Endothelialization of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of WPI Supplementation on Proliferation and Antioxidant Levels in HUVECs
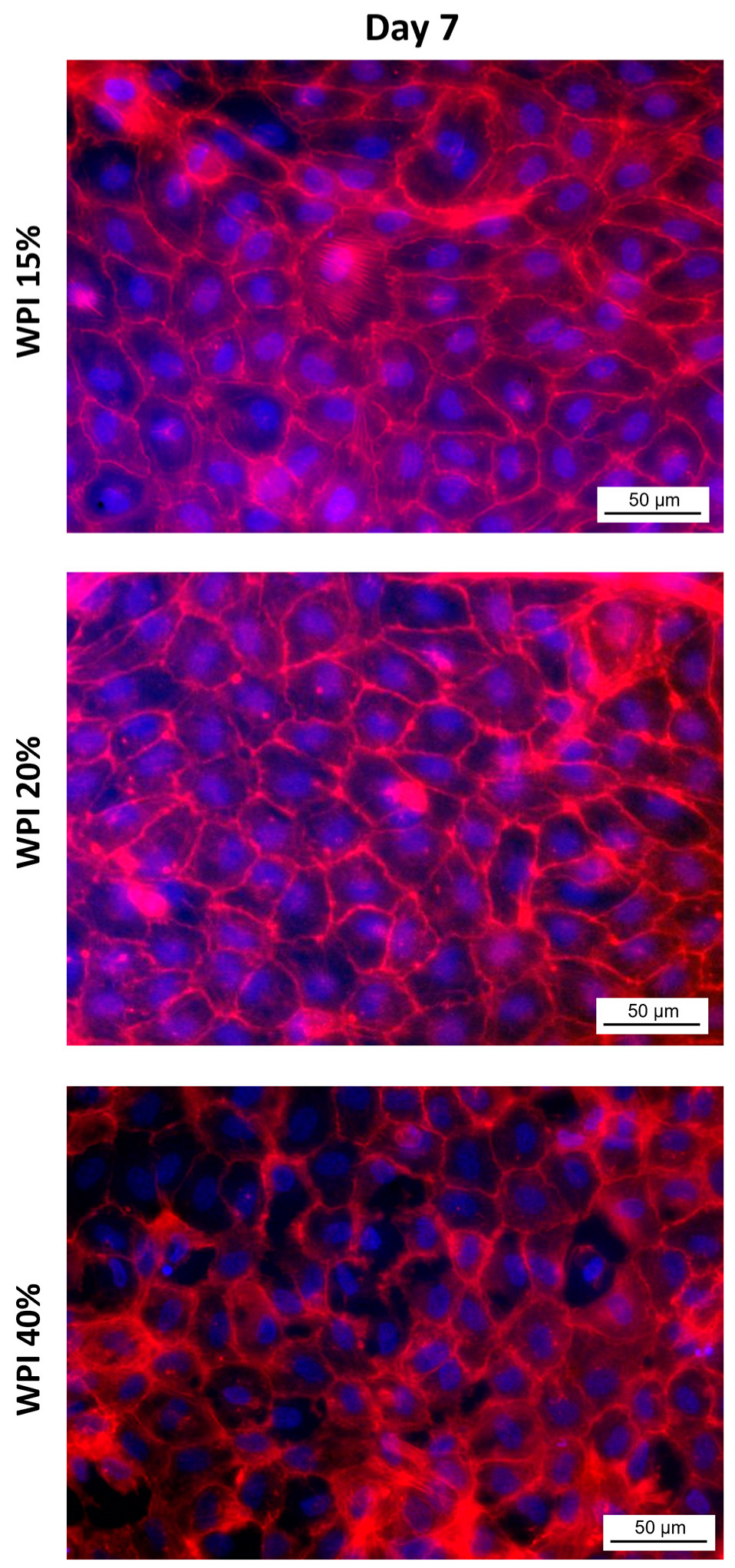
2.2. Endothelialization of Flat WPI Hydrogels
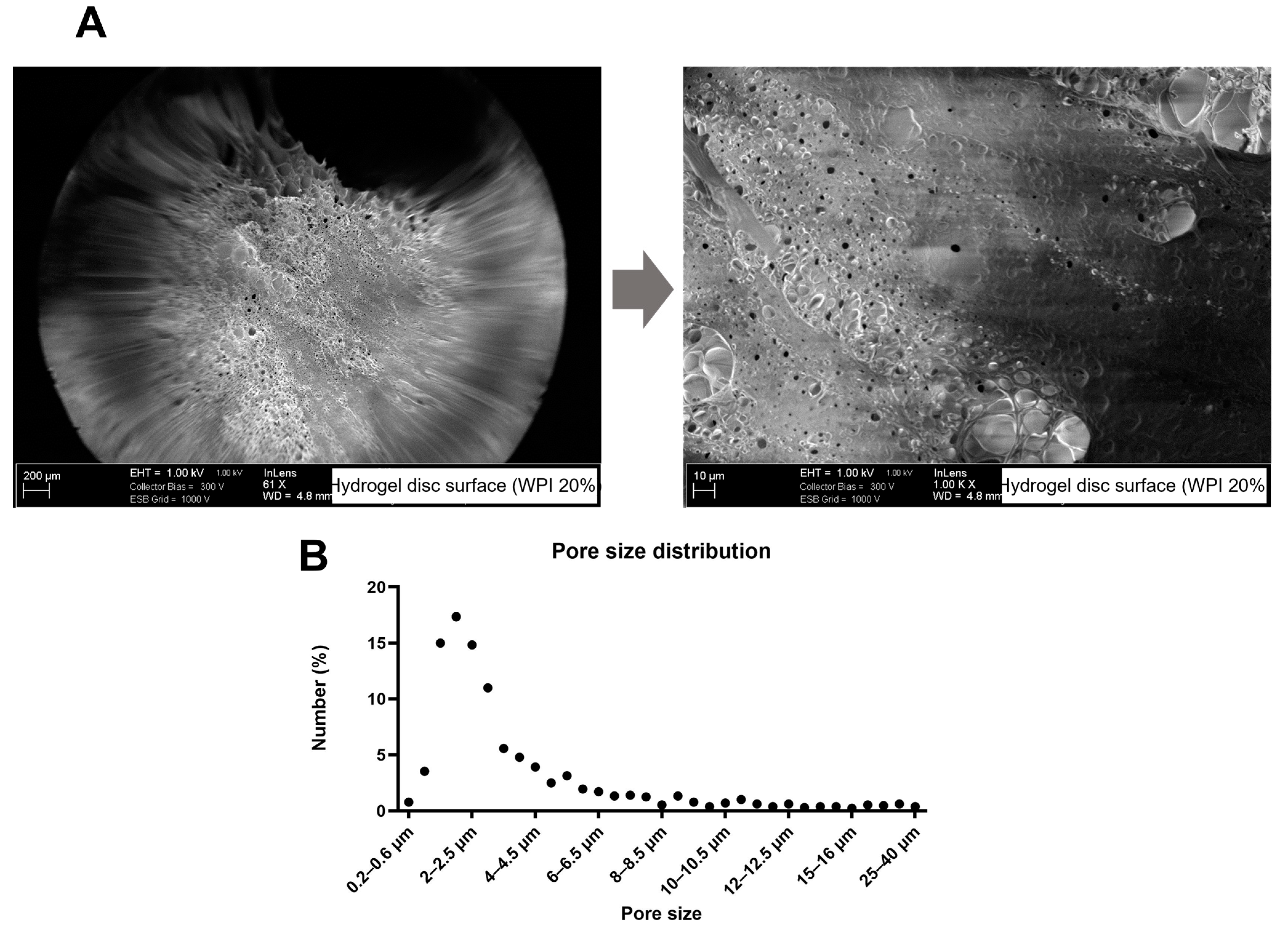
2.3. WPI Hydrogel Characterization
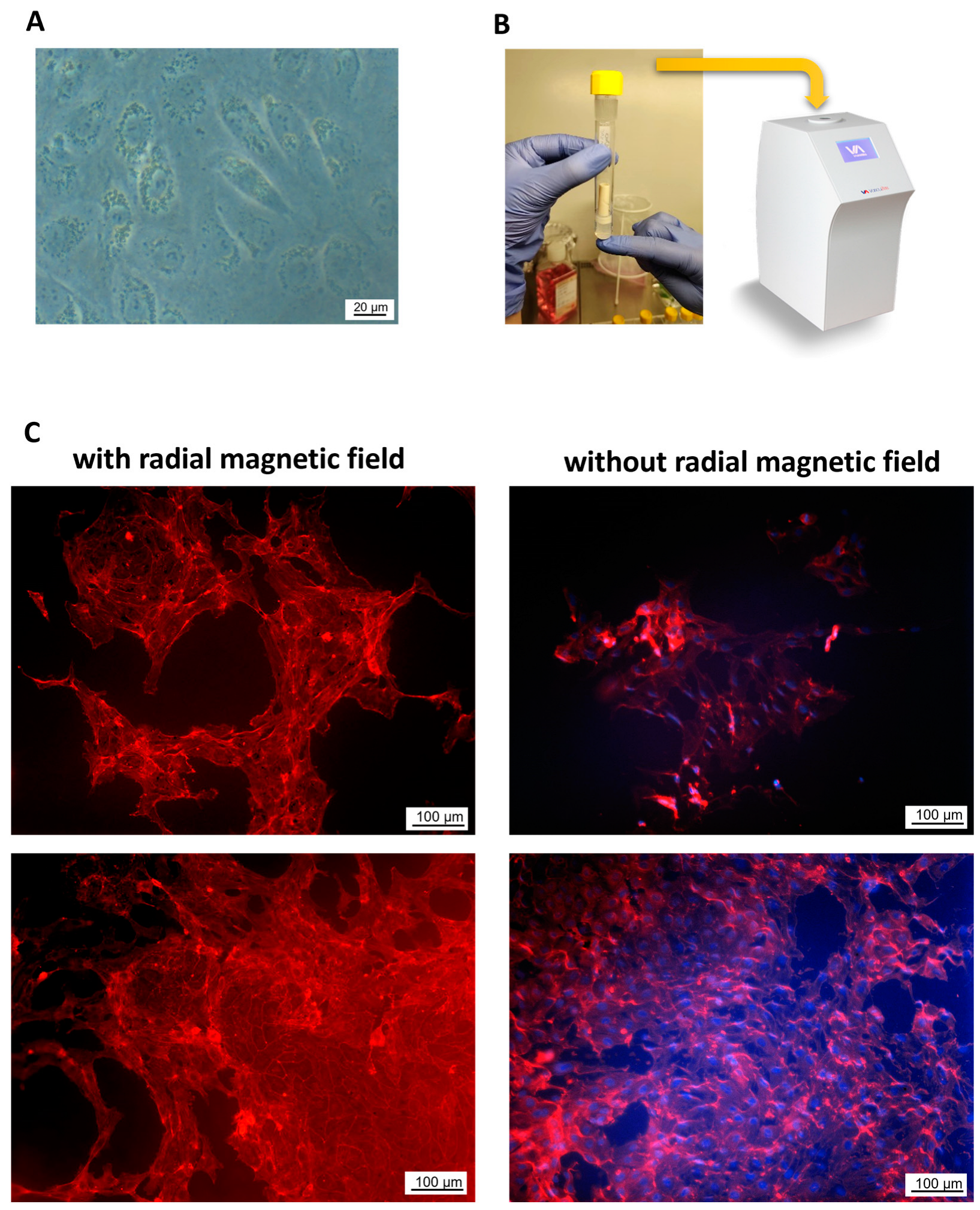
2.4. Endothelialization of Tubular WPI Constructs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Whey Protein Isolate Supplementation
4.2. Cell Isolation and Culture
4.3. Real-Time Cell Analysis
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analyses
4.4.1. Preparation of 2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin Diacetate (DCFH-DA) Probe for Intracellular ROS Detection
4.4.2. Preparation of Staining Solutions and Analysis of Flow Cytometry Data
4.5. WPI Hydrogel Preparation
4.6. Cell Seeding on 2D WPI Scaffolds
4.7. Cell Staining and Image Analysis
4.8. Mitochondrial Activity
4.9. Compressive Testing of Hydrogels
4.10. SEM Analysis of Hydrogels
4.11. Preparation of Tubular Scaffolds
4.12. Rotational Cell Seeding on 3D Scaffolds
4.13. Magnetic Cell Seeding on the Tubular Scaffolds
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Appendix A
References
- Chai, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, X. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Their Characteristics and the Mechanisms behind Them. Gels 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic-Stojanovic, S.; Nikolic, L.; Cakic, S. A Review of Patents and Innovative Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, S.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Natural-based nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: A review. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1143–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Horta, R.; Matesanz, A.; Gallardo, A.; Reinecke, H.; Jorcano, J.L.; Acedo, P.; Velasco, D.; Elvira, C. Technological advances in fibrin for tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231190288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ye, W.; Kang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Wound-Healing Material with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Functions, Constructed Using Keratin, Hyperbranched Polymers, and MnO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 29841–29853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Yip, R.C.S.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Current application and modification strategy of marine polysaccharides in tissue regeneration: A review. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 154, 213580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachimi Alaoui, C.; Rethore, G.; Weiss, P.; Fatimi, A. Sustainable Biomass Lignin-Based Hydrogels: A Review on Properties, Formulation, and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Baican, M. Lignins as Promising Renewable Biopolymers and Bioactive Compounds for High-Performance Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, D.; Yu, K.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, C.; et al. White-light crosslinkable milk protein bioadhesive with ultrafast gelation for first-aid wound treatment. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Das, P.; Mukherjee, J.; Banerjee, D.; Ghosh, P.R.; Kumar Das, P.; Bhattacharya, R.N.; Nandi, S.K. Waste-derived biomaterials as building blocks in the biomedical field. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Azoia, N.G.; Coelho, L.; Freixo, R.; Batista, P.; Pintado, M. Proteins Derived from the Dairy Losses and By-Products as Raw Materials for Non-Food Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, T.E.L.; Vandrovcova, M.; Krocilova, N.; Keppler, J.K.; Zarubova, J.; Skirtach, A.G.; Bacakova, L. Application of whey protein isolate in bone regeneration: Effects on growth and osteogenic differentiation of bone-forming cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garraud, O.; Hozzein, W.N.; Badr, G. Wound healing: Time to look for intelligent, ‘natural’ immunological approaches? BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, E.; Mros, S.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.D.; Ali, A. Melt-electrowriting with novel milk protein/PCL biomaterials for skin regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, M.T.; Piva, H.L.; Tedesco, A.C. Design of new protein drug delivery system (PDDS) with photoactive compounds as a potential application in the treatment of glioblastoma brain cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 110, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Guo, Q.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F.; Van der Meeren, P. Assembly of propylene glycol alginate/beta-lactoglobulin composite hydrogels induced by ethanol for co-delivery of probiotics and curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovskaya, D.; Bezchasnyuk, A.; Mochalova, M.; Tsygankov, P.; Lebedev, A.; Zorkina, Y.; Zubkov, E.; Ochneva, A.; Gurina, O.; Silantyev, A.; et al. Preparation of Protein Aerogel Particles for the Development of Innovative Drug Delivery Systems. Gels 2022, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, H.; Tian, C.; Tu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. Whey protein concentrate doped electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) fibers for antibiotic release improvement. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, R.J.S.; Domingues, M.A.F.; Ohara, A.; Okuro, P.K.; dos Santos, J.G.; Brexo, R.P.; Sato, H.H. Whey protein as a key component in food systems: Physicochemical properties, production technologies and applications. Food Struct. 2017, 14, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.; Pavlovic, M.; Zivic, M.; Filipovic, Z.; Gorjanovic, S.; Hranisavljevic, S.; Dojcinovic, M. Processing of whey from dairy industry waste. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2005, 3, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadek, M.; Charuza, K.; Kudlackova, R.; Aveyard, J.; D’Sa, R.; Serafim, A.; Stancu, I.C.; Iovu, H.; Kerns, J.G.; Allinson, S.; et al. Modification of heat-induced whey protein isolate hydrogel with highly bioactive glass particles results in promising biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrochano, A.R.; Buckin, V.; Kelly, P.M.; Giblin, L. Invited review: Whey proteins as antioxidants and promoters of cellular antioxidant pathways. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4747–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genc, H.; Hazur, J.; Karakaya, E.; Dietel, B.; Bider, F.; Groll, J.; Alexiou, C.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Detsch, R.; Cicha, I. Differential Responses to Bioink-Induced Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells and Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keeffe, M.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Antioxidant effects of enzymatic hydrolysates of whey protein concentrate on cultured human endothelial cells. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 36, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, E.; Luce, A.; Balestrieri, A.; Mele, L.; Anastasio, C.; D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Campanile, G. Whey Improves In Vitro Endothelial Mitochondrial Function and Metabolic Redox Status in Diabetic State. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashoush, I.S.; El Batawy, O.I.; El-Shourbagy, G.A. Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effect of pomegranate peel and whey powders in rats. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2013, 58, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Paik, H.D.; Yoon, Y.C.; Park, E. Whey Protein Inhibits Iron Overload-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh-Sharafabad, F.; Sharifi Zahabi, E.; Tarighat-Esfanjani, A. Role of whey protein in vascular function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of human intervention studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R. Effect of whey protein on the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji-Naito, K.; Jack, R.W. Concentrated bovine milk whey active proteins facilitate osteogenesis through activation of the JNK-ATF4 pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bu, T.; Ren, Y.; Yu, S.