Advances in Flotation Reagents for Cassiterite Separation: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Surface Chemistry and Crystalline Structure
2.1. Crystalline Structure
2.2. Surface Chemistry
3. Collectors
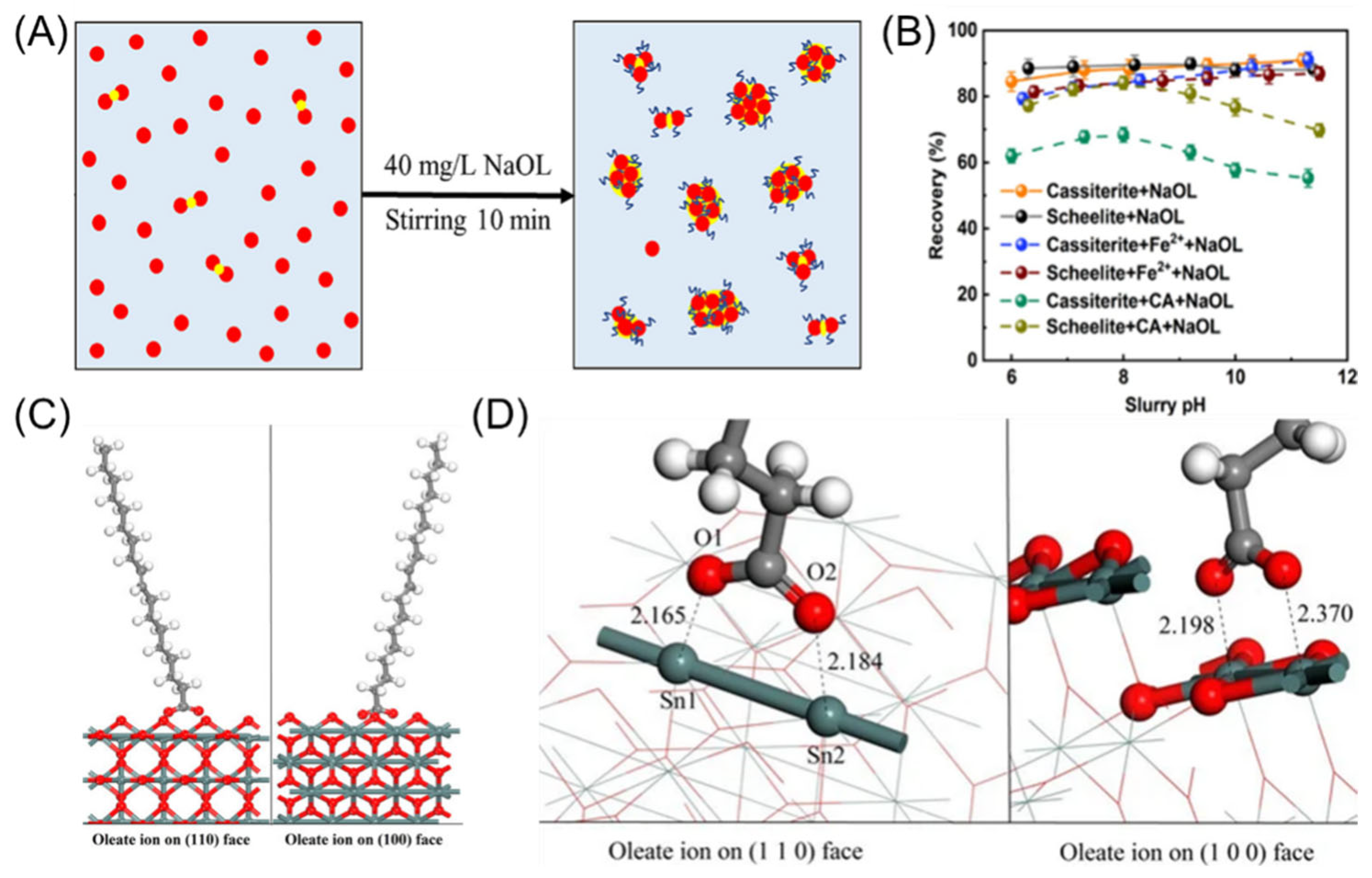
3.1. Fatty Acid Collectors
3.2. Phosphonic Acid Collectors
3.3. Sulphosuccinamate Collectors
3.4. Hydroxamic Acid Collectors
3.5. Combined Collectors
3.6. Other Collectors
4. Depressants
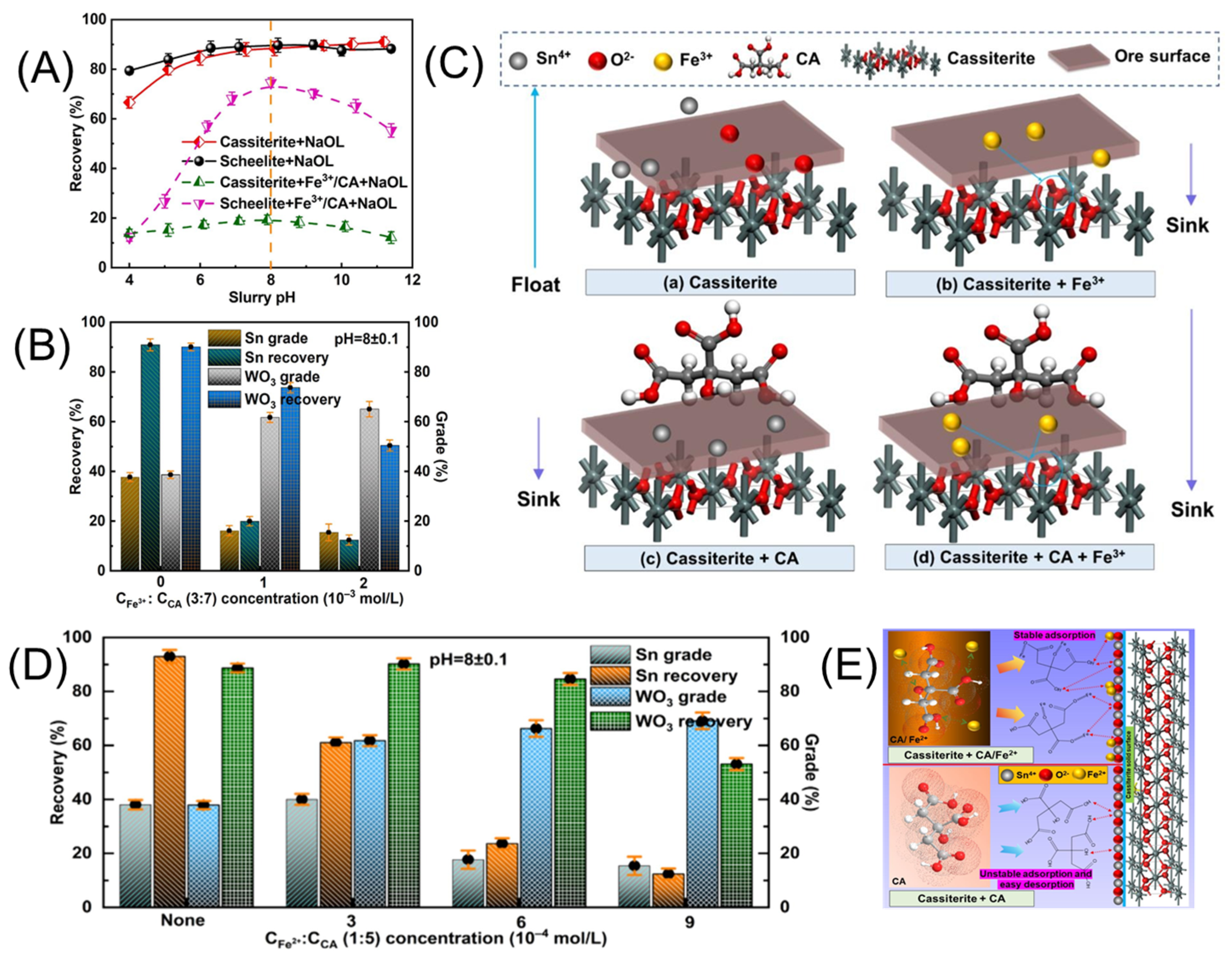
4.1. Inorganic Depressants
4.2. Organic Depressants
4.3. Combined Depressants
5. Activators
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- (1)
- To overcome the challenges posed by cassiterite collectors, such as high costs, toxicity, insufficient selectivity, and collecting efficiency, future research should prioritize the computational design of collectors. We propose that the future development of cassiterite flotation reagents should be guided by a “targeted action mechanism”, adopting a rational design approach driven by the synergy of quantum chemistry and molecular simulation. This strategy aims to achieve precise recognition and efficient adsorption of reagents on the cassiterite surface. Compared with traditional empirical methods, this approach can unveil the binding mechanisms between reagent molecules and the electronic structure characteristics of cassiterite at the atomic scale, thereby laying a solid theoretical foundation for the development of highly selective reagents.
- (2)
- Additionally, developing biodegradable collectors derived from natural compounds should be emphasized to minimize environmental impact while preserving flotation performance. We believe that bio-based and biodegradable flotation reagents represent a critical breakthrough for the green transformation of cassiterite flotation. Naturally derived surfactants—such as saponins, flavonoids, tannic acid, and alginates—exhibit excellent biocompatibility and environmental friendliness. Moreover, some of these molecules contain functional groups capable of complexation or hydrophobic interactions with metal mineral surfaces, endowing them with potential collecting or depressing capabilities. In addition, functionalized biopolymers, such as modified chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose, possess polymer chain structures that enable multipoint adsorption. These materials demonstrate strong mineral surface recognition and controllable release properties, making them promising candidates for the next generation of green flotation reagents.
