Synthesis, Experimental and Computational Evaluation of SERAAK1 as a 5-HT2A Receptor Ligand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Computational Studies on the Compound SERAAK1
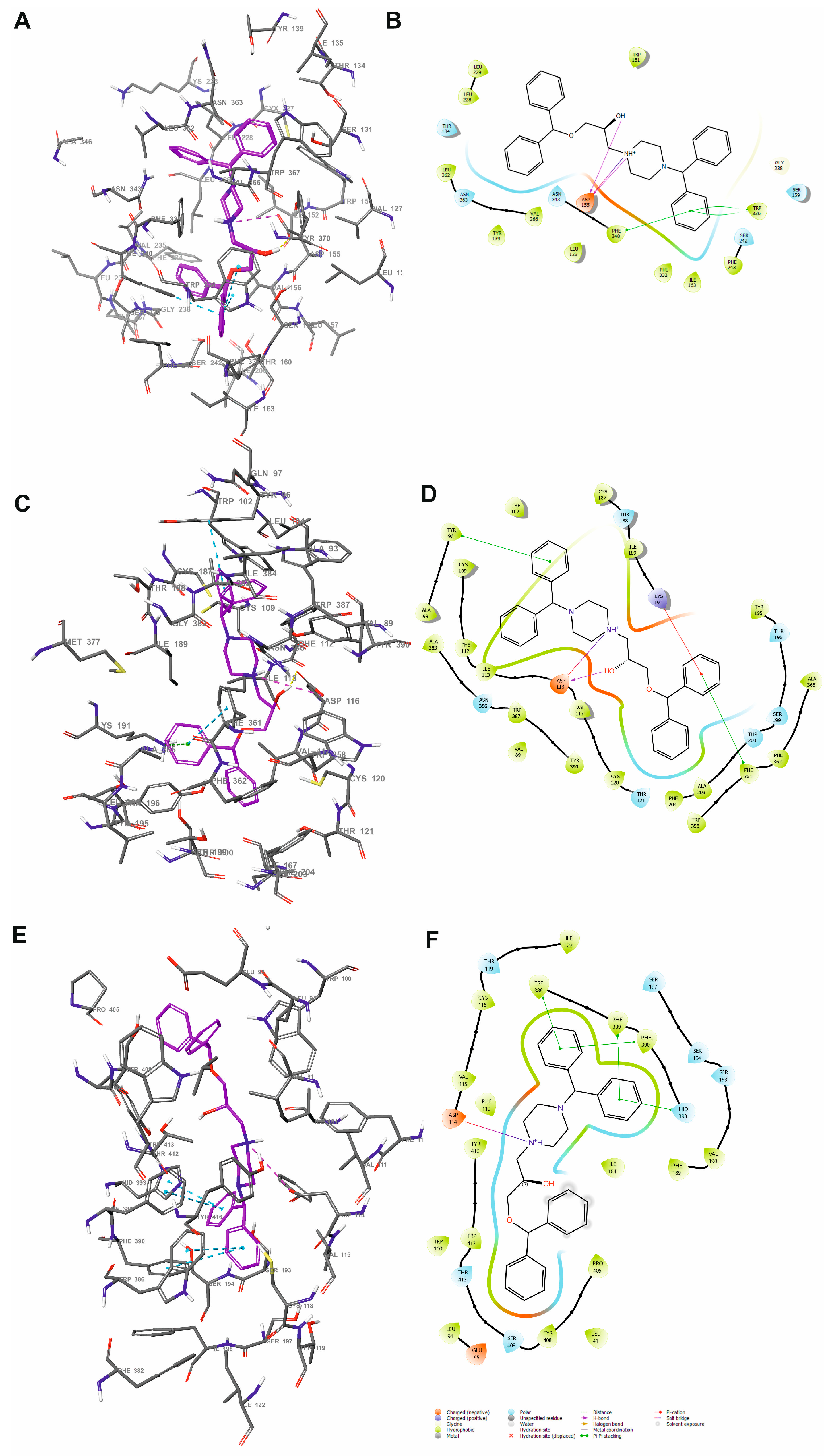
2.1.1. Molecular Docking to the Structure of the 5-HT2A Receptor in an Inactive Conformation
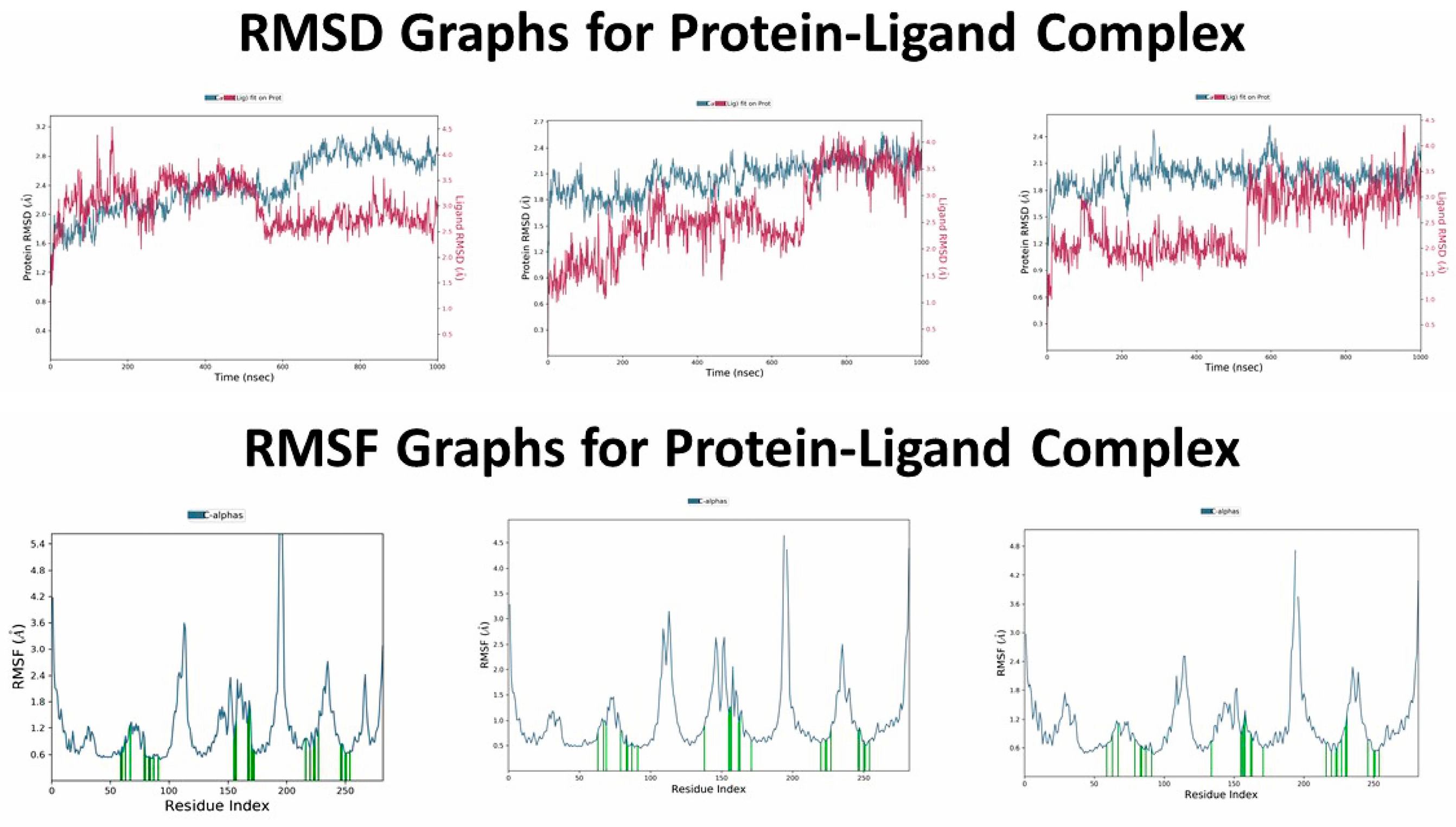
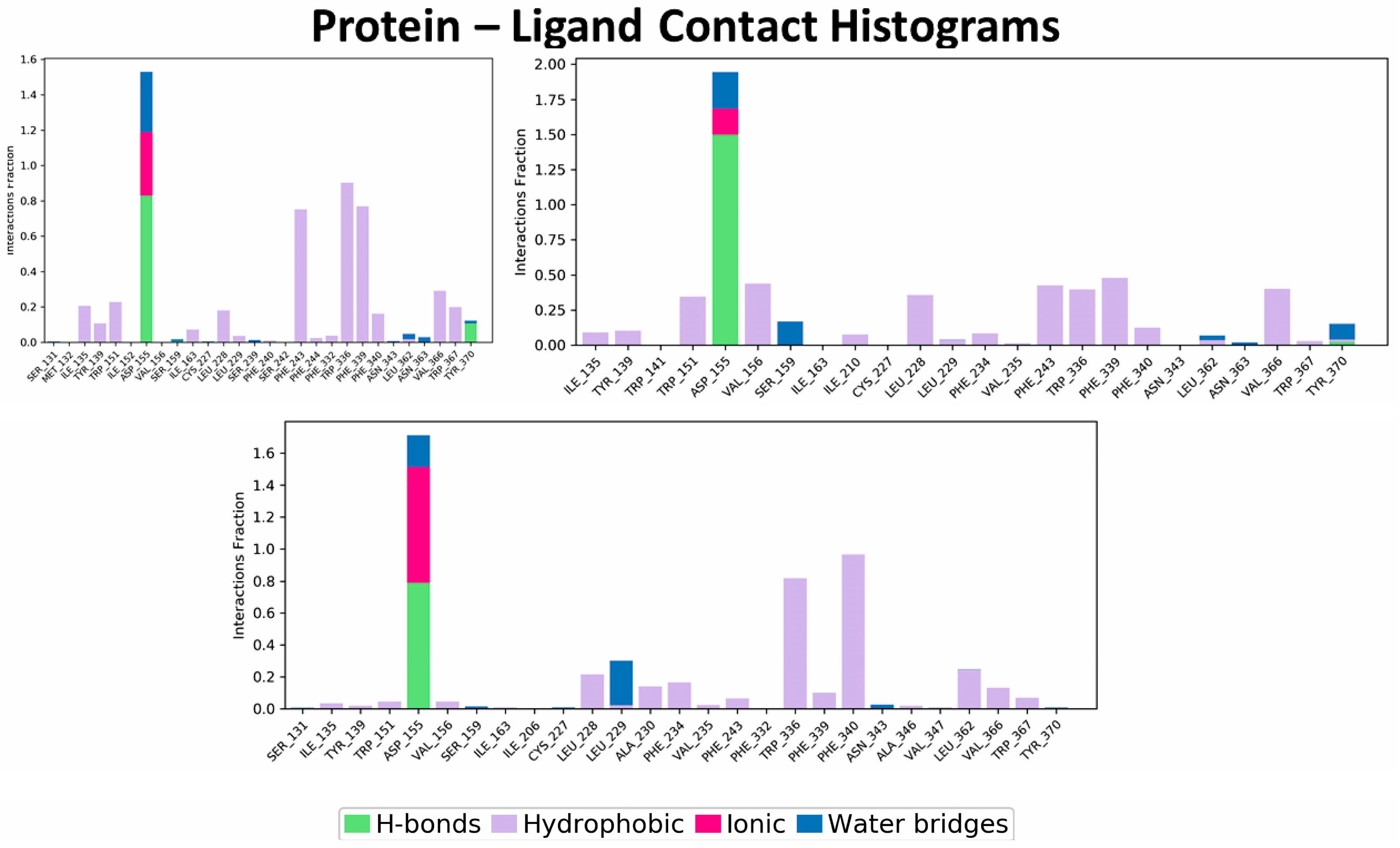
2.1.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the SERAAK1 Complex with the 5-HT2A Receptor
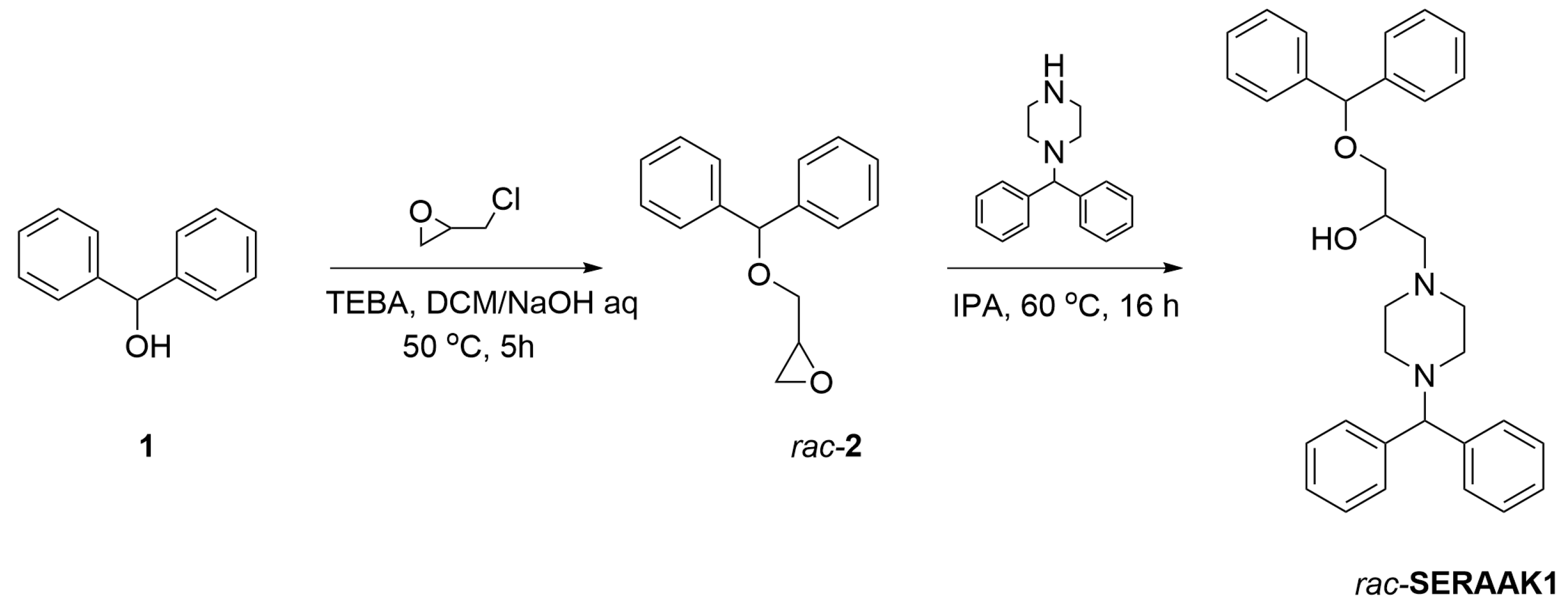
2.2. Synthesis of SERAAK1
2.3. ADMET Evaluation of SERAAK1
2.3.1. Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activity Assay
2.3.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.3.3. Permeability Assays
2.4. Behavioral Studies
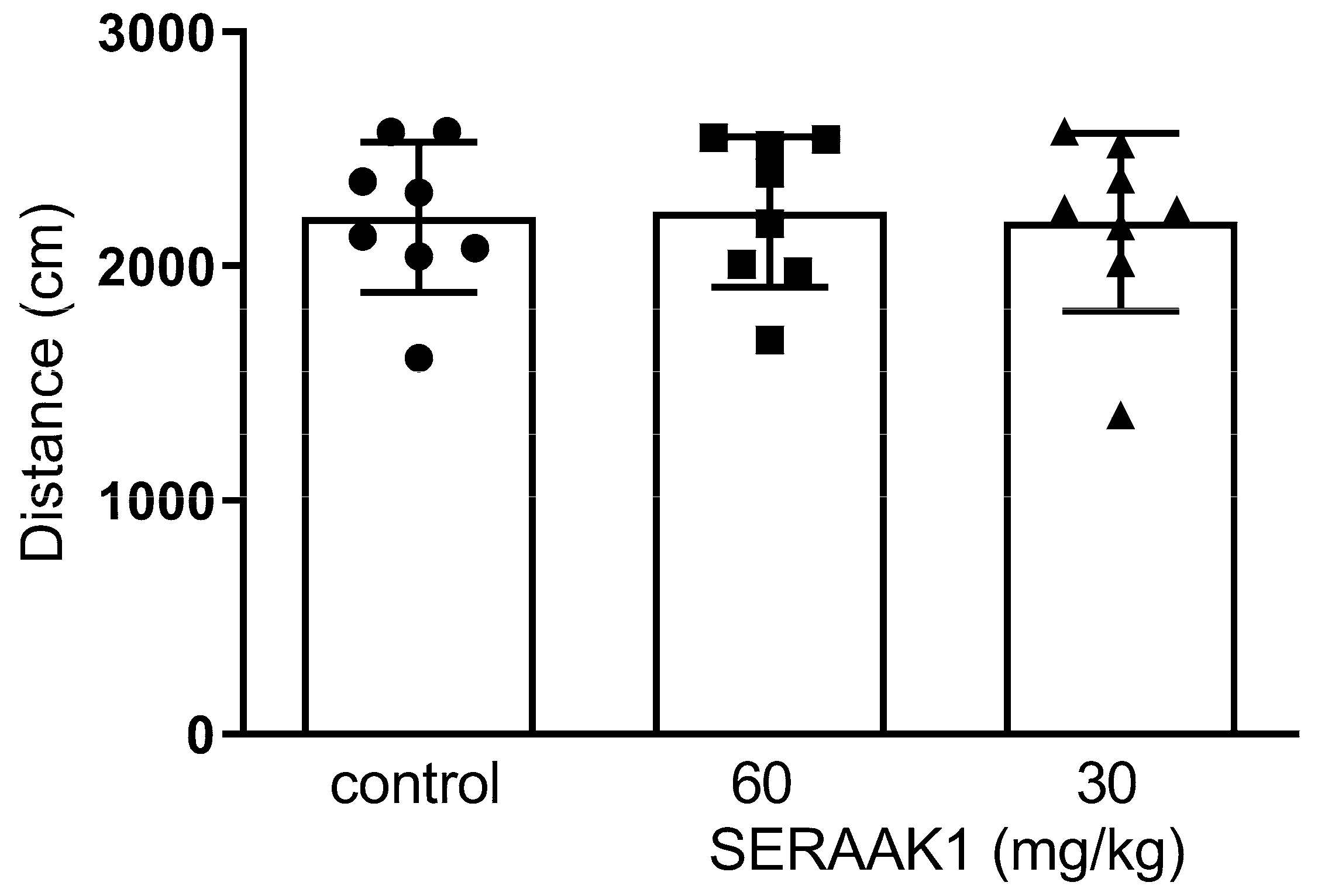
2.4.1. SERAAK1 Effects on Spontaneous Locomotor Activity in Mice
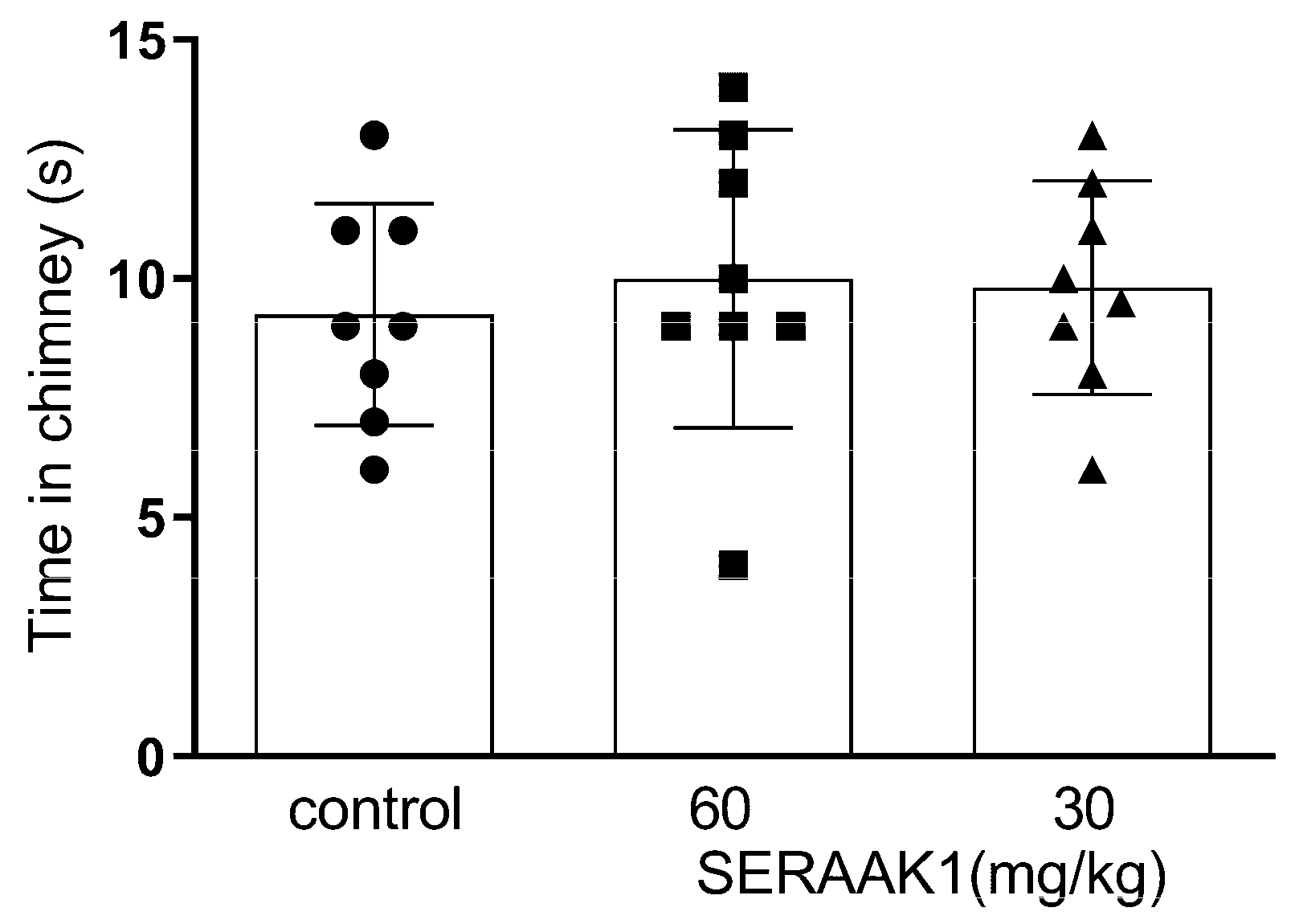
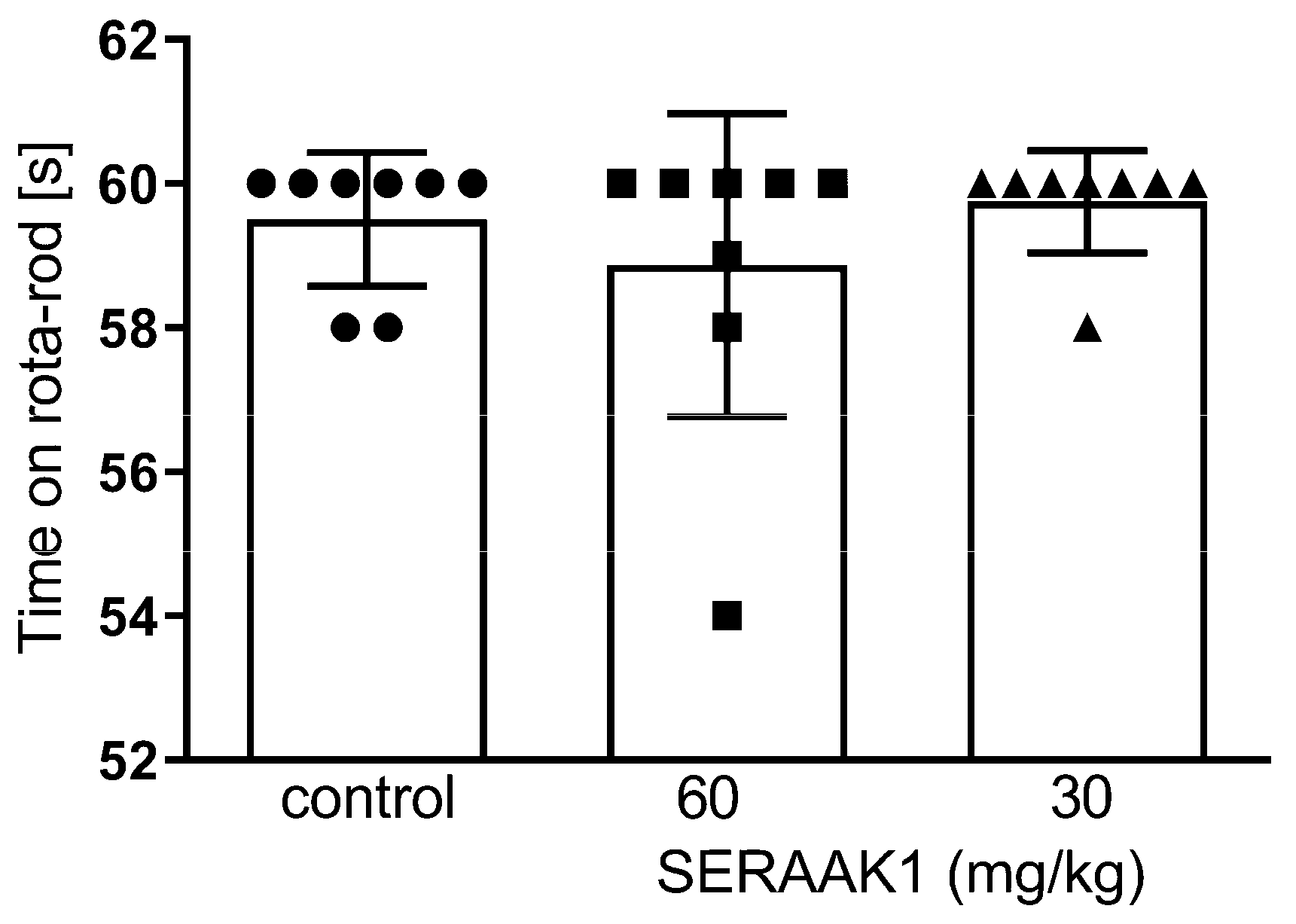
2.4.2. SERAAK1 Effects on Motor Coordination in Mice
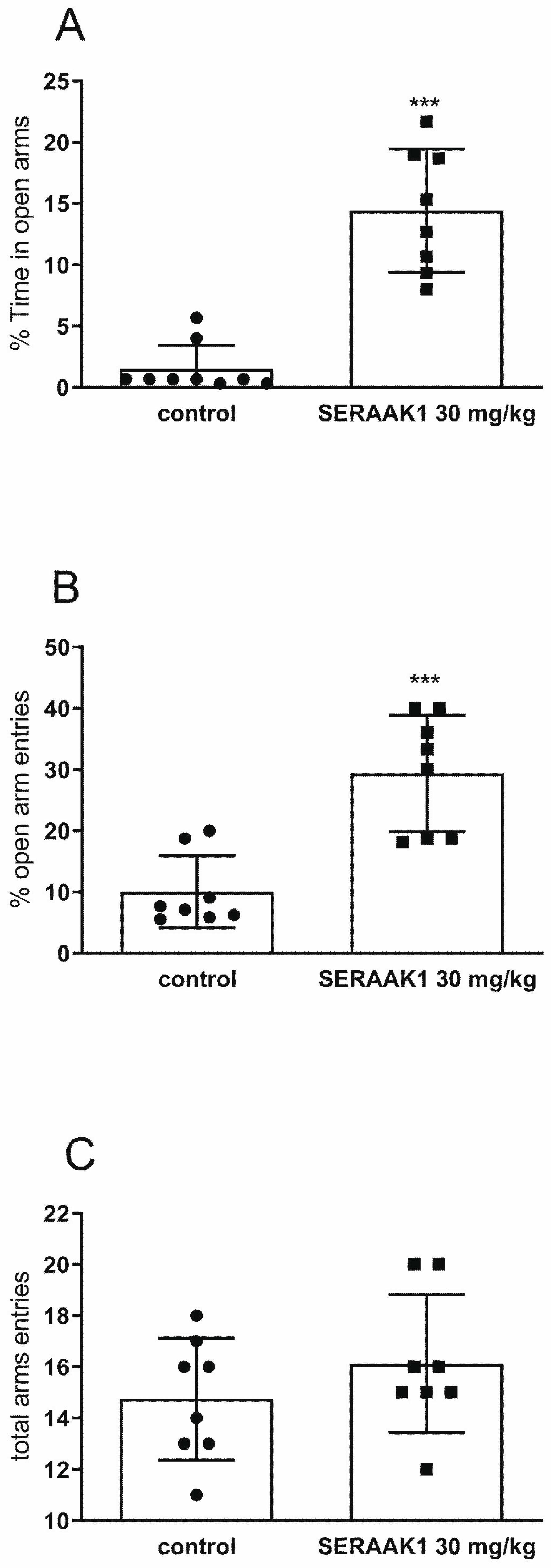
2.4.3. Effect of Acute Administration on Anxiety-like Behavior
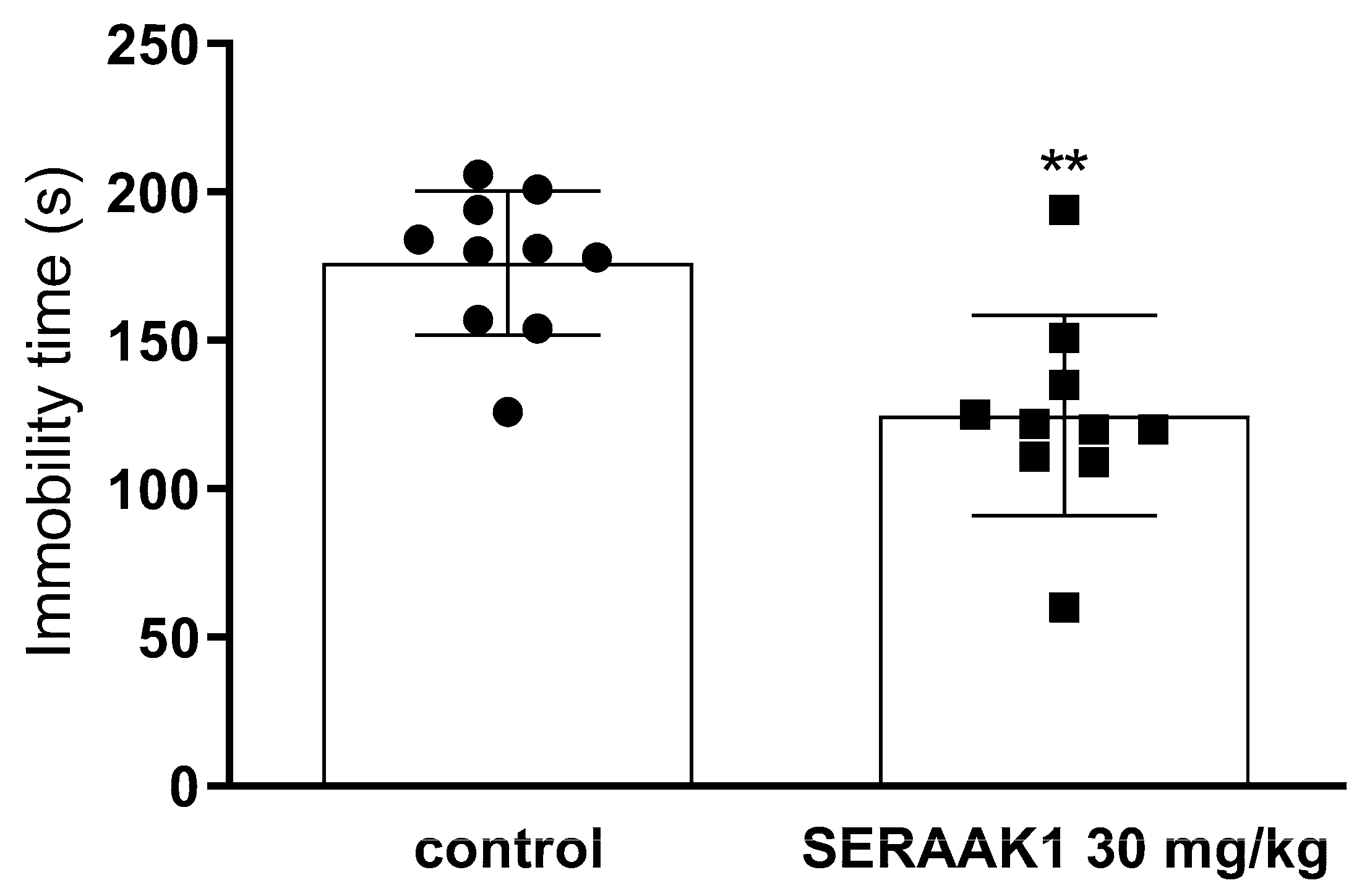
2.4.4. Total Immobility Duration in the Forced Swim Test
2.4.5. Effect of Acute Administration on Amphetamine-Induced Hyperactivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Modeling
4.2. SERAAK1 Synthetic Procedure
4.3. ADMET Parameters
4.3.1. Influence on Cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2D6 Activity
4.3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4.3.3. Membrane Permeability Evaluation
4.4. Behavioral Studies Protocols
4.4.1. Drugs
4.4.2. Animals
4.4.3. Spontaneous Locomotor Activity and Amphetamine-Induced Hyperactivity
4.4.4. Motor Coordination
4.4.5. Elevated Plus Maze Test (EPM Test)
4.4.6. Forced Swim Test (FST, Porsolt’s Test)
4.4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPM | elevated plus maze test |
| FST | forced swim test |
