Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
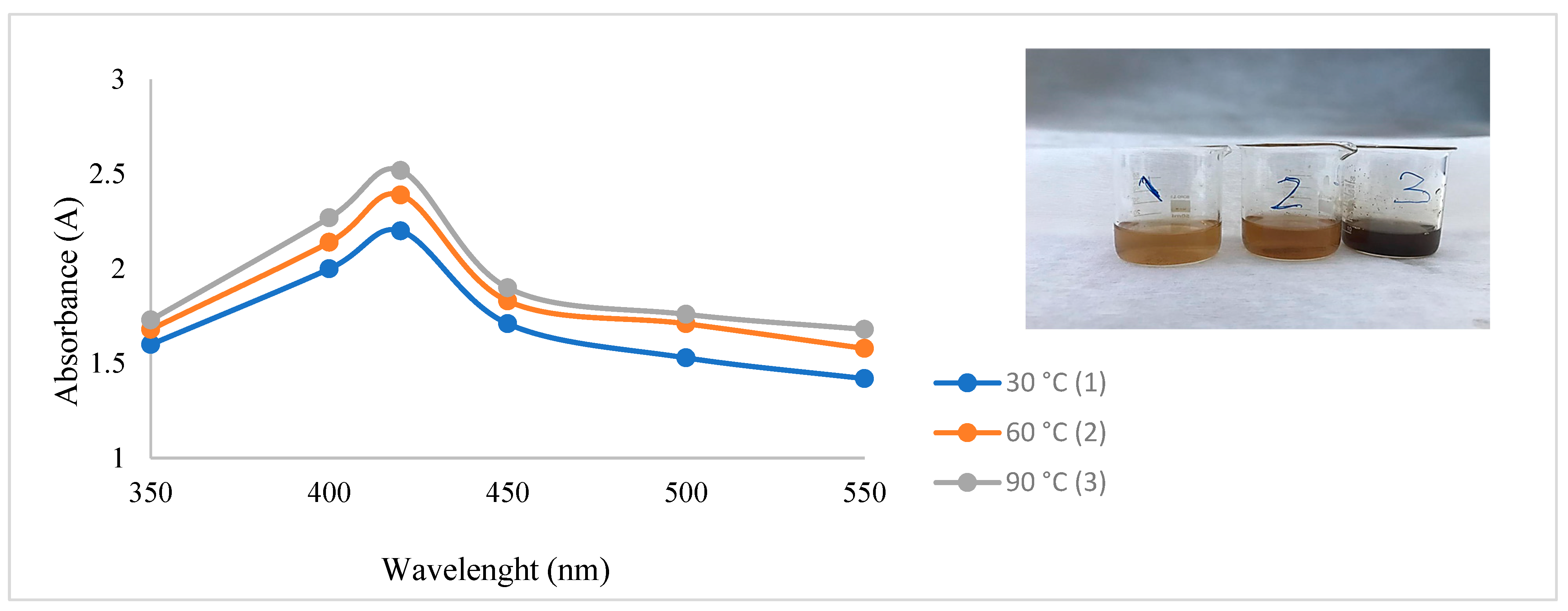
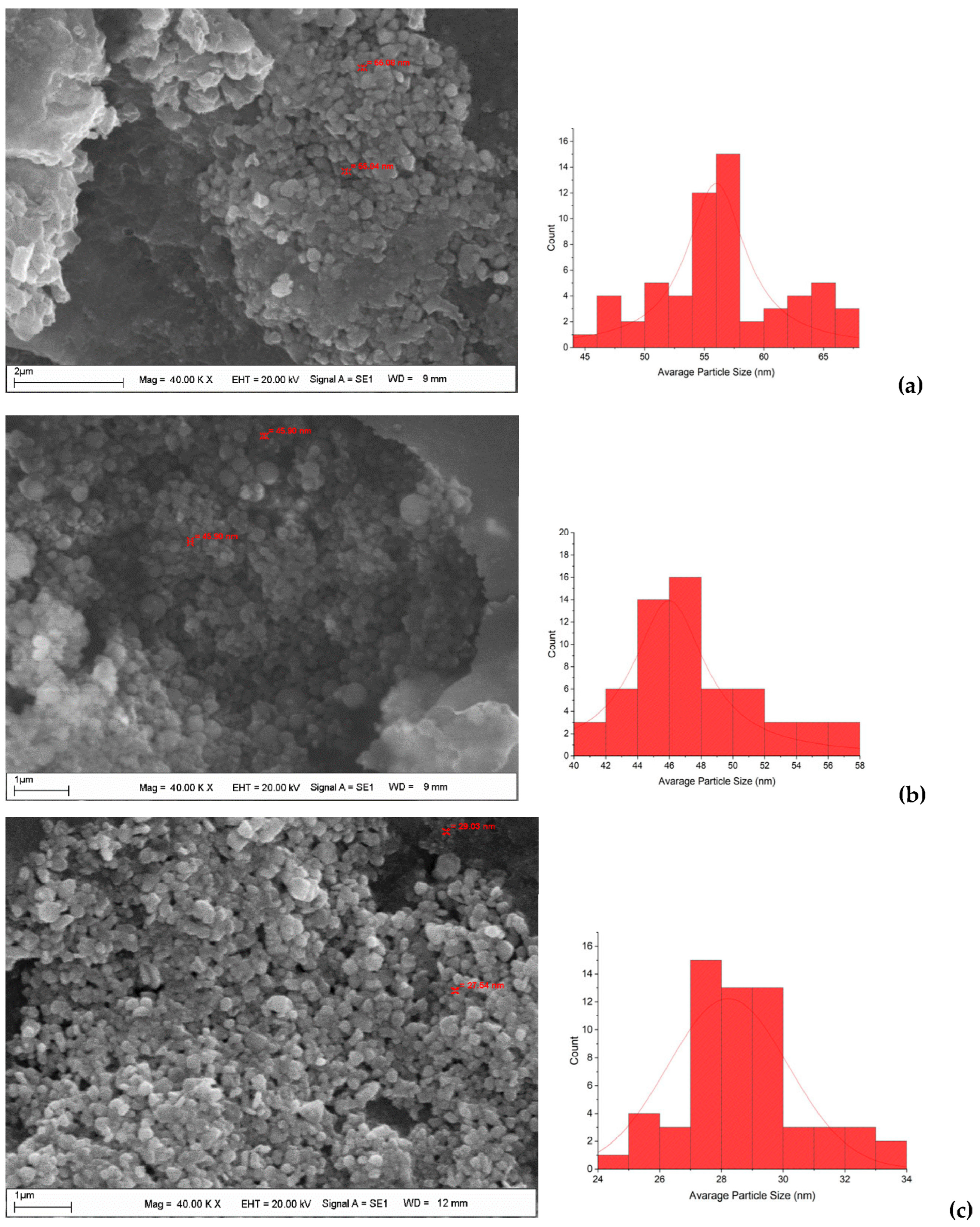
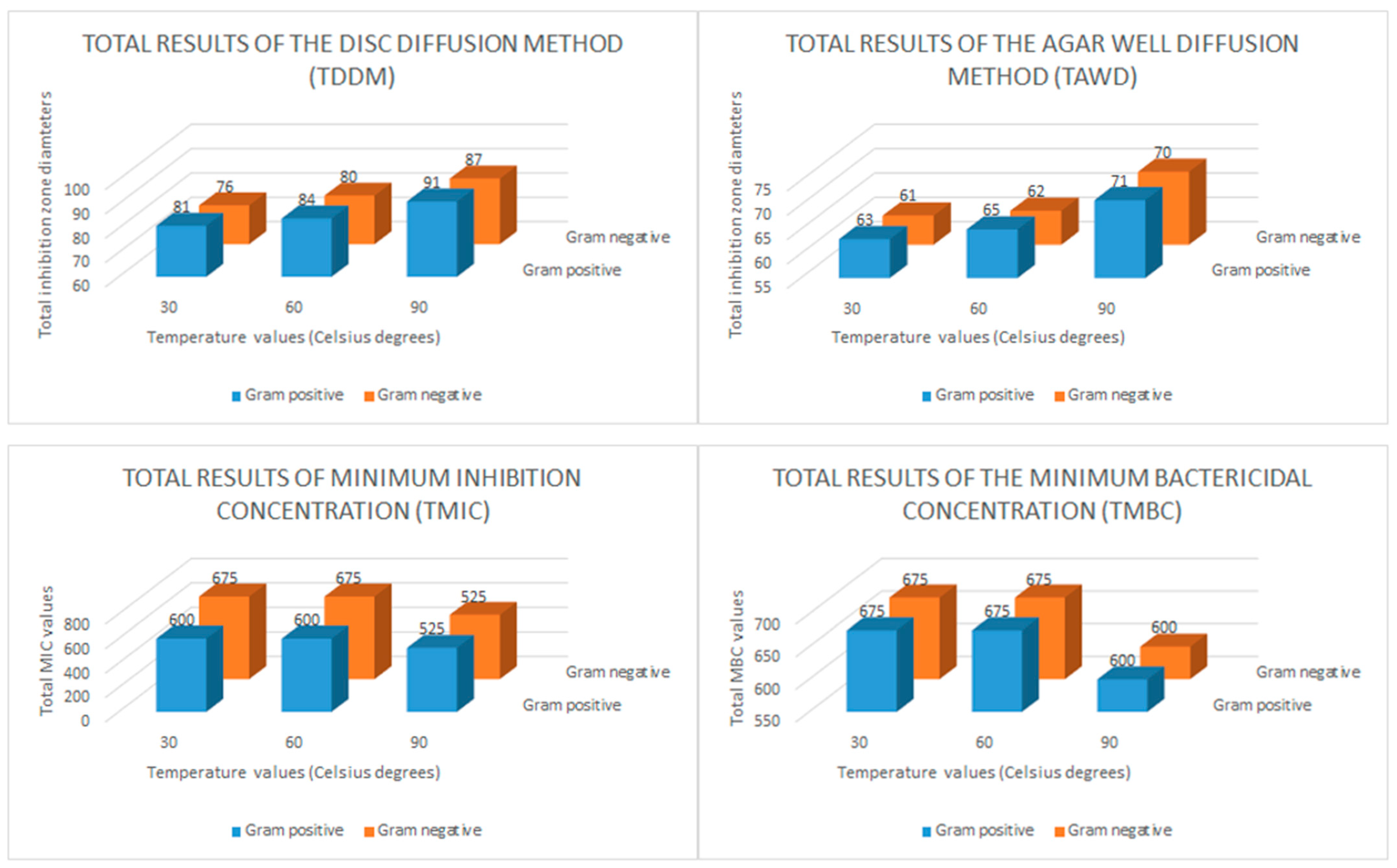
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Green Synthesis of Chestnut (Castanea Sativa) Honey-Based Silver Nanoparticles (CH-AgNPs)
4.2. Characterization of CH-AgNPs
4.3. The Total Phenolic Content of Chestnut (Castanea Sativa) Honey Extract and CH-AgNPs
4.4. DPPH·Free Radical Scavenging Activity
4.5. Collagenase Inhibition
4.6. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Inhibition
4.7. Antibacterial Activity
4.7.1. Microorganisms and Growth Conditions
4.7.2. The Disk Diffusion Method (DDM)
4.7.3. The Agar Well Diffusion Method (AWD)
4.7.4. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.7.5. The Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bedlovičová, Z.; Strapáč, I.; Baláž, M.; Salayová, A. A brief overview on antioxidant activity determination of silver nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from seed extract of Brassica nigra and its antibacterial activity. Nusant. Biosci. 2015, 7, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröfel, A.; Kratošová, G.; Šafařík, I.; Šafaříková, M.; Raška, I.; Shor, L.M. Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles–a review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Lin, Z.H.; Ma, X.X. Evidence of the production of silver nanoparticles via pretreatment of Phoma sp. 3.2883 with silver nitrate. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, S.; Joseph, S.; Koshy, E.P.; Mathew, B. Green synthesis and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles using Mussaenda glabrata leaf extract and their environmental applications to dye degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 17347–17357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, S.; Pennemann, H.; Schonfeld, F. Theoretical and experimental characterization of a low-Reynolds number split-and-recombine mixer. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2006, 2, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Mourato, C.; Sanches, S.; Noronha, J.P.; Crespo, M.B.; Pereira, I.A. Biogenic platinum and palladium nanoparticles as new catalysts for the removal of pharmaceutical compounds. Water Res. 2017, 108, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiny, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. DNA damage and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis of A549 lung carcinoma cells induced by biosynthesised silver and platinum nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27775–27787. [Google Scholar]
- Longoria, E.C.; Velasquez, S.M.; Nestor, A.V.; Berumen, E.A.; Borja, M.A. Production of platinum nanoparticles and nanoaggregates using Neurospora crassa. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, K.; Nazir, S.; Ahmad, A.; Li, B.; Khan, A.U.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Rahman, A.U. Facile and green synthesis of phytochemicals capped platinum nanoparticles and in vitro their superior antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2017, 166, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Kim, B.S. