Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
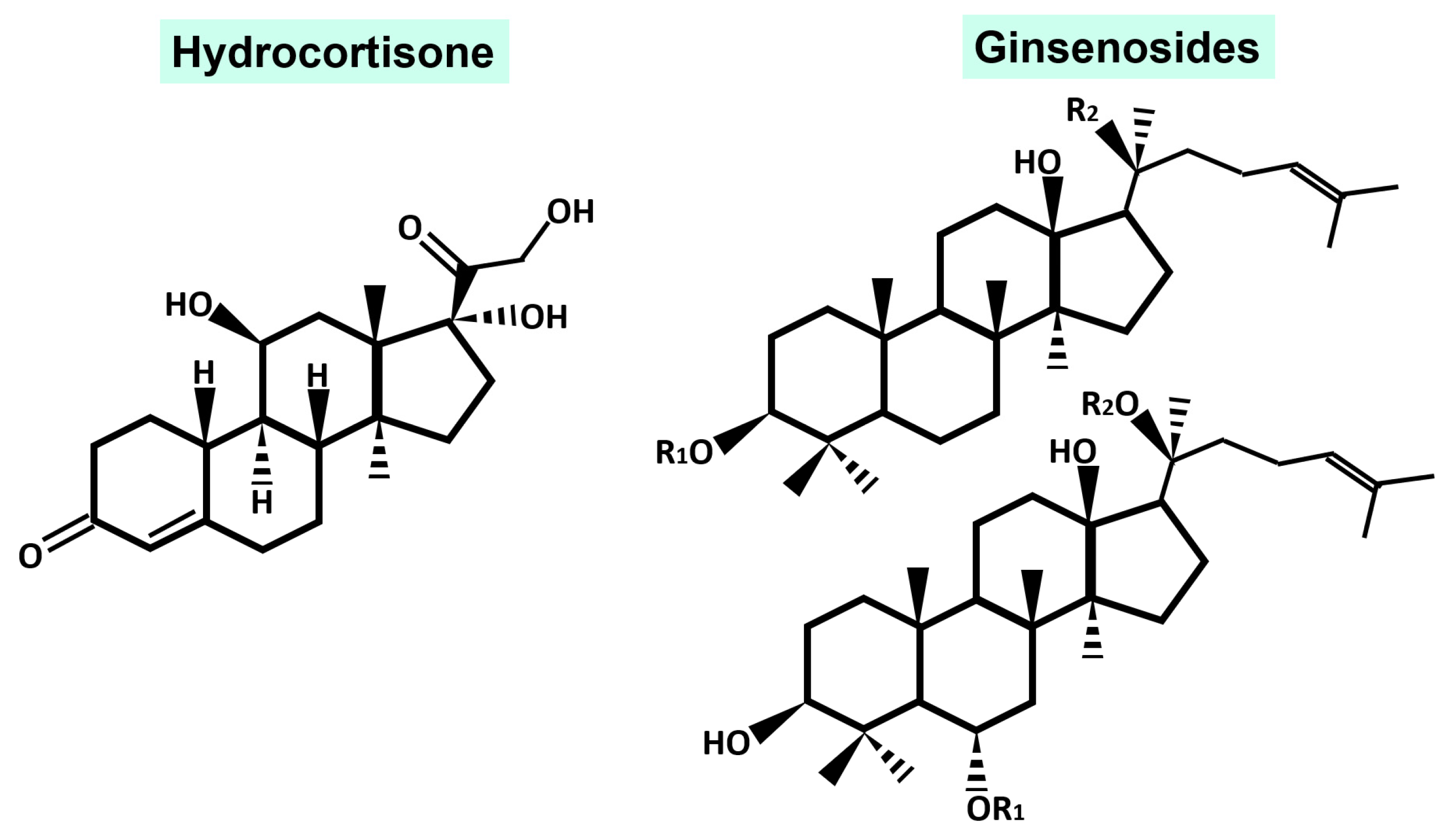
2. Phytochemical Characteristic
3. Immunomodulatory Activity
| Species | Molecular Group | Compound/Extract | Experimental Model | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panax quinquefolius L. | Polysaccharides | Extract | Wistar rats | ↑ Macrophages activity | [34] |
| Polysaccharides | Extract | Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells | ↑ Pro-inflammatory cytokines | [35] | |
| Polysaccharides | Extract | Mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes | Cytokines regulation | [36] | |
| Polysaccharides | Extract | Sprague–Dawley rats Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | Cytokines regulation | [37] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Polysaccharides | Acidic fraction | C57BL/6 mice macrophages | Cytokines regulation | [38] |
| Polysaccharides | Acidic fraction | C57BL/6 mice | Enhanced phagocytic effect | [41] | |
| Polysaccharides | Acidic fraction | C57BL/6 mice dendritic cells | ↑ CD86 | [43] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rh1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | Glucocorticoid receptor stimulus | [47] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rh1 | Hartley guinea pigs, SD rats, and ICR mice | ↓ NO ↓ PGE2 | [48] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rh1 | Mouse embryo fibroblasts 3T3-L1 cells | ↓ TNF-α ↓ IL-1β ↓ IL-6 | [49] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rh1 | Hairless mice | ↓ Infiltration of inflammatory cells ↓ IgE levels | [50] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rb1 | EV71 mice model | ↑ Cellular immune response ↑ Humoral immune response | [27] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rg1 | C57BL/6 mice C57BL/6 mice hepatocytes | ↑ Nrf2 ↑ Detoxifying enzymes | [55] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rg3 | BALB/c mice | Improve immune system | [51] | |
| Ginsenosides | Rg3 | Patients with non-small cell lung cancer | Regulate cell cycle | [52] | |
| Ginsenosides | Standardized G-115 extract | BALB/c pathogen-free mice | ↑TLR4 | [40] | |
| Ginsenosides | Compound K | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line Human Embryonic Kidney cell line (HEK293 cells) | ↓ iNOS ↓ TNF-α | [58] | |
| Ginsenosides | Compound K | Sprague–Dawley rats Kunming mice | Cytokines regulation | [61] | |
| Ginsenosides | Compound K | DBA/1 OlaHsd mice | ↓ Th1 response (in arthritis) | [62] | |
| Ginsenosides | Compound K | DBA/1 mice | Alleviates inflammatory response | [63] | |
| - | Extract | Clinical trial | ↑ Chemotaxis | [31] | |
| - | Extract | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line BALB/c mice | Cytokines regulation | [28] | |
| - | Extract | Balb/C mice C57 B1/6J mice C57 B1/6J nu/nu mice | ↑ Antibody formation ↑ NK | [29] | |
| - | Extract | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | Cytokines regulation | [32] | |
| - | Extract | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↑ Immunomodulators | [33] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer Eleutherococcus senticosus Rupr. & Maxim | - | Extract | Mouse J774A.1 macrophages | ↑ lL-12 | [30] |
4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
| Species | Molecular Group | Compound/Extract | Experimental Model | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside | Rg1 | ICR mice | Suppression NLRP1 inflammasome activation | [75] |
| Ginsenoside | Rg1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ IL-6 | [78] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rg1 | C57BL/6 mice | Inhibition NF-κB pathway | [79] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rg1 | ICR mice | Inhibition NF-κB pathway ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 | [80] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside Ginsenoside | Rg3 Rg5 | BV-2 microglial cells Neuro-2a cells NCI-H292 cells | Suppression TNF-α and NF-κB ↓ MUC5AC and ↓ MUC5AC mRNA | [76,81] |
| Ginsenoside | Rd | Sprague–Dawley rats | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 | [82] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rd | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 | [83] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb1 | Sprague–Dawley rats | ↑ IκB | [86] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | Suppression TNF-α | [88] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb1 | ICR mice | Inhibition NF-κB pathway | [87] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb1 y Rb2 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ TNF-α | [90] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb2, Rd, Re and Rg1 | Murine N9 microglial cell line | ↓ TNF-α ↓ NO | [91] | |
| Ginsenoside | Re and Rh1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 | [48] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rh2 | BV-2 microglial cells | ↓ NO ↓ COX-2 ↓ TNF-α ↓ IL-1β | [93] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rp1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 ↓ IL-1β | [94] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside | Rp1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ IL-1β ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 ↓ TNF-α | [95] |
| - | Root water extract (saponin fraction) | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 ↓ TNF-α | [71] | |
| - | Berry extract | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ iNOS ↓ COX-2 ↓ IL-1β ↓ IL-6 ↓ TNF-α | [72] | |
