Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability
Abstract
1. Introduction
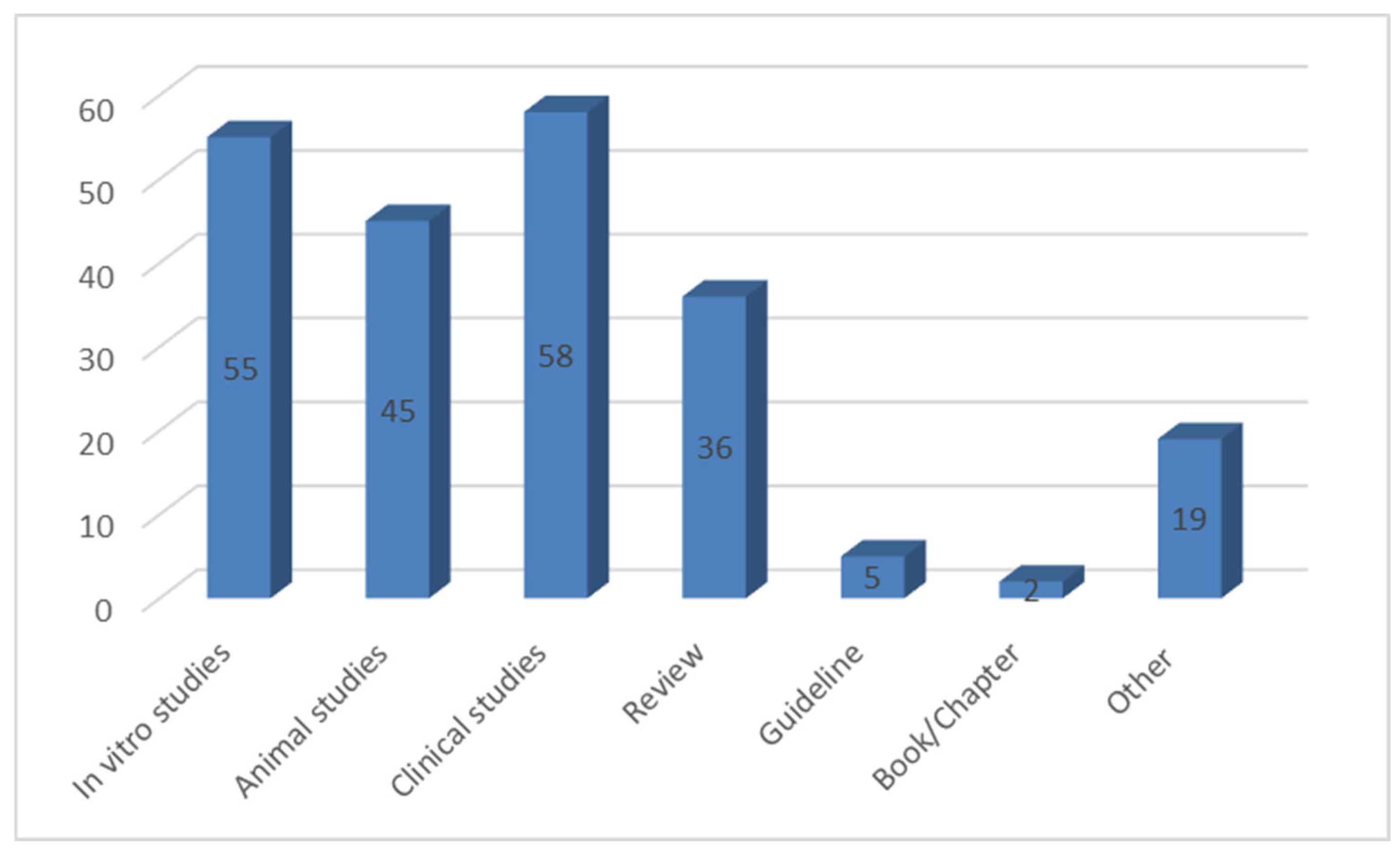
2. Materials and Methods
3. Zn in the Human Body
3.1. Dietary Recommendations for Zn
3.2. Zn Deficiency and Toxicity
3.3. Dietary Sources of Zn
4. Assessment of Trace-Elements Absorption—Differences Between Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability
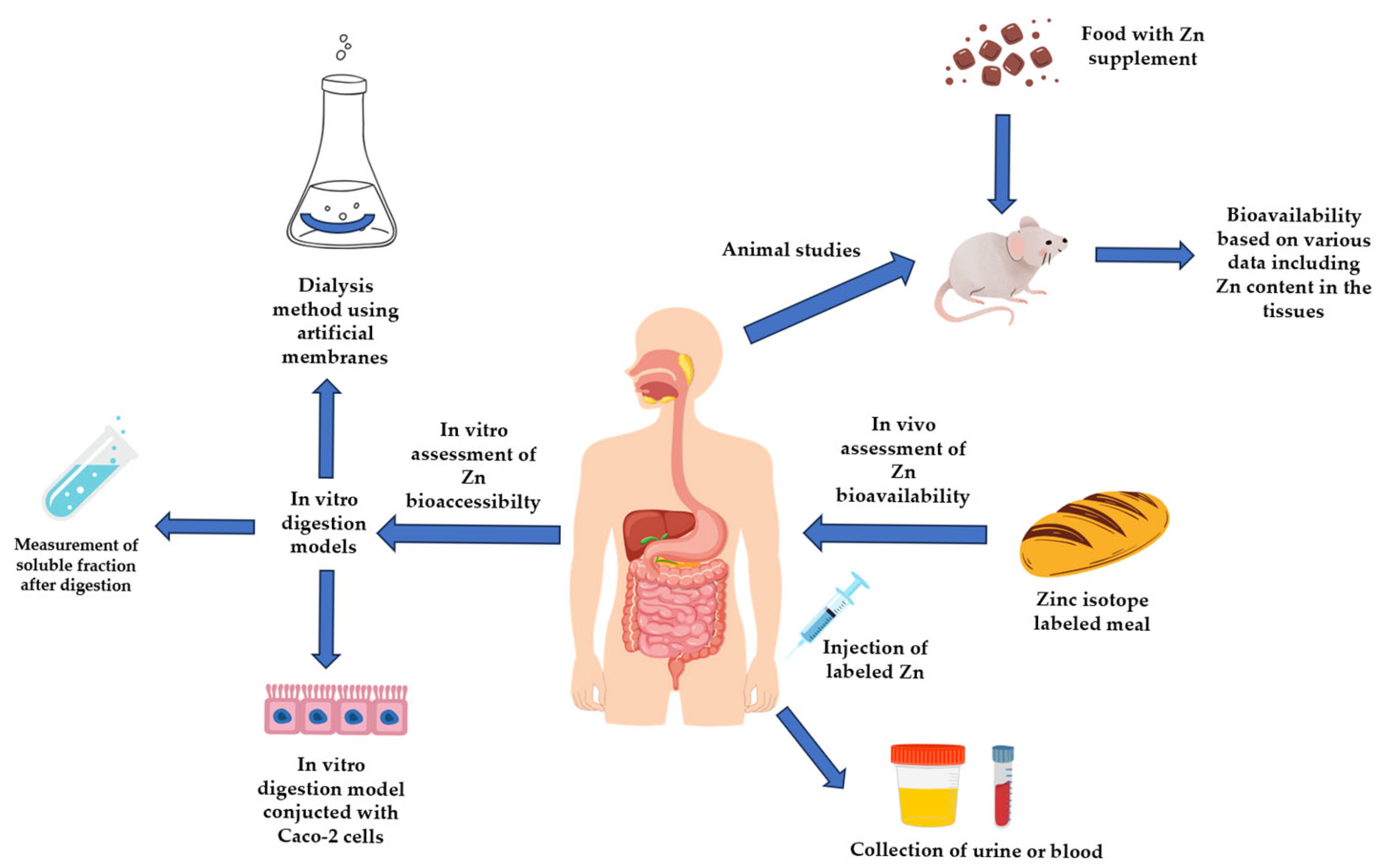
4.1. In Vitro Methods of Zinc Bioaccessibility Assessment
4.2. In Vivo Methods of Zn Bioavailability Assessment
4.2.1. Studies Performed in Animal Models
4.2.2. Clinical Studies
5. Bioaccessibility/Bioavailability of Zinc
5.1. The Influence of Phytates and Dietary Fiber
5.1.1. The Influence of Phytates on the Bioavailability of Zn
5.1.2. The Influence of Dietary Fiber on the Bioavailability of Zn
5.2. The Influence of Proteins and Peptides
5.2.1. The Influence of Proteins on the Bioavailability of Zn
5.2.2. The Influence of Peptides on the Bioavailability of Zn
5.3. The Influence of Other Elements
5.4. Bioaccessibility/Bioavailability Depending on Different Chemical Forms of Zn
5.4.1. In Vitro Studies
5.4.2. Animal Studies
5.4.3. Human Studies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectrometry |
| AE | Acrodermatitis enteropathica |
| ALP | Plasma Alkaline Phosphatase |
| AUC | The Area Under the Curve |
| CPP | Casein Phosphopeptide |
| CuZn-SOD | CuZn Superoxide Dismutase |
| DMT1 | Divalent Metal Ion Transporter |
| FZA | Fractional Zinc Absorption |
| FAZ | Fractional Absorption of Zinc |
| HPIC | High-performance Ion Chromatography |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma-emission coupled Spectrometry |
| PRI | Population Reference Intake |
| RDA | Recommended Dietary Allowances |
| SEC-ICP-MS | Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry |
| TAZ | Total Absorption of Zinc |
| UL | Tolerable Upper Intake Level |
References
- Gibson, R.S.; Hess, S.Y.; Hotz, C.; Brown, K.H. Indicators of Zinc Status at the Population Level: A Review of the Evidence. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxfield, L.; Shukla, S.; Crane, J.S. Zinc Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Knez, M.; Stangoulis, J.C.R. Dietary Zn Deficiency, the Current Situation and Potential Solutions. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 36, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belay, A.; Gashu, D.; Joy, E.J.M.; Lark, R.M.; Chagumaira, C.; Likoswe, B.H.; Zerfu, D.; Ander, E.L.; Young, S.D.; Bailey, E.H.; et al. Zinc Deficiency Is Highly Prevalent and Spatially Dependent over Short Distances in Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, P.M.; Marcelino, G.; Santana, L.F.; de Almeida, E.B.; Guimarães, R.d.C.A.; Pott, A.; Hiane, P.A.; Freitas, K.d.C. Minerals in Pregnancy and Their Impact on Child Growth and Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Ali, I.; Rust, P.; Kundi, M.; Ekmekcioglu, C. Selenium, Zinc, and Manganese Status in Pregnant Women and Its Relation to Maternal and Child Complications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, W.; Jiang, S.; Fang, H.; Yu, D.; Yang, L. Study on the Zinc Nutritional Status and Risk Factors of Chinese 6–18-Year-Old Children. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, M.; Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Glibetic, M.; Tako, E. The Linoleic Acid: Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid Ratio (LA:DGLA)—An Emerging Biomarker of Zn Status. Nutrients 2017, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkembi, B.; Huppertz, T. Influence of Dairy Products on Bioavailability of Zinc from Other Food Products: A Review of Complementarity at a Meal Level. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.K.; Pfaender, S.; Hagmeyer, S.; Tarana, L.; Mattes, A.-K.; Briel, F.; Küry, S.; Boeckers, T.M.; Grabrucker, A.M. Characterization of Zinc Amino Acid Complexes for Zinc Delivery in Vitro Using Caco-2 Cells and Enterocytes from hiPSC. Biometals 2017, 30, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-González, R.; Romarís-Hortas, V.; García-Sartal, C.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; del Carmen Barciela-Alonso, M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Evaluation of an in Vitro Method to Estimate Trace Elements Bioavailability in Edible Seaweeds. Talanta 2010, 82, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; Romarís-Hortas, V.; Moscoso-Pérez, C.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. In-Vivo and in-Vitro Testing to Assess the Bioaccessibility and the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Selenium and Mercury Species in Food Samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemrani, B.; Bines, J.E. Recent Insights into Trace Element Deficiencies: Causes, Recognition and Correction. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 36, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saper, R.B.; Rash, R. Zinc: An Essential Micronutrient. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 79, 768. [Google Scholar]
- Gapys, B.; Raszeja-Specht, A.; Bielarczyk, H. Role of Zinc in Physiological and Pathological Processes of the Body. J. Lab. Diagn. 2014, 50, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and Human Health: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Roles of Zinc Transporters in Zinc Homeostasis and Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, C. Zinc: Physiology, Deficiency, and Parenteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Duan, M.; Fang, B.; Zhao, G.; Leng, X.; Zhang, T. Zinc Homeostasis and Regulation: Zinc Transmembrane Transport through Transporters. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 7627–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, D.G.; Hufnagl, K.; Comberiati, P.; Roth-Walter, F. Lack of Iron, Zinc, and Vitamins as a Contributor to the Etiology of Atopic Diseases. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1032481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, R.; Tay, F.; Zeder, C.; Brnić, M.; Hurrell, R.F. Zinc Absorption by Young Adults from Supplemental Zinc Citrate Is Comparable with That from Zinc Gluconate and Higher than from Zinc Oxide. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Shames, D.M.; Lowe, N.M.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Sutherland, B.; Abrams, S.A.; Turnlund, J.R.; Jackson, M.J. Effect of Acute Zinc Depletion on Zinc Homeostasis and Plasma Zinc Kinetics in Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhorn, V.; Haase, H.; Maares, M. Interaction and Competition for Intestinal Absorption by Zinc, Iron, Copper, and Manganese at the Intestinal Mucus Layer. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 84, 127459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W. Zinc Biochemistry: From a Single Zinc Enzyme to a Key Element of Life. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallee, B.L.; Falchuk, K.H. The Biochemical Basis of Zinc Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 1993, 73, 79–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.G.; Park, S.; Lim, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Song, S.Y.; Roh, T.