Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System
Abstract
1. Introduction
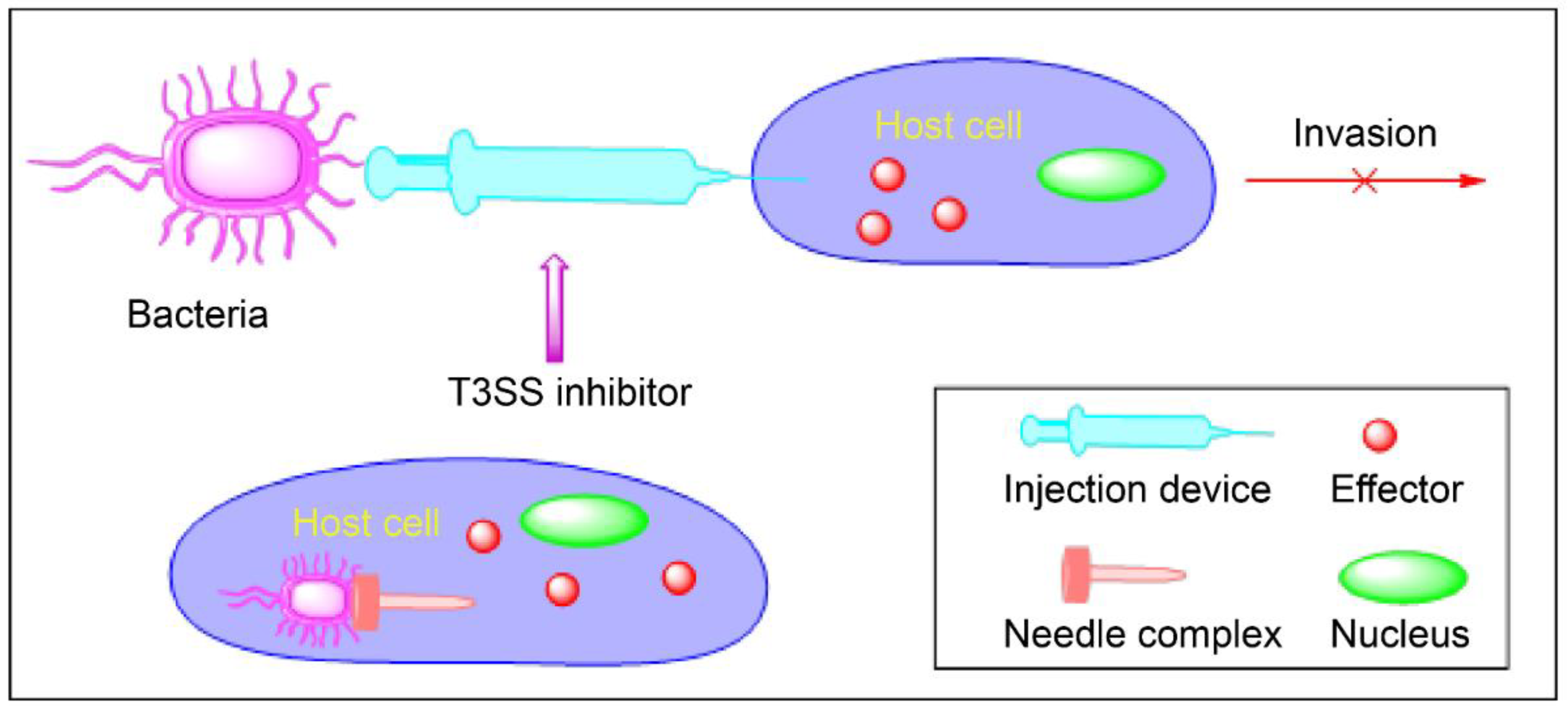
2. Virulence Blockers
3. Type 3 Secretion Systems
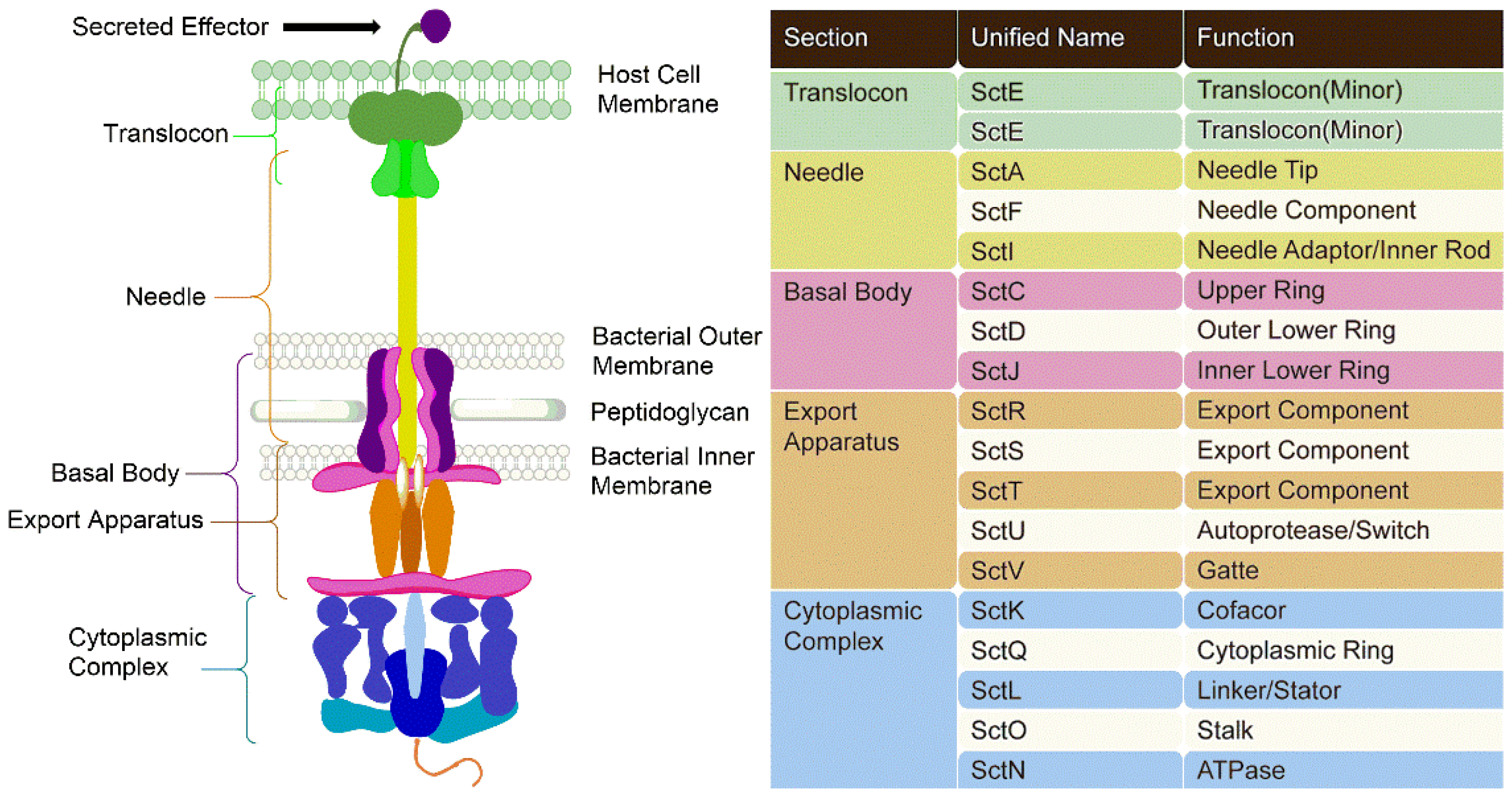
3.1. Components of T3SSs
3.2. Mechanism of Action of T3SSs
4. Inhibitors of T3SSs
5. Synthesized Inhibitors of T3SSs
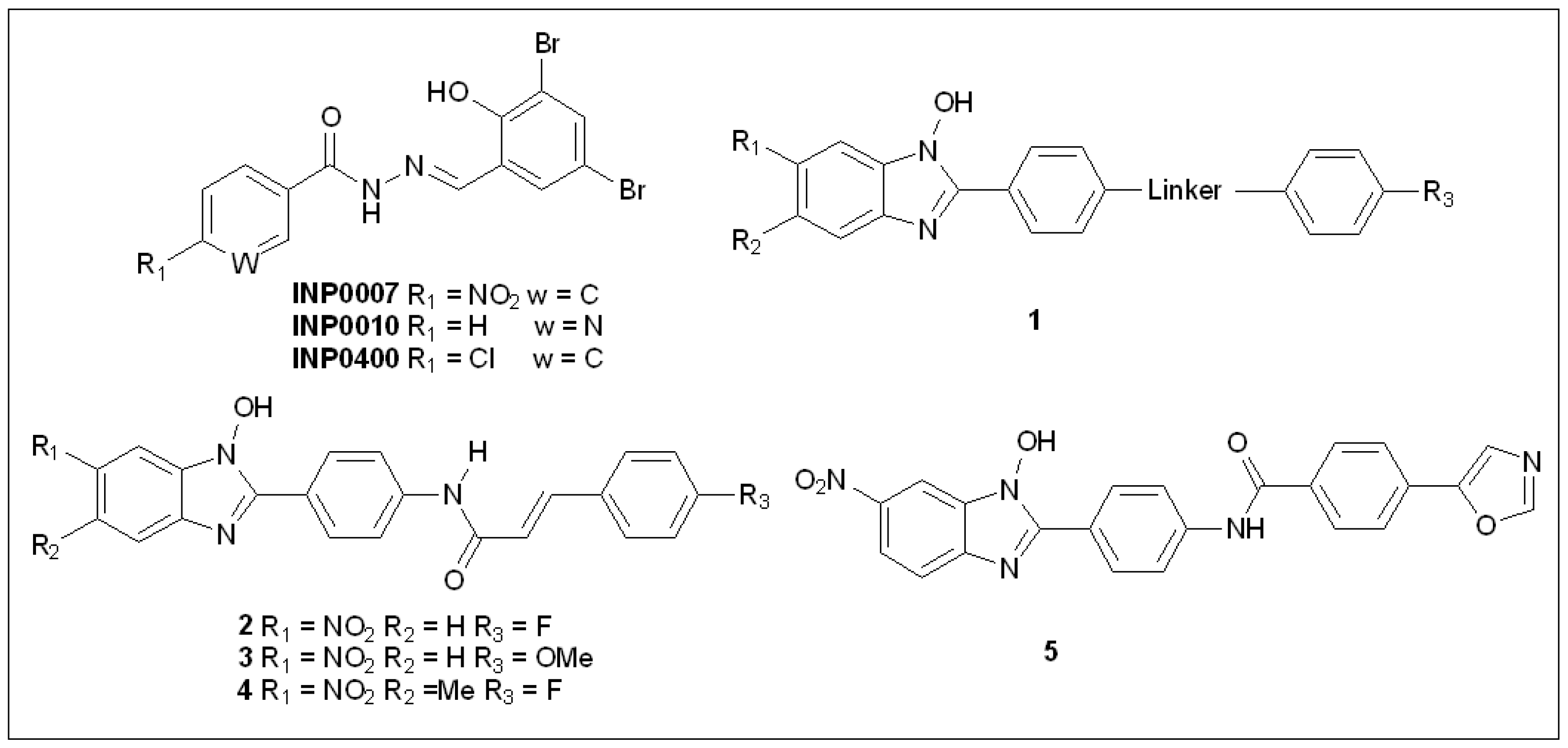
5.1. Salicylidene Acyl Hydrazides
5.2. N-Hydroxybenzimidazoles
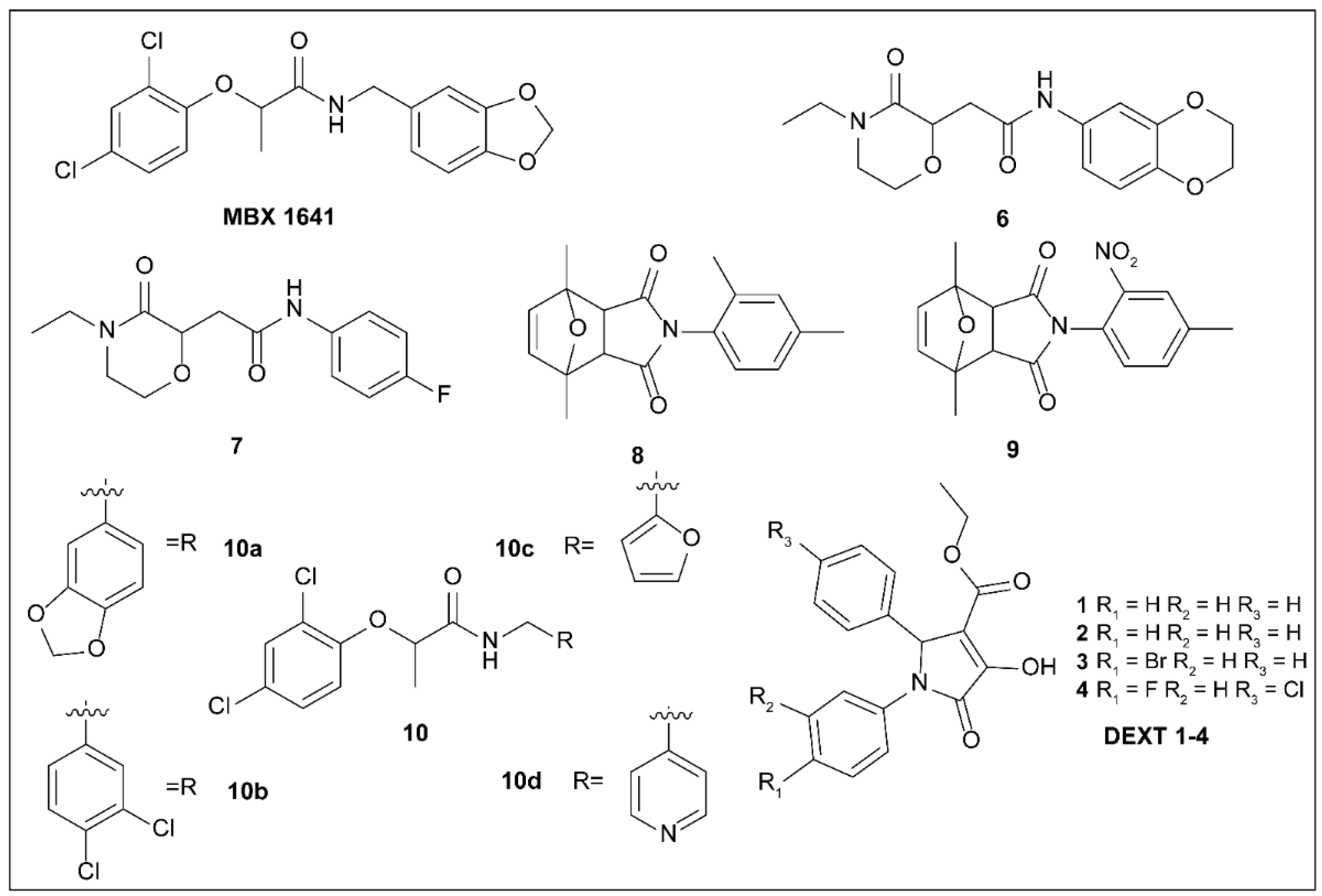
5.3. Phenoxyacetamides
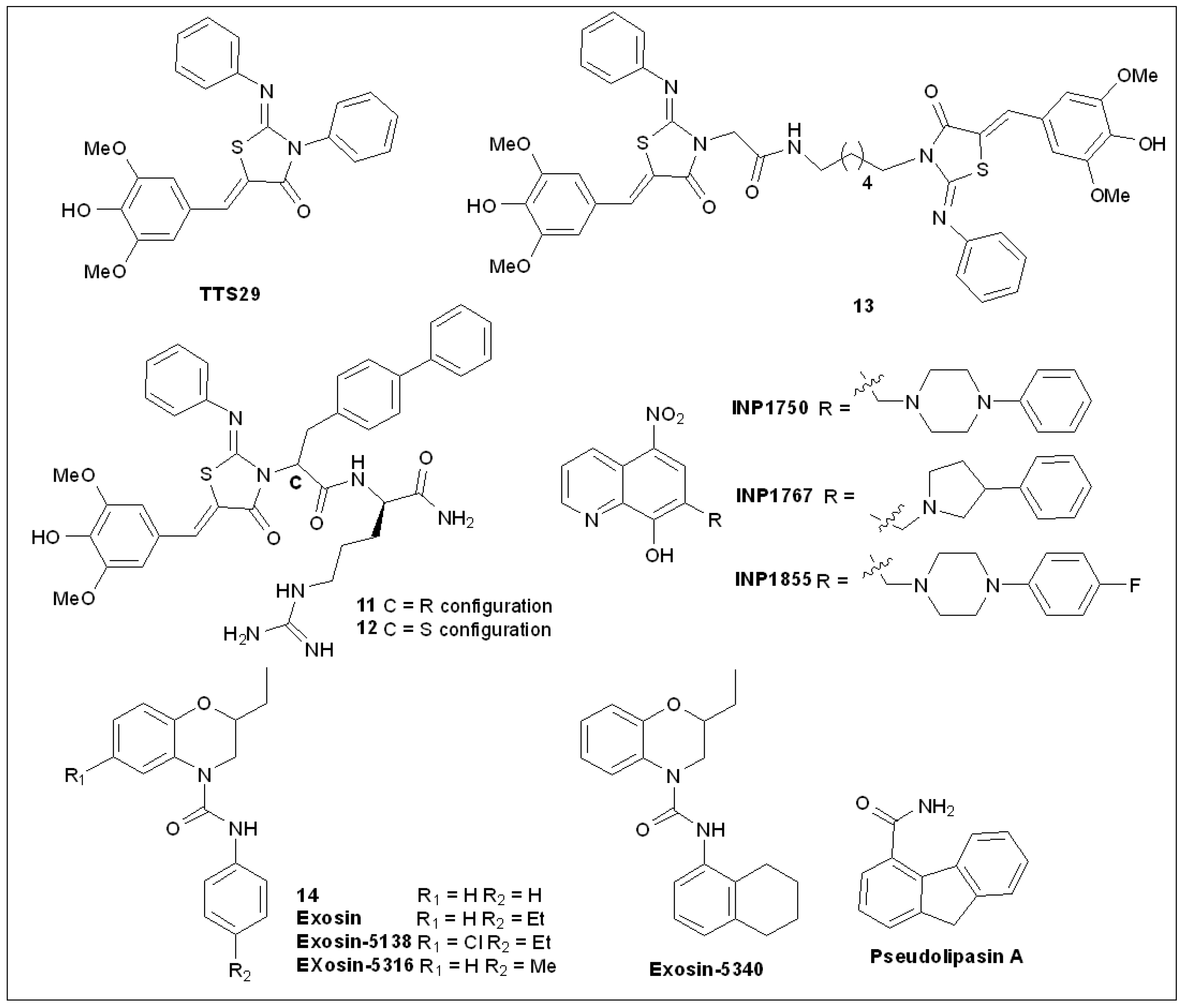
5.4. 2-Imino-5-Arylidenethiazolidinones
5.5. 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives
5.6. 2,3-Dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-4-carboxamides
5.7. Pseudolipasin A
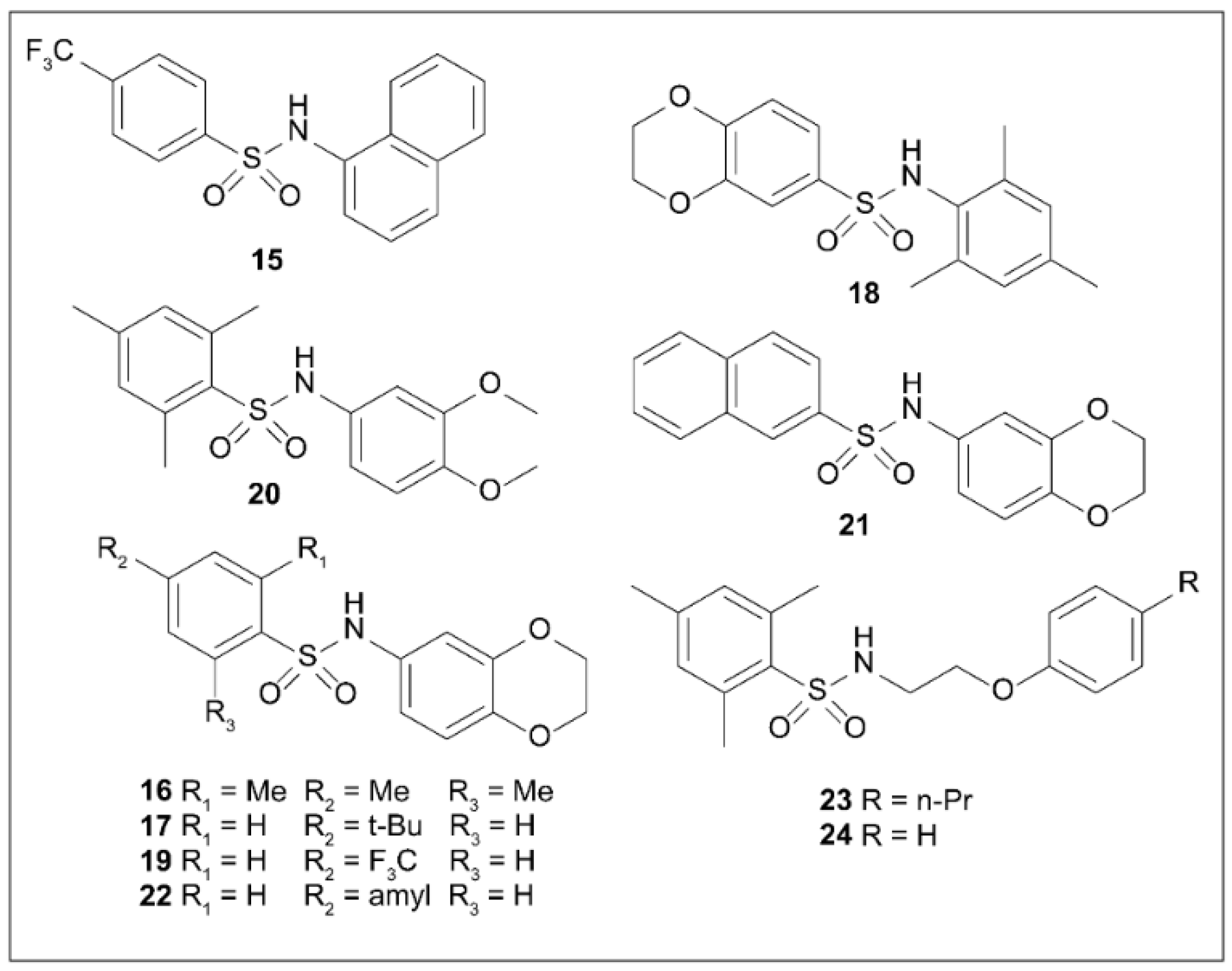
5.8. Arylsulfonamides
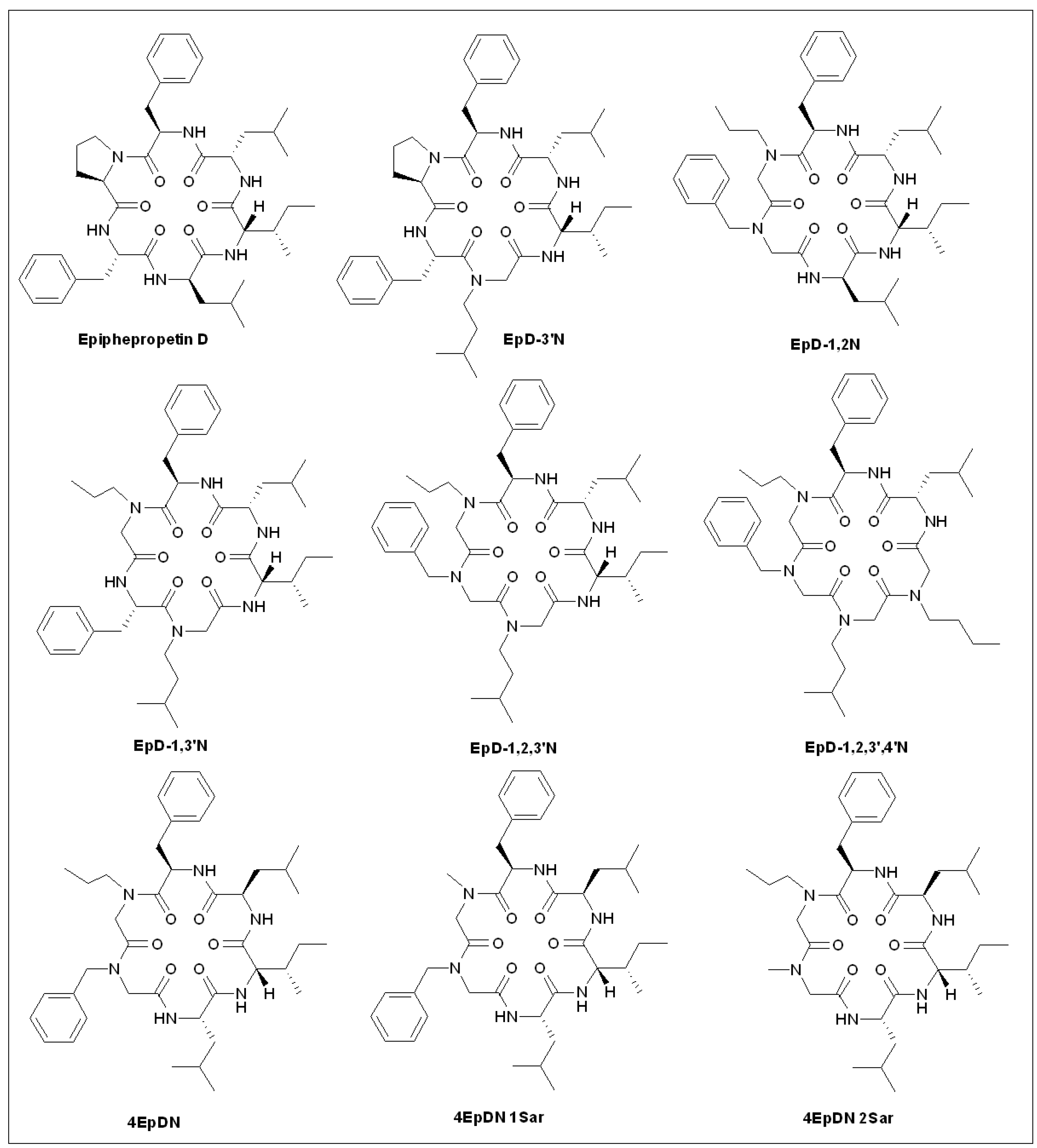
5.9. Epiphepropetin D Derivatives
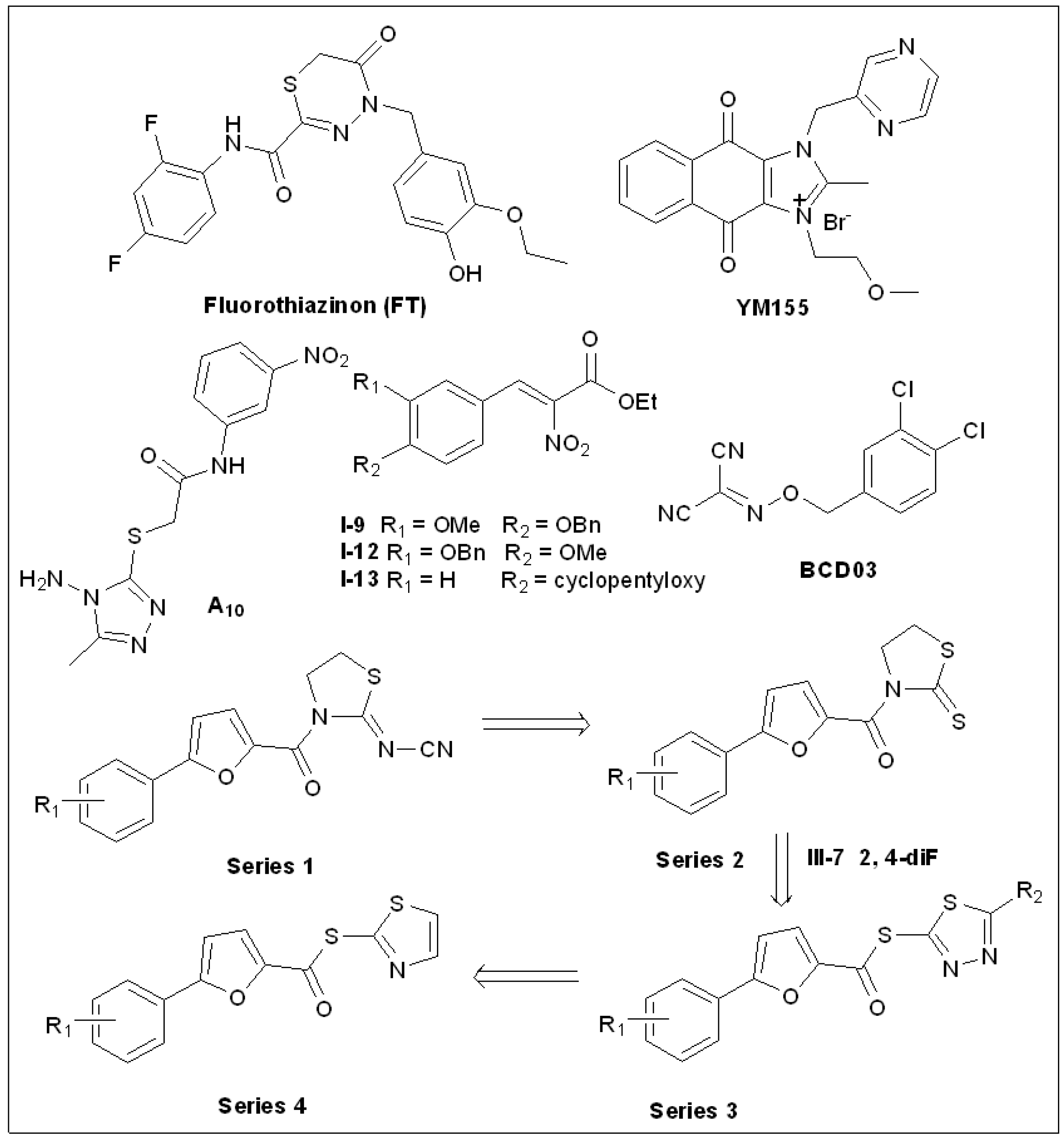
5.10. Fluorothiazinon (FT)
5.11. Sepantronium Bromide (YM155)
5.12. 1,2,4-Triazole Thioether(A10)
5.13. Thiazolidin-2-Cyanamide Derivatives and Analogs
5.14. 2-Nitro-3-Arylacrylates
5.15. Benzyloxy Carbonimidoyl Dicyanides
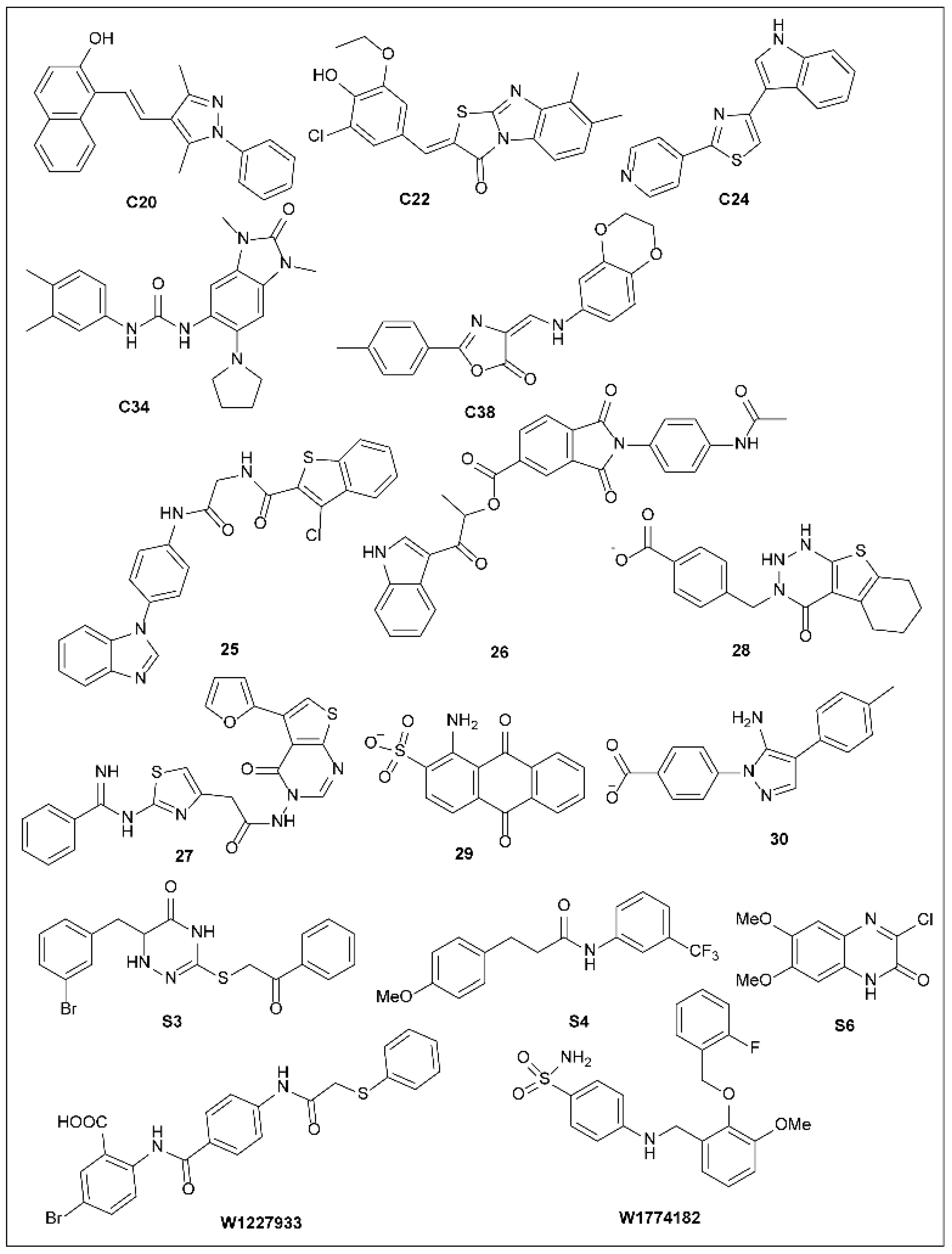
5.16. Other Synthetic T3SS Inhibitors
6. Naturally Occurring T3SS Inhibitors
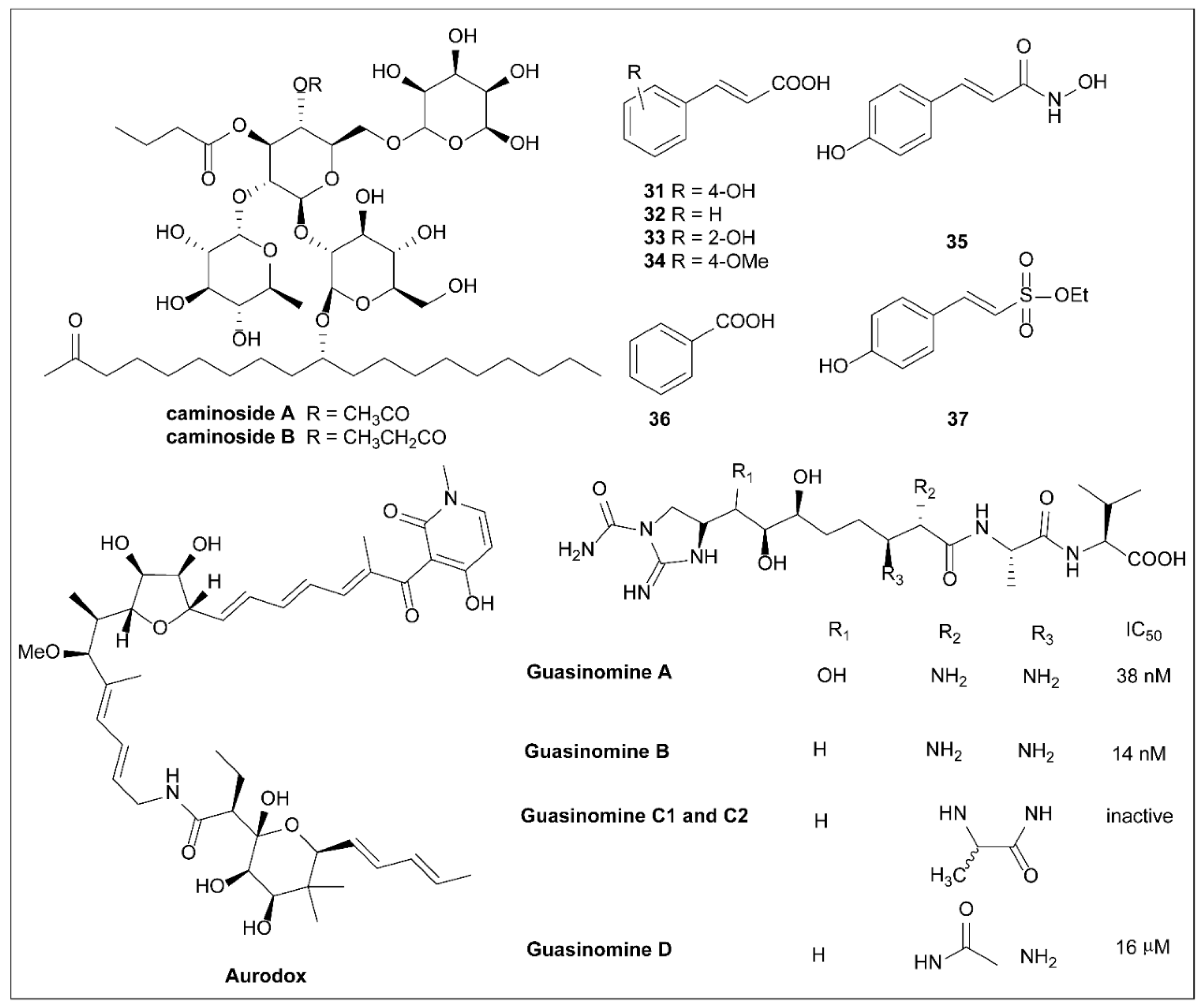
6.1. Caminosides
6.2. Plant Phenolic Compounds
6.3. Aurodox
6.4. Guasinomines
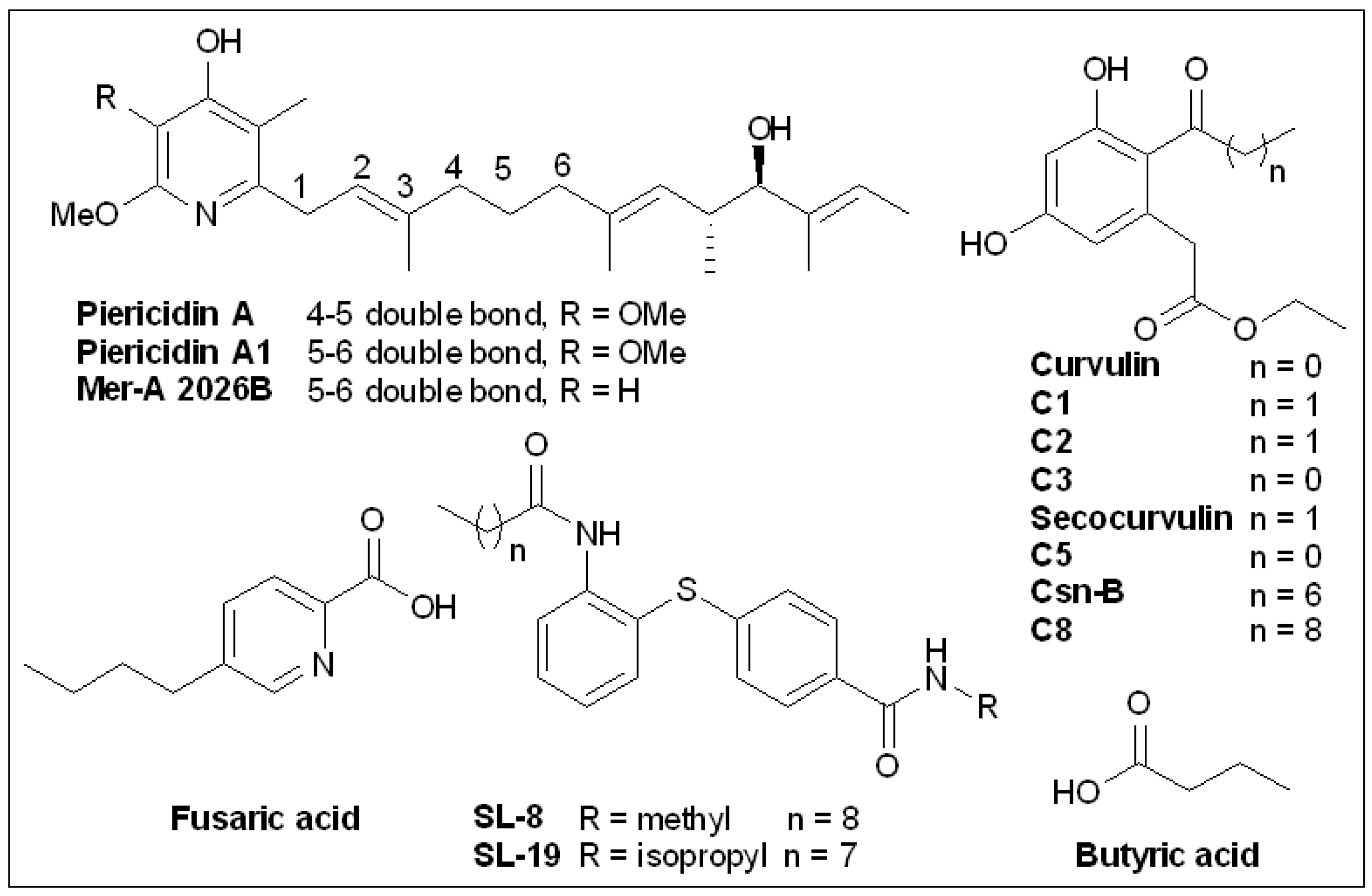
6.5. Piericidins
6.6. Cytosporone B and Derivatives
6.7. Butyric Acid
6.8. Fusaric Acid and Derivatives
6.9. (-)-Hopeaphenol
6.10. Sanguinarine Chloride
6.11. Thymol and Carbvacrol
6.12. Syringaldehyde
6.13. Paeonol
6.14. Cinnamaldehyde
6.15. Flavonoids
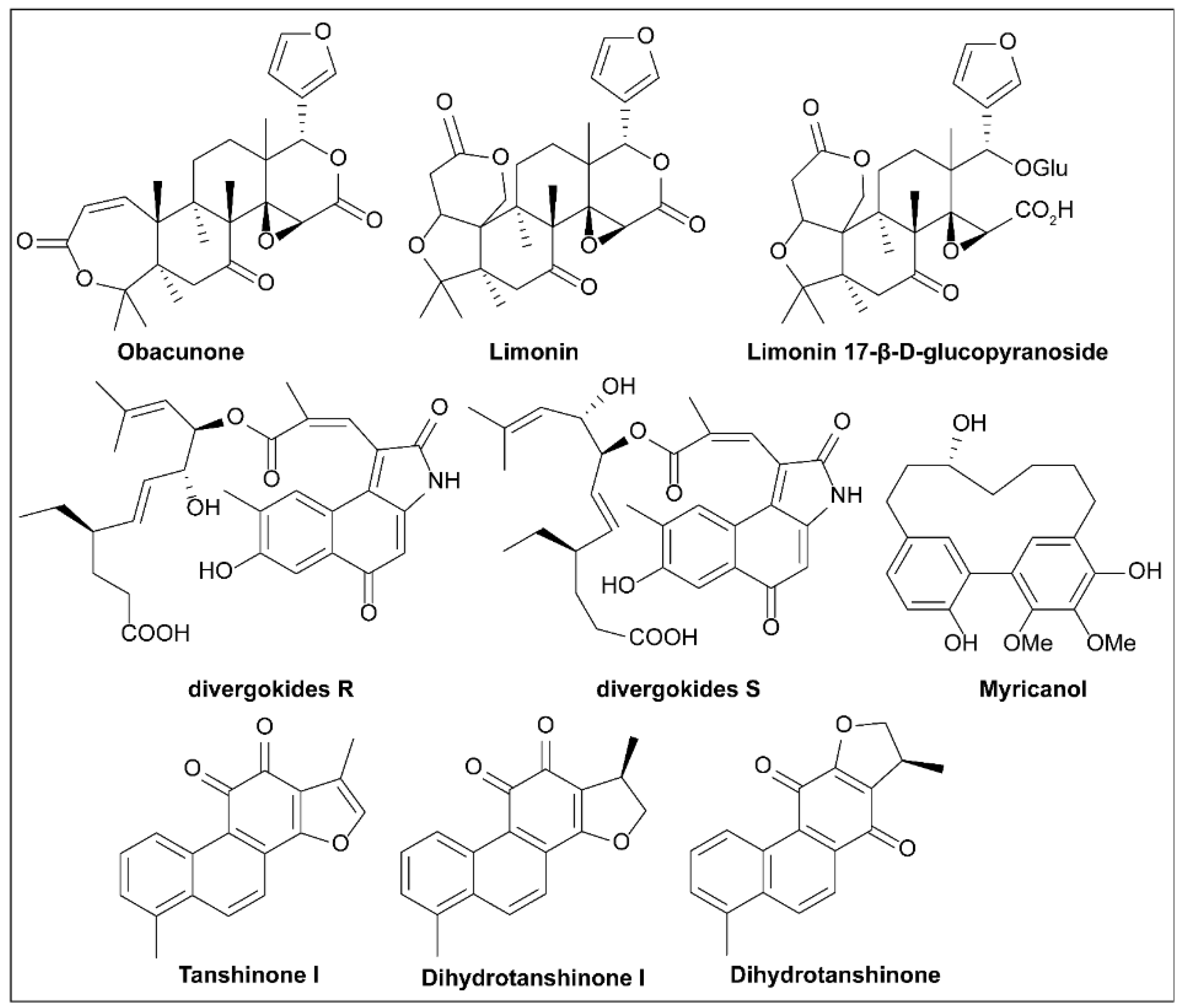
6.16. Limonoids
6.17. Divergokide R and Divergokide S
6.18. Tanshinones
6.19. Myricanol
6.20. Tannic Acid
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodward, S.E.; Krekhno, Z.; Finlay, B.B. Here, there, and everywhere: How pathogenic Escherichia coli sense and respond to gastrointestinal biogeography. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Novel therapeutic strategies for treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Fan, S.-S.; Jiang, S.; Xiang, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, L.-H.; Cui, Z.-N. Small Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Targeting the Type III Secretion System of Xanthomonas oryzae on Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigvert, M.; Solé, M.; López-Garcia, B.; Coll, N.S.; Beattie, K.D.; Davis, R.A.; Elofsson, M.; Valls, M. Type III secretion inhibitors for the management of bacterial plant diseases. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.E.; Jeon, B.J.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, B.S. Inhibitory Activity of Sedum middendorffianum-Derived 4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid and Vanillic Acid on the Type III Secretion System of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Núñez, J.L.; Pérez-López, M.; Espinosa, N.; Campos-Hernández, N.; García-Contreras, R.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; Cortes-López, H.; Vázquez-Sánchez, M.; Quezada, H.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; et al. Anti-Virulence Properties of Plant Species: Correlation between In Vitro Activity and Efficacy in a Murine Model of Bacterial Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, A.; Teotia, S.; Singh, D. Tools for engineering resistance against pathogens in plants. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J. Antibiotic use and its consequences for the normal microbiome. Science 2016, 352, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, B.J.E.; Strynadka, N.C.J. On the road to structure-based development of anti-virulence therapeutics targeting the type III secretion system injectisome. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Projan, S.J.; Bradford, P. Late stage antibacterial drugs in the clinical pipeline. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L.; Isler, B.; Stewart, A. New treatment options for multiresistant gram negatives. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotinger, J.; Pendergrass, H.; May, A. Molecular Targets and Strategies for Inhibition of the Bacterial Type III Secretion System (T3SS); Inhibitors Directly Binding to T3SS Components. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaich, S. Antivirulence as a new antibacterial approach for chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, P.; Elofsson, M.; Rosell, S.; Wolf-Watz, H. Virulence blockers as alternatives to antibiotics: Type III secretion inhibitors against Gram-negative bacteria. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, X. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Type III Secretion System. Molecules 2015, 20, 17659–17674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoroge, J.; Sperandio, V. Jamming bacterial communication: New approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Pierson, E.; Hung, D.T. Targeting virulence: A new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewngam, P.; Chiou, J.; Chatterjee, P.; Otto, M. Alternative approaches to treat bacterial infections: Targeting quorum-sensing. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotinger, J.A.; Morris, S.T.; May, A.E. The Case against Antibiotics and for Anti-Virulence Therapeutics. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, B.; Wong, T.Y.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Jarrell, E.T.; Leppla, S.H.; Collier, R.J.; Liddington, R.C.; Cantley, L.C. The structural basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity of the anthrax lethal factor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoop, W.L.; Xiong, Y.; Wiltsie, J.; Woods, A.; Guo, J.; Pivnichny, J.V.; Felcetto, T.; Michael, B.F.; Bansal, A.; Cummings, R.T.; et al. Anthrax lethal factor inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7958–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayeri, M.; Wiggins, J.F.; Lindeman, R.E.; Leppla, S.H. Cisplatin Inhibition of Anthrax Lethal Toxin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2658–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kantha, S.S. A centennial review; the 1890 tetanus antitoxin paper of von Behring and Kitasato and the related developments. Keio J. Med. 1991, 40, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, G.J.A.; Young, J.A.T. Antitoxins: Novel strategies to target agents of bioterrorism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, D.T.; Shakhnovich, E.A.; Pierson, E.; Mekalanos, J.J. Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Vibrio cholerae Virulence and Intestinal Colonization. Science 2005, 310, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peach, K.C.; Bray, W.M.; Shikuma, N.J.; Gassner, N.C.; Lokey, R.S.; Yildiz, F.H.; Linington, R.G. An image-based 384-well high-throughput screening method for the discovery of biofilm inhibitors in Vibrio cholerae. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorasia, D.G.; Veith, P.D.; Hanssen, E.G.; Glew, M.D.; Sato, K.; Yukitake, H.; Nakayama, K.; Reynolds, E.C. Structural Insights into the PorK and PorN Components of the Porphyromonas gingivalis Type IX Secretion System. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasica, A.M.; Goulas, T.; Mizgalska, D.; Zhou, X.; de Diego, I.; Ksiazek, M.; Madej, M.; Guo, Y.; Guevara, T.; Nowak, M.; et al. Structural and functional probing of PorZ, an essential bacterial surface component of the type-IX secretion system of human oral-microbiomic Porphyromonas gingivalis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, G.P.; Reeves, P.J. Membrance traffic wardens and protein secretion in Gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, K.G.; Girón, J.; Jerse, A.; McDaniel, T.K.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Kaper, J.B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli contains a putative type III secretion system necessary for the export of proteins involved in attaching and effacing lesion formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7996–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, G.R.; Van Gijsegem, F. Assembly and Function of Type III Secretory Systems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 735–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvaux, M.; Hébraud, M.; Henderson, I.R.; Pallen, M.J. Type III secretion: What’s in a name? Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, B.; Sekirov, I.; Finlay, B.B. Type III Secretion Systems and Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.R.; Wolf-Watz, H. The Yersinia Yop virulon: A bacterial system for subverting eukaryotic cells. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölin, I.; Portnoy, D.; Wolf-Watz, H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect. Immun. 1985, 48, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.R. Yersinia type III secretion: Send in the effectors. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, G.R. The type III secretion injectisome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraidt, O.; Marlovits, T.C. Three-Dimensional Model of Salmonella’s Needle Complex at Subnanometer Resolution. Science 2011, 331, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Diepold, A. A Unified Nomenclature for Injectisome-Type Type III Secretion Systems. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 427, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkin, V.E.; Schmied, W.H.; Schraidt, O.; Marlovits, T.C.; Egelman, E.H. The Structure of the Salmonella typhimurium Type III Secretion System Needle Shows Divergence from the Flagellar System. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Browne, S.H.; Hasegawa, P.; Okamoto, S.; Fierer, J.; Guiney, D.G. Identification of SalmonellaSPI-2 secretion system components required for SpvB-mediated cytotoxicity in macrophages and virulence in mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteyn, B.; West, N.P.; Browning, D.F.; Cole, J.A.; Shaw, J.G.; Palm, F.; Mounier, J.; Prévost, M.-C.; Sansonetti, P.; Tang, C.M. Modulation of Shigella virulence in response to available oxygen in vivo. Nature 2010, 465, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissim-Eliraz, E.; Nir, E.; Shoval, I.; Marsiano, N.; Nissan, I.; Shemesh, H.; Nagy, N.; Goldstein, A.M.; Gutnick, M.; Rosenshine, I.; et al. Type Three Secretion System-Dependent Microvascular Thrombosis and Ischemic Enteritis in Human Gut Xenografts Infected with Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00558-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Murphy, K.R.; Torhan, M.C.; Bowlin, N.O.; Williams, J.D.; Bowlin, T.L.; Moir, D.T.; Hauser, A.R. Impact of Type III Secretion Effectors and of Phenoxyacetamide Inhibitors of Type III Secretion on Abscess Formation in a Mouse Model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01202-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, M.; Chan, Y.; Shen, W.; Li, Y. The Functions of Effector Proteins in Yersinia Virulence. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, J.R.; Fernández, L.; Wasney, G.A.; Vuckovic, M.; Reffuveille, F.; Hancock, R.E.; Strynadka, N.C. The Structure of a Type 3 Secretion System (T3SS) Ruler Protein Suggests a Molecular Mechanism for Needle Length Sensing. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1676–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, K.; Ohishi, M.; Ogino, T.; Tamano, K.; Sasakawa, C.; Abe, A. Supermolecular structure of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion system and its direct interaction with the EspA-sheath-like structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11638–11643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, J.R.C.; Worrall, L.J.; Sgourakis, N.G.; DiMaio, F.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Felise, H.B.; Vuckovic, M.; Yu, A.C.; Miller, S.I.; Baker, D.; et al. A Refined Model of the Prototypical Salmonella SPI-1 T3SS Basal Body Reveals the Molecular Basis for Its Assembly. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, I.; Börnicke, J.; Heidemann, J.; Svergun, D.; Horstmann, J.A.; Erhardt, M.; Tuukkanen, A.; Uetrecht, C.; Kolbe, M. Molecular Organization of Soluble Type III Secretion System Sorting Platform Complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3787–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.; Pardo, J.P.; Espinosa, N.; Pérez-Hernández, G.; González-Pedrajo, B. Enzymatic characterization of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion ATPase EscN. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 468, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzdzion, L.; Krezel, H.; Wrzeszcz, K.; Grzegorek, I.; Nowinska, K.; Chodaczek, G.; Swietnicki, W. Design of small molecule inhibitors of type III secretion system ATPase EscN from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2017, 64, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.C.; Ochoa, C.D.; Morrow, K.A.; Robson, M.J.; Prasain, N.; Zhou, C.; Alvarez, D.F.; Frank, D.W.; Balczon, R.; Stevens, T. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme Y impairs endothelial cell proliferation and vascular repair following lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L915–L924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, P.J.; Singh, V.; Davidson, A.C.; Koronakis, V. Swiss Army Pathogen: The Salmonella Entry Toolkit. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.R. The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Infection by injection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.E. Common Themes in the Design and Function of Bacterial Effectors. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, Y.A.; Sadik, A.Y.; Ellermeier, J.R.; Slauch, J.M. Integrating Global Regulatory Input Into the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System. Genetics 2012, 190, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izoré, T.; Job, V.; Dessen, A. Biogenesis, Regulation, and Targeting of the Type III Secretion System. Structure 2011, 19, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.E.; Wolf-Watz, H. Protein delivery into eukaryotic cells by type III secretion machines. Nature 2006, 444, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, L.K.; Dossa, P.D.; Hang, H.C. Small molecules aimed at type III secretion systems to inhibit bacterial virulence. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Ouyang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Khalique, A.; He, C.; Liang, X.; Shu, G.; Yin, L. Type 3 secretion system 1 of Salmonella typhimurium and its inhibitors: A novel strategy to combat salmonellosis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 34154–34166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawara, H. Possible drugs for the treatment of bacterial infections in the future: Anti-virulence drugs. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, D.T.; Opperman, T.J.; Aron, Z.D.; Bowlin, T.L. Adjunctive therapy for multidrug-resistant bacterial infections: Type III secretion system and efflux inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.C.; Finlay, B.B. Targeting the type III secretion system to treat bacterial infections. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goure, J.; Broz, P.; Attree, O.; Cornelis, G.R.; Attree, I. Protective Anti-V Antibodies Inhibit Pseudomonas and Yersinia Translocon Assembly within Host Membranes. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, D.G.; Anderson, G.W.; Mauro, J.; Welkos, S.; Andrews, G.P.; Adamovicz, J.; Friedlander, A.M. Protection against experimental bubonic and pneumonic plague by a recombinant capsular F1-V antigen fusion protein vaccine. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Yahr, T.; Ohara, M.; Kurahashi, K.; Gropper, M.A.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Frank, D.W. Active and passive immunization with the Pseudomonas V antigen protects against type III intoxication and lung injury. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shime, N.; Sawa, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Faure, K.; Allmond, L.R.; Karaca, T.; Swanson, B.L.; Spack, E.G.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P. Therapeutic Administration of Anti-PcrV F(ab′)2in Sepsis Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5880–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, B.; Luyt, C.-E.; Dugard, A.; Wolff, M.; Diehl, J.-L.; Jaber, S.; Forel, J.-M.; Garot, D.; Kipnis, E.; Mebazaa, A.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of an anti-PcrV PEGylated monoclonal antibody fragment in mechanically ventilated patients colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatila, F.; Yalçın, H.T.; Özyurt, C.; Evran, S.; Çakır, B.; Yaşa, I.; Nalbantsoy, A. Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) Aptamer targeting SipA protein inhibits Salmonella Enteritidis invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horna, G.; Ruiz, J. Type 3 secretion system as an anti-Pseudomonal target. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Mahmoodi, S. A Novel Design of Multi-epitope Peptide Vaccine Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2022, 19, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Beckett, V.; Konstan, M.; Accurso, F.; Burns, J.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Milla, C.; VanDevanter, D.; Chmiel, J. KB001-A, a novel anti-inflammatory, found to be safe and well-tolerated in cystic fibrosis patients infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milla, C.E.; Chmiel, J.F.; Accurso, F.J.; VanDevanter, D.R.; Konstan, M.W.; Yarranton, G.; Geller, D.E. Anti-PcrV antibody in cystic fibrosis: A novel approach targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infection. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.O.; Yu, X.Q.; Robbie, G.J.; Wu, Y.; Shoemaker, K.; Yu, L.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Keller, A.E.; Anude, C.; Hernandez-Illas, M.; et al. Phase 1 study of MEDI3902, an investigational anti–Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV and Psl bispecific human monoclonal antibody, in healthy adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 629.e1–629.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheremet, A.B.; Nesterenko, L.N.; Zigangirova, N.A. The Type Three Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a Target for Development of Antivirulence Drugs. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 2020, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergrass, H.A.; May, A.E. Natural Product Type III Secretion System Inhibitors. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotinger, J.A.; May, A.E. Antibodies Inhibiting the Type III Secretion System of Gram-Negative Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibodies 2020, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zhang, L.; Kirienko, N.V. High-Throughput Approaches for the Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Antivirulents. mBio 2021, 12, e2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, P.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Chini, A.; Martínez, J.L.; Hernando-Amado, S. Discovery of inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through the search for natural-like compounds with a dual role as inducers and substrates of efflux pumps. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7396–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, M.; Kan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C. Identification of Novel Type Three Secretion System (T3SS) Inhibitors by Computational Methods and Anti-Salmonella Evaluations. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 764191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.N.; Lau, T.; Lentz, A.; Sherry, J.; Cabrera-Cortez, A.; Hug, K.; Lalljie, A.; Engel, J.; Lokey, R.S.; Auerbuch, V. Developing Cyclic Peptomers as Broad-Spectrum Type III Secretion System Inhibitors in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0169020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, D.M.; McLean, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sarsby, J.; Haneef, A.S.; Fernig, D.G.; Winstanley, C.; Berry, N.G.; Kaye, S.B. A pipeline to evaluate inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin U. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, A.M.; Nordfelth, R.; Uvell, H.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Elofsson, M. Targeting Bacterial Virulence: Inhibitors of Type III Secretion in Yersinia. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.; Nordfelth, R.; Dubinina, E.; Bergman, T.; Gustafsson, M.; Magnusson, K.E.; Wolf-Watz, H. Modulation of Virulence Factor Expression by Pathogen Target Cell Contact. Science 1996, 273, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordfelth, R.; Kauppi, A.M.; Norberg, H.A.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Elofsson, M. Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Targeting Type III Secretion. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3104–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschiol, S.; Bailey, L.; Gylfe, A.; Sundin, C.; Hultenby, K.; Bergström, S.; Elofsson, M.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Normark, S.; Henriques-Normark, B. A small-molecule inhibitor of type III secretion inhibits different stages of the infectious cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14566–14571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, A.; Robertson, M.L.; Lowden, M.; Ibarra, J.A.; Puente, J.L.; Finlay, B.B. Transcriptional Inhibitor of Virulence Factors in Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, D.L.; Layton, A.N.; Field, T.R.; Bowen, A.J.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Elofsson, M.; Stevens, M.P.; Galyov, E.E. Inhibition of Type III Secretion in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium by Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2631–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.K.; Garrity-Ryan, L.K.; Bartlett, V.J.; Grier, M.C.; Verma, A.K.; Medjanis, G.; Donatelli, J.E.; Macone, A.B.; Tanaka, S.K.; Levy, S.B.; et al. N-Hydroxybenzimidazole Inhibitors of the Transcription Factor LcrF in Yersinia: Novel Antivirulence Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5626–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logsdon, L.K.; Mecsas, J. Requirement of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Effectors YopH and YopE in Colonization and Persistence in Intestinal and Lymph Tissues. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4595–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrity-Ryan, L.K.; Kim, O.K.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Bartlett, V.J.; Verma, A.K.; Fisher, M.L.; Castillo, C.; Songsungthong, W.; Tanaka, S.K.; Levy, S.B.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitors of LcrF, a Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Transcription Factor, Attenuate Virulence and Limit Infection in a Murine Pneumonia Model. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.R.; Engel, J.N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces type-III-secretion-mediated apoptosis of macrophages and epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 78, 5530–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, C.M.; Hauser, A.R. Relative Contributions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoU, ExoS, and ExoT to Virulence in the Lung. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6969–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, D.; Williams, J.D.; Majgier-Baranowska, H.; Patel, I.; Peet, N.P.; Huang, J.; Lory, S.; Bowlin, T.L.; Moir, D.T. Discovery and Characterization of Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, C.; Che, Y.; Gu, L.; Ren, J.; Hu, K.; Sun, X.; Yang, C.-H.; et al. Synthesis and Bioactivity of Novel Inhibitors for Type III Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Rodríguez, N.A.; Muñoz-Cázares, N.; Castro-Torres, V.A.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; García-Contreras, R.; Quezada, H.; Castillo-Juárez, I.; Martínez-Vázquez, M. Anti-Pathogenic Properties of the Combination of a T3SS Inhibitory Halogenated Pyrrolidone with C-30 Furanone. Molecules 2021, 26, 7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felise, H.B.; Nguyen, H.V.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Barry, K.C.; Jackson, S.R.; Blanc, M.-P.; Bronstein, P.A.; Kline, T.; Miller, S.I. An Inhibitor of Gram-Negative Bacterial Virulence Protein Secretion. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, T.; Felise, H.B.; Barry, K.C.; Jackson, S.R.; Nguyen, H.V.; Miller, S.I. Substituted 2-Imino-5-arylidenethiazolidin-4-one Inhibitors of Bacterial Type III Secretion. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7065–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, T.; Barry, K.C.; Jackson, S.R.; Felise, H.B.; Nguyen, H.V.; Miller, S.I. Tethered thiazolidinone dimers as inhibitors of the bacterial type III secretion system. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enquist, P.-A.; Gylfe, A.; Hägglund, U.; Lindström, P.; Norberg-Scherman, H.; Sundin, C.; Elofsson, M. Derivatives of 8-hydroxyquinoline—Antibacterial agents that target intra- and extracellular Gram-negative pathogens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3550–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.; Gylfe, A.; Sundin, C.; Muschiol, S.; Elofsson, M.; Nordström, P.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Lugert, R.; Waldenström, A.; Wolf-Watz, H.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of type III secretion inYersiniablock theChlamydia pneumoniaeinfection cycle. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlgren, M.K.; Zetterström, C.E.; Gylfe, A.; Linusson, A.; Elofsson, M. Statistical molecular design of a focused salicylidene acylhydrazide library and multivariate QSAR of inhibition of type III secretion in the Gram-negative bacterium Yersinia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2686–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoldo, A.; Curak, J.; Kittanakom, S.; Chevelev, I.; Lee, V.T.; Sahebol-Amri, M.; Koscik, B.; Ljuma, L.; Roy, P.J.; Bedalov, A.; et al. Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exoenzyme S Using a Yeast Phenotypic Screen. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharajah, A.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P.; Van Bambeke, F. Targeting the Type Three Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.T.; Pukatzki, S.; Sato, H.; Kikawada, E.; Kazimirova, A.A.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Arm, J.P.; Frank, D.W.; Lory, S. Pseudolipasin A Is a Specific Inhibitor for Phospholipase A 2 Activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cytotoxin ExoU. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.M.; Six, D.; Dennis, E.A.; Ghosh, P.; Matsumoto, K.; Shionyu, M.; Go, M.; Shimizu, K.; Shinomura, T.; Kimata, K.; et al. In Vivo Phospholipase Activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cytotoxin ExoU and Protection of Mammalian Cells with Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41326–41332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Baek, J.; Song, J.; Byeon, H.; Min, H.; Min, K.H. Identification of arylsulfonamides as ExoU inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3823–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.C.; Wong, W.R.; Dupzyk, A.J.; Bray, W.M.; Linington, R.G.; Auerbuch, V. An NF-κB-Based High-Throughput Screen Identifies Piericidins as Inhibitors of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Type III Secretion System. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwochert, J.; Lao, Y.; Pye, C.R.; Naylor, M.R.; Desai, P.V.; Valcarcel, I.C.G.; Barrett, J.A.; Sawada, G.; Blanco, M.-J.; Lokey, R.S. Stereochemistry Balances Cell Permeability and Solubility in the Naturally Derived Phepropeptin Cyclic Peptides. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.; Schwochert, J.; Lao, Y.; Lau, T.; Lloyd, C.; Luu, J.; Kooner, O.; Morgan, J.; Lokey, S.; Auerbuch, V. Synthetic Cyclic Peptomers as Type III Secretion System Inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00060-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigangirova, N.A.; Zayakin, E.S.; Kapotina, L.N.; Kost, E.A.; Didenko, L.V.; Davydova, D.Y.; Rumyanceva, J.P.; Gintsburg, A.L. Development of Chlamydial Type III Secretion System Inhibitors for Suppression of Acute and Chronic Forms of Chlamydial Infection. Acta Nat. 2012, 4, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, L.N.; Zigangirova, N.; Zayakin, E.S.; Luyksaar, S.; Kobets, N.V.; Balunets, D.V.; Shabalina, L.; Bolshakova, T.N.; Dobrynina, O.Y.; Gintsburg, A.L. A small-molecule compound belonging to a class of 2,4-disubstituted 1,3,4-thiadiazine-5-ones suppresses Salmonella infection in vivo. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigangirova, N.A.; Nesterenko, L.N.; Sheremet, A.B.; Soloveva, A.V.; Luyksaar, S.I.; Zayakin, E.S.; Balunets, D.V.; Gintsburg, A.L. Fluorothiazinon, a small-molecular inhibitor of T3SS, suppresses salmonella oral infection in mice. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; El Qaidi, S.; McDonald, P.; Roy, A.; Hardwidge, P. YM155 Inhibits NleB and SseK Arginine Glycosyltransferase Activity. Pathogens 2021, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.-B.; Wang, P.-Y.; Fang, Z.-M.; Wang, J.-J.; Guo, D.-X.; Ji, J.; Zhou, X.; Qi, P.-Y.; Liu, L.-W.; Yang, S. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,4-Triazole Thioethers as Both Potential Virulence Factor Inhibitors against Plant Bacterial Diseases and Agricultural Antiviral Agents against Tobacco Mosaic Virus Infections. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15108–15122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Tian, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiang, X.; Ahmed, W.; Tang, R.; Cui, Z.-N. Synthesis and bioactivity of 1,3-thiazolidine-2-thione derivatives against type III secretion system of Xanthomonas oryzae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3364–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Tian, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiang, X.; Lin, Y.; Ahmed, W.; Tang, R.; Cui, Z.-N. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives as type III secretion system inhibitors against Xanthomonas oryzae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 160, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Tao, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.-H.; Cui, Z.-N. Synthesis and bioactivity of thiazolidin-2-cyanamide derivatives against type III secretion system of Xanthomonas oryzae on rice. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 149, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; He, M.; Xiang, X.-W.; Adnan, M.; Cui, Z.-N. Novel S-Thiazol-2-yl-furan-2-carbothioate Derivatives as Potential T3SS Inhibitors Against Xanthomonas oryzae on Rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11867–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Ahmed, W.; Xiang, X.; Song, G.; Cui, Z.-N. Discovery of Ethyl 2-Nitro-3-Arylacrylates Molecules as T3SS Inhibitor Reducing the Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria Xanthomonas. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-N.; Chen, L.; Si, N.-G.; Jiang, W.-J.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Liu, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-Q. Identification of Benzyloxy Carbonimidoyl Dicyanide Derivatives as Novel Type III Secretion System Inhibitors via High-Throughput Screening. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, D.E.; Davis, A.J.; Castillo, C.; Mecsas, J. Identification and Characterization of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Yop Translocation in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swietnicki, W.; Carmany, D.; Retford, M.; Guelta, M.; Dorsey, R.; Bozue, J.; Lee, M.S.; Olson, M.A. Identification of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Yersinia pestis Type III Secretion System YscN ATPase. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.C.; Linington, R.G.; Auerbuch, V. Chemical Inhibitors of the Type Three Secretion System: Disarming Bacterial Pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5433–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyom, R.; Roytrakul, S.; Thinwang, P. A small molecule, C24H17ClN4O2S, inhibits the function of the type III secretion system in Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlen, S.; Zapol’Skii, V.A.; Bilitewski, U.; Dersch, P. Identification of Translocation Inhibitors Targeting the Type III Secretion System of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0095821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, A.V.; Luyksaar, S.I.; Kapotina, L.N.; Kirsanov, D.D.; Zayakin, E.S.; Karyagina, A.S.; Zigangirova, N.A. Identification of chlamydial T3SS inhibitors through virtual screening against T3SS ATPase. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grado, M.; Rosenberger, C.M.; Gauthier, A.; Vallance, B.A.; Finlay, B.B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Induces Expression of the Early Growth Response Factor by Activating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6217–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, J.B.; Linington, R.G.; Andersen, R.J.; Molinski, T.F. Stereochemical Assignment in Acyclic Lipids Across Long Distance by Circular Dichroism: Absolute Stereochemistry of the Aglycone of Caminoside A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 5946–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linington, R.G.; Robertson, M.; Gauthier, A.; Finlay, B.B.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Caminoside A, an Antimicrobial Glycolipid Isolated from the Marine Sponge Caminus sphaeroconia. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 4089–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linington, R.G.; Robertson, M.; Gauthier, A.; Finlay, B.B.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F.; van Soest, A.R.; Andersen, R.J. Caminosides B−D, Antimicrobial Glycolipids Isolated from the Marine Sponge Caminus sphaeroconia. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Akashi, T.; Ayabe, S.-I. Flavonoids of Leguminous Plants: Structure, Biological Activity, and Biosynthesis. J. Plant Res. 2000, 113, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, Q.; Selimi, D.; Wang, Q.; Charkowski, A.O.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.-H. The Plant Phenolic Compound p -Coumaric Acid Represses Gene Expression in the Dickeya dadantii Type III Secretion System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hutchins, W.; Wu, X.; Liang, C.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Khokhani, D.; Chen, X.; Che, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Derivative of plant phenolic compound inhibits the type III secretion system of Dickeya dadantii via HrpX/HrpY two-component signal transduction and Rsm systems. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhani, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Yamazaki, A.; Hutchins, W.; Zhou, S.-S.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.-H. Discovery of Plant Phenolic Compounds That Act as Type III Secretion System Inhibitors or Inducers of the Fire Blight Pathogen, Erwinia amylovora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5424–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.E.; Jeon, B.J.; Park, M.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Kwon, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, B.S. Inhibition of the type III secretion system of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 by resveratrol oligomers identified in Vitis vinifera L. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Lehr, H.H.; Teitel, S.; Maehr, H.; Grunberg, E. A new antibiotic X-5108 of Streptomyces origin. I. Production, isolation and properties. J. Antibiot. 1973, 26, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinali, G. Synthetic analogs of aurodox and kirromycin active on elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. J. Antibiot. 1981, 34, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Iwatsuki, M.; Nagai, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Shiomi, K.; Ōmura, S.; Abe, A. A small-molecule inhibitor of the bacterial type III secretion system protects against in vivo infection with Citrobacter rodentium. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, R.E.; O’boyle, N.; Connolly, J.P.R.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Roe, A.J. Characterization of the Mode of Action of Aurodox, a Type III Secretion System Inhibitor from Streptomyces goldiniensis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00595-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolle, R.E.; Nicolaou, K.C. Total synthesis of elfamycins: Aurodox and efrotomycin. 2. Coupling of key intermediates and completion of the synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, M.; Ikeda, A.; Nakajima, A.; Ōno, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Hirose, T.; Sunazuka, T. Towards the total synthesis of aurodox: Preparation of the key hemiacetal-lactone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 66, 152799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, M.; Uchida, R.; Yoshijima, H.; Ui, H.; Shiomi, K.; Kim, Y.-P.; Hirose, T.; Sunazuka, T.; Abe, A.; Tomoda, H.; et al. Guadinomines, Type III secretion system inhibitors, produced by Streptomyces sp. K01-0509. II: Physico-chemical properties and structure elucidation. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, M.; Uchida, R.; Yoshijima, H.; Ui, H.; Shiomi, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Abe, A.; Tomoda, H.; Ōmura, S. Guadinomines, Type III secretion system inhibitors, produced by Streptomyces sp. K01-0509. I: Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Sunazuka, T.; Tsuchiya, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kojima, Y.; Mori, R.; Iwatsuki, M.; Ōmura, S. Total Synthesis and Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Guadinomines B and C2. Chem. A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8220–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, T.C.; May, A.E.; Zaleta-Rivera, K.; Ruby, J.G.; Skewes-Cox, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; DeRisi, J.L.; Iwatsuki, M.; Omura, S.; Khosla, C. Molecular Insights into the Biosynthesis of Guadinomine: A Type III Secretion System Inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17797–17806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Takahashi, N.; Miyamoto, S.; Mori, R.; Suzuki, S.; Nagatsu, J. Isolation and Physiological Activities of Piericidin A, A Natural Insecticide Produced by Streptomyces. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1963, 27, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Suzuki, A.; Tamura, S. Structure of Piericidin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 2066–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Wu, M.; Crane, F.; Takahashi, H.; Tamura, S.; Folkers, K. Piericidin A: A new inhibitor of mitochondrial electron transport. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1966, 25, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.M.; Duncan, M.C.; Johnson, K.S.; Diepold, A.; Lam, H.; Dupzyk, A.J.; Martin, L.R.; Wong, W.R.; Armitage, J.P.; Linington, R.G.; et al. Piericidin A1 Blocks Yersinia Ysc Type III Secretion System Needle Assembly. mSphere 2017, 2, e00030-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.F.; Wagenaar, M.M.; Singh, M.P.; Janso, J.E.; Clardy, J. The Cytosporones, New Octaketide Antibiotics Isolated from an Endophytic Fungus. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 4043–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Du, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, B.; Huang, D.; Li, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Weimer, B.C.; et al. Cytosporone B is an agonist for nuclear orphan receptor Nur77. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Z.; Liu, Q.-F.; Li, L.; Wang, W.-J.; Yao, L.-M.; Yang, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Zhan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, M.-Q.; et al. The orphan receptor TR3 suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis in mice by downregulating Wnt signalling. Gut 2012, 61, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Cao, X.; Rico-Bautista, E.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Bobkov, A.; Wolf, D.A.; Zhang, X.-K.; Dawson, M.I. Relative impact of 3- and 5-hydroxyl groups of cytosporone B on cancer cell viability. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lv, C.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. Cytosporone B, an Inhibitor of the Type III Secretion System of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ji, X.; Ding, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, H. Total Synthesis of Cytosporone B. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Morishita, T.; Ohshita, J. An Aryne Route to Cytosporone B and Phomopsin C. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 508–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamberlam, C.E.M.; Meza, A.; Leite, C.B.; Marques, M.R.; De Lima, D.P.; Beatriz, A. Total synthesis and allelopathic activity of cytosporones A-C. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Delius, M.; Le, C.M.; Dong, V.M. Rhodium-Phosphoramidite Catalyzed Alkene Hydroacylation: Mechanism and Octaketide Natural Product Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15022–15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Shen, Y. An Efficient Synthesis of Cytosporone B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, A.; dos Santos, E.A.; Gomes, R.S.; de Lima, D.; Beatriz, A. Cytosporones and Related Compounds, A Review: Isolation, Biosynthesis, Synthesis and Biological Activity of Promising Fungal Resorcinolic Lipids. Curr. Org. Synth. 2015, 12, 618–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnhoff, M.; Miller, C.P.; Martin, W.R. Resistance of the mouse’s intestinal tract to experimental salmonella infection. I. Factors which interfere with the initiation of infection by oral inoculation. J. Exp. Med. 1964, 120, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; O’Riordan, M.X.D. Chapter Three. Regulation of bacterial pathogenesis by intestinal short-chain fatty acids. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Sariaslani, S., Gadd, G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 85, pp. 93–118. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.H.; Pomare, E.W.; Branch, W.J.; Naylor, C.P.; Macfarlane, G.T. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, N.; Tashiro, K.; Kuhara, S.; Hayashi, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Tobe, T. Regulation of virulence by butyrate sensing in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2009, 155, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, C.-H.; Wang, S.; Roland, K.L.; Curtiss, R. Leucine-Responsive Regulatory Protein (Lrp) Acts as a Virulence Repressor in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1278–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordone, A.; Lucchini, S.; De Felice, M.; Ricca, E. Direct and indirect control of Lrp on LEE pathogenicity genes of Citrobacter rodentium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, M.; Yen, H.; Tobe, T. LeuO enhances butyrate-induced virulence expression through a positive regulatory loop in enterohaemorrhagicEscherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumann, E. Fusaric acid as a wilt toxin. Phytopathology 1957, 47, 342–357. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Ling, N.; Wang, M.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Fusaric acid is a crucial factor in the disturbance of leaf water imbalance in Fusarium-infected banana plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 60, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutcher, F.K.; Puckhaber, L.S.; Stipanovic, R.D.; Bell, A.A.; Nichols, R.L.; Lawrence, K.S.; Liu, J. Microbial Resistance Mechanisms to the Antibiotic and Phytotoxin Fusaric Acid. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Guo, Z.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Fusaric acid modulates Type Three Secretion System of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Structural optimization of natural product fusaric acid to discover novel T3SS inhibitors of Salmonella. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 582, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterström, C.E.; Hasselgren, J.; Salin, O.; Davis, R.A.; Quinn, R.J.; Sundin, C.; Elofsson, M. The Resveratrol Tetramer (-)-Hopeaphenol Inhibits Type III Secretion in the Gram-Negative Pathogens Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Vijayan, V.; Pant, P.; Sharma, M.; Vikram, N.; Kaur, P.; Singh, T.P.; Sharma, S. Identification of potential drug candidates to combat COVID-19: A structural study using the main protease (mpro) of SARS-CoV-2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 6649–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Beattie, K.D.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Holla, H.; Healy, P.C.; Sykes, M.; Shelper, T.; Avery, V.M.; et al. Solving the Supply of Resveratrol Tetramers from Papua New Guinean Rainforest Anisoptera Species That Inhibit Bacterial Type III Secretion Systems. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, C.; Zetterström, C.E.; Vo, D.D.; Brkljača, R.; Urban, S.; Elofsson, M. Exploring resveratrol dimers as virulence blocking agents—Attenuation of type III secretion in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babich, H.; Zuckerbraun, H.L.; Barber, I.B.; Babich, S.B.; Borenfreund, E. Cytotoxicity of Sanguinarine Chloride to Cultured Human Cells from Oral Tissue. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 78, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Gandhi, A.; Fimognari, C.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bishayee, A. Alkaloids for cancer prevention and therapy: Current progress and future perspectives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Deng, X.; Chu, X. Natural compound sanguinarine chloride targets the type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannadi, A.; Sajjadi, S.E.; Kabouche, A. Thymus fontanesii Boiss. & Reut.—A Potential Source of Thymol-Rich Essential Oil in North Africa. Z. Nat. C 2004, 59, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Luo, Z.-Q.; Deng, X. The Herbal Compound Thymol Protects Mice from Lethal Infection by Salmonella Typhimurium. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovagnoni, G.; Rossi, B.; Tugnoli, B.; Ghiselli, F.; Bonetti, A.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. Thymol and Carvacrol Downregulate the Expression of Salmonella typhimurium Virulence Genes during an In Vitro Infection on Caco-2 Cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.C.; Chung, H.H.; Huang, C.H.; Cheng, J.T. Decrease of Hyperglycemia by Syringaldehyde in Diabetic Rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Chu, X.; Yao, X.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, X. Inhibition of the type III secretion system by syringaldehyde protects mice from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Shin, Y.-W.; Bae, E.-A.; Han, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Kang, S.-S.; Kim, N.-H. Antiallergic effect of the root of Paeonia lactiflora and its constituents paeoniflorin and paeonol. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.X.; Tong, X.; Zeng, J.; Tu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, M.; Deng, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Nie, H.; et al. Paeonol Suppresses Neuroinflammatory Responses in LPS-Activated Microglia Cells. Inflammation 2016, 39, 1904–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Li, S.; Wei, H.