| Glycolipoprotein complex | Gintonin | SH-SY5Y Human neuroblastoma cell line | ↓ ROS formation | [97] | |
| Panax japonicum C.A. Meyer | Saponines | Chikusetsusaponine Iva | THP-1 human monocyte-like cells | ↓ iNOS ↓ TNF-α ↓ IL-6 ↓ IL-1β | [85] |
| Panax notoginseng Burk. | Ginsenosides | Rb1 | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓TNF-α ↓ IL-6 ↓COX-2 ↓ IL-1β | [89] |
5. Anti-Cancer Activity
| Species | Molecular Group | Compound/Extract | Experimental Model | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside | Rh1 | Mouse lymphoid neoplasma cell line (P388) | Cytotoxic effect | [102] |
| Ginsenoside | Rh1 | Human leukemia (THP-1) cell line | ↑ apoptosis | [103] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rh2 | B16 melanoma cell line | ↓ cell growth | [104] | |
| Ginsenoside Ginsenoside | Rh2 Rh2 | Murine melanoma (B16F10) cell line, Human breast cancer line (MDA-MB-231)cell, and Hepatocyte derived cellular carcinoma (HuH-7) cell line | Anti-proliferation Anti-invasion Anti-metastasis | [106] | |
| Diverse cancer models | Cell cycle, autophagy, migration and angiogenesis Alleviates chemotherapy effects | [107] | |||
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside | Rg1 | Osteosarcoma MG-63 cells | Oncogenes inhibition | [109] |
| Ginsenoside | Rg3 | Breast cancer model | Anti-proliferation | [113] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rg5 | Hepatic Adenocarcinoma SK-HEP-1 cells | ↑ p21Cip/WAF1 ↓ cyclin E ↓ CDK2 ↓ CDC25A | [116] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Ginsenoside | Compound K | Mouse high-metastatic melanoma B16-BL6 Human myeloid leukemia K562 Human liver cancer HepG2 Human high-metastatic lung carcinoma 95-D | ↓ tumor cells | [120] |
| Ginsenoside | Compound K |
mouse highly metastatic melanoma (B16-BL6) Human liver cancer (HepG2) Human myeloid leukemia (K562) Human highly metastatic lung cancer (95-D) | ↓ tumor cells | [121] | |
| Ginsenoside | Compound K | Lung cancer cells A549 and H1975 | ↑ autophagy ↑apoptosis | [122] | |
| Ginsenoside | Compound K | Bladder cancer T24 cells | ↑apoptosis | [123] | |
| Ginsenosides | Compound K and Rb1 | SKOV-3 and HEYA8 cells | ↓ tumor cells survival | [126] | |
| Ginsenoside | Rb3 and Rd | ApcMin/+ mice | ↓ oncogenic signaling molecules (iNOS, STAT3/pSTAT3, Src/pSrc) | [128] | |
| Ginsenoside | Re, Rg1, Rc, Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rd, Rg3, Rg5 and Rk1 | Human lung cancer cells Human breast cancer cells | ↑ apoptosis ↓ cell proliferation ↑ p21 | [133,134,135,136] | |
| - | Extract | Immortalized human keratinocytes (HaCaT )cells | ↑ cell viability | [118] | |
| Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer | Alkaloid | - | C57BL/6 mouse spleen lymphocytes | Reparation damaged cells | [119] |
| Polyacetylene compounds | Panaxydol | Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line | ↓ tumor cells | [124] | |
| Panax quinquefolius L. | Ginsenoside | Rg3 | SW-480 (Leibovitz’s L-15), HT-29 (McCoy’s 5A), and non-small cell lung (NSCLC, DMEM) | Anti-proliferation | [125] |
| Panax notoginseng Burk | Ginsenoside | Notoginsenoside R1 | Sprague–Dawley rats | Cell protection | [132] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| Panax | P. |
| Nitric Oxide | NO |
| Glucose | Glu |
| Arabinose in pyranose form | Arbp |
| Xylose | Xyl |
| Arabinose in furanose form | Arbf |
| Rhamnose | Rham |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | HPLC |
| Thin Layer Chromatography/High Performance Liquid Chromatography | TLC/HPLC |
| Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | UHPLC |
| Two-Dimensional High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | HPLC 2D |
| Natural Killer cell | NK cell |
| Interleukin | IL |
| Tumor necrosis factor α | TNF-α |
| Inducible nitric oxide synthase | iNOS |
| Cyclooxygenase-2 | COX-2 |
| Nuclear factor κB | NF-κB |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinases | MAPK |
| Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase | PI3K |
| Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay | ELISA |
| T helper type 1 | Th1 |
| Cluster of differentiation 86 | CD86 |
| Matrix metalloproteinase 1 | MMP-1 |
| Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 | ERK 1/2 |
| interferon gamma | IFN-γ |
| Immunoglobulin | Ig |
| Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 | Nrf2 |
| Protein kinase B | PKB or Akt |
| Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand | RANKL |
| Human Embryonic Kidney cell line | HEK293 cells |
| Prostaglandin E2 | PEG2 |
| Toll Like receptor | TLR4 |
| Reactive oxygen species | ROS |
| glutathione | GSH |
| Messenger RNA | mRNA |
| Lipopolysaccharide | LPS |
| c-Jun N-terminal kinase | JNK |
| Glutathione Peroxidase | GPxs |
| Superoxide dismutase | SOD |
| Human lung mucoepidermoid carcinoma cell line | NCI-H292 |
| Catalase | CAT |
| nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor | NLRP |
| interferon-inducible protein | AIM2 |
| interleukin receptor-associated kinase | IRAK |
| IkappaB kinase | IκB |
| Gq protein alpha subunit | GαQ |
| Inositol triphosphate | IP3 |
| B-cell lymphoma 2 | Bcl2 |
| signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | STAT3 |
| mouse double minute 2 homolog | MDM2 |
| Hepatic Adenocarcinoma | SK-HEP-1 cells |
| Murine melanoma cell line | B16F10 |
| Human breast cancer cell line | MDA-MB-231 |
| Hepatocyte derived cellular carcinoma cell line | HuH-7 |
| Immortalized human keratinocytes cell line | HaCaT |
