Evaluation of the Chemosensoric Properties of Commercially Available Dog Foods Using Electronic Sensors and GC-MS/O Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
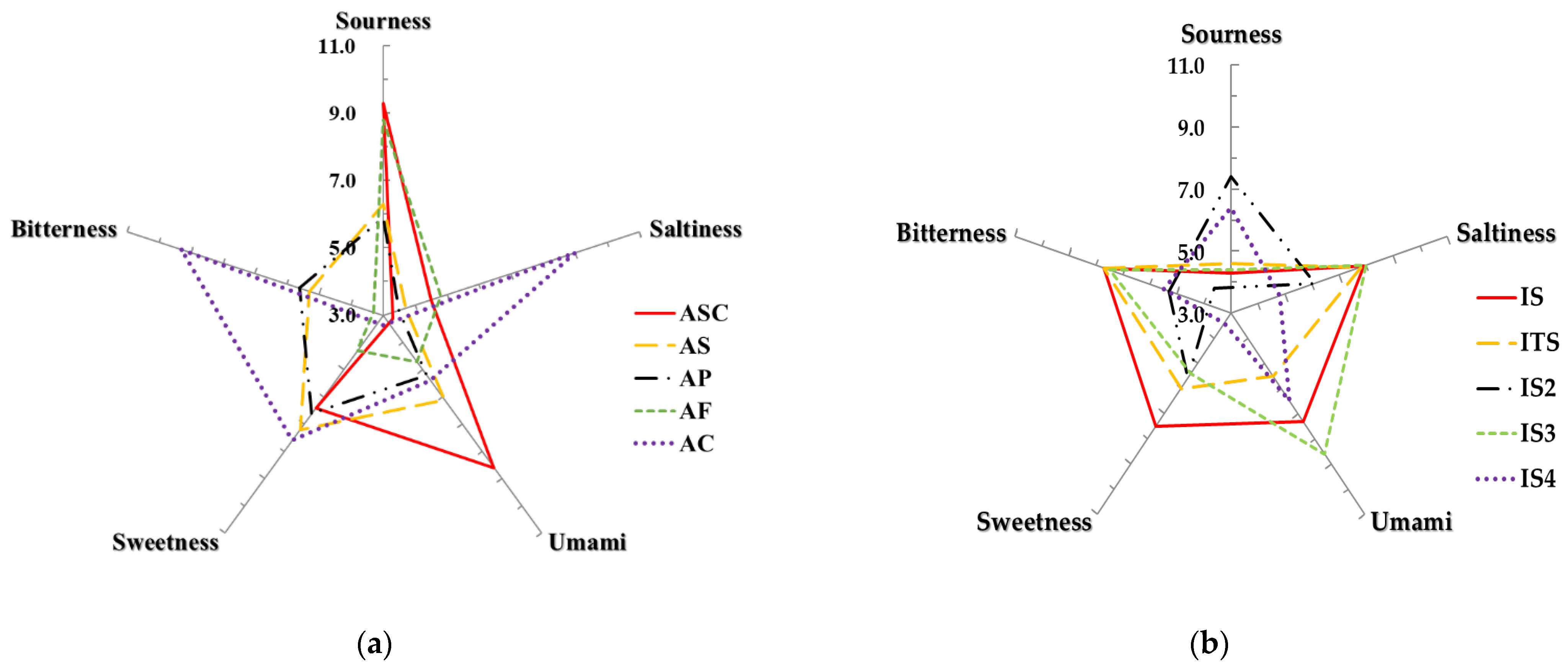
2.1. E-Tongue Analysis
2.2. E-Nose Analysis
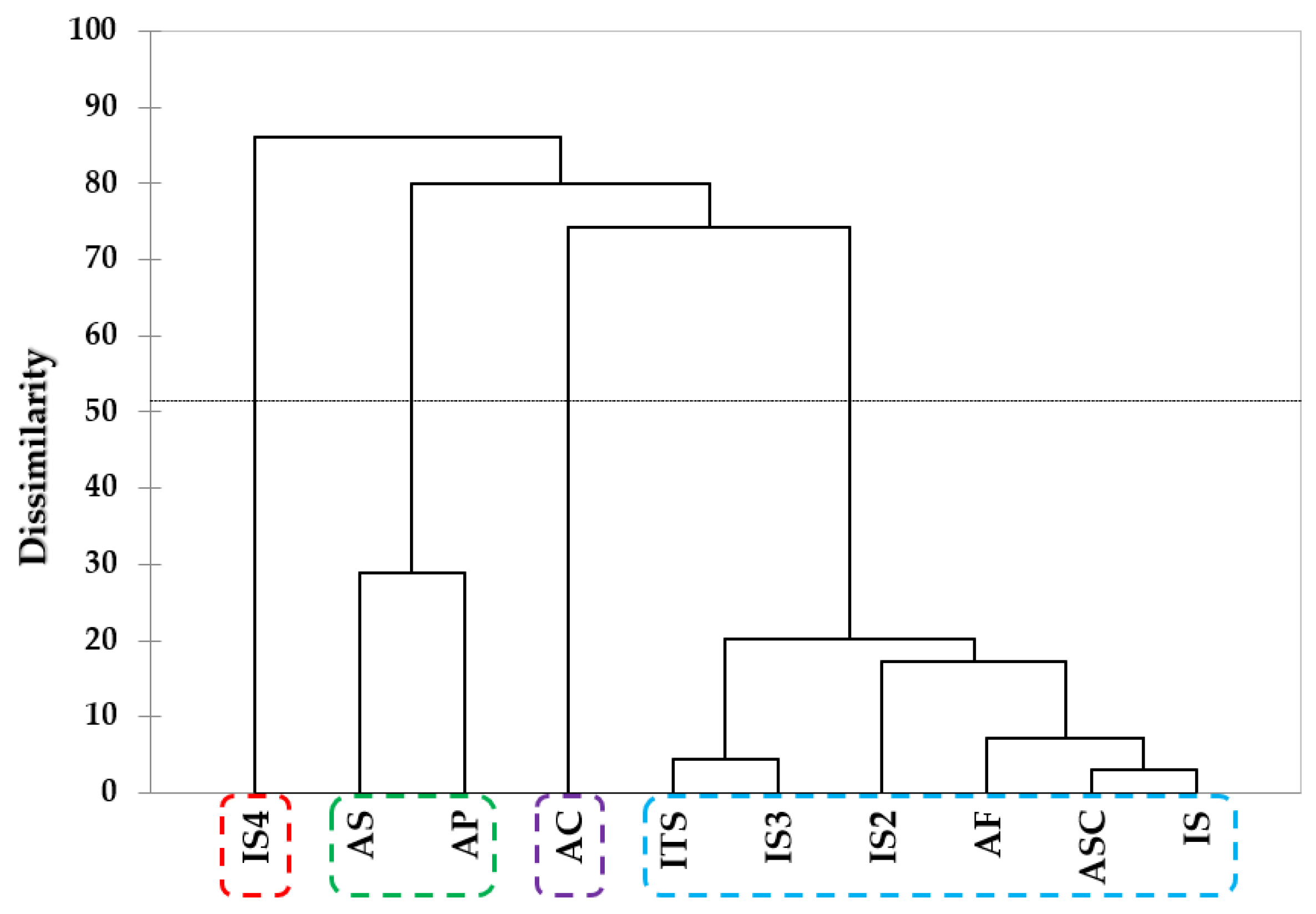
2.3. Analyses of Taste Components and Volatile Compounds Patterns via Multivariate Analyses
2.4. GC-MS Analysis
2.5. GC-O Analysis
2.6. Analyses of Odor Active Compound Patterns via Multivariate Analyses
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Electronic Tongue (E-Tongue) Analysis
3.3. Electronic Nose (E-Nose) Analysis
3.4. GC-MS Coupled with GC-Olfactometry (GC-O)
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- APPA. Pet Industry Market Size, Trends & Ownership Statistics: Actual Sales within the U.S. Market in 2021. Pet Industry Market Size, Trends & Ownership Statistics. 2021. Available online: americanpetproducts.org (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- AVMA. U.S. Pet Ownership Statistics. U.S. Pet Ownership & Demographics Sourcebook. U.S. Pet Ownership Statistics|American Veterinary Medical Association. 2018. Available online: avma.org (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Boutet, S. Innovation in Pet Nutrition and Ingredients. Petfood Industry. 2014. Available online: http://www.petfoodindustry.com/Innovation_in_pet_nutrition_and_ingredients.html (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Buff, P.R.; Carter, R.A.; Bauer, J.E.; Kersey, J.H. Natural pet food: A review of natural diets and their impact on canine and feline physiology. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 3781–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, G. Rendered Products in Pet Food. Essential Rendering. 2006, pp. 159–178. Available online: http://assets.nationalrenderers.org/essential_rendering_pet_food.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Gibson, M.W.; Sajid, A. Pet food processing: Understanding transformations in starch during extrusion and baking. Cereal Foods World 2013, 58, 232–236. Available online: http://www.aaccnet.org/publications/plexus/cfw/pastissues/2013/Pages/CFW-58-5-0232.aspx (accessed on 3 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Zicker, S.C. Evaluating Pet Foods: How Confident Are You When You Recommend a Commercial Pet Food? Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2008, 23, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Govil, K.; Thakur, D.; Kumar, A.; Saini, K.S.P. Scientific dog feeding for good health and its preparation: A review. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierska, K.; Biel, W.; Witkowicz, R.; Karakulska, J.; Stachurska, X. Evaluation of nutritional value and microbiological safety in commercial dog food. Veter-Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobie, C.; Péron, F.; LaRose, C. Assessing Food Preferences in Dogs and Cats: A Review of the Current Methods. Animals 2015, 5, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Dzanis, D. The Association of American Feed Control Officials Dog and Cat Food Nutrient Profiles: Substantiation of Nutritional Adequacy of Complete and Balanced Pet Foods in the United States. J. Nutr. 1994, 124 (Suppl. S12), 2535S–2539S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAFCO. Association of American Feed Control Officials. Dog and Cat Nutrient Profiles. Official Publications of the Association of American Feed Control Officials Incorporated; AAFCO: Oxford, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D.M.; Prescott, J. Odor/taste integration and the perception of flavor. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 166, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.B.; Møller, P.; Flint, A.; Martens, M.; Raben, A. Effect of sensory perception of foods on appetite and food intake: A review of studies on humans. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, E.K.; DeChant, M.T.; Perry, E.B. When the Nose Doesn’t Know: Canine Olfactory Function Associated With Health, Management, and Potential Links to Microbiota. Front. Veter-Sci. 2018, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmanov, A.; Bosak, N.; Lin, C.; Matsumoto, I.; Ohmoto, M.; Reed, D.; Nelson, T. Genetics of Taste Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, J.W.S. Sensory and experiential factors in the design of foods for domestic dogs and cats. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1991, 50, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.; Hecht, J.; Dedrick, A. Smelling more or less: Investigating the olfactory experience of the domestic dog. Learn. Motiv. 2013, 44, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houpt, K.A.; Hintz, H.F.; Shepherd, P. The role of olfaction in canine food preferences. Chem. Senses 1978, 3, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Martin, G.K.; Roberts, W.A. The olfactory capability of dogs to discriminate between different quantities of food. Learn. Behav. 2021, 49, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basque, C.; Cambou, S.; Peron, F.; Le Paih, L.; Marzin, C.; Hanaoka, K.; Callejon, L.; Prost, C.; Lethuaut, L. Food preference and olfactory discrimination tests: A complementary approach to understand the drivers of hedonic responses in dogs. J. Sens. Stud. 2018, 34, e12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M. Analysis of Volatiles in Food Products. Separations 2021, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress-Rogers, E.; Brimelow, C.J. (Eds.) Instrumentation and Sensors for the Food Industry; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2001; Volume 65. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Moazzem, M.S. Recent Applications of Potentiometric Electronic Tongue and Electronic Nose in Sensory Evaluation. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Hu, R.; Long, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Chu, Z. Comparative evaluation of the volatile profiles and taste properties of roasted coffee beans as affected by drying method and detected by electronic nose, electronic tongue, and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2018, 272, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, C.G.; Hong, S.J.; Shin, E.-C. Comparative Evaluation of the Volatile Profiles and Taste Properties of Commercial Coffee Products Using Electronic Nose, Electronic Tongue, and GC/MSD. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 50, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, J. GC-O-MS technique and its applications in food flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eles, V.; Hullár, I.; Romvári, R. Electronic nose and tongue for pet food classification. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2013, 78, 225–228. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/106910 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Oladipupo, B.; Stough, J.; Guthrie, N.; Gouma, P. Application of Combined Electronic Nose and Tongue Technology in Petfood Flavor Development and Quality Control. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Kolkata, India, 6–10 January 2011; Volume 1362, pp. 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, K.; Adhikari, K.; Di Donfrancesco, B. Volatile Compounds in Dry Dog Foods and Their Influence on Sensory Aromatic Profile. Molecules 2013, 18, 2646–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhong, F.; Li, Y. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Dog Foods by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, Acceptance Test, and Preference Test. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9195–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, B.D.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Gas chromatography–olfactometry in food flavour analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1186, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheli, F.; Novacco, M.; Bontempo, V.; Dell’Orto, V. Pet Food Industry: E-nose and E-tongue Technology for Quality Control. In Proceedings of the 2st International Conference on Advances in Sensors, Actuators, Metering and Sensing (ALLSENSORS 2017), Barcelona, Spain, 19–23 March 2017; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Samant, S.S.; Crandall, P.G.; Arroyo, S.E.J.; Seo, H.-S. Dry Pet Food Flavor Enhancers and Their Impact on Palatability: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Nsor-Atindana, J.; Masamba, K.G.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Optimization of key aroma compounds for dog food attractant. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 225, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettasinghe, M.; Vasanthan, T.; Temelli, F.; Swallow, K. Volatile flavour composition of cooked by-product blends of chicken, beef and pork: A quantitative GC–MS investigation. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheli, F.; Bontempo, V.; Pinotti, L.; Ottoboni, M.; Tretola, M.; Baldi, A.; Dell’Orto, V. Feed analysis and animal nutrition: Electronic nose as a diagnostic tool. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 68, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Alegría-Morán, R.A.; Guzmán-Pino, S.A.; Egaña, J.I.; Muñoz, C.; Figueroa, J. Food Preferences in Dogs: Effect of Dietary Composition and Intrinsic Variables on Diet Selection. Animals 2019, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazi, I.; Isnaini, N.L.; Mutmainnah, M.; Ainur, A. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Method for Classification of Beef and Pork Aroma Based on Electronic Nose. Indones. J. Halal Res. 2019, 1, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utama, D.T.; Jang, A.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, S.-M.; Lee, S.K. Distinguishing Aroma Profile of Highly-Marbled Beef according to Quality Grade using Electronic Nose Sensors Data and Chemometrics Approach. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ruth, S.M. Methods for gas chromatography-olfactometry: A review. Biomol. Eng. 2001, 17, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceña, L.; Vera, L.; Guasch, J.; Busto, O.; Mestres, M. Chemical Characterization of Commercial Sherry Vinegar Aroma by Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography−Olfactometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Li, T.; Song, H. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in four commercial oyster sauce by SGC/GC × GC–O–MS, AEDA, and OAV. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 107, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.M.; Hong, S.J.; Jeong, H.; Yoon, S.; Shin, E.-C. Chemical Sensory Properties of Radishes in Varying Storage Periods and Temperatures Using Electronic Sensors and Multivariate Analyses. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 51, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.-C.; Craft, B.D.; Pegg, R.B.; Phillips, R.D.; Eitenmiller, R.R. Chemometric approach to fatty acid profiles in Runner-type peanut cultivars by principal component analysis (PCA). Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.-C.; Pegg, R.B.; Phillips, R.D.; Eitenmiller, R.R. Commercial Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Cultivars in the United States: Phytosterol Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9137–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Volatile Compounds | RT (1) | Relative Intensity | Odor Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (min) | ASC | DS | DP | DF | DC | IS | ITS | IS2 | IS3 | IS4 | ||
