Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
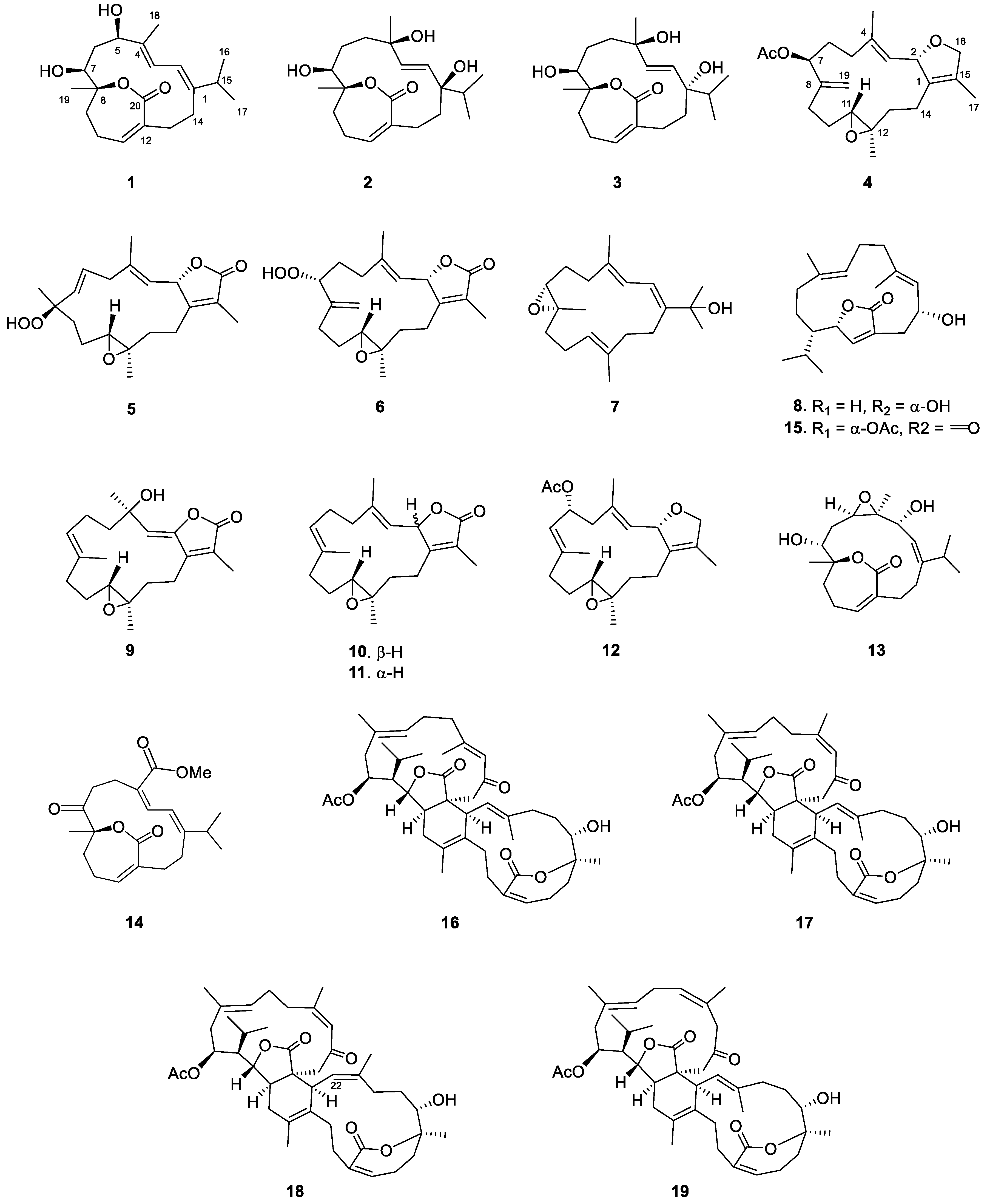
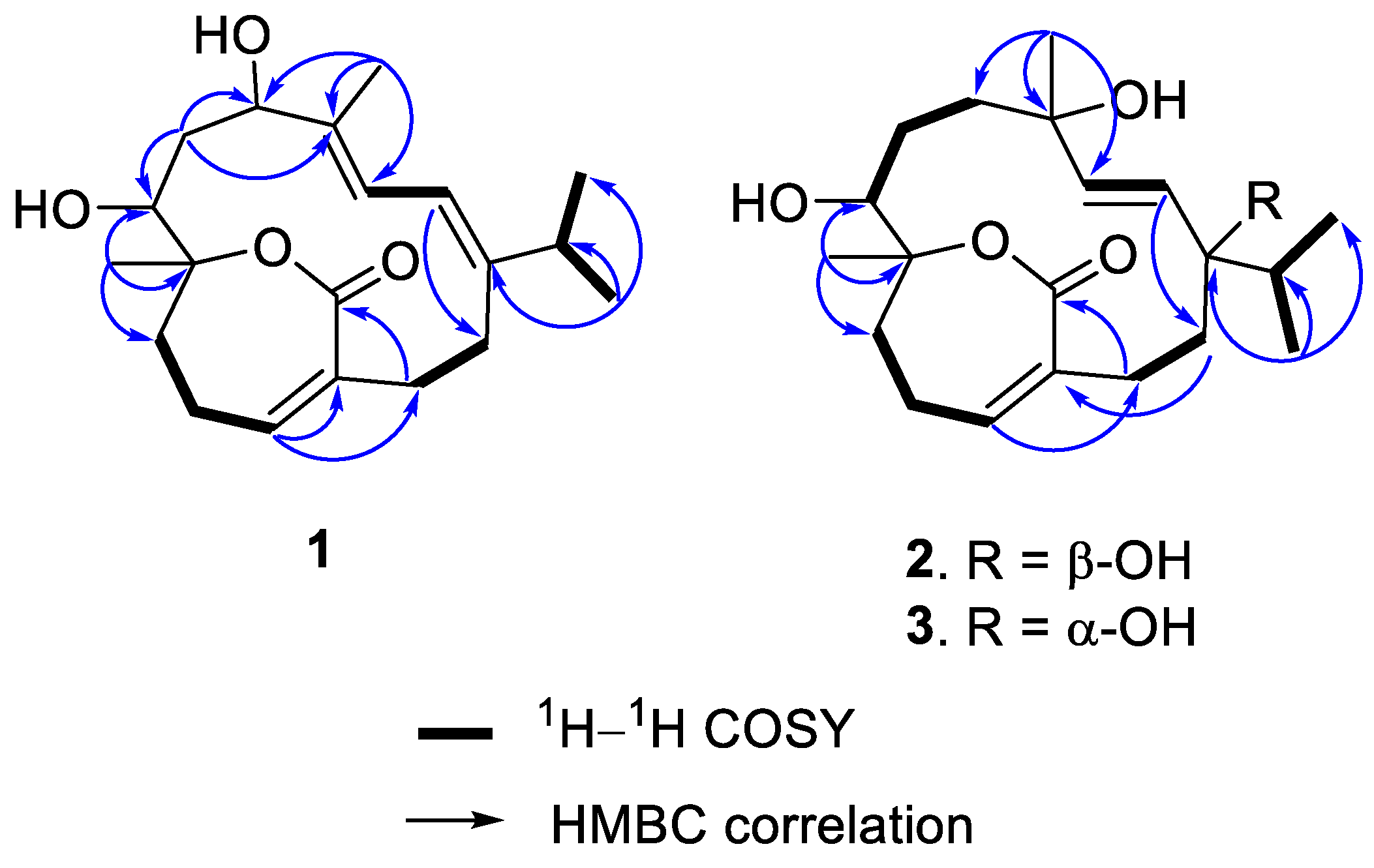
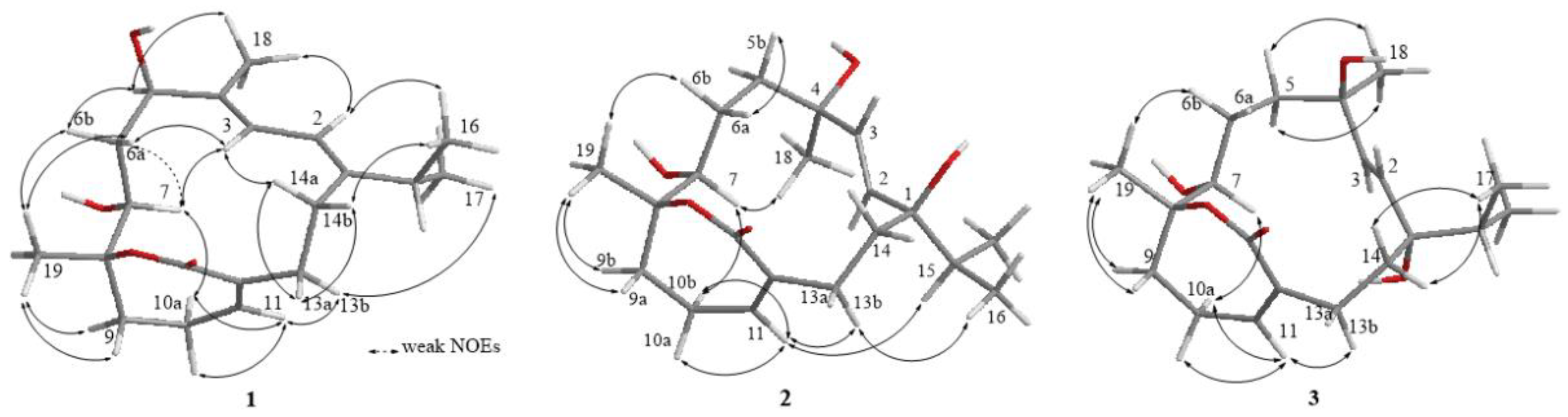
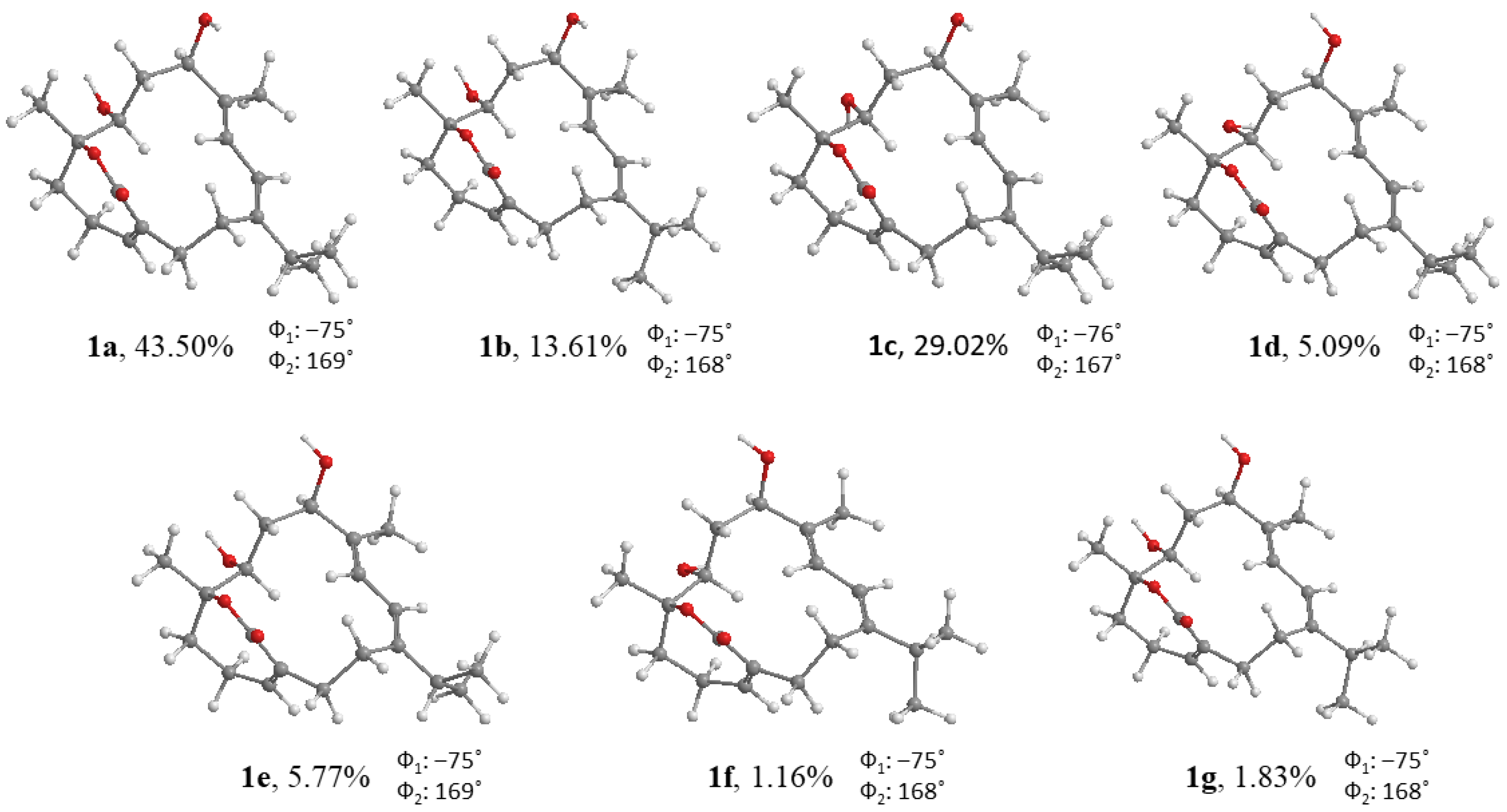
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Computational Method
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinesen, Z.D. Patterns in the distribution of soft corals across the central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 1983, 1, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E. Soft coral abundance on the central Great Barrier Reef: Effects of Acanthaster planci, space availability, and aspects of the physical environment. Coral Reefs 1997, 16, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Tursch, A. The soft coral community on a sheltered reef quadrat at Laing Island (Papua New Gunea). Mar. Biol. 1982, 68, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, M.A.; Capra, M.F.; Carlisle, C.H.; Lawn, I.; Coll, J.C. Stimulation of contractions in the polyps of the soft coral Xenia elongata by compounds extracted from other Alcyonacean soft corals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1989, 94, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, B.G.; Coll, J.C.; Sammarco, P.W. Complementary (secondary) metabolites in a soft coral: Sex-specific variability, inter-clonal variability, and competition. Mar. Ecol. 2006, 27, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Hsieh, M.K.; Duh, C.Y. Polyoxygenated cembrane diterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6140–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Lin, C.C.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Isolation and structure elucidation of cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, S.R.; Weng, J.R.; Tu, T.H.; Cheng, Y.B.; Wu, S.H.; Sheu, J.H. New hydroquinone monoterpenoid and cembranoid-related metabolites from the soft coral Sarcophyton tenuispiculatum. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.C.; Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. Cherbonolides M and N from a Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chao, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Dai, C.F.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Wu, S.H.; Sheu, J.H. New biscembranoids sardigitolides A–D and known cembranoid-related compounds from Sarcophyton digitatum: Isolation, structure elucidation, and bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chen, S.R.; Cheng, Y.B.; Hwang, T.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Dai, C.F.; et al. Cembranoid-related diterpenes, novel secoditerpenes, and an unusual bisditerpene from a Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton Tortuosum. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chao, C.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Chang, F.R.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. An unprecedented cembranoid with a novel tricyclo [9.3.0.02,12]tetradecane skeleton and related diterpenes from the soft coral Sarcophyton cinereum. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 95, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, H.; Mao, S.; Guo, Y. Cembrane-type diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton mililatensis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.C.; Hawes, G.B.; Liyanage, N.; Oberhasli, W.; Wells, R.J. A new cembranoid diterpene from a Sarcophyton species. Aust. J. Chem. 1977, 30, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Guo, Y.W.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G. Sarcophytonolides E–H, cembranolides from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton latum. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory cembranolides from a Formosa soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Yamada, K.; Ishitsuka, M.O.; Fujita, Y.; Kakisawa, H. New cembranoids from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia mayi. Chem. Lett. 1990, 37, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, A.; Hertzer, C.; Kehraus, S.; Nietzer, S.; Rohde, S.; Schupp, P.J.; Wägele, H.; König, G.M. Secondary metabolome and its defensive role in the aeolidoidean Phyllodesmium longicirrum, (Gastropoda, Heterobranchia, Nudibranchia). Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, G.H.; Sun, Z.H.; Zou, Y.H.; Yin, S. New cembrane-type diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Molecules 2016, 21, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.F.; Lan, L.F.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Guo, Y.W. Sartrolides A–G and bissartrolide, new cembranolides from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 7381–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuto, U.; Masayoshi, N.; Mitsuru, N.; Tetsuo, I.; Tsunao, H. Ketoemblide and sarcophytolide, two new cembranolides with ε-lactone function from the soft coral Sarcophyta elegans. Chem. Lett. 1983, 12, 613–616. [Google Scholar]
- Takamura, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Endo, N.; Fukuda, Y.; Kadota, I. Total synthesis of sarcophytonolide H and isosarcophytonolide D: Structural revision of isosarcophytonolide D and structure−antifouling activity relationship of sarcophytonolide H. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Uvaranil, C.; Su, J.H.; Lu, M.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, S.L.; Sheu, J. Glaucumolides A and B, biscembranoids with new structural type from a cultured soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Cai, F.Y.; Lauro, G.; Tang, H.; Su, L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, H.H.; Mándi, M.; Kurtán, T.; Riccio, R.; et al. Immunomodulatory biscembranoids and assignment of their relative and absolute configurations: Data set modulation in the density functional theory/nuclear magnetic resonance approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, H.; Wright, A.D.; Beil, W.; König, G.M. Two new bicyclic cembranolides from a new Sarcophyton species and determination of absolute configuration of sarcoglaucol-16-one. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Sensitivity analysis of DP4+ with the probability distribution terms: Development of a universal and customizable method. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 8544–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.C.; Sung, P.J.; Suh, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Sheu, J.H.; Yang, L.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of natural products isolated from soft corals of Taiwan between 2008 and 2012. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4083–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.C.; Li, R.N.; Lin, L.C.; Tang, J.Y.; Su, J.H.; Sheu, J.H.; Chang, H.W. Comparison of antioxidant and anticancer properties of soft coral-derived Sinularin and dihydrosinularin. Molecules 2021, 26, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, F.; Saliu, F.; Maggioni, D.; Montano, S.; Seveso, D.; Lavorano, S.; Zoia, L.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Galli, P. Cytotoxic compounds from Alcyoniidae: An overview of the last 30 years. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, G.R.; Caton, M.C.; Nova, M.P.; Parandoosh, Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth and viability in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 204, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 a | 2 b | 2 c | 3 b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) |
| 2 | 6.13 d (11.6) | 5.40 d (16.4) | 5.37 d (16.4) | 5.44 d (16.0) |
| 3 | 5.82 d (11.6) | 5.53 d (16.4) | 5.52 d (16.4) | 5.43 d (16.0) |
| 5 | 4.19 (11.0, 8.0, 4.0) | 1.84 m | 1.98 m | 1.74 m |
| 1.73 m | 1.82 m | |||
| 6 | 2.30 m | 1.66 m | 1.66 m | 1.82 m |
| 1.89 m | 1.46 m | 1.66 m | 1.37 m | |
| 7 | 4.11 dd (9.2, 8.4) | 3.92 d (10.8) | 3.75 d (10.0) | 3.79 d |
| 9 | 2.21 m | 2.24 m | 2.23 m | 2.20 m |
| 2.06 m | 1.95 m | 2.00 m | 1.89 m | |
| 10 | 2.58 m | 2.69 m | 2.53 m | 2.67 m |
| 2.40 m | 2.52 m | 2.50 m | 2.45 m | |
| 11 | 6.08 t (3.6) | 6.55 t (3.9) | 6.51 t (5.0) | 6.49 s |