- (3)
- Exploring the synergistic effects of combining multiple reagents could further enhance selectivity and collecting efficiency. For instance, pairing fatty acids with chelating agents or surfactants could strengthen hydrophobic interactions and reduce reagent consumption. The activation of gangue minerals by metal ions complicates the effective separation of cassiterite from gangue minerals, undermining selectivity. A key strategy for developing selective depressants lies in investigating their electrochemical properties and surface adsorption mechanisms to elucidate their interactions with cassiterite and gangue minerals. Focus should be placed on synthetic polymers and functionalized biopolymers that exhibit selective interactions with gangue minerals, enabling better control over flotation selectivity without inhibiting cassiterite. Integrating depressants with adaptive control systems could dynamically adjust reagent dosages based on real-time monitoring of mineral surface properties, further enhancing separation efficiency.
- (4)
- Metal ions present in flotation pulp can either enhance or hinder cassiterite flotation by altering surface potential and forming complexes that affect mineral selectivity. To optimize the effects of metal ions, reagents that regulate the zeta potential and maintain electrostatic conditions favorable for cassiterite flotation should be developed. Understanding how metal ions influence surface charge can facilitate the design of more efficient flotation environments. Research should also focus on alternative activators, such as rare earth elements or non-toxic chelating agents, to replace traditional pollutant activators like Pb2+, thereby enhancing flotation performance while minimizing environmental risks. Additionally, ion-specific reagents can be designed to selectively target harmful ions in the pulp, mitigating their impact on cassiterite flotation without compromising other process parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ju, H.; Lee, J. High-temperature liquid sn-air energy storage cell. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yu, R.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; An, Q.; Xu, W.; et al. Dynamic behavior of spatially confined sn clusters and its application in highly efficient sodium storage with high initial coulombic efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2307151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Gao, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Guo, Z. Supergravity separation for recovering pb and sn from electronic waste. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, S.; Pugnant, A.; Xiang, H.; Fontmorin, J.; Yu, E.H. Low cost and efficient alloy electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction to formate. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Usman, M.; Rehman, J.U.; Tahir, M.B. A first-principles study to investigate the physical properties of sn-based hydride perovskites XSnH3 (x = k, li) for hydrogen storage application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.E.; Auping, W.L.; Kleijn, R.; Kwakkel, J.H.; Sprecher, B. Reassessing tin circularity and criticality. J. Ind. Ecol. 2024, 28, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, H. Separation of arsenic from tin anode slime by vacuum distillation. Vacuum 2024, 222, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tan, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Measuring the sustainability of tin in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, M.; Helbig, C.; Marschall, R. Supply risk considerations for photoelectrochemical water splitting materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 2238–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wu, K.; Xu, F.; Fan, S.; Yang, P.; Ma, J. Cobalt doping in MOF-derived carbon-loaded tin nanomaterials for enhanced electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 5334–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amosah, M.E.; Yvon, M.; Zhou, J.; Galvin, K.P. The role of enhanced desliming and gravity separation as a precursor to flotation in the upgrading of cassiterite from tailings. Miner. Eng. 2024, 208, 108581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, L. A novel technology for the recovery and separation of cassiterite- and iron-containing minerals from tin-containing tailing. Minerals 2024, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Tian, Y.; Xu, B. Green and efficient removal of arsenic and recovery of tin from hazardous waste tin refined copper slag. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2023; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2023.
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2024; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2024.
