A Detailed Thermodynamic Description of Ion Pair Binding by a Calix[4]arene Derivative Containing Urea and Amide Functionalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Complexation of Alkali Metal Cations with Host Calixarene in Acetonitrile
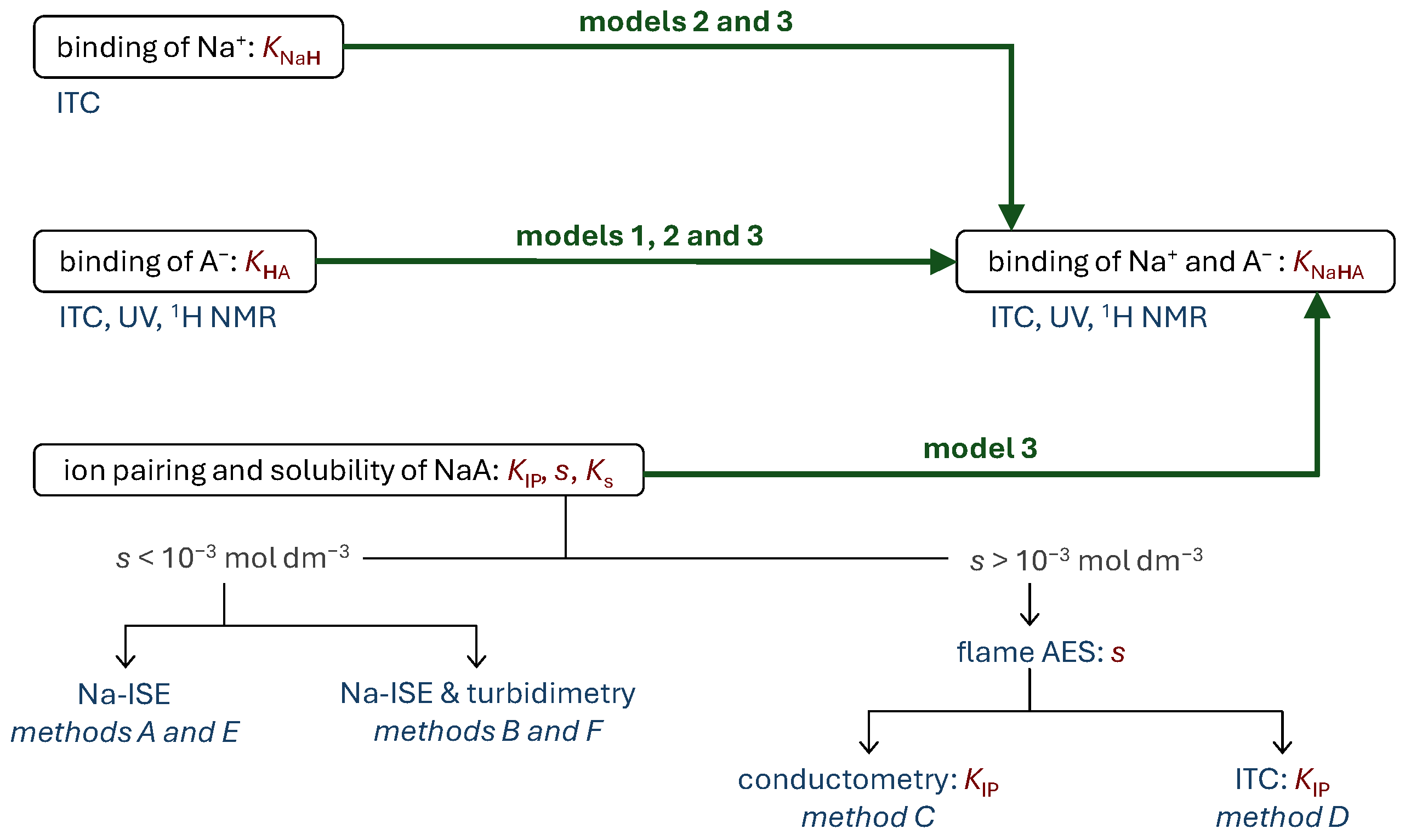
2.2. Solubility of Selected Sodium Salts and Related Ion Pairing in Acetonitrile
2.2.1. Sodium Chloride
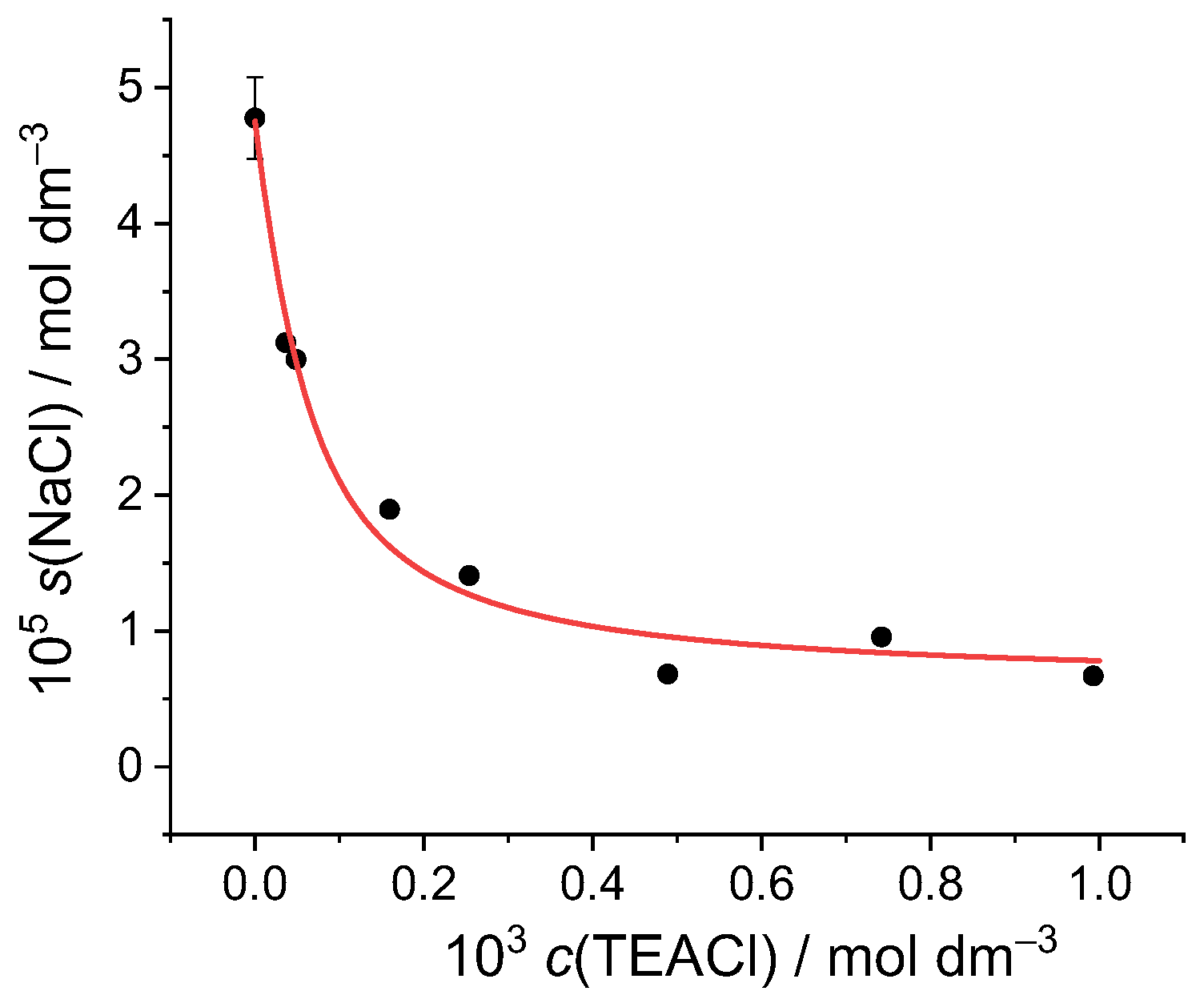
Method A
Method B
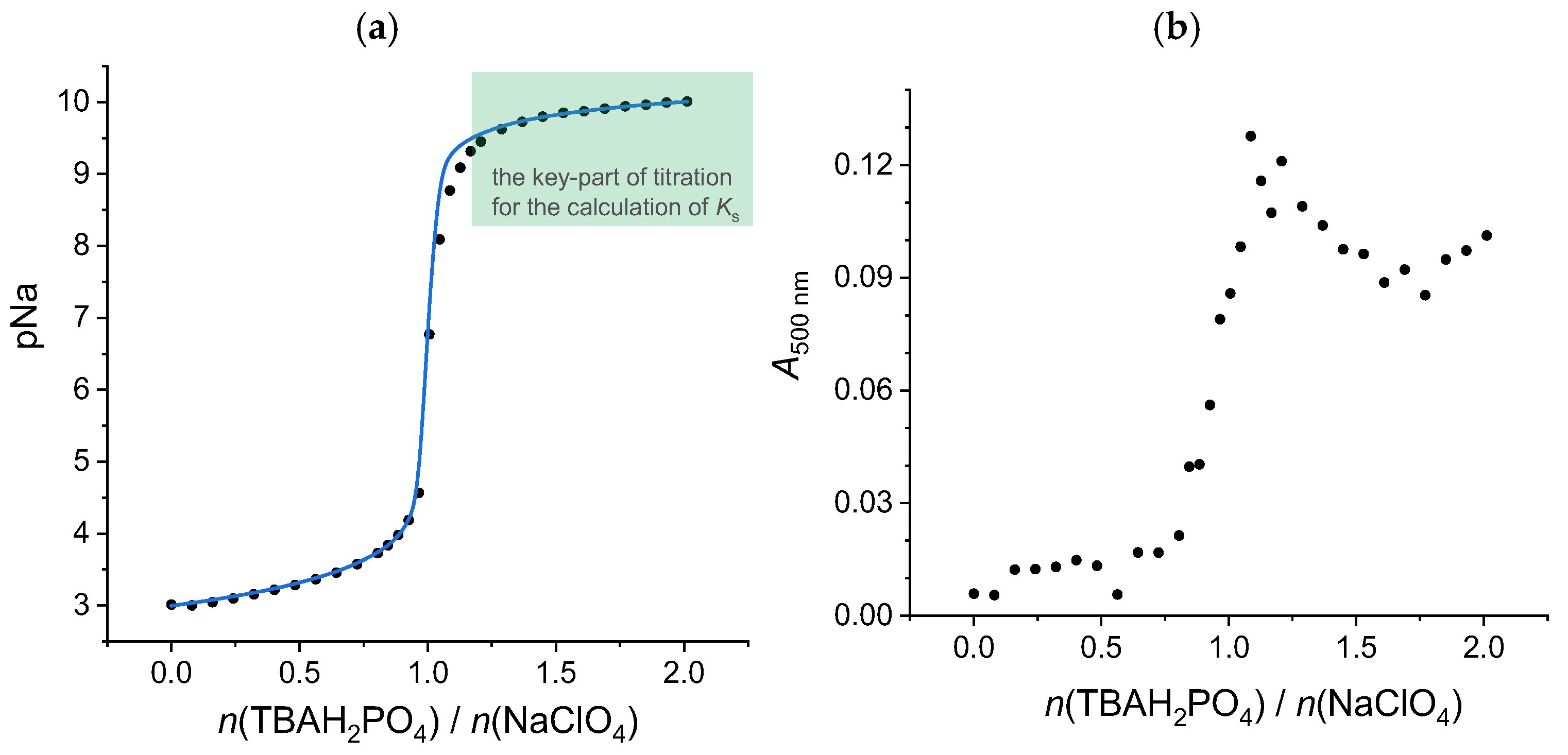
2.2.2. Sodium Hydrogen Sulfate
Method C
Method D
2.2.3. Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate
Method E
Method F
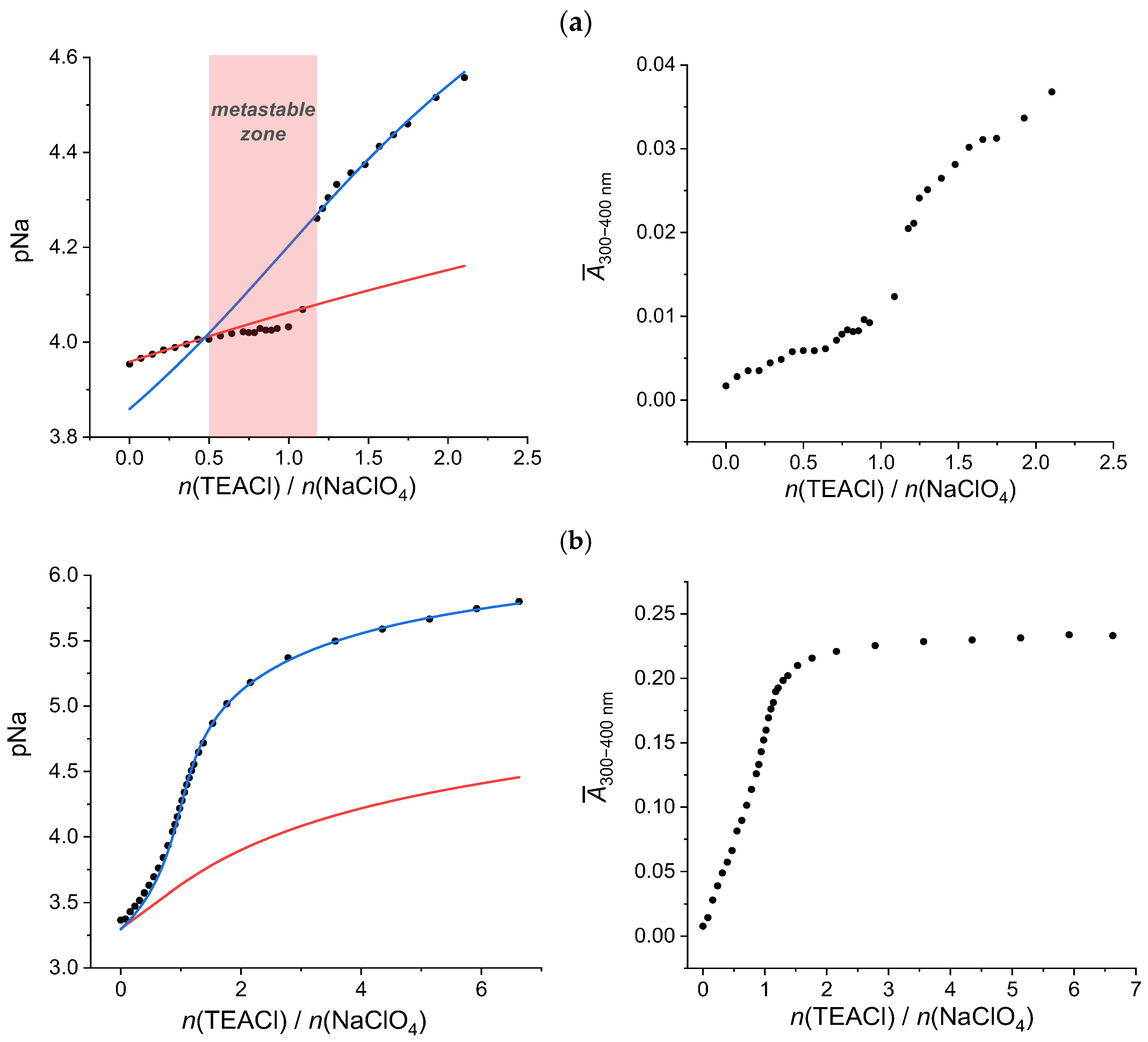
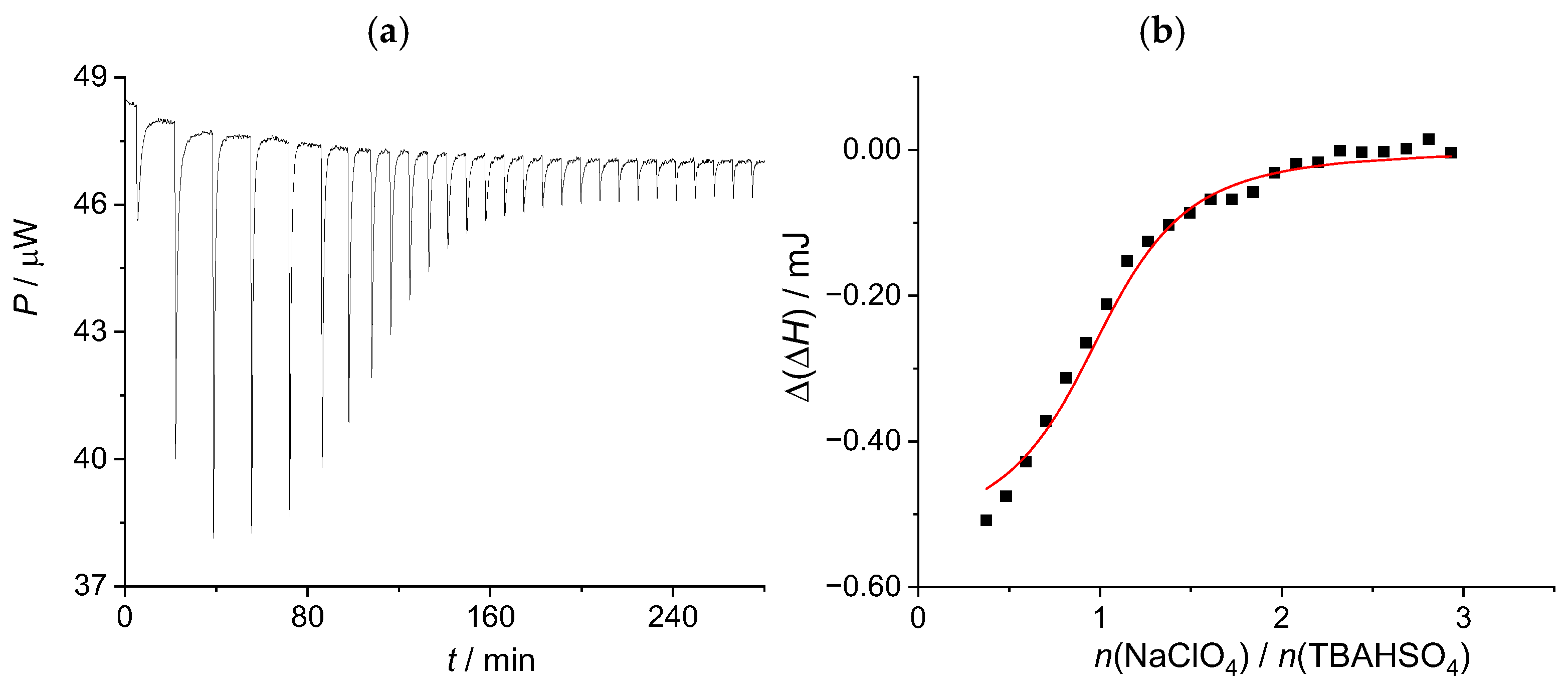
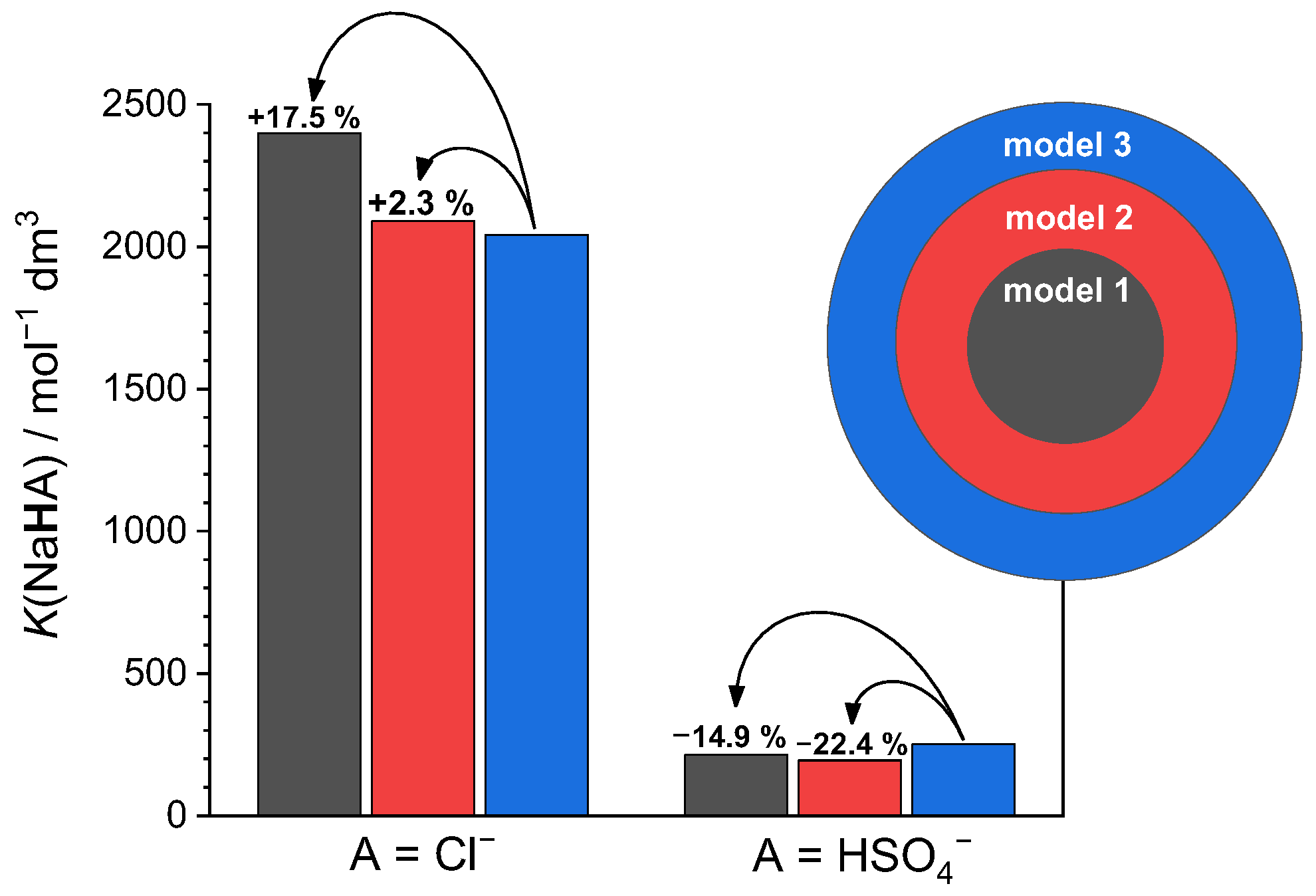
2.3. Cooperativity in Binding of Sodium Ion Pairs by Host Calixarene in Acetonitrile
2.3.1. Sodium Chloride
2.3.2. Sodium Hydrogen Sulfate
2.3.3. Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Complexation of Alkali Metal Cations with Host Calixarene in Acetonitrile
3.3. Solubility and Ion Pairing of Sodium Salts in Acetonitrile
3.3.1. Sodium Chloride
Potentiometry—Method A
Potentiometry-Turbidimetry—Method B
3.4. Sodium Hydrogen Sulfate
3.4.1. Flame AES
3.4.2. Conductometry—Method C
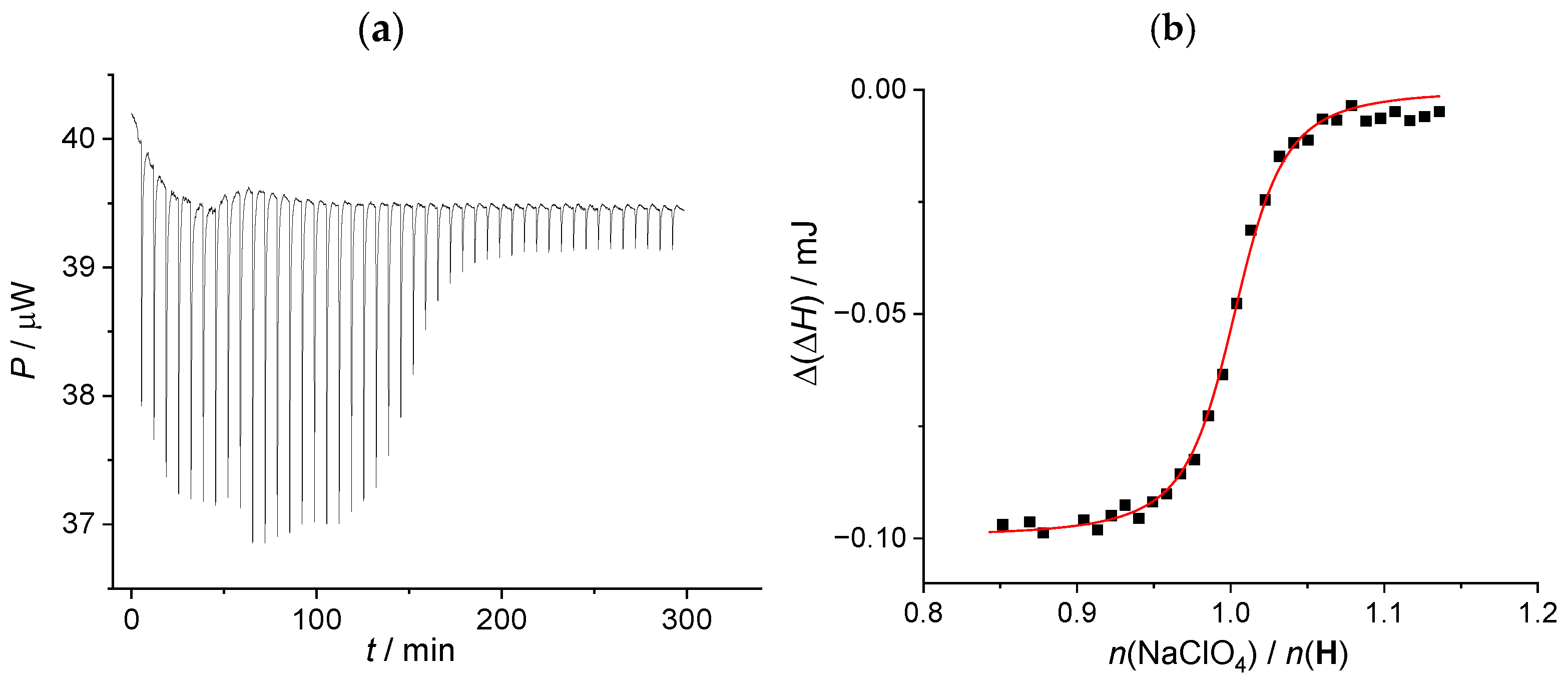
3.4.3. ITC—Method D
3.5. Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate
3.5.1. Potentiometry—Method E
3.5.2. Potentiometry–Turbidimetry—Method F
3.6. Cooperativity in Ion Pair Binding Measurements
3.6.1. ITC
3.6.2. UV
3.6.3. NMR
3.7. Molecular Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.K.; Sessler, J.L. Ion pair receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3784–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cort, A.D. Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials; Gale, P.A., Steed, J.W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, A.J.; Beer, P.D. Heteroditopic Receptors for Ion-Pair Recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5052–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Vargas-Zúñiga, G.I.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Sessler, J.L. Macrocycles as Ion Pair Receptors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9753–9835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.J.; Docker, A.; Beer, P.D. From Heteroditopic to Multitopic Receptors for Ion-Pair Recognition: Advances in Receptor Design and Applications. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 1824–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagay, S.A.; Khan, L.; Ali, R. Recent Advancements in Ion-Pair Receptors. Chem. Asian J. 2023, 18, e202201080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, A.; Tay, H.M.; Beer, P.D. Mechanically Interlocked Host Systems for Ion-Pair Recognition. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 11849–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y.; Hefter, G. Ion Pairing. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4585–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, C.J.; Bizjak, A.; Vlachy, V.; Dill, K.A. Ion Pairing in Molecular Simulations of Aqueous Alkali Halide Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6782–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.N.; Tembe, B.L. Solvation Structure of Sodium Chloride (Na+–Cl−) Ion Pair in Acetonitrile (AN)–Dimethyl Formamide (DMF) Mixtures. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, T.; Saiki, T.; Iwabuchi, J.; Akine, S. Stepwise and Dramatic Enhancement of Anion Recognition with a Triple-Site Receptor Based on the Calix[4]Arene Framework Using Two Different Cationic Effectors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5507–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, B.; Guan, Y.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sharma, B.P.; Liang, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Highly Selective Lithium Extraction by Forming Ion Pairs Using 2,9-Dialkyl-1,10-Phenanthrolines and a Hydrophobic Anion. AIChE J. 2025, 71, e18704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerder, J.; Vreekamp, R.H.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; Verboom, W.; Van Duynhoven, J.P.M.; Reinhoudt, D.N. The Pinched Cone Conformation of Calix[4]Arenes: Noncovalent Rigidification of the Calix[4]Arene Skeleton. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 3476–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, M.; Ménand, M.; Le Gac, S.; Luhmer, M.; Dalla, V.; Jabin, I. Calix[6]Tris(Thio)Ureas: Heteroditopic Receptors for the Cooperative Binding of Organic Ion Pairs. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 7067–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, V.; Tay, H.M.; Manawadu, D.; Pancholi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Beer, P.D. Lithium Chloride Selective Ion-Pair Recognition by Heteroditopic [2]Rotaxanes. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 14219–14225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J.; Bos, J.E.; Wezenberg, S.J. Stimulus-Controlled Anion Binding and Transport by Synthetic Receptors. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 8530–8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, B.; Sengupta, A.; Liu, Y.; McDonald, K.P.; Pink, M.; Anderson, J.R.; Raghavachari, K.; Flood, A.H. Electrostatic and Allosteric Cooperativity in Ion-Pair Binding: A Quantitative and Coupled Experi-ment-Theory Study with Aryl-Triazole-Ether Macrocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9746–9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docker, A.; Tay, H.M. Determining Ion-Pair Binding Affinities of Heteroditopic Receptor Systems. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202402844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, H.M.; Tse, Y.C.; Docker, A.; Gateley, C.; Thompson, A.L.; Kuhn, H.; Zhang, Z.; Beer, P.D. Halogen-Bonding Heteroditopic [2]Catenanes for Recognition of Alkali Metal/Halide Ion Pairs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Kwon, S.-R.; Kim, S.K. Calix[4]Pyrrole Bis-Crowns as Ion Pair Receptors: Cation Selectivity Modulated by Counter Anions. Org. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 6096–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Muriel, R.; Romero, J.R.; Li, Y.; Aragay, G.; Ballester, P. The Effect of Solvent on the Binding of Anions and Ion-Pairs with a Neutral [2]Rotaxane. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 9986–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.F. Progress in Physical Organic Chemistry; Streitwieser, A., Taft, R.W., Jr., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967; pp. 45–92. [Google Scholar]
