Behaviors and Mechanisms of Adsorption of MB and Cr(VI) by Geopolymer Microspheres under Single and Binary Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
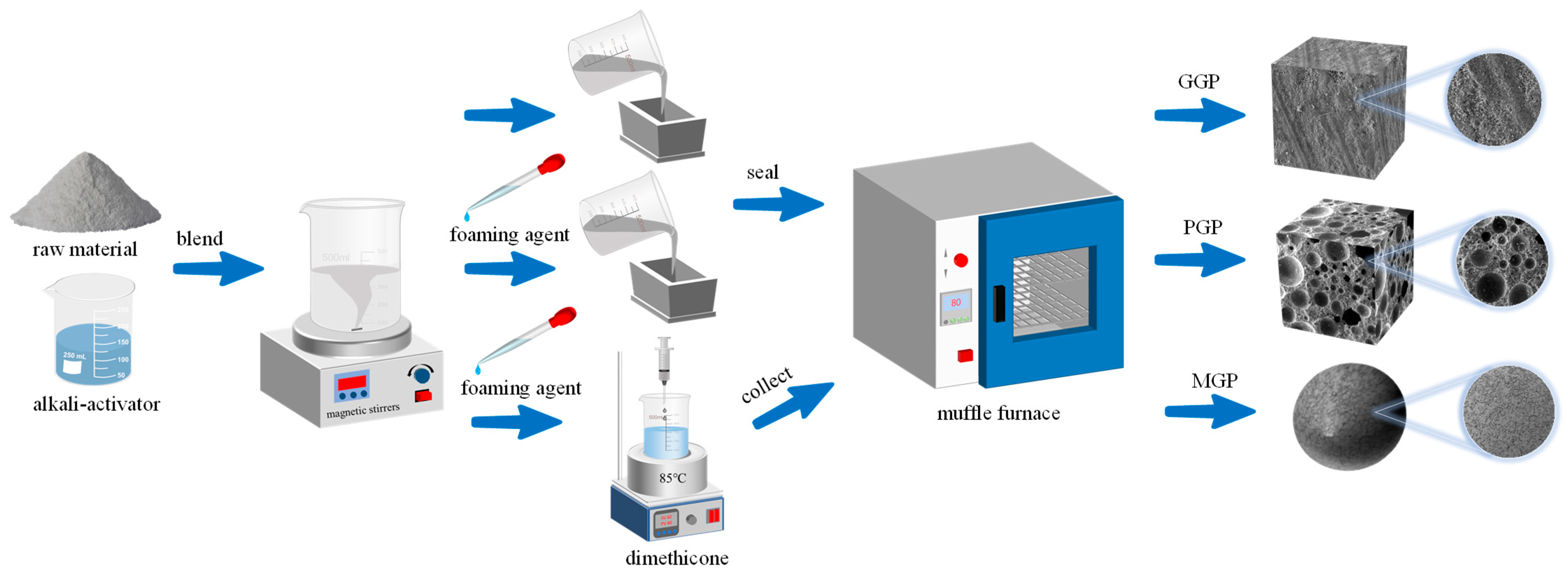
2.1. Structures and Morphologies of the Geopolymers
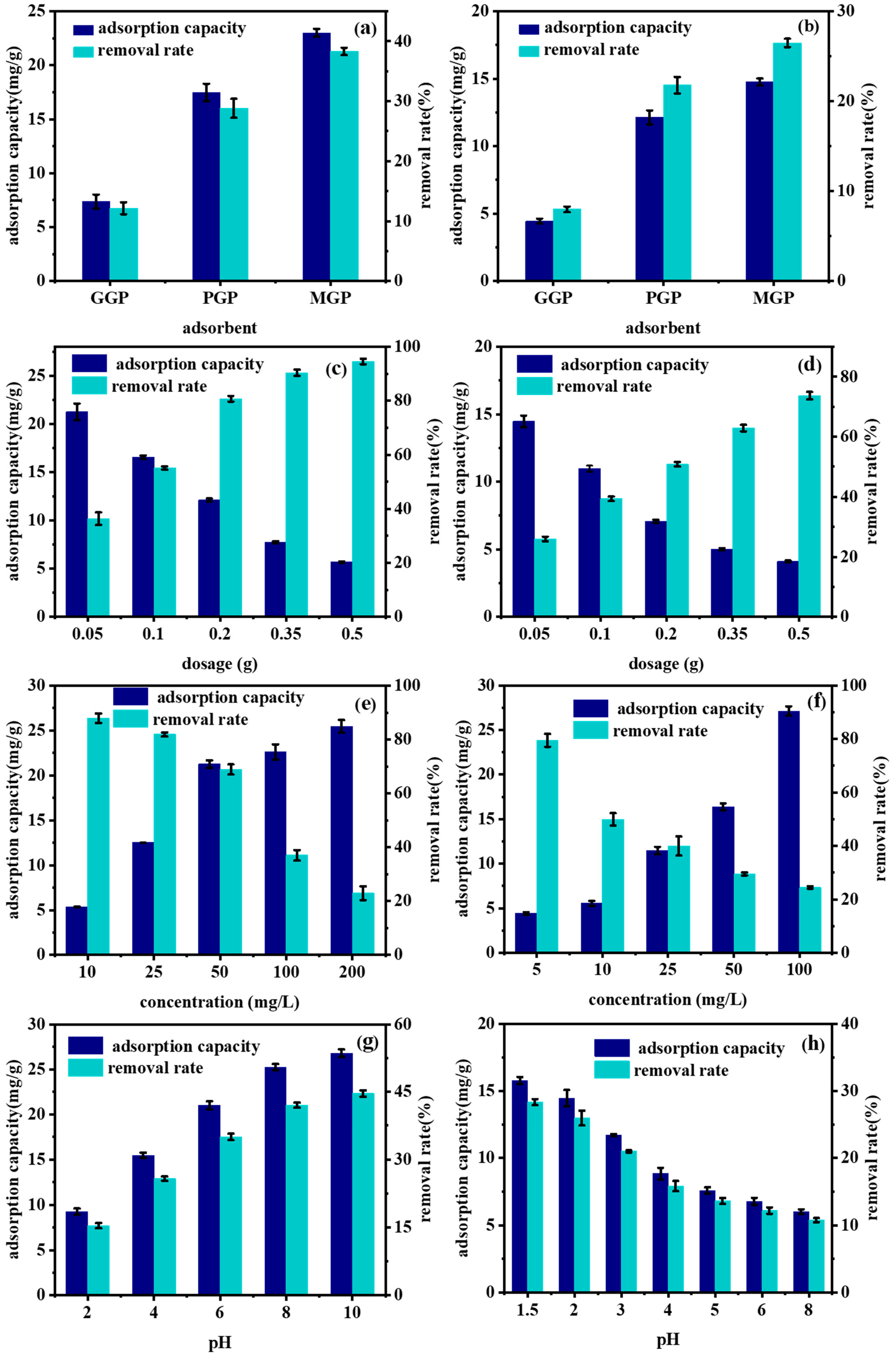
2.2. Factors on the Adsorption of Geopolymers for Methylene Blue and Cr(VI)
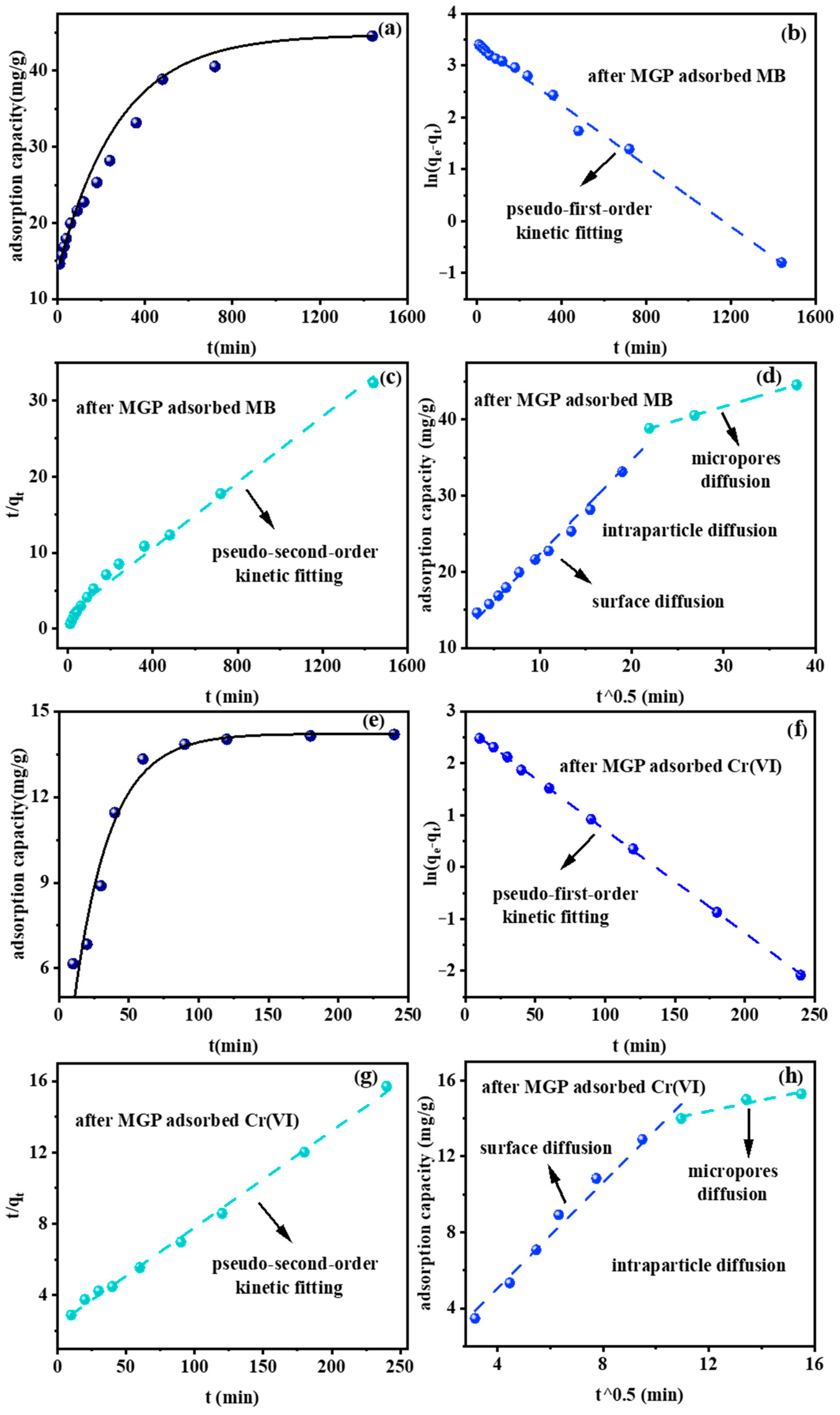
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics of FA-Based Geopolymer Microspheres for Methylene Blue and Cr(VI)
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms of FA-Based Geopolymer Microspheres for Methylene Blue and Cr(VI)
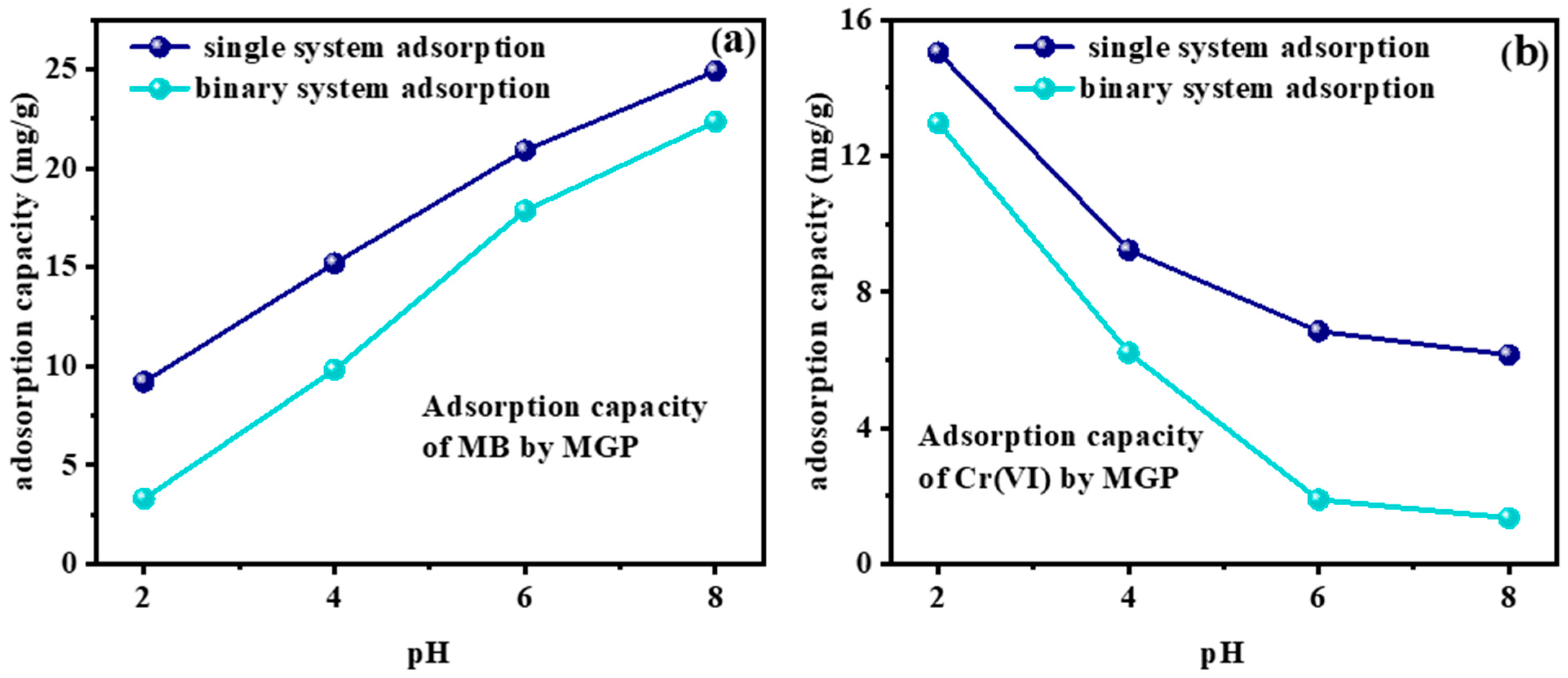
2.5. Competitive Adsorption
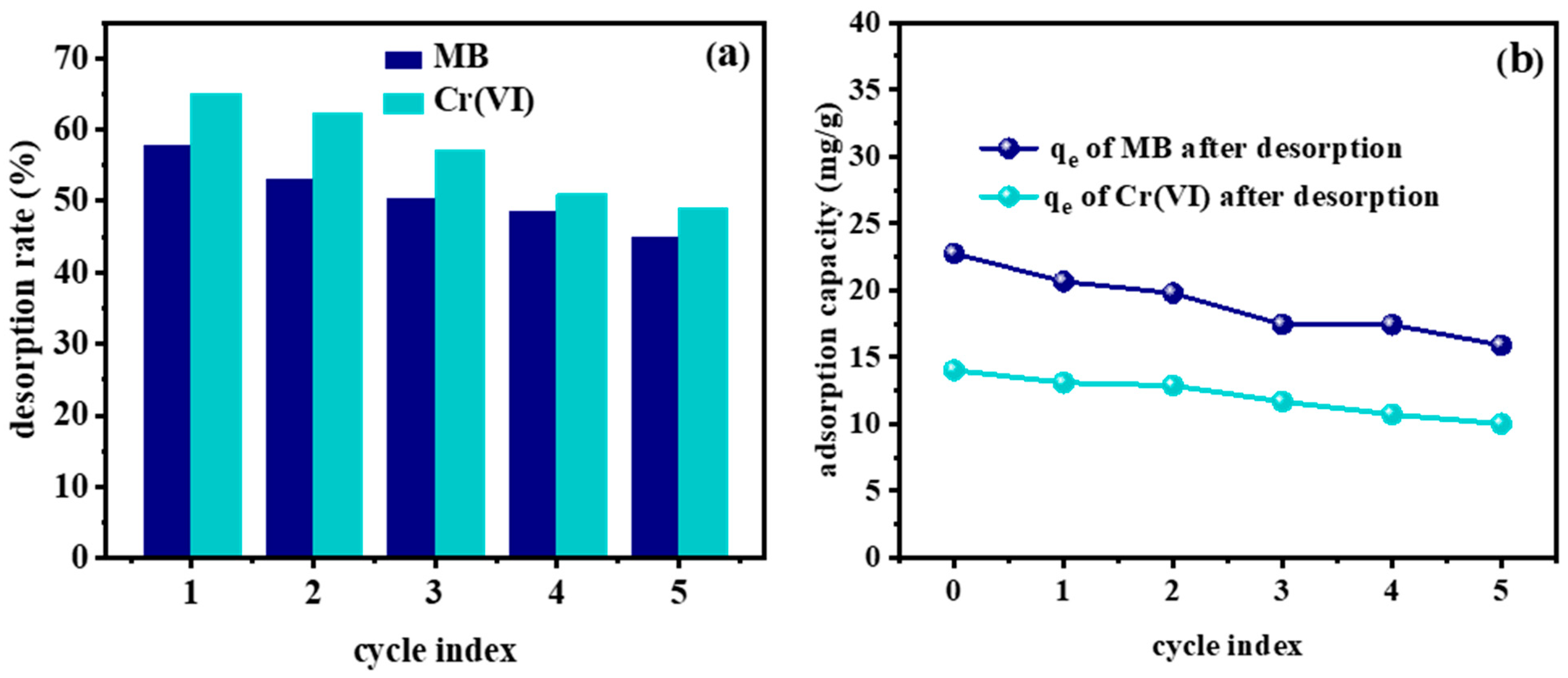
2.6. Desorption Rate and Regeneration
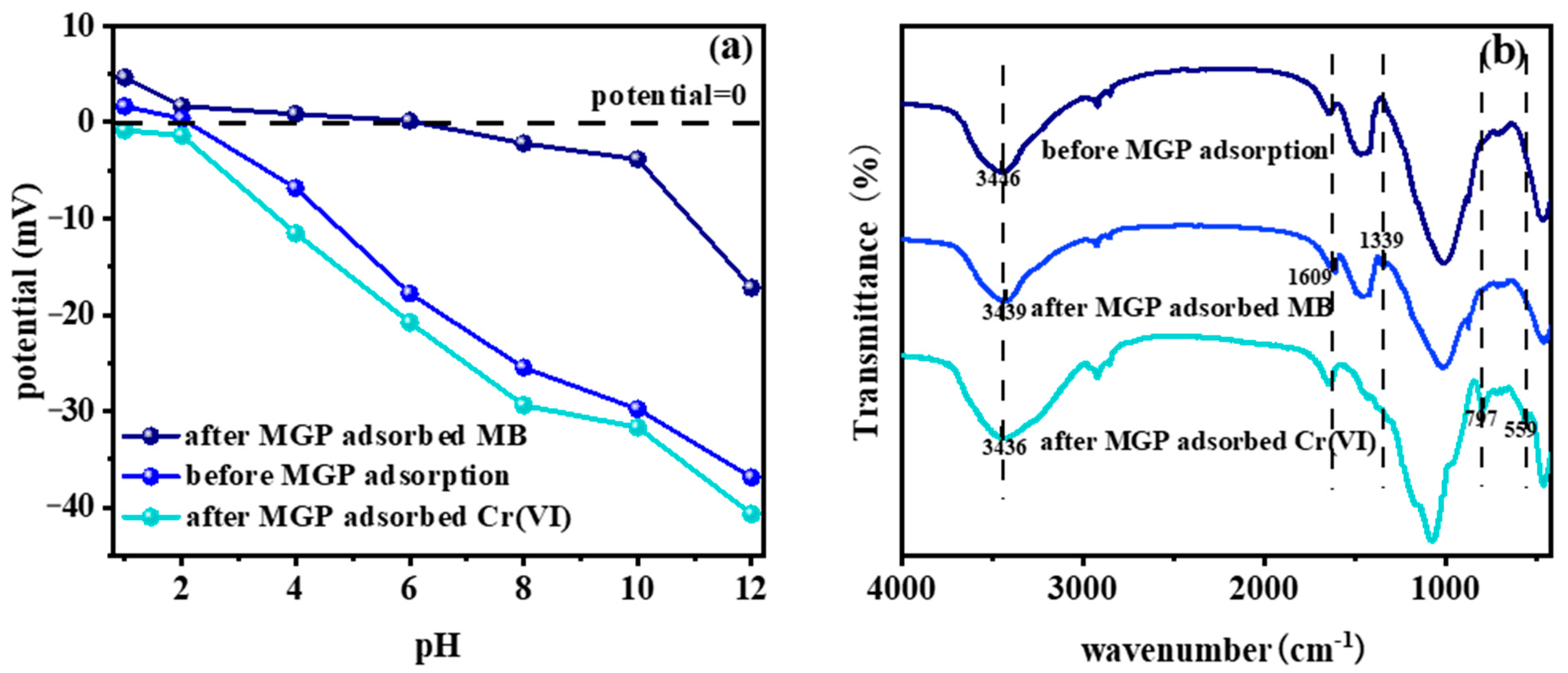
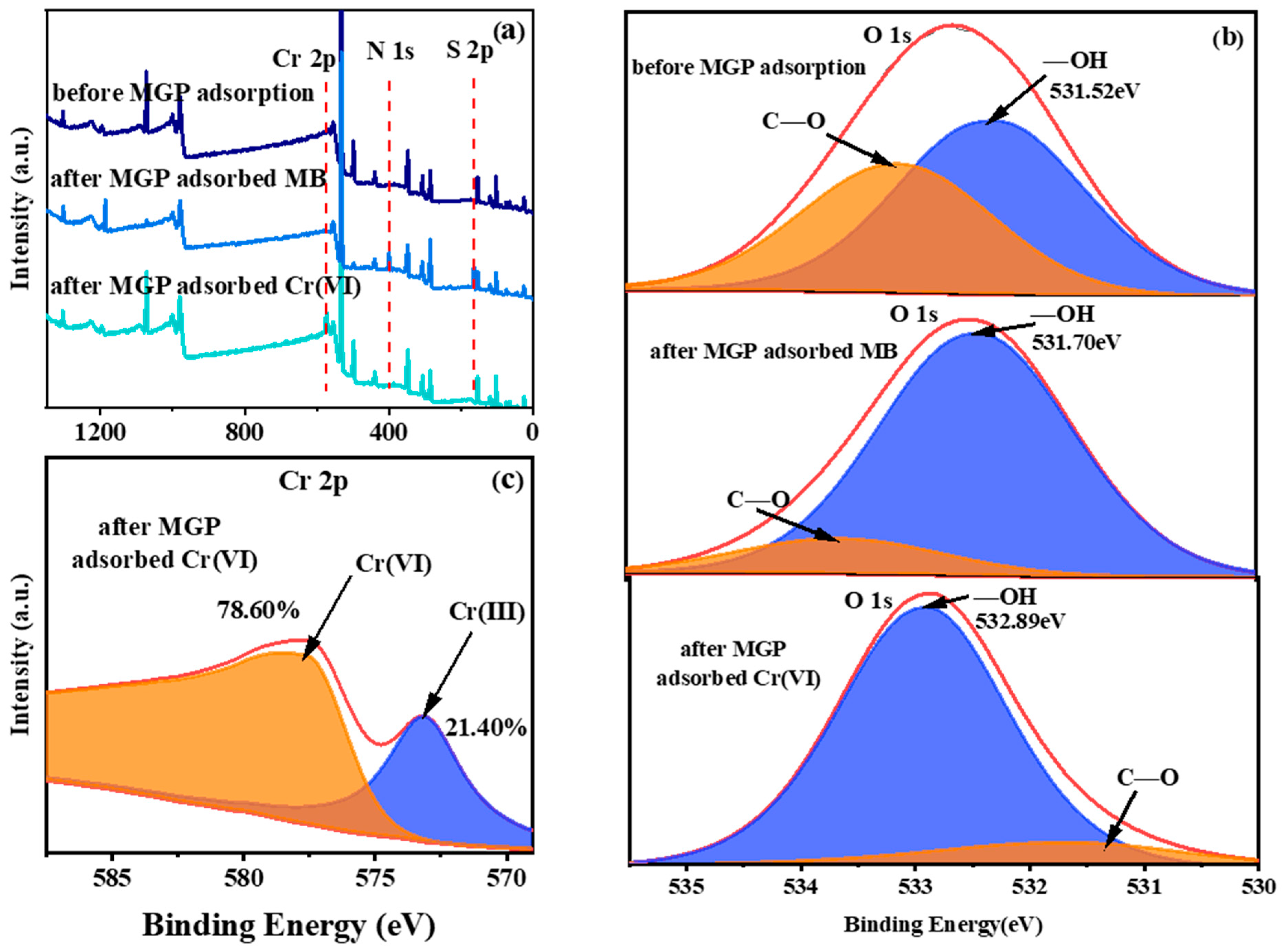
2.7. Adsorption Mechanism Analysis
2.8. Comparison of Adsorption Properties of Geopolymer Adsorbents
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, L.; Bu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Vo, T.T.; Li, D. From pollution to solutions: Insights into the sources, transport and management of plastic debris in pristine and urban rivers. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Drinking-Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Cui, M.-H.; Sangeetha, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, A.-J. Efficient azo dye wastewater treatment in a hybrid anaerobic reactor with a built-in integrated bioelectrochemical system and an aerobic biofilm reactor: Evaluation of the combined forms and reflux ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, A.A.; Alihosseini, F. Application of dye saturated clay adsorbent from dyeing wastewater as textile printing pigment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 3152–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Cheng, S.; Su, T.; Zuo, G.; Zhao, W.; Qi, X.; Wei, W.; Dong, W. Fenton-like catalyst Fe3O4@polydopamine-MnO2 for enhancing removal of methylene blue in wastewater. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, H.; et al. Hydrogels for the removal of the methylene blue dye from wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G.; Pan, B. Synergetic adsorption and electrochemical classified recycling of Cr(VI) and dyes in synthetic dyeing wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechi, N.; Khemis, I.B.; Dotto, G.L.; Franco, D.; Sellaoui, L.; Lamine, A.B. Investigation of the adsorption mechanism of methylene blue (MB) on Cortaderia selloana flower spikes (FSs) and on Cortaderia selloana flower spikes derived carbon fibers (CFs). J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momina; Mohammad, S.; Suzylawati, I. Study of the adsorption/desorption of MB dye solution using bentonite adsorbent coating. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Corona, A.; Rangel, R.; Alvarado-Gil, J.J.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; Quintana, P.; Rodríguez-Gattorno, G. Photocatalytic performance of nitrogen doped ZnO structures supported on graphene oxide for MB degradation. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, R.D.; Purohit, L.P. Novel ZnO tetrapod-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of phenolic compounds and MB dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hua, Y.; Su, X.; Komarneni, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y. Cr(VI) adsorption by montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124–125, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Gao, X. Adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) on woody-activated carbons. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L. Effect of reduced graphene oxide doping on photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) and photocatalytic oxidation of tetracycline by ZnAlTi layered double oxides under visible light. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Fu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J. Integration of g-C3N4 into cellulose/graphene oxide foams for efficient photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 169, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alouani, M.; Saufi, H.; Moutaoukil, G.; Alehyen, S.; Nematollahi, B.; Belmaghraoui, W.; Taibi, M.H. Application of geopolymers for treatment of water contaminated with organic and inorganic pollutants: State-of-the-art review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Sreekumari, S.S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from industrial effluents using activated carbon derived from waste coconut buttons. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Lin, L.D. Adsorption capacity and removal efficiency of heavy metal ions by Moso and Ma bamboo activated carbons. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Jaya Kumar, N.S.; Sahu, J.N.; Ganesan, P.; Mubarak, N.M.; Mazari, S.A. Synthesis and characterization of hydrochars produced by hydrothermal carbonization of oil palm shell. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 1916–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acisli, O.; Acar, I.; Khataee, A. Preparation of a fly ash-based geopolymer for removal of a cationic dye: Isothermal, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 83, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, P.; Sellaoui, L.; Franco, D.; Netto, M.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Bajahzar, A.; Belmabrouk, H.