| GPCR | G protein coupled receptor |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| POPC | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| RMSD | root mean square deviation |
| RMSF | root mean square fluctuation |
| SPC | simple point charge |
| TEBA | Benzyltriethylammonium chloride |
References
- Bamalan, O.A.; Moore, M.J.; Khalili, Y.A. Physiology, Serotonin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa/St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, D.; Rudge, S. The Role of Serotonin in Depression and Anxiety. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1995, 9 (Suppl. S4), 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich, A.; Brown, S.L.; Kahn, R.; van Praag, H.M. The Role of Serotonin in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1988, 14, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Alonso, M.; Sarriés-Serrano, U.; Miquel-Rio, L.; Yanes Castilla, C.; Paz, V.; Meana, J.J.; Perello, M.; Bortolozzi, A. New Insights into the Effects of Serotonin on Parkinson’s Disease and Depression through Its Role in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Span. J. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnäs, K.; Halldin, C.; Hall, H. Autoradiographic Distribution of Serotonin Transporters and Receptor Subtypes in Human Brain. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2004, 22, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carhart-Harris, R.L.; Nutt, D.J. Serotonin and Brain Function: A Tale of Two Receptors. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 1091–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosienko, V.; Beis, D.; Pasqualetti, M.; Waider, J.; Matthes, S.; Qadri, F.; Bader, M.; Alenina, N. Life without Brain Serotonin: Reevaluation of Serotonin Function with Mice Deficient in Brain Serotonin Synthesis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisstaub, N.V.; Zhou, M.; Lira, A.; Lambe, E.; González-Maeso, J.; Hornung, J.