Efficient Degradation of Ciprofloxacin in Water over Copper-Loaded Biochar Using an Enhanced Non-Radical Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
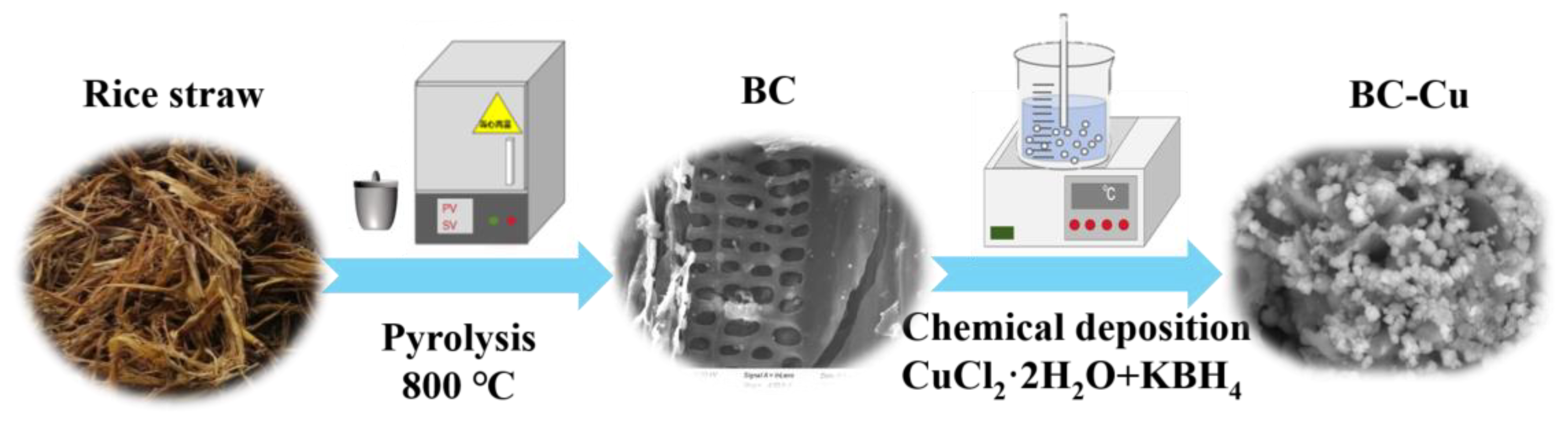
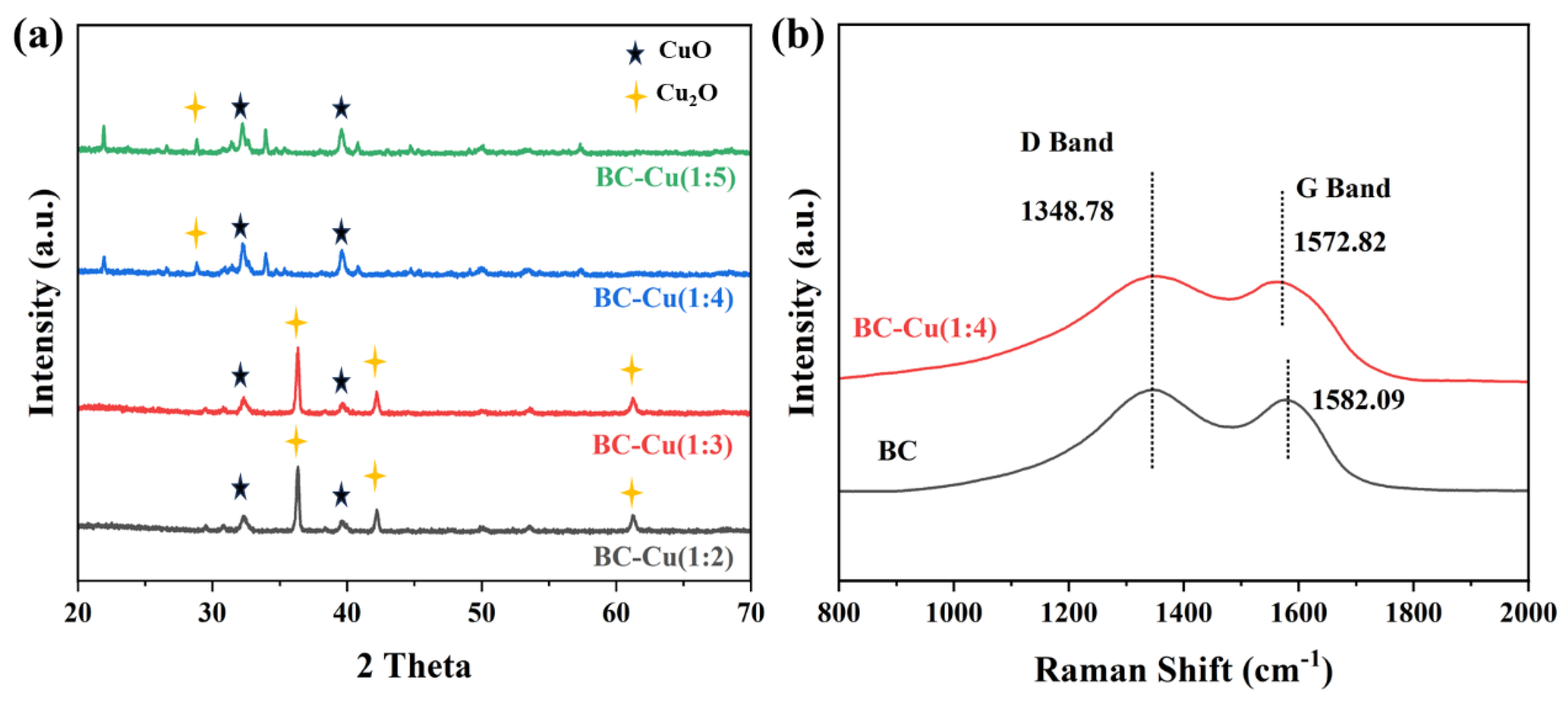
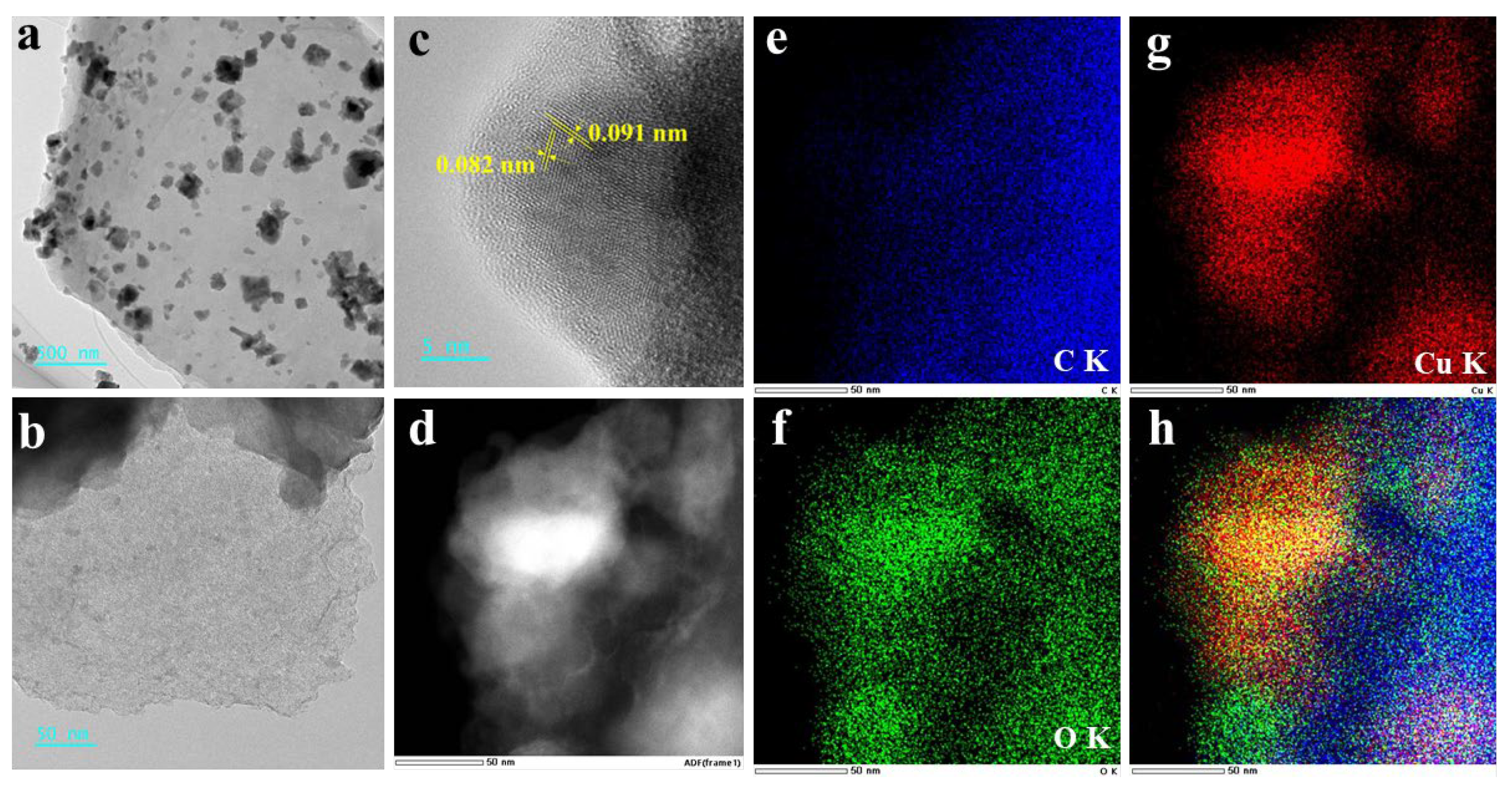
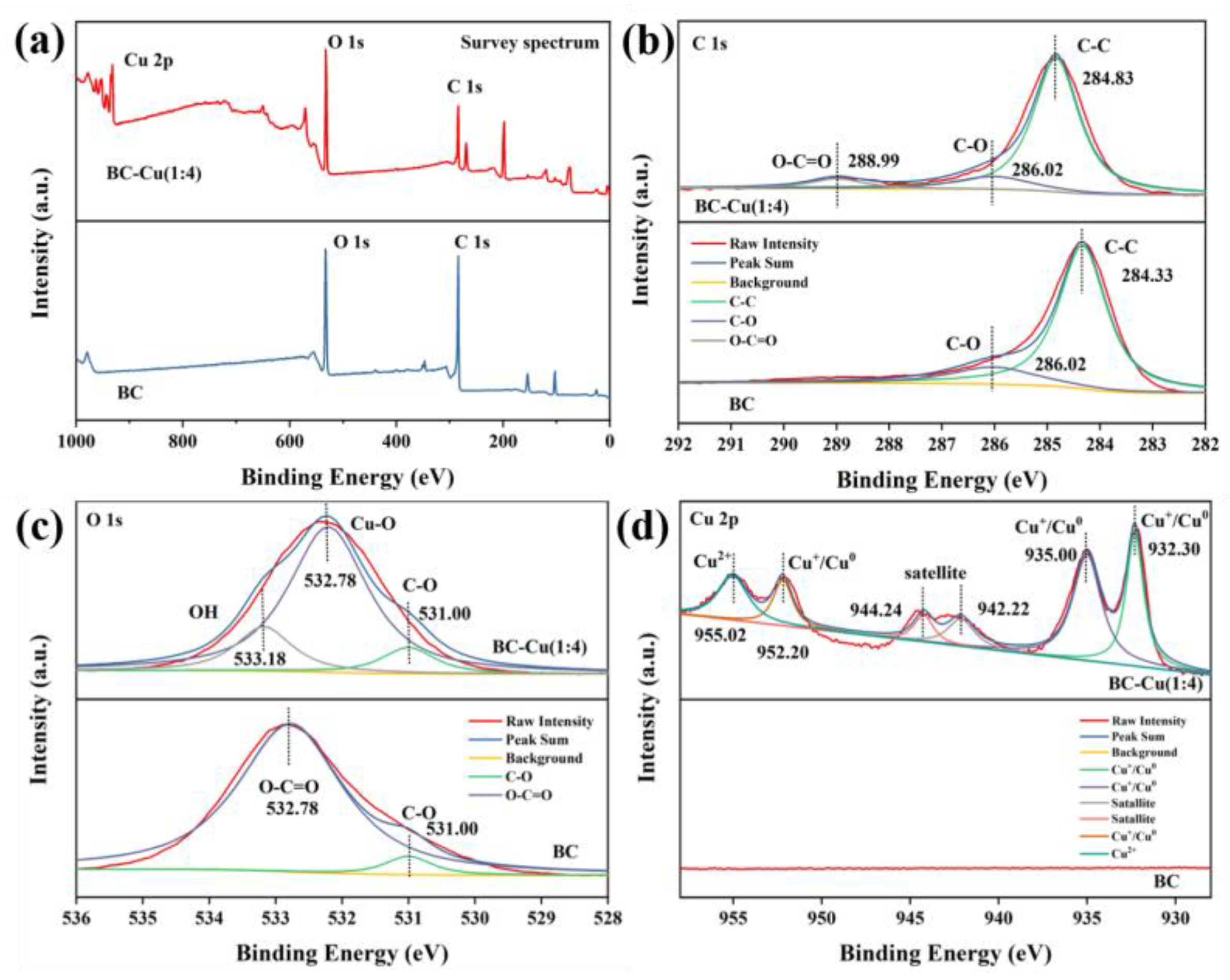
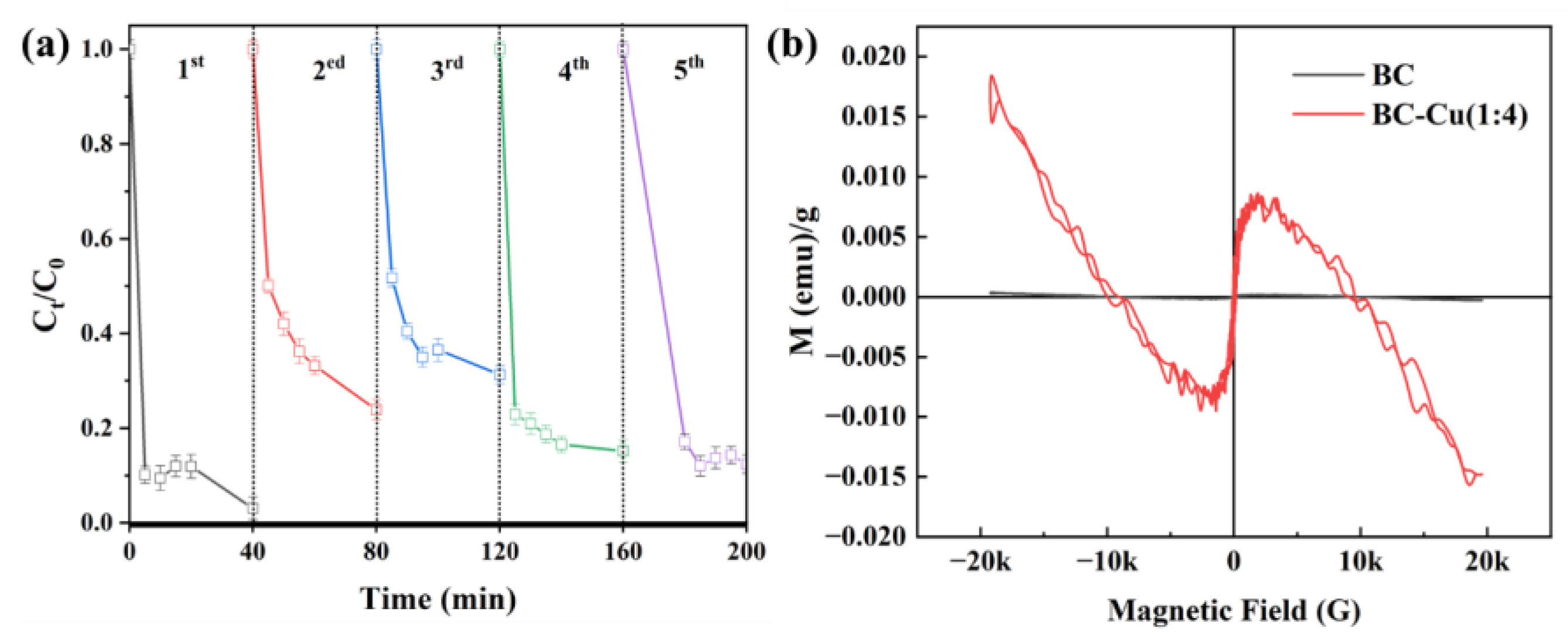
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
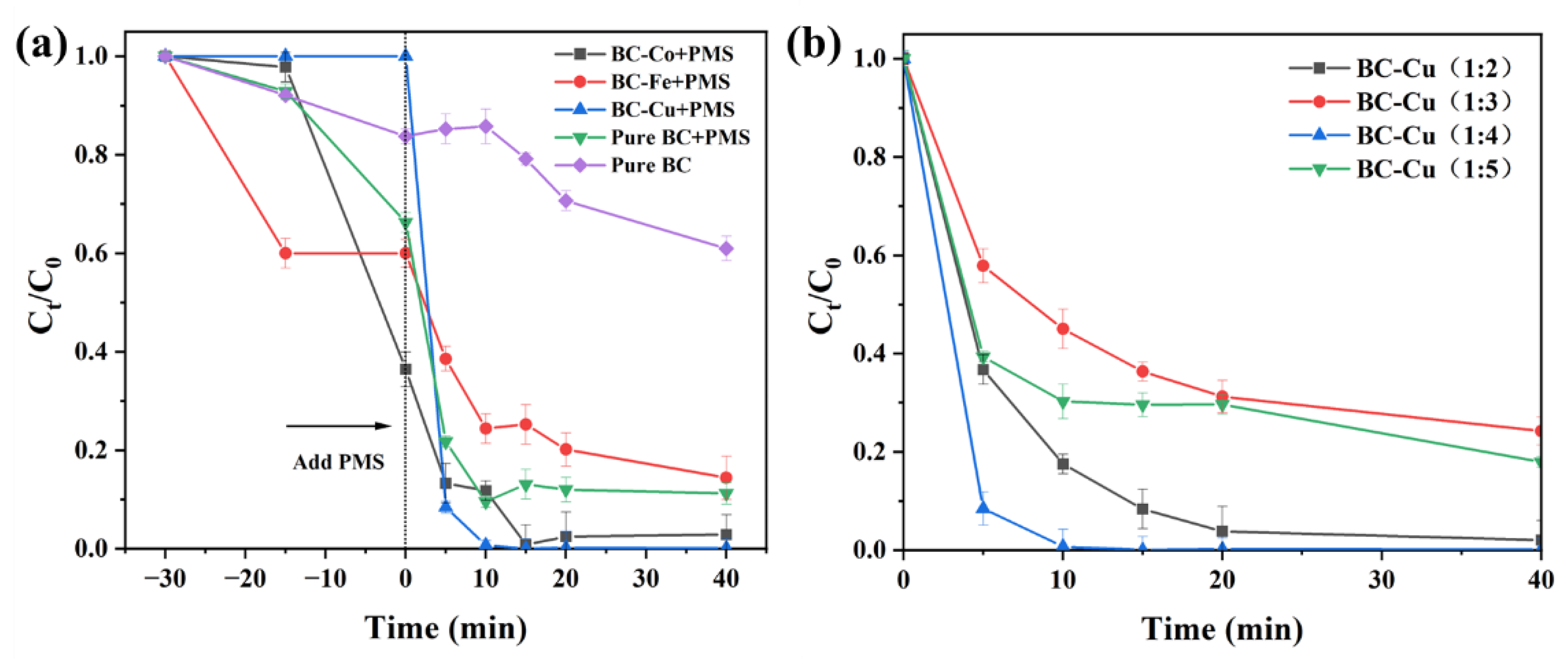
2.2. Catalytic Performance Test
2.2.1. Catalytic Performance of Samples
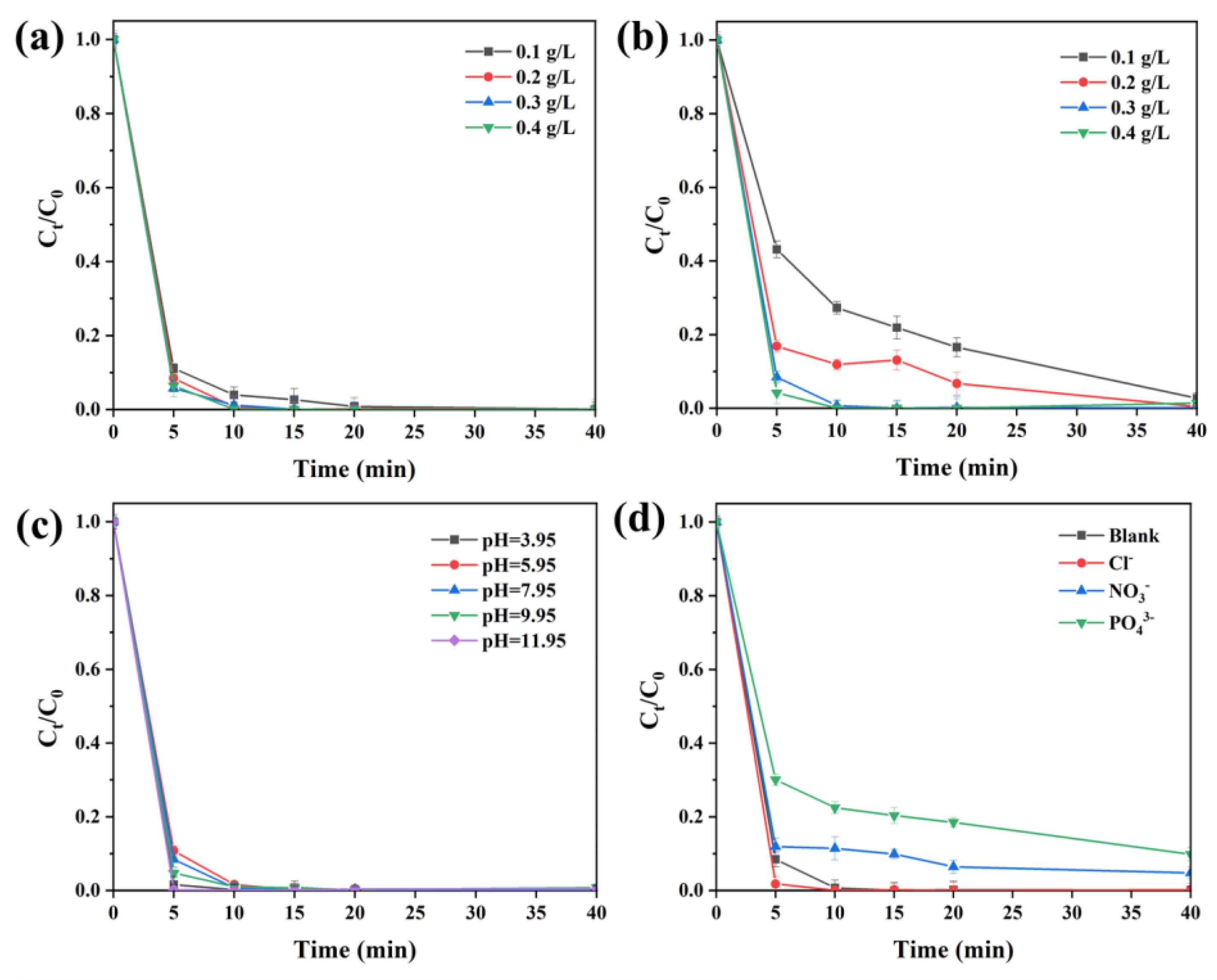
2.2.2. Effects of Other Parameters on CIP Degradation
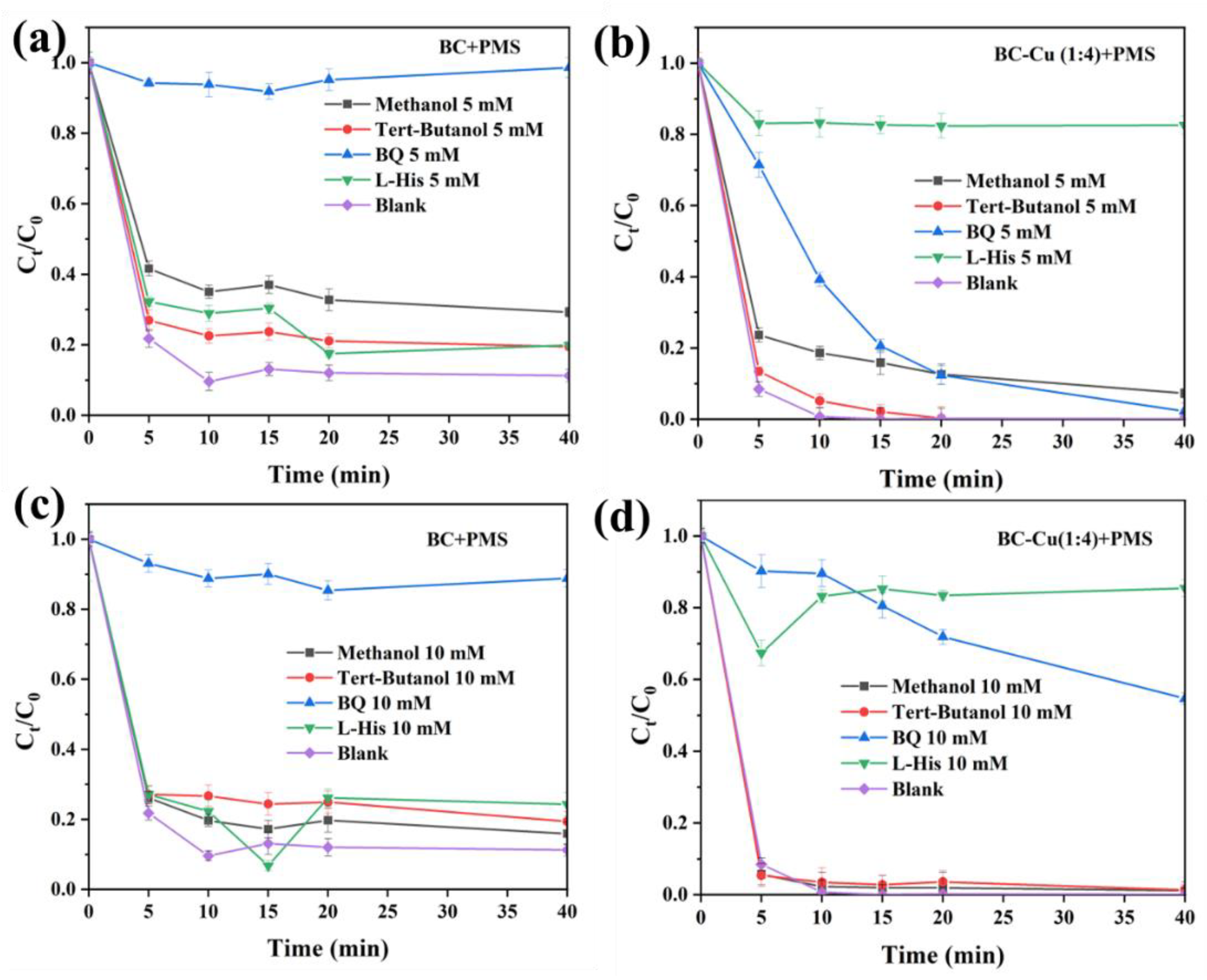
2.2.3. The Possible Mechanism of CIP Degradation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Materials
Preparation of Biochar and Cu-Loaded Biochar
3.3. Characterization Methods
3.4. Degradation Procedure
3.5. Analysis Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.G.; Choi, D.; Cheon, S.; Ko, S.O.; Kang, S.; Oh, S. Addition of biochar into activated sludge improves removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, G.; Pan, L.; Li, C.; You, F.; Wang, Y. Ciprofloxacin adsorption by biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and bamboo waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22806–22817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Tian, X.; Lin, L.; Ding, R.; Yan, W.; Zhao, F. Functional role of mixed-culture microbe in photocatalysis coupled with biodegradation: Total organic carbon removal of ciprofloxacin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Qin, P.; Guo, X.; Bi, B.; Wang, L.; Xi, B.; Wu, F.; et al. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in typical urban water of Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Liu, L.; Xing, X. Interaction of ciprofloxacin chlorination products with bacteria in drinking water distribution systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, L.; Li, L. Complete degradation and detoxification of ciprofloxacin by a micro-/nanostructured biogenic Mn oxide composite from a highly active Mn2+-oxidizing pseudomonas strain. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Nghiem, L.D.; Oh, S. Aerobic biotransformation of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin by Bradyrhizobium sp. isolated from activated sludge. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, J.; Xie, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Chang, H.; Wang, C. Novel BiOBr by compositing low-cost biochar for efficient ciprofloxacin removal: The synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis on the degradation kinetics and mechanism insight. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15369–15379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsirai, T.; Qiblawey, H.; Buzatu, P.; Al-Marri, M.; Judd, S.J. Cleaning of ceramic membranes for produced water filtration. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2018, 166, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, P.; Liu, P.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Liu, L.; Zou, W. Green synthesis of stable Fe, Cu oxide nanocomposites from loquat leaf extracts for removal of Norfloxacin and Ciprofloxacin. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Labrada, K.; Richard, R.; Andriantsiferana, C.; Valdés, H.; Jáuregui-Haza, U.; Manero, M.H. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin degradation in aqueous system by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.C.; Yu, F.; Wang, L.C.; Xing, Q.J.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Zou, J.P.; Dai, W.L.; Li, Y.; Suib, S.L. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants coupled with simultaneous photocatalytic H2 evolution over graphene quantum dots/Mn-N-TiO2/g-C3N4 composite catalysts: Performance and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 227, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.M.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Teixeira, S.; Petrovykh, D.Y.; Cuniberti, G.; Pereira, L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Photocatalytic microporous membrane against the increasing problem of water emerging pollutants. Materials 2019, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourshaban-Mazandarani, M.; Ahmadian, M.; Nasiri, A.; Poormohammadi, A. CuCoFe2O4@ AC magnetic nanocomposite as a novel heterogeneous Fenton-like nanocatalyst for Ciprofloxacin degradation from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseman-Bashiz, E.; Rezaee, A.; Moussavi, G. Ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous solutions using modified electrochemical Fenton processes with iron green catalysts. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yan, P.; Dong, J.; Duan, W.; Xu, L.; Li, H. A photoelectrochemical aptasensor of ciprofloxacin based on Bi24O31C10/BiOCl heterojunction. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Quan, W. Effects of straw return and straw biochar on soil properties and crop growth: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 986763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghioud, H.; Fryda, L.; Djelal, H.; Assadi, A.; Kane, A. A comprehensive review of biochar in removal of organic pollutants from wastewater: Characterization, toxicity, activation/functionalization and influencing treatment factors. J. Water. Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhamadou, S.; Dalhatou, S.; Obada, D.O.; Fryda, L.; Mahieu, A.; Bonnet, P.; Caperaa, C.; Kane, A.; Massai, H.; Zeghioud, H. Synthesis of piliostigma reticulatum decorated TiO2 based composite and its application towards Cr (VI) adsorption and bromophenol blue degradation: Nonlinear kinetics, equilibrium modelling and optimisation photocatalytic parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Bai, Y.; Guan, Y. Facile assembled N, S-codoped corn straw biochar loaded Bi2WO6 with the enhanced electron-rich feature for the efficient photocatalytic removal of ciprofloxacin and Cr (VI). Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Tu, G.; Zhao, D.; Tsang, P.E.; Fang, Z. Pyrolysis of different biomass pre-impregnated with steel pickling waste liquor to prepare magnetic biochars and their use for the degradation of metronidazole. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; He, X.; Peng, H.; Wen, J.; Lv, S. Efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin using Ga2S3/S-modified biochar via the high-temperature sulfurization. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Du, Q.; Sui, L.; Cheng, K. One-step fabrication of artificial humic acid-functionalized colloid-like magnetic biochar for rapid heavy metal removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, T.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, M.; Long, H. An efficient adsorbent: Simultaneous activated and magnetic ZnO doped biochar derived from camphor leaves for ciprofloxacin adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, M.; Guo, R.; Xi, B. Perdisulfate-assisted advanced oxidation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by bio-inspired iron encapsulated biochar catalyst. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 592, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Luo, J.; An, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S.; Li, Z. Circular utilization of Co (II) adsorbed composites for efficient organic pollutants degradation by transforming into Co/N-doped carbonaceous catalyst. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Qin, F.; Luo, H.; Huang, C.; Qin, D.; Ouyang, Z. Periodate activated by manganese oxide/biochar composites for antibiotic degradation in aqueous system: Combined effects of active manganese species and biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zeng, H.; Deng, Y.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, D. Unveiling the synergistic effect of internal Fe single atoms and introduced Fe3C in Enteromorpha derived biochar with enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation property towards nitenpyram removal. Biochar 2023, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Singh, N.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Berns, A.E. Effect of deashing on physico-chemical properties of wheat and rice straw biochars and potential sorption of pyrazosulfuron-ethyl. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Hao, X.; Cui, F. A stable and easily prepared copper oxide catalyst for degradation of organic pollutants by peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wang, R.; Ji, G.; Wu, H.; Qu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. From green tide to biochar: Thermal decomposition kinetics and TG-FTIR study of microalgae from Chaohu Lake. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 8083–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Idrees, M.; Hussain, Q.; Kong, J. Adsorption of copper (II) by using derived-farmyard and poultry manure biochars: Efficiency and mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 689, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hong, P.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Sun, B.; Zhu, S.