| Acids and esters (14) | ||||||||||||
| Hexanoic acid | 7.65 | 1 | 0 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| Butanoic acid | 8.143 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | Dogfood, Bitter |
| 3-Methyl-butanoic acid | 9.594 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Salty |
| Isovaleric acid | 9.765 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Salty |
| 2-Methyl-octanoic acid | 10.07 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Dogfood |
| 2-Methyl-butanoic acid | 10.086 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | Salty |
| Pentanoic acid | 11.005 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Salty, Dogfood |
| Propyl-propanedioic acid | 11.112 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2-Amino-4-methylbenzoic acid | 11.409 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Dogfood |
| 4-Methyl-pentanoic acid | 12.873 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Salty |
| Heptanoic acid | 14.084 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Bitter |
| Sobutyl octyl carbonate | 15.261 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Roasted |
| Sorbic Acid | 16.864 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| Heptanoic acid, ethyl ester | 17.545 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| Alcohols (5) | ||||||||||||
| Heptanol | 13.52 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 13.839 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 4-Methyl-phenol | 16.815 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Alcohols |
| 9-Octadecen-1-ol | 18.722 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| 4-Terpineol | 19.938 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Spicy |
| Aldehydes (8) | ||||||||||||
| 3-Methoxy-propanal | 7.717 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| Hexanal | 7.951 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Bitter |
| Heptanal | 11.27 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | Dogfood |
| Benzaldehyde | 13.217 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Dogfood, Bitter |
| Octanal | 14.587 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| 2,4-Heptadienal | 14.834 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | 15.9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| Nonanal | 17.72 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | Roasted, Bitter |
| Hydrocabons (21) | ||||||||||||
| Methylbenzene | 6.991 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Bitter, Dogfood |
| Ethylbenzene | 9.932 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sour |
| 4-Methyl-octane | 9.992 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 1,4-Dimethyl-benzene | 10.177 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Salty |
| 1,3-Dimethyl-benzene | 10.262 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood, Roasted |
| Pulegone | 11.637 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| Sulfonylbis-methane | 11.808 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2-Decene | 13.648 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 2,2,4,6,6-Pentamethylheptan | 14.176 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | Dogfood, Bitter |
| 3,3-Dimethylhexane | 15.563 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Dogfood |
| 2-Methyldecane | 16.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | Bitter |
| 2,2,3,4-Tetramethylpentane | 16.269 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Roasted |
