Investigation on the Underlying Mechanisms of the Mechanical and Electrical Enhancement of Nano-SiO2-Doped Epoxy Resins: A Molecular Simulation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
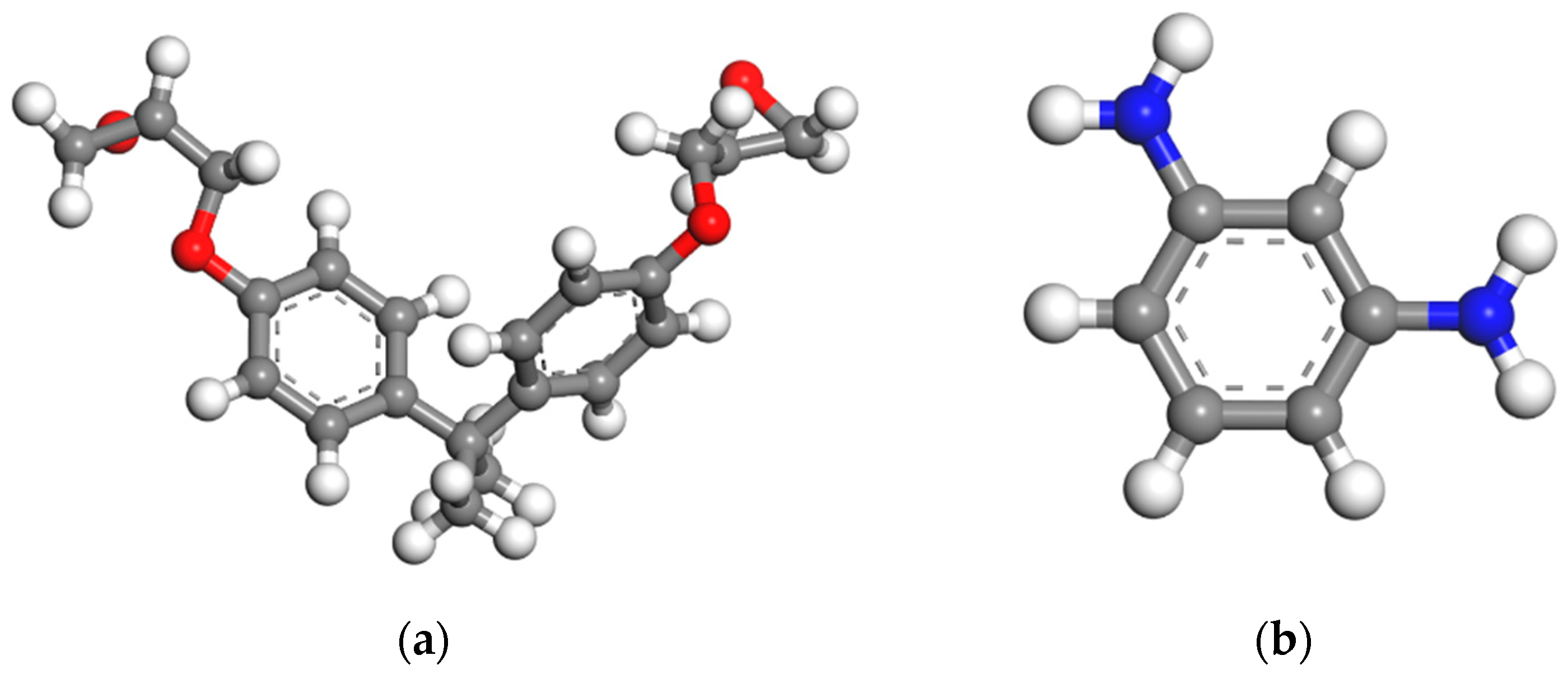
2.1. Molecular Modeling and Simulation Details
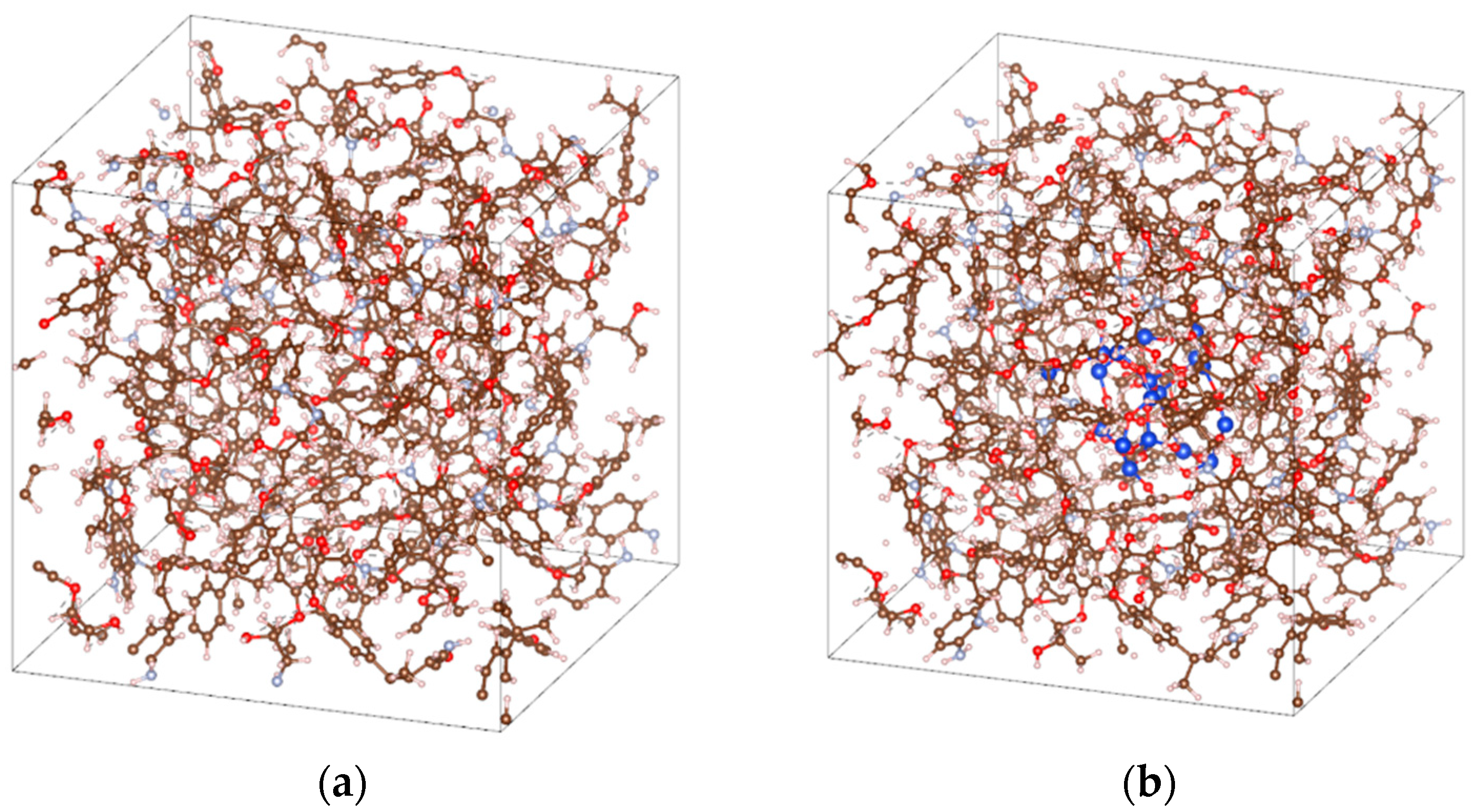
2.1.1. EP/SiO2 Nanocomposite
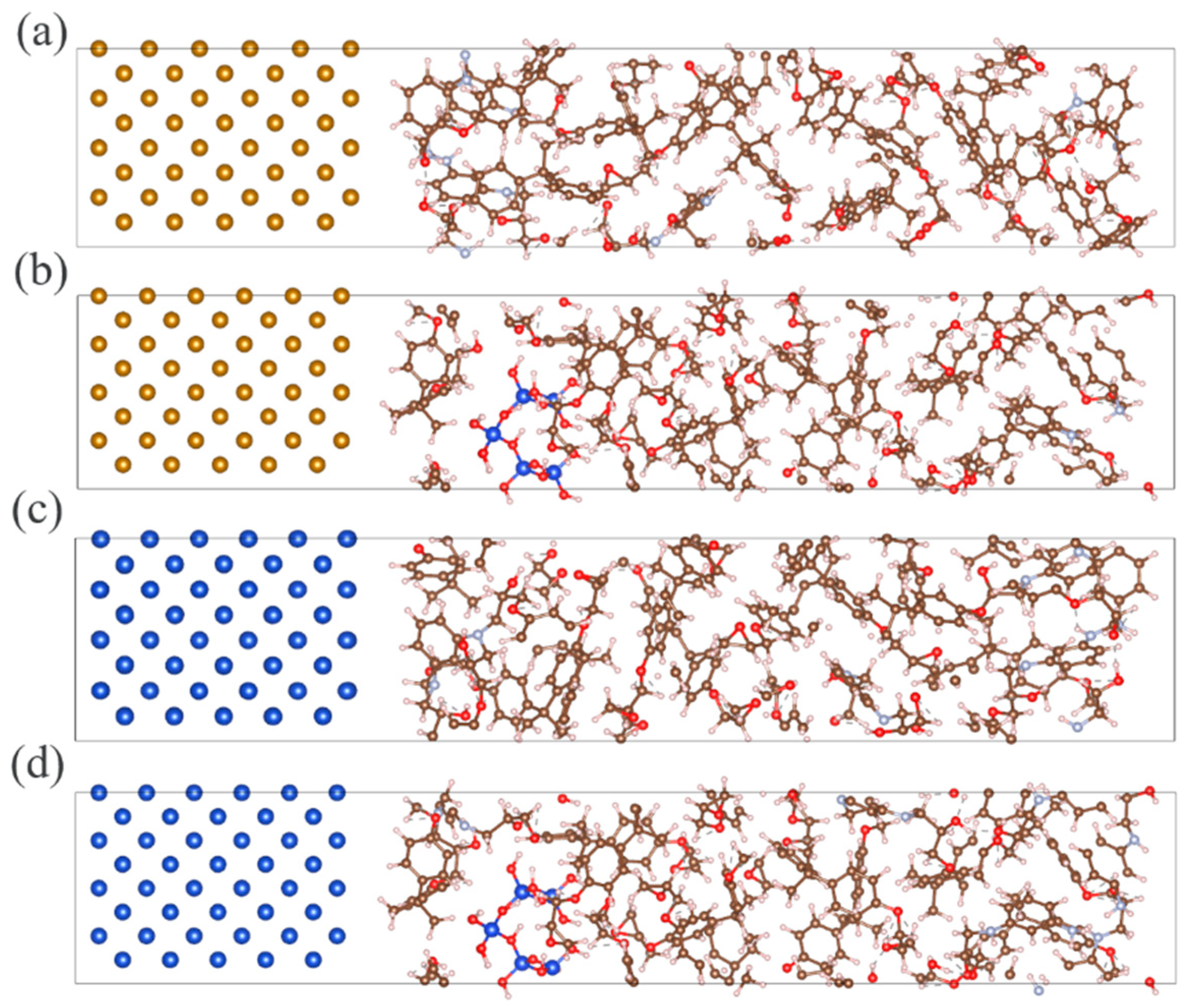
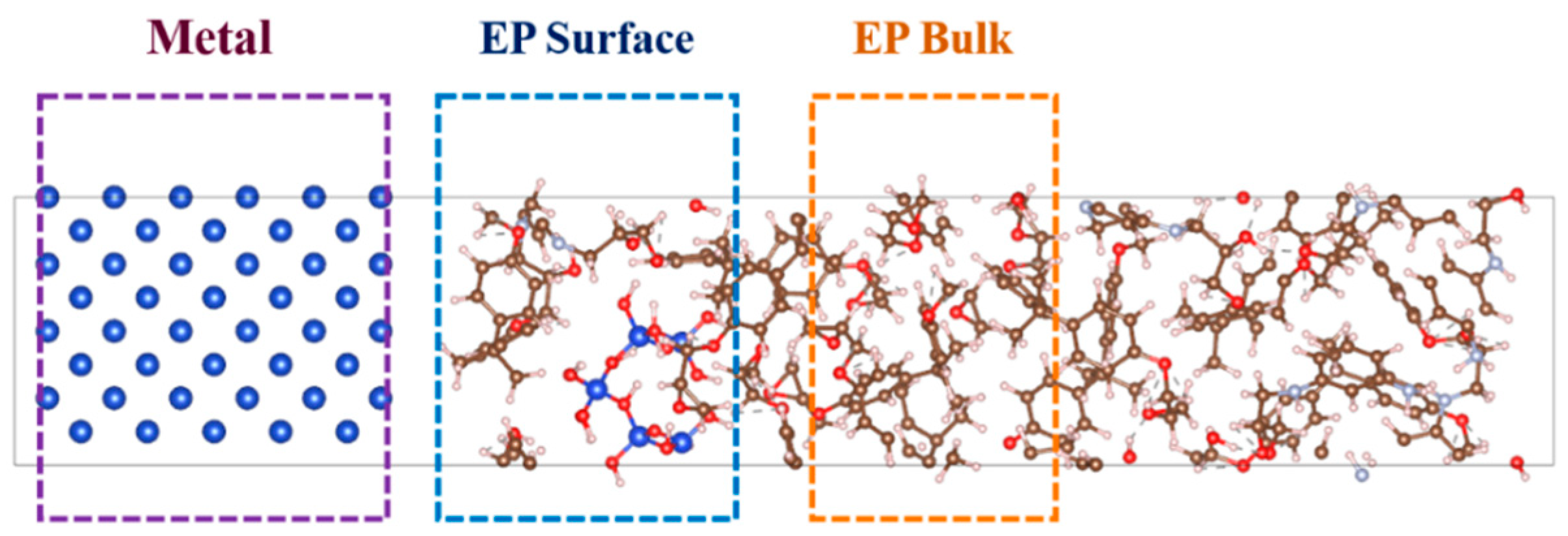
2.1.2. Interfacial Models Between EP/SiO2 Nanocomposite Layer and Metal Layer (Cu or Fe)
2.2. Mechanical Properties of EP/SiO2 Nanocomposite
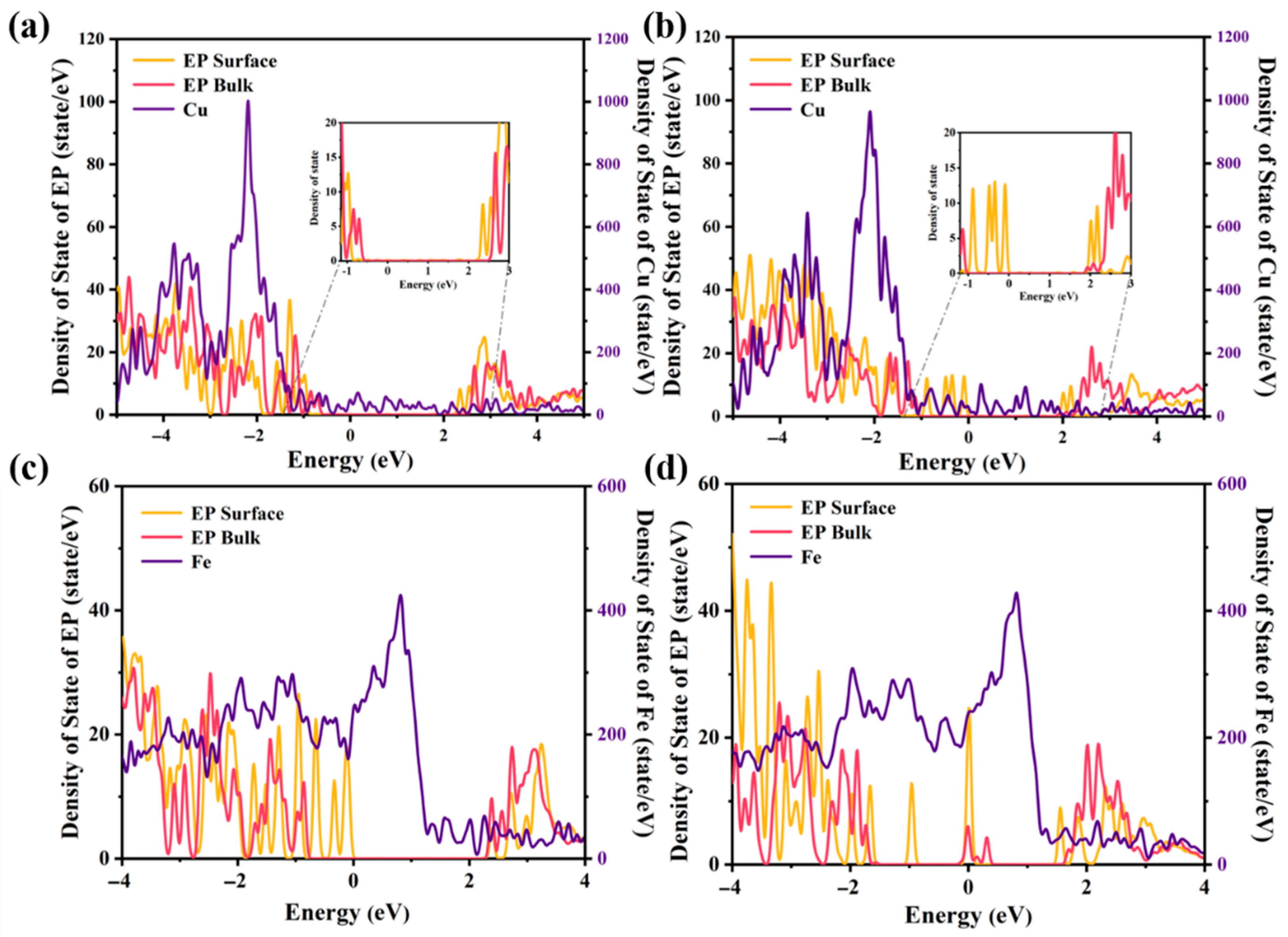
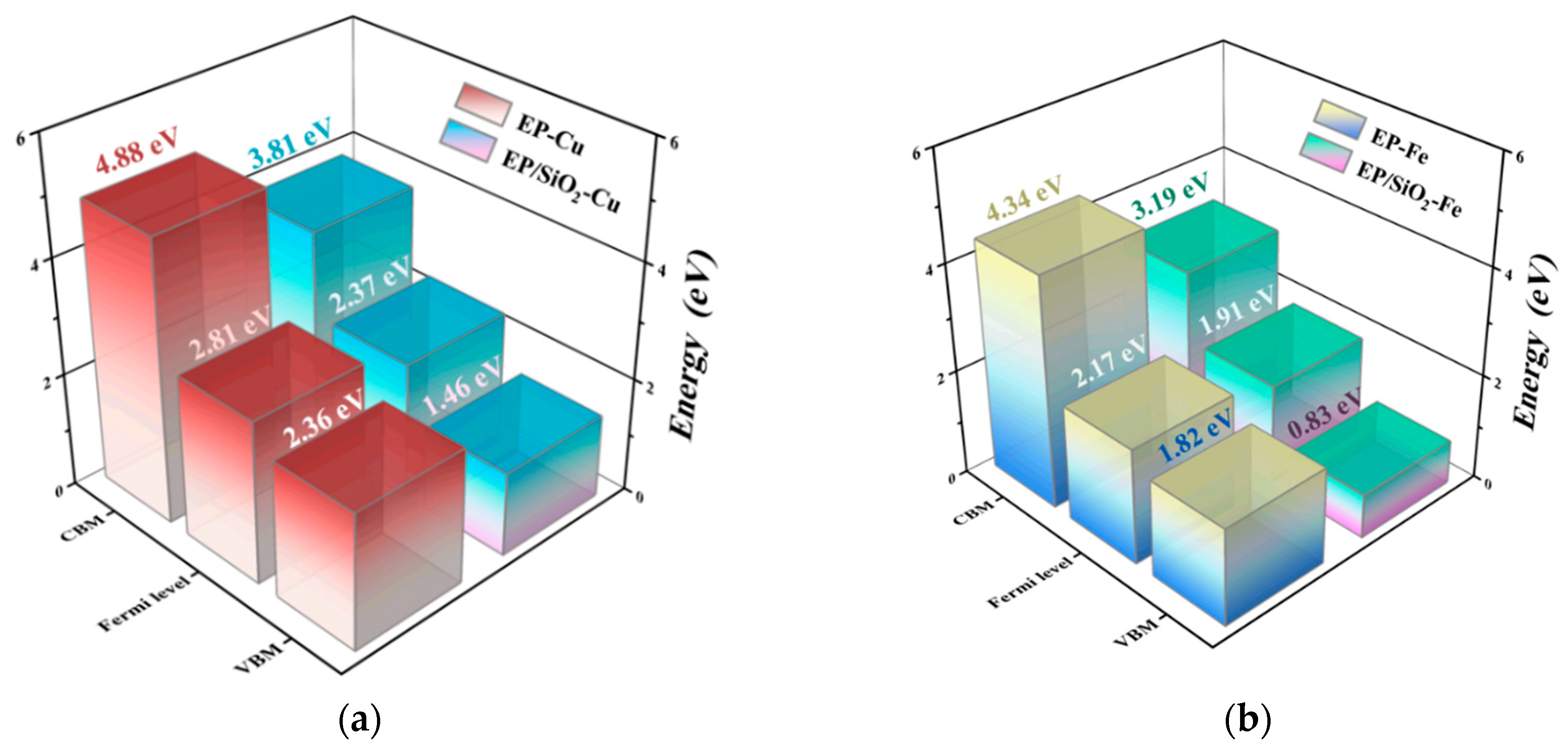
2.3. Electronic Properties Across Different Metal/EP Interfaces with/Without Nano-SiO2 Doping
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohki, Y. Development of Epoxy Resin Composites with High Thermal Conductivity. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2010, 26, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capricho, J.C.; Fox, B.; Hameed, N. Multifunctionality in Epoxy Resins. Polym. Rev. 2019, 60, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhang, H.; Tzounis, L.; Santagiuliana, G.; Bilotti, E.; Papageorgiou, D.G. Multifunctional Epoxy Nanocomposites Reinforced by Two-Dimensional Materials: A Review. Carbon 2021, 185, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S. Nonlinear Dielectric Response and Conductivity Characteristics of Epoxy Resin in High Voltage AC Electric Field. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 58, 015301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-W.; Zeng, R.-C.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.-H.; Wang, G.-L.; Jia, S.