-P.; Sibille, E.; Underwood, M.; Itohara, S.; Dauer, W.T.; et al. Cortical 5-HT2A Receptor Signaling Modulates Anxiety-like Behaviors in Mice. Science 2006, 313, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cinalli, D.; Cohen, S.J.; Knapp, K.D.; Rios, L.M.; Martínez-Hernández, J.; Luján, R.; Stackman, R.W. Examination of the Hippocampal Contribution to Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor-Mediated Facilitation of Object Memory in C57BL/6J Mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 109, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondej, M.; Stępnicki, P.; Kaczor, A.A. Multi-Target Approach for Drug Discovery against Schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesseveur, G.; Repérant, C.; David, D.J.; Gardier, A.M.; Sanchez, C.; Guiard, B.P. 5-HT₂A Receptor Inactivation Potentiates the Acute Antidepressant-like Activity of Escitalopram: Involvement of the Noradrenergic System. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 226, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Jha, M.K.; Radhakrishnan, R. Role of Psychedelics in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 46, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, D.J.; Peill, J.M.; Weiss, B.; Godfrey, K.; Carhart-Harris, R.L.; Erritzoe, D. Psilocybin and Other Classic Psychedelics in Depression. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 66, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Stackman, R.W. The Role of Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors in Memory and Cognition. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, A.; Terrón, J.A.; Hong, E. Effects of the 5-HT Receptor Antagonists GR127935 (5-HT1B/1D) and MDL100907 (5-HT2A) in the Consolidation of Learning. Behav. Brain Res. 1997, 89, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.H.; Darby-King, A.; Hodge, E. 5-HT2 Receptor Involvement in Conditioned Olfactory Learning in the Neonate Rat Pup. Behav. Neurosci. 