- Fosu, A.Y.; Bartier, D.; Diot, F.; Kanari, N. Insight into the extractive metallurgy of tin from cassiterite. Materials 2024, 17, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.; Zheng, Y.; Miller, C.F.; Xu, X.; Moyen, J.; Wang, X. Formation of tin ore deposits; A reassessment. Lithos 2021, 402–403, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.I.; Eswaraiah, C.; Jeon, H.; Mishra, B.K.; Miller, J.D. Selection of gravity separators for the beneficiation of the uljin tin ore. Miner. Process Extr. Metall. Rev. 2017, 38, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.I.; Sreenivas, T.; Jeon, H.; Baek, S.; Mishra, B.K. A review of cassiterite beneficiation fundamentals and plant practices. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, T.; Embrechts, M.; Leißner, T.; Chehreh Chelgani, S.; Osbahr, I.; Möckel, R.; Peuker, U.A.; Rudolph, M. A study of the reprocessing of fine and ultrafine cassiterite from gravity tailing residues by using various flotation techniques. Miner. Eng. 2016, 96–97, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Li, H. Efficient selective flotation separation of fluorite from calcite using ferrous and ferric species as combined depressant. Miner. Eng. 2024, 205, 108451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ni, C.; Yao, J.; Chang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Ren, Z.; Shao, P.; et al. Hydroxypropyl amine surfactant: A novel flotation collector for efficient separation of scheelite from calcite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 167, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. A review of malachite flotation: Advanced reagents and sustainable practices. Miner. Eng. 2025, 228, 109317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, F. The role of gellan gum in the selective flotation separation of fluorite from calcite: An experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Powder Technol. 2024, 432, 119156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Sun, R.; Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X. Flotation separation of fluorite and calcite using anhydrous glucose and aluminum sulfate as a combined depressant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 624, 157089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xing, D.; Deng, J.; Jin, D.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Qin, G.; Liu, X. Effect of sulfuric acid pretreatment on flotation performance of calcite and fluorite. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, X.; Yao, J.; Yin, W.; Yin, C.; Sun, W.; Du, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. Application of dodecylbenzenesulfonate isopropanolamine as an environmentally friendly collector in direct flotation separation of magnesite from quartz. Miner. Eng. 2025, 229, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tong, X.; Xie, X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Zhang, S. Effects of grinding media on the flotation performance of cassiterite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 168, 106919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, X.; Yu, B.; Sha, J.; Gao, R.; Qi, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; et al. Flotation separation of quartz and feldspar under weak alkaline conditions using amine ether as a novel collector. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 315, 121873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Bao, L.; Shen, Y.; Butt, S.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis, flotation behavior, and structure-performance relationship of three hydroxyl-containing cationic collectors. Miner. Eng. 2025, 231, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Qiu, T.; Yan, H.; Li, Y. Flotation separation of bastnaesite from fluorite with an eco-friendly depressant polyepoxysuccinic acid and its depression mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 152941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W. Selective flotation separation of fluorite from calcite by using sesbania gum as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2021, 174, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Liu, C. Evaluation of 2-phosphatebutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid as a depressant in the flotation separation of fluorite from barite. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W. Synthesis of modified polystyrene nanoparticles and their application in fine cassiterite flotation. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 681, 132608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lv, J.; Kong, L.; Ni, L.; Qin, L. Enhancing flotation separation of fine-grained cassiterite and calcite with cetylpyridine bromide as a dispersant. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, W.H.; Khan, A.A. Rutile-type compounds. IV. SiO2, GeO2 and a comparison with other rutile-type structures. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1971, 27, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, M.; Feng, K.; Liu, P.; Guo, J.; Feng, J. Behavior of lead ions in cassiterite flotation using octanohydroxamic acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8723–8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, J.; Gillan, M.J. Energetics and structure of stoichiometric SnO2 surfaces studied by first-principles calculations. Surf. Sci. 2000, 463, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, T.T.; Rantala, T.S.; Lantto, V. Electronic structure of SnO2 (110) surface. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2000, 3, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Renno, A.D.; Foucaud, Y.; Rudolph, M. Study of the influence of the crystallographic orientation of cassiterite observed with colloidal probe atomic force microscopy and its implications for hydrophobization by an anionic flotation collector. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 4212–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Gong, G. Activation effect of pb2+ in cassiterite flotation with styrene phosphonic acid as collector. Chin. J. Eng. 2019, 41, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Holtham, P.N.; Tran, T. Froth flotation of monazite and xenotime. Miner. Eng. 1993, 6, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordens, A.; Cheng, Y.P.; Waters, K.E. A review of the beneficiation of rare earth element bearing minerals. Miner. Eng. 2013, 41, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.L.; Nash, G.R.; Hadler, K.; Fitzpatrick, R.S.; Anderson, C.G.; Wall, F. Zeta potentials of the rare earth element fluorcarbonate minerals focusing on bastnasite and parisite. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmulski, M. The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. IX. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 296, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, G.A. The isoelectric points of solid oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems. Chem. Rev. 1965, 65, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. VII. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 251, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. VIII. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. X. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 319, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Ren, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, X. Adsorption mechanism of mixed salicylhydroxamic acid and tributyl phosphate collectors in fine cassiterite electro-flotation system. J. Cent. South Univ. 2012, 19, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, P.G.; Buchanan, A.S. An application of the microelectrophoresis method to the study of the surface properties of insoluble oxides. Aust. J. Chem. 1957, 10, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazy, P.; Degoul, P.; Houot, R. Evaluation of cassiterite ores by flotation: Correlation tests with physico-chemical parameters. Second Tech. Conf. Tin Bangkok International Tin Council London: London, UK. 1969, 3, 939–960. [Google Scholar]