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Yang, K. A Low-Phenylalanine-Containing Whey Protein Hydrolysate Stimulates Osteogenic Activity through the Activation of p38/Runx2 Signaling in Osteoblast Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziadek, M.; Kudlackova, R.; Zima, A.; Slosarczyk, A.; Ziabka, M.; Jelen, P.; Shkarina, S.; Cecilia, A.; Zuber, M.; Baunnbach, T.; et al. Novel multicomponent organic-inorganic WPI/gelatin/CaP hydrogel composites for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 2479–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.; Keppler, J.K.; Brackman, G.; Dawood, D.; Vandrovcova, M.; Fawzy El-Sayed, K.; Coenye, T.; Schwarz, K.; Clarke, S.A.; Skirtach, A.G.; et al. Whey Protein Complexes with Green Tea Polyphenols: Antimicrobial, Osteoblast-Stimulatory, and Antioxidant Activities. Cells Tissues Organs 2018, 206, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.; Jackson, K.G.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Givens, D.I. The effects of whey proteins, their peptides and amino acids on vascular function. Nutr. Bull. 2022, 47, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnellmann, R.; Ntekoumes, D.; Choudhury, M.I.; Sun, S.; Wei, Z.; Gerecht, S. Stiffening Matrix Induces Age-Mediated Microvascular Phenotype Through Increased Cell Contractility and Destabilization of Adherens Junctions. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, K.; Tarczynska, M.; Truszkiewicz, W.; Gaweda, K.; Douglas, T.E.L.; Ginalska, G. Freeze-Dried Curdlan/Whey Protein Isolate-Based Biomaterial as Promising Scaffold for Matrix-Associated Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation-A Pilot In-Vitro Study. Cells 2022, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yue, K.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017, 57, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Pan, S. Substrate Stiffness of Bone Microenvironment Controls Functions of Pre-Osteoblasts and Fibroblasts In Vitro. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, F.; Jing, Z.; Shen, D.; He, P.; Chen, T.; Wu, T.; Jia, H.; Mo, D.; et al. Three-Dimensional Matrix Stiffness Activates the Piezo1-AMPK-Autophagy Axis to Regulate the Cellular Osteogenic Differentiation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 4735–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.R.; Ceccarelli, J.; Vigen, M.L.; Gudur, M.; Singh, R.; Deng, C.X.; Putnam, A.J.; Stegemann, J.P. Effects of hydroxyapatite on endothelial network formation in collagen/fibrin composite hydrogels in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.W.