Recent Advances in Cancer Therapeutic Copper-Based Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Antitumor Bioactivity of Copper Nanomaterials
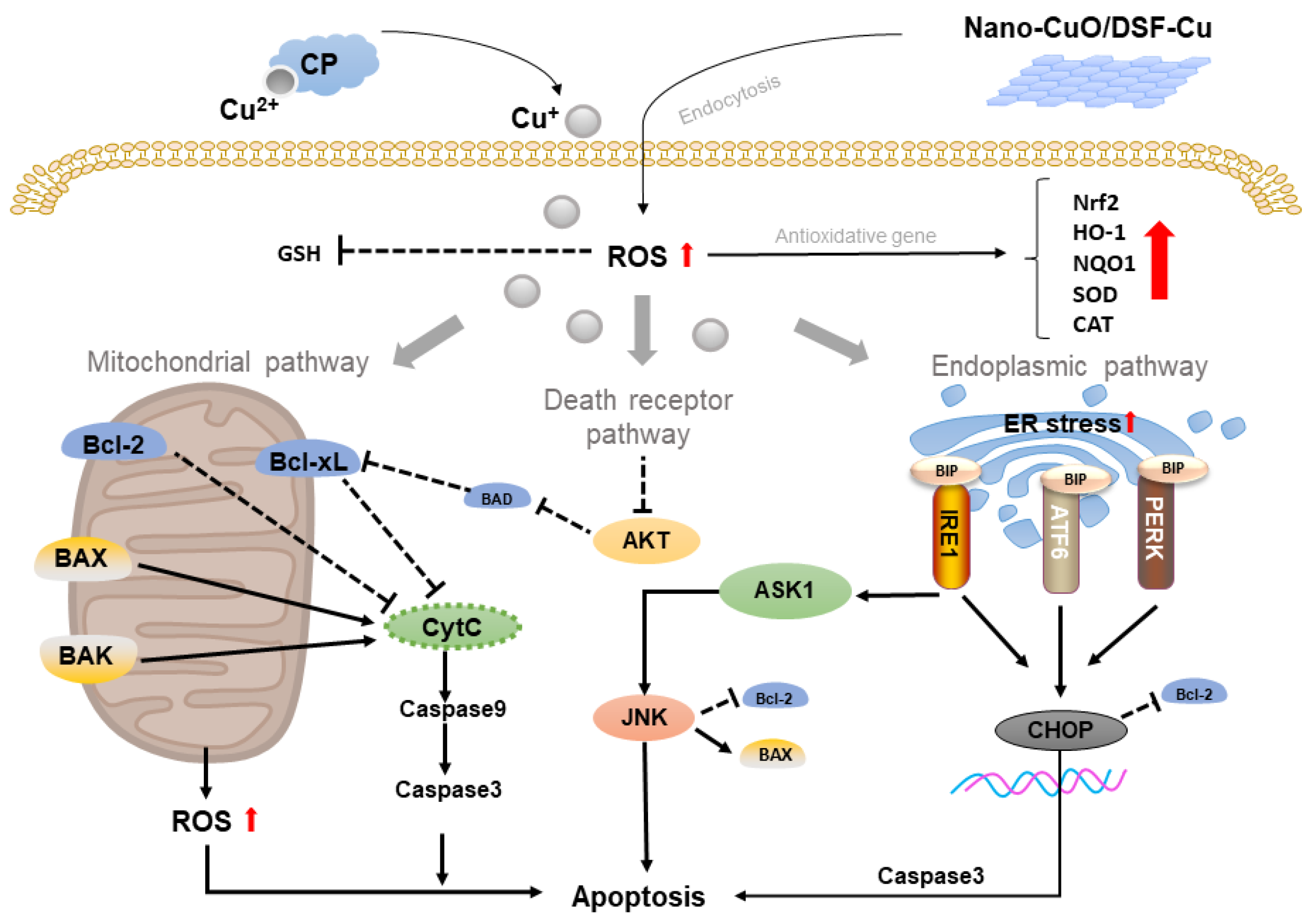
2.1. Copper-Based Apoptosis
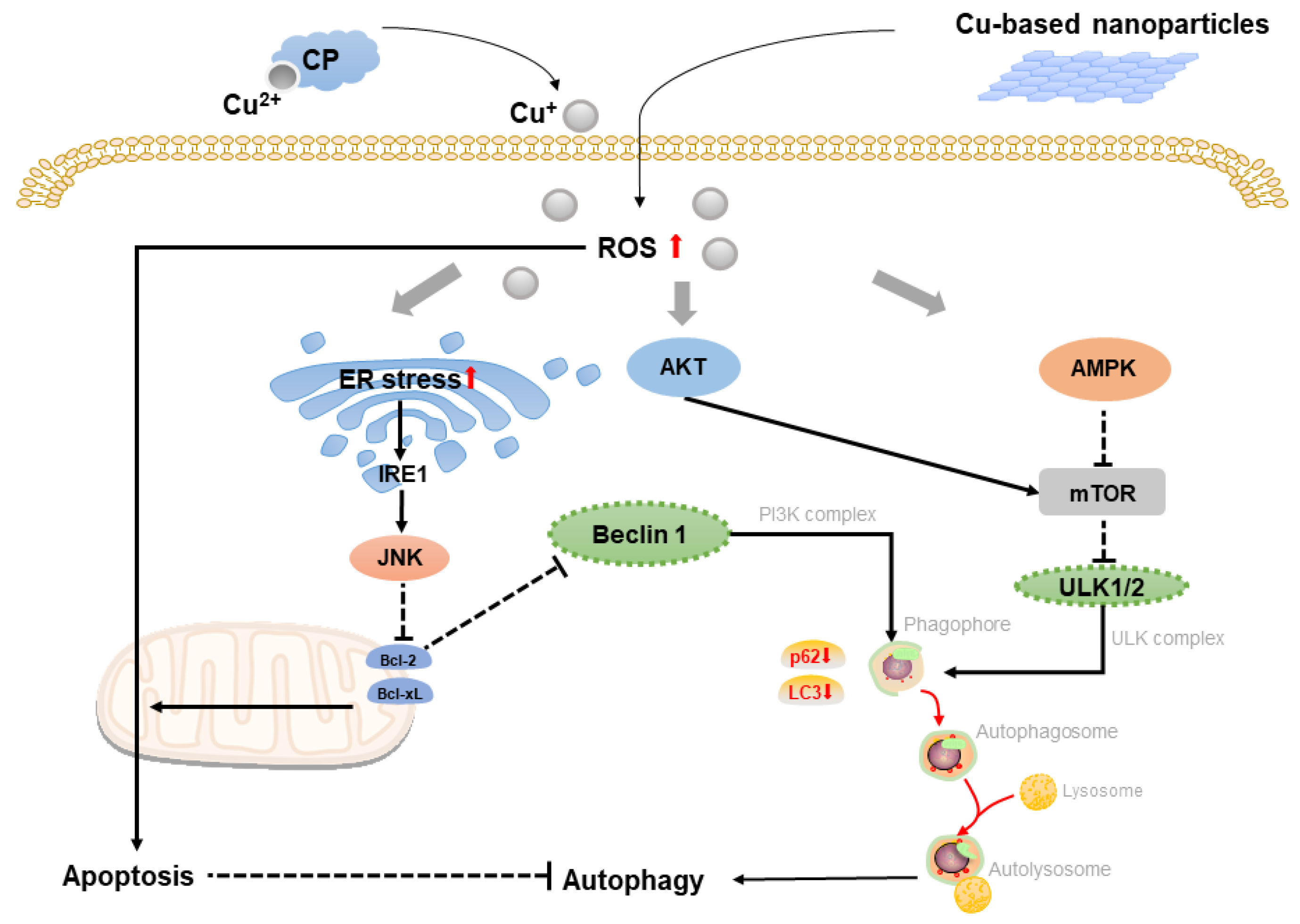
2.2. Copper-Based Autophagy
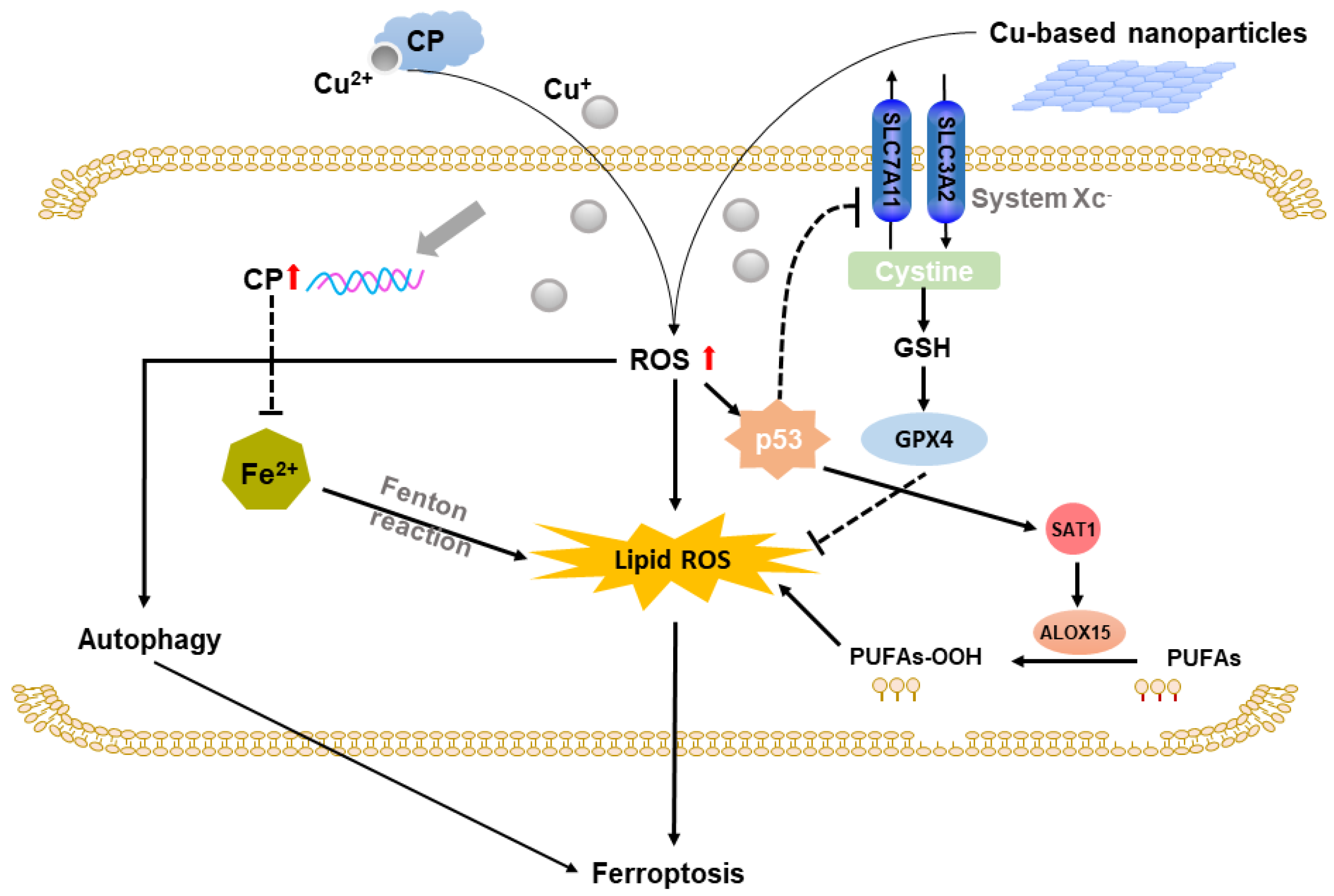
2.3. Copper-Based Ferroptosis
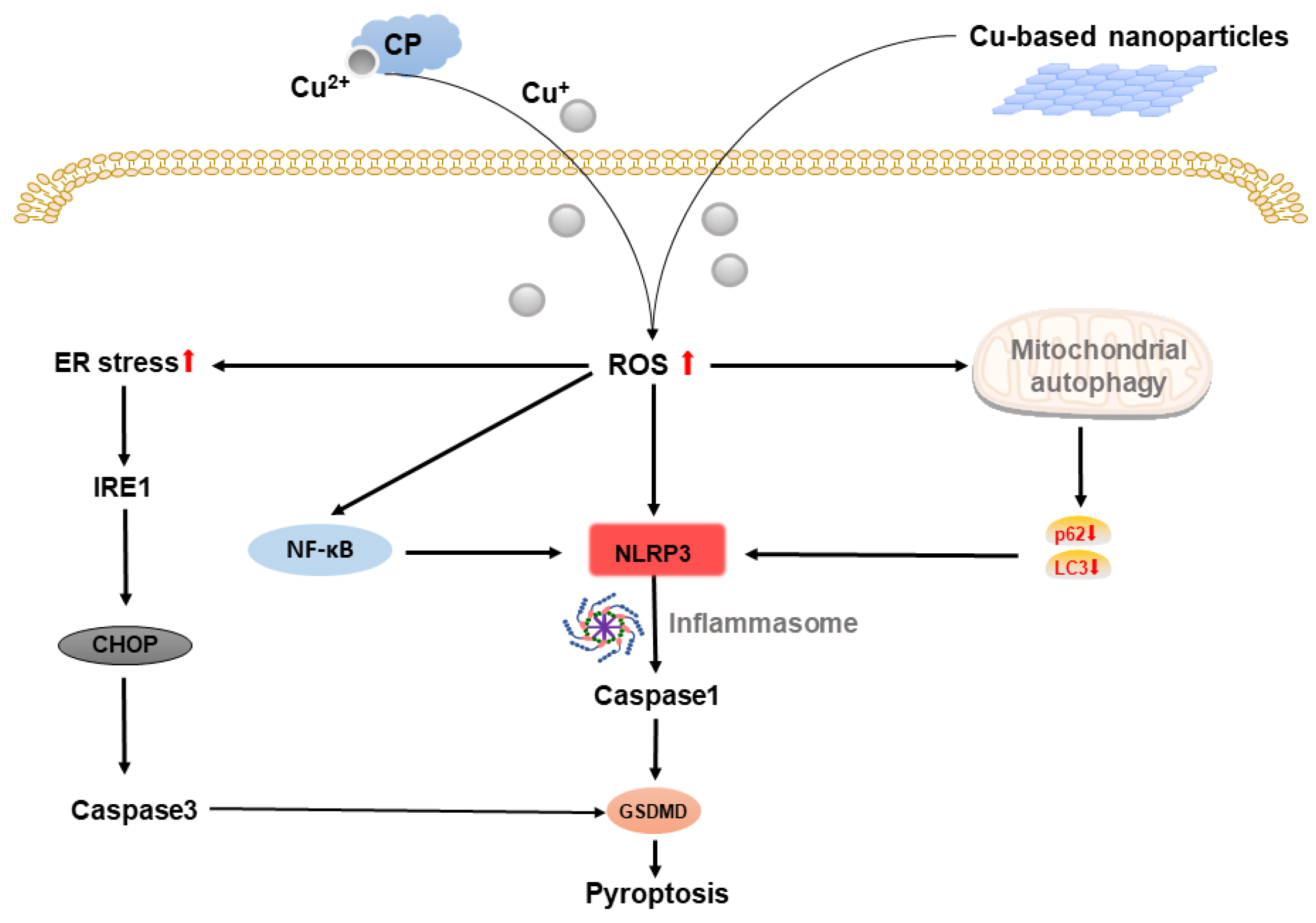
2.4. Copper-Based Pyroptosis
2.5. Copper-Based Paraptosis
2.6. Copper-Based Cuproptosis
3. Multifunctional Applications Based on Copper-Based Cell Death
3.1. Copper-Complexes Chemotherapy
3.2. Chemodynamic Therapy

3.3. Phototherapy
3.3.1. Photodynamic Therapy
3.3.2. Photothermal Therapy
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linder, M.C.; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 797S–811S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, E.I.; Heppner, D.E.; Johnston, E.M.; Ginsbach, J.W.; Cirera, J.; Qayyum, M.; Kieber-Emmons, M.T.; Kjaergaard, C.H.; Hadt, R.G.; Tian, L. Copper Active Sites in Biology. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3659–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lai, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Fang, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, K.; Nie, H.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; et al. Exposure to Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Triggers Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)-Stress Induced Toxicology and Apoptosis in Male Rat Liver and BRL-3A Cell. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polishchuk, E.V.; Merolla, A.; Lichtmannegger, J.; Romano, A.; Indrieri, A.; Ilyechova, E.Y.; Concilli, M.; De Cegli, R.; Crispino, R.; Mariniello, M.; et al. Activation of Autophagy, Observed in Liver Tissues from Patients with Wilson Disease and From ATP7B-Deficient Animals, Protects Hepatocytes from Copper-Induced Apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1173–1189.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, A.; Mumper, R.J. Elevated Copper and Oxidative Stress in Cancer Cells as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.C.; Crowe, M.S.; Turski, M.L.; Hobbs, G.A.; Yao, X.; Chaikuad, A.; Knapp, S.; Xiao, K.; Campbell, S.L.; Thiele, D.J.; et al. Copper Is Required for Oncogenic BRAF Signalling and Tumorigenesis. Nature 2014, 509, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.C.; Crowe, M.S.; Greenberg, D.N.; Counter, C.M. Copper Chelation Inhibits BRAFV600E-Driven Melanomagenesis and Counters Resistance to BRAFV600E and MEK1/2 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gouw, A.M.; LaGory, E.L.; Guo, S.; Attarwala, N.; Tang, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Gao, Z.; Casey, K.M.; et al. Mitochondrial Copper Depletion Suppresses Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Coy, S.; Petrova, B.; Dreishpoon, M.; Verma, A.; Abdusamad, M.; Rossen, J.; Joesch-Cohen, L.; Humeidi, R.; Spangler, R.D.; et al. Copper Induces Cell Death by Targeting Lipoylated TCA Cycle Proteins. Science 2022, 375, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Reconciling the Chemistry and Biology of Reactive Oxygen Species. