Localized Therapeutic Approaches Based on Micro/Nanofibers for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic
3. Cancer Therapies
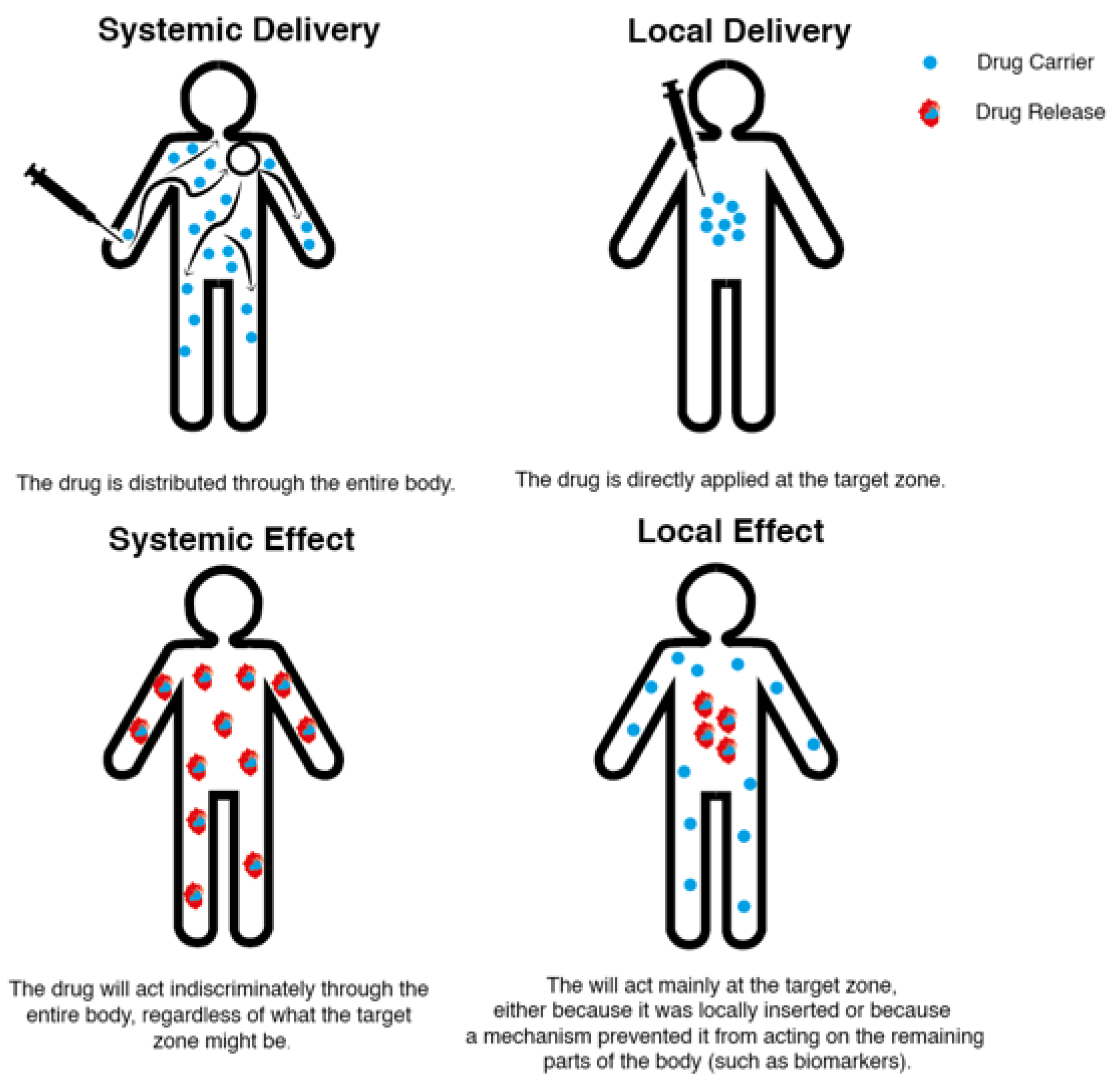
4. Local and Systemic Drug Delivery Systems
4.1. Fibrous Structures as Localized Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
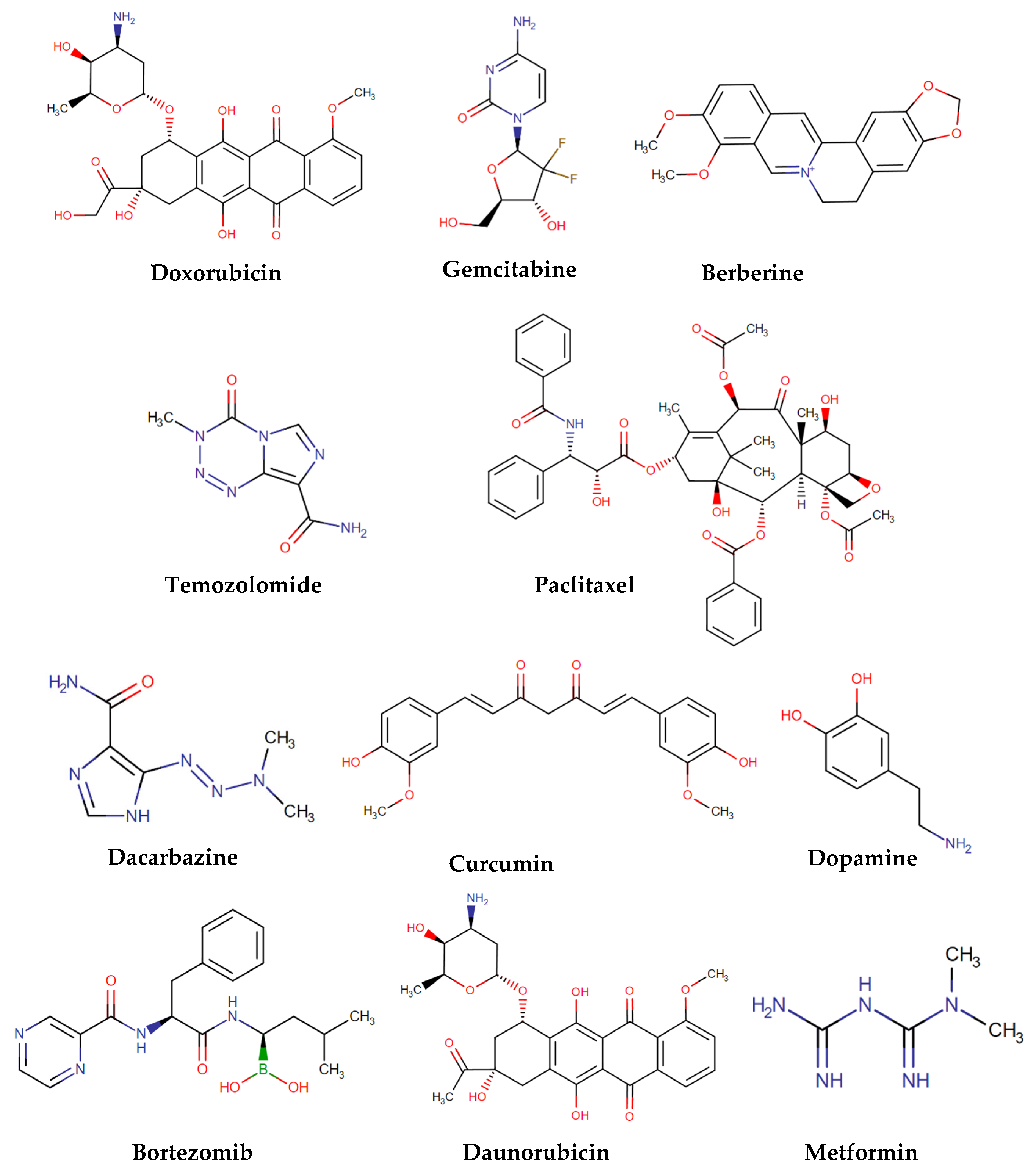
| Fiber | Nanoparticle | Released Drug | Type of Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH | Silver | ---- | ---- | [54] |
| CH-PVA | ---- | DOX | Ovarian | [55] |
| CH | ---- | Gemcitabine | Pancreatic | [56] |
| CH | ---- | Berberine | Cervical | [57] |
| CH-PVA | ---- | HAp/DOX | Bone cancer | [58] |
| CH-PU | MIL-53 | Temozolomide and PTX | --- | [59] |
| PVA-Silk | ---- | DOX | Breast | [60] |
| PVA | ---- | Dacarbazine | Glioblastoma | [61] |
| PCL-PVA | ---- | PTX | Colon | [62] |
| PLGA | ---- | PTX | Brain | [63] |
| PLGA | Gold | DOX | ---- | [64] |
| PLGA | MSNs | Curcumin | Breast | [65] |
| PCL-PLGA | ---- | DOX | ---- | [66] |
| Poly(NIPAAm-co-HMAAm | MNPs | DOX | Melanoma | [67] |
| CH | Fe3O4 | ---- | ---- | [68] |
| PLGA | MIONs | Dopamine and bortezomib | ---- | [69] |
| PLA | MNPs | Daunorubicin | Leukemia | [70] |
| PCL | MIONs and carbogenic nanodots | DOX | ---- | [71] |
| PCL | MNPs | PTX | --- | [72] |
| Cellulose acetate | Fe3O4 | ---- | ---- | [73] |
| PCL | Fe3O4 | DOX | --- | [74] |
| PCL | Fe3O4 | --- | --- | [75] |
| Cellulose | MNPs | DOX | ---- | [76] |
| PCL | MNPs | DOX and 17-allylamino-17-desmethoxygeldanamycin | ---- | [77] |
| N-isopropylacrylamide and N-hydroxymethylacrylamide | MNPs | Metformin | Skin melanoma | [78] |
| PCL | MNPs | DOX | ---- | [79] |
4.1.1. Chitosan Fibrous Structures as Localized Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
4.1.2. Polyvinyl Alcohol Fibrous Structures as Localized Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
4.1.3. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Fibrous Structures as Localized Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
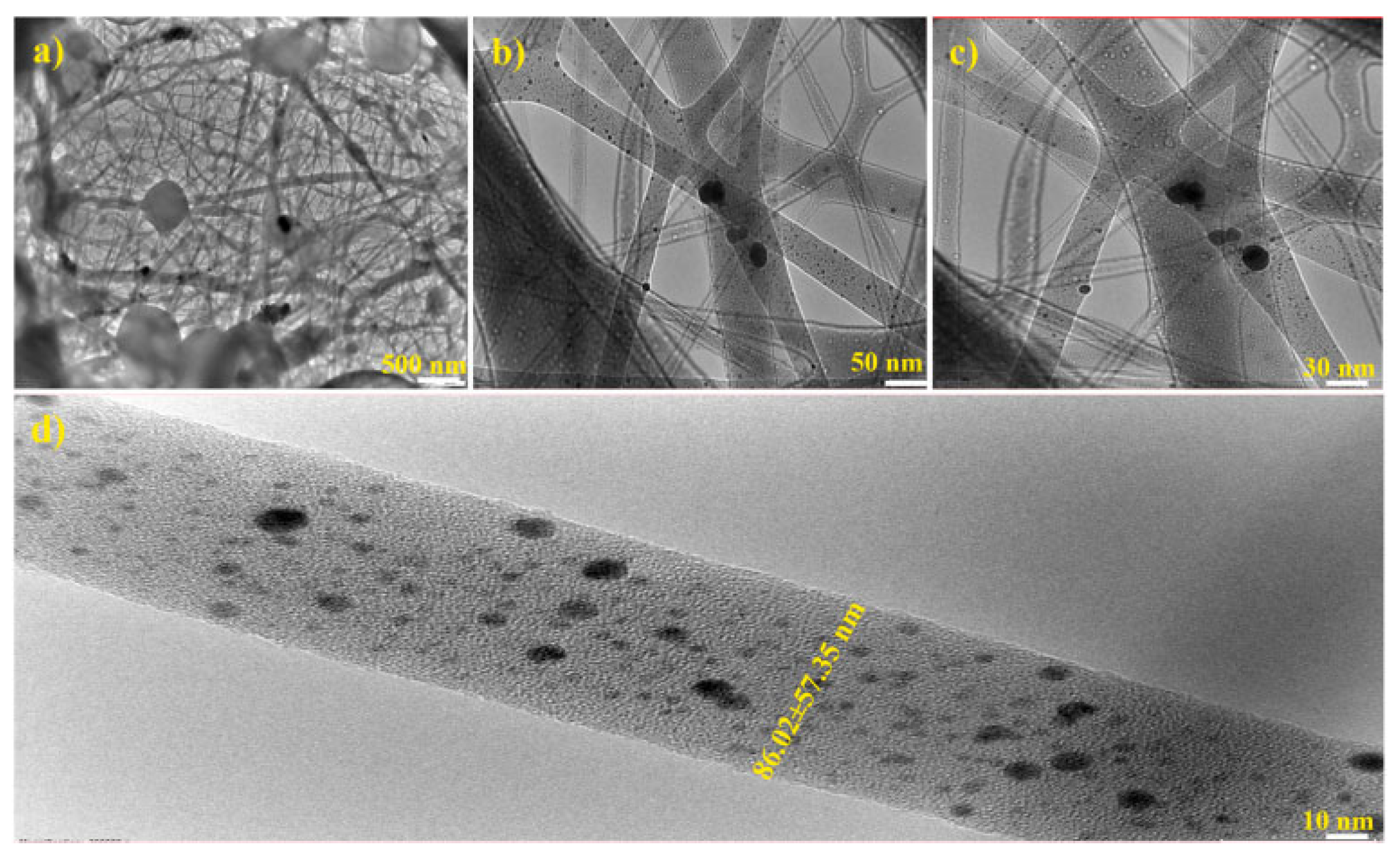
4.1.4. Magnetic NPs Combined with Fibrous Structures as Localized Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
4.2. Nanofibers Theranostic Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer Statistics for the Year 2020: An Overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Weinberg, R.A. The Biology of Cancer, 2nd ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 14–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, D.; DeVita, V.T.; Lawrence, T.S.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Ovid Technologies, Inc. Cancer “Principles & Practice of Oncology”, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 91–92. ISBN 978-1-4963-9463-7. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, B.; Ozpolat, B.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G. Nanotechnology in Cancer Therapy. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.M.; Shiri, S.; Farsinejad, S. Metastasis Review: From Bench to Bedside. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 8483–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.D.; Lima, E.; Boto, R.E.; Ferreira, D.; Fernandes, J.R.; Almeida, P.; Ferreira, L.F.V.; Silva, A.M.; Reis, L.V. Red and Near-Infrared Absorbing Dicyanomethylene Squaraine Cyanine Dyes: Photophysicochemical Properties and Anti-Tumor Photosensitizing Effects. Materials 2020, 13, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization List of Priority Medical Devices for Cancer Management; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-156546-2.