1996, 110, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, Y.O.; Ordyan, N.E. Blockade of 5-HT2A/2C-Type Receptors Impairs Learning in Female Rats in the Course of Estrous Cycle. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 150, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.G.; Quinn, J.L.; Li, L.; Dave, K.D.; Schindler, E.A.; Aloyo, V.J.; Harvey, J.A. Intrahippocampal LSD Accelerates Learning and Desensitizes the 5-HT(2A) Receptor in the Rabbit, Romano et al. Psychopharmacology 2010, 212, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchborn, T.; Schröder, H.; Höllt, V.; Grecksch, G. Repeated Lysergic Acid Diethylamide in an Animal Model of Depression: Normalisation of Learning Behaviour and Hippocampal Serotonin 5-HT2 Signalling. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, A.R.; Maglione, M.; Bagley, S.; Suttorp, M.; Hu, J.-H.; Ewing, B.; Wang, Z.; Timmer, M.; Sultzer, D.; Shekelle, P.G. Efficacy and Comparative Effectiveness of Atypical Antipsychotic Medications for Off-Label Uses in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2011, 306, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwoski, G.; Kothiwale, S.; Meiler, J.; Lowe, E.W. Computational Methods in Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 334–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zięba, A.; Bartuzi, D.; Stępnicki, P.; Matosiuk, D.; Wróbel, T.M.; Laitinen, T.; Castro, M.; Kaczor, A.A. Discovery and in Vitro Evaluation of Novel Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands Identified Through Virtual Screening. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB-6A93: Crystal Structure of 5-HT2AR in Complex with Risperidone. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6A93 (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Kimura, K.T.; Asada, H.; Inoue, A.; Kadji, F.M.N.; Im, D.; Mori, C.; Arakawa, T.; Hirata, K.; Nomura, Y.; Nomura, N.; et al. Structures of the 5-HT2A Receptor in Complex with the Antipsychotics Risperidone and Zotepine. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Javitch, J.A. The Binding Site of Aminergic G Protein-Coupled Receptors: The Transmembrane Segments and Second Extracellular Loop. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 437–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Zhou, X.E.; Cheng, X.; Simon, I.A.; Shen, D.-D.; Yen, H.-Y.; Robinson, C.V.; et al. Structural Insights into the Lipid and Ligand Regulation of Serotonin Receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Che, T.; Levit, A.; Shoichet, B.K.; Wacker, D.; Roth, B.L. Structure of the D2 Dopamine Receptor Bound to the Atypical Antipsychotic Drug Risperidone. Nature 2018, 555, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aier, I.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Raj, U. Structural Insights into Conformational Stability of Both Wild-Type and Mutant EZH2 Receptor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Lu, X.; Lan, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S. G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs): Advances in Structures, Mechanisms and Drug Discovery. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.D.Y.; Terry, D.B.; Smith, L.H. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of ADME and PK Properties During Lead Selection and Lead Optimization—Guidelines, Benchmarks and Rules of Thumb. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C., Baell, J., Brimacombe, K., Chung, T.D.Y., Coussens, N.P., Dahlin, J.L., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company: BeIndianapolis, Indiana; The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Beers, J.L.; Geffert, R.M.; Jackson, K.D. A Review of CYP-Mediated Drug Interactions: Mechanisms and In Vitro Drug-Drug Interaction Assessment. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug-Like Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-12-369520-8.