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of Cancer Cell Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Pleiotropic Physiological Signalling Agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokare, A.D.; Choi, W. Review of Iron-Free Fenton-like Systems for Activating H2O2 in Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Pei, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, J.; Yu, W.; Qiao, N.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Guo, J.; et al. Copper Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway in Chicken Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Vitro 2019, 54, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Song, Y.; Kang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wang, J.; Song, C.; Guo, H. MtROS-Mediated Akt/AMPK/MTOR Pathway Was Involved in Copper-Induced Autophagy and It Attenuates Copper-Induced Apoptosis in RAW264.7 Mouse Monocytes. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; He, E.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Q. The Disulfiram/Copper Complex Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Tumour Growth in Human Osteosarcoma by Activating the ROS/JNK Signalling Pathway. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L. Copper Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis of Hippocampal Neuron via PCREB/BDNF/ and Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, H. Copper Induces Spleen Damage Through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, DNA Damage, and Inflammation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Bi, S.; Deng, M.; Chen, K.; Shi, P.; Feng, L.; He, J.; Pu, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, H.; et al. Disulfiram/Copper Shows Potent Cytotoxic Effects on Myelodysplastic Syndromes via Inducing Bip-Mediated Apoptosis and Suppressing Autophagy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 902, 174107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Luzio, A.; Félix, L.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Serotonergic System Changes in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Gills after Long-Term Exposure to Microplastics and Copper. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 258, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-Eating and Self-Killing: Crosstalk between Autophagy and Apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariño, G.; Niso-Santano, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Self-Consumption: The Interplay of Autophagy and Apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Yin, H.; Cui, H.; Deng, H.; Liu, H.; Jian, Z.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Induction of Autophagy via the ROS-Dependent AMPK-MTOR Pathway Protects Copper-Induced Spermatogenesis Disorder. Redox Biol. 2022, 49, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Zhu, H.; Sheng, F.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, J. Activation of the MAPK11/12/13/14 (P38 MAPK) Pathway Regulates the Transcription of Autophagy Genes in Response to Oxidative Stress Induced by a Novel Copper Complex in HeLa Cells. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.; Posimo, J.M.; Gudiel, A.A.; Cicchini, M.; Feldser, D.M.; Brady, D.C. Copper Is an Essential Regulator of the Autophagic Kinases ULK1/2 to Drive Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, C. Lysosomal Deposition of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Triggers HUVEC Cells Death. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Qiu, W.; Li, Z. Inhibiting Autophagy Flux and DNA Repair of Tumor Cells to Boost Radiotherapy of Orthotopic Glioblastoma. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Solís, C.; Jimenez-Farfan, D.; Rodriguez-Enriquez, S.; Fernandez-Valverde, F.; Cruz-Salgado, A.; Ruiz-Azuara, L.; Sotelo, J. Copper Compound Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis of Glioma Cells by Reactive Oxygen Species and JNK Activation. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis Turns 10: Emerging Mechanisms, Physiological Functions, and Therapeutic Applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2401–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Kim, K.J.; Gaschler, M.M.; Patel, M.; Shchepinov, M.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Peroxidation of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Lipoxygenases Drives Ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4966–E4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Chan, S.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Disulfiram/Copper Induces Antitumor Activity against Both Nasopharyngeal Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts through ROS/MAPK and Ferroptosis Pathways. Cancers 2020, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, W.; Yang, C.; Jing, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Overcoming the Compensatory Elevation of NRF2 Renders Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells More Vulnerable to Disulfiram/Copper-Induced Ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Liao, L.; et al. COMMD10 Inhibits HIF1α/CP Loop to Enhance Ferroptosis and Radiosensitivity by Disrupting Cu-Fe Balance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Dai, C.; Hu, R.; Ding, L.; Feng, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, J.; Chen, Y. Engineering Dual Catalytic Nanomedicine for Autophagy-Augmented and Ferroptosis-Involved Cancer Nanotherapy. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Gao, W.; Shao, F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, R. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Cell Death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2114–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Tian, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yu, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, Y.; Ma, P.; et al. Pyroptosis: A New Frontier in Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-K.; Li, C.-Y.; Lin, I.-L.; Syue, W.-J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Cheng, K.-C.; Teng, Y.-N.; Lin, Y.-H.; Yen, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-C. Inflammation-Related Pyroptosis, a Novel Programmed Cell Death Pathway, and Its Crosstalk with Immune Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8813–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deigendesch, N.; Zychlinsky, A.; Meissner, F. Copper Regulates the Canonical NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Gao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tong, H.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Cheng, N.; et al. Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Prevents Copper-Induced Neuropathology in a Murine Model of Wilson’s Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L. Copper Induces Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation through ROS/NF-ΚB Pathway and Mitophagy Disorder. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 168, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C. The Unfolded Protein Response: Controlling Cell Fate Decisions under ER Stress and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Cui, J.; Meng, X.; Jiang, P.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Cell Death and Tumor: Association between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Apoptosis Pathway in Tumors. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardito, S.; Bassanetti, I.; Bignardi, C.; Elviri, L.; Tegoni, M.; Mucchino, C.; Bussolati, O.; Franchi-Gazzola, R.; Marchiò, L. Copper Binding Agents Acting as Copper Ionophores Lead to Caspase Inhibition and Paraptotic Cell Death in Human Cancer Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6235–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Huo, H.; Han, Q.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Hu, L.; et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Contributes to Copper-Induced Pyroptosis via Regulating the IRE1α-XBP1 Pathway in Pig Jejunal Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J. Programmed Cell Death, Redox Imbalance, and Cancer Therapeutics. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubah, O.C.; Wallace, H.M. Cancer Therapy: Targeting Mitochondria and Other Sub-Cellular Organelles. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.W.G.; Ichim, G.; Green, D.R. Die Another Way—Non-Apoptotic Mechanisms of Cell Death. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; Shiloh, Y. Programs for Cell Death: Apoptosis Is Only One Way to Go. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, C.; Pellei, M.; Colavito, D.; Alidori, S.; Lobbia, G.G.; Gandin, V.; Tisato, F.; Santini, C. Synthesis, Characterization, and in Vitro Antitumor Properties of Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Phosphine Copper(I) Complexes Containing the New Bis(1,2,4-Triazol-1-Yl)Acetate Ligand. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7317–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, C.; Gandin, V.; Pellei, M.; Colavito, D.; Papini, G.; Lobbia, G.G.; Del Giudice, E.; Porchia, M.; Tisato, F.; Santini, C. In Vitro Antitumor Activity of the Water Soluble Copper(I) Complexes Bearing the Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Phosphine Ligand. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardito, S.; Isella, C.; Medico, E.; Marchiò, L.; Bevilacqua, E.; Hatzoglou, M.; Bussolati, O.; Franchi-Gazzola, R. The Thioxotriazole Copper(II) Complex A0 Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Paraptotic Death in Human Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24306–24319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, V.; Pellei, M.; Tisato, F.; Porchia, M.; Santini, C.; Marzano, C. A Novel Copper Complex Induces Paraptosis in Colon Cancer Cells via the Activation of ER Stress Signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, V.; Tisato, F.; Dolmella, A.; Pellei, M.; Santini, C.; Giorgetti, M.; Marzano, C.; Porchia, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Anticancer Activity of Copper(I) Complexes with Homoscorpionate Tridentate Tris(Pyrazolyl)Borate and Auxiliary Monodentate Phosphine Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4745–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Hinokitiol Copper Complex Inhibits Proteasomal Deubiquitination and Induces