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Deng, X. Identification of the natural product paeonol derived from peony bark as an inhibitor of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium type III secretion system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Kozukue, N.; Harden, L.A. Cinnamaldehyde Content in Foods Determined by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5702–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, P.S.; Prabuseenivasan, S.; Ignacimuthu, S. Cinnamaldehyde—A potential antidiabetic agent. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Deng, X.; Chu, X.; Zhou, T. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits type three secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by affecting the expression of key effector proteins. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-C.; Chu, X.-L.; Su, J.-Q.; Cui, Z.-Q.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Yu, Z.-J.; Wu, Z.-M.; Cai, M.-L.; Li, H.-X.; Zhang, Z.-J. Baicalin protects mice against Salmonella typhimurium infection via the modulation of both bacterial virulence and host response. Phytomedicine 2018, 48, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, L.K.; Lara-Tejero, M.; RoseFigura, J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yount, J.S.; Lefebre, M.; Dossa, P.D.; Kato, J.; Guan, F.; et al. Antibacterial Flavonoids from Medicinal Plants Covalently Inactivate Type III Protein Secretion Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, L.K.; Yount, J.S.; Hang, H.C. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits bacterial virulence and invasion of host cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Licoflavonol is an inhibitor of the type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Pillai, S.D.; Jayaraman, A.; Patil, B.S. Citrus flavonoid represses Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 and motility in S. Typhimurium LT2. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, R.; Liu, Y.; Cong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Anti-virulence activities of biflavonoids from Mesua ferrea L. flower. Drug Discov. Ther. 2019, 13, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knekt, P.; Kumpulainen, J.; Järvinen, R.; Rissanen, H.; Heliövaara, M.; Reunanen, A.; Hakulinen, T.; Aromaa, A. Flavonoid intake and risk of chronic diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöthlings, U.; Murphy, S.P.; Wilkens, L.R.; Henderson, B.E.; Kolonel, L.N. Flavonols and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.; Sangwan, V.; Borja-Cacho, D.; Dudeja, V.; Vickers, S.; Saluja, A. Myricetin induces pancreatic cancer cell death via the induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2011, 308, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Lv, Y.; Dou, X.; Wassy, S.L.; Jia, G.; Wei, L.; Yu, Q.; Deng, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J. Myricetin inhibits the type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium by downregulating the Salmonella pathogenic island I gene regulatory pathway. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manners, G.D. Citrus Limonoids: Analysis, Bioactivity, and Biomedical Prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8285–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.-G.; Luo, X.-D. Meliaceous Limonoids: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7437–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Yan, X.; Tu, Q.; Di, Y.; Yuan, C.; Fang, X.; Ben-David, Y.; Xia, L.; Gong, J.; Shen, Y.; et al. Isolation and Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Perforanoid A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 7539–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Nhiem, N.X.; Subedi, L.; Oh, I.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H. Isolation of bioactive limonoids from the fruits of Melia azedarach. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 22, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Pillai, B.; Patil, B.S. Grapefruit bioactive limonoids modulate E. coli O157:H7 TTSS and biofilm. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 140, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floss, H.G. From Ergot to Ansamycins45 Years in Biosynthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminov, R. History of antimicrobial drug discovery: Major classes and health impact. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha, B.R.; Fonseca, L.P.; Calado, C.R.C. Antibiotic Discovery: Where Have We Come from, Where Do We Go? Antibiotics 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Li, S.; Guo, Z.; Sun, M.; Lu, C. Overexpression of div8 increases the production and diversity of divergolides in Streptomyces sp. W112. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98209–98214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.; Liao, C.; Wu, W.; et al. Tanshinones: First-in-Class Inhibitors of the Biogenesis of the Type 3 Secretion System Needle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Antibiotic Therapy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Lu, C. Myricanol Inhibits the Type III Secretion System of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium by Interfering With the DNA-Binding Activity of HilD. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 571217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.; Booth, B.W. Biomedical applications of tannic acid. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1503–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Lv, Q.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, J. Tannic Acid Inhibits Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection by Targeting the Type III Secretion System. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 784926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, C.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Gao, F.; Zhu, C.; Jia, X.; Tong, M.; Dong, P.; et al. Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System. Molecules 2022, 27, 8348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238348
Lv C, Li Y, Wei Y, Wang J, Yu H, Gao F, Zhu C, Jia X, Tong M, Dong P, et al. Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238348
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Chao, Ying Li, Yuxia Wei, Jiayu Wang, Hui Yu, Feng Gao, Chao Zhu, Xiangdi Jia, Mingqiong Tong, Pingxuan Dong, and et al. 2022. "Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238348
APA StyleLv, C., Li, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, J., Yu, H., Gao, F., Zhu, C., Jia, X., Tong, M., Dong, P., Gao, Q., & Geng, L. (2022). Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System. Molecules, 27(23), 8348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238348