-Y.; Sung, J.-H.; Suh, W.; Ham, S.-J.; Lim, K.-H.; et al. ZNF224, Krüppel like Zinc Finger Protein, Induces Cell Growth and Apoptosis-Resistance by down-Regulation of P21 and P53 via miR-663a. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31177–31190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-H.; Sermersheim, M.; Li, H.; Lee, P.H.U.; Steinberg, S.M.; Ma, J. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrajnowska, D.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B. Role of Zinc in Immune System and Anti-Cancer Defense Mechanisms. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Cai, L.; Mu, L.-N.; Lu, Q.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Cui, Y.; Sul, J.H.; Zhou, X.-F.; Ding, B.-G.; Elashoff, R.M.; et al. Dietary Mineral and Trace Element Intake and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus in a Chinese Population. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 55, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y. Association between Serum Zinc Levels and Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Słowińska, K.; Płaczkowska, S.; Prescha, A.; Pawełczyk, K.; Porębska, I.; Kosacka, M.; Pawlik-Sobecka, L.; Grajeta, H. Serum and Whole Blood Zn, Cu and Mn Profiles and Their Relation to Redox Status in Lung Cancer Patients. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 45, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbard, A. Zinc in Cancer Therapy Revisited. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2022, 24, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molenda, M.; Kolmas, J. The Role of Zinc in Bone Tissue Health and Regeneration—A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 5640–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Steiner, D.F.; Philipson, L.H. Insulin Biosynthesis, Secretion, Structure, and Structure-Activity Relationships. In Endotext; MDText.Com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaka, A.; Fujitani, Y. Role of Zinc Homeostasis in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severo, J.S.; Morais, J.B.S.; de Freitas, T.E.C.; Andrade, A.L.P.; Feitosa, M.M.; Fontenelle, L.C.; de Oliveira, A.R.S.; Cruz, K.J.C.; do Nascimento Marreiro, D. The Role of Zinc in Thyroid Hormones Metabolism. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickram, S.; Rohini, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Nancy Veenakumari, D.; Archana, K.; Anbarasu, K.; Jeyanthi, P.; Thanigaivel, S.; Gulothungan, G.; Rajendiran, N.; et al. Role of Zinc (Zn) in Human Reproduction: A Journey from Initial Spermatogenesis to Childbirth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacik, A.; Tirpak, F.; Tomka, M.; Miskeje, M.; Tvrda, E.; Arvay, J.; Andreji, J.; Slanina, T.; Gabor, M.; Hleba, L.; et al. Trace Elements Content in Semen and Their Interactions with Sperm Quality and RedOx Status in Freshwater Fish Cyprinus carpio: A Correlation Study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, V.; Pullakhandam, R.; Nair, K.M. Coordinate Expression and Localization of Iron and Zinc Transporters Explain Iron–Zinc Interactions during Uptake in Caco-2 Cells: Implications for Iron Uptake at the Enterocyte. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaiah, P.; Aslam, M.F.; Mashurabad, P.C.; Sharp, P.A.; Pullakhandam, R. Zinc Induces Iron Uptake and DMT1 Expression in Caco-2 Cells via a PI3K/IRP2 Dependent Mechanism. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, V.; Pullakhandam, R.; Nair, K.M. Iron-Zinc Interaction during Uptake in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Line: Kinetic Analyses and Possible Mechanism. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 46, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, L.A.; Parnell, W.R.; Thomson, C.D.; Green, T.J.; Gibson, R.S. Serum Zinc Is a Major Predictor of Anemia and Mediates the Effect of Selenium on Hemoglobin in School-Aged Children in a Nationally Representative Survey in New Zealand. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergul, A.B.; Turanoglu, C.; Karakukcu, C.; Karaman, S.; Torun, Y.A. Increased Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children with Zinc Deficiency. Eurasian J. Med. 2018, 50, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, R.; Yong, V.W.; Xue, M. The Important Role of Zinc in Neurological Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, L.I.; Ferrao, K.; Mehta, K.J. Role of Zinc in Health and Disease. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, K.R.; Brown, K.H. Estimating the Global Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency: Results Based on Zinc Availability in National Food Supplies and the Prevalence of Stunting. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Romeo, J.; Malavolta, M.; Costarelli, L.; Giacconi, R.; Diaz, L.-E.; Marcos, A. Zinc: Dietary Intake and Impact of Supplementation on Immune Function in Elderly. Age 2013, 35, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-309-15742-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ewa, R.; Stoś, K.; Woźniak, A.; Mojska, H. Normy żywienia dla populacji Polski; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warszawa, Poland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosz, M.; Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Charzewska, J. Normy Żywienia Dla Populacji Polski i Ich Zastosowanie; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warszawa, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65870-28-5. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 92-4-154612-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs, H.; Schmit, J.; Rink, L. Zinc Toxicity: Understanding the Limits. Molecules 2024, 29, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Zinc. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3844. [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft Für Ernährung e. V. Zink. Available online: https://www.dge.de/wissenschaft/referenzwerte/zink/ (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- ANSES Dietary Reference Values for Vitamins and Minerals. Available online: https://www.anses.fr/en/content/dietary-reference-values-vitamins-and-minerals (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Nutrient Requirements for Indians; Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR): New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Sandstead, H.H. Zinc Requirements and the Risks and Benefits of Zinc Supplementation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; King, J.C.; Lowe, N. A Review of Dietary Zinc Recommendations. Food Nutr. Bull. 2016, 37, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, H. Zinc Deficiency and Clinical Practice—Validity of Zinc Preparations. Yakugaku Zasshi 2008, 128, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B. Dietary Factors Influencing Zinc Absorption. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1378S–1383S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.; Golik, A. Zinc Balance and Medications Commonly Used in the Management of Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2006, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, M.; Samman, S. Chapter Three—Vegetarian Diets Across the Lifecycle: Impact on Zinc Intake and Status. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Henry, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 74, pp. 93–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chouraqui, J.-P. Risk Assessment of Micronutrients Deficiency in Vegetarian or Vegan Children: Not So Obvious. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufingerl, N.; Eilander, A. Nutrient Intake and Status in Adults Consuming Plant-Based Diets Compared to Meat-Eaters: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, J.P. Iron, Zinc, and Physical Performance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 188, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C. Zinc: An Essential but Elusive Nutrient. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 679S–684S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoh, N.Z.; Rink, L. Zinc in Infection and Inflammation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.; Samman, S. Zinc and Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokines: Implications for Cardiometabolic Disease. Nutrients 2012, 4, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennigar, S.R.; Kelley, A.M.; McClung, J.P. Metallothionein and Zinc Transporter Expression in Circulating Human Blood Cells as Biomarkers of Zinc Status: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morata, I.; Sobel, M.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Howe, C.G.; Sanchez, T.R. A State-of-the-Science Review on Metal Biomarkers. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambidge, M. Human Zinc Deficiency. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1344S–1349S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tako, E. Dietary Trace Minerals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Sekiguchi, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Akai, R.; Iwawaki, T.; Makiguchi, T.; Yokoo, S.; Ishikawa, O.; Motegi, S. Zinc Deficiency Exacerbates Pressure Ulcers by Increasing Oxidative Stress and ATP in the Skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 95, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andino, D.; Moy, J.; Gaynes, B.I. Serum Vitamin A, Zinc and Visual Function in Children with Moderate to Severe Persistent Asthma. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grüngreiff, K.; Gottstein, T.; Reinhold, D. Zinc Deficiency—An Independent Risk Factor in the Pathogenesis of Haemorrhagic Stroke? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, K.Y.; Castellanos, X.; Humphries, L.L.; Austin, J. Altered Zinc Metabolism in Mood Disorder Patients. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 26, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swardfager, W.; Herrmann, N.; Mazereeuw, G.; Goldberger, K.; Harimoto, T.; Lanctôt, K.L. Zinc in Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.-H.; Park, Y. Associations between Dietary Pattern and Depression in Korean Adolescent Girls. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2015, 28, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisławska, M.; Szkup-Jabłońska, M.; Jurczak, A.; Wieder-Huszla, S.; Samochowiec, A.; Jasiewicz, A.; Noceń, I.; Augustyniuk, K.; Brodowska, A.; Karakiewicz, B.; et al. The Severity of Depressive Symptoms vs. Serum Mg and Zn Levels in Postmenopausal Women. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 157, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maserejian, N.N.; Hall, S.A.; McKinlay, J.B. Low Dietary or Supplemental Zinc Is Associated with Depression Symptoms among Women, but Not Men, in a Population-Based Epidemiological Survey. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, S.M.; Ruusunen, A.; Tolmunen, T.; Voutilainen, S.; Tuomainen, T.-P.; Kauhanen, J. Dietary Zinc Intake and the Risk of Depression in Middle-Aged Men: A 20-Year Prospective Follow-up Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, N.; Lubec, G.; Singewald, N. Zinc Deficiency Induces Enhanced Depression-like Behaviour and Altered Limbic Activation Reversed by Antidepressant Treatment in Mice. Amino Acids 2009, 36, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassabehji, N.M.; Corniola, R.S.; Alshingiti, A.; Levenson, C.W. Zinc Deficiency Induces Depression-like Symptoms in Adult Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Moxey, A.; Nowak, G.; Vashum, K.; Bailey, K.; McEvoy, M. The Efficacy of Zinc Supplementation in Depression: Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, e31–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwek, M.; Dudek, D.; Paul, I.A.; Sowa-Kućma, M.; Zięba, A.; Popik, P.; Pilc, A.; Nowak, G. Zinc Supplementation Augments Efficacy of Imipramine in Treatment Resistant Patients: A Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 118, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; D’Amico, F.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S. Gut Microbiome–Micronutrient Interaction: The Key to Controlling the Bioavailability of Minerals and Vitamins? Biofactors 2022, 48, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Martono, P.D.; Kameo, S.; Suradji, E.W.; Koyama, H. Effect of Probiotic L. Plantarum IS-10506 and Zinc Supplementation on Humoral Immune Response and Zinc Status of Indonesian Pre-School Children. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Gnoni, A.; De Vito, D.; Dipalma, G.; Cantore, S.; Gargiulo Isacco, C.; Saini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Topi, S.; Scarano, A.; et al. Effect of Probiotics on the Occurrence of Nutrition Absorption Capacities in Healthy Children: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glutsch, V.; Hamm, H.; Goebeler, M. Zinc and Skin: An Update. JDDG J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The Essential Toxin: Impact of Zinc on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.; Członkowska, A.; Gaskin, S.; Granzotto, A.; Sensi, S.L.; Hoogenraad, T.U. The Role of Zinc in the Treatment of Wilson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosmire, G.J. Zinc Toxicity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porea, T.J.; Belmont, J.W.; Mahoney, J.; Donald, H. Zinc-Induced Anemia and Neutropenia in an Adolescent. J. Pediatr. 2000, 136, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, K.; Przygodna, B.; Nadolna, I.; Iwanow, K. Tabele Składu i Wartości Odżywczej Żywności, 2nd ed.; PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.M.d.C.C.; Vicente, A.F.d.R.B. Meat Nutritional Composition and Nutritive Role in the Human Diet. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, J.L.d.P.; Baptista, D.P.; Orlando, E.A.; Gigante, M.L.; Pallone, J.A.L. Effect of Processing on the Bioaccessibility of Essential Minerals in Goat and Cow Milk and Dairy Products Assessed by Different Static in Vitro Digestion Models. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemianowski, K.; Szpendowski, J.; Tońska, E. Chudy twaróg kwasowy jako źródło wybranych składników mineralnych w diecie osób dorosłych. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2015, 96, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Suliburska, J.; Krejpcio, Z. Evaluation of the Content and Bioaccessibility of Iron, Zinc, Calcium and Magnesium from Groats, Rice, Leguminous Grains and Nuts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, A.; Zaręba, S.; Wyszogrodzka-Koma, L. Ocena Zawartości Miedzi i Cynku w Wybranych Produktach Zbożowych. Bromatol. Chem. Toksykol. 2011, 44, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Golan, Y.; Kambe, T.; Assaraf, Y.G. The Role of the Zinc Transporter SLC30A2/ZnT2 in Transient Neonatal Zinc Deficiency. Metallomics 2017, 9, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, Y.; Assaraf, Y.G. Genetic and Physiological Factors Affecting Human Milk Production and Composition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marze, S. Bioavailability of Nutrients and Micronutrients: Advances in Modeling and In Vitro Approaches. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Sesmaisons, A. de Approaches Used to Estimate Bioavailability When Deriving Dietary Reference Values for Iron and Zinc in Adults. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.G.; King, J.C. The Molecular Basis for Zinc Bioavailability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Capella, J.M.; Buniowska, M.; Barba, F.J.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A. Analytical Methods for Determining Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T.; Carriere, F.; Day, L.; Deglaire, A.; Egger, L.; Freitas, D.; Golding, M.; Le Feunteun, S.; Macierzanka, A.; Menard, O.; et al. Correlation between in Vitro and in Vivo Data on Food Digestion. What Can We Predict with Static in Vitro Digestion Models? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2239–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawiec, P.; Sawicki, J.; Łasińska-Pracuta, P.; Czop, M.; Sowa, I.; Iłowiecka, K.; Koch, W. In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Se from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawiec, P.; Sawicki, J.; Łasińska-Pracuta, P.; Czop, M.; Sowa, I.; Helon, P.; Pietrzak, K.; Koch, W. In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Cr from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements from the Polish Market. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórska, J.; Pietrzak, K.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Czop, M.; Laszuk, J.; Koch, W. Influence of Diet on the Bioavailability of Active Components from Zingiber Officinale Using an In Vitro Digestion Model. Foods 2023, 12, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskwa, J.; Naliwajko, S.K.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Soroczyńska, J.; Socha, K.; Koch, W.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R. In Vitro Assessment of the Bioaccessibility of Zn, Ca, Mg, and Se from Various Types of Nuts. Foods 2023, 12, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajkowska, S.; Moskwa, J.; Socha, K.; Leśniewska, B. Evaluation of the Bioaccessibility of Essential and Toxic Trace Elements in Basil, Peppermint, and Rosemary Using an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 6189–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheftel, J.; Loechl, C.; Mokhtar, N.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Use of Stable Isotopes to Evaluate Bioefficacy of Provitamin A Carotenoids, Vitamin A Status, and Bioavailability of Iron and Zinc. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Food Bioactive Compounds; Overview and Assessment by in Vitro Methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaimat, A.S.; Barciela-Alonso, M.C.; Herbello-Hermelo, P.; Domínguez-González, R.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. In Vitro Assessment of Major and Trace Element Bioaccessibility in Tea Samples. Talanta 2021, 225, 122083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.D.; Schricker, B.R.; Rasmussen, R.R.; Van Campen, D. An in Vitro Method for Estimation of Iron Availability from Meals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2248–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ośko, J.; Pierlejewska, W.; Grembecka, M. Comparison of the Potential Relative Bioaccessibility of Zinc Supplements—In Vitro Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ośko, J.; Nasierowska, K.; Grembecka, M. Application of In Vitro Digestion Models in the Evaluation of Dietary Supplements. Foods 2024, 13, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuenemann, E.C. Dynamic Digestion Models: General Introduction. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., López-Expósito, I., Kleiveland, C., Lea, T., Mackie, A., Requena, T., Swiatecka, D., Wichers, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-15791-7. [Google Scholar]
- Brigide, P.; Torres, L.C.R.; Canniati Brazaca, S.G.; Figliuzzi, R.S.; Costa, N.M.B. Bioaccessibility of Minerals in Combinations of Biofortified Foods with Fe, Zn and Vitamin A. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4083–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Yuwei, L.; Zhenping, H.; Qian, W. Impact of Heat Processing on the Bioavailability of Zinc and Iron from Cereals and Pulses. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Effects of Dietary Supplements on the Bioaccessibility of Se, Zn and Cd in Rice: Preliminary Observations from In Vitro Gastrointestinal Simulation Tests. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H. Caseinophosphopeptides Overcome Calcium Phytate Inhibition on Zinc Bioavailability by Retaining Zinc from Coprecipitation as Zinc/Calcium Phytate Nanocomplexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Ahluwalia, A. Advances and Current Challenges in Intestinal in Vitro Model Engineering: A Digest. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etcheverry, P.; Grusak, M.A.; Fleige, L.E. Application of in Vitro Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability Methods for Calcium, Carotenoids, Folate, Iron, Magnesium, Polyphenols, Zinc, and Vitamins B6, B12, D, and E. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maares, M.; Haase, H. A Guide to Human Zinc Absorption: General Overview and Recent Advances of In Vitro Intestinal Models. Nutrients 2020, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latunde-Dada, G.O.; Kajarabille, N.; Rose, S.; Arafsha, S.M.; Kose, T.; Aslam, M.F.; Hall, W.L.; Sharp, P.A. Content and Availability of Minerals in Plant-Based Burgers Compared with a Meat Burger. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maares, M.; Keil, C.; Pallasdies, L.; Schmacht, M.; Senz, M.; Nissen, J.; Kieserling, H.; Drusch, S.; Haase, H. Zinc Availability from Zinc-Enriched Yeast Studied with an in Vitro Digestion/Caco-2 Cell Culture Model. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 71, 126934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-Y.; Pai, T.