A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dioxins and Furans Occurrence in River Sediments from a Secondary Steel Recycling Craft Village in Northern Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
| No. | Country | River Name | Concentration (ng/kg d.w) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Turkey | Yeşilırmak River | 3.47–33.8 (TEQ) | [25] |
| 2 | China | Daliao River | 0.28–29.01 | [26] |
| China | Dongting Lake | 130–891 (TEQ) | [27] | |
| 3 | Canada | Niagara river | 160–620 (TEQ) | [28] |
| 4 | Italy | Venice Lagoon | 0.5–2857 | [29] |
| 5 | Hong Kong | Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve | 5000–6900 | [30] |
| 6 | Germany | Elbe river | 1500 (TEQ) | [17] |
| 7 | France | Rhone River | <1–73,020 | [31] |
| 8 | USA | Saginaw River | 57–46,500 | [19] |
| Shiawassee River | 11–438 | |||
| 9 | Japan | Kankazi River | 68–6100 | [32] |
| 10 | Korea | Yeongsan river | 1140 | [33] |
| Nakdong River | 2940 | |||
| 11 | Vietnam | Cau River | 321 | [34] |
2. Results
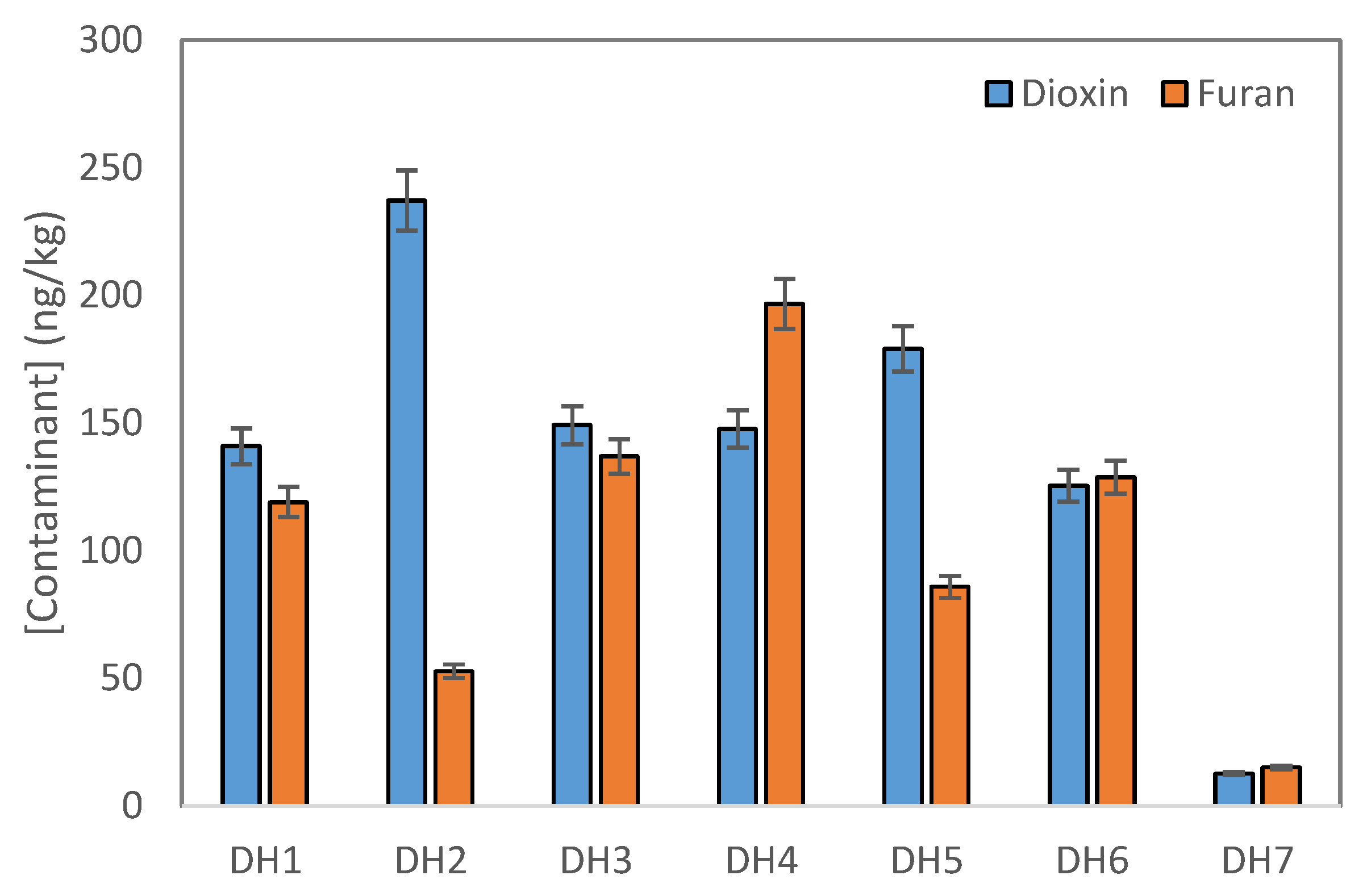
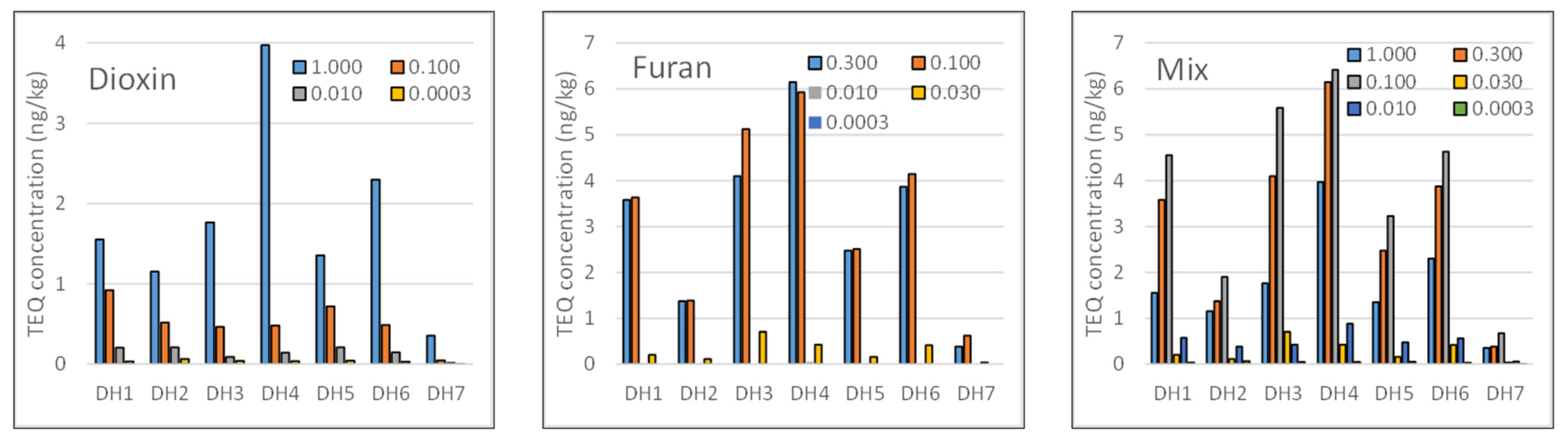
2.1. Occurrence of Dioxin/Furan Contaminants
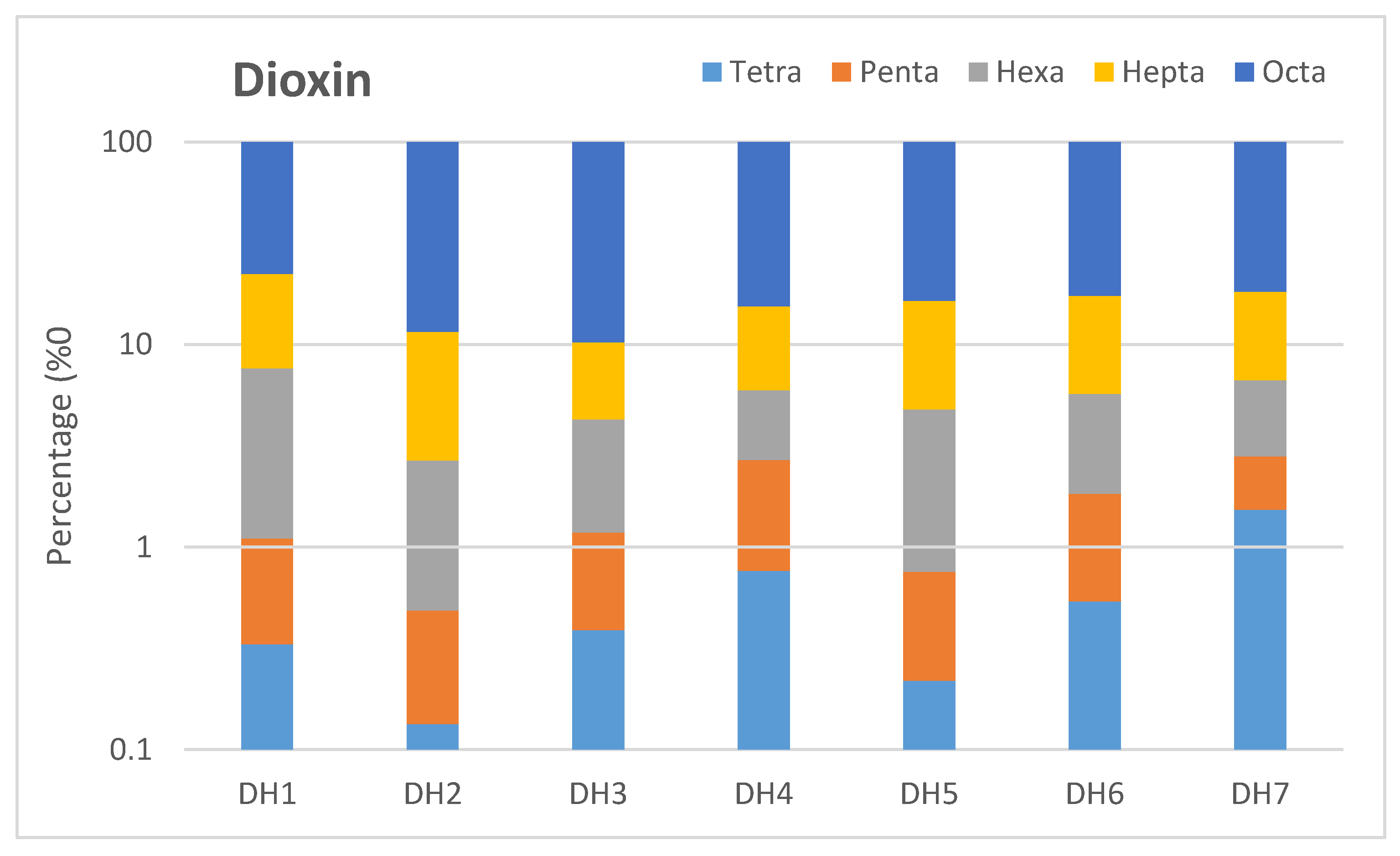
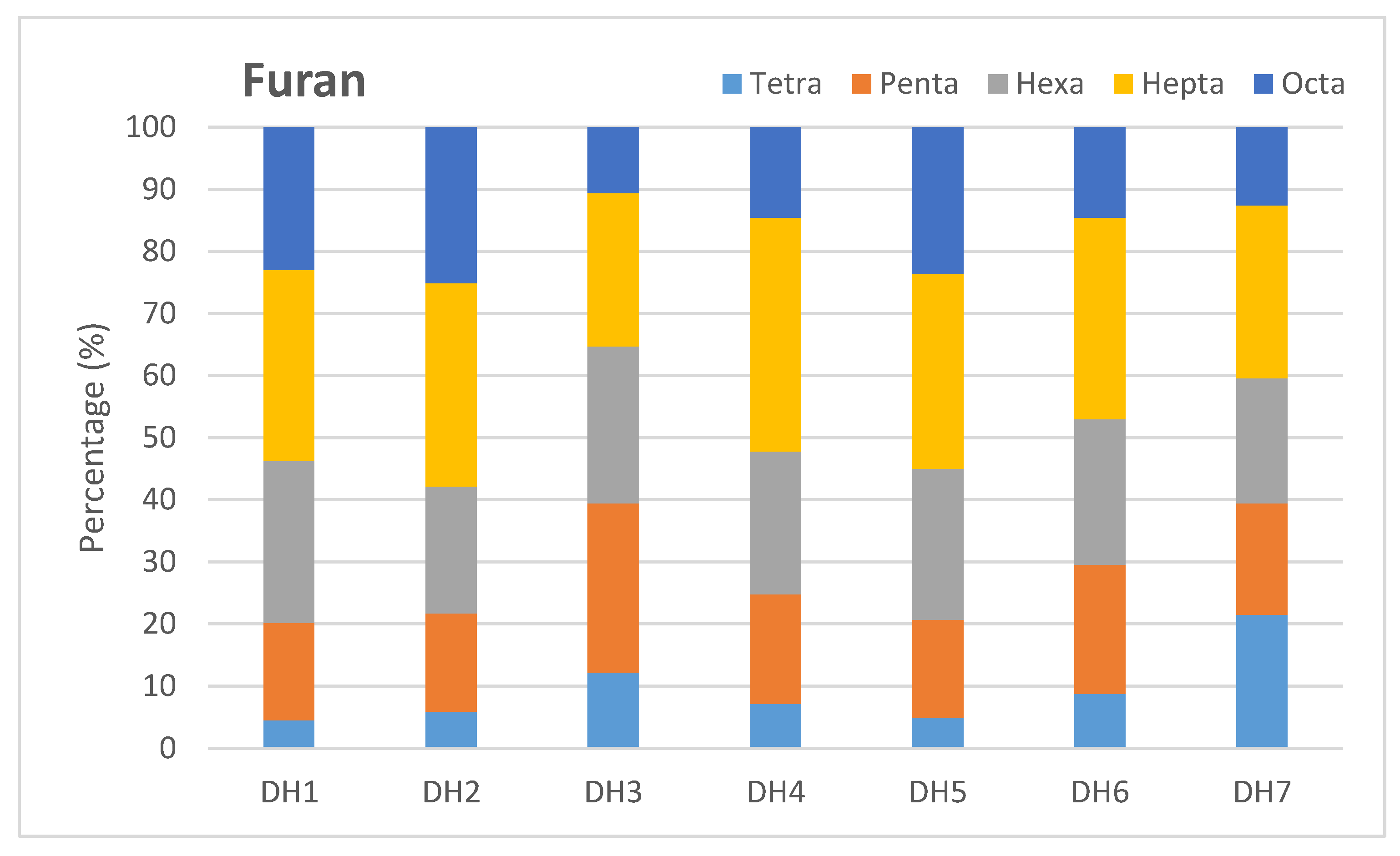
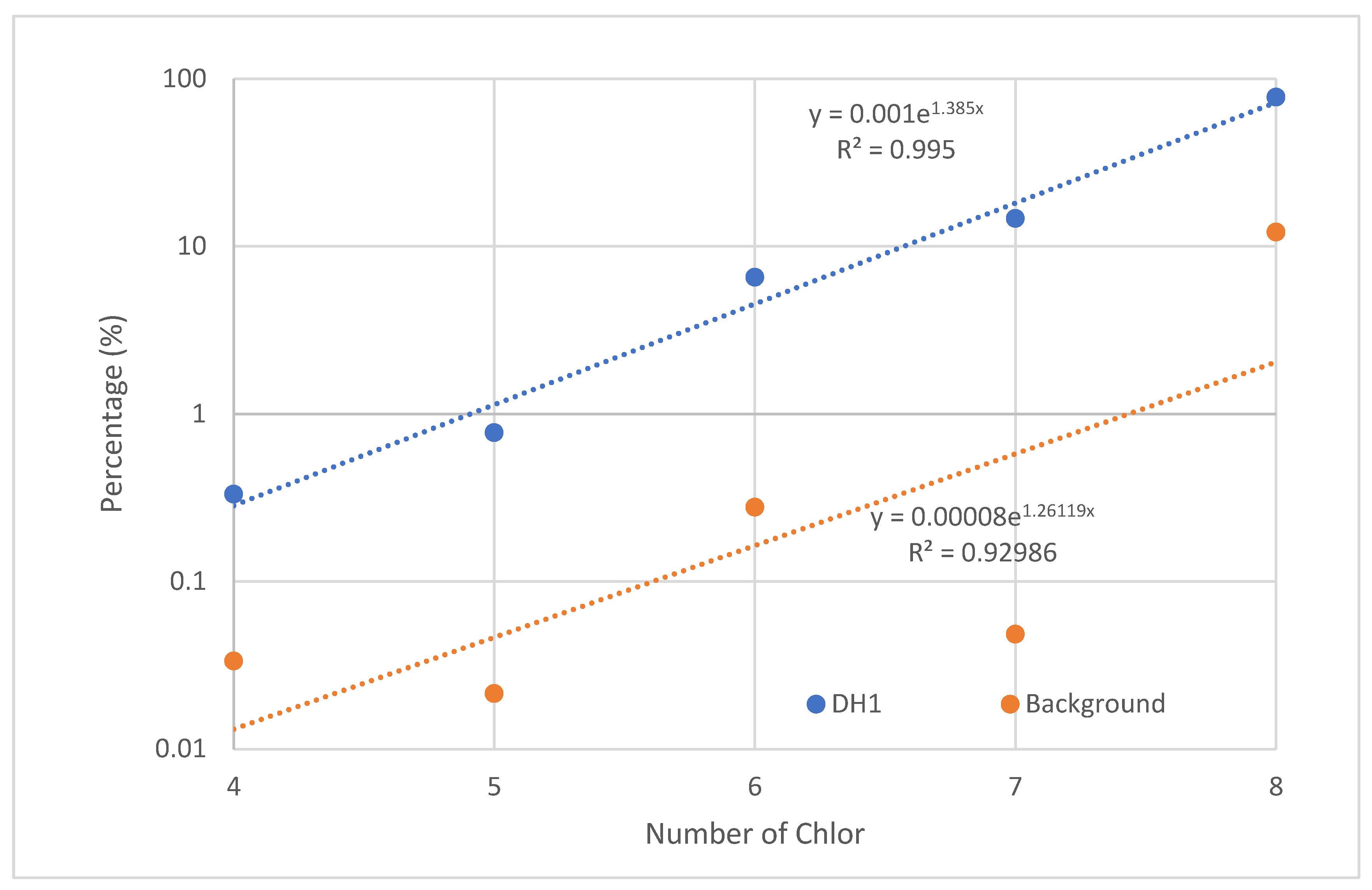
2.2. Distribution of Dioxins and Furans
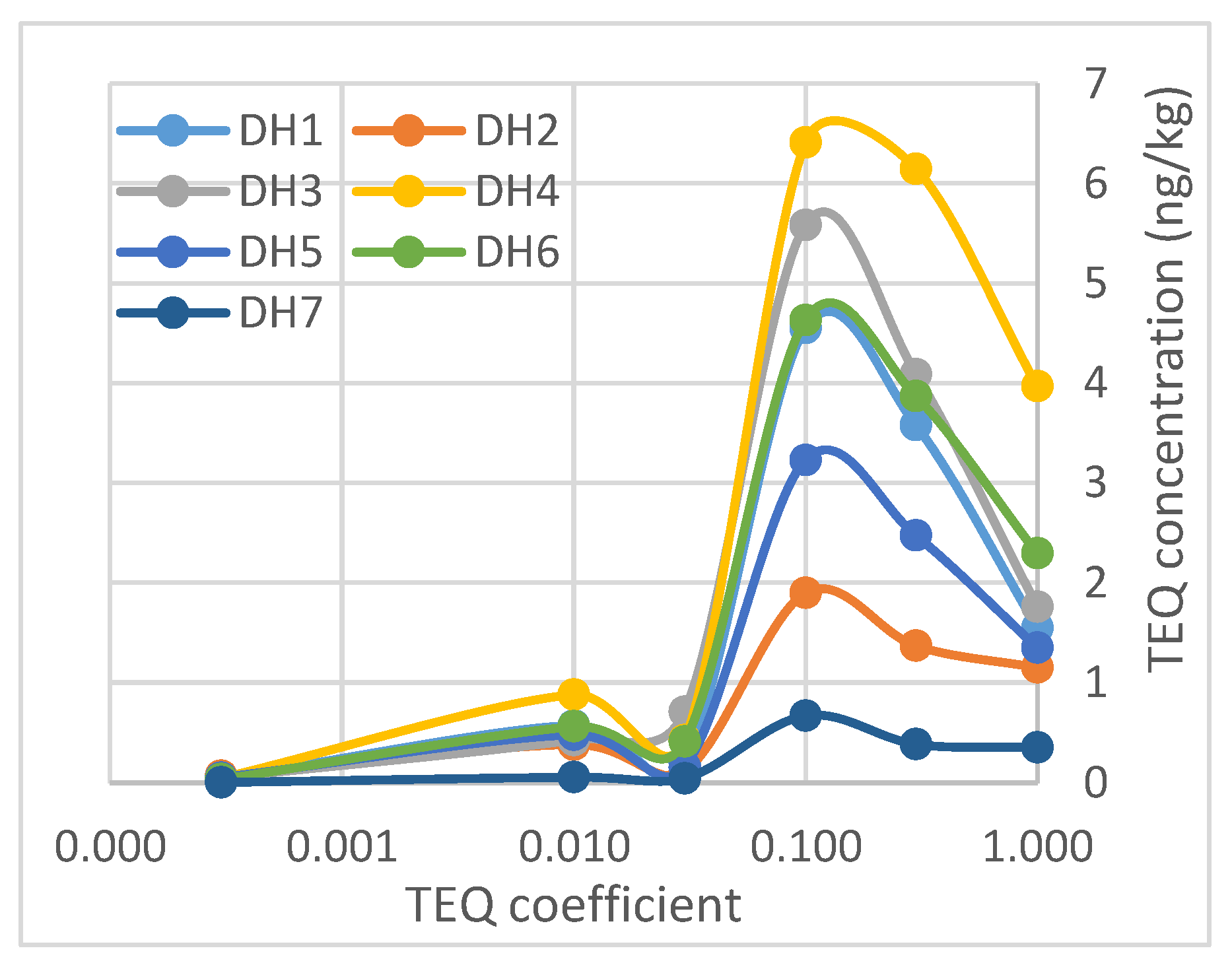
2.3. World Health Organization (WHO) TEQ for the PCDD/F
3. Discussions
- -
- Adding dioxin pollution parameters to the mandatory list for regular environmental pollution control in areas related to wastewater discharge from the production activities of the Da Hoi craft village. Although this study only monitored dioxin/furan in sediment, we recommend monitoring pollution in soil, water, air, and sediment because dioxin/furan seems to be present in all sample matrices.