- Chen, X.; Murawski, A.; Patel, K.; Crespi, C.L.; Balimane, P.V. A Novel Design of Artificial Membrane for Improving the PAMPA Model. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Shimizu, N.; Matsushita, S.; Murata, T. The Assessment of Mouse Spontaneous Locomotor Activity Using Motion Picture. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissier, J.-R.; Tardy, J.; Diverres, J.-C. Une Nouvelle Méthode Simple Pour Explorer l’action «tranquillisante»: Le Test de La Cheminée. Med. Exp. 2008, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, F.; Tripod, J.; Meier, R. Pharmacological characteristics of the soporific doriden. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1955, 85, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The Use of the Elevated plus Maze as an Assay of Anxiety-Related Behavior in Rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, R.G. The Use of a Plus-Maze to Measure Anxiety in the Mouse. Psychopharmacology 1987, 92, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Dao, D.T.; Arad, M.; Terrillion, C.E.; Piantadosi, S.C.; Gould, T.D. The Mouse Forced Swim Test. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samer, C.; Daali, Y.; Wagner, M.; Hopfgartner, G.; Eap, C.; Rebsamen, M.; Rossier, M.; Hochstrasser, D.; Dayer, P.; Desmeules, J. The Effects of CYP2D6 and CYP3A Activities on the Pharmacokinetics of Immediate Release Oxycodone. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. CYTOCHROME P-450 3A4: Regulation and Role in Drug Metabolism. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicali, E.J.; Smith, D.M.; Duong, B.Q.; Kovar, L.G.; Cavallari, L.H.; Johnson, J.A. A Scoping Review of the Evidence Behind CYP2D6 Inhibitor Classifications. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin-Zimmerman, I.; Wronska, M.; Wang, B.; Irizar, H.; Thygesen, J.H.; Bhat, A.; Denaxas, S.; Fatemifar, G.; Finan, C.; Harju-Seppänen, J.; et al. The Influence of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genetic Variation on Diabetes Mellitus Risk in People Taking Antidepressants and Antipsychotics. Genes 2021, 12, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Y.L.; Ho, H.K.; Chan, A. Metabolism-Related Pharmacokinetic Drug−drug Interactions with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Current Understanding, Challenges and Recommendations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Huang, S.-M. Predicting Drug–Drug Interactions: An FDA Perspective. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.C.; Chenge, J.; Chen, T. Structural Perspectives of the CYP3A Family and Their Small Molecule Modulators in Drug Metabolism. Liver Res. 2019, 3, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzumanian, V.A.; Kiseleva, O.I.; Poverennaya, E.V. The Curious Case of the HepG2 Cell Line: 40 Years of Expertise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Suarez, L.; Awabdh, S.A.; Coumoul, X.; Chauvet, C. The SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line, a Relevant in Vitro Cell Model for Investigating Neurotoxicology in Human: Focus on Organic Pollutants. NeuroToxicology 2022, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorović Vukotić, N.; Đorđević, J.; Pejić, S.; Đorđević, N.; Pajović, S.B. Antidepressants- and Antipsychotics-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.G. Drug Discovery and Evaluation: Pharmacological Assays; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; ISBN 978-3-540-42396-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ari, C.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Diamond, D.M.; Kindy, M.; Park, C.; Kovács, Z. Elevated Plus Maze Test Combined with Video Tracking Software to Investigate the Anxiolytic Effect of Exogenous Ketogenic Supplements. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 143, e58396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, R.H. Buspirone: Back to the Future. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2015, 53, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, M.Z.; Marciniak, M. Ligandy receptora 5-HT1a jako potencjalne leki przeciwdepresyjne. Prospect. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 13, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, V.; Maisonnette, S.; Morato, S.; Castrechini, P.; Brandão, M.L. Effects of Blockade of 5-HT2 Receptors and Activation of 5-HT1A Receptors on the Exploratory Activity of Rats in the Elevated plus-Maze. Psychopharmacology 1992, 107, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Véliz, G.; Alarcón, T.; Espinoza, C.; Dussaubat, N.; Mora, S. Ketanserin and Anxiety Levels: Influence of Gender, Estrous Cycle, Ovariectomy and Ovarian Hormones in Female Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 58, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, T.F.; Awouters, F. Central 5-HT2 Antagonists: A Preclinical Evaluation of a Therapeutic Potential. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 1990, 2, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceulemans, D.L.; Hoppenbrouwers, M.L.; Gelders, Y.G.; Reyntjens, A.J. The Influence of Ritanserin, a Serotonin Antagonist, in Anxiety Disorders: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study versus Lorazepam. Pharmacopsychiatry 1985, 18, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, E.L.; Barnfield, A.M.; Curzon, G. Evidence That MCPP-Induced Anxiety in the plus-Maze Is Mediated by Postsynaptic 5-HT2C Receptors but Not by Sympathomimetic Effects. Neuropharmacology 1994, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebel, G.; Rodgers, R.J.; Perrault, G.; Sanger, D.J. Risk Assessment Behaviour: Evaluation of Utility in the Study of 5-HT-Related Drugs in the Rat Elevated plus-Maze Test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 57, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partyka, A.; Jarosz, J.; Wasik, A.; Jastrzębska-Więsek, M.; Zagórska, A.; Pawłowski, M.; Wesołowska, A. Novel Tricyclic[2,1-f]Theophylline Derivatives of LCAP with Activity in Mouse Models of Affective Disorders. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajdel, P.; Marciniec, K.; Maślankiewicz, A.; Grychowska, K.; Satała, G.; Duszyńska, B.; Lenda, T.; Siwek, A.; Nowak, G.; Partyka, A.; et al. Antidepressant and Antipsychotic Activity of New Quinoline- and Isoquinoline-Sulfonamide Analogs of Aripiprazole Targeting Serotonin 5-HT1A/5-HT2A/5-HT7 and Dopamine D2/D3 Receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, B.; Domeney, A.M.; Naylor, R.J. Locomotor Hyperactivity Caused by Dopamine Infusion into the Nucleus Accumbens of Rat Brain: Specificity of Action. Psychopharmacology 1984, 82, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, A.R. Mesolimbic Dopamine and Its Control of Locomotor Activity in Rats: Differences in Pharmacology and Light/Dark Periodicity between the Olfactory Tubercle and the Nucleus Accumbens. Psychopharmacology 1986, 88, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusljic, S.; van den Buuse, M.; Gogos, A. Reassessment of Amphetamine- and Phencyclidine-Induced Locomotor Hyperactivity as a Model of Psychosis-like Behavior in Rats. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.F.; Heron-Maxwell, C.L.; Shaw, G. 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonism Reduces Hyperactivity Induced by Amphetamine, Cocaine, and MK-801 but Not D1 Agonist C-APB. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1999, 63, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2023-3: Epik 2023; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2023.