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallela, P.N.V.K.; Ummey, S.; Ruddaraju, L.K.; Pammi, S.V.N.; Yoon, S.G. Ultra Small, mono dispersed green synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Sida cordifolia plant and investigation of antibac-terial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 124, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, G.H.; Akyüz, G.; Kaymazlar, E.; Andac, M. An Investigation of green synthesis of silver nanoparti-cles using Turkish honey against pathogenic bacterial strains. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, R.; Chandran, K.; Harper, S.L.; Yun, S.I.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Plant extract synthesized silver nanopar-ticles: An ongoing source of novel biocompatible materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.A.; Ripari, N.; Conte, F.L.; da Silva Honorio, M.; Sartori, A.A.; Matucci, R.H.; Sforcin, J.M. An overview about apitherapy and its clinical applications. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolayli, S.; Keskin, M. Natural bee products and their apitherapeutic applications. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2020, 66, 175–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoncelj, J.; Doberšek, U.; Jamnik, M.; Golob, T. Evaluation of the phenolic content, antioxidant activity and colour of Slovenian honey. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernel, G.; Bloch, D.; Matwijczuk, A.; Cieśla, J.; Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Florek, M.; Gagoś, M. Biodirected synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous honey solutions and evaluation of their antifungal activity against pathogenic Candida spp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, S.; Karlidag, S.; Mayda, N.; Ozkok, A. Comparison of biochemical and antimicrobial activities of different honey samples. Czech J. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badet, C.; Quero, F. The in vitro effect of manuka honeys on growth and adherence of oral bacteria. Clin. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, S.; Jafari Najafabadi, F.; Zarepour, A.; Zarrabi, A. Is Astragalus gossypinus honey a natural antibacterial and cytotoxic agent? An investigation on A. gossypinus honey biological activity and its green synthesized silver nanoparticles. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deeb, N.M.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; El-Aassara, M.R.; Hafez, E.E. Novel trend in colon cancer therapy using silver nanoparticles synthesized by honey bee. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 265. [Google Scholar]
- González Fá, A.J.; Juan, A.; Di Nezio, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles prepared with honey: The role of carbohydrates. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiza, H.; Azizan, A.; Mohidin, A.H.; Halin, D.S.C. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using local honey. Nano Hybrids 2017, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Honey mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghramh, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Kilany, M. Study of anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and silver nanoparticles production by Sidr honey from three different sources. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikar, S.K.; Giri, D.D.; Pal, D.B.; Mishra, P.K.; Upadhyay, S.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A review. Green Sustain. Chem. 2016, 6, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in photosynthetic plants. J. Nanopart. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, P.; Koh, S.; Anniyev, T.; Greeley, J.; More, K.; Yu, C. Lattice-strain control of the activity in de alloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, R.; Rizwana, K.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Ultra-rapid photocatalytic activity of Azadirachta indica engineered colloidal titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci. 2014, 5, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Umoren, S.A.; Johnson, A.S. Sunlight- mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using honey and its promising anticorrosion potentials for mild steel in acidic environments. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.; Nawaz, S.; Jan, H.; Uddin, N.; Ali, A.; Anjum, S.; Abbasi, B.H. Synthesis of bio-mediated silver nanoparticles from Silybum marianum and their biological and clinical activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayguna, A.; Gülbagcaa, F.; Ozerb, L.Y.; Ustaogluc, B.; Altunogluc, Y.C.; Balogluc, M.C.; Atalard, M.N.; Almae, M.H.; Sena, F. Biogenic platinum nanoparticles using black cumin seed and their potential usage as antimicrobial and anticancer agent. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depciuch, J.; Stec, M.; Maximenko, A.; Drzymała, E.; Pawlyta, M.; Baran, J.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. Synthesis method-dependent photothermal e_ects of colloidal solutions of platinumnanoparticles used in photothermal anticancer therapy. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2020, 34, e5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Aygün, A.; Gündüz, H.; Sahin, K.; Demir, E.; Akocak, S.; Sen, F. Cytotoxic effects of platinum nanoparticles obtained from pomegranate extract by the green synthesis method on the MCF-7 cell line. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venu, R.; Ramulu, T.S.; Anandakumar, S.; Rani, V.S.; Kim, C.G. Bio-directed synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using aqueous honey solutions and their catalytic applications. Colloid Surf. A 2011, 384, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, B.; Muthukumarasamy, A.; Chidambaram, S.; Sugumaran, A.; Ramachandran, K.; Rasu Manimuthu, T. Cytotoxic potentials of biologically fabricated platinum nanoparticles from Streptomyces sp. on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, V.S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Prakash, S.; Ahila, N.K.; Vinoj, G.; Selvam, S.; Kumar, G.; Kannapiran, E.; Rajendran, R.B. Synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using seaweed Padina gymnospora and their catalytic activity as PVP/PtNPs nanocomposite towards biological applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami-Shabani, M.; Gholami-Shabani, Z.