Novel Azaborine-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)
Abstract
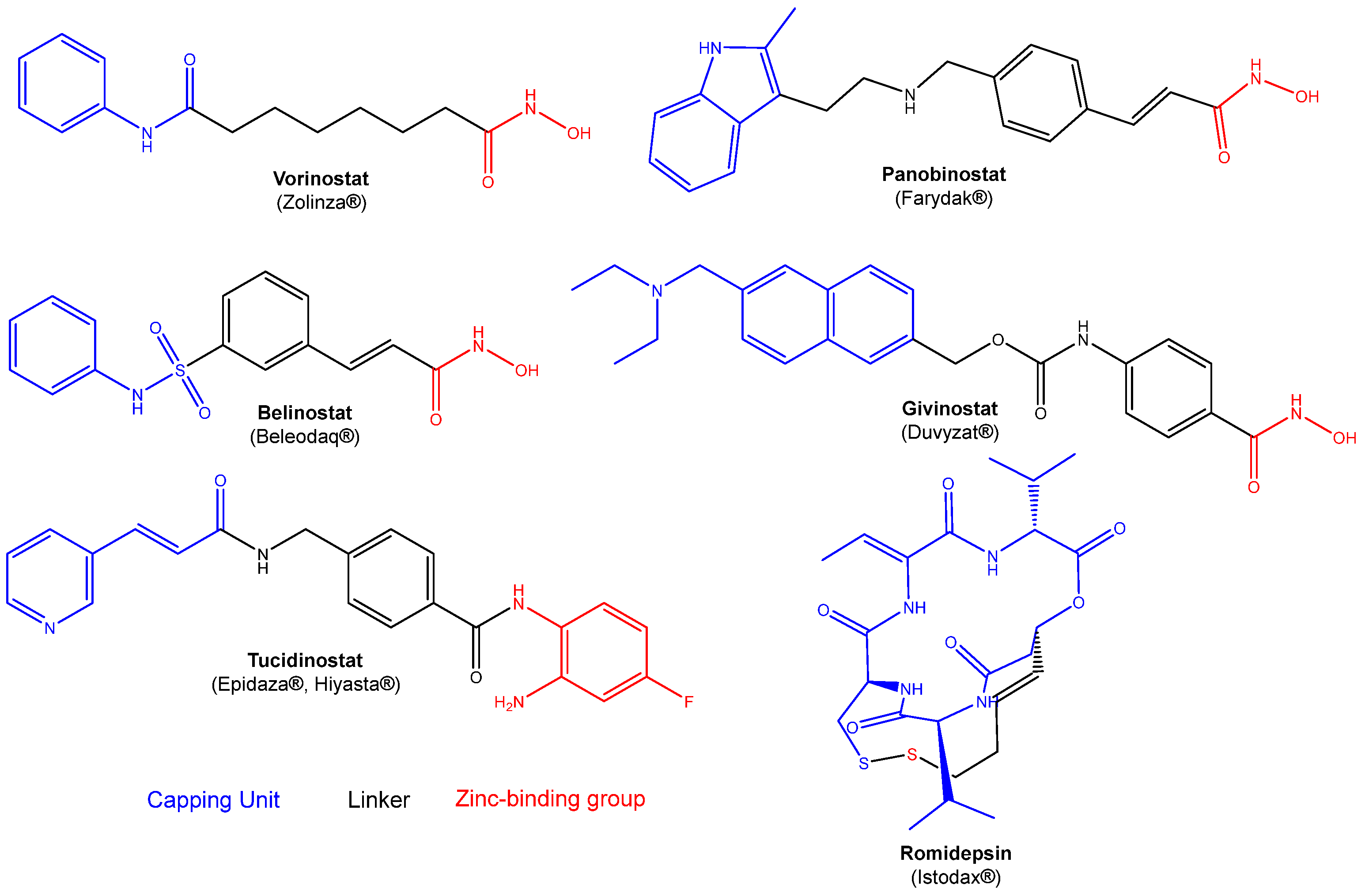
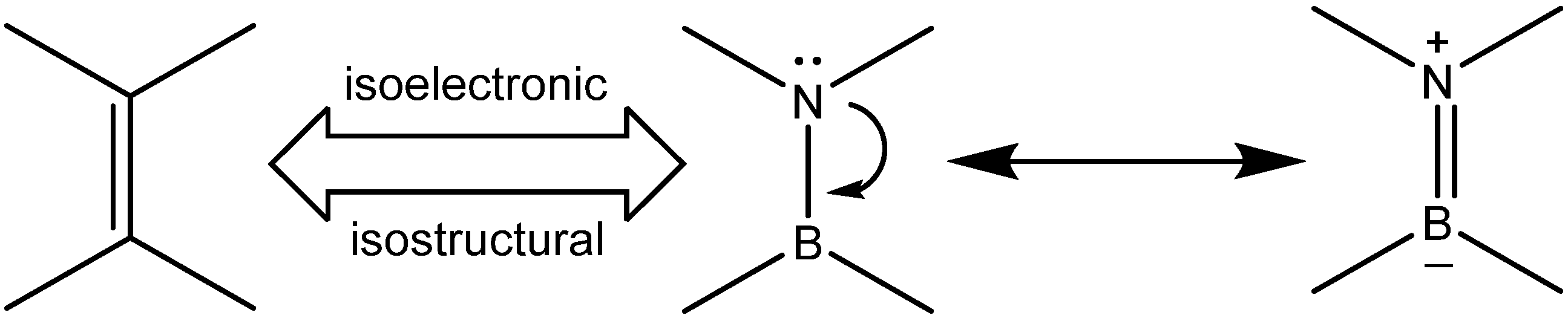
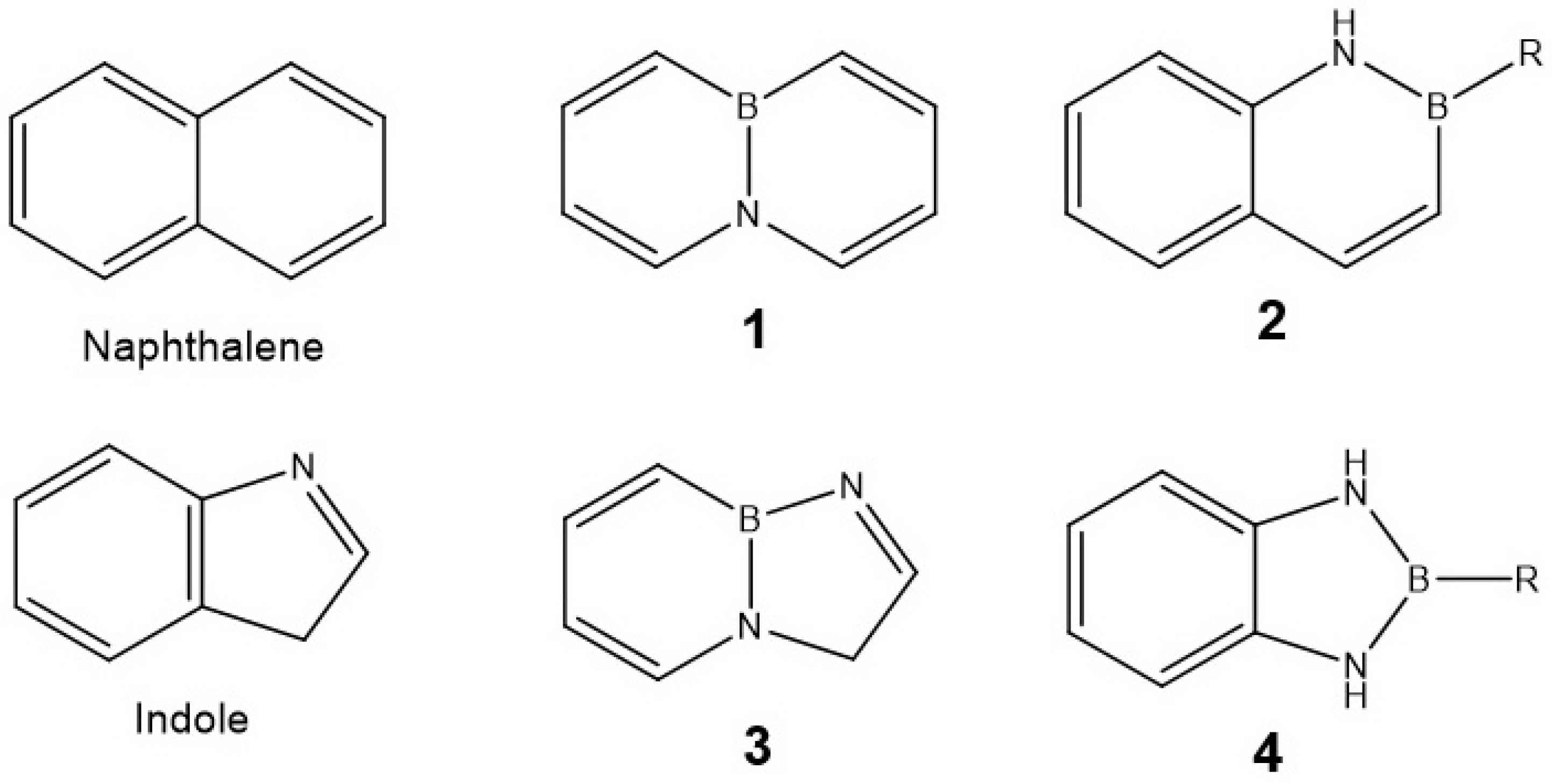
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis
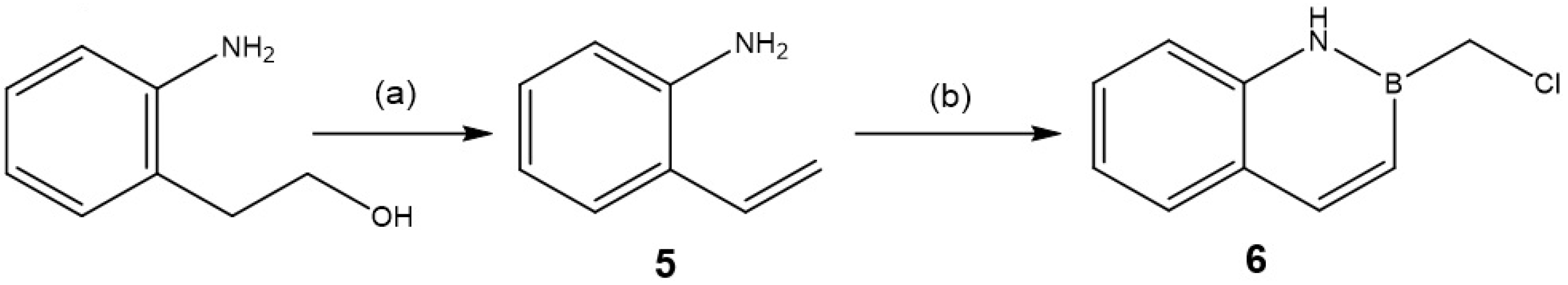
2.1.1. Synthesis and Functionalization of BN-Naphthalene Azaborine Building Block
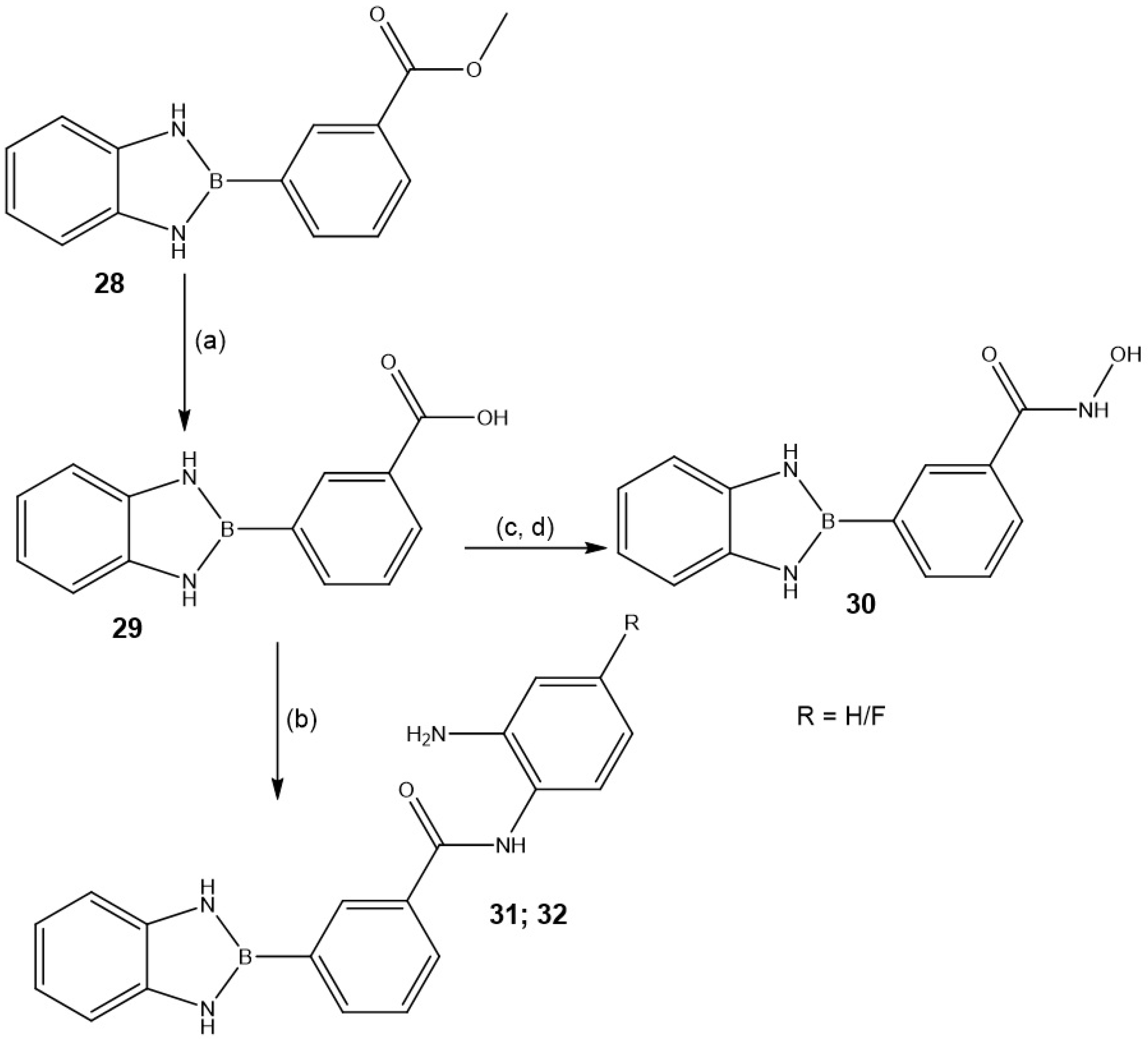
2.1.2. Synthesis and Functionalization of BN-Indole Azaborine Building Block
2.2. Assessment of Inhibitory Activity
2.2.1. IC50 Measurement of BN-Naphthalene-Based Compounds
2.2.2. IC50 Measurement of BN-Indole-Based Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregory, P.D.; Wagner, K.; Hörz, W. Histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 265, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, N.; Choukrallah, M.-A.; Matthias, P. Multiple roles of class I HDACs in proliferation, differentiation, and development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertos, N.R.; Wang, A.H.; Yang, X.-J. Class II histone deacetylases: Structure, function, and regulation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 79, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Faller, D.V. Transcription Regulation by Class III Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)-Sirtuins. Transl. Oncogenom. 2008, 3, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Cueto, M.A.; Asselbergs, F.; Atadja, P. Cloning and functional characterization of HDAC11, a novel member of the human histone deacetylase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25748–25755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Cohen, M.H.