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger LLC. Protein Preparation Wizard, Epik Version 2.1; Software at Stanford: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sparaco, R.; Kędzierska, E.; Kaczor, A.A.; Bielenica, A.; Magli, E.; Severino, B.; Corvino, A.; Gibuła-Tarłowska, E.; Kotlińska, J.H.; Andreozzi, G.; et al. Synthesis, Docking Studies and Pharmacological Evaluation of Serotoninergic Ligands Containing a 5-Norbornene-2-Carboxamide Nucleus. Molecules 2022, 27, 6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2021-4: Desmond Molecular Dynamics System; D.E. Shaw Research: Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Szczepańska, K.; Pockes, S.; Podlewska, S.; Höring, C.; Mika, K.; Latacz, G.; Bednarski, M.; Siwek, A.; Karcz, T.; Nagl, M.; et al. Structural Modifications in the Distal, Regulatory Region of Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists Leading to the Identification of a Potent Anti-Obesity Agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magli, E.; Kędzierska, E.; Kaczor, A.A.; Severino, B.; Corvino, A.; Perissutti, E.; Frecentese, F.; Saccone, I.; Massarelli, P.; Gibuła-Tarłowska, E.; et al. Synthesis, Docking Studies, and Pharmacological Evaluation of 5HT2C Ligands Containing the N’-Cyanoisonicotinamidine or N’-Cyanopicolinamidine Nucleus. Arch. Pharm. 2019, 352, e1800373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Anton, G.; Blavet, N.; Jalfre, M. Behavioural Despair in Rats: A New Model Sensitive to Antidepressant Treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 47, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

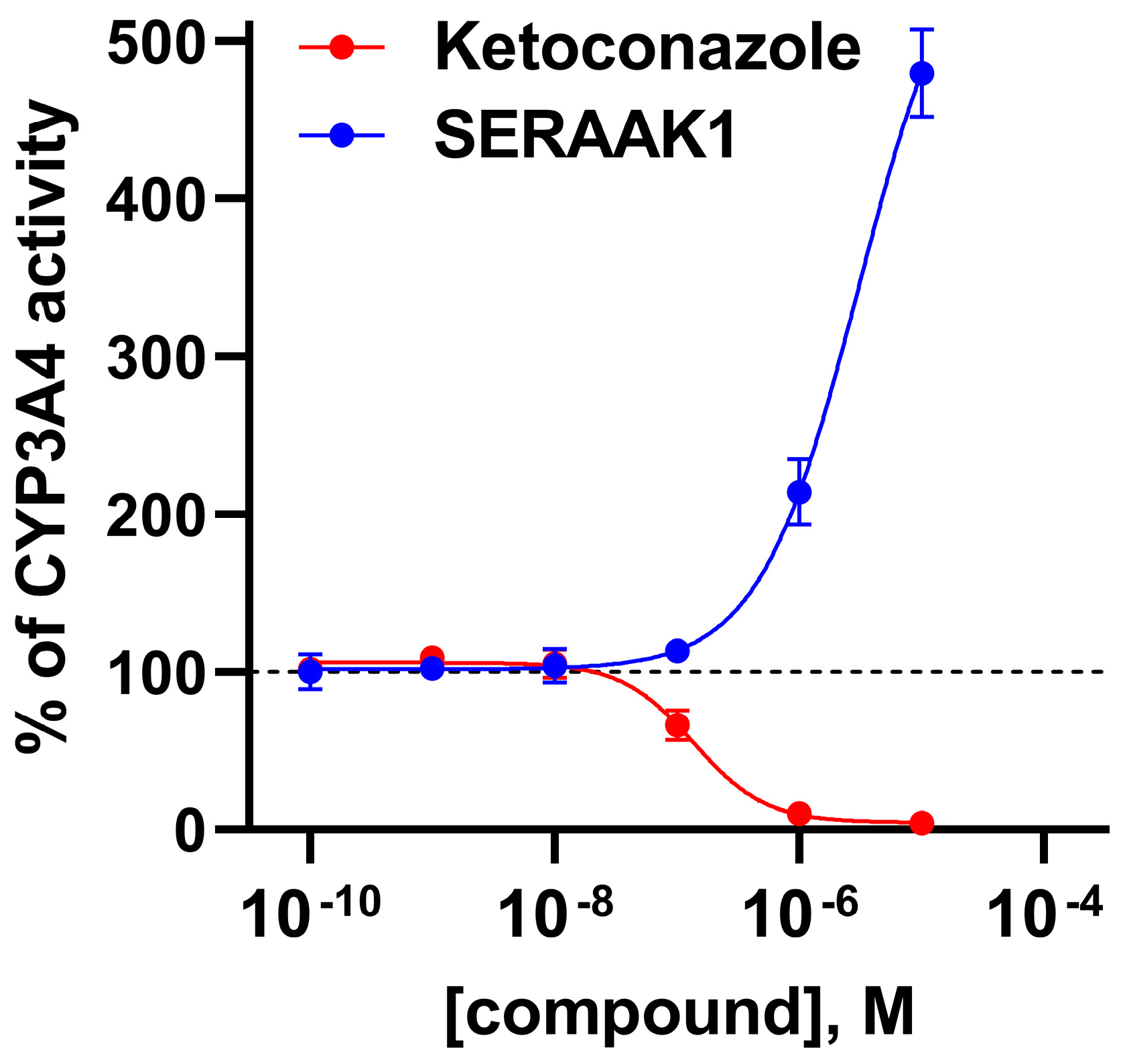
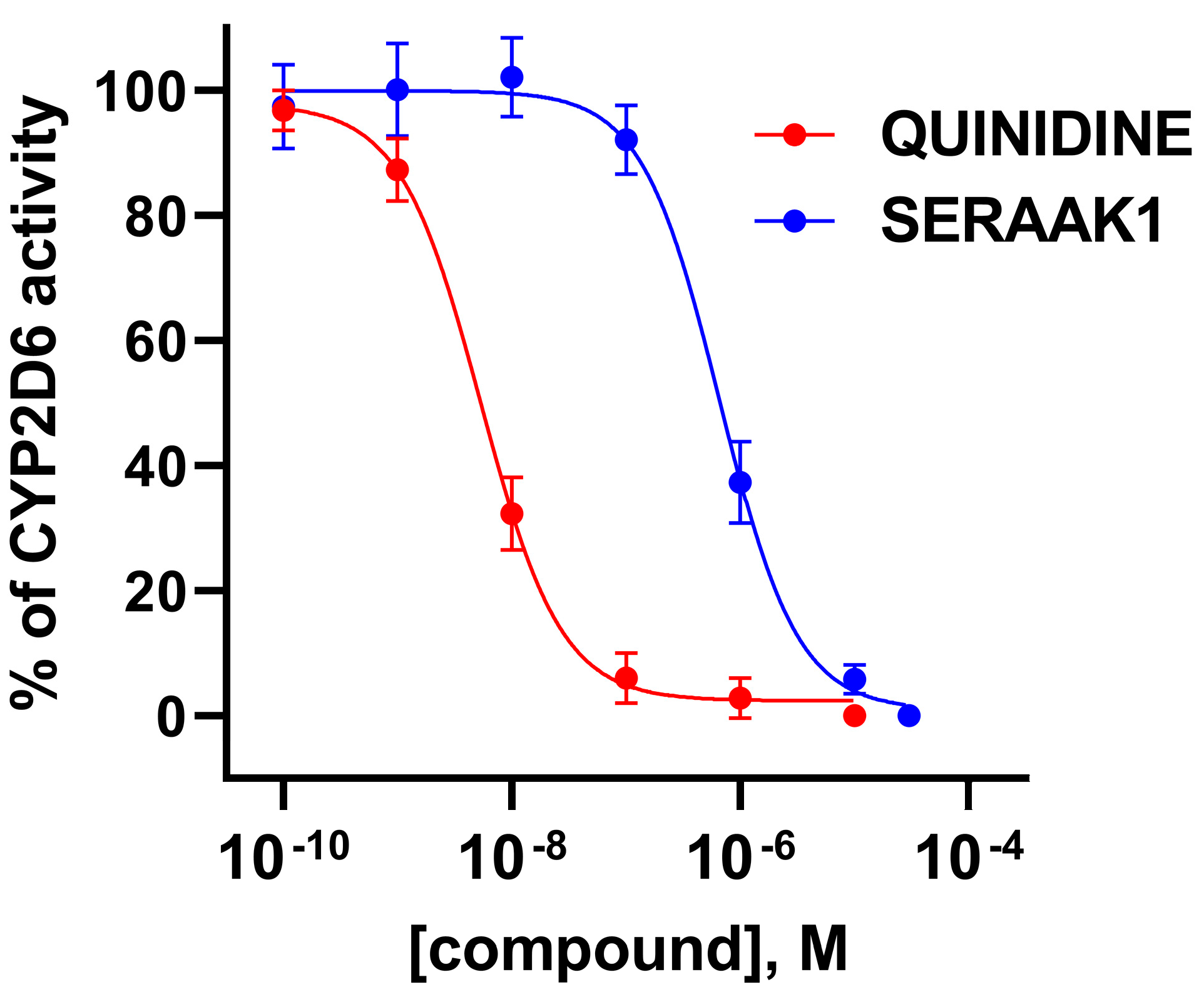
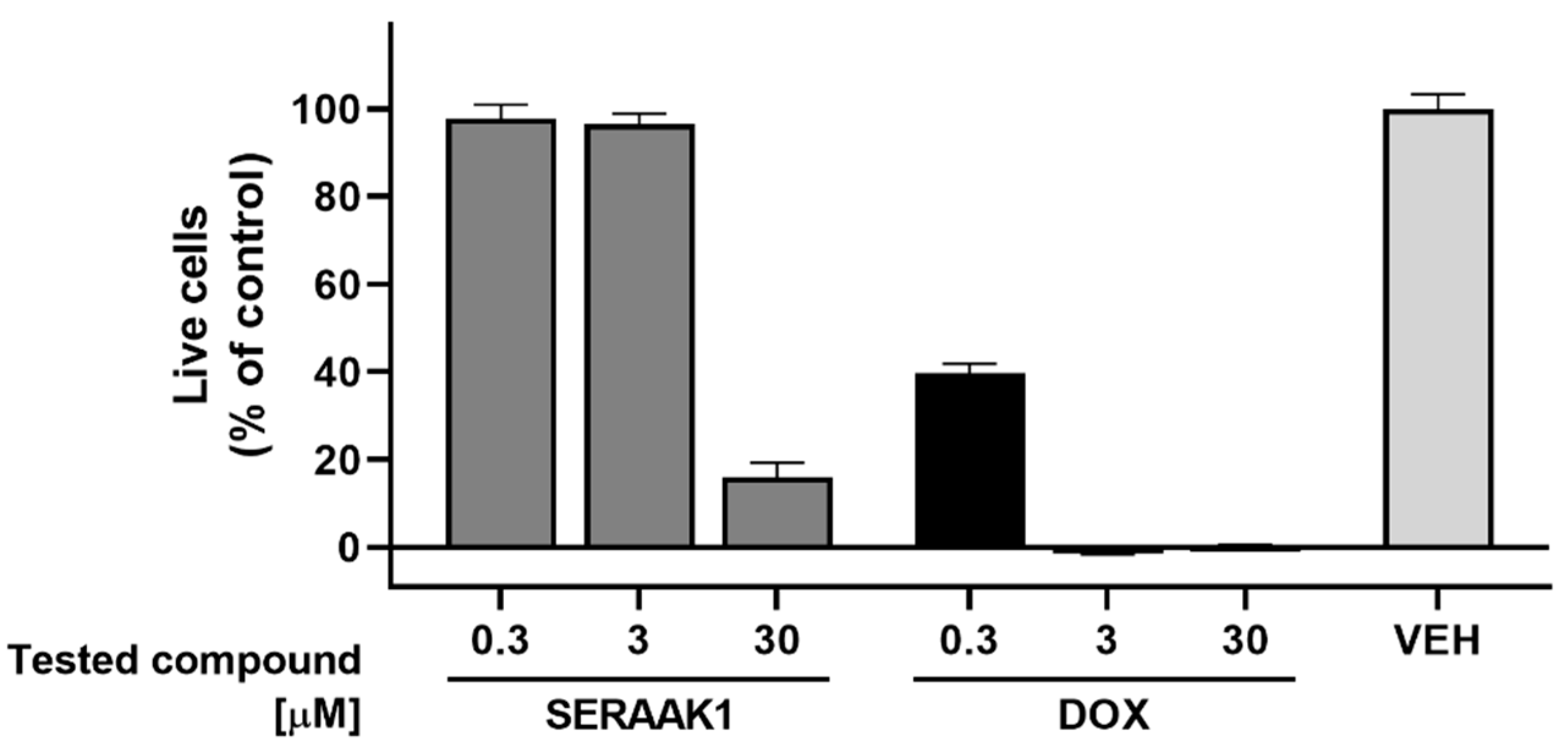
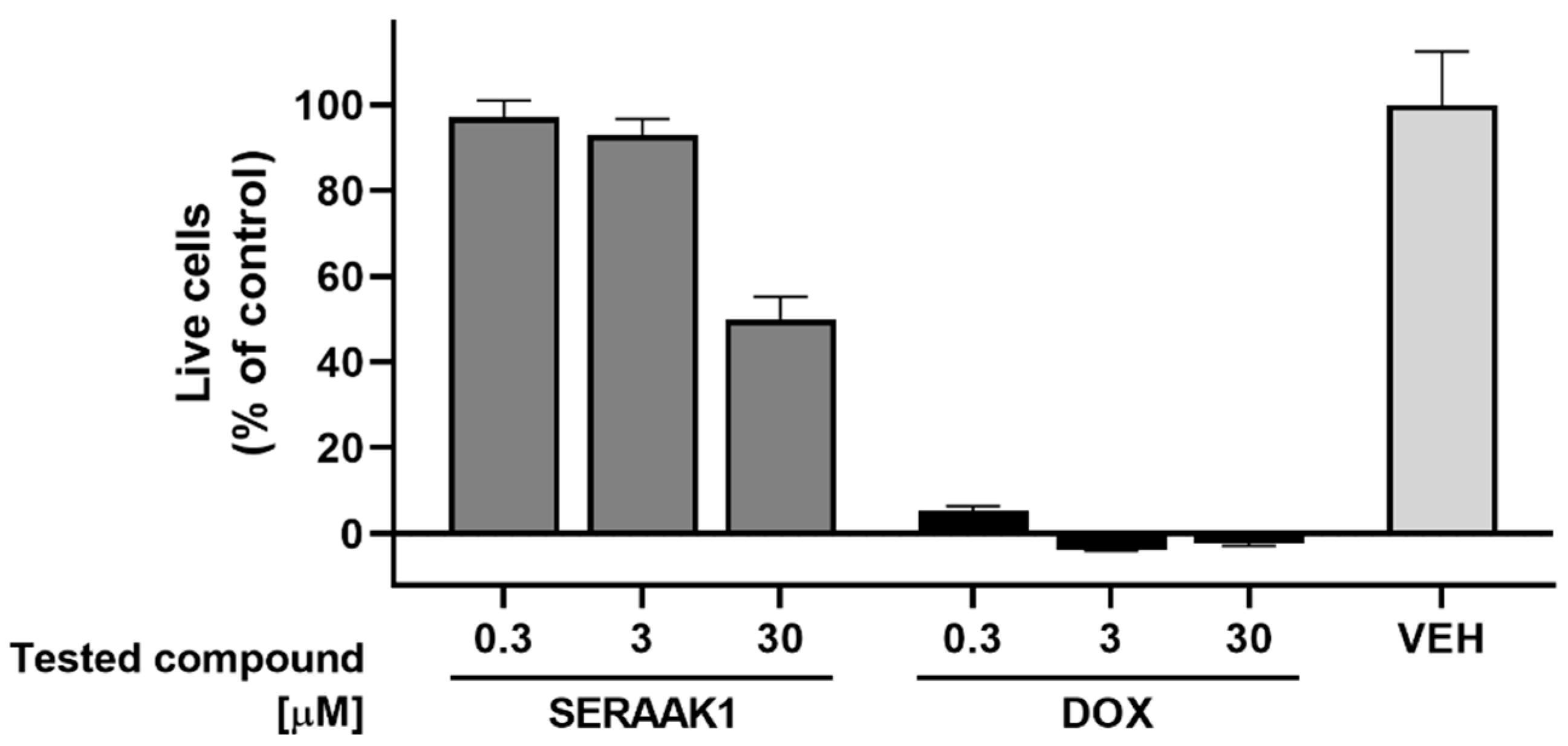