- -
- Early investment in building centralized solid and wastewater treatment systems in the Da Hoi craft village area, as the current waste collection and transportation methods may spread dioxin/furan pollutants to other areas. Furthermore, waste from steel recycling activities should be considered hazardous waste. Therefore, organizations collecting, transporting, and treating hazardous waste must be licensed.
- -
- Issuing guidelines for steel recycling, especially regarding furnace temperature, because at low temperatures ranging from 450 to 800 °C, the formation of dioxin/furan is very high [47]. Therefore, the recommended temperature in steel recycling should be higher than 1200 °C to reduce the formation of these compounds. With the current dioxin/furan-contaminated sediment, detailed and extensive monitoring is required to accurately assess the level and load of pollution. Then, the dredging of mud and sediment around Da Hoi village can be carried out to dispose of dioxins as hazardous waste. This is a massive workload that requires further investment and time to implement.
- -
- To protect the health of the people and prevent the widespread dispersion of pollutants, it is necessary to stop all sand mining activities, water extraction for domestic and agricultural use, as well as fishing and aquaculture in this area.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
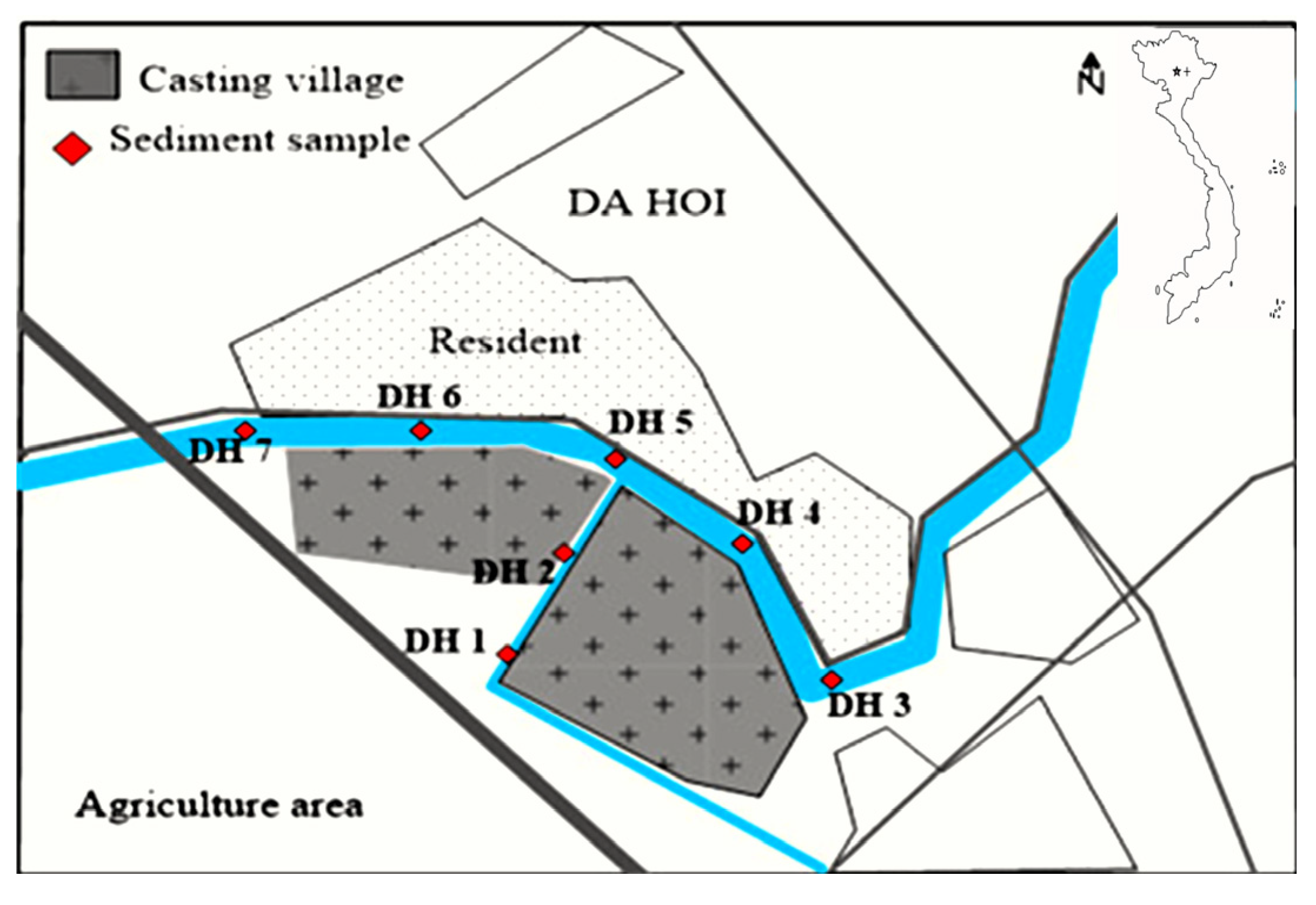
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Sample Analysis
4.4. Validation of Analytical Method
4.5. Calculation of TEQ
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CVs | Craft villages |
| DH | Da Hoi |
| DLCs | Dioxin-Like Compounds |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| HRGC/HRMS | High-Resolution Gas Chromatography/High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry |
| PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PCDDs | polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins |
| PCDFs | polychlorinated dibenzofurans |
| PCDD/F | polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin/polychlorinated dibenzofuran |
| TEFs | toxicity equivalence factors |
| TEQ | Toxic equivalent |
| SSR | Secondary Steel Recycling |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| 2, 3, 7, 8-PCDD | 2,3,7,8-substituted-polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 2,3,7,8-TCDD | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD | 1,2,3,7,8-pentachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD | 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD | 1,2,3,6,7,8-hexachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD | 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD | 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-heptachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| OCDD | Octachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 2, 3, 7, 8-PCDF | 2,3,7,8-substituted-polychlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 2,3,7,8-TCDF | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF | 1,2,3,7,8-pentachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF | 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF | 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF | 1,2,3,6,7,8-hexachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF | 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF | 2,3,4,6,7,8-hexachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF | 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-heptachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF | 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-heptachlorinated dibenzofuran |
| OCDF | Octachlorinated dibenzofuran |
References
- Nguyen, T.L. Environmental pollution in Vietnam’s craft villages. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 175, 06012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Anh. 2917. Available online: https://danviet.vn/bac-ninh-lang-nghe-truyen-thong-ngap-trong-o-nhiem-7777744041.htm (accessed on 9 February 2017).
- Thi Tham, N.; Manh Thang, H.; Thu Ha, D.; Thanh Canh, N.; Qui Duong, N. Pollution risk of heavy metal for agricultural land in iron reprocessing village Chau Khe, Tu Son town, Bac Ninh province. J. Vietnam. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Strezov, V.; Evans, T.; Salian, K.; Taylor, M.P. Formation and distribution of dioxins in agglomerated products and emitted dust during iron ore sintering. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.T.N.; Hoang, A.Q.; Nghiem, X.T.; Tu, B.M.; Dao, T.N.; Vu, D.N. Residue concentrations and profiles of PCDD/Fs in ash samples from multiple thermal industrial processes in Vietnam: Formation, emission levels, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17719–17730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.T.N.; Anh, H.Q.; Nghiem, X.T.; Tu, B.M.; Dao, T.N.; Nguyen, M.H. Characterization of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in flue gas from thermal industrial processes in Vietnam: A comprehensive investigation on emission profiles and levels. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT—National Technical Regulation on Industrial Waste Water; Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2011; No. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. QCVN 08:2023/BTNMT—National Technical Regulation on Surface Water Quality; Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2023; No. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomisto, J. Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds: Toxicity in humans and animals, sources, and behaviour in the environment. Wiki J. Med. 2019, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, K.; Ormerod, R.; Starke, G.; Zeise, K. Australian Inventory of Dioxin Emissions; Department of the Environment and Heritage: Brisbane, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, T.L.; Thuong, V.N.; Nam, D.V.; Thuy, M.L.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Trung, Q.N.; Long, P.D. Assessment of dioxin and furan level in serum blood of labor in contaminated site during three continuous months working. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2020, 58, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, I.; Ueda, Y.; Honda, K.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Nguyen, H.M.; Nam, D.V.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Pham, T.P.T.; Takenaka, N.; et al. Contamination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans in Jatropha curcas cultivation areas and their transfer from soil to seed in the Ba Vi, Quang Tri, and Trang Bang regions of Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2021, 1, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group. Chemical Agents and Related Occupations: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Working Group: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Han, C. Water Quality Ecological Risk Assessment with Sedimentological Approach. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, N.; Takagi, Y.; Oshima, S.; Ueda, Y.; Watanabe, I.; Binh, M.D.; Trung, N.Q.; Honda, K. The rapid analysis for dioxin derived from agent orange in soil~II analytical method with flow immunosensor. Organohalogen Compd. 2013, 75, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, H.T.; Kadokami, K.; Pan, S.; Matsuura, N.; Nguyen, T.Q. Screening and analysis of 940 organic micro-pollutants in river sediments in Vietnam using an automated identification and quantification database system for GC–MS. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, R.; Bergemann, M.; Stachel, B.; Umlauf, G. Dioxin in the river Elbe. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattore, E.; Viganò, L.; Mariani, G.; Guzzi, A.; Benfenati, E.; Fanelli, R. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in River Po sediments. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Yun, S.H.; Ostaszewski, A.; McCabe, J.M.; Mackenzie-Taylor, D.; Taylor, A.B. Dioxin-like toxicity in the Saginaw River watershed: Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls in sediments and floodplain soils from the Saginaw and Shiawassee Rivers and Saginaw Bay, Michigan, USA. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, M.; Imamura, K.; Takenaka, N.; Maeda, Y.; Viet, P.H.; Kondo, A.; Bandow, H. Characteristics of the abundance of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in sediment samples from selected Asian regions in Can Gio, Southern Vietnam and Osaka, Japan. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, G.; Someya, M.; Matsukami, H.; Tue, N.M.; Uchida, N.; Tuyen, L.H.; Viet, P.H.; Takahashi, S.; Tanabe, S.; Brouwer, A.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of dioxins and dioxin-like compounds in surface soils and river sediments from e-waste-processing sites in a village in northern Vietnam: Heading towards the environmentally sound management of e-waste. Emerg. Contam. 2016, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thuong, N.; Hung, N.X.; Mo, N.T.; Thang, N.M.; Huy, P.Q.; Van Binh, H.; Nam, V.D.; Van Thuy, N.; Son, L.K.; Minh, N.H. Transport and bioaccumulation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans at the Bien Hoa Agent Orange hotspot in Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14431–14441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, A.; Someya, M.; Kunisue, T.; Takahashi, S.; Tuyen, B.C.; Takada, H.; Tanabe, S. Contamination status of dioxins in sediments from Saigon River estuary, Vietnam. In Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry-Environmental Research in Asia; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. QCVN 43:2012/BTNMT—National Technical Regulation on Sediment Quality; Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2012; No. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dinç, B.; Çelebi, A.; Avaz, G.; Canlı, O.; Güzel, B.; Eren, B.; Yetis, U. Spatial distribution and source identification of persistent organic pollutants in the sediments of the Yeşilırmak River and coastal area in the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ni, Y.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soils and sediments from Daliao River Basin, China. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q. Declining polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans levels in the sediments from Dongting Lake in China. Chemosphere 2008, 73, S176–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burniston, D.; Klawunn, P.; Hill, B.; Marvin, C. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in Niagara River suspended sediments. Chemosphere 2015, 123, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, L.; Frignani, M.; Raccanelli, S.; Carraro, C. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in surficial sediments of the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.F.; Gaus, C.; A Prange, J.; Päpke, O.; Poon, K.F.; Lam, M.; Lam, P.K. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in sediments from Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Metre, P.C.; Babut, M.; Mourier, B.; Mahler, B.J.; Roux, G.; Desmet, M. Declining dioxin concentrations in the Rhone river basin, France, attest to the effectiveness of emissions controls. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12723–12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, M. Distribution characteristics and source identification of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in the waters from River Kanzaki, running through Osaka urban area, Japan. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cha, J.; Yoon, S.J.; Hong, S.; Khim, J.S. Instrumental and bioanalytical characterization of dioxin-like activity in sediments from the Yeongsan River and the Nakdong River estuaries, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, S.; Romanelli, M.; Piazza, R.; Vecchiato, M.; Pizzini, S.; Tranchida, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Romano, S.; Bellucci, L.G. Dataset for the assessment of selected POP’s pollution and effectiveness of environmental policies in the Bắc Giang Province and Cầu River (Northern Vietnam). Data Brief 2019, 27, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Håkansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Stage. Environmental Protection Agency. Interim Procedures for Estimating Risks Associated with Exposures to Mixtures of Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and -dibenzofurans (CDDs and CDFs) and 1989 Update; EPA/625/3-89/016 (NTIS PB90145756); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlborg, U.G.; Becking, G.; Birnbaum, L.; Brouwer, A.A.; Derks, H.; Feeley, M.; Golor, G.; Hanberg, A.; Larsen, J.; Liem, A. Toxic equivalency factors for dioxin-like PCBs: Report on WHO-ECEH and IPCS consultation, December 1993. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Xuyen, N.; Le Minh Thuy, N.X.H.; Ngoc Tung, N.; Quang Trung, N.; Duc Nam, V.; Thi Ngoc Mai, P.; Minh Huong Giang, D.; Van Thuong, N. Development of an analytical procedure for determination of dioxin/furans in milk by using high-resolution gas chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRGC/HRMS). J. Anal. Sci. 2019, 24, 4B. [Google Scholar]
- Dat, N.D.; Minh, N.H.; Nguyen, K.-A. Characteristics of PCDD/Fs in soil and sediment samples collected from A-So former airbase in Central Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment; Office of National Steering Committee (Office 33). Comprehensive Report Agent Orange/Dioxin Contamination at Three Hotspots: Bien Hoa, Da Nang, Phu Cat Airbases; Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment; Office of National Steering Committee (Office 33): Ha Noi, VietNam, 2013; No. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gaus, C.; Brunskill, G.J.; Weber, R.; Päpke, O.; Müller, J.F. Historical PCDD inputs and their source implications from dated sediment cores in Queensland (Australia). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4597–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- People’s Committee of Bac Ninh Province. Decision No. 222/QD-UBND on the Approval of the Comprehensive Environmental Protection Plan of Bac Ninh Province, Phase 2019–2025; People’s Committee of Bac Ninh Province: Bac Ninh City, Vietnam, 2019. Available online: https://iza.bacninh.gov.vn/news/-/details/141248/quyet-inh-so-222-q-ubnd-ngay-09-5-2019-cua-ubnd-tinh-bac-ninh-ve-viec-phe-duyet-e-an-tong-the-bao-ve-moi-truong-tinh-bac-ninh-giai-oan-2019-2025-21485060 (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Vietnam Federation of Science and Technology Associations. 2010. Available online: https://vusta.vn/lang-nghe-sat-thep-da-hoi-loi-giai-nao-cho-su-phat-trien-ben-vung-p72662.html (accessed on 13 January 2010).