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA approval summary: Vorinostat for treatment of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarz, R.L.; Frye, R.; Turner, M.; Wright, J.J.; Allen, S.L.; Kirschbaum, M.H.; Zain, J.; Prince, H.M.; Leonard, J.P.; Geskin, L.J.; et al. Phase II multi-institutional trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin as monotherapy for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5410–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Rahman, F.; Piekarz, R.; Peer, C.; Frye, R.; Robey, R.W.; Gardner, E.R.; Figg, W.D.; Bates, S.E. Romidepsin: A new therapy for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and a potential therapy for solid tumors. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010, 10, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Z.; Kwitkowski, V.E.; Del Valle, P.L.; Ricci, M.S.; Saber, H.; Habtemariam, B.A.; Bullock, J.; Bloomquist, E.; Li Shen, Y.; Chen, X.-H.; et al. FDA Approval: Belinostat for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Kanellias, N.; Kastritis, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Efficacy of Panobinostat for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 7131802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N. Givinostat: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hong, J.H.; Ning, Z.; Pan, D.; Fu, X.; Lu, X.; Tan, J. Therapeutic potential of tucidinostat, a subtype-selective HDAC inhibitor, in cancer treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 932914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A.D.G. Rings in drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.W.; Gallego, R.A.; Edwards, M.P. Lipophilic