| Examined Compound | CYP3A4 Activity Inhibition, Evaluated in the Concentration of 10 µM [% of Inhibition ± SEM] |
|---|---|
| Ketoconazole | 100 ± 1 |
| SERAAK1 | −352 ± 9 [a] |
| Examined Compound | CYP2D6 Activity Inhibition, Evaluated in the Concentration of 10 µM [% of Inhibition ± SEM] |
|---|---|
| Quinidine | 100 ± 1 |
| SERAAK1 | 95 ± 1 |
| Examined Compound | Pe ± SD [×10−6 cm/s] |
|---|---|
| Caffeine | 12.4 ± 0.6 |
| Sulpiride | 0.011 ± 0.002 |
| SERAAK1 | <0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zięba, A.; Kędzierska, E.; Jastrzębski, M.K.; Karcz, T.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Sumara, A.; Laitinen, T.; Wróbel, T.M.; Fornal, E.; Castro, M.; et al. Synthesis, Experimental and Computational Evaluation of SERAAK1 as a 5-HT2A Receptor Ligand. Molecules 2025, 30, 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102165
Zięba A, Kędzierska E, Jastrzębski MK, Karcz T, Olejarz-Maciej A, Sumara A, Laitinen T, Wróbel TM, Fornal E, Castro M, et al. Synthesis, Experimental and Computational Evaluation of SERAAK1 as a 5-HT2A Receptor Ligand. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102165
Chicago/Turabian StyleZięba, Agata, Ewa Kędzierska, Michał K. Jastrzębski, Tadeusz Karcz, Agnieszka Olejarz-Maciej, Agata Sumara, Tuomo Laitinen, Tomasz M. Wróbel, Emilia Fornal, Marián Castro, and et al. 2025. "Synthesis, Experimental and Computational Evaluation of SERAAK1 as a 5-HT2A Receptor Ligand" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102165
APA StyleZięba, A., Kędzierska, E., Jastrzębski, M. K., Karcz, T., Olejarz-Maciej, A., Sumara, A., Laitinen, T., Wróbel, T. M., Fornal, E., Castro, M., & Kaczor, A. A. (2025). Synthesis, Experimental and Computational Evaluation of SERAAK1 as a 5-HT2A Receptor Ligand. Molecules, 30(10), 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102165








