Rosmarinosin A Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
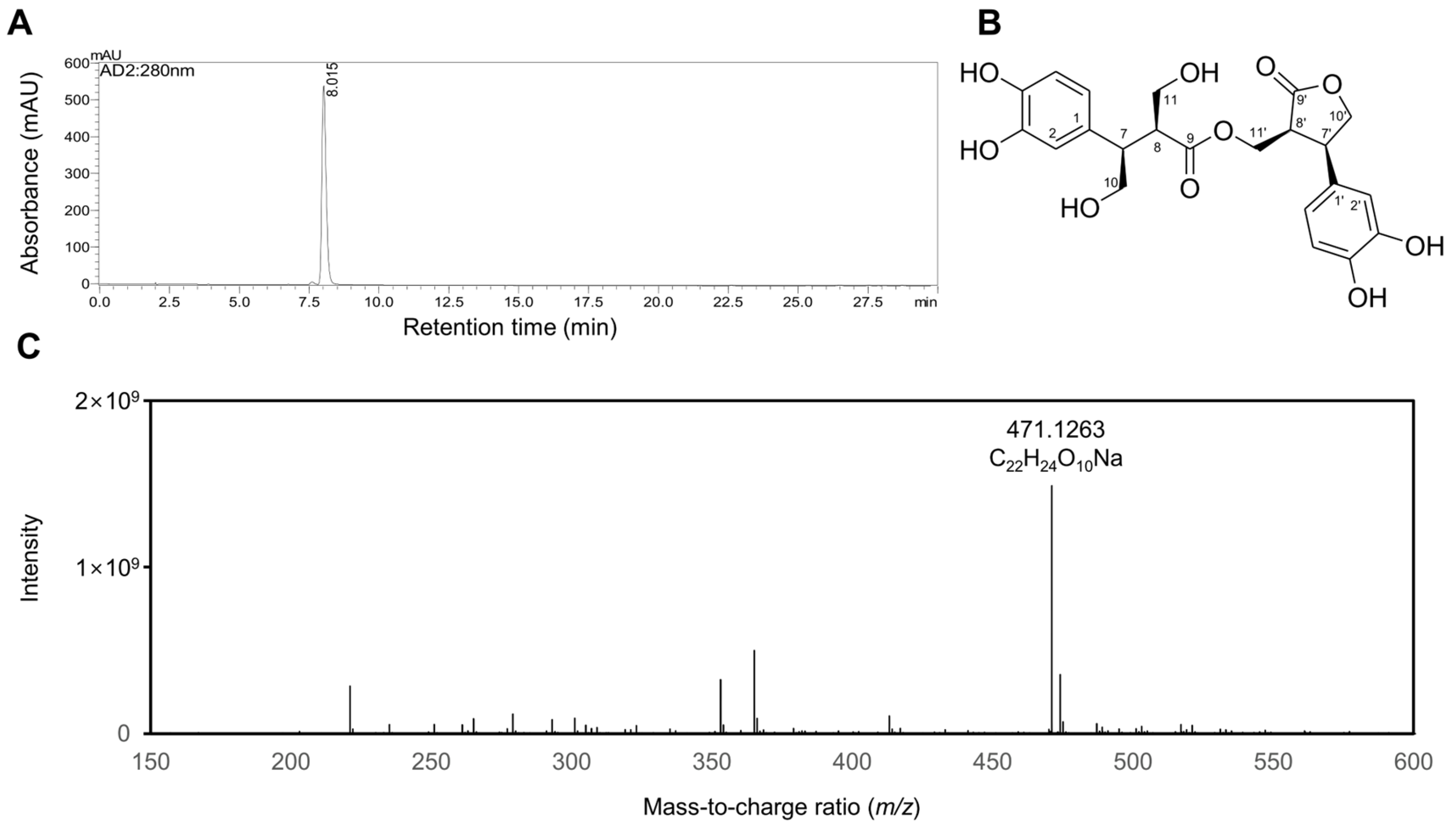
2.1. Characterization of Rosmarinosin A
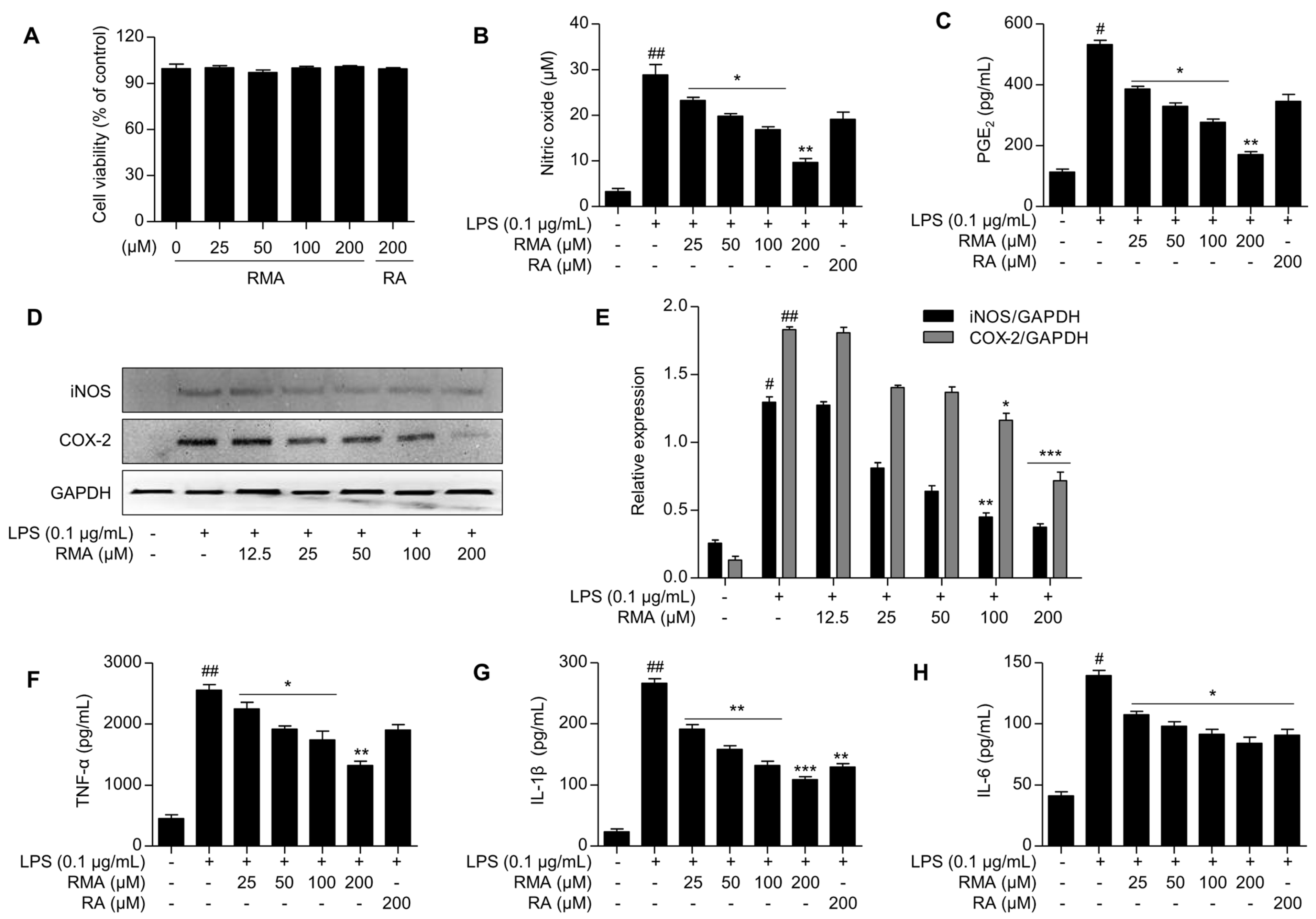
2.2. Effects of Rosmarinosin A on LPS-Stimulated NO and PGE2 Production
2.3. Effects of Rosmarinosin A on LPS-Stimulated Expression of iNOS and COX-2 Proteins
2.4. Effects of Rosmarinosin A on LPS-Stimulated Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
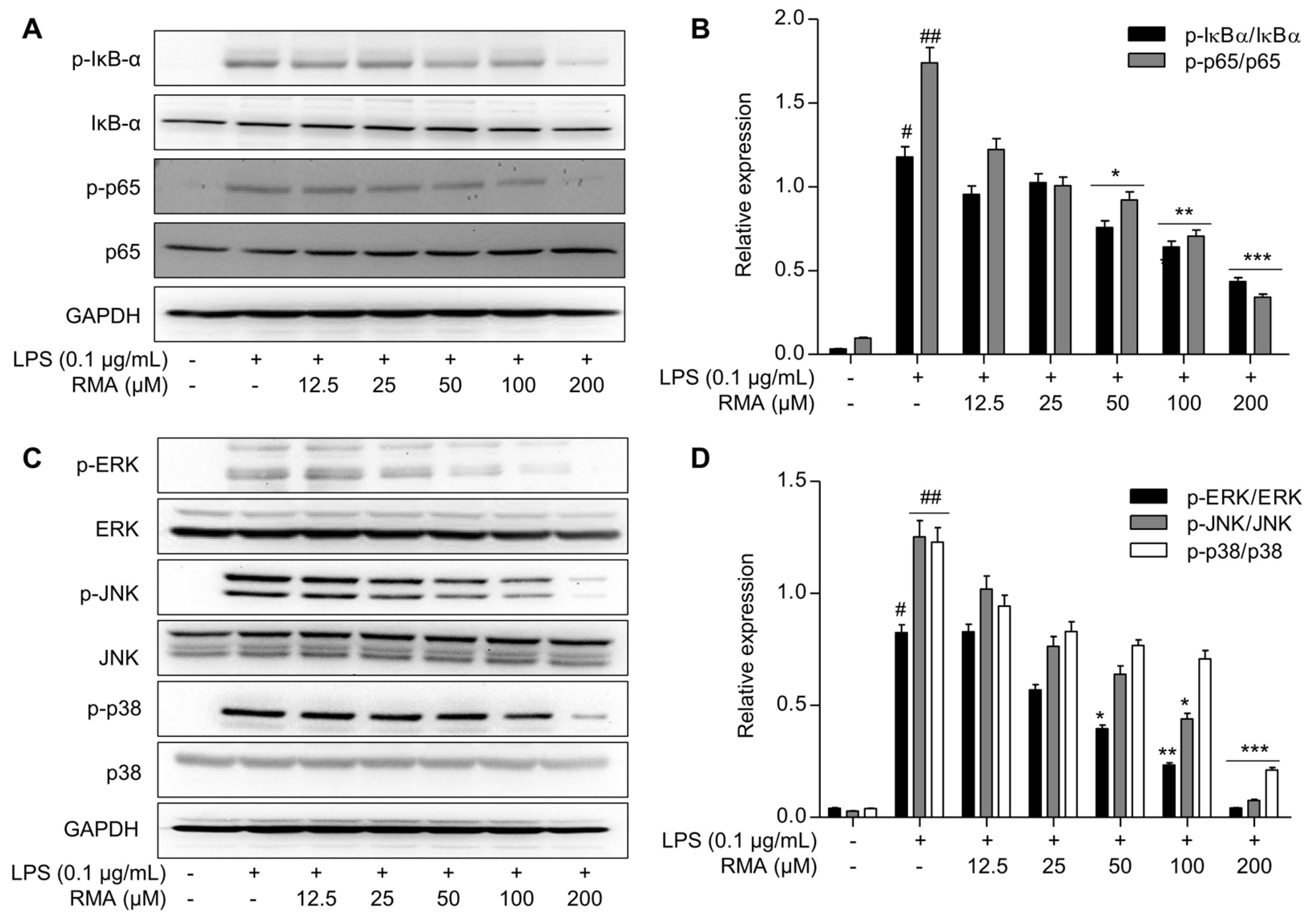
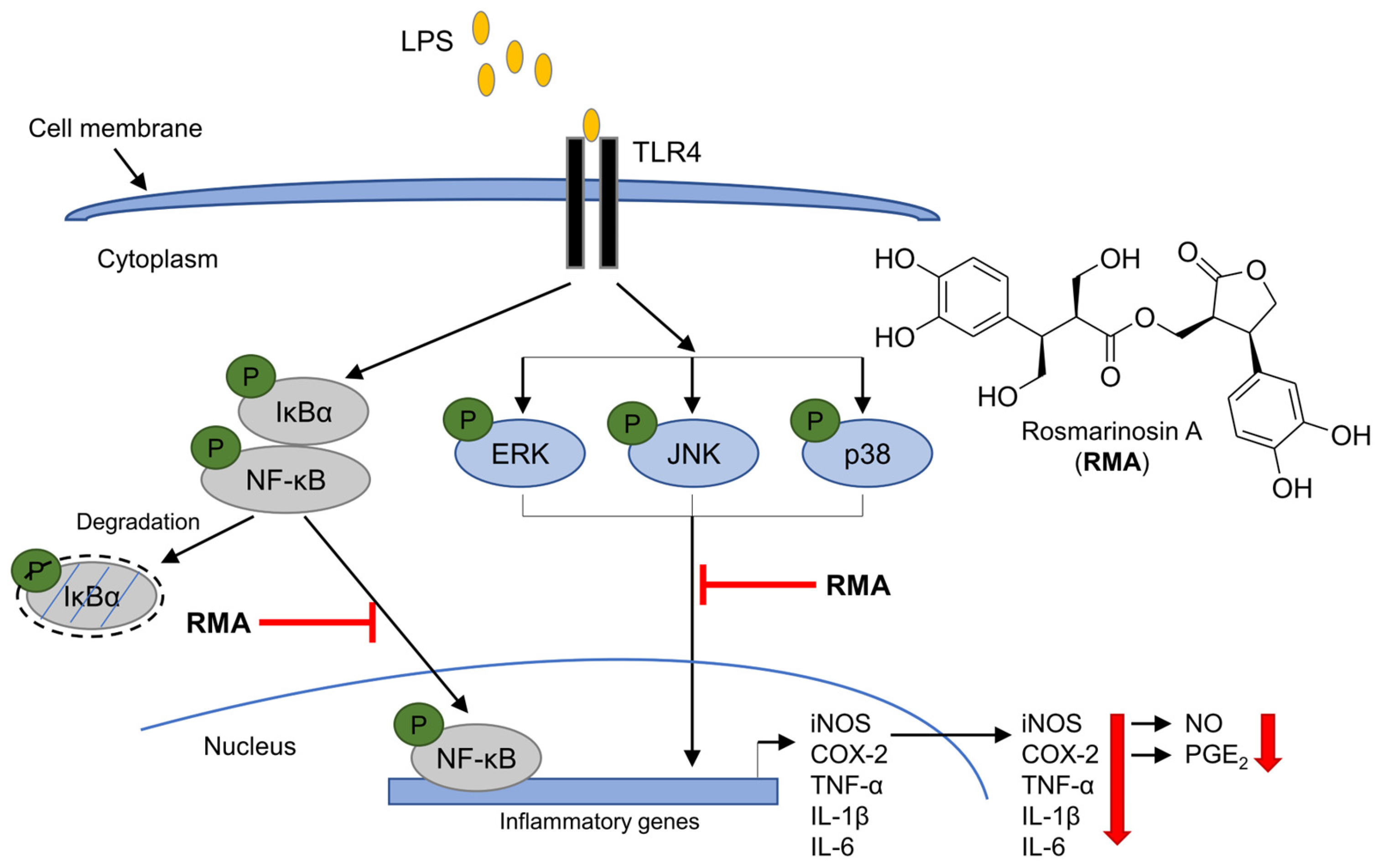
2.5. Effects of Rosmarinosin A on LPS-Stimulated Expression of NF-κB and MAPK-Pathway-Related Proteins
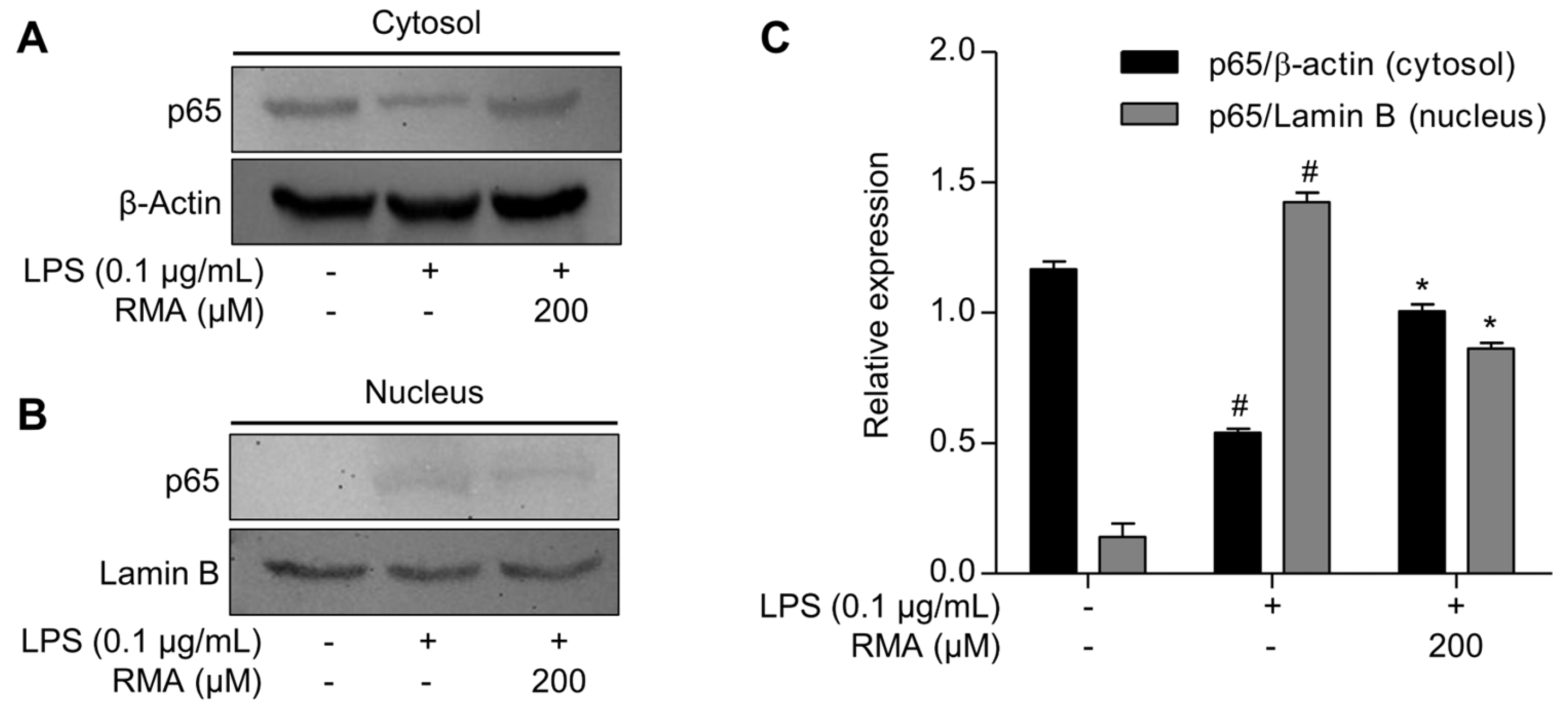
2.6. Effects of Rosmarinosin A on LPS-Stimulated NF-κB Transcriptional Activity via Nuclear Translocation of the p65 Subunit
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Preparation of Rosmarinosin A
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Preparation of Nuclear and Cytosolic Extraction