Efficiency as an Important Metric in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6401–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, A.A.; Shegokar, R. Polyethylene glycol (PEG): A versatile polymer for pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1257–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrostowska, A.; Xu, S.; Lamm, A.N.; Mazière, A.; Weber, C.D.; Dargelos, A.; Baylère, P.; Graciaa, A.; Liu, S.-Y. UV-photoelectron spectroscopy of 1,2- and 1,3-azaborines: A combined experimental and computational electronic structure analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10279–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustra, Z.X.; Liu, S.-Y. The State of the Art in Azaborine Chemistry: New Synthetic Methods and Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Dietz, R. 546. New heteroaromatic compounds. Part III. 2,1-Borazaro-naphthalene (1,2-dihydro-1-aza-2-boranaphthalene). J. Chem. Soc. 1959, 3, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, J.S.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Mazière, A.; Lovinger, G.J.; Li, B.; Zakharov, L.N.; Dargelos, A.; Graciaa, A.; Chrostowska, A.; Liu, S.-Y. Two BN Isosteres of Anthracene: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15414–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, F.J.R.; Tovar, F.; Austin, N.; Tresadern, G.; Trabanco, A.A. Benzazaborinines as Novel Bioisosteric Replacements of Naphthalene: Propranolol as an Example. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9287–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, B.A.; Schrank, C.L.; Wuest, W.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of an antibacterial azaborine retinoid isostere. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 62, 152667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, E.R.; Zakharov, L.N.; Liu, S.-Y. Boron in disguise: The parent “fused” BN indole. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11508–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, E.R.; Liu, S.-Y. BN isosteres of indole. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Han, C.; Mohammed, S.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Sun, F.; Du, Y. Indole-containing pharmaceuticals: Targets, pharmacological activities, and SAR studies. RSC Med. Chem. 2024, 15, 788–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, S.; Saha, T.; Singh, S.K. Naphthalene, a versatile platform in medicinal chemistry: Sky-high perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Nettleton, D.O.; Karki, R.G.; Zécri, F.J.; Liu, S.-Y. Medicinal Chemistry Profiling of Monocyclic 1,2-Azaborines. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, S.J.; Schrock, R.R.; Hoveyda, A.H. Enantioselective synthesis of cyclic secondary amines through Mo-catalyzed asymmetric ring-closing metathesis (ARCM). Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4899–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander, G.A.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Amani, J. Accessing an azaborine building block: Synthesis and substitution reactions of 2-chloromethyl-2,1-borazaronaphthalene. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5636–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, G.H.M.; Molander, G.A. Synthesis of Functionalized 1,3,2-Benzodiazaborole Cores Using Bench-Stable Components. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kasuya, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Ota, Y.; Zhan, P.; Asamitsu, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Okamoto, T.; Miyata, N. Identification of highly selective and potent histone deacetylase 3 inhibitors using click chemistry-based combinatorial fragment assembly. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.-Q.; Li, Z.-B.; Newman, M.J.; Shan, S.; Wang, X.-H.; Pan, D.-S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Du, X.; Lu, X.-P. Chidamide (CS055/HBI-8000): A new histone deacetylase inhibitor of the benzamide class with antitumor activity and the ability to enhance immune cell-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsack, F.; Sukumari-Ramesh, S. Entinostat improves acute neurological outcomes and attenuates hematoma volume after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Brain Res. 2021, 1752, 147222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Dul, E.; Sung, C.-M.; Chen, Z.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Zhang, G.-F.; Johanson, K.; Liu, R.; Lago, A.; Hofmann, G.; et al. Identification of novel isoform-selective inhibitors within class I histone deacetylases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, Y.; Maeda, T.; Kawai, Y.; Nakashima, D.; Oikawa, T.; Shimoke, K.; Ikeuchi, T.; Kuwajima, H.; Uesato, S. Synthesis and cancer antiproliferative activity of new histone deacetylase inhibitors: Hydrophilic hydroxamates and 2-aminobenzamide-containing derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, V.; Theruvath, J.; Pauck, D.; Picard, D.; Qin, N.; Blümel, L.; Maue, M.; Bartl, J.; Ahmadov, U.; Langini, M.; et al. Tacedinaline (CI-994), a class I HDAC inhibitor, targets intrinsic tumor growth and leptomeningeal dissemination in MYC-driven medulloblastoma while making them susceptible to anti-CD47-induced macrophage phagocytosis via NF-kB-TGM2 driven tumor inflammation. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Soragni, E.; Chou, C.J.; Barnes, G.; Jones, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; Pandolfo, M. Two new pimelic diphenylamide HDAC inhibitors induce sustained frataxin upregulation in cells from Friedreich’s ataxia patients and in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweipert, M.; Nehls, T.; Wurster, E.; Böltner, J.; Anton, K.; Lammer, P.; Lermyte, F.; Meyer-Almes, F.-J. The pivotal role of histidine 976 in human histone deacetylase 4 for enzyme function and ligand recognition. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 153, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänsch, N.; Sugiarto, W.O.; Muth, M.; Kopranovic, A.; Desczyk, C.; Ballweg, M.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Brenner-Weiss, G.; Meyer-Almes, F.-J. Switching the Switch: Ligand Induced Disulfide Formation in HDAC8. Chemistry 2020, 26, 13249–13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
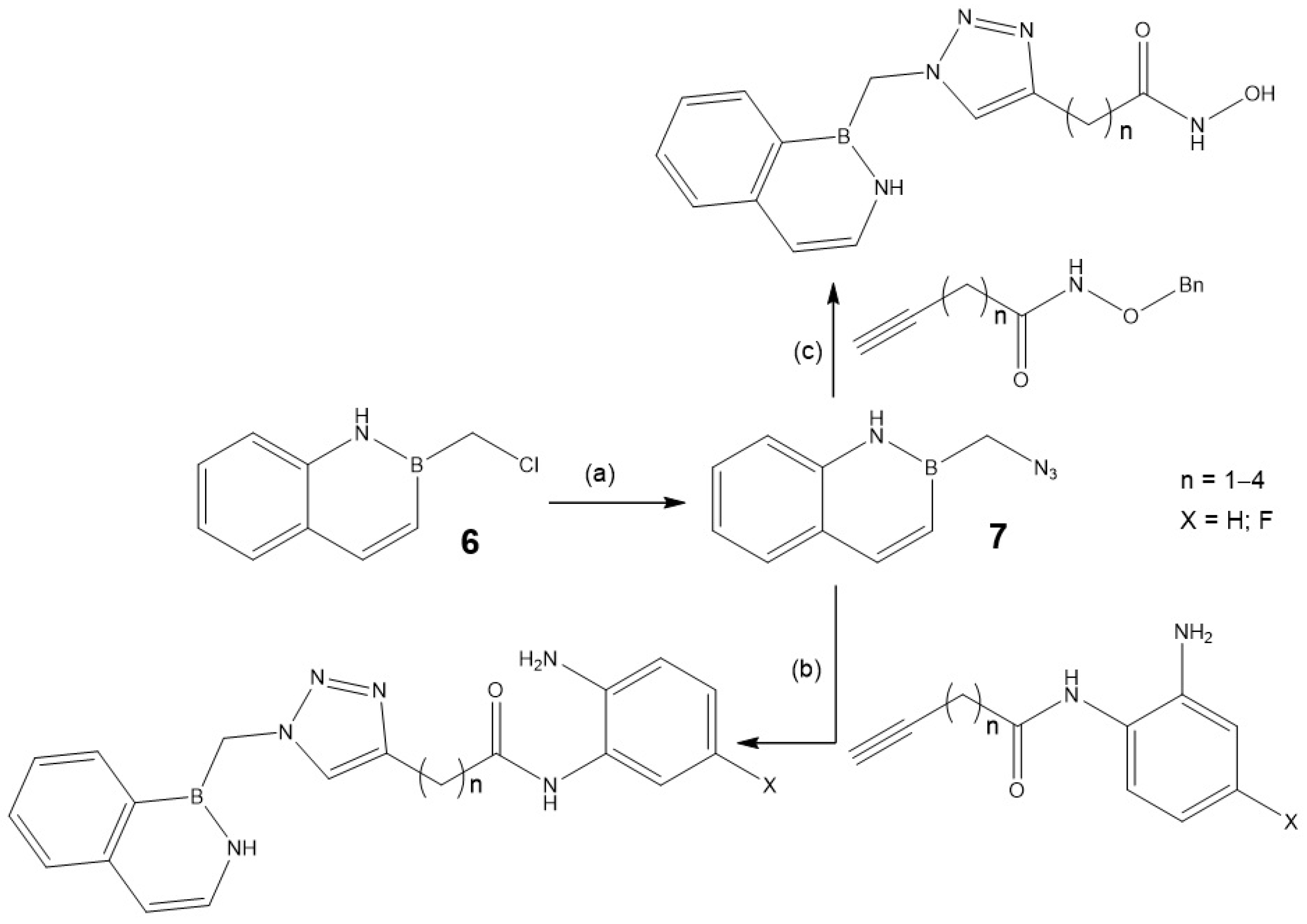



| Entry | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 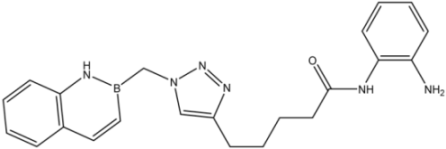 | 20 |
| 9 | 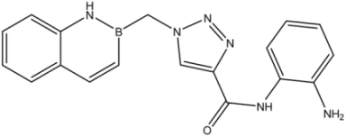 | 56 |
| 10 | 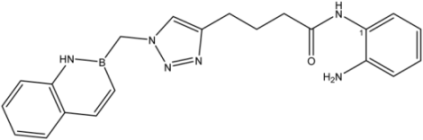 | 45 |
| 11 | 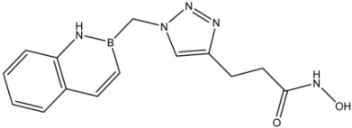 | 27 |
| 12 | 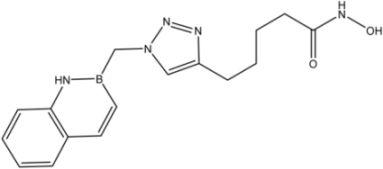 | 39 |
| 13 | 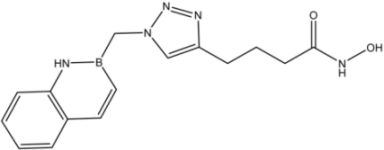 | 48 |
| 14 | 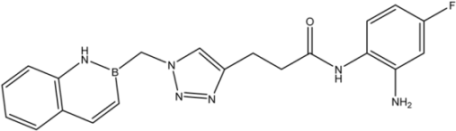 | 9 |
