161 | 0.437 | 0.6157 |
| AS-KOH-SP | 476 | 0.185 | 0.120 | 0.065 | 0.4766 |
| AS-RAW-MW | 147 | 0.144 | 0.037 | 0.107 | 0.5871 |
| AS-KOH-MW | 45 | 0.050 | 0.012 | 0.038 | 0.5945 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pertile, E.; Dvorský, T.; Václavík, V.; Berkyová, L.; Balvín, P. Almond Shell-Derived Biochar for Lead Adsorption: Comparative Study of Pyrolysis Techniques and Sorption Capacities. Molecules 2025, 30, 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204121
Pertile E, Dvorský T, Václavík V, Berkyová L, Balvín P. Almond Shell-Derived Biochar for Lead Adsorption: Comparative Study of Pyrolysis Techniques and Sorption Capacities. Molecules. 2025; 30(20):4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204121
Chicago/Turabian StylePertile, Eva, Tomáš Dvorský, Vojtěch Václavík, Lucie Berkyová, and Petr Balvín. 2025. "Almond Shell-Derived Biochar for Lead Adsorption: Comparative Study of Pyrolysis Techniques and Sorption Capacities" Molecules 30, no. 20: 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204121
APA StylePertile, E., Dvorský, T., Václavík, V., Berkyová, L., & Balvín, P. (2025). Almond Shell-Derived Biochar for Lead Adsorption: Comparative Study of Pyrolysis Techniques and Sorption Capacities. Molecules, 30(20), 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30204121








