Smart Responsive Microneedles for Controlled Drug Delivery
Abstract
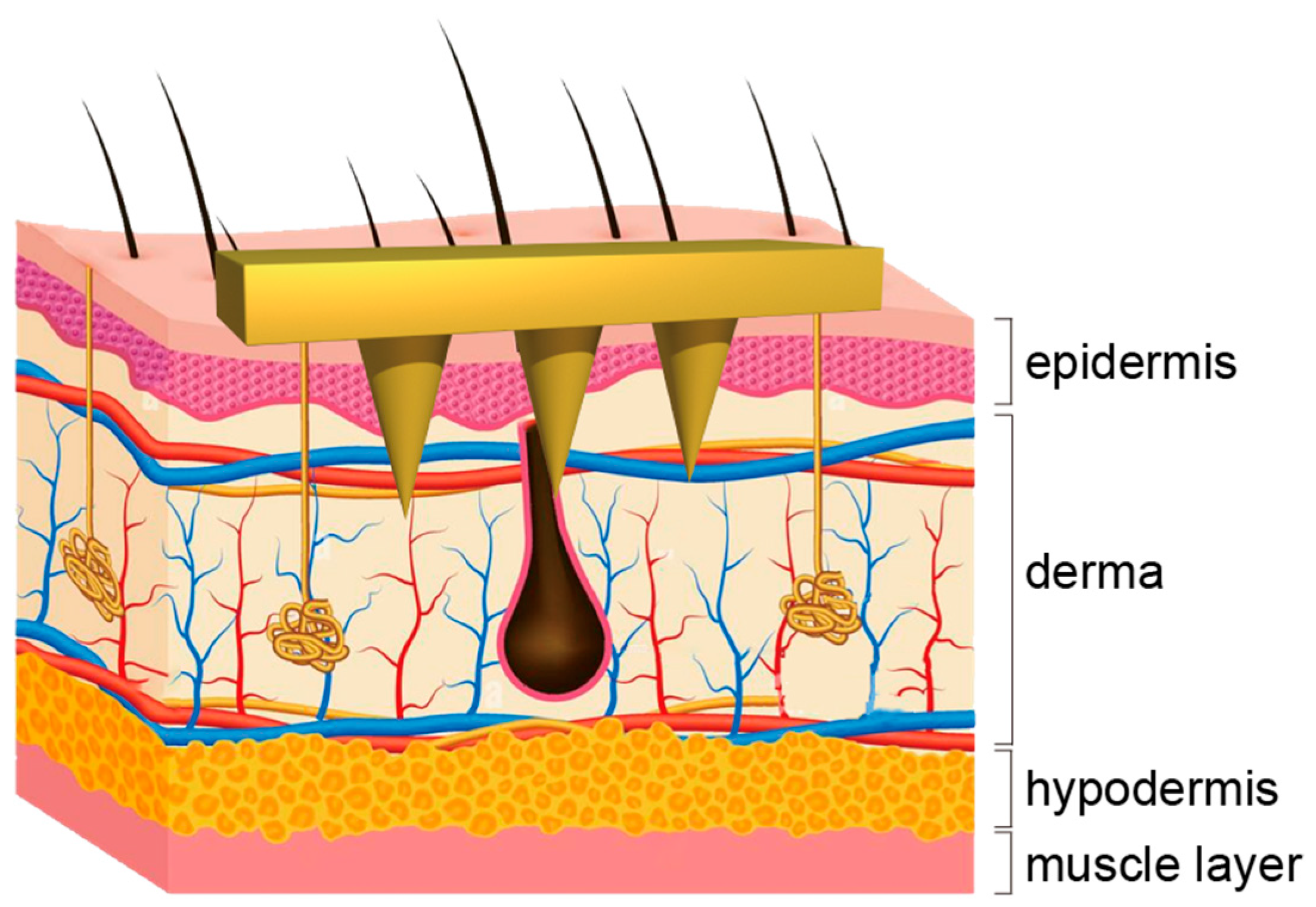
:1. Introduction
2. Endogenous Stimulus-Responsive Microneedles
2.1. Response to Glucose Concentration
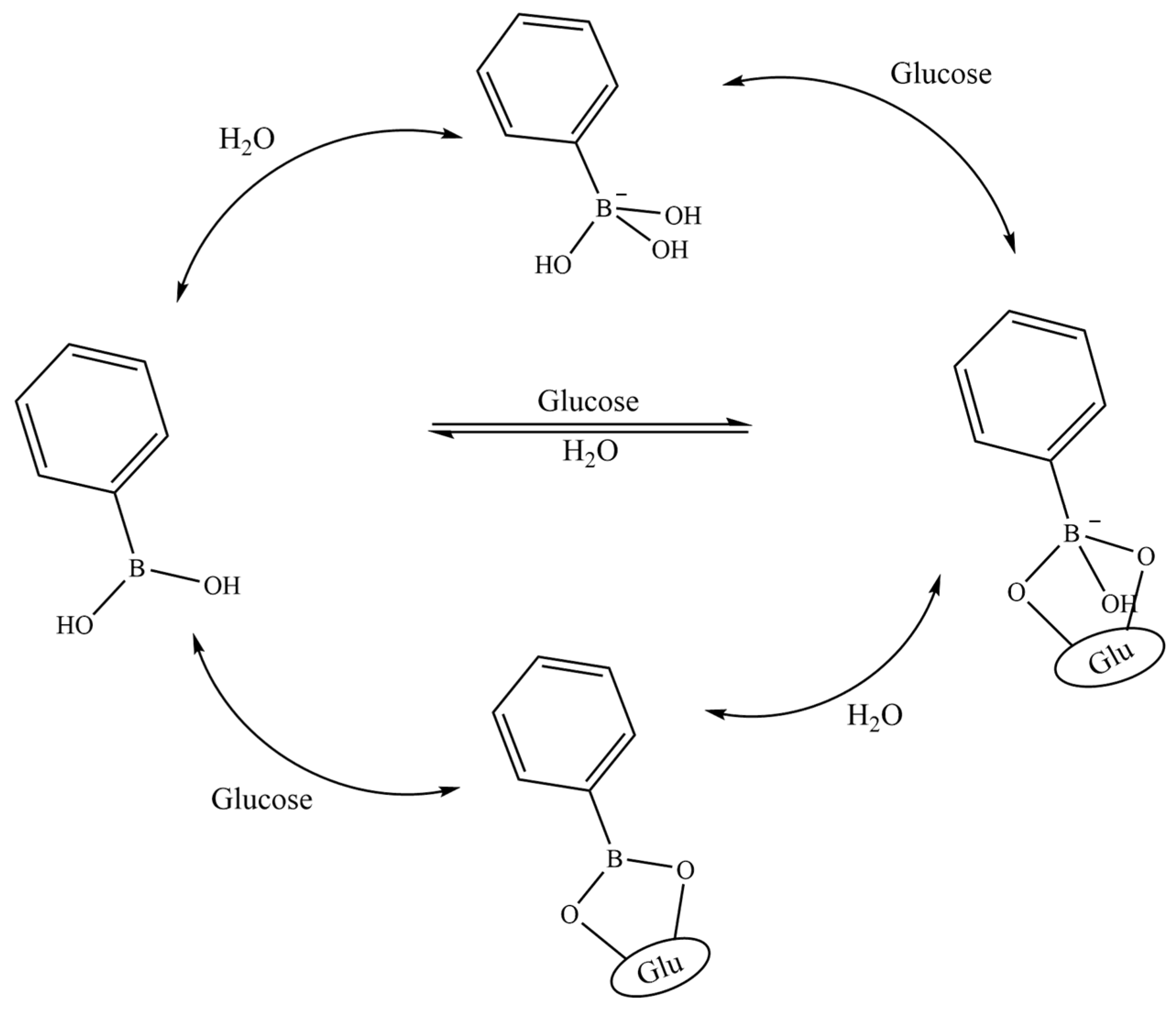
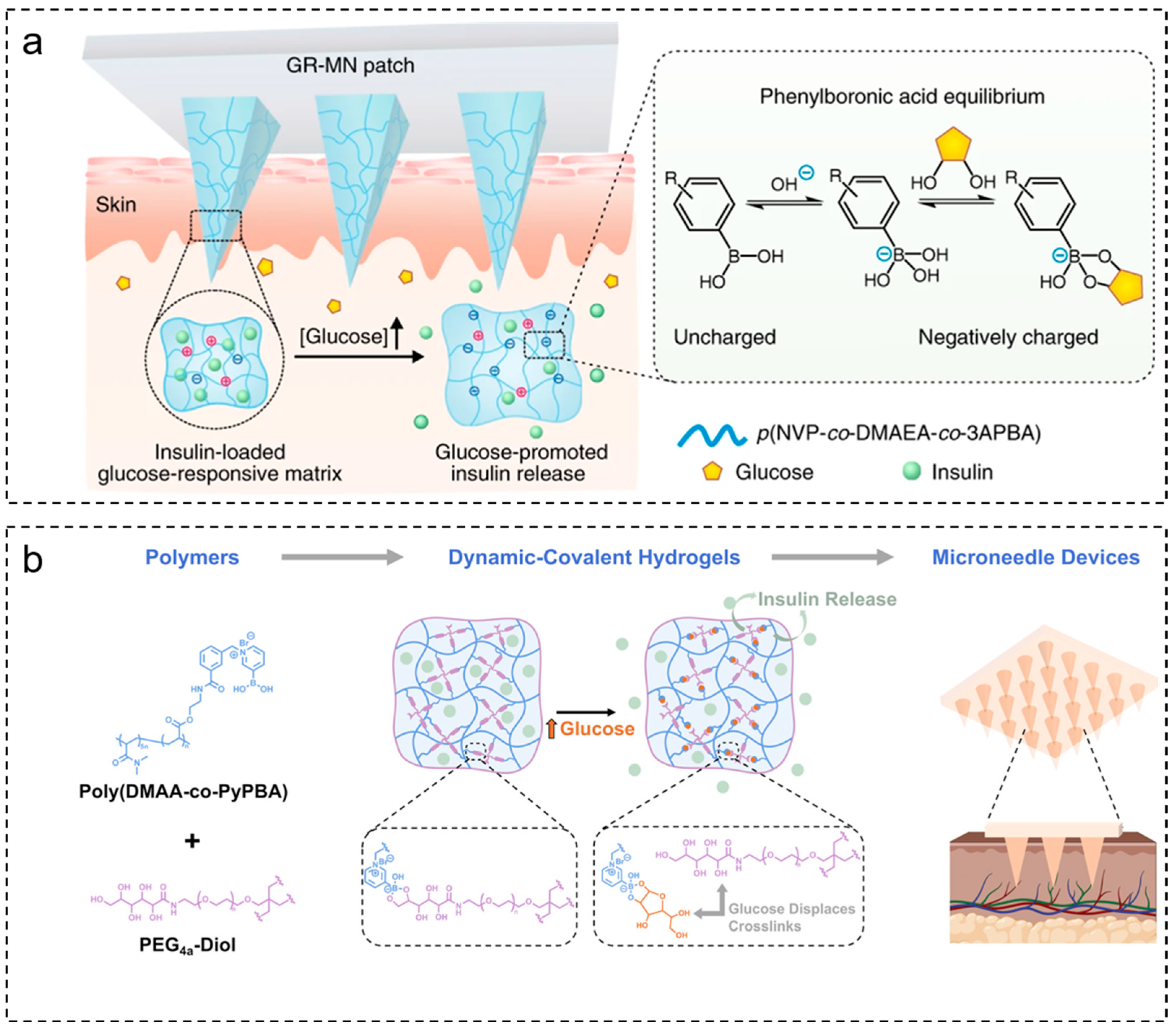
2.1.1. Glucose-Sensitive Microneedles Based on PBA
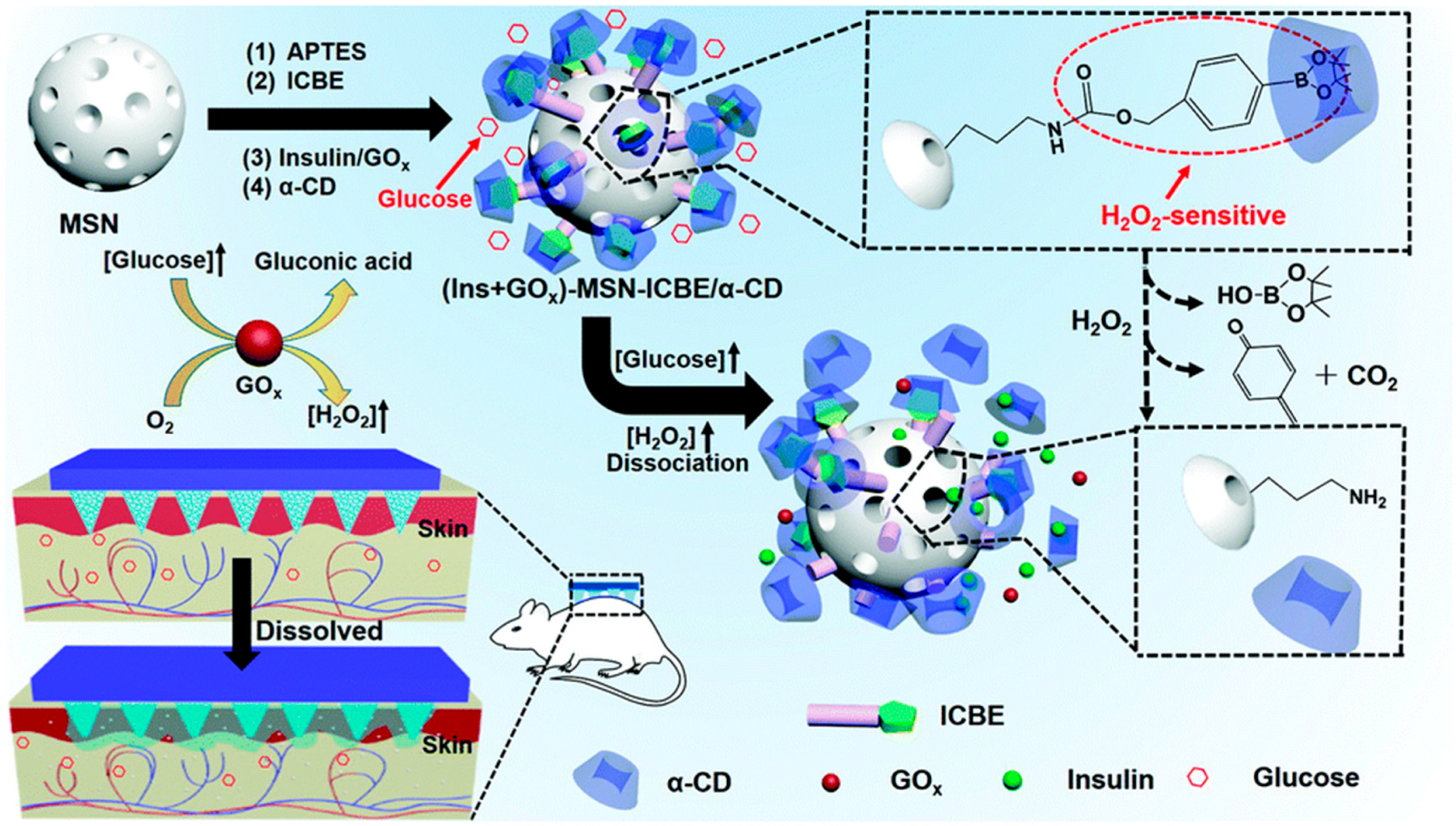
2.1.2. Glucose-Sensitive Microneedles Based on GOx
2.1.3. Glucose-Sensitive Materials Based on ConA
2.2. Response to pH
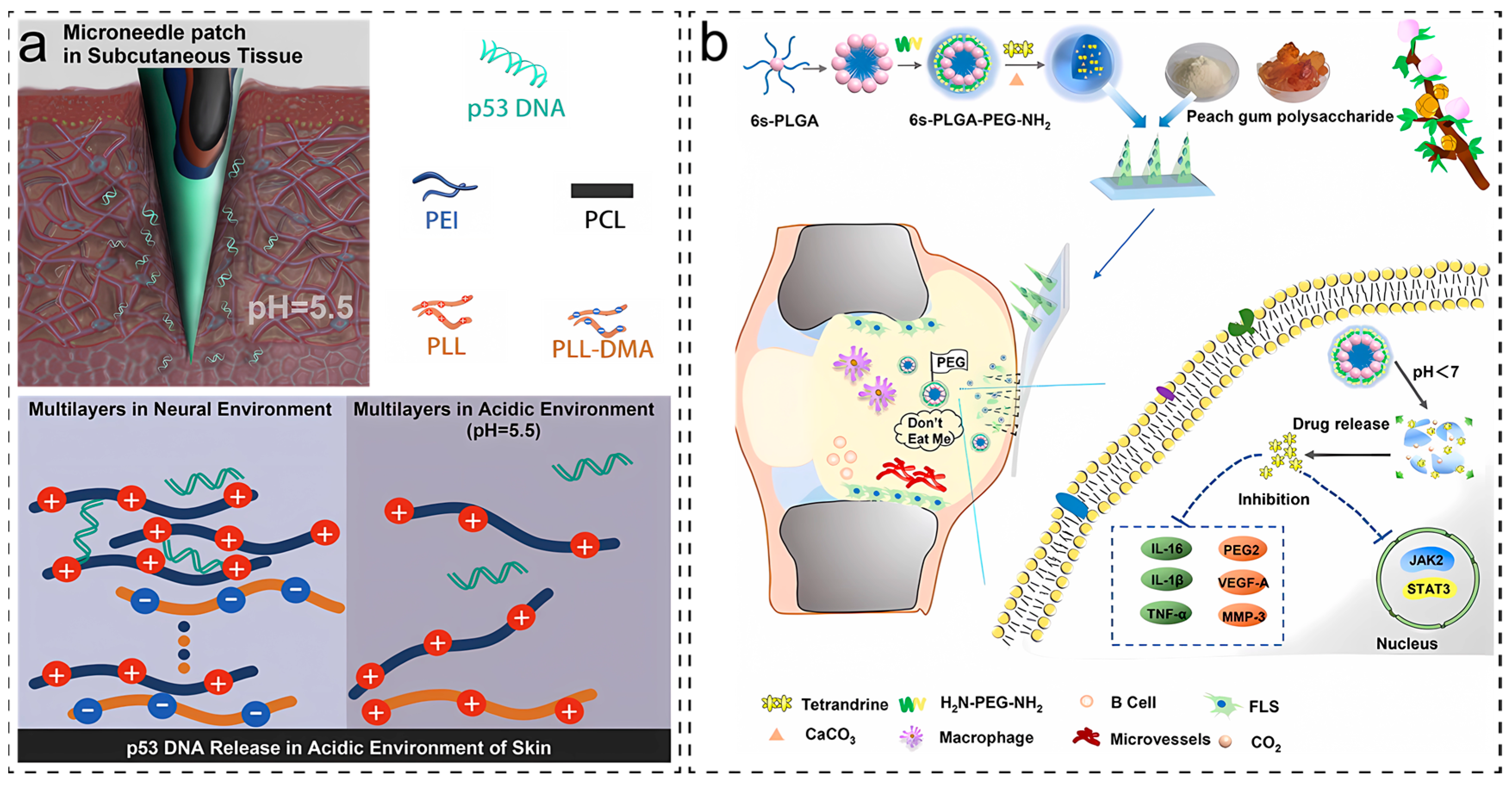
2.3. Response to Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
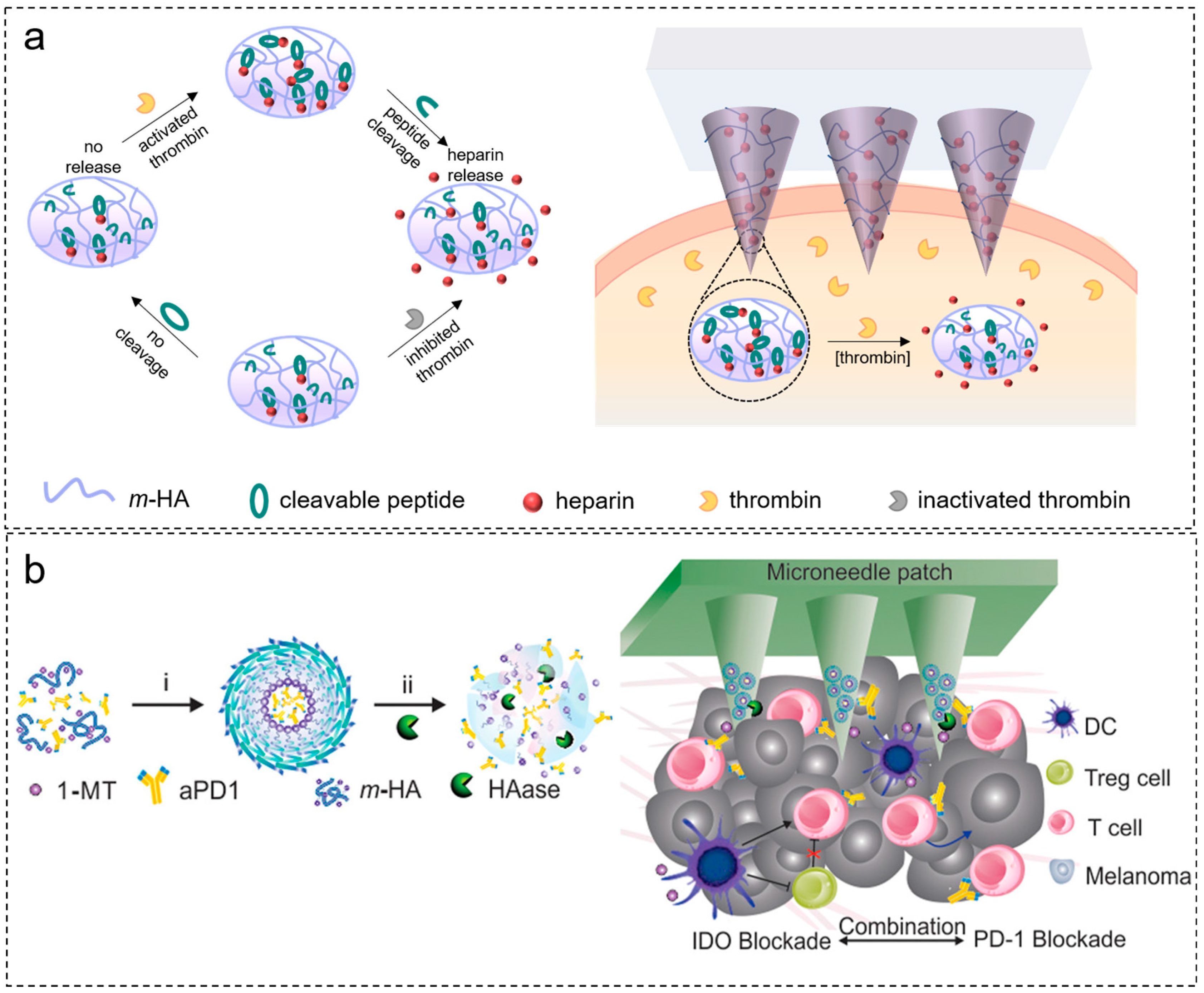
2.4. Response to Enzymes
3. Exogenous Stimulus-Responsive Microneedles
3.1. Response to Temperature
3.2. Response to Light
3.3. Response to Electricity
3.4. Response to Magnetic
4. Application of Smart Responsive Microneedles
4.1. Blood Glucose Control
4.2. Wound Repair
4.3. Cancer Treatment
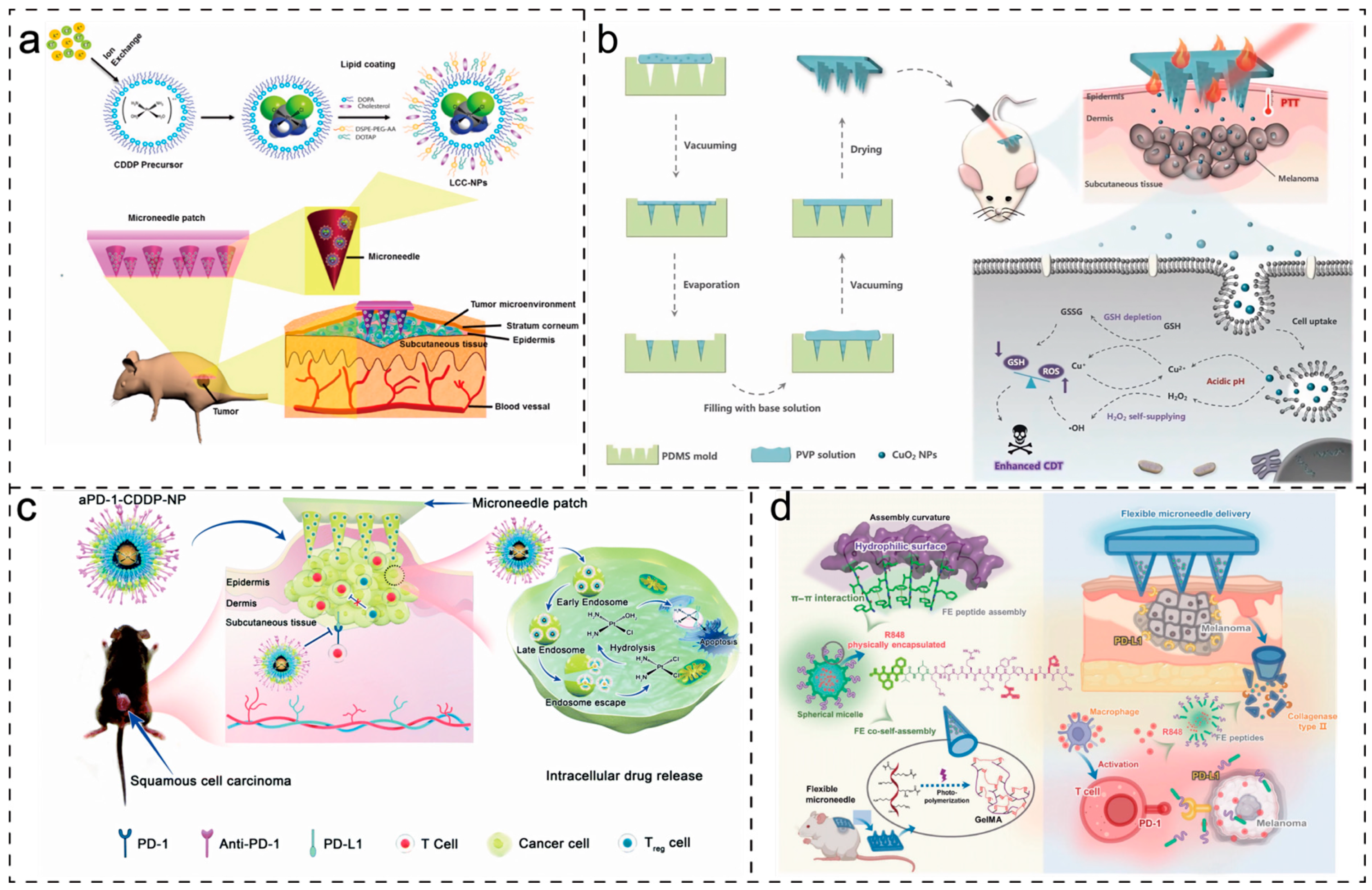
4.4. Treatment of Other Diseases
5. Development Trends and Clinical Transformation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Baik, S.; Kim, D.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Device-Assisted Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Microfabrication, Drug Delivery, and Safety. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Larraňeta, E. Slowly Dissolving Intradermal Microneedles. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystrova, S.; Luttge, R. Micromolding for Ceramic Microneedle Arrays. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Fakhraei Lahiji, S.; Jang, J.; Jang, M.; Jung, H. Micro-Pillar Integrated Dissolving Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated Microneedles: A Novel Approach to Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioris, K.; Raja, W.K.; Pritchard, E.M.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, B.; Chambre, L.; Harrington, K.; Kluge, J.; Valenti, L.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin Microneedle Patches for the Sustained Release of Levonorgestrel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 5375–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Kuang, D.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Lu, S. Swellable Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizidou, E.Z.; Williams, N.A.; Barrow, D.A.; Eaton, M.J.; McCrory, J.; Evans, S.L.; Allender, C.J. Structural Characterisation and Transdermal Delivery Studies on Sugar Microneedles: Experimental and Finite Element Modelling Analyses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, D.; Damiri, F.; Rojekar, S.; Zehravi, M.; Ramproshad, S.; Dhoke, D.; Musale, S.; Mulani, A.A.; Modak, P.; Paradhi, R.; et al. Recent Advancements in Microneedle Technology for Multifaceted Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadon, D.; Permana, A.D.; Courtenay, A.J.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Tekko, I.A.; McAlister, E.; Anjani, Q.K.; Utomo, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Development, Evaluation, and Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Polymeric Microarray Patches for Transdermal Delivery of Vancomycin Hydrochloride. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3353–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machekposhti, S.A.; Soltani, M.; Najafizadeh, P.; Ebrahimi, S.A.; Chen, P. Biocompatible Polymer Microneedle for Topical/Dermal Delivery of Tranexamic Acid. J. Control. Release 2017, 261, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, J.T.; Kim, C.B.; Shin, Y.-R.; Park, P.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.M.; Park, J.H. Microneedle Array Patch (MAP) Consisting of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Processability and Sustained Release. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Tao, X.; Tan, G.; Tian, B.; Zhang, L.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Electro-Responsive Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Controlled Release of Insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Goodson, J.L.; Rota, P.A.; Orenstein, W.A. A Microneedle Patch for Measles and Rubella Vaccination: A Game Changer for Achieving Elimination. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 41, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Tran, V.; Morhenn, V.; Hung, S.; Andersen, B.; Ito, E.; Wesley Hatfield, G.; Benson, N.R. Use of RT-PCR and DNA Microarrays to Characterize RNA Recovered by Non-Invasive Tape Harvesting of Normal and Inflamed Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Wu, V.; Zeng, Y.; Wen, D.; Miedema, J.R.; et al. Dual Self-Regulated Delivery of Insulin and Glucagon by a Hybrid Patch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29512–29517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, W.; Zhou, D.; Li, J.X.; Huang, Y.C.; Lin, R.; Gu, Z.; Du, J.Z. Microneedle-Array Patch with pH-Sensitive Formulation for Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, R.; Han, X.; Wen, D.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Gu, Z. Shrinking Fabrication of a Glucose-Responsive Glucagon Microneedle Patch. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Sheng, T.; Hou, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Glucose-Responsive Microneedle Patch for Closed-Loop Dual-Hormone Delivery in Mice and Pigs. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, E.; Friedrich, E.E.; Ramadan, M.H.; Erdos, G.; Mathers, A.R.; Ozdoganlar, O.B.; Washburn, N.R.; Falo, L.D. Tip-Loaded Dissolvable Microneedle Arrays Effectively Deliver Polymer-Conjugated Antibody Inhibitors of Tumor-Necrosis-Factor-Alpha Into Human Skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3453–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, T.; Yang, F.; Chen, D.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, R.; Du, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, Y.; Dai, X.; Niu, X.; et al. Synergistically Detachable Microneedle Dressing for Programmed Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, D.; Tan, Q. Transdermal Drug Delivery via Microneedles to Mediate Wound Microenvironment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 195, 114753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, C.H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Cao, D.D.; Chen, B.Z.; Guo, X.D.; Zhang, W. Multifunctional Covalent Organic Framework-Based Microneedle Patch for Melanoma Treatment. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 3846–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, G.; Yuan, J.; Jing, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Xie, G.; et al. A Smart Silk-Based Microneedle for Cancer Stem Cell Synergistic Immunity/Hydrogen Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Gong, Y.; Cao, P.; Wei, C.; Xiao, F.; Wu, D.; Chen, W.; et al. Smart Hydrothermally Responsive Microneedle for Topical Tumor Treatment. J. Control. Release 2023, 358, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Organization of Glucose-Responsive Systems and Their Properties. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7855–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, A.; Lebrun, A.; Smietana, M.; Laurencin, D. A Multinuclear NMR Perspective on the Complexation between Bisboronic Acids and Bisbenzoxaboroles with Cis-Diols. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, S.H.; Vakili, O.; Ahmadi, N.; Soltani Fard, E.; Mousavi, P.; Khalvati, B.; Maleksabet, A.; Savardashtaki, A.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Movahedpour, A. Glucose Oxidase: Applications, Sources, and Recombinant Production. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, S.C.; Mix, D.; Baudyš, M.; Kim, S.W. Glucose-Induced Release of Glycosylpoly(Ethylene Glycol) Insulin Bound to a Soluble Conjugate of Concanavalin A. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Feng, J. Progress in the Preparation and Evaluation of Glucose-Sensitive Microneedle Systems and Their Blood Glucose Regulation. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 5410–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Mao, W.; Ye, Y.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Buse, J.B.; Langer, R.; Gu, Z. Glucose-Responsive Insulin Patch for the Regulation of Blood Glucose in Mice and Minipigs. Nat. Biomed. Eng 2020, 4, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Monroe, T.; Yu, S.; Dong, P.; Xian, S.; Webber, M.J. Polymeric Microneedle Arrays with Glucose-Sensing Dynamic-Covalent Bonding for Insulin Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4401–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ma, Q.; He, D.; Liu, G.; Tang, D.