Paraptosis-like Cell Death in Human Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 815, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, W.; Chen, P.; Huang, Y.; Li, F. Disulfiram Copper Nanoparticles Prepared with a Stabilized Metal Ion Ligand Complex Method for Treating Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41118–41128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Gao, W.; Pu, Y.; He, B. Reversal of Cisplatin Chemotherapy Resistance by Glutathione-Resistant Copper-Based Nanomedicine via Cuproptosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6296–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.-Y.; Zeng, L.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. An Enzyme-Engineered Nonporous Copper(I) Coordination Polymer Nanoplatform for Cuproptosis-Based Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2204733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Tian, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Luo, M.; Ding, N.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. Brain-Targeted HFn-Cu-REGO Nanoplatform for Site-Specific Delivery and Manipulation of Autophagy and Cuproptosis in Glioblastoma. Small 2022, 19, e2205354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, C.; Pellei, M.; Gandin, V.; Porchia, M.; Tisato, F.; Marzano, C. Advances in Copper Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 815–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clioquinol and Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Complex with Copper to Form Proteasome Inhibitors and Apoptosis Inducers in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Research. Available online: https://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/bcr1322 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Chen, D.; Peng, F.; Cui, Q.C.; Daniel, K.G.; Orlu, S.; Liu, J.; Dou, Q.P. Inhibition of Prostate Cancer Cellular Proteasome Activity by a Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate-Copper Complex Is Associated with Suppression of Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milacic, V.; Chen, D.; Giovagnini, L.; Diez, A.; Fregona, D.; Dou, Q.P. Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate-Zinc(II) and -Copper(II) Complexes Induce Apoptosis in Tumor Cells by Inhibiting the Proteasomal Activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 231, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-H.; Lin, J.-K.; Liang, Y.-C.; Pan, M.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y. Involvement of Activating Transcription Factors JNK, NF-KappaB, and AP-1 in Apoptosis Induced by Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate/Cu Complex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 594, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; An, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; You, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B. A CD44-Targeted Cu(II) Delivery 2D Nanoplatform for Sensitized Disulfiram Chemotherapy to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 8139–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Balash, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. In Situ Triggering Antitumor Efficacy of Alcohol-Abuse Drug Disulfiram through Cu-Based Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2016–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Bu, W. Chemodynamic Therapy: Tumour Microenvironment-Mediated Fenton and Fenton-like Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, T. Chemodynamic Therapy Combined with Multifunctional Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Tumor Treatment. Chemistry 2021, 27, 13953–13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Sun, B. Glutathione-Triggered Nanoplatform for Chemodynamic/Metal-Ion Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9413–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Duan, J.; Li, Z.; Kong, Y.; Sang, Y.; Liu, H.; Bu, W.; et al. Self-Assembled Copper-Amino Acid Nanoparticles for in Situ Glutathione “AND” H2O2 Sequentially Triggered Chemodynamic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, A.; Ma, W.; Ma, K.; Lv, Y.-K.; Peng, P.; Zang, S.-Q.; Li, B. Atom-Precise Fluorescent Copper Cluster for Tumor Microenvironment Targeting and Transient Chemodynamic Cancer Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.-Y.; Jia, C.-P.; Mo, A.-N.; Liang, H.; Chen, Z.-F. Chemodynamic Therapy Agents Cu(II) Complexes of Quinoline Derivatives Induced ER Stress and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in SK-OV-3 Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Cheng, Y.; Qi, F.; Wu, Y.; Han, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H. Biodegradable Copper-Based Nanoparticles Augmented Chemodynamic Therapy through Deep Penetration and Suppressing Antioxidant Activity in Tumors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bian, Y.; Liang, S.; Yuan, M.; Dong, S.; He, F.; Gai, S.; Yang, P.; Cheng, Z.; Lin, J. One-Step Integration of Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Calcium and Copper Peroxides Nanocomposite for Enhanced Chemodynamic/Ion-Interference Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-H.; Li, C.-Q.; Hou, X.-L.; Xie, X.-T.; Zhang, B.; Wu, G.-Y.; Jin, F.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Liu, B. Tumor Microenvironment-Activated Theranostics Nanozymes for Fluorescence Imaging and Enhanced Chemo-Chemodynamic Therapy of Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55780–55789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.-Y.; Jia, C.-P.; Liao, L.-Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Hou, C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liang, H.; Chen, Z.-F. Copper(II) Complexes of Halogenated Quinoline Schiff Base Derivatives Enabled Cancer Therapy through Glutathione-Assisted Chemodynamic Therapy and Inhibition of Autophagy Flux. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 5134–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
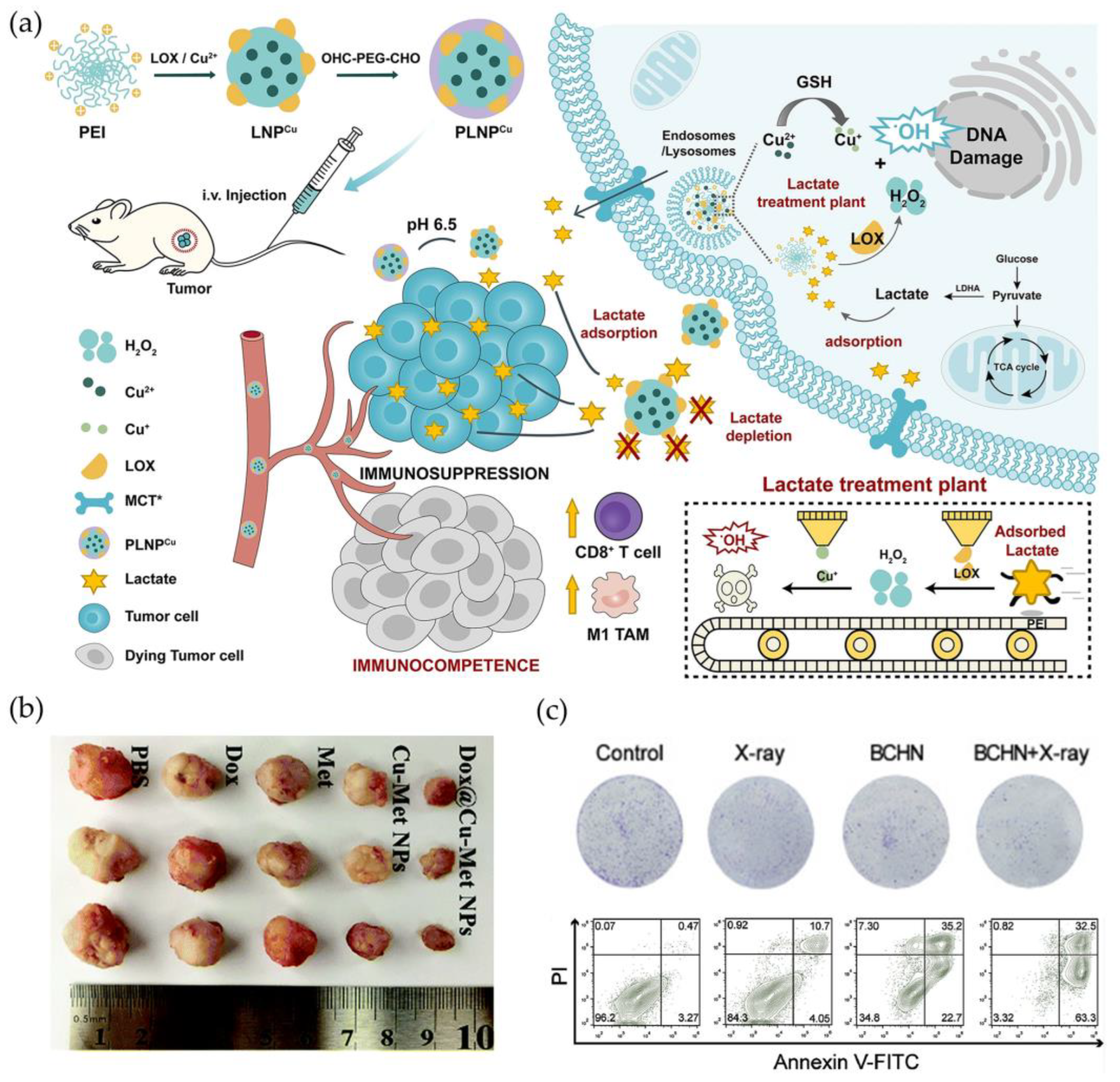
- He, R.; Zang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zheng, X.; Chong, G.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Nanofactory for Metabolic and Chemodynamic Therapy: Pro-Tumor Lactate Trapping and Anti-Tumor ROS Transition. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Zhang, L.-M.; Liu, C.-C.; Wu, Q.-N.; Li, S.-P.; Lei, X.-P.; Huang, Y.-G.; Feng, G.-N.; Yu, X.-Y.; Sun, X.-Q.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Hydrogen Peroxide Self-Providing Copper Nanodots for Combination of Chemotherapy and Acid-Induced Chemodynamic Therapy against Breast Cancer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 593, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-H.; Wan, Y.; Qi, C.; He, J.; Li, C.; Yang, C.; Xu, H.