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, A.U. An overview of inflammation: Mechanism and consequences. Front. Biol. 2011, 6, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Alhamlan, F.S.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory interleukins in infectious diseases: A comprehensive review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puppala, E.R.; Prasad, N.; Prakash, A.N.; Abubakar, M.; Syamprasad, N.P.; Gangasani, J.K.; Naidu, V.G.M. Mesua assamica (King & Prain) kosterm. bark ethanolic extract attenuates rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulating TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2/iNOS and activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathways: A comprehensive study on in-vitro and in-vivo models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdulkhaleq, L.A.; Assi, M.A.; Abdullah, R.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Hezmee, M.N.M. The crucial roles of inflammatory mediators in inflammation: A review. Vet. World 2018, 11, 627. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.C.; Rizer, J.; Selenica, M.L.B.; Reid, P.; Kraft, C.; Johnson, A.; Morgan, D. LPS-induced inflammation exacerbates phospho-tau pathology in rTg4510 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Qi, M.P.; Liu, R.N.; Zhu, X.F.; Hu, C.M. Indirubin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation via TLR4 abrogation mediated by the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Lian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Roles of ROS metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway in quality maintenance of postharvest Pleurotus eryngii under hyperoxia stress. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 207, 112617. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, C.; Mei, X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1456913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.; Simmonds, M.S. Rosmarinic acid. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Muhammad Amir, R.; Martins, N. Therapeutic potential of rosmarinic acid: A comprehensive review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.P.; Inyushkina, Y.V.; Fedoreyev, S.A. Rosmarinic acid and its derivatives: Biotechnology and applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, G.H.; Cho, J.H.