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Li, Z. Adsorption of acid green and procion red on a magnetic geopolymer based adsorbent: Experiments, characterization and theoretical treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadeck Netto, M.; Leindcker Rossatto, D.; Jahn, S.L.; Stoffels Mallmann, E.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Luiz Foletto, E. Preparation of a novel magnetic geopolymer/zero–valent iron composite with remarkable adsorption performance towards aqueous Acid Red 97. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, S.; Hermann, D.T.; Shikuku, V.O.; Otieno, S. Synthesis, characterization and application of acid and alkaline activated volcanic ash-based geopolymers for adsorptive remotion of cationic and anionic dyes from water. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20965–20973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanile, A.; Liguori, B.; Ferone, C.; Caputo, D.; Gigli, L.; Aprea, P. From geopolymers to zeolites: Synthesis and characterization of foamed FAU-X monoliths. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 349, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candamano, S.; Coppola, G.; Mazza, A.; Caranqui, J.C.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Alexis, F.; Algieri, C. Batch and fixed bed adsorption of methylene blue onto foamed metakaolin-based geopolymer: A preliminary investigation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L. The adsorption properties of steel slag-based porous geopolymer for Cu2+ removal. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Rao, F.; Yang, L.; Zhong, S. Comparison of ternary and dual combined waste-derived alkali activators on the durability of volcanic ash-based geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 136, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Rao, F.; Yang, L.; Zhong, S. Consolidation of phosphorus tailings and soluble fluorine & phosphorus with calcium carbide residue-mirabilite waste as a green alkali activator. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Rao, F.; Zheng, Y. Immobilization of fluorinion in phosphorus tailings-blast furnace slag based geopolymers activated by waste alkalis. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 146, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Wang, K.; Wei, H.; Wei, D.; Wei, X.; Wei, B.; Shao, L.; Fujita, T.; Cui, X. Efficient preparation of red mud-based geopolymer microspheres (RM@GMs) and adsorption of fluoride ions in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Tong, L.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Zheng, Y. Eco-friendly geopolymer materials: A review of performance improvement, potential application and sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Tian, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Review on the impact of metakaolin-based geopolymer’s reaction chemistry, nanostructure and factors on its properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, S.; Jiang, S.; Huang, K.; Ren, X.; Du, X.; Xing, P. Green Synthesis of the Metakaolin/slag Based Geopolymer for the Effective Removal of Methylene Blue and Pb (II). Silicon 2022, 14, 6965–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En-naji, S.; Ghazi, S.; Mabroum, H.; Mabroum, S.; Khatib, K.; Taha, Y.; Lodeiro, I.G.; Hakkou, R. Design of acid-geopolymers based on clays by-products for methylene blue removal from wastewater. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 245, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, H.; He, P.Y.; Meng, Q. Development of porous and reusable geopolymer adsorbents for dye wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Olhero, S.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Novais, R.M. 3D-printed red mud/metakaolin-based geopolymers as water pollutant sorbents of methylene blue. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Synthesis of porous biomass fly ash-based geopolymer spheres for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, W.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Liang, W.; Nie, Y.; Shen, C.; Ai, S. A novel aminated lignin/geopolymer supported with Fe nanoparticles for removing Cr(VI) and naphthalene: Intermediates promoting the reduction of Cr(VI). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Improved simultaneous adsorption of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) of organic modified metakaolin-based geopolymer. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4811–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Wang, T.; Li, J. Potentiality of the porous geopolymer sphere in adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solutions: Behaviors and mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Rohani, S.; Lu, J. Fe3O4@SiO2@CS-TETA functionalized graphene oxide for the adsorption of methylene blue (MB) and Cu(II). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.H.; Mo, K.H.; Lai, S.H.; Ling, T.C. Synthesis of porous geopolymer sphere for Ni(II) removal. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29055–29063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xia, B.; Suo, X.; Peng, W.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fan, G. Facile preparation of α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate whisker from by-product gypsum in chloride-free salt solution system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Shi, R.; Wang, W.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fan, G. Preparation of α-hemihydrate gypsum whiskers from phosphogypsum using atmospheric pressure nitrate solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoujo, H.T.; Shikuku, V.O.; Tome, S.; Akiri, S.; Kengne, N.M.; Abdpour, S.; Janiak, C.; Etoh, M.A.; Dina, D. Synthesis of pozzolan and sugarcane bagasse derived geopolymer-biochar composites for methylene blue sequestration from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medri, V.; Papa, E.; Mor, M.; Vaccari, A.; Murri, A.N.; Piotte, L.; Melandri, C.; Landi, E. Mechanical strength and cationic dye adsorption ability of metakaolin-based geopolymer spheres. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 193, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Biomass fly ash geopolymer monoliths for effective methylene blue removal from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.W.; Lee, M.L.; Ko, M.S.; Ueng, T.H.; Yang, S.F. The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
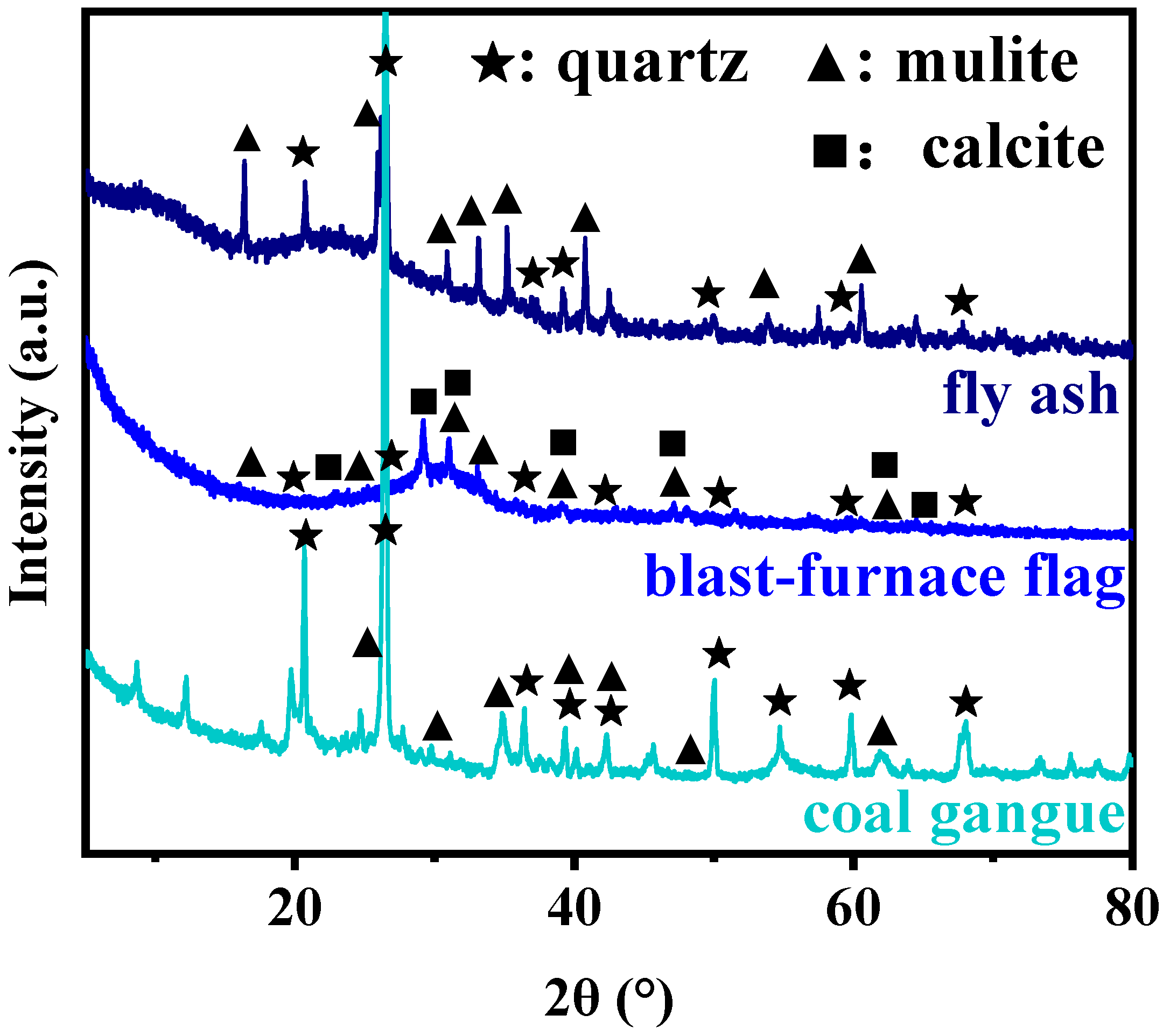
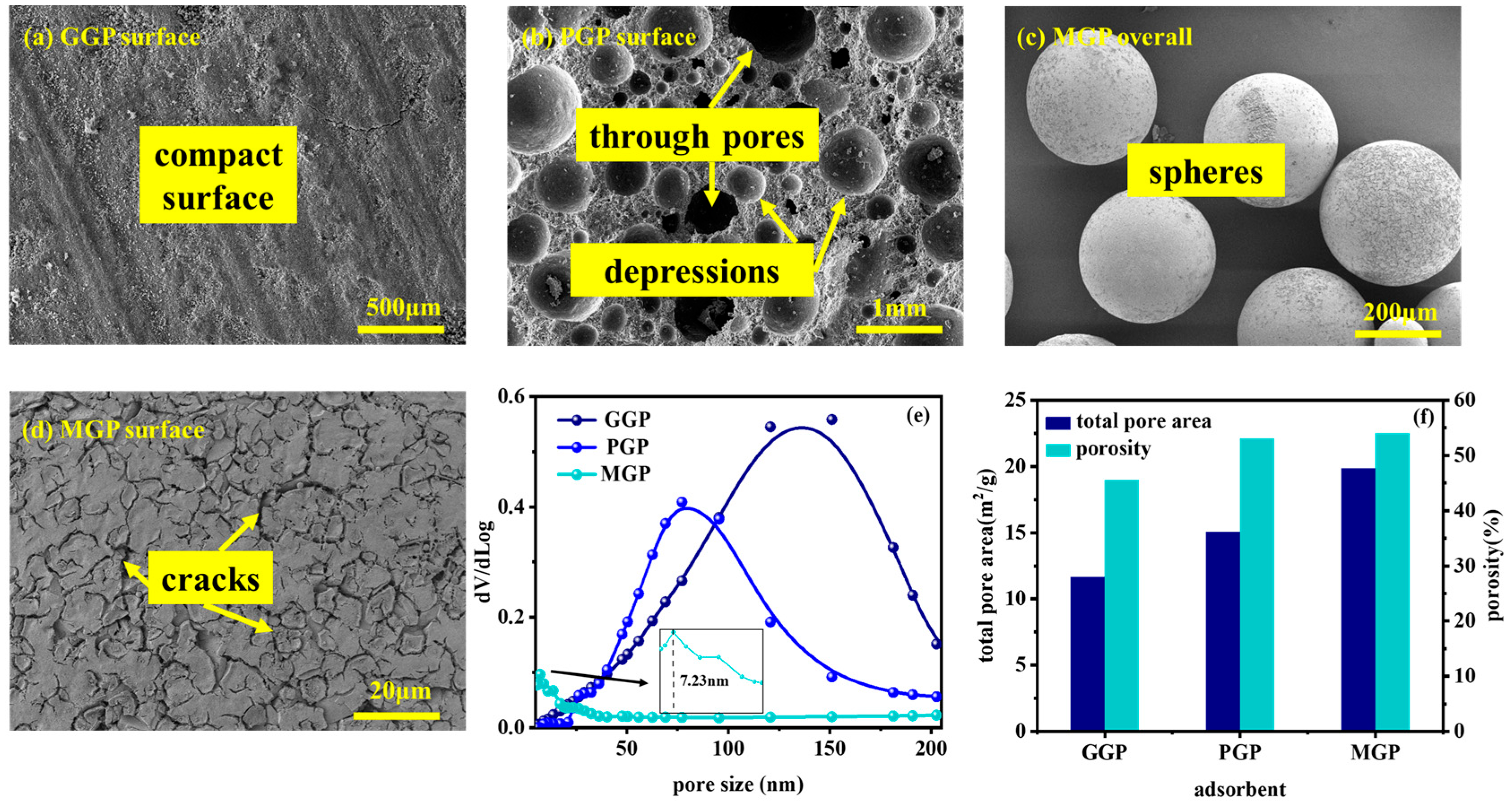


| Components(%) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 63.99 | 25.06 | 0.56 | 1.30 | 3.72 |
| FA | 53.08 | 28.64 | 0.04 | 2.39 | 1.58 |
| BFS | 30.57 | 15.09 | 38.55 | 1.60 | 0.37 |
| Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic | Intraparticle Diffusion | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qe | R2 | K2 | qe | R2 | Ki1 | P1 | R12 | Ki2 | P2 | R22 |
| 0.003 | 30.44 | 0.99 | 0.00024 | 46.19 | 0.99 | 1.24 | 9.98 | 0.99 | 0.36 | 31.04324 | 0.9998 |
| 0.020 | 14.44 | 0.9998 | 0.00124 | 18.44 | 0.996 | 1.4 | −0.56 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 10.92 | 0.87 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | KF | n | R2 |
| 33.06 | 0.06 | 0.99 | 5.45 | 2.8 | 0.95 |
| 29.64 | 0.08 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.97 |
| Raw Materials | Shape | Pollutants | Maximum Adsorption Capacity | Reusability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG, FA and BFS | Microsphere | MB and Cr(VI), single and binary | 26.8 mg/g 27.12 mg/g | Five cycles | This work |