- Minh Hoa, H. Current Situation and Solutions for Improving the Environmental Quality of Craft Villages in Bac Ninh Province. Environmental Magazine, Issue 9/2014. 2014. Available online: https://tapchimoitruong.vn/chuyen-muc-3/Hi%E1%BB%87n-tr%E1%BA%A1ng-v%C3%A0-gi%E1%BA%A3i-ph%C3%A1p-c%E1%BA%A3i-thi%E1%BB%87n-ch%E1%BA%A5t-l%C6%B0%E1%BB%A3ng-m%C3%B4i-tr%C6%B0%E1%BB%9Dng-l%C3%A0ng-ngh%E1%BB%81-t%E1%BB%89nh-B%E1%BA%AFc-Ninh-16360 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Office for Cleaner Production and Sustainable Consumption. 2017. Available online: http://scp.gov.vn/tin-tuc/t2149/bac-ninh-giai-phap-de-phat-trien-lang-nghe-ben-vung.html (accessed on 26 September 2017).
- Le Van. 2019. Available online: https://kinhtevadubao.vn/de-phat-trien-ben-vung-lang-nghe-bac-ninh-5354.html (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Shibamoto, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Katami, T. Dioxin formation from waste incineration. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 190, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- United Stage. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1613: Tetra-through-Octa-Chlorinated Dioxins and Furans by Isotope Dilution HRGC/HRMS, Revision B; United Stage. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Engineering and Analysis Division: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- United Stage. Environmental Protection Agency. Definition and Procedure for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit, Revision 2; United Stage. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]

| Code | N Coordinates | E Coordinates | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| DH1 | 21°07′02″ | 105°55′16″ | On the canal |
| DH2 | 21°07′11″ | 105°55′20″ | On the canal |
| DH3 | 21°07′19″ | 105°55′03″ | Before steel recycling area |
| DH4 | 21°07′18″ | 105°55′16″ | Middle steel recycling area |
| DH5 | 21°07′15″ | 105°55′24″ | Middle steel recycling area |
| DH6 | 21°07′03″ | 105°55′36″ | Middle steel recycling area |
| DH7 | 21°06′56″ | 105°55′41″ | After steel recycling area |
| No | Congener | TEF Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2378-TCDD | 1 |
| 2 | 12378-PeCDD | 1 |
| 3 | 123478-HxCDD | 0.1 |
| 4 | 123678-HxCDD | 0.1 |
| 5 | 123789-HxCDD | 0.1 |
| 6 | 1234678-HpCDD | 0.01 |
| 7 | OCDD | 0.0003 |
| 8 | 2378-TCDF | 0.1 |
| 9 | 12378-PeCDF | 0.03 |
| 10 | 23478-PeCDF | 0.3 |
| 11 | 123478-HxCDF | 0.1 |
| 12 | 123678-HxCDF | 0.1 |
| 13 | 123789-HxCDF | 0.1 |
| 14 | 234678-HxCDF | 0.1 |
| 15 | 1234678-HpCDF | 0.01 |
| 16 | 1234789-HpCDF | 0.01 |
| 17 | OCDF | 0.0003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.X.; Nguyen, X.T.; Mai, H.T.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Vu, N.D.; Pham, T.T.P.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Nguyen, D.T.; Duong, N.T.; Hoang, A.L.T.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dioxins and Furans Occurrence in River Sediments from a Secondary Steel Recycling Craft Village in Northern Vietnam. Molecules 2024, 29, 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081788
Nguyen HX, Nguyen XT, Mai HTH, Nguyen HT, Vu ND, Pham TTP, Nguyen TQ, Nguyen DT, Duong NT, Hoang ALT, et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dioxins and Furans Occurrence in River Sediments from a Secondary Steel Recycling Craft Village in Northern Vietnam. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081788
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hung Xuan, Xuyen Thi Nguyen, Hang Thi Hong Mai, Huong Thi Nguyen, Nam Duc Vu, Thao Thi Phuong Pham, Trung Quang Nguyen, Dat Tien Nguyen, Nam Thanh Duong, Anh Le Tuan Hoang, and et al. 2024. "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dioxins and Furans Occurrence in River Sediments from a Secondary Steel Recycling Craft Village in Northern Vietnam" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081788
APA StyleNguyen, H. X., Nguyen, X. T., Mai, H. T. H., Nguyen, H. T., Vu, N. D., Pham, T. T. P., Nguyen, T. Q., Nguyen, D. T., Duong, N. T., Hoang, A. L. T., Nguyen, T. N., Le, N. V., Dao, H. V., Ngoc, M. T., & Bui, M. Q. (2024). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Dioxins and Furans Occurrence in River Sediments from a Secondary Steel Recycling Craft Village in Northern Vietnam. Molecules, 29(8), 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081788