References
- Mancuso, C.; Santangelo, R. Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius: From pharmacology to toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.-S. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.W.; Wong, A.S.-T. Pharmacology of ginsenosides: A literature review. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Burgos, E.; Fernandez-Moriano, C.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Potential Neuroprotective Activity of Ginseng in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 10, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Abid, S.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Panax ginseng Cultivars in Korea and China. Molecules 2020, 25, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Youn, S.H.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Han, C.-K.; Haidere, M.F.; Kim, J.K.; Min, H.; Jung, Y.-J.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Hyun, S.H.; et al. Adaptogenic effects of Panax ginseng on modulation of immune functions. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mi, X.; Du, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Gao, M.; Yang, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, H.; Yang, G. Design, Synthesis, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of 12-Dehydropyxinol Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, X.; Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Hua, H.; Li, D. Dammarane-type leads panaxadiol and protopanaxadiol for drug discovery: Biological activity and structural modification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 189, 112087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, A.G.; Konstantinou, M.; Tzortziou, M.; Tsialtas, I.; Kalousi, F.D.; Garagounis, C.; Hayes, J.M.; Psarra, A.-M.G. Potential Dissociative Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity for Protopanaxadiol and Protopanaxatriol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Sellaturay, S.; Sriprasad, S. The history of ginseng in the management of erectile dysfunction in ancient China (3500-2600 BCE). Indian, J. Urol. 2012, 28, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, A.M.; Naval, M.V.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Ginseng: Revisión. Farm. Prof. 2003, 17, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Iglesias, I.; Lozano, R.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Current uses and knowledge of medicinal plants in the Autonomous Community of Madrid (Spain): A descriptive cross-sectional study. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Bryant, D.L.; Farone, A.L. Panax quinquefolius (North American Ginseng) Polysaccharides as Immunomodulators: Current Research Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2020, 25, 5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Phytochemical analysis of Panax species: A review. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.-Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.-Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, D.-A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Qi, H.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Mi, J.; Li, X. Gut Microbiota: Therapeutic Targets of Ginseng Against Multiple Disorders and Ginsenoside Transformation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.T.X.; Cui, X.M.; Song, Z.H.; Zhao, K.J.; Ji, Z.N.; Lo, C.K.; Tsim, K.W.K. Chemical Assessment of Roots of Panax notoginseng in China: Regional and Seasonal Variations in Its Active Constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4617–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-Z.; Ye, M.; Qiao, X.; Liu, C.-F.; Miao, W.-J.; Bo, T.; Tao, H.-Y.; Guo, D.-A. A strategy for efficient discovery of new natural compounds by integrating orthogonal column chromatography and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis: Its application in Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium and Panax notoginseng to characterize 437 potential new ginsenosides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 739, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, M.; Ling, X.; Li, L. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Panax notoginseng Flower Saponins Quantified Using LC/MS/MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.-L.; Pan, H.-Q.; Wang, H.; Yao, S.; Yang, W.-Z.; Hou, J.-J.; Jin, Q.-H.; Wu, W.-Y.; Guo, D.-A. Global profiling combined with predicted metabolites screening for discovery of natural compounds: Characterization of ginsenosides in the leaves of Panax notoginseng as a case study. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.S.; Passos, C.P.; Madureira, P.; Vilanova, M.; Coimbra, M.A. Structure–function relationships of immunostimulatory polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, L.B.; Park, J.U.; Duy, L.X.; Nguyet, N.T.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, Y.H. Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng modulate T cell function via the regulation of NF-AT-mediated IL-2 production. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, D.N.H.; Truong, D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Quynh, L.N.; Tran, L.; Nguyen, H.D.; Shamandy, B.E.; Le, T.M.H.; Tran, D.K.; Sayed, D.; et al. Ginsenoside Rh1: A Systematic Review of Its Pharmacological Properties. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Kim, J.; Quan, H.; Yin, M.; Jeong, S.; Choi, J.I.; Jang, E.A.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Bae, H.B. Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes Fc gamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis of T bacteria by macrophages via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.; Gao, H.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, S. Ginsenoside Rb1 is an immune-stimulatory agent with antiviral activity against enterovirus 71. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.-G.; Jang, M.; Cho, C.-W.; Hong, H.-D.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, S.-Y.; Jung, S.K.; Rhee, Y.K. White ginseng extract induces immunomodulatory effects via the MKK4-JNK pathway. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.H.; Cammisuli, S.; Baggiolini, M. Immunomodulatory effects of Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer in the mouse. Agents Actions 1984, 15, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Actor, J.K.; Indrigo, J.; Olsen, M.; Dasgupta, A. Asian and Siberian ginseng as a potential modulator of immune function: An in vitro cytokine study using mouse macrophages. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 327, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, F.; Ferrara, F.; Dugnani, S.; Falchi, M.; Santoro, G.; Fraschini, F. Immunomodulatory effects of two extracts of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1990, 16, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.I.; Shin, H.M. Wild Panax Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Protects Against Methotrexate–Induced Cell Regression by Enhancing the Immune Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, Y.; Eo, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Jeon, K.S.; Jeong, J.B. Wild simulated ginseng activates mouse macrophage, RAW264.7 cells through TRL2/4-dependent activation of MAPK, NF kappaB and PI3K/AKT pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assinewe, V.; Arnason, J.; Aubry, A.; Mullin, J.; Lemaire, I. Extractable polysaccharides of Panax quinquefolius L. (North American ginseng) root stimulate TNFa production by alveolar macrophages. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, H.R.; Sham, J.; Chau, L.A.; Madrenas, J. High molecular weight polysaccharides are key immunomodulators in North American ginseng extracts: Characterization of the ginseng genetic signature in primary human immune cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.F.; Wong, M.H.T.; Stryjecki, C.; De Boer, A.; Lui, E.M.K.; Mutch, D. Unraveling the adipocyte inflammomodulatory pathways activated by North American ginseng. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azike, C.G.; Charpentier, P.A.; Lui, E.M. Stimulation and Suppression of Innate Immune Function by American Ginseng Polysaccharides: Biological Relevance and Identification of Bioactives. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Yun, Y.S.; Yang, H.O.; Rhee, D.K.; Pyo, S. Immunostimulating effects of acidic polysaccharides extract of Panax ginseng on macrophage function. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2002, 24, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannacci, M.; Lucini, V.; Colleoni, F.; Martucci, C.; Grosso, S.; Sacerdote, P.; Scaglione, F. Panax ginseng C.A. Mayer G115 modulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mice throughout the increase of macrophage toll-like receptor 4 expression during physical stress. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Bae, K.; Jung, I.; Kim, C.; Yun, Y.; Song, J. Anti-Septicaemic Effect of Polysaccharide from Panax ginseng by Macrophage Activation. J. Infect. 2002, 45, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Sohn, E.; Park, J.D.; Kim, B.O.; Moon, E.Y.; Rhee, D.K.; Pyo, S. Red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) in combination with IFN-gamma results in enhanced macrophage function through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jung, I.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Chung, H.-Y.; Lee, I.-R.; Yun, Y.-S. Acidic Polysaccharide from Panax ginseng, Ginsan, Induces Th1 Cell and Macrophage Cytokines and Generates LAK Cells in Synergy with rIL-2. Planta Medica 1998, 64, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Byon, Y.-Y.; Ko, E.-J.; Song, J.-Y.; Yun, Y.-S.; Shin, T.; Joo, H.-G. Immunomodulatory Activity of Ginsan, a Polysaccharide of Panax Ginseng, on Dendritic Cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 13, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; Cha, S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenosides are active ingredients in Panax ginseng with immunomodulatory properties from cellular to organismal levels. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Chen, J.; Su, C.; Zha, L. Advances in the Bioactivities of Phytochemical Saponins in the Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yan, S.-J.; Zhang, H.-T.; Li, N.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, X.-X.; Ma, Q.; Qiu, X.-C.; Fan, Q.-Y.; et al. Ginsenoside Rh2 enhances the antitumor immunological response of a melanoma mice model. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 13, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, J.; Liu, D.; Cheng, B.; Fang, F.; Weng, L.; Wang, C.; Ling, C. Ginsenoside Rh1 potentiates dexamethasone’s anti-inflammatory effects for chronic inflammatory disease by reversing dexamethasone-induced resistance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-K.; Choo, M.