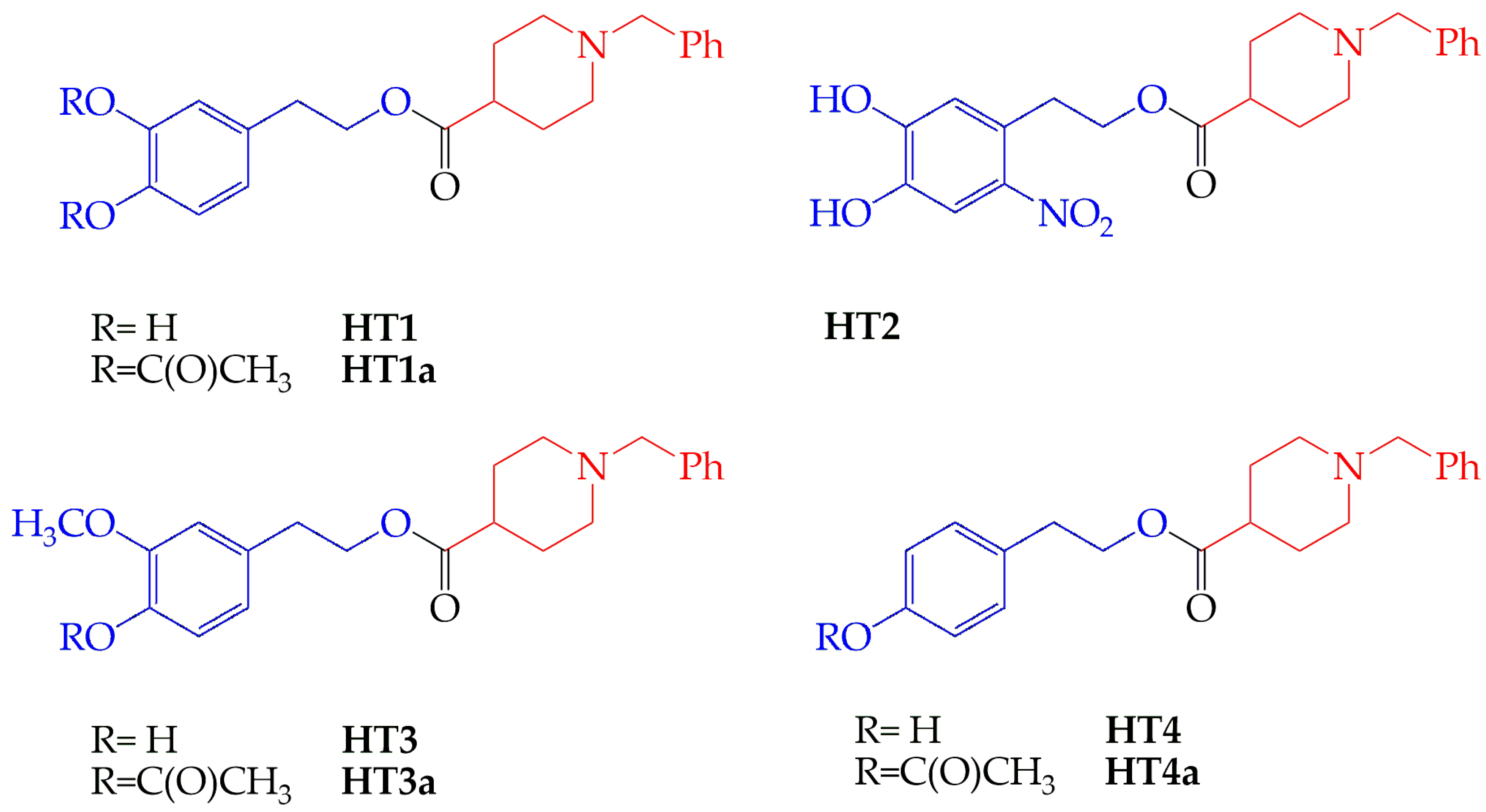
Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives of Donepezil on the Activity of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Oxidative Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of HT Hybrids on Monoamine Oxidases Activity
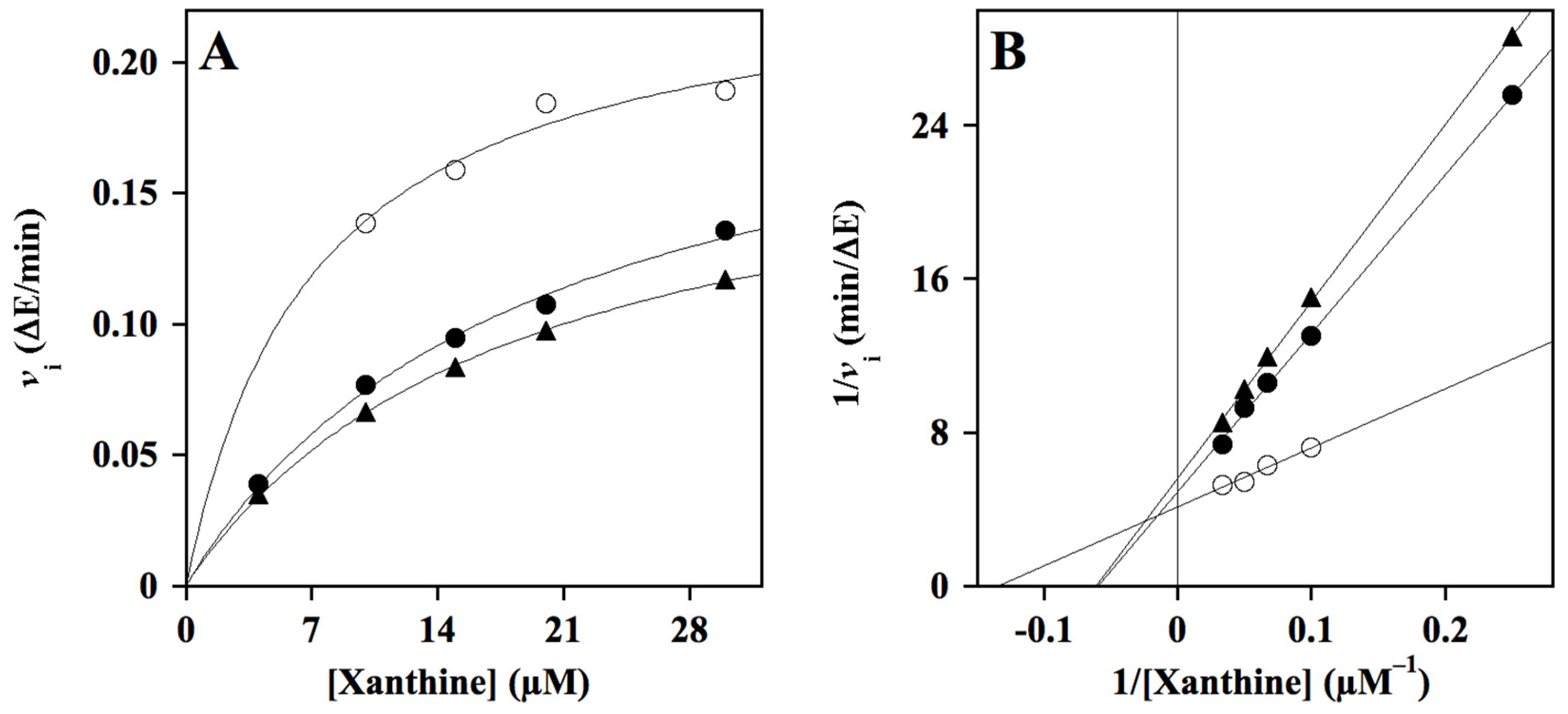
2.2. Effect of HT Hybrids on Xanthine Oxidase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Monoamine Oxidase Assay
4.2.2. Xanthine Oxidase Assay
4.2.3. Kinetics Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortese-Krott, M.M.; Koning, A.; Kuhnle, G.G.C.; Nagy, P.; Bianco, C.L.; Pasch, A.; Wink, D.A.; Fukuto, J.M.; Jackson, A.A.; van Goor, H.; et al. The Reactive Species Interactome: Evolutionary Emergence, Biological Significance, and Opportunities for Redox Metabolomics and Personalized Medicine. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, N.J.; Sato, T.; Takeda, N.; Hirata, H.; Matsumoto, S. Hyperpolarized 13C Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Tool for Imaging Tissue Redox State, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cellular Metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 36, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngum, J.A.; Tatang, F.J.; Toumeni, M.H.; Nguengo, S.N.; Simo, U.S.F.; Mezajou, C.F.; Kameni, C.; Ngongang, N.N.; Tchinda, M.F.; Dongho Dongmo, F.F.; et al. An overview of natural products that modulate the expression of non-coding RNAs involved in oxidative stress and inflammation-associated disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1144836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.B.; Samal, R.R.; Bhol, N.K.; Duttaroy, A.K. Cellular Red-Ox system in health and disease: The latest update. Biomed. Parmacother. 2023, 162, 114606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, A.I.; Dao, V.T.; Daiber, A.; Maghzal, G.J.; Di Lisa, F.; Kaludercic, N.; Leach, S.; Cuadrado, A.; Jaquet, V.; Seredenina, T.; et al. Reactive Oxygen-Related Diseases: Therapeutic Targets and Emerging Clinical Indications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, R.R. Monoamine oxidases: The biochemistry of the proteins as targets in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2189–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, K.F. 90 years of monoamine oxidase: Some progress and some confusion. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 1519–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colibus, L.; Li, M.; Binda, C.; Lustig, A.; Edmondson, D.; Mattevi, A. Three-dimensional structure of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): Relation to the structures of rat MAO A and human MAO B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12684–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Inaba-Hasegawa, K. Type A and B monoamine oxidase in age-related neurodegenerative disorders: Their distinct roles in neuronal death and survival. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C.; Chen, K.; Ridd, M.J. Monoamine oxidase: From genes to behavior. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.U.; Kim, S.; Sim, J.; Yang, S.; An, H.; Nam, M.H.; Jang, D.P.; Lee, C.J. Redefining differential roles of MAO-A in dopamine degradation and MAO-B in tonic GABA synthesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, T.L. A neuroscientific update on monoamine oxidase and its inhibitors. CNS Spectr. 