- Olmstead, W.N.; Bordwell, F.G. Ion-Pair Association Constants in Dimethyl Sulfoxide. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M. Elucidation of Specific Ion Association in Nonaqueous Solution Environments. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 1539–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelens, S.; Vacca, A.; Venturi, C. Binding of Ionic Species: A General Approach to Measuring Binding Constants and Assessing Affinities. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumcharern, G.; Tuntulani, T.; Coles, S.J.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Kilburn, J.D. A Novel Ditopic Receptor and Reversal of Anion Binding Selectivity in the Presence and Absence of Bound Cation. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4971–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregović, N.; Cindro, N.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. Complexation of Fluoride Anion and Its Ion Pairs with Alkali Metal Cations by Tetra-Substituted Lower Rim Calix[4]Arene Tryptophan Derivative. Supramol. Chem. 2016, 28, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, H.M.; Docker, A.; Hua, C.; Beer, P.D. Selective Sodium Halide over Potassium Halide Binding and Extraction by a Heteroditopic Halogen Bonding [2]Catenane. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 13074–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Namor, A.F.D.; Cabaleiro, M.C.; Vuano, B.M.; Salomona, M.; Pieroni, O.I.; Tanaka, D.A.P.; Ng, C.Y.; Tanco, M.A.L.; Rodríguez, N.M.; García, J.D.C.; et al. Thermodynamic and Electrochemical Aspects of the Interactions of Functionalised Calix(4)Arenes and Metal Cations in “Allosteric Media”. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Namor, A.F.D.; Cleverley, R.M.; Zapata-Ormachea, M.L. Thermodynamics of Calixarene Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2495–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, B.; Pourabdollah, K.; Dalali, N. Analytical Applications of Calixarenes from 2005 Up-to-Date. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2011, 69, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, B.; Pourabdollah, K.; Dallali, N. A Review of Calixarene Applications in Nuclear Industries. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 287, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, N.Y.; Possanza, A.L. Calixarene-Based Anionic Receptors: Highlights from 2011. Supramol. Chem. 2013, 25, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, P.; Sessler, J.L.; Wang, M.-X. Calixarenes and Beyond; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- de Namor, A.F.D.; Hamdan, W.A.; Webb, O.; Bance-Soualhi, R.; Howlin, B.; Al Hakawati, N. Calix[4]Arene Urea Derivatives: The Pathway from Fundamental Studies to the Selective Removal of Fluorides and Phosphates from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požar, J.; Cvetnić, M.; Usenik, A.; Cindro, N.; Horvat, G.; Leko, K.; Modrušan, M.; Tomišić, V. The Role of Triazole and Glucose Moieties in Alkali Metal Cation Complexation by Lower-Rim Ter-tiary-Amide Calix[4]Arene Derivatives. Molecules 2022, 27, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrušan, M.; Cindro, N.; Usenik, A.; Leko, K.; Glazer, L.; Tomaš, R.; Horvat, G.; Požar, J.; Tomišić, V. Complexation of Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metal Cations by Fluorescent Glycoconjugated Calix[4]Arene Derivative: Thermodynamic and Computational Studies. Croat. Chem. Acta 2024, 97, P1–P15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregović, N.; Cindro, N.; Frkanec, L.; Užarević, K.; Tomišić, V. Thermodynamic Study of Dihydrogen Phosphate Dimerisation and Complexation with Novel Urea- and Thiourea-Based Receptors. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 15863–15871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Egboluche, T.K.; Hossain, M.A. Urea- and Thiourea-Based Receptors for Anion Binding. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narikiyo, H.; Gon, M.; Tanaka, K.; Chujo, Y. Development of Fluorescence Sensors for Quantifying Anions Based on Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane That Contains Flexible Side Chains with Urea Structures. Polym. J. 2024, 56, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.J.; et al. Biomimetic Charge-Neutral Anion Receptors for Reversible Binding and Release of Highly Hydrated Phosphate in Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202406946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Deplazes, E.; Clegg, J.K.; Wu, X. A Charge-Neutral Organic Cage Selectively Binds Strongly Hydrated Sulfate Anions in Water. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindro, N.; Požar, J.; Barišić, D.; Bregović, N.; Pičuljan, K.; Tomaš, R.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. Neutral Glycoconjugated Amide-Based Calix[4]Arenes: Complexation of Alkali Metal Cations in Water. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leko, K.; Usenik, A.; Cindro, N.; Modrušan, M.; Požar, J.; Horvat, G.; Stilinović, V.; Hrenar, T.; Tomišić, V. Enhancing the Cation-Binding Ability of Fluorescent Calixarene Derivatives: Structural, Thermodynamic, and Computational Studies. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 43074–43087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, G.; Stilinović, V.; Kaitner, B.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. The Effect of Specific Solvent-Solute Interactions on Complexation of Alkali-Metal Cations by a Lower-Rim Calix[4]Arene Amide Derivative. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 12702–12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sviben, I.; Galić, N.; Tomišić, V.; Frkanec, L. Extraction and Complexation of Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metal Cations by Lower-Rim Calix[4]Arene Diethylene Glycol Amide Derivatives. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 6099–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelizzi, N.; Casnati, A.; Friggeri, A.; Ungaro, R. Synthesis and Properties of New Calixarene-Based Ditopic Receptors for the Simultaneous Complexation of Cations and Carboxylate Anions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1998, 2, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Nam, K.C. A Bifunctional 1,3-Alternate Calix[4]Arene Receptor Containing Urea and Crown Ether Moieties. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 640–642. [Google Scholar]
- Tongraung, P.; Chantarasiri, N.; Tuntulani, T. Calix[4]Arenes Containing Urea and Crown/Urea Moieties: Effects of the Crown Ether Unit and Na+ towards Anion Binding Ability. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, P.R.A.; Beer, P.D. Ion-Pair Recognition by a Ditopic Calix[4]Semitube Receptor. Dalton Trans. 2003, 2249–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisstoffels, L.A.J.; De Jong, F.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Sivelli, S.; Gazzola, L.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R. Facilitated Transport of Hydrophilic Salts by Mixtures of Anion and Cation Carriers and by Ditopic Carriers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 10142–10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerder, J.; Fochi, M.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Urea-Derivatized p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arenes: Neutral Ligands for Selective Anion Complexation. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 7815–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerder, J.