-L. Significantly Enhancing the Through-Plane Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Dielectrics by Constructing Aramid Nanofiber/Boron Nitride Three-Dimensional Interconnected Framework. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 136, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, R.; Xing, Z.; Hao, J.; Hu, X.; Min, D.; Li, S.; Wu, Q. Effect of Morphology and Traps on DC Conductivity and Breakdown of Polyethylene Nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2020, 27, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guan, J.; Ding, R. Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Resin Impregnated Paper Insulation in Different Stages of Partial Discharge Development. Polym. Compos. 2019, 41, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, S.; Yu, S.; Lu, Y.-C.; Xu, P.; Chu, B.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Wong, C.-P. Nanoparticles with Rationally Designed Isoelectronic Traps as Fillers Significantly Enhance Breakdown Strength and Electrostatic Energy Density of Polymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 195, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, L.; Du, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W. Enhancing Dielectric Strength of Thermally Conductive Epoxy Composites by Preventing Interfacial Charge Accumulation Using Micron-Sized Diamond. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, F.; Hin, C. Toward a Unified Theory Correlating Electronic, Thermodynamic, and Mechanical Properties at Defective Al/SiO2 Nanodevice Interfaces: An Application to Dielectric Breakdown. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6836–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.-B.; Hong, Z.; Awais, M.; Paramane, A. Enhancement of Insulation Properties of Cross-Linked Polyethylene Utilizing Aromatic Voltage Stabilizers with Electron-Withdrawing and Electron-Donating Groups. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Loi, M.A. The Role of the Interfaces in Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 7, 1901469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Xu, H.; Cheng, C.; Wu, K. A First-Principles Study of the Formation and Regulation of the Electric Double Layers at Cu (0 0 1)/Mineral Oil Interfaces. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 345302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, V.; Giangrande, P.; Galea, M. Influence of Insulation Thermal Aging on the Temperature Assessment in Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, D.; Zhang, G. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Interface Properties and Key Physical Properties of Nanodielectrics Manufactured With Epoxy Resin Doped With Metal Nanoparticles. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34231–34239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, X.; Xue, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, Z.; Tusiime, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J. Simultaneous Optimization of the Thermal Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites through PES and AgNP Functionalized BNs. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 248, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallal, H.A.; Abdul-Hamead, A.A.; Othman, F.M. Effect of Nano Powder (Al2O3-CaO) Addition on the Mechanical Properties of the Polymer Blend Matrix Composite. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Shendye, P.; Markert, B. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Silica Aerogel Nanocomposites Reinforced by Glass Fibers, Graphene Sheets and Carbon Nanotubes: A Comparison Study on Mechanical Properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 190, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, M.F.; Zhang, L.W.; Liew, K.M. Carbon Nanotube-Geopolymer Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Study of the Influence of Interfacial Chemical Bonding upon the Structural and Mechanical Properties. Carbon 2020, 161, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S.-C.; Tsai, J.-L. Characterizing Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Graphene/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Du, B.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Yan, B. Influence of Micro@Nano-Al2O3 Structure on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Conductivity, and Electrical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 51, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitichatpayak, D.; Makcharoen, W.; Vittayakorn, N.; Vittayakorn, W. Influence of Various Nanofillers on Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2022, 61, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xing, W.; Zhang, T.; Chi, Q. Research on Molecular Dynamics and Electrical Properties of High Heat-Resistant Epoxy Resins. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 160, 094902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M. Ultra-High Modulus Epoxy Resin Reinforced by Intensive Hydrogen Bond Network: From Design, Synthesis, Mechanism to Applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 231, 109815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rao, Z. A Molecular Dynamics Study on Heat Conduction of Crosslinked Epoxy Resin Based Thermal Interface Materials for Thermal Management. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 172, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Fu, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, B.; Lu, L.