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Ren, K.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Ji, J. The substrate stiffness at physiological range significantly modulates vascular cell behavior. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 214, 112483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, A.M.; Joseph, J.; Nair, M.B.; Nair, S.V.; Vijayakumar, M.; Menon, D. Coupled benefits of nanotopography and titania surface chemistry in fostering endothelialization and reducing in-stent restenosis in coronary stents. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 142, 213149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubey, A.; Marton, D.; Sprague, E.A. Human aortic endothelial cell response to 316L stainless steel material microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, L.; Yuan, F.; Tan, J.; Yuan, G.; Pei, J. Nano-micrometer surface roughness gradients reveal topographical influences on differentiating responses of vascular cells on biodegradable magnesium. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Wieser, A.; Reakasame, S.; Detsch, R.; Dietel, B.; Alexiou, C.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Cicha, I. Cell specificity of magnetic cell seeding approach to hydrogel colonization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, H.; Aigner, J.; Hopfner, U.; Wintermantel, E. Direct magnetic tubular cell seeding: A novel approach for vascular tissue engineering. Cells Tissues Organs 2006, 183, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, H.; Aigner, J.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Hopfner, U.; Wintermantel, E. Vascular tissue engineering with magnetic nanoparticles: Seeing deeper. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Genç, H.; Friedrich, B.; Alexiou, C.; Pietryga, K.; Cicha, I.; Douglas, T.E.L. Endothelialization of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration. Molecules 2023, 28, 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207052
Genç H, Friedrich B, Alexiou C, Pietryga K, Cicha I, Douglas TEL. Endothelialization of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207052
Chicago/Turabian StyleGenç, Hatice, Bernhard Friedrich, Christoph Alexiou, Krzysztof Pietryga, Iwona Cicha, and Timothy E. L. Douglas. 2023. "Endothelialization of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207052
APA StyleGenç, H., Friedrich, B., Alexiou, C., Pietryga, K., Cicha, I., & Douglas, T. E. L. (2023). Endothelialization of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration. Molecules, 28(20), 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207052