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Riazi, G.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. Biogenic Approach using Sheep Milk for the Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles: The Role ofMilk Protein in Platinum Reduction and Stabilization. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, P.; Shim, J.; Kim, K.; Oh, B.T. Prunus yedoensis tree gum mediated synthesis of platinumnanoparticles with antifungal activity against phytopathogens. Mater. Lett. 2016, 174, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, K.; Miotto, D.; Kim, L.; Sjaarda, C.; Maldonado-Alvarez, L.; Fukś, H. Active macromolecules of honey form colloidal particles essential for honey antibacterial activity and hydrogen peroxide production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balciunaitiene, A.; Viskelis, P.; Viskelis, J.; Streimikyte, P.; Liaudanskas, M.; Bartkiene, E.; Lele, V. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of Artemisia absinthium L., Humulus lupulus L. and Thymus vulgaris L., physico-chemical characterization, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. Processes 2021, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Sharma, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extracts of Ananas comosus. Green Sustain. Chem. 2012, 2, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Brahim, J.S.; Mohammed, A.E. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and antibacterial potentials of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using bee’s honey from two different floral sources in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desouky, T.A.; Ammar, H.A. Honey mediated silver nanoparticles and their inhibitory effect on aflatoxins and ochratoxin A. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 083–090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Balaji, K.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venkatesan, R. Fungal based synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An effect of temperature on the size of particles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 74, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Madhu, G.; John, E.; Kuttinarayanan, S.V.; Nair, S.K. Optical and antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized via green route using honey. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Mankad, V.; Gupta, S.K.; Jha, P.K. Size distribution of silver nanoparticles: UV-visible spectroscopic assessment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2012, 4, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Zaka, M.; Hashmi, S.S.; Khan, Z. Biogenic synthesis of Au, Ag and Au–Ag alloy nanoparticles using Cannabis sativa leaf extract. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Nazir, M.; Muhammad, W.; Hashmi, S.S.; Abbasi, R.; Rahman, L.; Hano, C. A comparative evaluation of the antiproliferative activity against Hepg2 liver carcinoma cells of plant-derived silver nanoparticles from basil extracts with contrasting anthocyanin contents. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Narasimha, G.; Dillip, G.R.; Praveen, B.; Shreedhar, B.; Lakshmi, C.S.; Raju, B.D.