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Nanocatalytic Theranostics with Glutathione Depletion and Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Species Generation for Efficient Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Cao, D.; Wang, Z. Biodegradable Copper-Metformin Nanoscale Coordination Polymers for Enhanced Chemo/Chemodynamic Synergistic Therapy by Reducing Oxygen Consumption to Promote H2O2 Accumulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1988–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Song, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Ouyang, R.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Biodegradable BiOCl Platform for Oxidative Stress Injury-Enhanced Chemodynamic/Radiation Therapy of Hypoxic Tumors. Acta Biomater. 2021, 129, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Birge, R.R. Protein-Based Artificial Retinas. Trends Biotechnol. 1993, 11, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Xia, Z.; Guo, S. Recent Advances on Black Phosphorus for Biomedicine and Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsher, D.W. Cancer Revoked: Oncogenes as Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Song, J.; Nie, L.; Chen, X. Reactive Oxygen Species Generating Systems Meeting Challenges of Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6597–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, J.; Guo, S. Triplet Photosensitizers: From Molecular Design to Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5323–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Primo, F.L.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Copper-Doped Carbon Dots for Optical Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 13394–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Hou, C.; Ding, Z.; Wen, C.; Zhang, L.-J.; Jiang, B.-P.; Shen, X.-C. A Chloroplast-Inspired Nanoplatform for Targeting Cancer and Synergistic Photodynamic/Photothermal Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocakoglu, K.; Er, Ö.; Yurt Lambrecht, F.; Yılmaz Süslüer, S.; Kayabasi, C.; Gündüz, C.; Yılmaz, O. Evaluation of Cancer Imaging Potential and Photodynamic Therapy Efficacy of Copper (II) Benzyloxypheophorbide-a. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-M.; Akram, W.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Liao, Y.-H.; Ye, Y.; Liu, H.-Y. DNA Interaction and Photodynamic Antitumor Activity of Transition Metal Mono-Hydroxyl Corrole. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.-K.; Chiu, C.-I.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-J.; Venkatesan, P.; Huang, P.-H.; Lai, P.-S.; Lin, C.-C. Photocytotoxic Copper(II) Complexes with Schiff-Base Scaffolds for Photodynamic Therapy. Chemistry 2018, 24, 4111–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yin, W.; Xu, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.; Tan, C.; Dai, Z.; et al. Ultrathin 2D Copper(I) 1,2,4-Triazolate Coordination Polymer Nanosheets for Efficient and Selective Gene Silencing and Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Pandey, N.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Amador, E.H.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Xiao, E.; et al. Study of Copper-Cysteamine Based X-ray Induced Photodynamic Therapy and Its Effects on Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration in a Clinical Mimic Setting. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 7, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Li, Y.; Younis, M.R.; Fu, L.-H.; He, T.; Lei, S.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Synthetic Biology-Instructed Transdermal Microneedle Patch for Traceable Photodynamic Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles: From Sensors to Theranostics. Small 2014, 10, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, Q.; Yu, Z.; Gao, X.; Pan, W.; Wan, X.; Tang, B. Nuclear-Targeted Photothermal Therapy Prevents Cancer Recurrence with Near-Infrared Triggered Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5197–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, Y.; Du, S.; Wu, Y.; Shen, P.; Yan, T.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Zha, Z.; Han, X. Controlled CRISPR-Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Delivery for Sensitized Photothermal Therapy. Small 2021, 17, e2101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Adachi, M.; Wen, X.; Erwin, B.; Mawlawi, O.; Lai, S.Y.; Li, C. Single Agent Nanoparticle for Radiotherapy and Radio-Photothermal Therapy in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Biomaterials 2015, 57, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yang, K.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, P.; Jia, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, X.; Han, X. Synergistic Photothermal Cancer Immunotherapy by Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein-Based Copper Sulfide Nanotherapeutic Platform Targeting PTPN2. Biomaterials 2021, 279, 121233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, W.; Xu, Z.; Si, Y.; Li, Q.; Qi, X.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tian, G. CuO Dot-Decorated Cu@Gd2O3 Core-Shell Hierarchical Structure for Cu(i) Self-Supplying Chemodynamic Therapy in Combination with MRI-Guided Photothermal Synergistic Therapy. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Su, Z.; Wang, C. Tailored Surfaces on 2D Material: UFO-Like Cyclodextrin-Pd Nanosheet/Metal Organic Framework Janus Nanoparticles for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Guan, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Meng, X.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhou, S. Defective Porous Carbon Polyhedra Decorated with Copper Nanoparticles for Enhanced NIR-Driven Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Small 2020, 16, e1905184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aishajiang, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D. Recent Advances in Cancer Therapeutic Copper-Based Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy. Molecules 2023, 28, 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052303
Aishajiang R, Liu Z, Wang T, Zhou L, Yu D. Recent Advances in Cancer Therapeutic Copper-Based Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052303
Chicago/Turabian StyleAishajiang, Reyida, Zhongshan Liu, Tiejun Wang, Liang Zhou, and Duo Yu. 2023. "Recent Advances in Cancer Therapeutic Copper-Based Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052303
APA StyleAishajiang, R., Liu, Z., Wang, T., Zhou, L., & Yu, D. (2023). Recent Advances in Cancer Therapeutic Copper-Based Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy. Molecules, 28(5), 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052303