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Carbon framework-encapsulated copper oxide particles to activate peroxymonosulfate for the efficient degradation of tetracycline. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 552, 149424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.D.; Liu, X.T.; Ma, J.; Lin, C.Y.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, H.J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by base: Implications for the degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, E.; Philippou, K.; Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I. Copper adsorption by magnetized pine-needle biochar. Processes 2019, 7, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhan, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Tang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, S.; Zhuang, X. A green strategy for porous biochar fabrication with superior capacity for peroxydisulfate activation to degrade sulfadiazine: The cooperative role of C-sp3 and specific surface area. Biochar 2023, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Bo, S.; Qin, Y.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S. Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lai, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, F.; et al. Role of radical and non-radical pathway in activating persulfate for degradation of p-nitrophenol by sulfur-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ni, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, S.; et al. Lignocellulosic biomass derived N-doped and CoO-loaded carbocatalyst used as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate activator for ciprofloxacin degradation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Mohamed, A.K.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; et al. Carbon defects in biochar facilitated nitrogen doping: The significant role of pyridinic nitrogen in peroxymonosulfate activation and ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 135864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, T.; Yang, Q.; Qiu, R.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Lei, X.; Zhao, Z. Efficient Degradation of Ciprofloxacin in Water over Copper-Loaded Biochar Using an Enhanced Non-Radical Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248094
Guo T, Yang Q, Qiu R, Gao J, Shi J, Lei X, Zhao Z. Efficient Degradation of Ciprofloxacin in Water over Copper-Loaded Biochar Using an Enhanced Non-Radical Pathway. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248094
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ting, Qinyu Yang, Ruoqi Qiu, Jie Gao, Jingzhuan Shi, Xiaoyun Lei, and Zuoping Zhao. 2023. "Efficient Degradation of Ciprofloxacin in Water over Copper-Loaded Biochar Using an Enhanced Non-Radical Pathway" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248094
APA StyleGuo, T., Yang, Q., Qiu, R., Gao, J., Shi, J., Lei, X., & Zhao, Z. (2023). Efficient Degradation of Ciprofloxacin in Water over Copper-Loaded Biochar Using an Enhanced Non-Radical Pathway. Molecules, 28(24), 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248094