2013, 18, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Ayyannan, S.R. Monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors as potential neurotherapeutic agents: An overview and update. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1603–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Mateeva, A.; Zlatkov, A.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Structure-Based Design of Novel MAO-B Inhibitors: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, J.L.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Ruiz-Galdon, M.; Molina-Vega, M.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Reyes-Engel, A. Monoamino oxidase alleles correlate with the presence of essential hypertension among hypogonadic patients. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro Julve, M.; Miralles Albors, P.; Ortonobes Roig, S.; Vives, R.; Falgueras, L.; Gómez-Valent, M. Hypertensive crisis following the administration of tedizolid: Possible serotonin syndrome. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2020, 27, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Matveychuk, D.; MacKenzie, E.M.; Duchcherer, M.; Mousseau, D.D.; Baker, G.B. An update on amine oxidase inhibitors: Multifaceted drugs. Progr. Neuro-Psychoph. Biol. Psych. 2013, 44, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaludercic, N.; Mialet-Perez, J.; Paolocci, N.; Parini, A.; Di Lisa, F. Monoamine oxidases as sources of oxidants in the heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 73, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camell, C.D.; Sander, J.; Spadaro, O.; Lee, A.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Wing, A.; Goldberg, E.L.; Youm, Y.H.; Brown, C.W.; Elsworth, J.; et al. Inflammasome-driven catecholamine catabolism in macrophages blunts lipolysis during ageing. Nature 2017, 550, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, S.; Di Sante, M.; Di Lisa, F.; Kaludercic, N. Emerging role of monoamine oxidase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Z.; An, Q.; Zhao, J.; Shi, C. Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA): A promising target for prostate cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 563, 216188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlcek, P.; Bob, P.; Vales, K. Revisiting monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A potential dual-action therapy for patients with prostate cancer and comorbid depression? J. Psychophar. 2023, 37, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.A.; Granger, D.N. Xanthine oxidase: Biochemistry, distribution and physiology. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1986, 126, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hille, R.; Nishino, T. Flavoprotein structure and mechanism. 4. Xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, F.; Fernandes, E.; Roleira, F. Progress Towards the Discovery of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 9, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, E.E.; Khoo, N.K.H.; Hundley, N.J.; Malik, U.Z.; Freeman, B.A.; Tarpey, M.M. Hydrogen peroxide is the major oxidant product of xanthine oxidase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enroth, C.; Eger, B.T.; Okamoto, K.; Nishino, T.; Nishino, T.; Pai, E.F. Crystal structures of bovine milk xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase: Structure-based mechanism of conversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10723–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.K.; Curhan, G. Gout: Epidemiology and lifestyle choices. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2005, 17, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.A.; Jolly, M. Hyperuricemia and associated diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. 2006, 32, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce Cokal, B.; Yurtdas, M.; Keskin Guler, S.; Gunes, H.N.; Atac Ucar, C.; Aytac, B.; Durak, Z.E.; Yoldas, T.K.; Durak, I.; Cubukcu, H.C. Serum glutathione peroxidase, xanthine oxidase, and superoxide dismutase activities and malondialdehyde levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganoni, S.; Schwarzschild, M.A. Urate as a Marker of Risk and Progression of Neurodegenerative Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Fontanella, R.A.; Scisciola, L.; Pesapane, A.; Taktaz, F.; Franzese, M.; Puocci, A.; Ceriello, A.; Prattichizzo, F.; Rizzo, M.R.; et al. Targeting redox imbalance in neurodegeneration: Characterizing the role of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4872–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, L.A.; McKay, L.E.; Peter, K.N.; Seyfarth, L.M.; Berkowitz, L.A.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. Attenuation of Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in a C. elegans Parkinson’s Model through Regulation of Xanthine Dehydrogenase (XDH-1) Expression by the RNA Editase, ADR-2. J. Develop. Biol. 2023, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, J.L.; Willicott, K.; Craig, M.L.; Greene, M.R.; DuGay, C.N.; Caldwell, G.A.; Caldwell, K.A. Xanthine Dehydrogenase Is a Modulator of Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Response to Bacterial Metabolite Exposure in C. elegans. Cells 2023, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Joshi, G.; Kler, H.; Kalra, S.; Kaur, M.; Arya, R. Toward an Understanding of Structural Insights of Xanthine and Aldehyde Oxidases: An Overview of their Inhibitors and Role in Various Diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1073–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, R.; Cerchia, C.; Nasso, R.; Romanelli, V.; De Vendittis, E.; Masullo, M.; Lavecchia, A. Novel reversible inhibitors of xanthine oxidase targeting the active site of the enzyme. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G. The Inhibitory Activity of Natural Products to Xanthine Oxidase. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (DHNB) is a potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: A potential therapeutic agent for treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Hase-Aoki, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Zhao, L.; Kasahara, Y.; Kondo, S.; Becker, M.A. Selectivity of febuxostat, a novel non-purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Colombo, F.; Biella, S.; Stockley, C.; Restani, P. Polyphenols and Human Health: The Role of Bioavailability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, C.G.; Croft, K.D.; Kennedy, D.O.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliara, V.; De Rosa, M.; Di Donato, P.; Nasso, R.; D’Errico, A.; Cammarota, F.; Poli, A.; Masullo, M.; Arcone, R. Inhibition of Interleukin-6-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Invasive Ability of Lemon Peel Polyphenol Extract in Human Primary Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Samtiya, M.; Dhewa, T.; Mishra, V.; Aluko, R.E. Health benefits of polyphenols: A concise review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Community. Council Regulation No. 432/2012. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, L136, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zaluski, M.; Karcz, T.; Drabczyńska, A.; Vielmuth, C.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Mordyl, B.; Siwek, A.; Satała, G.; Müller, C.E.; et al. Xanthine-Dopamine Hybrid Molecules as Multitarget Drugs with Potential for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olla, S.; Siguri, C.; Fais, A.; Era, B.; Fantini, M.C.; Di Petrillo, A. Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Oxidative Endogen Enzymes: A Focus on Putative Binding Modes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, P.; Oliverio, M.; Maiuolo, J.; Bonacci, S.; De Luca, G.; Masullo, M.; Arcone, R.; Procopio, A. Novel Hydroxytyrosol-Donepezil Hybrids as Potential Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Agents. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 741444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Costanzo, P.; Masullo, M.; D’Errico, A.; Nasso, R.; Bonacci, S.; Mollace, V.; Oliverio, M.; Arcone, R. Hydroxytyrosol-Donepezil Hybrids Play a Protective Role in an In Vitro Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Model and in Neuronal Differentiated Human SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.S.; Harvey, R.J. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD001190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaiuto, E.; Milelli, A.; Cozza, G.; Tumiatti, V.; Marchetti, C.; Agostinelli, E.; Fimognari, C.; Hrelia, P.; Minarini, A.; Di Paolo, M.L. Novel polyamine analogues: From substrates towards potential inhibitors of monoamine oxidases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 70, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Awale, S.; Tezuka, Y.; Ueda, J.Y.; Tran, Q.; Kadota, S. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors from the flowers of Chrysanthemum sinense. Planta Medica 2006, 72, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsari, C.; Trader, D.J.; Tait, A.; Costi, M.P. Designing Chimeric Molecules for Drug Discovery by Leveraging Chemical Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1908–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Qu, W.; Sun, H. Donepezil-based multi-functional cholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, H.; Caunca, M.R. Mediterranean Diet in Preventing Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokras, N.; Poulogiannopoulou, E.; Sotiropoulos, M.G.; Paravatou, R.; Goudani, E.; Dimitriadou, M.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Doxastakis, G.; Perrea, D.N.; Hloupis, G.; et al. Behavioral and Neurochemical Effects of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Total Phenolic Content and Sideritis Extract in Female Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, E.; Madrona, A.; Palma-Valdés, R.; Espartero, J.L.; Santiago, M. Effect of intracerebral hydroxytyrosol and its nitroderivatives on striatal dopamine metabolism: A study by in vivo microdialysis. Life Sci. 2015, 134, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobzar, O.L.; Mischenko, I.M.; Tatarchuk, A.V.; Vdovin, V.S.; Lukashov, S.S.; Yarmoluk, S.M.; Vovk, A.I. Nitro-Substituted Aurones As Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors. Ukr. Bioorg. Acta 2021, 16, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.M.; Glowinski, I.B. Acetylation, deacetylation and acyltransfer. Environ. Health Perspect. 