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Lü, F. Micro-Structure and Thermomechanical Properties of Crosslinked Epoxy Composite Modified by Nano-SiO2: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Polymers 2018, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, R.L.C.; Spenley, N.A.; Robertson, S.H. Compass Iii: Automated Fitting Workflows and Extension to Ionic Liquids. Mol. Simul. 2020, 47, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzi, N.; Ebrahim, M. Mechanical Properties and Glass Transition Temperature of Metal-Organic Framework-Filled Epoxy Resin: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 314, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of Ab-Initio Total Energy Calculations for Metals and Semiconductors Using a Plane-Wave Basis Set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab Initio Molecular-Dynamics Simulation of the Liquid-Metal-Amorphous-Semiconductor Transition in Germanium. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics for Liquid Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Lv, C.; Shan, M.; Zhang, H.; Ling, C.; Zhou, X.; Jiao, Z. Glass Transition Temperature of Functionalized Graphene–Polymer Composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 71, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, P. Study of the Glass Transition Temperature and the Mechanical Properties of PET/Modified Silica Nanocomposite by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhang, X.; Qing, S.; Zheng, M.; Wang, H. Stability of Soluble Bulk Nanobubbles: Many-Body Dissipative Particle Dynamics Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 120979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, X. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Micro Mechanism of Functionalized SiO2 Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes Modified Epoxy Resin Adhesives. Polym. Compos. 2024, 46, 1587–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Wen, X.; Szymańska, K.; Mijowska, E.; Hao, C.; Tang, T.; Lei, Q. Polyhydric SiO2 Coating Assistant to Graft Organophosphorus onto Glass Fabric for Simultaneously Improving Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 243, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Lü, F.; Xie, Q.; Ruan, H.; Yang, X.; Liang, S. The Effects of Shape and Mass Fraction of Nano-SiO2 on Thermomechanical Properties of Nano-SiO2/DGEBA/MTHPA Composites: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 015339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. Free Volume: An Indicator of the Glass-Forming Ability in Binary Alloys. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M. A Molecular Dynamic Simulation Method to Elucidate the Interaction Mechanism of Nano-SiO2 in Polymer Blends. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 12889–12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillac, R.; Pullumbi, P.; Coudert, F.-X. ELATE: An Open-Source Online Application for Analysis and Visualization of Elastic Tensors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 275201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Dang, B.; He, J. Titanium Oxide Nanoparticle Increases Shallow Traps to Suppress Space Charge Accumulation in Polypropylene Dielectrics. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48720–48727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; He, J.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y. Large Improvement in Trap Level and Space Charge Distribution of Polypropylene by Enhancing the Crystalline—Amorphous Interface Effect in Blends. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. From Contact Electrification to Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 096502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, G.S.P.; Schein, L.B. General Model of Sphere-Sphere Insulator Contact Electrification. J. Electrost. 1995, 36, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zi, Y.; Wang, A.C.; Zou, H.; Dai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.-C.; Feng, P.; Li, D.; et al. On the Electron-Transfer Mechanism in the Contact-Electrification Effect. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, L.; Kresse, G. Density Functional Study of CO on Rh(111). Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2004, 70, 165405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyd, J.; Scuseria, G.E.; Ernzerhof, M. Hybrid Functionals Based on a Screened Coulomb Potential. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 8207–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, U.; Schuller, M.; Franck, C.M. Theoretical Investigation of HVDC Disc Spacer Charging in SF6 Gas Insulated Systems. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, T. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation Information for Authors. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2023, 30, C4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, G. Charge Accumulation Patterns on Spacer Surface in HVDC Gas-Insulated System: Dominant Uniform Charging and Random Charge Speckles. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, J.; Lin, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G.; He, J. Surface Charge Migration and Dc Surface Flashover of Surface-Modified Epoxy-Based Insulators. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 065301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


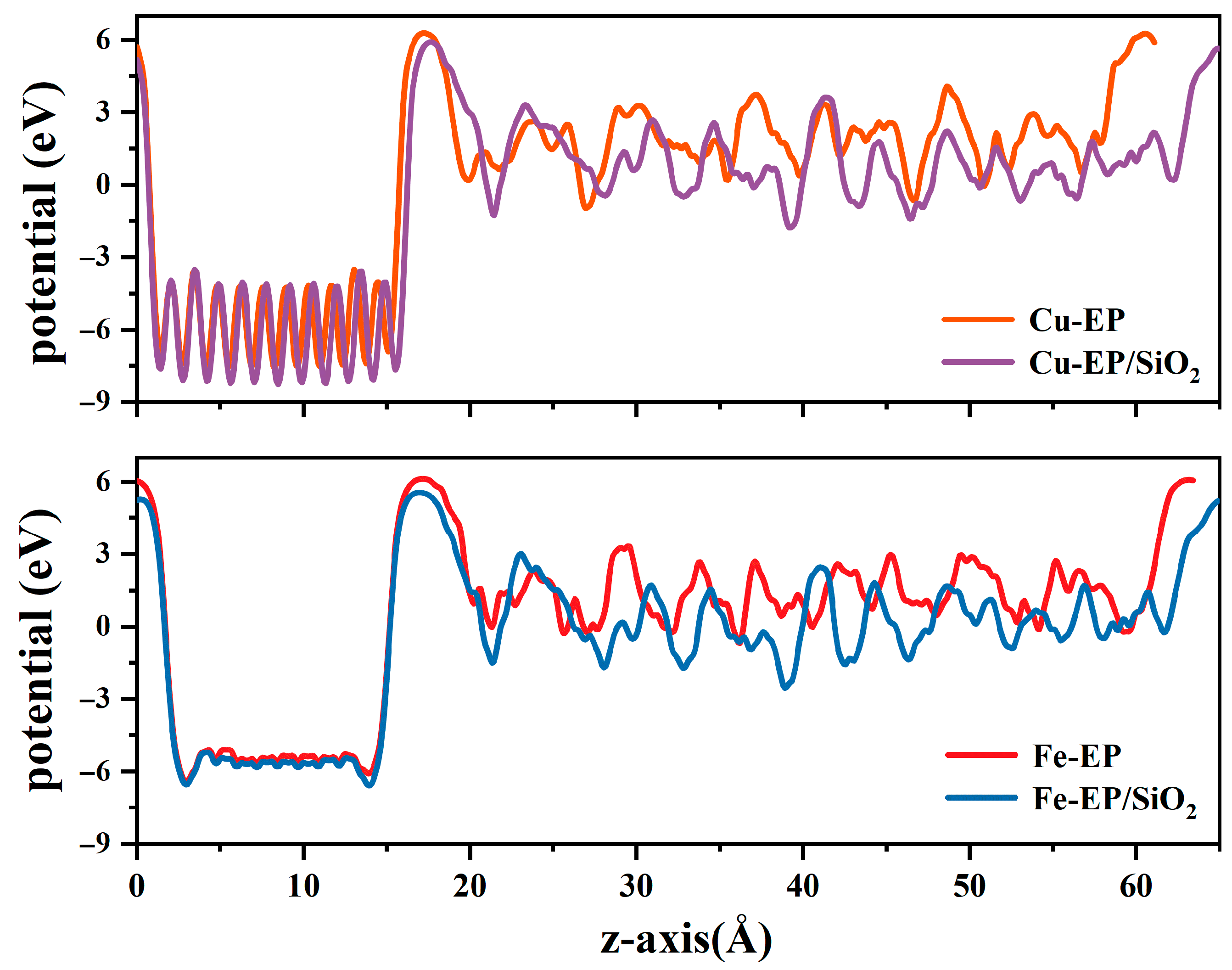
| Average Potential (eV) | Potential Shift (eV) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu-EP | −5.132 | 0 |
| Cu-EP/SiO2 | −5.566 | −0.434 |
| Fe-EP | −4.122 | 0 |
| Fe-EP/SiO2 | −4.381 | −0.259 |
| Average Potential (eV) | Potential Shift (eV) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu-EP | 2.025 | 0 |
| Cu-EP/SiO2 | 1.025 | −1.0 |
| Fe-EP | 1.482 | 0 |
| Fe-EP/SiO2 | 0.393 | −1.089 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, K.; Wang, Y.; Yan, W.; Cao, T.; Du, Y.; Wu, K.; Guo, L. Investigation on the Underlying Mechanisms of the Mechanical and Electrical Enhancement of Nano-SiO2-Doped Epoxy Resins: A Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142960
Cui K, Wang Y, Yan W, Cao T, Du Y, Wu K, Guo L. Investigation on the Underlying Mechanisms of the Mechanical and Electrical Enhancement of Nano-SiO2-Doped Epoxy Resins: A Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(14):2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142960
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Kunqi, Yang Wang, Wenchao Yan, Teng Cao, Yan Du, Kai Wu, and Li Guo. 2025. "Investigation on the Underlying Mechanisms of the Mechanical and Electrical Enhancement of Nano-SiO2-Doped Epoxy Resins: A Molecular Simulation Study" Molecules 30, no. 14: 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142960
APA StyleCui, K., Wang, Y., Yan, W., Cao, T., Du, Y., Wu, K., & Guo, L. (2025). Investigation on the Underlying Mechanisms of the Mechanical and Electrical Enhancement of Nano-SiO2-Doped Epoxy Resins: A Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules, 30(14), 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142960