-K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Rh1 Possesses Antiallergic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 133, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Kim, K.-A.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Rh1 Ameliorates High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Inhibiting Adipocyte Differentiation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jeong, Y.; Song, J.; Ji, G.E. Oral administration of ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by oxazolone in hairless mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Ginsenoside Rg3 improves cyclophosphamide-induced immunocompetence in Balb/c mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, R.; Tang, Y. Ginsenoside Rg3, a promising agent for NSCLC patients in the pandemic: A large-scale data mining and systemic biological analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ci, Y.; Han, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 can ameliorate the key in nti-in cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 in a cancer cachexia mouse model. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Weng, J.-H.; Mitchison, T.J. Immunomodulatory drug discovery from herbal medicines: Insights from organ-specific activity and xenobiotic defenses. Elife 2021, 10, e73673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Kong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Huo, X.; Ma, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 98, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, N. Hepataprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1—A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.W.; Min, H. Ginseng, the ‘Immunity Boost’: The Effects of Panax ginseng on Immune System. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Choi, E.; Shin, K.K.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, D.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, H.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, D.; et al. Compound K, a ginsenoside metabolite, plays an antiinflammatory role in macrophages by targeting the AKT1-mediated signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, H.-J. Ginsenoside Compound K: Insights into Recent Studies on Pharmacokinetics and Health-Promoting Activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-D.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Ouyang, D.-S.; Yang, G.-P. A review of biotransformation and pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Fitoterapia 2015, 100, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Si, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, A.; Wei, W. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects via downregulating COX2. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 27, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Song, K.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Kang, H.S.; Song, Y.W. Compound K, a Metabolite of Ginsenosides, Attenuates Collagen-induced Arthritis in Mice. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 22, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Liu, K.; Tai, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wei, W. Ginsenoside metabolite compound-K regulates macrophage function through inhibition of β-arrestin2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuong, T.T.; Yang, C.-S.; Yuk, J.-M.; Lee, H.-M.; Ko, S.-R.; Cho, B.-G.; Jo, E.-K. Glucocorticoid receptor agonist compound K regulates dectin-1-dependent inflammatory signaling through inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-S.; Ko, S.-R.; Cho, B.-G.; Shin, N.-M.; Yuk, J.-M.; Li, S.; Kim, J.-M.; Evans, R.M.; Jung, J.-S.; Song, N.-K.; et al. The ginsenoside metabolite compound K, a novel agonist of glucocorticoid receptor, induces tolerance to endotoxin-induced lethal shock. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Shin, J.A.; Jung, J.-S.; Hyun, J.-W.; Van Le, T.K.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, E.-M.; Kim, H.-S. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Compound K in Activated Microglia and Its Neuroprotective Effect on Experimental Stroke in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhong, W.; Wang, W.; Hu, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, B.; Hu, T.; Song, G. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K promotes recovery of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and inhibits inflammatory responses by suppressing NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Kim, M.; Ryu, J.; Choi, C. Ginsenosides compound K and Rh 2 inhibit tumor necrosis factor-α-induced activation of the NF-κB and JNK pathways in human astroglial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 421, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Eldaim, M.A.; Abd El Latif, A.S.; Hassan, A.; El-Borai, N.B. Ginseng attenuates fipronil-induced hepatorenal toxicity via its antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory activities in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45008–45017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.O.; Yang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Yi, Y.S.; Cho, J.Y. Korean Red Ginseng saponin fraction exerts anti-inflammatory effects by targeting the NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.-S.; Yi, Y.-S.; Son, Y.-J.; Yoo, S.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived components. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Kim, S.K.; Ban, J.Y. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Korean Ginseng Berry Extract in LPS-Activated RAW264.7 Macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, D.-H.; Nahar, J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Rupa, E.J.; Ramadhania, Z.M.; Han, Y.; Yang, D.-C.; Kang, S.C. Focused Review on Molecular Signalling Mechanisms of Ginsenosides on Anti-lung cancer and Anti-inflammatory Activities. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Qian, H.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Mao, W.; Guo, Q. Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 945129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Chu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, L. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevent and treat inflammatory diseases: A review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.S.; Yoo, Y.M.; Ahn, B.W.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-B.; Hwang, K.W.; Lee, D.I. Prevention of Inflammation-Mediated Neurotoxicity by Rg3 and Its Role in Microglial Activation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, R.; Li, W.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against neuronal degeneration induced by chronic dexamethasone treatment by inhibiting NLRP-1 inflammasomes in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xu, L.-H.; Ouyang, D.-Y.; Liu, K.-P.; Pan, H.; He, J.; He, X.-H. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages through differentially modulating the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chu, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, C.; Heng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J.; Wei, G.; et al. Anti-inflammatory function of ginsenoside Rg1 on alcoholic hepatitis through glucocorticoid receptor related nuclear factor-kappa B pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Jeong, J.-J.; Eun, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and its metabolites ginsenoside Rh1 and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.; Kim, Y.; Cha, B.; Brito, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Fatombi, B.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Lei, L.; et al. A systematic exploration of ginsenoside Rg5 reveals anti-inflammatory functions in airway mucosa cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Yang, Q.; Kong, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Xiong, L.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates early oxidative damage and sequential inflammatory response after transient focal ischemia in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Chung, J.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Ha, Y.M.; Bae, S.; Lee, E.K.; Jung, K.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.K.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits the expressions of iNOS and COX-2 by suppressing NF-κB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and mouse liver. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-S. New mechanisms of ginseng saponin-mediated anti-in ammatory action via targeting canonical in ammasome signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qi, J.; Li, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ning, Q. Inhibitory effects of Chikusetsusaponin IVa on lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory responses in THP-1 cells. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.; Ye, Q. Anti-in ammatory and anti-gouty-arthritic effect of free Ginsenoside Rb1 and nano Ginsenoside Rb1 against MSU induced gouty arthritis in experimental animals. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 332, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, E.-H.; Lee, I.-A.; Jung, I.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1 activation—The key step of inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhule, A.; Navarro, S.; Smith, J.R.; Shepherd, D.M. Panax notoginseng attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Yoo, E.S.; Baik, K.U.; Park, M.H.; Han, B.H. In Vitro Inhibitory Effect of Protopanaxadiol Ginsenosides on Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α Production and its Modulation by Known TNF-α Antagonists. Planta Medica 2001, 67, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Bi, X.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhan, J.Y.; Dong, Y.X.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, R.; Li, X. Differential effects of ginsenosides on NO and TNF-α production by LPS-activated N9 microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Ginsenoside Rh1 suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in IFN-γ-stimulated microglia via modulation of JAK/STAT and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.A.; Kim, E.J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 inhibit the activation of AP-1 and protein kinase A pathway in lipopolysaccharide/interferon-gamma-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Lee, Y.; Park, T.; Kim, H.; Rhee, M.; Cho, J. Ginsenoside Rp1, a ginsenoside derivative, blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1beta production via suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Lee, J.; Park, M.H.; Lee, Y.G.; Rho, H.S.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Rhee, M.H.; Park, Y.C.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenoside Rp 1, a ginsenoside derivative, blocks promoter activation of iNOS and Cox-2 genes by suppression of an IKKβ-mediated NF-κB pathway in HEK293 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Shin, T.