1983, 49, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, P.; Buendia, I.; Del Barrio, L.; Leon, R. Novel Multitarget Hybrid Compounds for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcan, H.O.; Kosar, M. The Hybrid Compounds as Multi-target Ligands for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Considerations on Donepezil. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.B.; de Moraes, L.G.C.; Pacheco, P.A.F.; Dos Santos, D.G.; Ribeiro, R.M.A.C.; Moreira, C.D.S.; da Rocha, D.R. Naphthoquinones as a Promising Class of Compounds for Facing the Challenge of Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhzem, A.H.; Woodman, T.J.; Blagbrough, I.S. Design and synthesis of hybrid compounds as novel drugs and medicines. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19470–19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noce, B.; Di Bello, E.; Fioravanti, R.; Mai, A. LSD1 inhibitors for cancer treatment: Focus on multi-target agents and compounds in clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1120911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekuś-Słomka, N.; Mikstacka, R.; Ronowicz, J.; Sobiak, S. Hybrid cis-stilbene Molecules: Novel Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidemberg, D.M.; Ferreira, M.A.; Takahashi, T.N.; Gomes, P.C.; Cesar-Tognoli, L.M.; da Silva-Filho, L.C.; Tormena, C.F.; da Silva, G.V.; Palma, M.S. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities of indolylalkaloid toxins from the venom of the colonial spider Parawixia bistriata: Functional characterization of PwTX-I. Toxicon 2009, 54, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmeyer, H.U.; Gawehn, K.; Grassl, M. Enzymes as Biochemical Reagents. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Bergmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, R.M.; Antenucci, L.; Gavagnin, M.; Raimo, G.; Amodeo, P. Structure–activity relationships of fraxamoside as an unusual xanthine oxidase inhibitor. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 ) as internal control of XO inhibition. Error standards have not been reported, as they were less than 3% for almost all the measurements. When the same data were analyzed in the semi-logarithmic plot (B), the squared correlation coefficient R2 of the straight lines ranged between 0.761 and 0.997, with the exception of that obtained for compound HT1a, where essentially no inhibition was observed.
) as internal control of XO inhibition. Error standards have not been reported, as they were less than 3% for almost all the measurements. When the same data were analyzed in the semi-logarithmic plot (B), the squared correlation coefficient R2 of the straight lines ranged between 0.761 and 0.997, with the exception of that obtained for compound HT1a, where essentially no inhibition was observed.
 ) as internal control of XO inhibition. Error standards have not been reported, as they were less than 3% for almost all the measurements. When the same data were analyzed in the semi-logarithmic plot (B), the squared correlation coefficient R2 of the straight lines ranged between 0.761 and 0.997, with the exception of that obtained for compound HT1a, where essentially no inhibition was observed.