| 13 | 3.17 t (12.2) | 2.90 td (12.0, 4.0) | 3.09 m | 2.72 m |
| 1.84 m | 2.22 m | 2.50 m | 2.38 m | |
| 14 | 2.57 td (12.2, 8.0) | 1.92 m | 1.90 m | 2.27 m |
| 2.13 m | 1.79 m | 1.81 m | 1.67 m | |
| 15 | 2.33 m | 1.70 m | 1.80 m | 1.60 m |
| 16 | 1.10 d (6.8) | 0.89 d (6.8) | 0.85 d (6.8) | 0.87 d (6.4) |
| 17 | 1.06 d (6.8) | 0.81 d (6.8) | 0.80 d (6.8) | 0.83 d (6.4) |
| 18 | 1.92 s | 1.26 s | 1.30 s | 1.25 s |
| 19 | 1.41 s | 1.29 s | 1.31 s | 1.26 s |
| 5-OH | 1.38 d (8.0) | |||
| 7-OH | 1.24 d (8.4) |
| 1 a | 2 b | 2 c | 3 b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | δC (mult.) | δC (mult.) | δC (mult.) | δC (mult.) |
| 1 | 149.9 (C) | 77.0 (C) | 74.5 (C) | 77.1 (C) |
| 2 | 118.5 (CH) | 135.1(CH) | 134.8 (CH) | 132.4 (CH) |
| 3 | 123.0 (CH) | 135.1(CH) | 133.4 (CH) | 135.1(CH) |
| 4 | 133.3 (C) | 74.9 (C) | 73.8 (C) | 74.0 (C) |
| 5 | 73.0 (CH) | 37.5 (CH2) | 34.0 (CH2) | 36.9 (CH2) |
| 6 | 36.0 (CH2) | 25.6 (CH2) | 25.6 (CH2) | 25.2 (CH2) |
| 7 | 67.5 (CH) | 71.7 (CH) | 72.2 (CH) | 70.2 (CH) |
| 8 | 83.0 (C) | 86.1 (C) | 83.9 (C) | 85.7 (C) |
| 9 | 34.1 (CH2) | 35.3 (CH2) | 36.6 (CH2) | 35.8 (CH2) |
| 10 | 27.3 (CH2) | 28.4 (CH2) | 27.9 (CH2) | 28.3 (CH2) |
| 11 | 140.5 (CH) | 144.8 (CH) | 144.0 (CH) | 145.2 (CH) |
| 12 | 133.2 (C) | 134.8 (C) | 134.2 (C) | 132.6 (C) |
| 13 | 37.4 (CH2) | 32.9 (CH2) | 32.0 (CH2) | 35.6 (CH2) |
| 14 | 27.2 (CH2) | 39.0 (CH2) | 38.0 (CH2) | 36.8 (CH2) |
| 15 | 35.7 (CH) | 38.4 (CH) | 40.1 (CH) | 43.4 (CH) |
| 16 | 22.1 (CH3) | 16.8 (CH3) | 16.7 (CH3) | 17.1 (CH3) |
| 17 | 22.8 (CH3) | 17.4 (CH3) | 16.9 (CH3) | 18.0 (CH3) |
| 18 | 17.2 (CH3) | 31.9 (CH3) | 32.0 (CH3) | 32.5 (CH3) |
| 19 | 22.0 (CH3) | 22.5 (CH3) | 21.7 (CH3) | 22.7 (CH3) |
| 20 | 166.5 (C) | 170.4 (C) | 168.7 (C) | 169.3 (C) |
| DP4+ (%) | ||||
| 1α4β-3 | 1β4α-3 | 1α4α-3 | 1β4β-3 | |