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum leaf extract and their characterization. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2011, 6, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Shameli, K.; Bin Ahmad, M.; Jaffar Al-Mulla, E.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Shabanzadeh, P.; Rustaiyan, A.; Zidan, M. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Callicarpa maingayi stem bark extraction. Molecules 2012, 17, 8506–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic-Pasti, T.; Leskovac, A.; Vasic, V. Myeloperoxidase inhibitors as potential drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 168–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.H.; Roberts, N.A.; Borkakoti, N. Collagenase inhibitors: Their design and potential therapeutic use. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1987, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.B.; Długosz, O.; Sałaga, M.; Banach, M.; Fichna, J. Silver nanoparticles based on blackcurrant extract show potent anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and in DSS-induced colitis in mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, R.A.; El-Sherif, Y.A.; Salama, M.M. A novel biochemical study of anti-ageing potential of Eucalyptus camaldulensis bark waste standardized extract and silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 191, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, H.; Zaman, G.; Usman, H.; Ansir, R.; Drouet, S.; Gigliolo-Guivarc’h, N.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Biogenically proficient synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) employing aqueous extract of Aquilegia pubiflora along with their in vitro antimicrobial, anti-cancer and other biological applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 950–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamer, S.; Romli, M.H.; Che-Hamzah, F.; Misni, N.; Joseph, N.M.; Al-Haj, N.A.; Amin-Nordin, S. Systematic review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and antibacterial activities: Application and theoretical perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Hano, C.; Nath, G.; Sharma, B. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Carissa carandas L. and their antioxidant and antimicrobial activity against human pathogenic bacteria. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Daneu, N.; Baláž, M.; Lukáčová Bujňáková, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using various medicinal plant extracts: Morphology and antibacterial efficacy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadhasan, M.; SankarBabu, V.R.; Naresh, R.; Umamaheswari, K.; Rajendiran, N. A sunlight-induced rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using sodium salt of N-cholyl amino acids and its antimicrobial applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 96, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, S.M.; Aiad, I.; El-Sukkary, M.M.; Soliman, E.A.; El-Awady, M.Y. Preparation of capped silver nanoparticles using sunlight and cationic surfactants and their biological activity. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeggi, U.M.; Badmus, J.A.; Botha, S.S.; Ismail, E.; Marnewick, J.L.; Africa, C.W.; Hussein, A.A. Biosynthesis, Characterization, and Biological Activities of Procyanidin Capped silver nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, S.S.; Dogiparthi, L.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Givotia moluccana leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 2018, 226, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Kaya, G.; Keskin, Ş. Green synthesis and biochemical properties of propolis based silver nanoparticles. Uludağ Arıcılık Dergisi 2022, 22, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiji, M.; Anagha, P.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Sunlight mediated rapid synthesis of small size range silver nanoparticles using Zingiber officinale rhizome extract and its antibacterial activity analysis. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2018, 48, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio Natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, M.; Muju, G.; Anantharaman, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Platymonas sp. and its antibacterial activity against biofouling causing bacterial strains. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2019, 9, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Baran, M.F.; Keskin, C.; Hatipoğlu, A.; Yavuz, Ö.; İrtegün Kandemir, S.; Eftekhari, A. Investigation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties and specification of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) gerived from Cicer arietinum L. green leaf extract. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, M. Synthesis, characterization and antidiabetic potential of bee pollen based silver nanoparticles. El-Cezeri 2022, 9, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M. Humulus lupulus L.(Hop) Based silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and enzyme inhibition effects. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2022, 21, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic—phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Meth. Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Cuendet, M.; Hostettmann, K.; Potterat, O. Iridoid glucosides with free radical scavenging properties from Fagraea blumei. Helv. Chim. Acta 1997, 80, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, P.B.; Tawata, S. Anti-oxidant, anti-aging, and anti-melanogenic properties of the essential oils from two varieties of Alpinia zerumbet. Molecules 2015, 20, 16723–16740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.M.; Pepato, M.T.; Brunetti, I.L. Free radical scavenging profile and myeloperoxidase inhibition of extracts from antidiabetic plants: Bauhinia for ficata and Cissus sicyoides. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, O.; Dolan, A.; Athman, R.; Power, A.; Gethin, G.; Cowman, S.; Humphreys, H. Comparison of the antimicrobial activity of Ulmo honey from Chile and Manuka honey against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, M.H. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlıdağ, S.; Keskin, M.; Bayram, S.; Mayda, N.; Özkök, A. Honey: Determination of volatile compounds, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Czech J. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecem-Bayram, N.; Yüzer, M.O.; Bayram, S. Melissopalynology analysis, physicochemical properties, multi-element content and antimicrobial activity of honey samples collected from Bayburt, Turkey. Uludag Bee J. 2019, 19, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Osés, S.M.; Pascual-Maté, A.; de la Fuente, D.; de Pablo, A.; Fernández-Muiño, M.A.; Sancho, M.T. Comparison of methods to determine antibacterial activity of honeys against Staphylococcus aureus. NJAS-Wagen. J. Life Sci. 2016, 78, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecem Bayram, N.; Çebi, N.; Çelik, S.; Gerçek, Y.C.; Bayram, S.; Tanuğur Samancı, A.E.; Özkök, A. Turkish royal jelly: Amino acid, physicochemical, antioxidant, multi-elemental, antibacterial and fingerprint profiles by analytical techniques combined with chemometrics. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
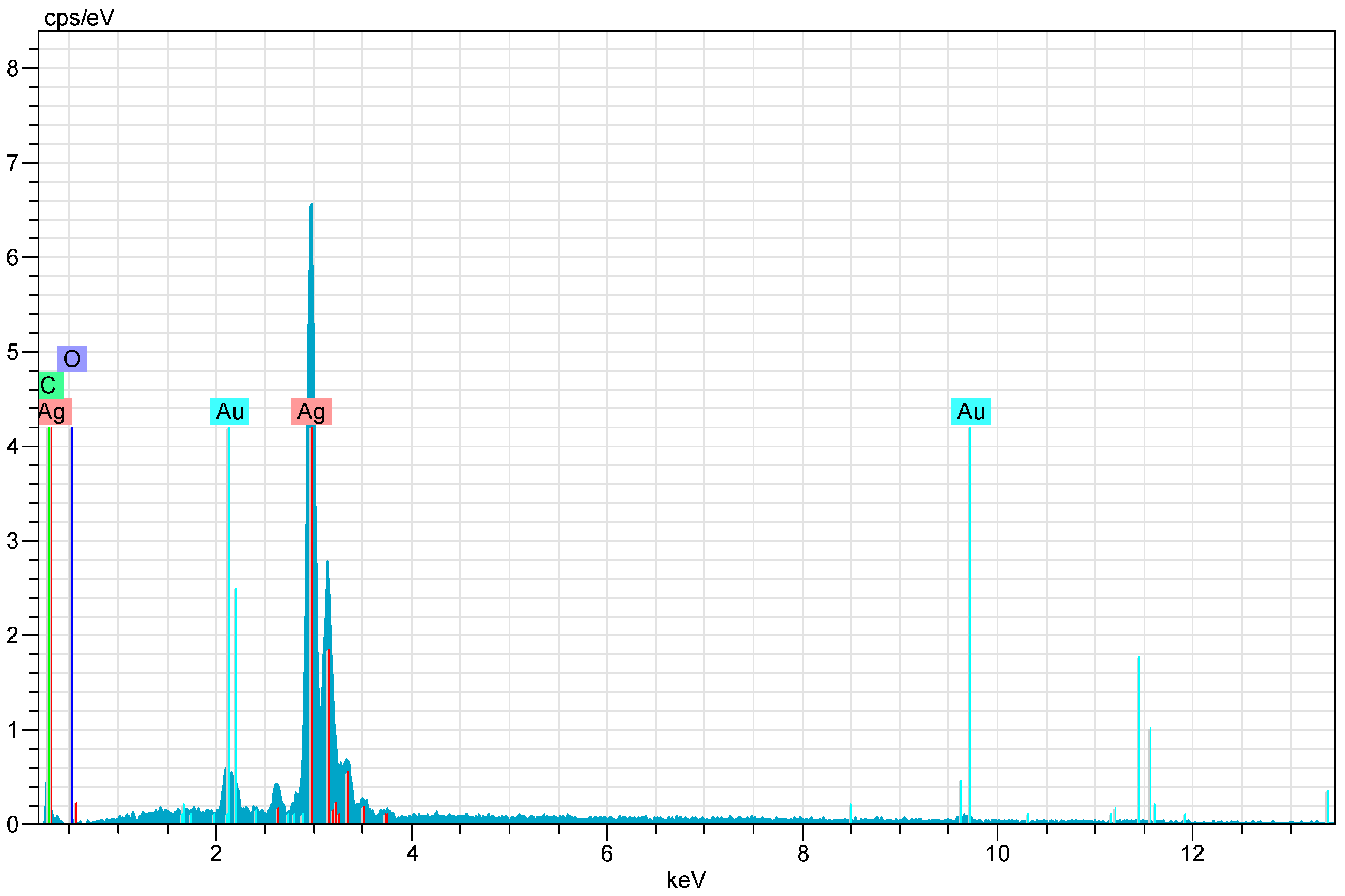

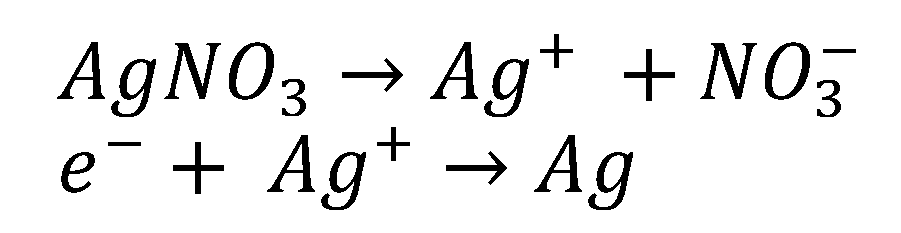
| El | AN | Series | unn. | C Norm. | C Atom. | C Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [wt.-%] | [wt.-%] | [at.-%] | [%] | |||
| Ag | 47 | L-series | 81.90 | 93.46 | 62.67 | 2.6 |
| C | 6 | K-series | 4.54 | 5.18 | 31.21 | 1.2 |
| O | 8 | K-series | 1.19 | 1.35 | 6.12 | 1.0 |
| Total: | 87.62 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||
| Peak Number | C. Honey Extract (cm−1) | 30 °C (cm−1) | 60 °C (cm−1) | 90 °C (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3275.35 | 3311.38 | 3324.14 | 3324.24 |
| 2 | 2935.82 | 2123.57 | 2117.04 | 2115.78 |
| 3 | 1644.03 | 1635.25 | 1635.17 | 1635.46 |
| 4 | 1416.61 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 1345.16 | - | - | - |
| 6 | 1258.26 | - | - | - |
| 7 | 1026.85 | - | - | - |
| 8 | 919.27 | - | - | - |
| 9 | 866.04 | - | - | - |
| 10 | 818.12 | - | - | - |
| 11 | 777.56 | - | - | - |
| 12 | 701.08 | - | - | - |
| Total Phenolic Content (mg GAE/g) | DPPH·IC50 Value (mg/mL) | Collagenase Inhibition (%) | Myloperoxidase Inhibition (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honey extract | 1.21 ± 0.02 a | 21.37 ± 0.01 a | 60.0 ± 1.4 a | 30.0 ± 1.0 a |
| CH-AgNPs (30 °C) | 0.92 ± 0.01 b | 15.08 ± 0.02 b | 68.7 ± 1.1 b | 34.0 ± 1.1 b |
| CH-AgNPs (60 °C) | 0.87 ± 0.01 c | 14.67 ± 0.01 c | 71.4 ± 1.3 c | 35.2 ± 1.0 c |
| CH-AgNPs (90 °C) | 0.84 ± 0.01 d | 13.71 ± 0.02 d | 74.2 ± 1.1 d | 36.4 ± 1.2 d |
| Trolox | - | 0.009 ± 0.001 | - | - |
| Oleanolic acid | - | - | 28.4 ± 1.98 | - |
| Quercetin | - | - | - | 48.6 ± 1.1 |
| Plant or Biological Source | Reaction Conditions | Average Size (nm) | Shape | Biomedical Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nigella sativa (black cumin, seeds) | 75 °C; 2 days | 3.47 | Spherical | Anticancer activity against human breast (MDA-MB-231) and cervical (HeLa) cancer cells Bactericidal against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria | [35] |
| Green tea (powder extract) | 50 °C; 4 h | 2 | Spherical | Anticancer activity against two human colon cancer cell lines (SW480 and SW620) | [36] |