) as internal control of XO inhibition. Error standards have not been reported, as they were less than 3% for almost all the measurements. When the same data were analyzed in the semi-logarithmic plot (B), the squared correlation coefficient R2 of the straight lines ranged between 0.761 and 0.997, with the exception of that obtained for compound HT1a, where essentially no inhibition was observed.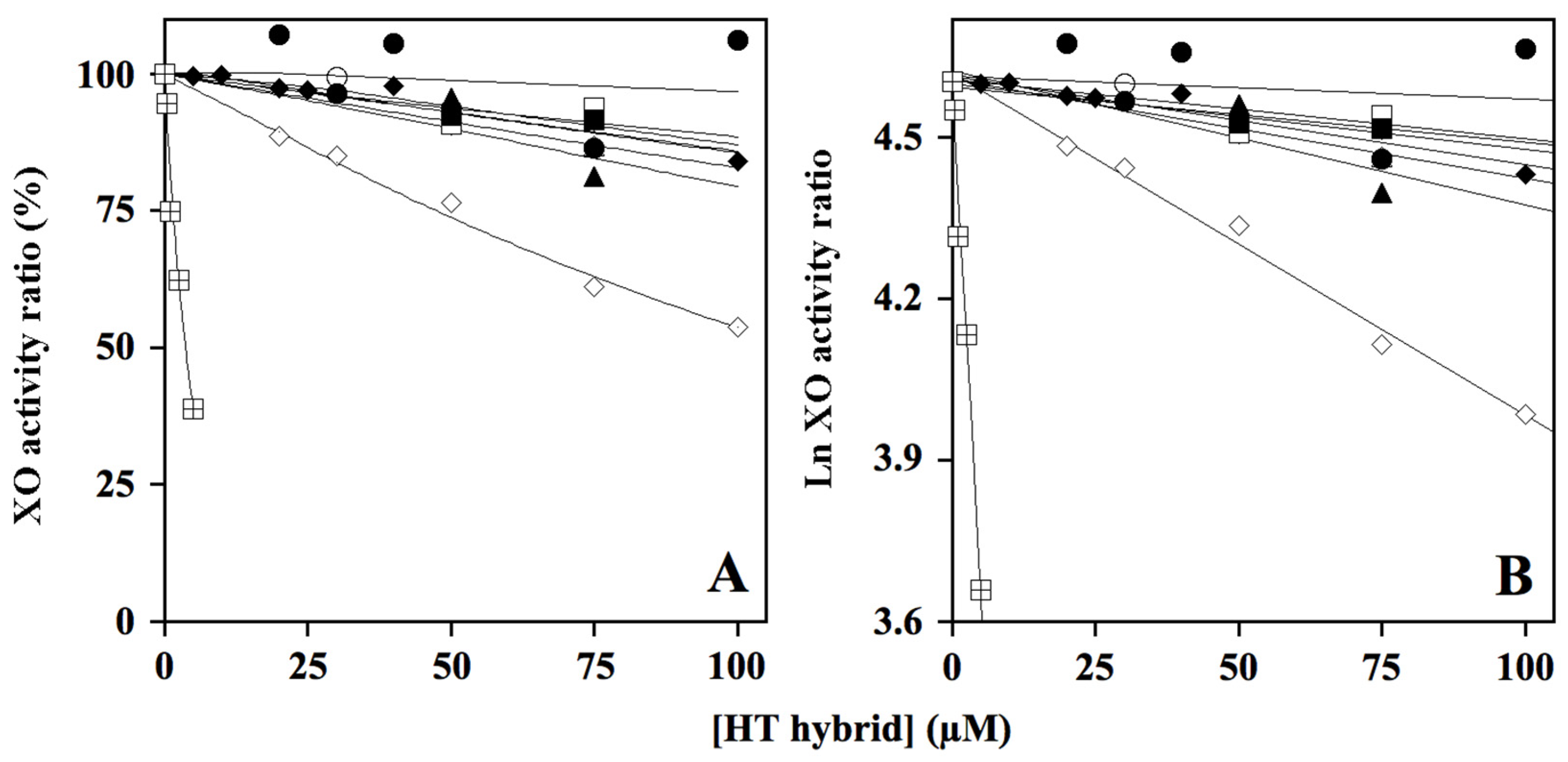
| Compound | IC50 µM ± SD (n) | |
|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | |
| HT1 | 54.1 ± 6.9 (10) | 125 ± 28 (10) |
| HT1a | 50.8 ± 11.0 (10) | 85 ± 33 (9) |
| HT2 | 322 ± 58 (10) | 184 ± 48 (8) |
| HT3 | 23.4 ± 6.3 (10) | 171 ± 44 (10) |
| HT3a | 44.3 ± 14.4 (10) | 174 ± 80 (10) |
| HT4 | 14.3 ± 2.2 (8) | 106 ± 22 (6) |
| HT4a | 57.0 ± 18.2 (10) | 86 ± 24 (6) |
| Donepezil | 67.6 ± 8.1 (10) | 40.0 ± 10.9 (10) |
| Clorgyline 1 | 0.15 ± 0.02 (3) | 4.3 ± 0.1 (3) |
| Seligiline 2 | 15.9 ± 0.1 (3) | 0.23 ± 0.05 (3) |
| Compound | Inhibition Type | Note | Ki, Calculated from | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KM Increase | Vmax Decrease | |||
| µM ± SE (n) | ||||
| HT1 | mixed | approaching competitive | 39.7 ± 14.3 (8) | |
| HT1a | mixed | approaching competitive | 36.5 ± 13.2 (8) | |
| HT2 | noncompetitive | - | 398 ± 56 (8) | |
| HT3 | mixed | approaching competitive | 7.6 ± 3.7 (8) | |
| HT3a | uncompetitive | - | 80.5 ± 30.4 (13) a | |
| HT4 | mixed | approaching competitive | 6.1 ± 1.6 (8) | |
| HT4a | mixed | approaching competitive | 15.6 ± 4.2 (8) | |
| Donepezil | mixed | approaching noncompetitive | 82.9 ± 10.0 (8) | |
| Clorgyline b | Inactivator [52] | - | 0.012 [52] | |
| Compound | Inhibition Type | Note | Ki, Calculated from | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KM Increase | Vmax Decrease | |||
| µM ± SE (n) | ||||
| HT1 | competitive | - | 163 ± 28 (8) | |
| HT1a | mixed | approaching competitive | 37.9 ± 13.1 (6) | |
| HT2 | uncompetitive | - | 186 ± 98 (12) a | |
| HT3 | mixed | approaching competitive | 115 ± 50 (6) | |
| HT3a | mixed | approaching competitive | 190 ± 37 (4) | |
| HT4 | uncompetitive | - | 128 ± 45 (14) a | |
| HT4a | competitive | - | 20.7 ± 2.8 (8) | |