| 15 | 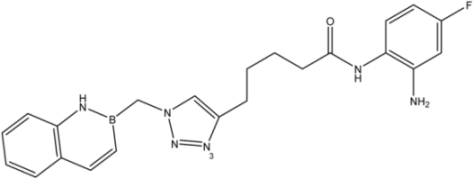 | 34 |
| Entry | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 16d |  | 40 |
| 17 | 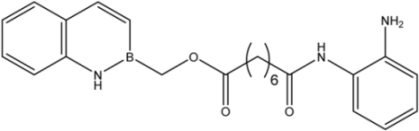 | 20 |
| 18 | 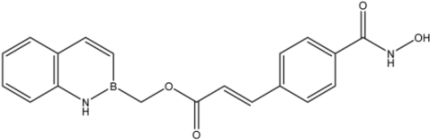 | 27 |
| 19 | 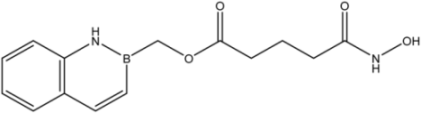 | 9 |
| 20 |  | 35 |
| 21 | 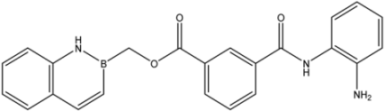 | 56 |
| 22 | 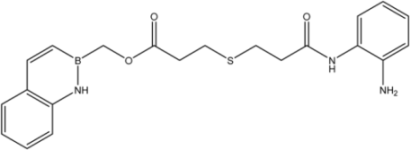 | 23 |
| 23 | 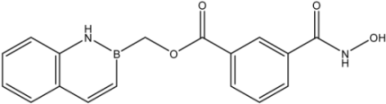 | 21 |
| Entry | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 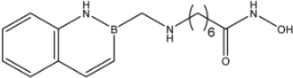 | 35 |
| 25 | 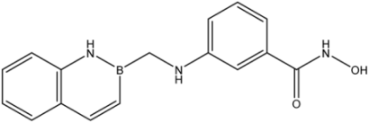 | 76 |
| 26 | 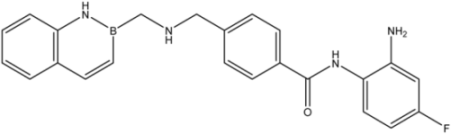 | 56 |
| 27 | 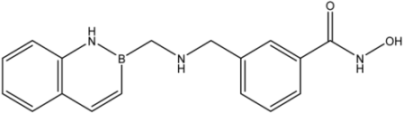 | 14 |
| Entry | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 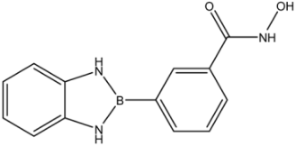 | 61 |
| 31; 32 |  | 68 (R = H) 60 (R = F) |
| 35 | 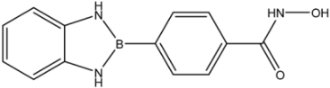 | 52 |
| Entry | Structure | IC50 (HDAC1) | IC50 (HDAC4) | IC50 (HDAC8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
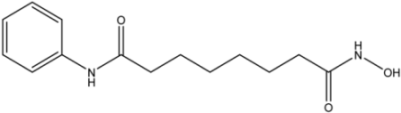 Vorinostat | 0.39 [33] | >10 | 0.66 | |
 Tucidinostat | 0.095 [34] | - | - | |
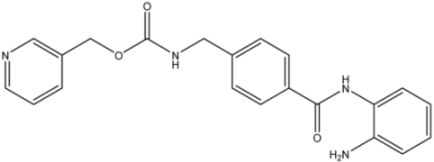 Entinostat | 0.46 [35] | - | >100 [36] | |
| 9 | 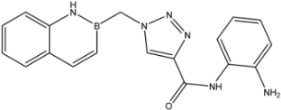 | >35 | 16.8 ± 1.6 | 20 ± 3 |
| 10 |  | >35 | 8.08 ± 1.59 | 19 ± 5 |
| 12 | 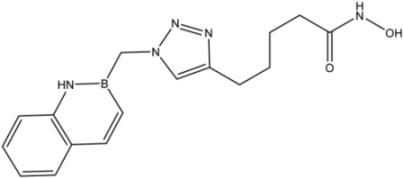 | >35 | 13.8 ± 4.3 | 6.2 ± 3.4 |
| 13 |  | >35 | 23.1 ± 4.9 | 3.3 ± 1.7 |
| 16d | 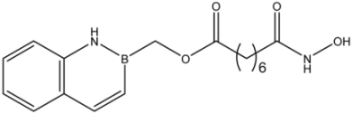 | >35 | 14.7 ± 1.7 | >35 |
| 17 | 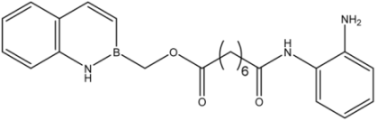 | 8.2 ± 2.5 | 16.5 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 3 |