| Punica granatum (pomegranate, crusts) | Room temperature Ultrasonication 24 h | 20.12 | Spherical and cubes | Antiproliferation effect and enhanced apoptosis against human breast adenocarcinoma cell line (MCF-7) | [37] |
| Honey | 100 °C for 2 and 4 h | 2.2 | Nanowires | --- | [38] |
| Streptomyces species (Gram-positive bacteria) | 50 °C; 24 h | 20–50 | Spherical | Anticancer activity against human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7) | [39] |
| Padina gymnospora (brown algae) | room temperature for 10 min | 5–50 | Truncated octahedral | Bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli, Lactococcus lactis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae | [40] |
| Sheep milk | room temperature for 3 h. | 9 | Spherical | --- | [41] |
| Prunus x yedoensis (gum extract) | pH 8; gum extract concentrations of 7% and 8% 30 min | 10–50 | Spherical | Antifungal against Colletotrichum acutatum and Cladosporium fulvum | [42] |
| MICROORGANISMS | Honey Extract (100 mg/mL) | CH-AgNPs (30 °C) | CH-AgNPs (60 °C) | CH-AgNPs (90 °C) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDM | AWD | MIC | MBC | DDM | AWD | MIC | MBC | DDM | AWD | MIC | MBC | DDM | AWD | MIC | MBC | ||
| Gram positive | B. cereus ATCC 14579 | - | - | - | - | 15 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 15 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 17 | 13 | 150 | 150 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 49452 | - | - | - | - | 14 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 16 | 12 | 150 | 150 | 16 | 12 | 150 | 150 | |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | - | - | - | - | 16 | 13 | 150 | 150 | 16 | 13 | 75 | 150 | 18 | 14 | 75 | 150 | |
| S. mutans ATCC 35668 | - | - | - | - | 18 | 14 | 75 | 75 | 19 | 15 | 75 | 75 | 20 | 16 | 75 | 75 | |
| S. salivarus ATCC 13419 | - | - | - | - | 18 | 14 | 75 | 150 | 18 | 14 | 150 | 150 | 20 | 16 | 75 | 75 | |
| Gram negative | A. baumannii ATCC BA1609 | - | - | - | - | 14 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 15 | 12 | 150 | 150 | 17 | 13 | 150 | 150 |
| E. coli ATCC BAA 25–23 | - | - | - | - | 15 | 12 | 150 | 150 | 16 | 12 | 150 | 150 | 18 | 14 | 75 | 150 | |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 9070 | - | - | - | - | 14 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 15 | 11 | 150 | 150 | 15 | 12 | 150 | 150 | |
| S. Typhimurium RSSK 95091 | - | - | - | - | 17 | 14 | 75 | 75 | 18 | 14 | 75 | 75 | 19 | 16 | 75 | 75 | |
| Y. enterocolitica ATCC 27729 | - | - | - | - | 16 | 13 | 150 | 150 | 16 | 13 | 150 | 150 | 18 | 15 | 75 | 75 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keskin, M.; Kaya, G.; Bayram, S.; Kurek-Górecka, A.; Olczyk, P. Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062762
Keskin M, Kaya G, Bayram S, Kurek-Górecka A, Olczyk P. Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062762
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeskin, Merve, Gülşen Kaya, Sinan Bayram, Anna Kurek-Górecka, and Paweł Olczyk. 2023. "Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062762
APA StyleKeskin, M., Kaya, G., Bayram, S., Kurek-Górecka, A., & Olczyk, P. (2023). Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules, 28(6), 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062762