| H | 100.00% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| C | 100.00% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| All data | 100.00% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Compound | P388 a | DLD-1 b | HuCCT-1 c | CCD966SK d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 3 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 4 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 5 | 15.2 ± 3.2 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 6 | 11.8 ± 4.6 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 7 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 8 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 9 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 10 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 11 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 12 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 13 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 14 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| 15 | >30 | >30 | >30 | 27.6 ± 7.8 |
| 16 | 16.7 ± 5.8 | >30 | 19.1 ± 6.4 | 21.3 ± 5.8 |
| 17 | 22.8 ± 9.7 | >30 | >30 | 26.1 ± 10.3 |
| 18 | 10.6 ± 1.9 | 9.9 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 18.8 ± 6.9 |
| 19 | >30 | >30 | >30 | 18.8 ± 6.8 |
| Doxorubicin | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, F.-R.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum. Molecules 2022, 27, 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061760
Chao C-H, Chen Y-J, Huang C-Y, Chang F-R, Dai C-F, Sheu J-H. Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum. Molecules. 2022; 27(6):1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061760
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Chih-Hua, Yi-Ju Chen, Chiung-Yao Huang, Fang-Rong Chang, Chang-Feng Dai, and Jyh-Horng Sheu. 2022. "Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum" Molecules 27, no. 6: 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061760
APA StyleChao, C.-H., Chen, Y.-J., Huang, C.-Y., Chang, F.-R., Dai, C.-F., & Sheu, J.-H. (2022). Cembranolides and Related Constituents from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton cinereum. Molecules, 27(6), 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061760