| 18 |  | 8.2 ± 1.8 | >35 | 0.52 ± 0.11 |
| 23 | 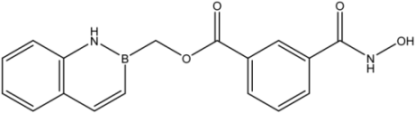 | 1.88 ± 0.11 | 7.3 ± 1.7 | 0.44 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 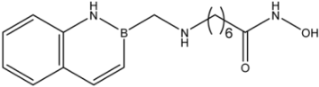 | 9.3 ± 2.3 | >35 | >35 |
| 25 | 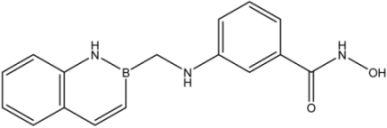 | >35 | 17 ± 3 | >35 |
| Entry | Structure | IC50 (HDAC1) | IC50 (HDAC4) | IC50 (HDAC8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 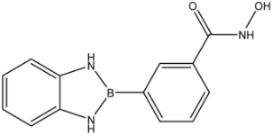 | 0.975 ± 0.394 | 1.35 ± 0.18 | 0.20 ± 0.02 |
| 31; 32 | 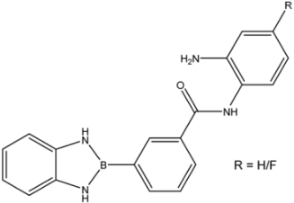 | >35 | >35 | >35 |
| 35 | 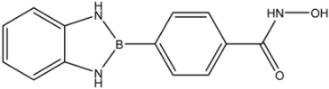 | >35 | >35 | >35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behringer, M.; Schweipert, M.; Peters, E.E.; Kopranovic, A.; Meyer-Almes, F.-J. Novel Azaborine-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). Molecules 2025, 30, 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194017
Behringer M, Schweipert M, Peters EE, Kopranovic A, Meyer-Almes F-J. Novel Azaborine-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). Molecules. 2025; 30(19):4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehringer, Martin, Markus Schweipert, Enna E. Peters, Aleksandra Kopranovic, and Franz-Josef Meyer-Almes. 2025. "Novel Azaborine-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)" Molecules 30, no. 19: 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194017
APA StyleBehringer, M., Schweipert, M., Peters, E. E., Kopranovic, A., & Meyer-Almes, F.-J. (2025). Novel Azaborine-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). Molecules, 30(19), 4017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194017