- Snider, J.W.; Datta, N.R.; Vujaskovic, Z. Hyperthermia and Radiotherapy in Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, W.; Zhu, P.; Dong, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, K.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, S. Fabrication of Dual PH/Redox-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Anticancer Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8001–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Ju, D.-D.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.-C.; Yan, X.; Long, Y.-Z.; Song, F. Flexible Inorganic Core-Shell Nanofibers Endowed with Tunable Multicolor Upconversion Fluorescence for Simultaneous Monitoring Dual Drug Delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yu, D.-G.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.W.A. Theranostic Fibers for Simultaneous Imaging and Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, G.S.; Luebbers, K.P. (Eds.) Cancer: Prevention, Early Detection, Treatment and Recovery, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-118-96288-6. [Google Scholar]
- How Cancer Is Diagnosed. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/diagnosis-staging/diagnosis#lab-tests-used-to-diagnose-cancer (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute Physical Exam. Available online: https://training.seer.cancer.gov/staging/sources/exam.html (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Nakamura, R.M. Cancer Diagnostics: Current and Future Trends; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-59259-791-8. [Google Scholar]
- Khleif, S.N.; Rixe, O.; Skeel, T.R. Skeel’s Handbook of Cancer Therapy; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tohme, S.; Simmons, R.L.; Tsung, A. Surgery for Cancer: A Trigger for Metastases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhier, A.; Astuccio, M.; Lahey, D.; Monfredo, N.; Johnson, A.; Callahan, W.; Partington, A.; Fellows, K.; Ouellette, L.; Zhidro, S.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Rho-Kinase Signaling with Y-27632 Blocks Melanoma Tumor Growth. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Monte, M.; Macias, R.; Romero, M.; Herraez, E.; Asensio, M.; Ortiz-Rivero, S.; Cives-Losada, C.; Di Giacomo, S.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; et al. Expression of Chemoresistance-Associated ABC Proteins in Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic and Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Allenby, T.; Lin, J.; Rosenberg, J.; Simone, N.L.; Schmitz, K.H. Exercise Therapy and Radiation Therapy for Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskar, R.; Lee, K.A.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.-W. Cancer and Radiation Therapy: Current Advances and Future Directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.; Roudaia, L.; Buhlaiga, N.; Del Rincon, S.V.; Papneja, N.; Miller, W.H. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy: From the Past, to the Present, to the Future. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Nechansky, A.; Kircheis, R. Cancer Immunotherapy. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Williams, S.; Stevens, A.; Rea, D.W. Endocrine Therapy for Early Breast Cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2004, 4, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deli, T.; Orosz, M.; Jakab, A. Hormone Replacement Therapy in Cancer Survivors–Review of the Literature. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.; Boto, R.E.; Ferreira, D.; Fernandes, J.R.; Almeida, P.; Ferreira, L.F.V.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M.; Reis, L.V. Quinoline- and Benzoselenazole-Derived Unsymmetrical Squaraine Cyanine Dyes: Design, Synthesis, Photophysicochemical Features and Light-Triggerable Antiproliferative Effects against Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Materials 2020, 13, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M.; Fangueiro, R.; Ferreira, D.P. Drug Delivery Systems for Photodynamic Therapy: The Potentiality and Versatility of Electrospun Nanofibers. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triesscheijn, M.; Baas, P.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Stewart, F.A. Photodynamic Therapy in Oncology. Oncologist 2006, 11, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, H.P.; Kotte, A.N.T.J.; Crezee, J. Planning, Optimisation and Evaluation of Hyperthermia Treatments. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, T.A.; Gopalakrishna, A.; Tsivian, M.; Van Noord, M.; Rasch, C.R.; Inman, B.A.; Geijsen, E.D. A Systematic Review of Regional Hyperthermia Therapy in Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; Stancu, A. Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles Dose Based on Tumor Size in Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia Cancer Therapy. Proc. IEEE Trans. 2009, 45, 5251–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Lim, M.; Goos, J.A.C.M.; Qiao, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Mansfeld, F.M.; Jackson, M.; Davis, T.P.; Kavallaris, M. Biologically Targeted Magnetic Hyperthermia: Potential and Limitations. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.K.; Kim, S.W. Recent Advances in Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Gu, H. Nanostructured Materials for Biomedical Applications. J. Nanomater. 2008, 2008, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, W.N.H. Magnetism in Medicine: A Handbook, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weynheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, T.; Kohane, D.S. Nanoscale Systems for Local Drug Delivery. Nano Today 2019, 28, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwer, L.; Hashizume, R.; Ozawa, T.; James, C.D. Systemic and Local Drug Delivery for Treating Diseases of the Central Nervous System in Rodent Models. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 42, e1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; De Jesus, O. Medication Routes of Administration. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.M.; Sahoo, S.K. Controlled Drug Delivery: Polymeric Biomaterials. Encycl. Biomed. Polym. Polym. Biomater. 2015, 11, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Vargason, A.M.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. The Evolution of Commercial Drug Delivery Technologies. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar, D.; Michalska, K. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes with Antibiotics and Antibacterial Agents as Drug-Delivery Systems—A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohane, D.S. Microparticles and Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.; Zahedi, P.; Allen, C.; Piquette-Miller, M. Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems for Localized Cancer Chemotherapy. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Bannerjee, S.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Sriwastawa, B. Drug Delivery Systems: An Updated Review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Martinez, E.; Cornejo Bravo, J.; Serrano Medina, A.; Pérez González, G.; Villarreal Gómez, L. A Summary of Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System: Drugs Loaded and Biopolymers Used as Matrices. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, F.; Sooriyarachchi, A.; Altural, H.; Montazami, R.; Rylander, M.; Hashemi, N. Fiber Based Approaches as Medicine Delivery Systems. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1411–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, O.M.; Rubinstein, I.; Onyuksel, H. Role of Nanotechnology in Targeted Drug Delivery and Imaging: A Concise Review. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2005, 1, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Lee, S.-E.; Kim, D.-H.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Park, J.-S. Recent Advances of Nanotechnology for the Delivery of Anticancer Drugs for Breast Cancer Treatment. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhu, C.; Edmonds, L.; Yang, H.; Cui, W.; Li, B. Microsol-Electrospinning for Controlled Loading and Release of Water-Soluble Drugs in Microfibrous Membranes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43220–43226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y. Time-Programmed DCA and Oxaliplatin Release by Multilayered Nanofiber Mats in Prevention of Local Cancer Recurrence Following Surgery. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-Y. Near-Infrared Light-Remote Localized Drug Delivery Systems Based on Zwitterionic Polymer Nanofibers for Combination Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Murugesan, B.; Pandiyan, N.; Chinnalagu, D.K.; Rangasamy, G.; Mahalingam, S. Electrospinning Cellulose Acetate/Silk Fibroin/Au-Ag Hybrid Composite Nanofiber for Enhanced Biocidal Activity against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanpui, P.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells at Low Silver Nanoparticle Concentrations Using Chitosan Nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, E.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gao, J.; Hao, X.; Pei, S.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, D. Biocompatible Core–Shell Electrospun Nanofibers as Potential Application for Chemotherapy against Ovary Cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 41, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, S.J.; Zuzic, A.; Foroughi, J.; Talebian, S.; Aghmesheh, M.; Moulton, S.E.; Vine, K.L. Preparation and in Vitro Assessment of Wet-Spun Gemcitabine-Loaded Polymeric Fibers: Towards Localized Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Tabaei, S.J.S.; Rahimi, M.; Taranejoo, S.; Ghanimatdan, M. Herbal Extract Incorporated Chitosan Based Nanofibers as a New Strategy for Smart Anticancer Drug Delivery System—An In Vitro Model. WCRJ 2020, 7, e1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qavamnia, S.S.; Rad, L.R.; Irani, M. Incorporation of Hydroxyapatite/Doxorubicin into the Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyurethane Nanofibers for Controlled Release of Doxurubicin and Its Anticancer Property. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzazzadeh, A.; Dizaji, B.F.; Kianinejad, N.; Nouri, A.; Irani, M. Fabrication of Poly(Acrylic Acid) Grafted-Chitosan/Polyurethane/Magnetic MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework Composite Core-Shell Nanofibers for Co-Delivery of Temozolomide and Paclitaxel against Glioblastoma Cancer Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, T.; Lou, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Ran, H. Drug Release from Core-Shell PVA/Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles Fabricated by One-Step Electrospraying. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, L.; Morás, A.M.; Arantes, P.R.; Masterson, K.; Cao, Z.; Nugent, M.; Moura, D.J. Electrospun PVA-Dacarbazine Nanofibers as a Novel Nano Brain-Implant for Treatment of Glioblastoma: In Silico and In Vitro Characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 143, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Jiang, J.; Ren, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Polycaprolactone/Polyvinyl Alcohol Core-Shell Nanofibers as a PH-Responsive Drug Carrier for the Potential Application in Chemotherapy against Colon Cancer. Mater. Lett. 2021, 291, 129516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, C.-H. Electrospun Micro- and Nanofibers for Sustained Delivery of Paclitaxel to Treat C6 Glioma in Vitro. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Seo, H.; Park, J.H.; Son, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.; Moon, G.D.; Hyun, D.C. Poly(d,l-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Hollow Fiber with Segmental Switchability of Its Chains Sensitive to NIR Light for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebian, Z.; Babazadeh, M.; Zarghami, N.; Mousazadeh, H. Anticancer Efficiency of Curcumin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles/Nanofiber Composites for Potential Postsurgical Breast Cancer Treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanom, J.; Rezk, A.I.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Near-Infrared Responsive Synergistic Chemo-Phototherapy from Surface-Functionalized Poly(ε-Caprolactone)–Poly(d,l-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Composite Nanofibers for Postsurgical Cancer Treatment. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Ebara, M.; Aoyagi, T. A Smart Hyperthermia Nanofiber with Switchable Drug Release for Inducing Cancer Apoptosis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5753–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-C.; Lin, F.-H.; Lin, J.-C. In Vitro Characterization of Magnetic Electrospun IDA-Grafted Chitosan Nanofiber Composite for Hyperthermic Tumor Cell Treatment. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, A.R.K.; Unnithan, A.R.; Yun, Y.-H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. An Implantable Smart Magnetic Nanofiber Device for Endoscopic Hyperthermia Treatment and Tumor-Triggered Controlled Drug Release. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, L.; Mahboobnia, K.; Irani, M. Fabrication of PLA/MWCNT/Fe3O4 Composite Nanofibers for Leukemia Cancer Cells. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Agarwal, S.; Srivastava, S.; Jain, S. The Combined Effect of Thermal and Chemotherapy on HeLa Cells Using Magnetically Actuated Smart Textured Fibrous System: Effect of Thermal and Chemotherapy on Hela Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 106, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, E.; Uto, K.; Lee, C.M.; Sakura, K.; Ebara, M. Hyperthermia Nanofiber Platform Synergized by Sustained Release of Paclitaxel to Improve Antitumor Efficiency. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.J.R.; Chaparro, C.I.P.; Silva, J.C.; Valente, M.A.; Borges, J.P.; Soares, P.I.P. Electrospun Composite Cellulose Acetate/Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Non-Woven Membranes for Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneet, K.; Tamasa, D.; Rangarajan, A.; Jain, S. Magnetic Nanofibers Based Bandage for Skin Cancer Treatment: A Non-Invasive Hyperthermia Therapy. Cancer Rep. 2020, 3, e1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.-X.; Yan, J.-S.; Wang, X.-X.; Hu, M.-Z.; Xiang, H.-F.; Long, Y.-Z. In Situ Melt Electrospun Polycaprolactone/Fe3O4 Nanofibers for Magnetic Hyperthermia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitha, N.S.; Sreeja, S.; Varghese, P.J.G.; Sailaja, G.S. A Dual Functional Superparamagnetic System with PH-Dependent Drug Release and Hyperthermia Potential for Chemotherapeutic Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 273, 125108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fujisawa, N.; Takanohashi, M.; Najmina, M.; Uto, K.; Ebara, M. A Smart Hyperthermia Nanofiber-Platform-Enabled Sustained Release of Doxorubicin and 17AAG for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadzadeh, S.; Babazadeh, M.; Zarghami, N.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Mousazadeh, H. An Implantable Smart Hyperthermia Nanofiber with Switchable, Controlled and Sustained Drug Release: Possible Application in Prevention of Cancer Local Recurrence. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serio, F.; Silvestri, N.; Kumar Avugadda, S.; Nucci, G.E.P.; Nitti, S.; Onesto, V.; Catalano, F.; D’Amone, E.; Gigli, G.; del Mercato, L.L.; et al. Co-Loading of Doxorubicin and Iron Oxide Nanocubes in Polycaprolactone Fibers for Combining Magneto-Thermal and Chemotherapeutic Effects on Cancer Cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, M.; Shabani, I.; Mohandesi, J.A. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Electrospun Nanofibers by Incorporation of Graphene Nanoplatelets. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 125, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösiger, P.; Tegl, G.; Richard, I.M.T.; Le Gat, L.; Huber, L.; Stagl, V.; Mensah, A.; Guebitz, G.M.; Rossi, R.M.; Fortunato, G. Enzyme Functionalized Electrospun Chitosan Mats for Antimicrobial Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Wang, Y.; Qi, H.; Shi, C.; Wei, G.; Xiao, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Teng, C.; et al. Nanocomposite Sponges of Sodium Alginate/Graphene Oxide/Polyvinyl Alcohol as Potential Wound Dressing: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 167, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei Mirakabad, F.S.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Yamchi, M.R.; Milani, M.; Zarghami, N.; Zeighamian, V.; Rahimzadeh, A.; Alimohammadi, S.; Hanifehpour, Y.; et al. PLGA-Based Nanoparticles as Cancer Drug Delivery Systems. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lee, C.-H.; Ko, H.-J.; Suh, J.-S.; Yoon, H.-G.; Lee, K.; Huh, Y.-M.; Haam, S. Multifunctional Magneto-Polymeric Nanohybrids for Targeted Detection and Synergistic Therapeutic Effects on Breast Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8836–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, S.C.; Saha, A.; Devi, P.S. PEGylated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for PH Responsive Drug Delivery Application. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 9715–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-L.; Liang, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chiang, C.-F.; Mo, L.-R.; Wei, S.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-Y. Doxorubicin-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Monitoring Magnet-Enhancing Tumor Chemotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Nanomedicine–Nanoscale Drugs and Delivery Systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 7906–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Quarta, A.; Espinosa, A.; Figuerola, A.; Wilhelm, C.; García-Hernández, M.; Genovese, A.; Falqui, A.; Alloyeau, D.; Buonsanti, R.; et al. Correlating Magneto-Structural Properties to Hyperthermia Performance of Highly Monodisperse Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by a Seeded-Growth Route. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4170–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, S.; Zeinali Sehrig, F.; Samiei, M.; Milani, M.; Abbasi, E.; Dadashzadeh, K.; Akbarzadeh, A. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Applications in Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2015, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbafzadeh, M.; Vakili, M. Application of Magnetic Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/Collagen Nanofibres for Drug Delivery Systems. Mol. Simul. 2022, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Meininger, A.; Jiang, H.; Moon, K.-S.; Wong, C.P. Magnetic Nanocomposite for Potential Ultrahigh Frequency Microelectronic Application. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xiao, T.; Luo, Z.; He, R.; Cao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. A Micro-/Nano-Chip and Quantum Dots-Based 3D Cytosensor for Quantitative Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.I.P.; Borges, J.P. Recent Advances in Magnetic Electrospun Nanofibers for Cancer Theranostics Application. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, S.; Su, W.; Chang, J. Multifunctional Nanoparticles Composed of A Poly( Dl-Lactide-Coglycolide) Core and A Paramagnetic Liposome Shell for Simultaneous Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Targeted Therapeutics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, M.; Galli, F.; Capriotti, G.; Mattei, M.; Cicconi, R.; Campagna, G.; Panzuto, F.; Signore, A. Theranostic Designed Near-Infrared Fluorescent Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles and Preliminary Studies with Functionalized VEGF-Nanoparticles. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Hong, S.G.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.; Moon, G.D.; Hyun, D.C. Poly(ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) Hollow Nanoparticles with Surface Sealability and On-Demand Pore Generability for Easy Loading and NIR Light-Triggered Release of Drug. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Mahyad, B.; Hashemzadeh, H.; Janfaza, S.; Gholikhani, T.; Tayebi, L. Biomedical Applications of TiO2 Nanostructures: Recent Advances. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3447–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, C.; Yang, M. Upconversion Luminescence Nanomaterials: A Versatile Platform for Imaging, Sensing, and Therapy. Talanta 2020, 208, 120157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Qi, H. An Injectable Silk Fibroin Nanofiber Hydrogel Hybrid System for Tumor Upconversion Luminescence Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Tang, X.; Wang, M.; Du, Z.; Chen, S.; Heng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Alifu, N.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C. Clinical Indocyanine Green-Based Silk Fibroin Theranostic Nanoprobes for in Vivo NIR-I/II Fluorescence Imaging of Cervical Diseases. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2023, 47, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Mallidi, S.; Zheng, X.; Rahmanzadeh, R.; Mir, Y.; Elrington, S.; Khurshid, A.; Hasan, T. Development and Applications of Photo-Triggered Theranostic Agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1094–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janib, S.M.; Moses, A.S.; MacKay, J.A. Imaging and Drug Delivery Using Theranostic Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.; Bértolo, E.; Núñez, C.; Pilla, V.; Santos, H.M.; Fernández-Lodeiro, J.; Fernández-Lodeiro, A.; Djafari, J.; Capelo, J.L.; Lodeiro, C. Green and Red Fluorescent Dyes for Translational Applications in Imaging and Sensing Analytes: A Dual-Color Flag. ChemistryOpen 2018, 7, 9–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolting, D.; Gore, J.; Pham, W. Near-Infrared Dyes: Probe Development and Applications in Optical Molecular Imaging. Curr. Org. Synth. 2011, 8, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic Nanoparticles in MR Imaging and Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzin, A.; Etesami, S.A.; Quint, J.; Memic, A.; Tamayol, A. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
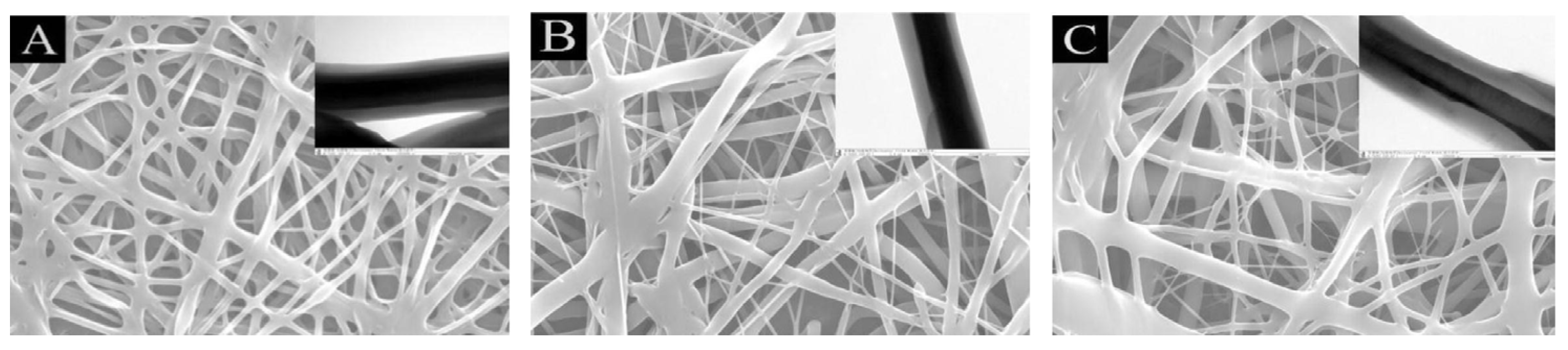
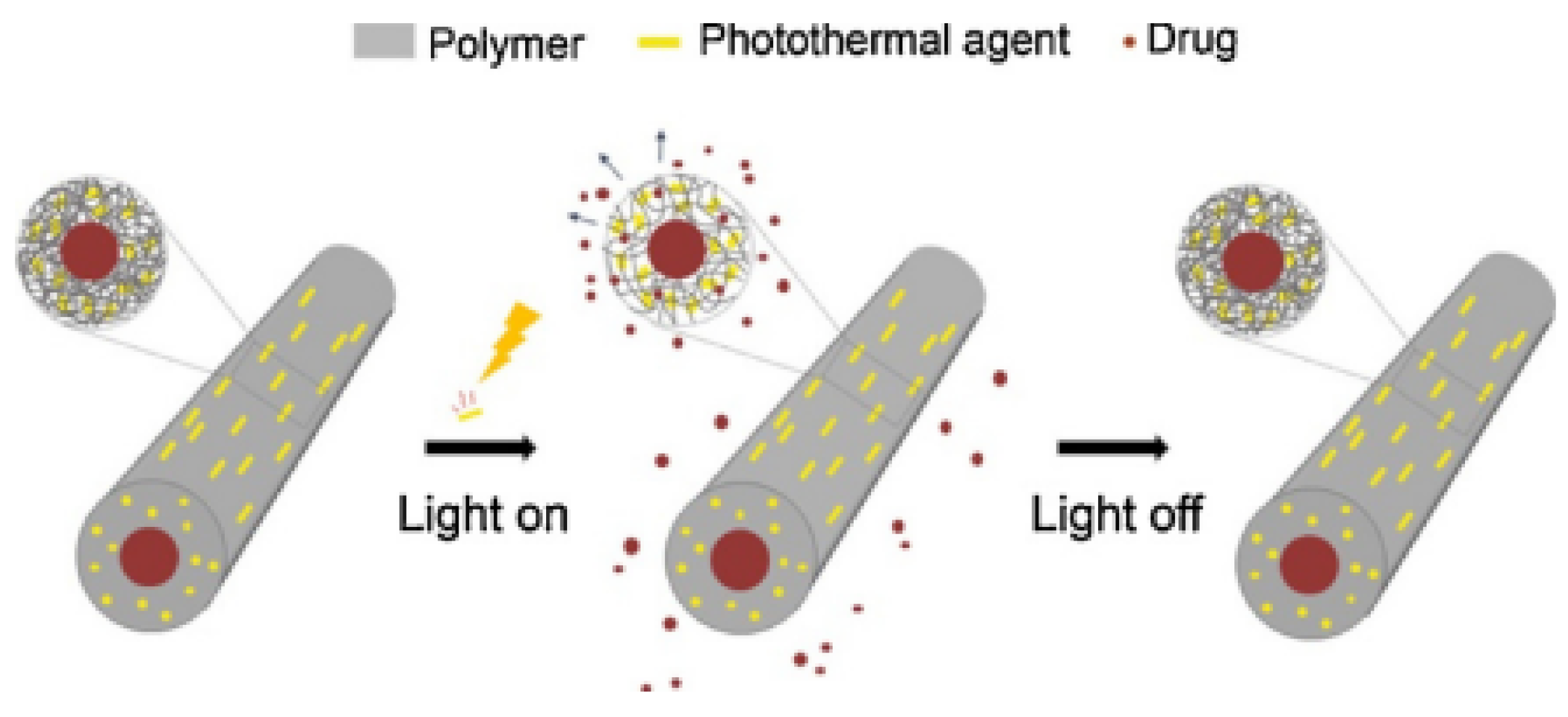
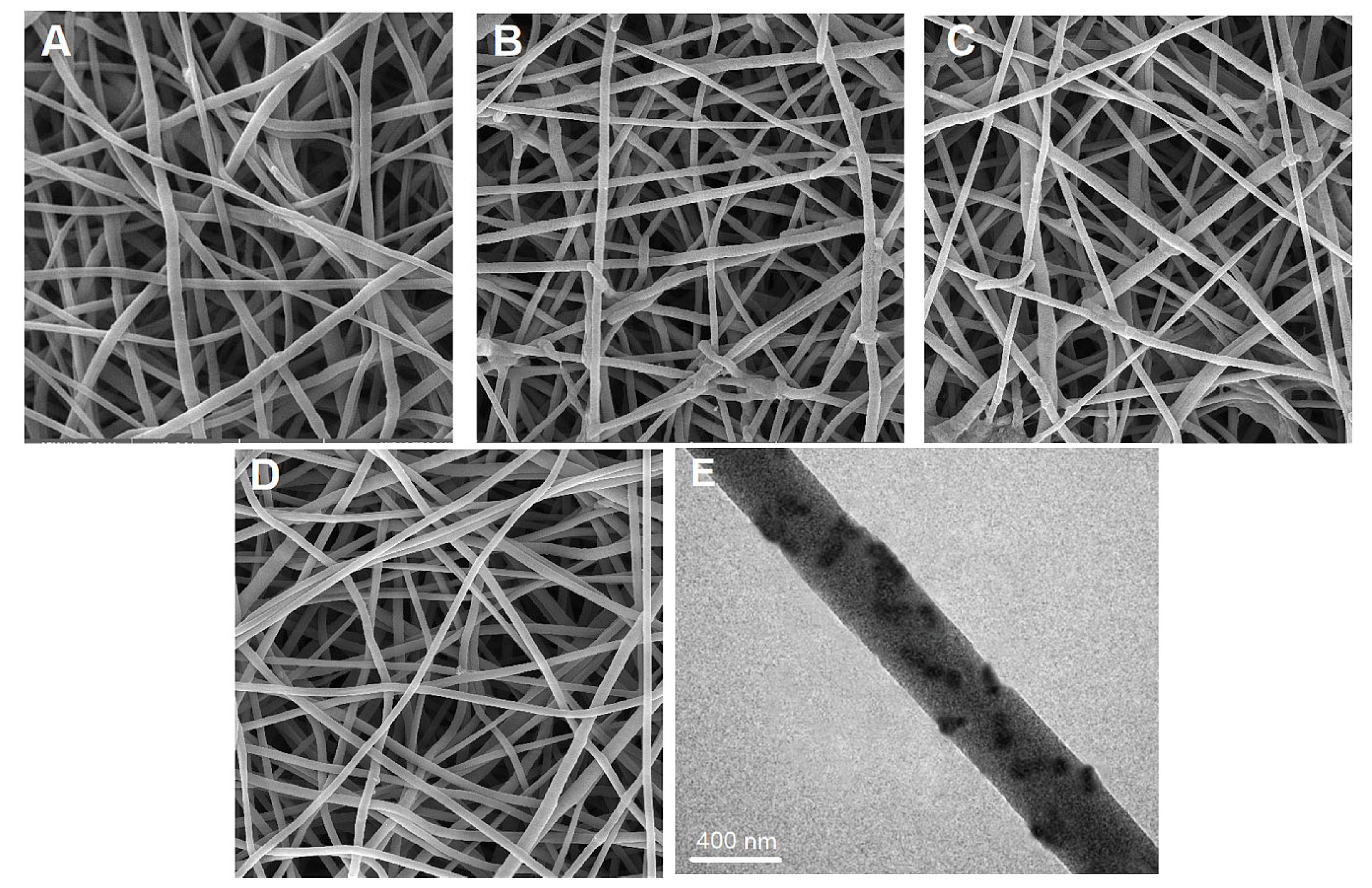



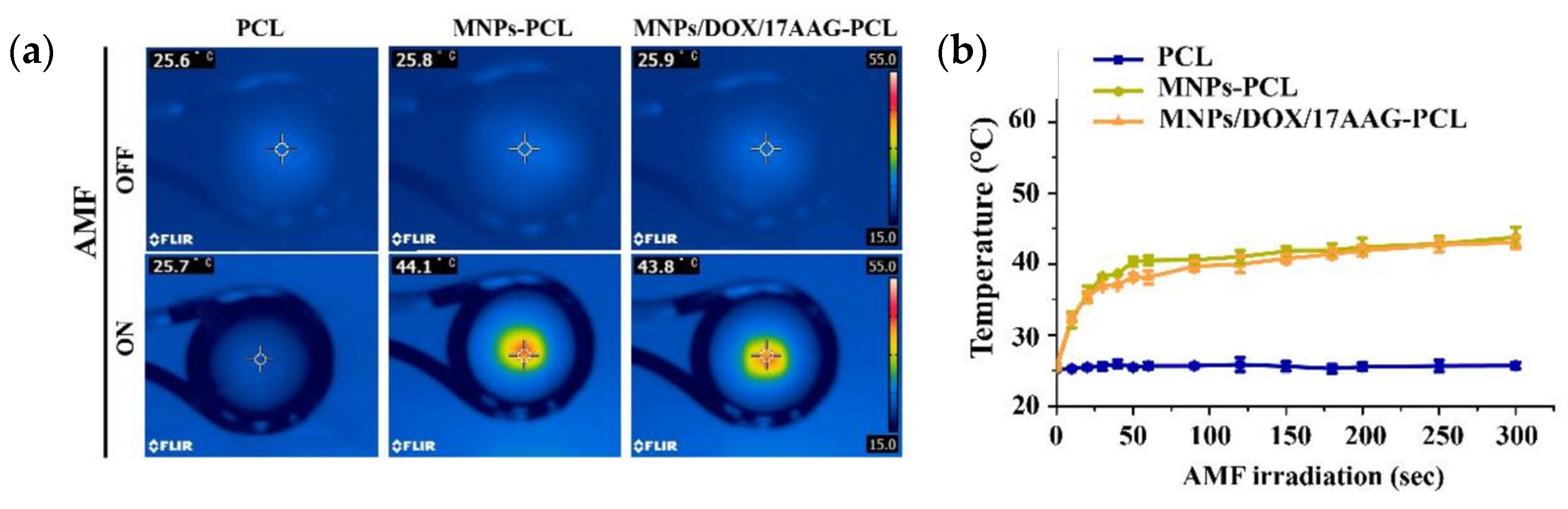

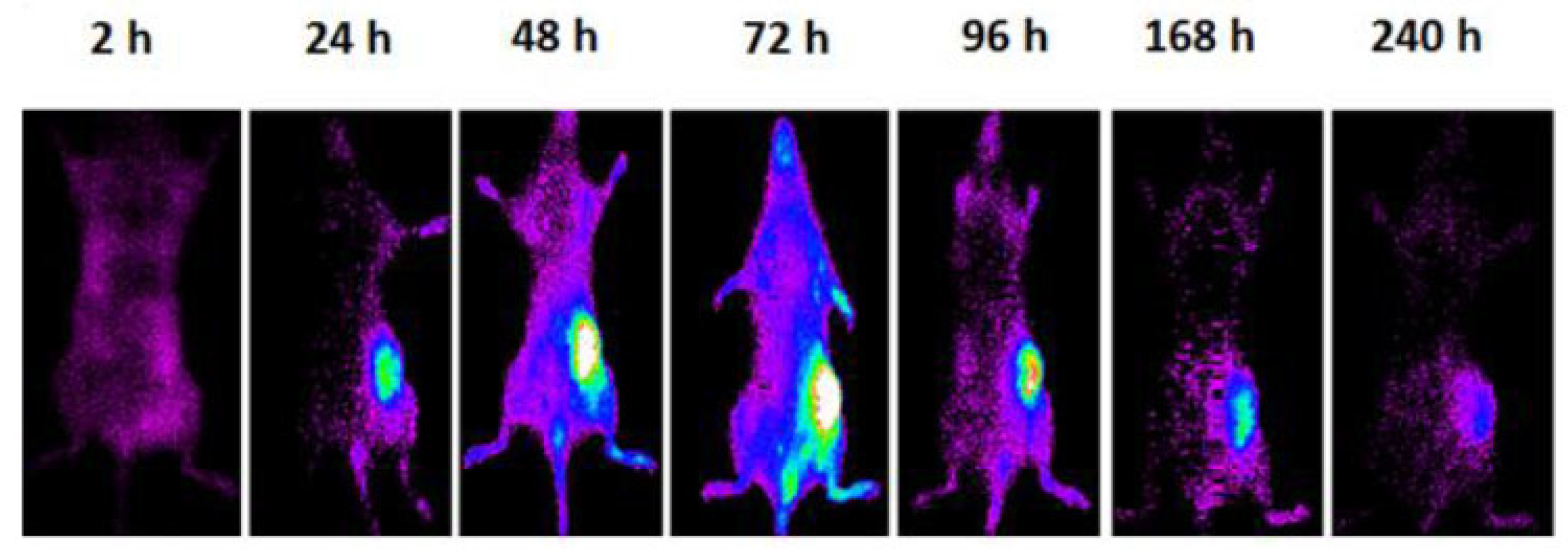
| Fe3O4 (wt%) | ΔT (°C) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 21.0 ± 0.4 |
| 9 | 25.2 ± 0.3 |
| 13 | 27.1 ± 0.5 |
| 17 | 31.1 ± 0.2 |
| 21 | 36.4 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, D.; Araújo, J.C.; Fangueiro, R.; Ferreira, D.P. Localized Therapeutic Approaches Based on Micro/Nanofibers for Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073053
Alves D, Araújo JC, Fangueiro R, Ferreira DP. Localized Therapeutic Approaches Based on Micro/Nanofibers for Cancer Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073053
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Diana, Joana C. Araújo, Raul Fangueiro, and Diana P. Ferreira. 2023. "Localized Therapeutic Approaches Based on Micro/Nanofibers for Cancer Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073053
APA StyleAlves, D., Araújo, J. C., Fangueiro, R., & Ferreira, D. P. (2023). Localized Therapeutic Approaches Based on Micro/Nanofibers for Cancer Treatment. Molecules, 28(7), 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073053