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. A New Glucose-Responsive Delivery System Based on Sulfonamide-Phenylboronic Acid for Subcutaneous Insulin Injection. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 157, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.; Jin, T.; Wu, H.; Hei, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhu, W. On-Demand Transdermal Insulin Delivery System for Type 1 Diabetes Therapy with No Hypoglycemia Risks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y. Glucose-Responsive Microneedle Patch With Variable Crosslinking Density and Flexible Core–Shell Structure for Insulin Delivery. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2202124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. Smart Microneedle Fabricated with Silk Fibroin Combined Semi-Interpenetrating Network Hydrogel for Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. A Porous Reservoir-Backed Boronate Gel Microneedle for Efficient Skin Penetration and Sustained Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Gels 2022, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Li, C. Phenylboronate-Diol Crosslinked Glycopolymeric Nanocarriers for Insulin Delivery at Physiological pH. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Jiang, F.; Cheng, K.; Qi, Z.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Lu, S. Synthesis of pH and Glucose Responsive Silk Fibroin Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Jiang, F.; Jia, T.; Qi, Z.; Xing, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Glucose-Responsive Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Insulin. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, G.; Yu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y. H2O2-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Integrated with Microneedle Patches for the Glucose-Monitored Transdermal Delivery of Insulin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-Array Patches Loaded with Hypoxia-Sensitive Vesicles Provide Fast Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Uppal, N.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Stabilization of Enzymes in Silk Films. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsemann, M.; Frenzel, L.P.; Baatout, D.; Claasen, J.; Theurich, S.; Kintzelé, L.; Becker, H.J.; Patz, M.; Pallasch, C.P.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.S.; et al. Impact of Hypoxia as Novel Microenvironmental Factor on Drug Susceptibility of Primary CLL Cells. Blood 2012, 120, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lai, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Tang, X.; Ci, J.; Sun, S.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Acidic pH Environment Induces Autophagy in Osteoblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Han, J.; Nie, J. Photo-Crosslinked Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogels Based on Methacrylate Modified Dextran–Concanavalin A and PEG Dimethacrylate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Du, S.; Chen, L.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. Design of Genipin-Crosslinked Microgels from Concanavalin A and Glucosyloxyethyl Acrylated Chitosan for Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Park, K. Glucose-Binding Property of Pegylated Concanavalin a. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, U.; Grdadolnik, J. The Hydration of Concanavalin A Studied by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1135, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Li, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Glucose-Responsive Biopolymer Nanoparticles Prepared by Co-Assembly of Concanavalin A and Amylopectin for Insulin Delivery. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, X. The Role of Internal and External Stimuli in the Rational Design of Skin-Specific Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Ding, H. pH-Responsive Nanoparticles for Cancer Immunotherapy: A Brief Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Weng, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Advances in Intelligent Stimuli-Responsive Microneedle for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, 2300014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.S.; Bharadwaj, P.; Bilal, M.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Taboada, P.; Bungau, S.; Kyzas, G.Z. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Theragnosis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Maaden, K.; Varypataki, E.M.; Romeijn, S.; Ossendorp, F.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Ovalbumin-Coated pH-Sensitive Microneedle Arrays Effectively Induce Ovalbumin-Specific Antibody and T-Cell Responses in Mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ruan, H.; Ruan, S.; Pei, L.; Jing, Q.; Wu, T.; Hou, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, N.; et al. Acid-Responsive PEGylated Branching PLGA Nanoparticles Integrated into Dissolving Microneedles Enhance Local Treatment of Arthritis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idelchik, M.D.P.S.; Begley, U.; Begley, T.J.; Melendez, J.A. Mitochondrial ROS Control of Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 47, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marañon, A.M.; Iannantuoni, F.; Abad-Jiménez, Z.; Canet, F.; Díaz-Pozo, P.; López-Domènech, S.; Jover, A.; Morillas, C.; Mariño, G.; Apostolova, N.; et al. Relationship between PMN-Endothelium Interactions, ROS Production and Beclin-1 in Type 2 Diabetes. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, K.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Lu, C.; Xu, H. ROS-Triggered Degradation of Selenide-Containing Polymers Based on Selenoxide Elimination. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Duan, S.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L. Recent Advances on Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Delivery and Diagnosis System. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2441–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, P.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Gu, Z. ROS-Responsive Microneedle Patch for Acne Vulgaris Treatment. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Qu, F.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, P.; Du, H.; Xie, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Gel-Based Microneedle Patches for Prolonged and Intelligent Psoriasis Management. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4346–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrawati, R. Enzyme-Responsive Polymer Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann Benore, M. What Is in a Name? (Or a Number?): The Updated Enzyme Classifications. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2019, 47, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Hanne, N.J.; Cui, Z.; Qian, C.; Wang, C.; Xin, H.; Cole, J.H.; Gallippi, C.M.; et al. Thrombin-Responsive Transcutaneous Patch for Auto-Anticoagulant Regulation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Hochu, G.M.; Xin, H.; Wang, C.; Gu, Z. Synergistic Transcutaneous Immunotherapy Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses through Delivery of Checkpoint Inhibitors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8956–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, D. A Dissolving Microneedle Patch for Antibiotic/Enzymolysis/Photothermal Triple Therapy against Bacteria and Their Biofilms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Li, C.; Zhou, W. Cross-Linking-Density-Changeable Microneedle Patch Prepared from a Glucose-Responsive Hydrogel for Insulin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4870–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Xue, L.; Liu, S.; Lei, Y. Assisted 3D Printing of Microneedle Patches for Minimally Invasive Glucose Control in Diabetes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Shi, Z.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Pan, G.; Lei, Y.; Xue, L. Responsive Hydrogel-Based Microneedle Dressing for Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Ul Amin, B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, W. Microneedle Patch Prepared from a Hydrogel by a Mild Method for Insulin Delivery. ChemNanoMat 2021, 7, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.L.; Cheng, K.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z.T.; Hou, X.L.; Song, L.B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, Y.D.; Xu, Q.R. The Eradication of Biofilm for Therapy of Bacterial Infected Chronic Wound Based on pH-Responsive Micelle of Antimicrobial Peptide Derived Biodegradable Microneedle Patch. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Hegarty, C.; Casimero, C.; Davis, J. Electrochemically Controlled Dissolution of Nanocarbon–Cellulose Acetate Phthalate Microneedle Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35540–35547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Hu, Y.C.; Chiang, W.L.; Chen, K.J.; Yang, W.C.; Liu, H.L.; Fu, C.C.; Sung, H.W. Multidrug Release Based on Microneedle Arrays Filled with pH-Responsive PLGA Hollow Microspheres. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5156–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Maaden, K.; Yu, H.; Sliedregt, K.; Zwier, R.; Leboux, R.; Oguri, M.; Kros, A.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J.A. Nanolayered Chemical Modification of Silicon Surfaces with Ionizable Surface Groups for pH-Triggered Protein Adsorption and Release: Application to Microneedles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, K.; Park, J.S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Jo, D.-G.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Polyplex-Releasing Microneedles for Enhanced Cutaneous Delivery of DNA Vaccine. J. Control. Release 2014, 179, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.T.T.; Kim, N.W.; Thambi, T.; Giang Phan, V.H.; Lee, M.S.; Yin, Y.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.S. Microneedle Arrays Coated with Charge Reversal pH-Sensitive Copolymers Improve Antigen Presenting Cells-Homing DNA Vaccine Delivery and Immune Responses. J. Control. Release 2018, 269, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Quan, G.; Lu, C.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Dissolving Microneedles Integrated with pH-Responsive Micelles Containing AIEgen with Ultra-Photostability for Enhancing Melanoma Photothermal Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5739–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Lyu, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Xin, X.; Yin, L. Topical Delivery of ROS-Responsive Methotrexate Prodrug Nanoassemblies by a Dissolvable Microneedle Patch for Psoriasis Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cheng, Z.; Yi, H. NIR Light-Activatable Dissolving Microneedle System for Melanoma Ablation Enabled by a Combination of ROS-Responsive Chemotherapy and Phototherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ju, S.; Ren, X.; Ding, C.; Zhao, J. ROS-Responsive Microneedles Loaded with Integrin Avβ6-Blocking Antibodies for the Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Control. Release 2023, 360, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Lu, C.; Qin, W.; Chen, M.; Quan, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Construction of a Core-Shell Microneedle System to Achieve Targeted Co-Delivery of Checkpoint Inhibitors for Melanoma Immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 104, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Qin, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, T.; Yin, S.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Feng, G.; et al. Enzyme-Responsive Microneedle Patch for Bacterial Infection and Accelerated Healing of Diabetic Wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Du, K.; Yin, Q. Multiple Morphologies of a Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)-Block-Poly(N,N-Dimethyl Aminoethyl Methacrylate) Copolymer with pH-Responsiveness and Thermoresponsiveness. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, H.; Sun, T.; Wang, H. Responsive Microneedles as a New Platform for Precision Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Shao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial and Angiogenic Chitosan Microneedle Array Patch for Promoting Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Feng, Y.H.; He, Y.T.; Hu, L.F.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Chen, B.Z.; Guo, X.D. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Microneedles for Controlled Transdermal Drug Delivery. Acta Biomater. 2022, 153, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Yang, F.; Han, R.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Qian, Z. Near-Infrared Responsive 5-Fluorouracil and Indocyanine Green Loaded MPEG-PCL Nanoparticle Integrated with Dissolvable Microneedle for Skin Cancer Therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; McGoldrick, N.; Migalska, K.