| Donepezil | mixed | approaching competitive | 15.3 ± 4.6 (6) | |
| Selegiline b | Inactivator [52] | 0.055 [52] | ||
| Compound | IC50 | Inhibition Type | Note | Ki |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated from KM Increase | ||||
| µM ± SE (n) | µM ± SE (n) | |||
| HT1 | 454 ± 22 (2) | |||
| HT1a | no inhibition | |||
| HT2 | 109 ± 20 (4) | mixed | approaching competitive | 63 ± 8 (4) |
| HT3 | 361 ± 1 (2) | |||
| HT3a | 282 ± 37 (2) | |||
| HT4 | 605 ± 35 (2) | |||
| HT4a | 438 ± 6 (2) | |||
| Donepezil | 424 ± 23 (2) | |||
| Allopurinol | 3.7 ± 0.5 (2) | Competitive [53] | - | 1.8 [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Errico, A.; Nasso, R.; Rullo, R.; Maiuolo, J.; Costanzo, P.; Bonacci, S.; Oliverio, M.; De Vendittis, E.; Masullo, M.; Arcone, R. Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives of Donepezil on the Activity of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Oxidative Damage. Molecules 2024, 29, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020548
D’Errico A, Nasso R, Rullo R, Maiuolo J, Costanzo P, Bonacci S, Oliverio M, De Vendittis E, Masullo M, Arcone R. Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives of Donepezil on the Activity of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Oxidative Damage. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020548
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Errico, Antonio, Rosarita Nasso, Rosario Rullo, Jessica Maiuolo, Paola Costanzo, Sonia Bonacci, Manuela Oliverio, Emmanuele De Vendittis, Mariorosario Masullo, and Rosaria Arcone. 2024. "Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives of Donepezil on the Activity of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Oxidative Damage" Molecules 29, no. 2: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020548
APA StyleD’Errico, A., Nasso, R., Rullo, R., Maiuolo, J., Costanzo, P., Bonacci, S., Oliverio, M., De Vendittis, E., Masullo, M., & Arcone, R. (2024). Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives of Donepezil on the Activity of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Oxidative Damage. Molecules, 29(2), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020548