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Complexation of Halide Anions and Tricarboxylate Anions by Neutral Urea-Derivatized p-Tert-Butylcalix[6]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 6448–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schazmann, B.; Diamond, D. Improved Nitrate Sensing Using Ion Selective Electrodes Based on Urea-Calixarene Ionophores. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, J.N.; Bhalla, V.; Kumar, M.; Mahajan, R.K.; Puri, R.K. A Chloride Selective Sensor Based on a Calix[4]Arene Possessing a Urea Moiety. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 2772–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, J.N.; Bhalla, V.; Kumar, M.; Puri, R.K.; Mahajan, R.K. Chloride Ion Recognition Using Thiourea/Urea Based Receptors Incorporated into 1,3-Disubstituted Calix[4]Arenes. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetnić, M.; Cindro, N.; Topić, E.; Bregović, N.; Tomišić, V. Supramolecular Handshakes: Characterization of Urea-Carboxylate Interactions Within Calixarene Frameworks. ChemPlusChem 2024, 89, e202400130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetnić, M.; Cindro, N.; Bregović, N.; Tomišić, V. Thermodynamics of Anion Binding by (Thio)Ureido-Calix[4]Arene Derivatives in Acetonitrile. ACS Phys. Chem. Au 2024, 4, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surina, A.; Čejka, J.; Salvadori, K.; Lhoták, P. Anion Recognition Using Meta-Substituted Ureidocalix[4]Arene Receptors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 8669–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, P.M.; Teixeira, F.A.; Segurado, M.A.P.; Ascenso, J.R.; Bernardino, R.J.; Brancatelli, G.; Geremia, S. Synthesis and Anion Binding Properties of New Dihomooxacalix[4]Arene Diurea and Dithiourea Re-ceptors. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6497–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, P.M.; Teixeira, F.A.; Segurado, M.A.P.; Ascenso, J.R.; Bernardino, R.J.; Michel, S.; Hubscher-Bruder, V. Bidentate Urea Derivatives of p-Tert-Butyldihomooxacalix[4]Arene: Neutral Receptors for Anion Complexation. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.A.; Marcos, P.M.; Ascenso, J.R.; Brancatelli, G.; Hickey, N.; Geremia, S. Selective Binding of Spherical and Linear Anions by Tetraphenyl(Thio)Urea-Based Dihomooxa-Calix[4]Arene Receptors. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11383–11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, A.S.; Miranda, A.S.; Ascenso, J.R.; Miranda, M.Q.; Félix, V.; Brancatelli, G.; Hickey, N.; Geremia, S.; Marcos, P.M. Anion Recognition by Partial Cone Dihomooxacalix[4]Arene-Based Receptors Bearing Urea Groups: Remarkable Affinity for Benzoate Ion. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 5657–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.S.; Marcos, P.M.; Ascenso, J.R.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Schurhammer, R.; Hickey, N.; Geremia, S. Dihomooxacalix[4]Arene-Based Fluorescent Receptors for Anion and Organic Ion Pair Recognition. Molecules 2020, 25, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.S.; Marcos, P.M.; Ascenso, J.R.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Menezes, F. Anion Binding by Fluorescent Ureido-Hexahomotrioxacalix[3]Arene Receptors: An NMR, Absorption and Emission Spectroscopic Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garozzo, D.; Gattuso, G.; Notti, A.; Pappalardo, A.; Pappalardo, S.; Parisi, M.F.; Perez, M.; Pisagatti, I. A Calix[5]Arene-Based Heterotetratopic Host for Molecular Recognition of Long-Chain, Ion-Paired α,ω-Alkanediyldiammonium Salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4892–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gac, S.; Ménand, M.; Jabin, I. Second Generation of Calix[6]Aza-Cryptands: Synthesis of Heteroditopic Receptors for Organic Ion Pairs. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5195–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatori, L.; Arduini, A.; Pochini, A.; Secchi, A.; Massera, C.; Ugozzoli, F. Monotopic and Heteroditopic Calix[4]Arene Receptors as Hosts for Pyridinium and Viologen Ion Pairs: A Solution and Solid-State Study. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3698–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulli, C.; Gattuso, G.; Liotta, C.; Notti, A.; Parisi, M.F.; Pisagatti, I.; Pappalardo, S. Calix[5]Arene-Based Heteroditopic Receptor for 2-Phenylethylamine Hydrochloride. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 4350–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerkerke, S.; Wouters, J.; Jabin, I. Selective Recognition of Phosphatidylcholine Lipids by a Biomimetic Calix[6]Tube Receptor. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 8720–8726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauwels, G.; Valkenier, H.; Davis, A.P.; Jabin, I.; Bartik, K. Repositioning Chloride Transmembrane Transporters: Transport of Organic Ion Pairs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6921–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, G.; Stilinović, V.; Hrenar, T.; Kaitner, B.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. An Integrated Approach (Thermodynamic, Structural, and Computational) to the Study of Complexation of Alkali-Metal Cations by a Lower-Rim Calix[4]Arene Amide Derivative in Acetonitrile. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 6264–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požar, J.; Nikšić-Franjić, I.; Cvetnić, M.; Leko, K.; Cindro, N.; Pičuljan, K.; Borilović, I.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. Solvation Effect on Complexation of Alkali Metal Cations by a Calix[4]Arene Ketone Derivative. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 8539–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; Chantooni, R.M., Jr. A Critical Study Involving Water, Methanol, Acetonitrile, N,N-Dimethylformamide, and Dimethyl Sulfoxide of Medium Ion Activity Coefficients, on the Basis of the TPA-TPB Assumption. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, J.; Iberl, L.; Rossmaier, J.; Gores, H.J.; Kaukal, B. Conductance of 1,1-Electrolytes in Acetonitrile Solutions From −40 °C to 35 °C. J. Sol. Chem. 1990, 19, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.-F.; Desnoyers, J.E. Application of the Bjerrum Association Model to Electrolyte Solutions. IV. Apparent Molar Heat Capacities and Compressibilities in Water and Aprotic Solventst. J. Sol. Chem. 1999, 28, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Namor, A.F.D.; Kowalska, D.; Castellano, E.E.; Piro, O.E.; Velarde, F.J.S.; Salas, J.V. Lower Rim Calix(4)Arene Ketone Derivatives and Their Interaction with Alkali Metal Cations. Structural and Thermodynamic (Solution and Complexation) Characterisation of the Tetraphenyl Ketone Derivative and Its Sodium Complex. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barišić, D.; Tomišić, V.; Bregović, N. Acid-Base Properties of Phosphoric and Acetic Acid in Aprotic Organic Solvents – A Complete Thermodynamic Characterisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1046, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K. Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alderighi, L.; Gans, P.; Ienco, A.; Peters, D.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Hyperquad Simulation and Speciation (HySS): A Utility Program for the Investigation of Equilibria Involving Soluble and Partially Soluble Species. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 184, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, G.; Frkanec, L.; Cindro, N.; Tomišić, V. A Comprehensive Study of the Complexation of Alkali Metal Cations by Lower Rim Calix[4]Arene Amide Derivatives. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 24316–24329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Namor, A.F.D.; De Sueros, N.A.; Mckervey, M.A.; Barrett, G.; Neu, F.A.; Schwing-Weill, M.J. The Solution Thermodynamics of Ethyl p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene Tetraacetate and Its Alkali Metal Complexes in Acetonitrile and Methanol. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1991, 1546–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Namor, A.F.D.; Chahine, S.; Kowalska, D.; Castellano, E.E.; Piro, O.E. Selective Interaction of Lower Rim Calix[4]Arene Derivatives and Bivalent Cations in Solution. Crystallographic Evidence of the Versatile Behavior of Acetonitrile in Lead(II) and Cadmium(II) Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12824–12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankshear, M.D.; Dudley, I.M.; Chan, K.M.; Cowley, A.R.; Santos, S.M.; Felix, V.; Beer, P.D. Cooperative and Ion-Pair Recognition by Heteroditopic Calix[4]Diquinone Receptors. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. Sec. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of Equilibria in Solution. Determination of Equilibrium Constants with the HYPERQUAD Suite of Programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frassineti, C.; Ghelli, S.; Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Moruzzi, M.S.; Vacca, A. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance as a Tool for Determining Protonation Constants of Natural Polyprotic Bases in Solution 1. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 231, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A Message-Passing Parallel Molecular Dynamics Implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; van der Spoel, D. GROMACS 3.0: A Package for Molecular Simulation and Trajectory Analysis. J. Mol. Model. 2001, 7, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, Flexible, and Free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; Van Der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A High-Throughput and Highly Parallel Open Source Molecular Simulation Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilárd, P.; Abraham, M.J.; Kutzner, C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Markidis, S., Laure, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Mackerell, A.D. CHARMM36 All-Atom Additive Protein Force Field: Validation Based on Comparison to NMR Data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical Sampling through Velocity Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernetti, M.; Bussi, G. Pressure Control Using Stochastic Cell Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swope, W.C.; Andersen, H.C.; Berens, P.H.; Wilson, K.R. A Computer Simulation Method for the Calculation of Equilibrium Constants for the Formation of Physical Clusters of Molecules: Application to Small Water Clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle Mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) Method for Ewald Sums in Large Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požar, J.; Horvat, G.; Čalogović, M.; Galić, N.; Frkanec, L.; Tomišić, V. Complexation of Oxonium and Ammonium Ions by Lower-Rim Calix[4]Arene Amino Acid Derivatives. Croat. Chem. Acta 2012, 85, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