| MK | Microsphere | MB, single | 4.2 mg/g | Not given | [46] |
| Biomass FA | Block | MB, single | 15.4 mg/g | Five cycles | [47] |
| Biomass FA | Microsphere | MB, single | 30.1 mg/g | One cycle | [37] |
| MK (organic, modified) | Powder | Cu(II) and Cr(VI), single and binary | 108.2 mg/g 95.3 mg/g | Not given | [39] |
| MK | Powder | Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Cr(III), single | 100 mg/g 75.74 mg/g 54.54 mg/g 10.15 mg/g | Not given | [48] |
| Samples | Proportion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG/g | FA/g | BFS/g | NaOH/g | Na2SiO3 9H2O/g | H2O/g | H2O2/mL | |
| GGP | 50 | 50 | — | 5.81 | 40 | 17.2 | — |
| PGP | 50 | 50 | — | 5.81 | 40 | 17.2 | 1.0 |
| MGP | 25 | 25 | 50 | 5.81 | 40 | 17.2 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; Rao, F.; Zhang, K.; Qin, Z.; Song, Z.; Na, Z. Behaviors and Mechanisms of Adsorption of MB and Cr(VI) by Geopolymer Microspheres under Single and Binary Systems. Molecules 2024, 29, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071560
Fang Y, Yang L, Rao F, Zhang K, Qin Z, Song Z, Na Z. Behaviors and Mechanisms of Adsorption of MB and Cr(VI) by Geopolymer Microspheres under Single and Binary Systems. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071560
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yi, Lang Yang, Feng Rao, Kaiming Zhang, Zhuolin Qin, Zhenguo Song, and Zhihui Na. 2024. "Behaviors and Mechanisms of Adsorption of MB and Cr(VI) by Geopolymer Microspheres under Single and Binary Systems" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071560
APA StyleFang, Y., Yang, L., Rao, F., Zhang, K., Qin, Z., Song, Z., & Na, Z. (2024). Behaviors and Mechanisms of Adsorption of MB and Cr(VI) by Geopolymer Microspheres under Single and Binary Systems. Molecules, 29(7), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071560