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.S.; Bai, H.W.; Chung, B.Y.; Kim, T.H. Gamma irradiation-assisted degradation of rosmarinic acid and evaluation of structures and anti-adipogenic properties. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Pimenta, A.I.; Calhelha, R.C.; Antonio, A.L.; Verde, S.C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C. Effects of gamma irradiation on cytotoxicity and phenolic compounds of Thymus vulgaris L. and Mentha x piperita L. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, E.B.; Jang, B.S.; Byun, E.H.; Sung, N.Y. Effect of gamma irradiation on the change of solubility and anti-inflammation activity of chrysin in macrophage cells and LPS-injected endotoxemic mice. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 127, 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, G.H.; Lee, H.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Chung, B.Y.; Bai, H.W. Novel aminopyridazine derivative of minaprine modified by radiolysis presents potent anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 and DH82 macrophage cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10887. [Google Scholar]
- Hirten, R.P.; Lin, K.C.; Whang, J.; Shahub, S.; Helmus, D.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Longitudinal assessment of sweat-based TNF-alpha in inflammatory bowel disease using a wearable device. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2833. [Google Scholar]
- Sardar, M.; Siddiqui, A.R.; Ahmad, N.; Mushtaq, M.; Shafeeq, S.; Nur-e-Alam, M.; Ul-Haq, Z. Unraveling Interleukin-1β inhibition: Computational insights into anti-inflammatory compound selection for inflammatory disorders. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2025, 135, 108925. [Google Scholar]
- Kerkis, I.; Silva, Á.P.D.; Araldi, R.P. The impact of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and mesenchymal stem cell-derived IL-6 on neurological conditions. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1400533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Ma, T. Function and inhibition of P38 MAP kinase signaling: Targeting multiple inflammation diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115973. [Google Scholar]
- Grela, E.; Kozłowska, J.; Grabowiecka, A. Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria–A review. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.; Kerber, S.; Kelm, M. Reevaluation of the Griess method for determining NO/NO−2 in aqueous and protein-containing samples. Nitric Oxide 1999, 3, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Jeong, G.H.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, K.-B.; Park, S.; Kim, T.H.; Bai, H.-W.; Chung, B.Y. Rosmarinosin A Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2025, 30, 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183752
Lee H, Jeong GH, Lee SS, Lee K-B, Park S, Kim TH, Bai H-W, Chung BY. Rosmarinosin A Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183752
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hanui, Gyeong Han Jeong, Seung Sik Lee, Kyung-Bon Lee, Sanghwa Park, Tae Hoon Kim, Hyoung-Woo Bai, and Byung Yeoup Chung. 2025. "Rosmarinosin A Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183752
APA StyleLee, H., Jeong, G. H., Lee, S. S., Lee, K.-B., Park, S., Kim, T. H., Bai, H.-W., & Chung, B. Y. (2025). Rosmarinosin A Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 30(18), 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183752