- Wottgen, E. Adsorption of phosphonic acids on cassiterite. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1969, 78, C91–C97. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, G.; Pommier, L.W. Studies on cassiterite flotation from bolivian ores. In Second Technical Conference on Tin; International Tin Council London: London, UK; Government of Thailand: Bangkok, Thailand, 1969; pp. 917–935. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Maksimov, D. Studies of the double layer on cassiterite and rutile. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 29, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, P.; Hernandez, J.G.; Montoya, J.A.; Navarrete, J.; Salmones, J.; Schifter, I.; Morales, J. Effect of tin content on silica mixed oxides: Sulfated and unsulfated catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 123, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doren, A.; Van Lierde, A.; de Cuyper, J.A. Influence of non-ionic surfactants on the flotation of cassiterite. Dev. Miner. Process. 1979, 2, 86–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gochin, R.J.; Solari, J.A. Dissolved air flotation for recovery of fine cassiterite. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. C-Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 1983, 92, C52–C58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, J. A review of flotation reagents for bastnäsite-(ce) rare earth ore. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 321, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L. Flotation separation of bastnaesite from calcite using a novel gemini surfactant as the collector. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Tian, J. An in-depth exploration of the impact of novel collector HPDDA on the low-temperature flotation behavior of bastnaesite and quantum chemical calculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Han, Z.; Shen, H.; Ran, W.; Xie, W.; Liang, Y. Exploring the separation mechanism of gemini surfactant in scheelite froth flotation at low temperatures: Surface characterization, DFT calculations and kinetic simulations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, H.; Schoenherr, J.; Schubert, H. Alkane dicarboxylic acids and aminonaphthol-sulfonic acids—A new reagent regime for cassiterite flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1985, 15, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gong, G.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y. New insights into the adsorption of oleate on cassiterite: A DFT study. Minerals 2017, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, Y.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, W. Hydrophobic agglomeration flotation of fine cassiterite induced by kerosene and sodium oleate. Powder Technol. 2024, 432, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. A novel mixed depressant for the flotation separation of scheelite and cassiterite: Adsorption mechanism and performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelgani, S.C.; Rudolph, M.; Leistner, T.; Gutzmer, J.; Peuker, U.A. A review of rare earth minerals flotation: Monazite and xenotime. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichen, G.; Jie, L.; Yuexin, H.; Yimin, Z.; Yanfeng, L.; Shuai, Y. Adsorption mechanism of oleate on cassiterite (100) surface:a density functional study. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2018, 47, 639–644. [Google Scholar]
- Guicheng, G.; Han, Y.; Liu, J. Quantum chemical study on adsorption of sodium oleate on cassiterite (211) surface. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 5, 639–644. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. Efficient flotation separation of cassiterite from fluorite using a novel depressant tetrasodium iminodisuccinate. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 721, 137264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, W. Surface analysis of cassiterite with sodium oleate in aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y. Effect of calcium ions on adsorption of sodium oleate onto cassiterite and quartz surfaces and implications for their flotation separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Nguyen, A.V. Flotation mechanism of lead-activated cassiterite with ricinoleic acid as a collector. Min. Metall. Explor. 2024, 41, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, G.D.; Poling, G.W.; Frost, D.C. Surface contaminants on cassiterite recovered from an industrial concentrator. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1989, 27, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.N.; Kirkup, J.L.; Davey, M.N.; Arthur, C. Flotation of cassiterite: Development of a flotation process. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1968, 77, C1–C13. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, G.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, S. In situ investigation of the adsorption of styrene phosphonic acid on cassiterite (110) surface by molecular modeling. Minerals 2017, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, H.; Bilsing, U. Cassiterite flotation using styrene phosphonic acid to produce high-grade concentrates at high recoveries from finely disseminated ores-comparison with other collectors and discussion of effective circuit configurations. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huang, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, H. A novel surfactant styryl phosphonate mono-iso-octyl ester with improved adsorption capacity and hydrophobicity for cassiterite flotation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y. Study on flotation performances and adsorption mechanism of 2-carboxyethylphenylphosphinic acid to cassiterite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, G.; Han, Y. Mechanism of HCA and CEPPA in flotation separation of cassiterite and fluorite. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; He, F.; Shang, Y.; Yin, W. Flotation behavior and adsorption mechanism of (1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-octenyl) phosphonic acid to cassiterite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gao, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J. Enhancing cassiterite flotation by 1-hydroxydodecylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HDDPA). Miner. Eng. 2024, 206, 108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangaonkar, P.R.; Kamarudin, H. Studies on the cassiterite-sulphosuccinamate flotation system. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1994, 42, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetic, V.M. Cassiterite flotation: A review. In Advances in Mineral Processing: A Half-Century of Progress in Application of Theory to Practice; Society for Mining Metallurgy: Englewood, CO, USA, 1986; pp. 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, G.D.; Poling, G.W. The chemistry of cassiterite flotation. In Advances in Mineral Processing: A Half-Century of Progress in Application of Theory to Practice; Society for Mining Metallurgy: Englewood, CO, USA, 1986; pp. 229–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zambrana, G.Z.; Medina, R.T.; Gutierrez, G.B.; Vargas, R.R. Recovery of minus ten micron cassiterite by liquid-liquid extraction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1974, 1, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Jeon, H.; Zeng, Q.; Jiang, E.; Wang, D. Influence of metal cations on cassiterite flotation. Geosyst. Eng. 1998, 1, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Wang, Y.; Meng, J.; Liu, J. Flotation and adsorption of novel gemini decyl-bishydroxamic acid on bastnaesite: Experiments and density functional theory calculations. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B. Donor properties of hydroxamic acids. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1978, 26, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderovich, V.A.; Ryaboi, V.I.; Kriveleva, E.D.; Coin, B.; Vainshenkar, V.I.; Dogadina, A.V. Influence of structural characterisation of hydroxamic acids on their dissociation and complex formation. J. Gen. Chem. USSR 1979, 49, 1530. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Yang, C. Flotation and surface behavior of cassiterite with salicylhydroxamic acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10778–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Q.; Zhu, J.G. Selective flotation of cassiterite with benzohydroxamic acid. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Han, H.; Ni, Y. Flotation separation of scheelite from gypsum using Pb-BHA complex collector. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, R. Study on the mechanism and application of a novel collector-complexes in cassiterite flotation. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Haisheng, H.; Yuehua, H.; Zhao, W.; Jianjun, W.; Li, W.; Wei, S.; Yue, Y.; Lei, S.; Ruohua, L.; et al. Beneficiation and purification of tungsten and cassiterite minerals using pb-BHA complexes flotation and centrifugal separation. Minerals 2018, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, P.; Ou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Flotation of cassiterite using alkyl hydroxamates with different carbon chain lengths: A theoretical and experimental study. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H. Optimization of conventional hydroxamic acid for cassiterite flotation: Application of structural modification under principle of isomerism. Miner. Eng. 2021, 167, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, P.; Yu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Kang, J.; Sun, W.; Tian, M. The application and adsorption selectivity of a novel collector 4-butoxy-n-hydroxybenzamide in cassiterite flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 679, 161272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y. Selective separation behavior and study on the interaction mechanism of 2-hydroxy-3-naphthylmethyl hydroxamic acid and cassiterite. Minerals 2024, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhong, H. Amide group enhanced self-assembly and adsorption of thioether-containing hydroxamic acid on cassiterite surface. AICHE J. 2023, 69, e18023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H. A novel surfactant 2-(benzylthio)-acetohydroxamic acid: Synthesis, flotation performance and adsorption mechanism to cassiterite, calcite and quartz. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 522, 146509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, G. A selective flotation of cassiterite with a dithiocarbamate-hydroxamate molecule and its adsorption mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 538, 147996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Sun, W. DHX collector for recovery of cassiterite: Mechanistic insights and practical implications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 127, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; He, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. A novel decanedioic hydroxamic acid collector for the flotation separation of bastnäsite from calcite. Miner. Eng. 2020, 151, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, F.; Fu, G.; Shang, X. Flotation performance of anisic hydroxamic acid as new collector for tungsten and tin minerals. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 3645–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Luo, D.; Deng, J.; Sun, S.; Song, S.; Jiang, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, K. An environmentally friendly strategy for the preparation of high-purity quartz using combined collector reverse flotation coupled with acid-leaching technology. Miner. Eng. 2025, 227, 109274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Synergistic adsorption mechanism of novel combined collector in flotation separation of fayalite from magnetite: Experiments and MD simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 680, 161442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, N.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, M.; Li, Y. A new combined collector of sodium oleate and 1,12-dodecanediamine for efficient flotation separation of spodumene from feldspar. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 673, 160905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, P.S.; Zawala, J.; Kowalczuk, P.B. Polymer-based collectors in flotation: A review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 335, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, D.; Tong, X.; Hu, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, G. A recipe of surfactant for the flotation of fine cassiterite particles. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, C.; Tian, Z.; Wu, C.; Qin, W. Cassiterite beneficiation in China: A mini-review. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Lv, J.; Xie, X. Study on the synergistic effect of sodium oleate/salicylaldoxime mixed collector co-adsorption on cassiterite flotation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, H.; Wei, Z.; Deng, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate as a new ligand to enhance the flotation of cassiterite in pb-BHA system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 675, 160966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wen, S. A novel combined collector for high-performance flotation of cassiterite: Experimental insights and MD simulations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Song, Z. A self-assembled surfactant for efficient flotation of cassiterite: Experimental study and DFT calculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wen, S. Experimental and MD study on the effect of SDS/OHA mixed collector co-adsorption on cassiterite flotation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Y. Research progress of flotation reagents and surface modification of ilmenite. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2021, 31, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Tian, Z. Flotation mechanism of mixed toluene arsonic acid on cassiterite. Min. Metall. Eng. 1989, 1, 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shi, Q.; Miao, B.; Liu, D.; Jin, S.; Wang, Z. Application of exopolysaccharide directionally synthesized by xanthomonas campestris as the green selective depressant for the clean flotation of talc: Statistical optimization and mechanism analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, Q.; Miao, B.; Zhang, G. Application of exopolysaccharides synthesized by xanthomonas campestris in an efficient separation system of refractory chalcopyrite and molybdenite. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Miao, B.; Li, B.; Li, S. Exopolysaccharide (EPS) synthesised from azotobacter vinelandii and its characterisation and application in bioflotation. Miner. Eng. 2024, 211, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, L.G.V.; Pino, G.A.H.; Torem, M.L. Electroflotation of cassiterite fines using a hydrophobic bacterium strain. Rem Rev. Esc. De Minas 2013, 66, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Han, Z.; Tian, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Wang, Z.; Shu, K. Multi-polar group cationic collector HTTPD: Mechanistic insights into selective flotation of bastnaesite. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Liu, C.; Fang, X.; Ren, Z.; Yang, L.; Shao, P.; Luo, X.; Zeng, G.; Duan, L.; Liu, T. A novel collector with wide pH adaptability and high selectivity towards flotation separation of scheelite from calcite. Miner. Eng. 2020, 158, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Liu, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, H. Hydrophobic intensification flotation: Comparison of collector containing two minerophilic groups with conventional collectors. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2536–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y. New insights into the dodecylamine adsorption on scheelite and calcite: An adsorption model. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Long, S. Cationic flotation of scheelite from calcite using quaternary ammonium salts as collector: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczuk, B.; González-Martín, M.L.; Bruque, J.M. Wettability of cassiterite in presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1994, 38, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Qiao, L.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, P.; Qin, W.; Jiao, F.; Liu, D. Enhanced adsorption of citric acid at the calcite surface by adding copper ions: Flotation separation of scheelite from calcite. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663, 131036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Su, H.; Mao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, D. Application of waste gypsum as novel selective depressant in the flotation separation of apatite from dolomite. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Shen, P.; Zheng, Q.; Qiao, L.; Dong, L.; Liu, D. Effective flotation separation of apatite from dolomite using a new eco-friendly depressant gallic acid. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, P.; Han, Y. Aluminium-Modified sodium silicate as a selective depressant in Fluorite-Dolomite Flotation: Experimental and DFT analysis. Miner. Eng. 2025, 228, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzpour, A.; Samadzadeh Yazdi, M.R.; Mohammadi, B.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. Calcite in froth flotation—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Gao, H.; Qin, X.; Bai, X. Depressants for separation of chalcopyrite and molybdenite: Review and prospects. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lauten, R.A. The depression of pyrite in selective flotation by different reagent systems—A literature review. Miner. Eng. 2016, 96–97, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thyabat, S. Empirical evaluation of the role of sodium silicate on the separation of silica from Jordanian siliceous phosphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 67, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y. Research status and prospective on separation technology of fine cassiterite. Met. Mine 2014, 10, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.P.; Song, B.X. A review on reagents and processes of fine-grained cassiterite flotation in mining engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 577, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tian, M.; Zheng, H.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Song, S.; He, D.; Jiang, X. Flotation of rutile from almandine using sodium fluorosilicate as the depressant. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 599, 124918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, D. Effects of sodium hexmetaphosphate on flotation separation of diaspore and kaolinite. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2005, 12, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Adsorption and depression mechanism of an eco-friendly depressant PBTCA on fluorite surface for the efficient separation of cassiterite from fluorite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. The application and mechanism of high-efficiency depressant na2ATP on the selective separation of cassiterite from fluorite by direct flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 169, 106963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Wen, S.; Guan, Z.; Feng, Q. Utilization of EDTMPA as an eco-friendly depressant for selective flotation separation of cassiterite from calcite in the oleate system. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 674, 131933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Q. Investigations on flotation separation of scheelite from calcite by using a novel depressant: Sodium phytate. Miner. Eng. 2018, 126, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Liu, W. Selective flotation of scheelite from calcite using xanthan gum as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Dong, L.; Qin, W.; Liu, W.; Hu, C. Flotation separation of scheelite from calcite using pectin as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2019, 136, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhai, J.; Yin, Z.; Guan, Q. Effect of phytic acid on the surface properties of scheelite and fluorite for their selective flotation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 573, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Zhu, H.; Jia, W. New insights into the carboxymethyl cellulose adsorption on scheelite and calcite: Adsorption mechanism, AFM imaging and adsorption model. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gong, G.C.; Han, Y.X. Influences of organic depressants on the floatability of fine cassiterite. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y. Depressing behaviors and mechanism of an eco-friendly depressant on flotation separation of cassiterite and fluorite. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Che, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Peng, W.; Wu, B.; Fan, G. Flotation separation of cassiterite from calcite using low-molecular-weight citrus pectin as depressant. Separations 2024, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. Exploring a clean organic carboxylic acid depressant for flotation separation of tungsten-tin minerals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, D. Surface pretreatment of scheelite and cassiterite by gallic acid to achieve high efficiency flotation separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 667, 160428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, L.; Shen, P.; Mao, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, D. Selective adsorption of soluble starch on the cassiterite surface for effective flotation separation of scheelite from cassiterite. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 48, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Bi, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yuan, J.; Yu, A.; Chen, L.; Bai, S.; Mao, Y. Application of calcium hypochlorite and carboxymethyl chitosan as combined depressants for selective flotation separation of chalcopyrite from pyrite at low alkalinity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lai, H.; Wei, X.; Shen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Liu, D. Adsorption mechanism of NA2S2O3 and FeSO4 as a combined depressant for galena in chalcopyrite-galena flotation separation. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 706, 135799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Cai, J. Review on research and application of fine cassiterite flotation with combined reagents. Metal Mine 2019, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, D. Enhanced flotation separation of cassiterite from calcite using metal-inorganic complex depressant. Minerals 2021, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jin, S. Utilization of phytic acid as a selective depressant for quartz activated by zinc ions in smithsonite flotation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Han, H. The inhibiting effect of pb-starch on chlorite flotation and its adsorption configuration based on DFT computation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. Synergistic effect and mechanism of ferric ion modified citric acid depressant in the flotation separation of scheelite from cassiterite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, S.; Gao, Y. Typical roles of metal ions in mineral flotation: A review. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 2081–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Jin, S.; Duan, N. Insights into the adsorption mechanism of benzohydroxamic acid in the flotation of rhodochrosite with pb2+ activation. Powder Technol. 2023, 427, 118705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Shao, Y.; Yu, J.; He, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, H. Adsorption differences and mechanism of pb-BHA and al-BHA in the flotation separation of ilmenite and titanaugite. Miner. Eng. 2023, 197, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S.; Cao, Q. Activation mechanism of lead ions in cassiterite flotation with salicylhydroxamic acid as collector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Gao, Z.; Han, H.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y. Improved flotation separation of cassiterite from calcite using a mixture of lead (II) ion/benzohydroxamic acid as collector and carboxymethyl cellulose as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2017, 113, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Guo, Z.; Tian, M.; Sun, W. Selective flotation separation of cassiterite and calcite through using cinnamohydroxamic acid as the collector and pb2+ as the activator. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666, 131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; He, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, G.; Cao, S.; Fan, G.; Li, G.; Cao, Y. Hardness of surface hydroxyls and its pivotal role in the flotation of cassiterite from quartz via lead ions activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 347, 127565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zhang, C.; Han, H.; Liu, R.; Gao, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Ji, B.; Hu, Y. Effects of the preassembly of benzohydroxamic acid with fe (III) ions on its adsorption on cassiterite surface. Miner. Eng. 2018, 127, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, L.; Gao, Z.; Sun, W.; Cao, X. Activation mechanism of zinc ions in cassiterite flotation with benzohydroxamic acid as a collector. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xie, X.; Tong, X.; Feng, D.; Lv, J.; Chen, Y.; Song, Q. The activation mechanism of fe(II) ion-modified cassiterite surface to promote salicylhydroxamic acid adsorption. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y. Effect and mechanism of cu (II) on flotation separation of cassiterite from fluorite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H. Interaction mechanism of magnesium ions with cassiterite and quartz surfaces and its response to flotation separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample Origin | Background Electrolyte | Measurement Technique | IEP | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | - | Electrophoresis | 7.3 | [51] |
| The Republic of Zimbabwe | KCl | Streaming potential | 3.4 | [52] |
| Congo | KCl | Streaming potential | 3.9 | [52] |
| France | KCl | Streaming potential | 4.5 | [52] |
| Germany | - | Electrophoresis | 5.6 | [53] |
| Bolivia | KCl | potentiometric titration | 4 | [54] |
| Canada | KNO3 | potentiometric titration | 5.4 | [55] |
| Germany | - | Electrophoresis | 3 | [56] |
| Bolivia | - | Streaming potential | 4.5 | [57] |
| Australia | - | Electrophoresis | 4.2 | [58] |
| Australia | KCl | Electrophoresis | 2.9 | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Ni, C. Advances in Flotation Reagents for Cassiterite Separation: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules 2025, 30, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112380
Wang X, Li H, Liu X, Tang Y, Ni C. Advances in Flotation Reagents for Cassiterite Separation: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112380
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xianchen, Hong Li, Xinhong Liu, Yuan Tang, and Chenquan Ni. 2025. "Advances in Flotation Reagents for Cassiterite Separation: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112380
APA StyleWang, X., Li, H., Liu, X., Tang, Y., & Ni, C. (2025). Advances in Flotation Reagents for Cassiterite Separation: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules, 30(11), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112380