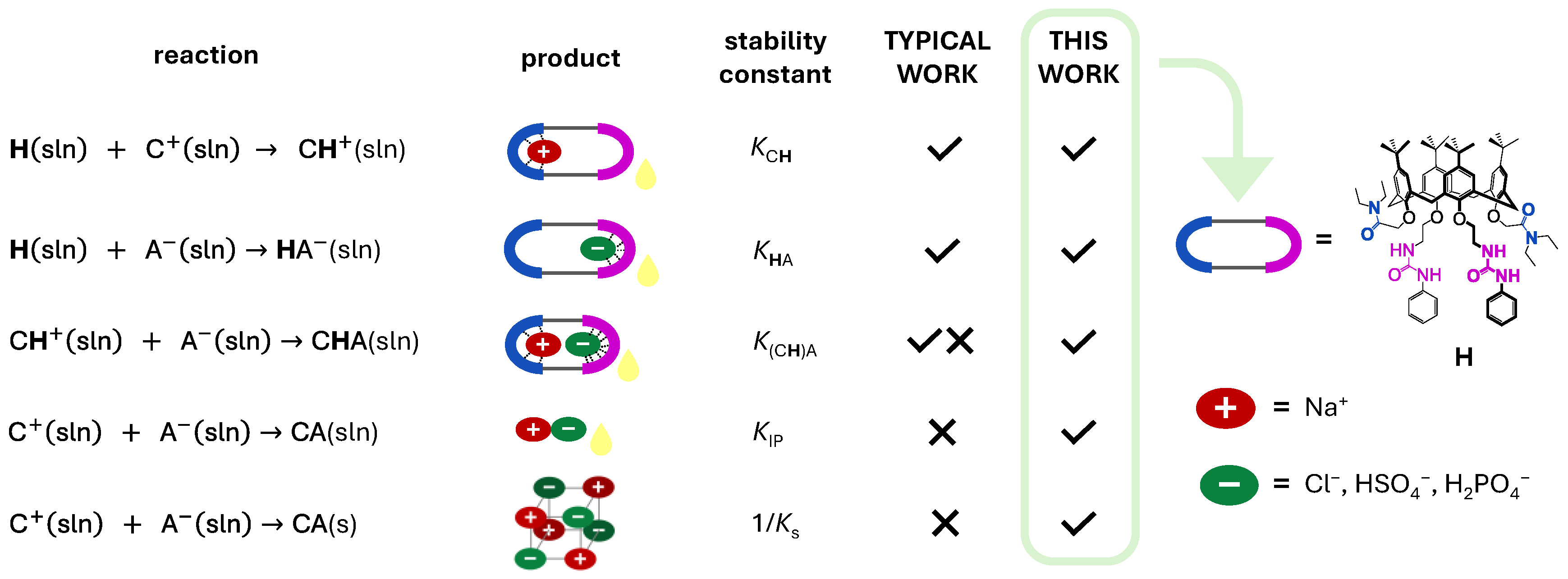
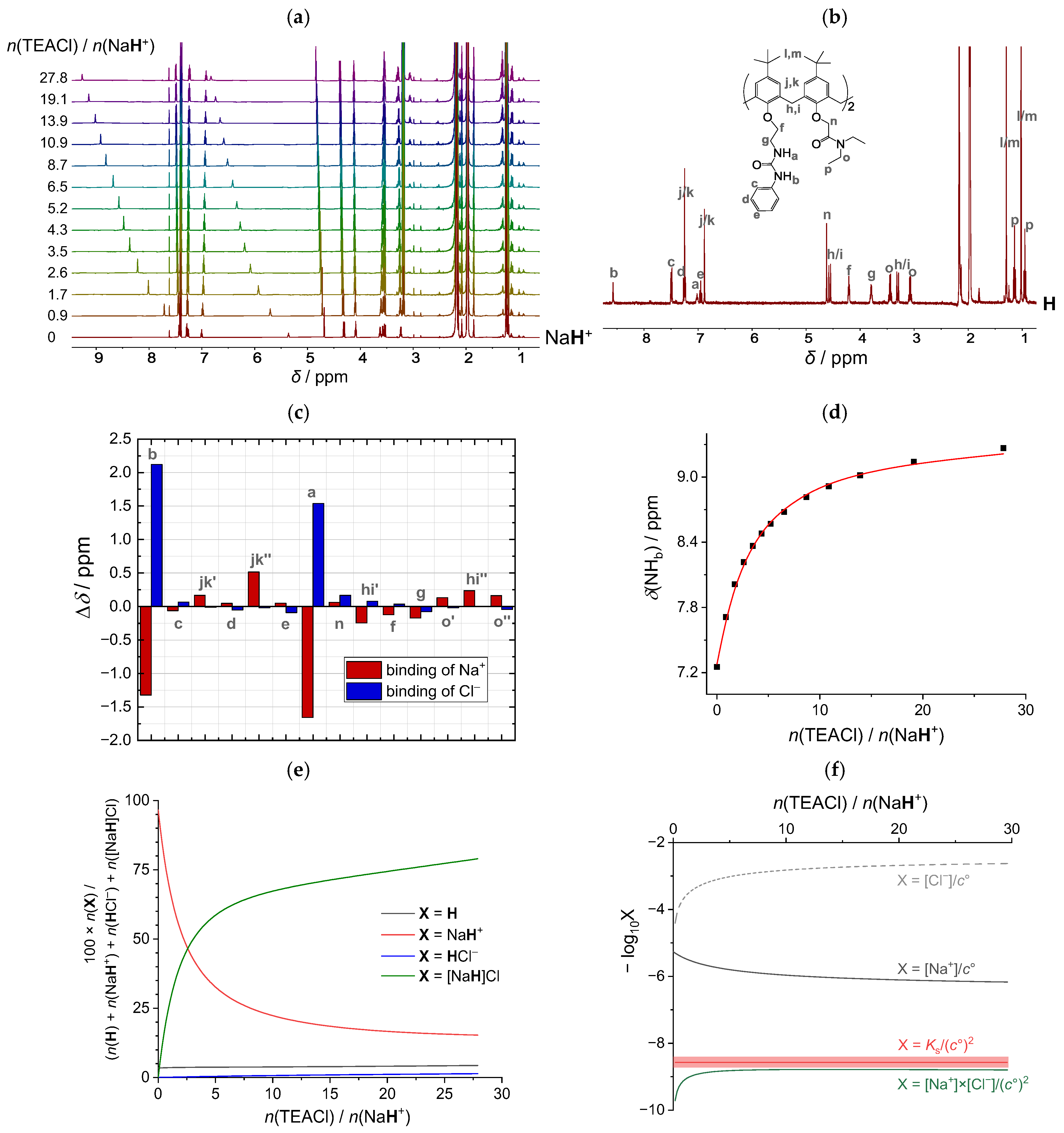


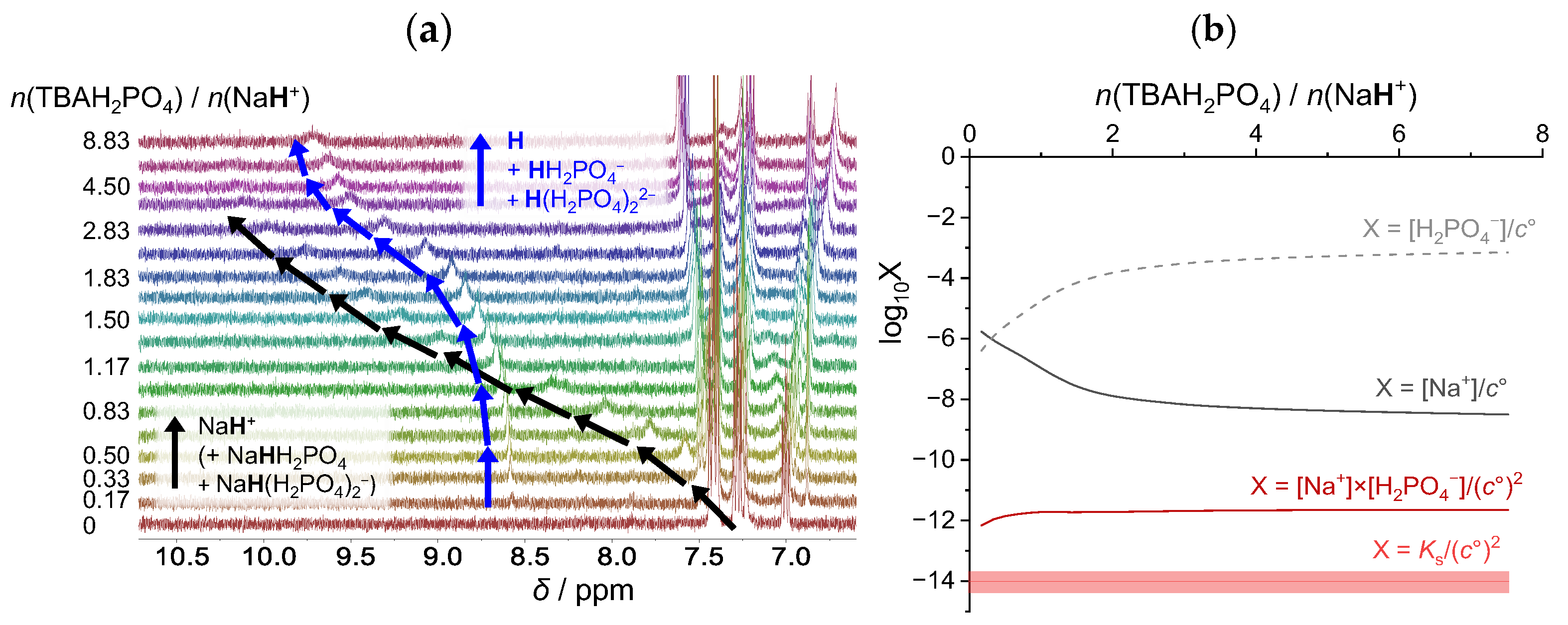
| Cation: | Li+ | Na+ | K+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| log KCH | ≥7 | 6.69(1) | 2.80(1) |
| ΔrG°/kJ mol−1 | ≤−43 | −38(1) | −15.9(4) |
| ΔrH°/kJ mol−1 | −36.4(1) | −47.6(9) | −36.8(3) |
| (−T·ΔrS°)/kJ mol−1 | ≤−7 | 9.2(9) | 20.9(3) |
| Method A | Method B | Average a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 105 s/mol dm−3 | 4.8(3) a | 7.4(2) b,c | 6(1) |
| −log (s/mol dm−3) | 4.32(3) a | 4.13(1) b | 4.22(9) |
| −log (Ks/mol2 dm−6) | 8.77(4) b | 8.41(3) a | 8.6(2) |
| log (KIP/mol−1 dm3) | 3.5(1) b | 3.5(1) a | 3.4(1) |
| Method | Flame AES | ||
| 103 s/mol dm−3 | 1.2(1) b | ||
| Method | C: conductometry | D: ITC | average |
| log (KIP/mol−1 dm3) | 4.22(2) a | 4.60 (6) b,c | 4.4(2) |
| average | |||
| −log (Ks/mol2 dm−6) | 7.24(6) d | 7.58(7) e | 7.4(2) |
| Method E | Method F | |
|---|---|---|
| 106 s/mol dm−3 | 2.7(3) a,b | 2.7 b |
| −log (Ks/mol2 dm−6) | 13.6(4) a | 13.7(1) a |
| log (KIP/mol−1 dm3) | 8.6(4) a | 8.1(1) a |
| A | Method | log KHA | log KNaHA | Δlog K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | NMR UV ITC | 2.06(1) b 2.22(3) b 2.47(6) b | 3.27(2) c 3.38(1) c, 3.32 (1) d, 3.31 (1) e 3.40(2) c | 1.21 1.09 0.93 |
| HSO4– | NMR UV | 1.72(2) b 1.74(3) b | 2.45(1) c 2.33(4) c, 2.29 (9) d, 2.40 (1) e | 0.73 0.66 |
| log K | ΔrH°/kJ mol−1 | −T·ΔrS°/kJ mol−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaH+ + Cl− | 3.40(2) a | −18.2(7) | −1.2(6) |
| Coord. Number for Na+ | Coord. Number for Cl− | Number of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds | % Structures with Included Solvent Molecule | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | − | − | 0.9 | 63 |
| HCl− | − | 4.0 | 0 | 2 |
| NaH⁺ | 6.0 | − | 0.1 | 99 |
| NaHCl | 5.4 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cvetnić, M.; Rinkovec, T.; Vianello, R.; Horvat, G.; Bregović, N.; Tomišić, V. A Detailed Thermodynamic Description of Ion Pair Binding by a Calix[4]arene Derivative Containing Urea and Amide Functionalities. Molecules 2025, 30, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112464
Cvetnić M, Rinkovec T, Vianello R, Horvat G, Bregović N, Tomišić V. A Detailed Thermodynamic Description of Ion Pair Binding by a Calix[4]arene Derivative Containing Urea and Amide Functionalities. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112464
Chicago/Turabian StyleCvetnić, Marija, Tamara Rinkovec, Robert Vianello, Gordan Horvat, Nikola Bregović, and Vladislav Tomišić. 2025. "A Detailed Thermodynamic Description of Ion Pair Binding by a Calix[4]arene Derivative Containing Urea and Amide Functionalities" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112464
APA StyleCvetnić, M., Rinkovec, T., Vianello, R., Horvat, G., Bregović, N., & Tomišić, V. (2025). A Detailed Thermodynamic Description of Ion Pair Binding by a Calix[4]arene Derivative Containing Urea and Amide Functionalities. Molecules, 30(11), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112464