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Irwin, N.J.; Donnelly, L.; McCoy, C.P. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays Made from Light-Responsive Materials for On-Demand Transdermal Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Andrabi, S.M.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Wong, S.L.; Wang, G.; Xie, J. Triggered Release of Antimicrobial Peptide from Microneedle Patches for Treatment of Wound Biofilms. J. Control. Release 2023, 356, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Huang, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, W.; Wen, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, C. Ferroferric Oxide Loaded Near-Infrared Triggered Photothermal Microneedle Patch for Controlled Drug Release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 617, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yin, Z.; Huang, H.; Liao, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, F. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Unfolding Microneedle Patch for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Myocardial Ischemia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40278–40289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Micro/Nano Needles for Advanced Drug Delivery. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2020, 30, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Zhang, X.P.; Zheng, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.Y.; Guo, X.D. Conductive Microneedle Patch with Electricity-Triggered Drug Release Performance for Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 31645–31654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, D.; Chen, B.Z.; Luo, R.; Liu, Z.; Qu, X.; Wang, C.; Shan, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Self-Powered Controllable Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, R.; Chao, S.; Xue, J.; Jiang, D.; Feng, Y.H.; Guo, X.D.; Luo, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Improved Pharmacodynamics of Epidermal Growth Factor via Microneedles-Based Self-Powered Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, R.; Chen, B. Multifunctional Chitosan–Magnetic Graphene Quantum Dot Nanocomposites for the Release of Therapeutics from Detachable and Non-Detachable Biodegradable Microneedle Arrays. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Magneto-Responsive Microneedle Robots for Intestinal Macromolecule Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kwon, S.; Park, S. Active Delivery of Multilayer Drug-Loaded Microneedle Patches Using Magnetically Driven Capsule. Med. Eng. Phys. 2020, 85, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chai, D.; Gao, M.; Xu, B.; Jiang, G. Thermal Ablation of Separable Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Metformin on Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomat. 2019, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.R.S.; Fallows, S.J.; McMillan, H.L.; Donnelly, R.F.; Jones, D.S. Microneedle-Mediated Intrascleral Delivery of in Situ Forming Thermoresponsive Implants for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Dong, K.; Lu, X.; Gao, B.; He, B. Bioinspired 3D-Printed MXene and Spidroin-Based Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Microneedle Scaffolds for Efficient Wound Management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 56525–56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.J.; He, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, K.; Yao, Y.; Lu, F. Light-Regulated Nitric Oxide Release from Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles Integrated with Graphene Oxide for Biofilm-Infected-Wound Healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ye, R.; Gong, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, Y.; Nie, G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, L. Iontophoresis-Driven Microneedle Patch for the Active Transdermal Delivery of Vaccine Macromolecules. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Huang, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Z.; Liang, X.J.; et al. Rolling Microneedle Electrode Array (RoMEA) Empowered Nucleic Acid Delivery and Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.J.; Kang, A.; Ahn, M.H.; Jun, H.; Baek, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Na, W.; Choi, S.O. Insertion-Responsive Microneedles for Rapid Intradermal Delivery of Canine Influenza Vaccine. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, R.; Gong, Y.; Fang, Z.; Wang, T.; Chen, W. Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Adjuvant-Free Schistosoma Japonicum-Egg Tip-Loaded Asymmetric Microneedle Patch (STAMP). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Gu, Z. Advances in Bioresponsive Closed-Loop Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratlie, K.M.; York, R.L.; Invernale, M.A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Materials for Diabetes Therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, A.J.; Bailey, C.J. Oral Antidiabetic Agents: Current Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2005, 65, 385–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wounds and Its Burden: An Updated Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y. Black Phosphorus-Loaded Separable Microneedles as Responsive Oxygen Delivery Carriers for Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5901–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, L.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D.; Yao, M.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Down-Regulating Scar Formation by Microneedles Directly via a Mechanical Communication Pathway. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10163–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, K.-H.; Aliu, A.; Walezko, N.; Aust, M. Medical Needling: Effect on Skin Erythema of Hypertrophic Burn Scars. Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast. Chir. 2019, 51, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S. Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Tumor Therapy. Small 2023, 19, 2301670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; She, J.; Lin, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Jin, L.; Xie, X.; Su, Y. Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Lipid-Coated Cisplatin Nanoparticles for Efficient and Safe Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33060–33069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Lin, S.; Niu, H.; Zhang, H.; Guan, L.; Shu, C.; Wu, A.; Bian, Y.; Zhu, Y. A Responsive Microneedle System for Efficient Anti-Melanoma by Combining Self-Enhanced Chemodynamic Therapy with Photothermal Therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, H.P.; Xu, K.; Lim, W.Q.; Chen, H.; Zheng, M.; Thng, T.G.S.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Y. Microneedle-Assisted Topical Delivery of Photodynamically Active Mesoporous Formulation for Combination Therapy of Deep-Seated Melanoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11936–11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Ogunnaike, E.A.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.; Hu, Q.; Ci, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Wen, D.; et al. Scattered Seeding of CAR T Cells in Solid Tumors Augments Anticancer Efficacy. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Zhu, W.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Jin, L.; Pu, J.J.; Xie, X.; She, J.; Lui, V.W.Y.; et al. Microneedles Loaded with Anti-PD-1–Cisplatin Nanoparticles for Synergistic Cancer Immuno-Chemotherapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 18885–18898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, B.; Wang, W. A Composite Peptide-Supramolecular Microneedle System for Melanoma Immunotherapy. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 5335–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, N.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X. Actively Separated Microneedle Patch for Sustained-Release of Growth Hormone to Treat Growth Hormone Deficiency. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, G.; Keum, T.; Seo, J.-E.; Bashyal, S.; Eum, N.-S.; Kweon, M.; Lee, S.; Sohn, D.; Lee, S. Iontophoretic Transdermal Delivery of Human Growth Hormone (hGH) and the Combination Effect of a New Type Microneedle, Tappy Tok Tok®. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.T.; Yin, Y.; Thambi, T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Giang Phan, V.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.S. Smart Vaccine Delivery Based on Microneedle Arrays Decorated with Ultra-pH-Responsive Copolymers for Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.J.; Arya, J.M.; McClain, M.A.; Frew, P.M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle Patches: Usability and Acceptability for Self-Vaccination against Influenza. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepens, B.; Vos, P.J.; Saelens, X.; Van Der Maaden, K. Vaccination with Influenza Hemagglutinin-Loaded Ceramic Nanoporous Microneedle Arrays Induces Protective Immune Responses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 136, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, R.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chiang, W.-H.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Hu, S.-H. Transdermal Composite Microneedle Composed of Mesoporous Iron Oxide Nanoraspberry and PVA for Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

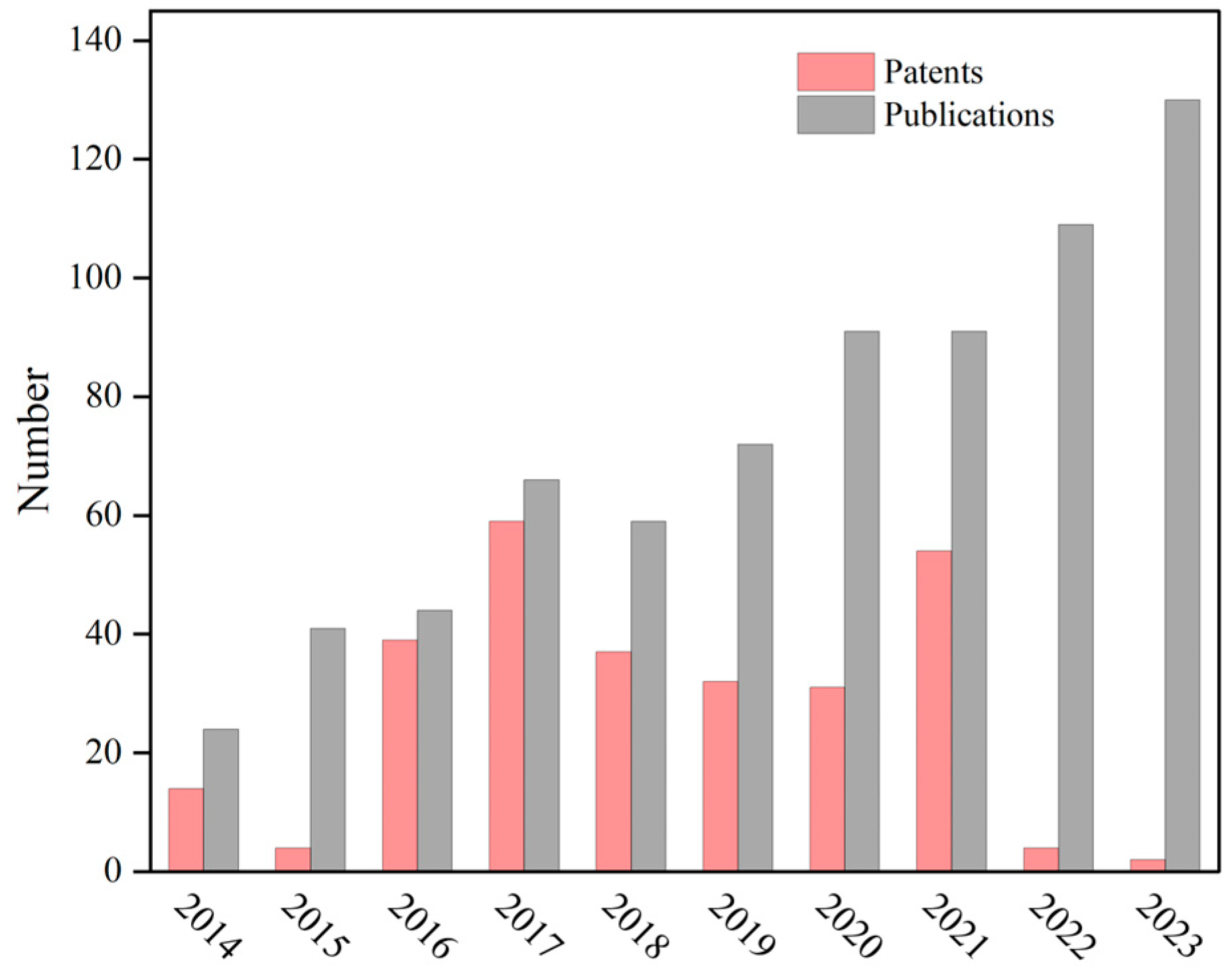
| Responsive Materials | Stimulus Types | Loaded Drugs | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-carboxy-4-fluorophenylboronicacid | Glucose | Porcine insulin | Blood glucose control | [73] |
| 3-aminophenylboronic acid | Glucose | Bovine insulin | Blood glucose control | [74] |
| 4-(2-acrylamidoethylcarbamoyl)-3-fluorophenylboronic acid | Glucose | Gluconic insulin | Diabetic wound | [75] |
| GOx/poly(ethylene glycol)-b-PHMEMA | Glucose/pH | Insulin | Blood glucose control | [22] |
| 3-carboxy-4-fluorophenylboronicacid | Glucose | Porcine insulin | Blood glucose control | [76] |
| 2,3-dimethylmaleic anhydride-polyethyleneimine-polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer | pH | Antimicrobial peptide | Chronic wound healing | [77] |
| Cellulose acetate phthalate | pH | N/A | N/A | [78] |
| NaHCO3 | pH | Alexa 488/Cy5 | N/A | [79] |
| Pyridine | pH | ovalbumin | N/A | [80] |
| Polydopamine | pH | DNA vaccine | Vaccine delivery | [81] |
| Oligo(sulfamethazine)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(amino urethane) | pH | DNA vaccine | Vaccine delivery | [82] |
| Copolymer methyl ether poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(β-aminoester) | pH | AIEgen (NIR950) | Tumor therapy | [83] |
| Thioketal | ROS | Methotrexate | Psoriasis therapy | [84] |
| Boronate moiety | ROS | Doxorubicin | Melanoma therapy | [85] |
| N1-(4-boronobenzyl)-N3-(4-boronophenyl)-N1, N1, N3, N3-tetramethylpropane-1,3-diaminium | ROS | avβ6-blocking antibody [10D5] | Pulmonary fibrosis | [86] |
| 1-methyl-DL-tryptophan-conjugated hyaluronic acid | Hyaluronidase | Anti-PD1 antibody | Cancer immunotherapy | [87] |
| Hyaluronic acid methacrylate | Hyaluronidase | Basic fibroblast growth factor | Bacterial infection/diabetic wounds | [88] |
| Responsive Materials | Stimulus Types | Loaded Drugs | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycaprolactone | Temperature | Metformin | Diabetes | [105] |
| Poloxamer formulations | Temperature | Fluorescein sodium | sustained ocular drug delivery | [106] |
| MXene | NIR | Mupirocin/human epidermal growth factor | Wound management | [107] |
| Graphene oxide | NIR | Nitric oxide | Wound healing | [108] |
| Ag/AgCl electrodes | Electric | Ovalbumin | COVID-19 | [109] |
| Electrode array | Electric | siRNA(PD-L1) alone or combined with aPD-1 or immunoadjuvant of CPG2395 | Cancer immunotherapy | [110] |
| Polycaprolactone/hyaluronic acid | Machine | Vaccine antigen of canine influenza virus | Vaccine immunity | [111] |
| Asymmetric microneedles loaded with Schistosoma japonicum egg tips on CA-CMC | Machine | Schistosoma japonicum egg | Type 1 diabetes mellitus | [112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Z.; Yan, Z.; Tan, G.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Smart Responsive Microneedles for Controlled Drug Delivery. Molecules 2023, 28, 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217411
Qi Z, Yan Z, Tan G, Kundu SC, Lu S. Smart Responsive Microneedles for Controlled Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217411
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Zhenzhen, Zheng Yan, Guohongfang Tan, Subhas C. Kundu, and Shenzhou Lu. 2023. "Smart Responsive Microneedles for Controlled Drug Delivery" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217411
APA StyleQi, Z., Yan, Z., Tan, G., Kundu, S. C., & Lu, S. (2023). Smart Responsive Microneedles for Controlled Drug Delivery. Molecules, 28(21), 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217411