-K.; Han, O. Effect of Bioactive Dietary Polyphenols on Zinc Transport across the Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3606–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.; Krüger, T.F.; Hjorth, T.P.; Buhl, E.H.; Sørensen, E.S. Milk Osteopontin Mediates Zinc Uptake in Intestinal Cells in the Presence of Phytic Acid. Int. Dairy J. 2025, 161, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpashree, B.G.; Arora, S.; Kapila, S.; Sharma, V. Physicochemical Characterization of Mineral (Iron/Zinc) Bound Caseinate and Their Mineral Uptake in Caco-2 Cells. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maares, M.; Keil, C.; Koza, J.; Straubing, S.; Schwerdtle, T.; Haase, H. In Vitro Studies on Zinc Binding and Buffering by Intestinal Mucins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Reynold, C.; Navarro-Alarcon, M.; de la Serrana, H.L.-G.; Perez-Valero, V.; Lopez-Martinez, M.C. In Vitro Determination of Zinc Dialyzability from Duplicate Hospital Meals: Influence of Other Nutrients. Nutrition 2008, 24, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Jyothi Lakshmi, A. Maximising the Bioaccessibility of Iron and Zinc of a Complementary Food Mix through Multiple Strategies. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Merwe, R.; Kruger, J.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Duodu, K.G.; Taylor, J.R.N. Improving Iron and Zinc Bioaccessibility through Food-to-Food Fortification of Pearl Millet with Tropical Plant Foodstuffs (Moringa Leaf Powder, Roselle Calyces and Baobab Fruit Pulp). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, C. Evidence for the Usefulness of in Vitro Dialyzability, Caco-2 Cell Models, Animal Models, and Algorithms to Predict Zinc Bioavailability in Humans. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2013, 75, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, B.G.; Perez-Corona, M.T.; Madrid, Y. Availability of Zinc from Infant Formula by in Vitro Methods (Solubility and Dialyzability) and Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9405–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białowąs, W.; Blicharska, E.; Drabik, K. Biofortification of Plant- and Animal-Based Foods in Limiting the Problem of Microelement Deficiencies—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, M.-Y.; Du, X.; Hotz, C.; Lönnerdal, B. Biofortification of Rice with Zinc: Assessment of the Relative Bioavailability of Zinc in a Caco-2 Cell Model and Suckling Rat Pups. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3650–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Li, R.; Jin, H.; You, H.J.; Ji, G.E. Effects of Selenium- and Zinc-Enriched Lactobacillus Plantarum SeZi on Antioxidant Capacities and Gut Microbiome in an ICR Mouse Model. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, H.; Bai, J.; Lv, L.; Xuan, Y.; et al. Comparison of Zinc Bioavailability in Zinc-Glycine and Zinc-Methionine Chelates for Broilers Fed with a Corn-Soybean Meal Diet. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 983954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, E.; Ferket, P.R.; Uni, Z. Changes in Chicken Intestinal Zinc Exporter mRNA Expression and Small Intestinal Functionality Following Intra-Amniotic Zinc-Methionine Administration. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.; Qin, X.; Ran-Ressler, R.; Brenna, J.T.; Glahn, R.P.; Tako, E. Dietary Zinc Deficiency Affects Blood Linoleic Acid: Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid (LA:DGLA) Ratio; a Sensitive Physiological Marker of Zinc Status in Vivo (Gallus gallus). Nutrients 2014, 6, 1164–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Tako, E. The In Ovo Feeding Administration (Gallus gallus)—An Emerging In Vivo Approach to Assess Bioactive Compounds with Potential Nutritional Benefits. Nutrients 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.; Kolba, N.; Tako, E. Assessing the Interactions between Zinc and Vitamin A on Intestinal Functionality, Morphology, and the Microbiome In Vivo (Gallus gallus). Nutrients 2023, 15, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liria-Domínguez, R.; Penny, M.; Kroon, P.A.; Burgos, G.; Dainty, J.; Zeder, C.; Zimmermann, M.B.; King, J.; Mithen, R.; Boy, E.; et al. Biofortified Yellow-Fleshed Potatoes Provide More Absorbable Zinc than a Commonly Consumed Variety: A Randomized Trial Using Stable Isotopes in Women in the Peruvian Highlands. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilaj, N.; Boit, T.; Andang’o, P.; Zeder, C.; Mwangi, M.N.; Hummel, M.; Velazco, O.N.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M.; Zimmermann, M.B.; et al. Zinc Absorption from Maize-Based Meals Enriched with Edible House Crickets: A Randomized Crossover Stable-Isotope Study in Kenyan Pre-School Children. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsma, E.F.; Moretti, D.; Ly, S.C.; Dekkers, R.; van den Heuvel, E.G.; Fitri, A.; Boelsma, E.; Stomph, T.J.; Zeder, C.; Melse-Boonstra, A. Zinc Absorption from Milk Is Affected by Dilution but Not by Thermal Processing, and Milk Enhances Absorption of Zinc from High-Phytate Rice in Young Dutch Women. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.Y.; Min, L.I.; Bing, L.X.; Xiang, R.T.; Dong, L.W.; Chun, Y.; Meng, W.U.; Li, Y.L.; Xia, M.Y.; Jun, W.; et al. Zinc Absorption from Representative Diet in a Chinese Elderly Population Using Stable Isotope Technique. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, C.D.; Miller, L.V.; Krebs, N.F.; Lei, S.; Hambidge, K.M. Zinc Absorption as a Function of the Dose of Zinc Sulfate in Aqueous Solution. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janet, R.H.; Matthys, L.; Johnson, L. Zinc Absorption, Mineral Balance, and Blood Lipids in Women Consuming Controlled Lactoovovegetarian and Omnivorous Diets for 8 Wk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, E.A.; Oliveira, A.F.; França, C.J.; Souza, G.B.; Nogueira, A.R.A. Bioaccessibility of Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Zn, and Crude Protein in Beef, Pork and Chicken after Thermal Processing. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiard, J.-C.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Charbonnier, L.; Mesnil, A.; Rainbow, P.S.; Wang, W.-X. Bioaccessibility of Essential and Non-Essential Metals in Commercial Shellfish from Western Europe and Asia. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2010–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melse-Boonstra, A. Bioavailability of Micronutrients From Nutrient-Dense Whole Foods: Zooming in on Dairy, Vegetables, and Fruits. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandström, B.; Cederblad, Å.; Lönnerdal, B. Zinc Absorption From Human Milk, Cow’s Milk, and Infant Formulas. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1983, 137, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogaska, A.; Reguła, J.; Suliburska, J.; Krejpcio, Z. Comparison of the In Vitro Bioavailability of Selected Minerals from Gluten-Free Breads Enriched with Grains and Synthetic Organic and Non-Organic Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regula, J.; Cerba, A.; Suliburska, J.; Tinkov, A.A. In Vitro Bioavailability of Calcium, Magnesium, Iron, Zinc, and Copper from Gluten-Free Breads Supplemented with Natural Additives. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 182, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste Contin Gomes, M.; Stampini Duarte Martino, H.; Tako, E. Effects of Iron and Zinc Biofortified Foods on Gut Microbiota In Vivo (Gallus gallus): A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, M.; Tako, E.; Glahn, R.P.; Kolba, N.; de Courcy-Ireland, E.; Stangoulis, J.C.R. Linoleic Acid:Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid Ratio Predicts the Efficacy of Zn-Biofortified Wheat in Chicken (Gallus gallus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.J.C.; Martino, H.S.D.; Kolba, N.; Cheng, J.; Agarwal, N.; Rocha, M.d.M.; Tako, E. Zinc Biofortified Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) Soluble Extracts Modulate Assessed Cecal Bacterial Populations and Gut Morphology In Vivo (Gallus gallus). Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2022, 27, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Roy, A. Enhancing Micronutrient Absorption through Simultaneous Fortification and Phytic Acid Degradation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 1235–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, K.; Isaksson, M.; Rossander-Hulthén, L.; Almgren, A.; Sandberg, A.-S. Absorption of Zinc and Retention of Calcium: Dose-Dependent Inhibition by Phytate. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambidge, K.M.; Miller, L.V.; Mazariegos, M.; Westcott, J.; Solomons, N.W.; Raboy, V.; Kemp, J.F.; Das, A.; Goco, N.; Hartwell, T.; et al. Upregulation of Zinc Absorption Matches Increases in Physiologic Requirements for Zinc in Women Consuming High- or Moderate-Phytate Diets during Late Pregnancy and Early Lactation. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Alba, V.; Lazarte, C.E.; Bergenståhl, B.; Granfeldt, Y. Phytate, Iron, Zinc, and Calcium Content of Common Bolivian Foods and Their Estimated Mineral Bioavailability. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlemmer, U.; Frølich, W.; Prieto, R.M.; Grases, F. Phytate in Foods and Significance for Humans: Food Sources, Intake, Processing, Bioavailability, Protective Role and Analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S330–S375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer Labba, I.-C.; Steinhausen, H.; Almius, L.; Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Sandberg, A.-S. Nutritional Composition and Estimated Iron and Zinc Bioavailability of Meat Substitutes Available on the Swedish Market. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertinato, J.; Griffin, P.; Huliganga, E.; Matias, F.M.G.; Dam, D.; Brooks, S.P.J. Calcium Exacerbates the Inhibitory Effects of Phytic Acid on Zinc Bioavailability in Rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, R.M.; Parker, H.M.; Erdman, J.W. Effects of Dietary Phytate, Calcium and Magnesium Levels on Zinc Bioavailability to Rats. J. Nutr. 1984, 114, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, C.; Peerson, J.M.; Brown, K.H.; Lönnerdal, B. Effect of a Micronutrient Fortificant Mixture and 2 Amounts of Calcium on Iron and Zinc Absorption from a Processed Food Supplement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hunt, J.R.; Beiseigel, J.M. Dietary Calcium Does Not Exacerbate Phytate Inhibition of Zinc Absorption by Women from Conventional Diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.V.; Krebs, N.F.; Hambidge, K.M. Mathematical Model of Zinc Absorption: Effects of Dietary Calcium, Protein and Iron on Zinc Absorption. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.L.; Díaz, M.; González, K.; Griffin, I.; Abrams, S.A.; Preciado, R. The Addition of Milk or Yogurt to a Plant-Based Diet Increases Zinc Bioavailability but Does Not Affect Iron Bioavailability in Women. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Costa-Bauza, A. Key Aspects of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate (Phytate) and Pathological Calcifications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Simonet, B.M.; Perelló, J.; Costa-Bauzá, A.; Prieto, R.M. Effect of Phytate on Element Bioavailability in the Second Generation of Rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2004, 17, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.I.; Xu, X.; Sulieman, A.A.; Na, Y.; Mahdi, A.A. The Effect of Fermentation Time on in Vitro Bioavailability of Iron, Zinc, and Calcium of Kisra Bread Produced from Koreeb (Dactyloctenium aegyptium) Seeds Flour. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyba, S.J.; Wegmüller, R.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Ceesay, K.; Prentice, A.M.; Brown, K.H.; Wessells, K.R. Effect of Exogenous Phytase Added to Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements (SQ-LNS) on the Fractional and Total Absorption of Zinc from a Millet-Based Porridge Consumed with SQ-LNS in Young Gambian Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brnić, M.; Wegmüller, R.; Zeder, C.; Senti, G.; Hurrell, R.F. Influence of Phytase, EDTA, and Polyphenols on Zinc Absorption in Adults from Porridges Fortified with Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brnić, M.; Hurrell, R.F.; Songré-Ouattara, L.T.; Diawara, B.; Kalmogho-Zan, A.; Tapsoba, C.; Zeder, C.; Wegmüller, R. Effect of Phytase on Zinc Absorption from a Millet-Based Porridge Fed to Young Burkinabe Children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, W.M.; Nguyen Trung, M.; Davids, M.; Liu, G.; Rios-Morales, M.; Jessen, H.; Fiedler, D.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Bui, T.P.N. Phytate Metabolism Is Mediated by Microbial Cross-Feeding in the Gut Microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1812–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lau, H.C.H.; Yu, J. Microbiota-Mediated Phytate Metabolism Activates HDAC3 to Contribute Intestinal Homeostasis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, S.; Su, L.; Huang, X.; Long, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Alteration in Gut Microbiota Associated with Zinc Deficiency in School-Age Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Hu, G.; He, F.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Fu, S. Phytic Acid Improves Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11401–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.; Karra, M.; Picone, T.; Chu, A.; Hancock, D.P.; Petocz, P.; Samman, S. Dietary Fiber Intake Increases the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Healthy and Diabetic Women. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 149, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiewlicz, J.; Rybicka, I. Minerals and Their Bioavailability in Relation to Dietary Fiber, Phytates and Tannins from Gluten and Gluten-Free Flakes. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcieszek, J.; Witkoś, K.; Ruzik, L.; Pawlak, K. Comparison of Copper and Zinc in Vitro Bioaccessibility from Cyanobacteria Rich in Proteins and a Synthetic Supplement Containing Gluconate Complexes: LC–MS Mapping of Bioaccessible Copper Complexes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gong, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, R.; Ren, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, F.; Cao, Y.; et al. Oyster-Derived Zinc-Binding Peptide Modified by Plastein Reaction via Zinc Chelation Promotes the Intestinal Absorption of Zinc. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y.; He, S.; Su, D.; Nag, A.; Zeng, Q.; Yuan, Y. Novel Zn-Binding Peptide Isolated from Soy Protein Hydrolysates: Purification, Structure, and Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ye, M.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, Q.; Yuan, Y. Development, Characterization and in Vivo Zinc Absorption Capacity of a Novel Soy Meal Hydrolysate-Zinc Complexes. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1211609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, E.; Alegría, A.; Barberá, R.; Farré, R. Speciation Analysis of Calcium, Iron, and Zinc in Casein Phosphopeptide Fractions from Toddler Milk-Based Formula by Anion Exchange and Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Flame Atomic-Absorption Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udechukwu, M.C.; Collins, S.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Prospects of Enhancing Dietary Zinc Bioavailability with Food-Derived Zinc-Chelating Peptides. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4137–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarshi, P.P.; Mao, Q.; Grant, R.W.; Hazels Mitmesser, S. Comparative Absorption and Bioavailability of Various Chemical Forms of Zinc in Humans: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, P.; Chan, W.N.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Leung, K.T.; Lo, K.W.; Yu, J.; Tse, G.M.K.; et al. Cellular Zinc Metabolism and Zinc Signaling: From Biological Functions to Diseases and Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mónica, A.; Lautaro, B.; Fernando, P.; Miguel, A. Calcium and Zinc Decrease Intracellular Iron by Decreasing Transport during Iron Repletion in an in Vitro Model. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolić, T.; Yazdani, M.; Mandić, S.; Distante, S. Iron Metabolism, Calcium, Magnesium and Trace Elements: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esamai, F.; Liechty, E.; Ikemeri, J.; Westcott, J.; Kemp, J.; Culbertson, D.; Miller, L.V.; Hambidge, K.M.; Krebs, N.F. Zinc Absorption from Micronutrient Powder Is Low but Is Not Affected by Iron in Kenyan Infants. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5636–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, L.J.; Dainty, J.R.; Hollands, W.J.; Bull, V.J.; Hoogewerff, J.A.; Foxall, R.J.; McAnena, L.; Strain, J.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J. Effect of High-Dose Iron Supplements on Fractional Zinc Absorption and Status in Pregnant Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.B.; Kroeun, H.; Houghton, L.A.; Gibson, R.S.; Harding, K.B.; De-Regil, L.M.; Kraemer, K.; Barr, S.I.; Karakochuk, C.D. Including 60 Mg Elemental Iron in a Multiple Micronutrient Supplement Blunts the Increase in Serum Zinc after 12 Weeks of Daily Supplementation in Predominantly Anemic, Nonpregnant Cambodian Women of Reproductive Age. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, F.J.; Brummer, R.-J.M.; Dainty, J.R.; Hoogewerff, J.A.; Bull, V.J.; Saris, W.H.M. Iron Supplements Inhibit Zinc but Not Copper Absorption in Vivo in Ileostomy Subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Z. Pentapeptide-Zinc Chelate from Sweet Almond Expeller Amandin Hydrolysates: Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics, Stability and Zinc Transport Ability In Vitro. Molecules 2022, 27, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyńska, B.; Krakowska, A.; Lazur, J.; Jękot, B.; Zimmer, Ł.; Szewczyk, A.; Sułkowska-Ziaja, K.; Poleszak, E.; Opoka, W. Bioaccessibility of Phenolic Compounds, Lutein, and Bioelements of Preparations Containing Chlorella Vulgaris in Artificial Digestive Juices. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deters, E.L.; VanDerWal, A.J.; VanValin, K.R.; Beenken, A.M.; Heiderscheit, K.J.; Hochmuth, K.G.; Jackson, T.D.; Messersmith, E.M.; McGill, J.L.; Hansen, S.L. Effect of Bis-Glycinate Bound Zinc or Zinc Sulfate on Zinc Metabolism in Growing Lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi Javid, S.; Moravej, H.; Ghaffarzadeh, M.; Esfahani, M.B. Comparison of Zinc Sulfate and Zinc Threonine Based on Zn Bioavailability and Performance of Broiler Chicks. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yi, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, N. Relative Bioavailability of Broiler Chickens Fed with Zinc Hydroxychloride and Sulfate Sources for Corn-Soybean Meal. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4114–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Cao, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Zinc Proteinate with Moderate Chelation Strength Enhances Zinc Absorption by Upregulating the Expression of Zinc and Amino Acid Transporters in Primary Cultured Duodenal Epithelial Cells of Broiler Embryos. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, J.L.; Díaz, M.; Muñoz, E.; Westcott, J.L.; González, K.E.; Krebs, N.F.; Caamaño, M.C.; Hambidge, M. Bioavailability of Zinc Oxide Added to Corn Tortilla Is Similar to That of Zinc Sulfate and Is Not Affected by Simultaneous Addition of Iron. Food Nutr. Bull. 2012, 33, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Romaña, D.L.; Lönnerdal, B.; Brown, K.H. Absorption of Zinc from Wheat Products Fortified with Iron and Either Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, M.; Spank, S.; Kluge, A.; Schappach, A.; Kirch, W. The Pharmacokinetics of Zinc from Zinc Gluconate: A Comparison with Zinc Oxide in Healthy Men. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 43, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.M.; Brewer, G.J.; Dressman, J.B.; Swidan, S.Z.; DuRoss, D.J.; Adair, C.H.; Barnett, J.L.; Berardi, R.R. Effect of Intragastric pH on the Absorption of Oral Zinc Acetate and Zinc Oxide in Young Healthy Volunteers. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSilvestro, R.A.; Koch, E.; Rakes, L. Moderately High Dose Zinc Gluconate or Zinc Glycinate: Effects on Plasma Zinc and Erythrocyte Superoxide Dismutase Activities in Young Adult Women. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandia, P.; Bour, D.; Maurette, J.M.; Donazzolo, Y.; Duchène, P.; Béjot, M.; Houin, G. A Bioavailability Study Comparing Two Oral Formulations Containing Zinc (Zn Bis-Glycinate vs. Zn Gluconate) After a Single Administration to Twelve Healthy Female Volunteers. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2007, 77, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacenza, F.; Giacconi, R.; Costarelli, L.; Malavolta, M. Preliminary Comparison of Fractional Absorption of Zinc Sulphate, Zinc Gluconate, and Zinc Aspartate after Oral Supple-Mentation in Healthy Human Volunteers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemek, M.; Kadi, A.; Merenkova, S.; Potoroko, I.; Messaoudi, I. Improving Dietary Zinc Bioavailability Using New Food Fortification Approaches: A Promising Tool to Boost Immunity in the Light of COVID-19. Biology 2023, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y.; Chang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, X. Pumpkin Skin Polysaccharide–Zn(II) Complex: Preparation, Characterization, and Suppression of Inflammation in Zebrafish. Foods 2022, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, H.; Min, W. Preparation, Characterization and Bioactivities of Athelia Rolfsii Exopolysaccharide-Zinc Complex (AEPS-Zinc). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Lu, Y.; Fu, J.; Ning, Z.; Yang, J.; Ren, J. Preparation and Characterization of Dictyophora Indusiata Polysaccharide–Zinc Complex and Its Augmented Antiproliferative Activity on Human Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6525–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J. Research Progress of Edible Mushroom Polysaccharide-Metal Trace Element Complexes. Food Chem X 2024, 24, 101711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, R.; Purpura, M.; Davis, J.; Keratsopoulos, N.; Parra, M.E.; Secrest, A.H.; Tinsley, G.M.; Taylor, L. Glycoprotein Matrix Zinc Exhibits Improved Absorption: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Ros, G.; Nieto, G. Fe, Zn and Se Bioavailability in Chicken Meat Emulsions Enriched with Minerals, Hydroxytyrosol and Extra Virgin Olive Oil as Measured by Caco-2 Cell Model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, B.K.S.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Chin, K.-Y. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Fracture Risk: A Review of Current Evidence and Mechanisms Involved. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, C.P.; Morgan, M.; Rudolph, D.S.; Hwang, A.; Albert, N.E.; Valenzano, M.C.; Wang, X.; Mercogliano, G.; Mullin, J.M. Proton Pump Inhibitors Interfere With Zinc Absorption and Zinc Body Stores. Gastroenterol. Res 2011, 4, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of Long-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy on Complete Blood Count Parameters and Selected Trace Elements: A Pilot Study. Available online: https://www.mp.pl/paim/issue/article/15101 (accessed on 16 June 2025).

| Factor of Deficiency | Individual Factor |
|---|---|
| Improper diet | Plant-based diet Poverty—lack of access to food Malnutrition |
| Altered intestinal absorption | Connatural—genetic mutation of ZnT transporters (Acrodermatitis enteropathica-AE) A diet high in absorption inhibitors (phytates, lignins, fiber) |
| Increased loss of Zn | Diarrhea and diarrhea-related diseases Renal diseases |
| Interactions with drugs and trace elements | Diuretics, angiotensin-receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitors, drugs and dietary supplements rich in Ca, Fe, Se, Cu |
| Diseases | Chronic inflammatory disease, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism |
| Increased demand | Pregnancy, lactation, preterm birth, the elderly, puberty |
| Others | Stress, burns, surgery, infections, intravenous and enteral alimentation |
| Method of Studies | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies | Simplicity | Partial reflection of the condition of the human digestive tract |
| Low cost | Exclusion of oral phase (very often) Colonic phase exclusion (mostly) | |
| Free from ethical aspects Multiple sample analysis Determining the impact of a specific food components High repeatability | Physiological factors, age, gender, and health condition are hard to evaluate | |
| In vivo studies | Expensive, complicated, time-consuming | |
| Physiological, health, gender, and age factors are considered | Limited by ethical aspects (especially in the case of assessing unsafe/toxic compounds) | |
| The influence of difficult-to-define and control factors | ||
| Low repeatability Difficult to extrapolate the results of animal studies to humans |
| Model | Zn Forms | Sample/Study Group | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro | Zn bis-glycinate, Zn sulfate Zn picolinate, Zn citrate, Zn methionine, Zn gluconate | Dietary supplements | Highest bioaccessibility for Zn bis-glycinate was 5.77–9.38%, lowest for Zn sulfate, 1.13% Better bioaccessibility for capsules (6.19%) than tablets (4.48%) | [116] |
| Zn-amino acid complexes (Zn-Aas)/ZnCl2 | Zn-amino acid complex | Better availability of amino acid complexes than ZnCl2, use of amino acid transporters by Zn-AAs | [10] | |
| Pentapeptide- Zn chelate from Sweet Almond Expeller Amandin/Zn-gluconate, ZnSO4 | Experimental material | Higher solubility and zinc transport capacity of Zn-chelate than zinc gluconate and sulfate. Better absorption of zinc gluconate than sulfate. | [198] | |
| Zn-osteopontin complex (Zn-OPN) | Experimental material | Increased zinc absorption in the presence of phytates compared to inorganic forms | [129] | |
| Organic form (Spirulina) and Zn-gluconate | Spirulina tablets | Better bioaccessible Zn from Spirulina tablets than from Zn-gluconate | [184] | |
| Succinyled sodium caseinate Zn complex (S.NaCN-Zn) | Experimental material | Higher bioaccessibility of S.NaCN-Zn than from ZnSO4 | [130] | |
| Zn contained in Chlorella vulgaris | Dietary supplements with Chlorella vulgaris | Negligible bioaccessibility of zinc | [199] | |
| Animal studies | Zn-methionine, Zn-glycinate | Broilers | Increased bioavailability in line with Zn-methionine, Zn-glycine, ZnSO4 | [140] |
| Zn-glycinate/ZnSO4 | Young lambs | The advantage of zinc glycinate | [200] | |
| Zn-threonine/ZnSO4 | Broiler chickens | The advantage of Zn-threonine | [201] | |
| Basic ZnCl2/ZnSO4 | Broilers | The advantage of basic ZnCl2 | [202] | |
| Zn-protein complex/ZnSO4 | Broilers | Better bioavailability from Zn-protein complex | [203] | |
| Clinical studies | Zinc oxide/ZnSO4 | 10 women aged 21–51 years | Similar absorption of Zn from both forms | [204] |
| Zinc oxide/ZnSO4 | 22 adult men | Similar absorption of Zn from both forms | [205] | |
| Zn citrate, Zn gluconate, Zinc oxide | 15 adults (male and female) aged 18–45 years | Zn absorption from gluconate is estimated at 60.9%, from citrate 61.3%, from zinc oxide 40.9% | [21] | |
| Zn glycinate, Zn gluconate | 30 women aged 18–24 years | Plasma Zn status increased in the glycinate group, with no changes in the gluconate and placebo groups | [208] | |
| Zn gluconate, Zn aspartate, ZnSO4 | 8 adults (male and female) aged 25–50 years | FZA for Zn aspartate was 34.58%, for Zn gluconate 19.13%, for sulfate 8.94% | [210] | |
| Zn glycinate, Zn gluconate | 12 women aged 18–40 years | The superiority of Zn bis-glycinate | [209] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokarczyk, J.; Koch, W. Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Molecules 2025, 30, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132742
Tokarczyk J, Koch W. Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132742
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokarczyk, Joanna, and Wojciech Koch. 2025. "Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132742
APA StyleTokarczyk, J., & Koch, W. (2025). Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Molecules, 30(13), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132742