| 3-Methylhexadecane | 16.476 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| 3,8-Dimethyldecane | 16.493 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| Undecane, 2,8-dimethyl- | 16.867 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Roasted |
| 2,3,6,7-Tetramethyloctane | 17.107 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Sweet |
| 3,3-Dimethylhexane | 17.266 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| Dimethyl-4-aniline | 18.001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2,3,5-Trimethyldecane | 18.877 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Salty |
| 2-Butyl-1-decene | 19.547 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Roasted |
| Dodecane | 20.472 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Dogfood, Salty |
| Heterocyclic compounds (8) | ||||||||||||
| Methoxy-phenyl-oxime | 11.343 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2,6-Dimethylpyrazine | 11.603 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2-Acetylpyrrole | 16.397 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Sweet |
| 2,6-Diethylpyrazine | 16.95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Sweet |
| 2-Ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-pyrazine | 16.971 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Roasted, Bitter |
| Tetramethyl-pyrazine | 17.213 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 2-3-Indole | 18.995 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | Roasted, Bitter |
| 1-2-Pyrrolidon | 20.862 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Bitter |
| Ketones (8) | ||||||||||||
| 2-Heptanone | 10.952 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| Dimethyl sulfone | 11.827 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one | 14.055 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Salty |
| 3,5-Octadiene-2-one | 16.71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| 2-Nonanone | 17.362 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bitter |
| 5-Methyl-2-cyclohexanone | 19.568 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Spicy |
| 2-Piperidinone | 19.813 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Dogfood |
| Chrysanthenone | 20.88 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Roasted |
| Furans (3) | ||||||||||||
| Furfural | 9.153 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Dogfood |
| 2-Furanmethanol | 9.758 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
| 2-Pentylfuran | 14.219 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Sweet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Youn, M.Y.; Yoon, S.; Hong, S.J.; Jo, S.M.; Kim, K.S.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, H.-W.; Shin, E.-C. Evaluation of the Chemosensoric Properties of Commercially Available Dog Foods Using Electronic Sensors and GC-MS/O Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145509
Jeong H, Youn MY, Yoon S, Hong SJ, Jo SM, Kim KS, Jeong EJ, Kim H-W, Shin E-C. Evaluation of the Chemosensoric Properties of Commercially Available Dog Foods Using Electronic Sensors and GC-MS/O Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145509
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyangyeon, Moon Yeon Youn, Sojeong Yoon, Seong Jun Hong, Seong Min Jo, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Hyun-Wook Kim, and Eui-Cheol Shin. 2023. "Evaluation of the Chemosensoric Properties of Commercially Available Dog Foods Using Electronic Sensors and GC-MS/O Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145509
APA StyleJeong, H., Youn, M. Y., Yoon, S., Hong, S. J., Jo, S. M., Kim, K. S., Jeong, E. J., Kim, H.-W., & Shin, E.-C. (2023). Evaluation of the Chemosensoric Properties of Commercially Available Dog Foods Using Electronic Sensors and GC-MS/O Analysis. Molecules, 28(14), 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145509