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Cho, H.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Pyo, M.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, C.-W.; et al. Gintonin, newly identified compounds from ginseng, is novel lysophosphatidic acids-protein complexes and activates G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors with high affinity. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Lee, R.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, D.-G.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Cho, Y.; Rhim, H.; Nah, S.-Y. Ginseng gintonin, aging societies, and geriatric brain diseases. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Guan, Y. Ginsenosides in cancer: A focus on the regulation of cell metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Lu, K.; Zong, G.; Xia, Y.; Han, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y. Ginseng polysaccharides: Potential antitumor agents. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.A.; Qin, J.-J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: In vitro and in vivo activities, structure–activity relationships, and molecular mechanisms of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-J.; Cho, K.-H.; Jung, W.-S.; Moon, S.-K.; Park, E.-K.; Kim, N.-H. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1, crocin, amygdalin, geniposide, puerarin, ginsenoside Re, hesperidin, poncirin, glycyrrhizin, and baicalin by human fecal microflora and its relation to cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, B.H.; Shin, I.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Kim, S.I.L.; Joe, C.O. Modulation of Protein Kinase C Activity in NIH 3T3 Cells by Plant Glycosides from Panax ginseng. Planta Medica 1997, 63, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, D.G.; Kitts, D.D. Structure–function relationship exists for ginsenosides in reducing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in the human leukemia (THP-1) cell line. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 406, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odashima, S.; Ohta, T.; Kohno, H.; Matsuda, T.; Kitagawa, I.; Abe, H.; Arichi, S. Control of phenotypic expression of cultured B16 melanoma cells by plant glycosides. Cancer Res 1985, 45, 2781–2784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chu, S.; Lin, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Anticancer property of ginsenoside Rh2 from ginseng. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.-K.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, K.-D.; Im, W.-T. Production of the Rare Ginsenoside Rh2-MIX (20(S)-Rh2, 20(R)-Rh2, Rk2, and Rh3) by Enzymatic Conversion Combined with Acid Treatment and Evaluation of Its Anti-Cancer Activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaodan, S.; Ying, C. Role of ginsenoside Rh2 in tumor therapy and tumor microenvironment immunomodulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. In vitro anti-cancer activity and structure–activity relationships of natural products isolated from fruits of Panax ginseng. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.-F.; Shi, S.-L.; Liu, Q.-R.; Tang, J.; Song, J.; Liang, Y. Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg1, cinnamic acid, and tanshinone IIA in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells: Nuclear matrix downregulation and cytoplasmic trafficking of nucleophosmin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Aung, H.; Ni, M.; Wu, J.-A.; Tong, R.; Wicks, S.; He, T.-C.; Yuan, C.-S. Red American Ginseng: Ginsenoside Constituents and Antiproliferative Activities of Heat-Processed Panax quinquefolius Roots. Planta Medica 2007, 73, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-I.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-Y.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, J.; Nah, S.-Y.; Kim, Y. Evidence that the tertiary structure of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 with tight hydrophobic packing near the chiral center is important for Na+ channel regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Smith, E.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Anti-Angiogenic Properties of Ginsenoside Rg3. Molecules 2020, 25, 4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Hardingham, J.E. Stereoselective Anti-Cancer Activities of Ginsenoside Rg3 on Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Models. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, P.Y.; Wong, D.Y.; Wu, P.; Leung, P.; Mak, N.; Yeung, H.; Liu, L.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Fan, T.; et al. The angiosuppressive effects of 20(R)- ginsenoside Rg3. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-M.; Cui, M.-H.; Xin, Y.; Gu, L.-P.; Jiang, X.; Su, M.-M.; Wang, D.-D.; Wang, W.-J. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on ovarian cancer metastasis. Chin. Med. J. 2008, 121, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Ginsenoside-Rg5 suppresses cyclin E-dependent protein kinase activity via up-regulating p21Cip/WAF1 and down-regulating cyclin E in SK-HEP-1 cells. Anticancer. Res. 1997, 17, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woo, L.K.; Nakamura, Y.; Donati, L. Effect of Korean Ginseng on the growth rate of cells. Arch. Ital. Patol. Clin. Tumori 1965, 8, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.D.; Ha, S.E.; Kang, J.R.; Park, J.K. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng Extract on Cell Death Responses in Peroxynitrite-Treated Keratinocytes. J. Ginseng Res. 2010, 34, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.K.; Kim, T.H.; Yoo, S.Y.; Koh, K.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Ji, Y.H. The Effects of Akaloid Fraction of Korean Ginseng on the Radiation-Induced DNA Strand Breaks. J. Korean Soc. Ther. Radiol. 1995, 13, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Feng, M.-Q.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhou, P. Studies on the preparation, crystal structure and bioactivity of ginsenoside compound K. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lv, G.; Huang, X.; Lin, H.; Ma, C.; Lin, Z.; Qu, P. Functional Mechanism of Ginsenoside Compound K on Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 15347354221101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, G.; Yang, Q.; Tang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Cong, Z. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K induces apoptosis and autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells via AMPK-mTOR and JNK pathways. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Liu, J.; Ye, S.; Xiao, S.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J. Compound K Induces Apoptosis of Bladder Cancer T24 Cells Via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated p38 MAPK Pathway. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharm. 2013, 28, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Seo, H.W.; Youn, S.H.; Kyung, J.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; In, G.; Park, C.-K.; Han, C.-K. Physiological and pharmacological features of the non-saponin components in Korean Red Ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Lyu, F.; Lou, L.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Jakowitsch, J.; Ma, Y. Anti-tumor activities of Panax quinquefolius saponins and potential biomarkers in prostate cancer. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wong, C.K.C.; Lai, H.-C.; Wong, A.S.T. Ginsenoside-Rb1 targets chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer stem cells via simultaneous inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25897–25914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, T.; Teng, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells by regulating microRNA-25. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 2895–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Khan, I.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Leong, W.; Ho, L.T.; Hsiao, W.L.W. Ginsenosides Rb3 and Rd reduce polyps formation while reinstate the dysbiotic gut microbiota and the intestinal microenvironment in ApcMin/+ mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, K.-G.; Harris, R.A.; Cho, W.-J.; Lee, J.-T.; Lee, I.-K. Scoparone Exerts Anti-Tumor Activity against DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells via Inhibition of STAT3 Activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-H.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, J.H.; Yang, H.O. KG-135, enriched with selected ginsenosides, inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in culture and inhibits xenograft growth in athymic mice. Cancer Lett. 2010, 289, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivoňová, M.K.; Vilčková, M.; Kliment, J.; Mahmood, S.; Jurečeková, J.; Dušenková, S.; Waczulíková, I.; Slezák, P.; Dobrota, D. Association of p53 and p21 polymorphisms with prostate cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Tang, H.-T.; Jia, Y.-T.; Ma, B.; Fu, J.-F.; Wang, Y.; Lv, K.-Y.; Xia, Z.-F. Notoginsenoside R1 Attenuates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Shock 2010, 34, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hill, D.L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H. Experimental therapy of prostate cancer with novel natural product anti-cancer ginsenosides. Prostate 2008, 68, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Anti-lung cancer effects of novel ginsenoside 25-OCH3-PPD. Lung Cancer 2009, 65, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Rayburn, E.R.; Zhao, Y.; Hill, D.L.; Zhang, R. 20(S)-25-methoxyl-dammarane-3β, 12β, 20-triol, a novel natural product for prostate cancer therapy: Activity in vitro and in vivo and mechanisms of action. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-S.; Wang, C.-Z.; Li, X.-L.; Wang, Q.-F.; Mehendale, S.R.; Fishbein, A.; Han, A.H.; Sun, S. The mitochondrial pathway is involved in American ginseng-induced apoptosis of SW-480 colon cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdés-González, J.A.; Sánchez, M.; Moratilla-Rivera, I.; Iglesias, I.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update. Molecules 2023, 28, 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093863
Valdés-González JA, Sánchez M, Moratilla-Rivera I, Iglesias I, Gómez-Serranillos MP. Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093863
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdés-González, Jose Antonio, Marta Sánchez, Ignacio Moratilla-Rivera, Irene Iglesias, and María Pilar Gómez-Serranillos. 2023. "Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093863
APA StyleValdés-González, J. A., Sánchez, M., Moratilla-Rivera, I., Iglesias, I., & Gómez-Serranillos, M. P. (2023). Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update. Molecules, 28(9), 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093863






