Optimized Route for the Fabrication of MnAlC Permanent Magnets by Arc Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the As-Cast MnAlC
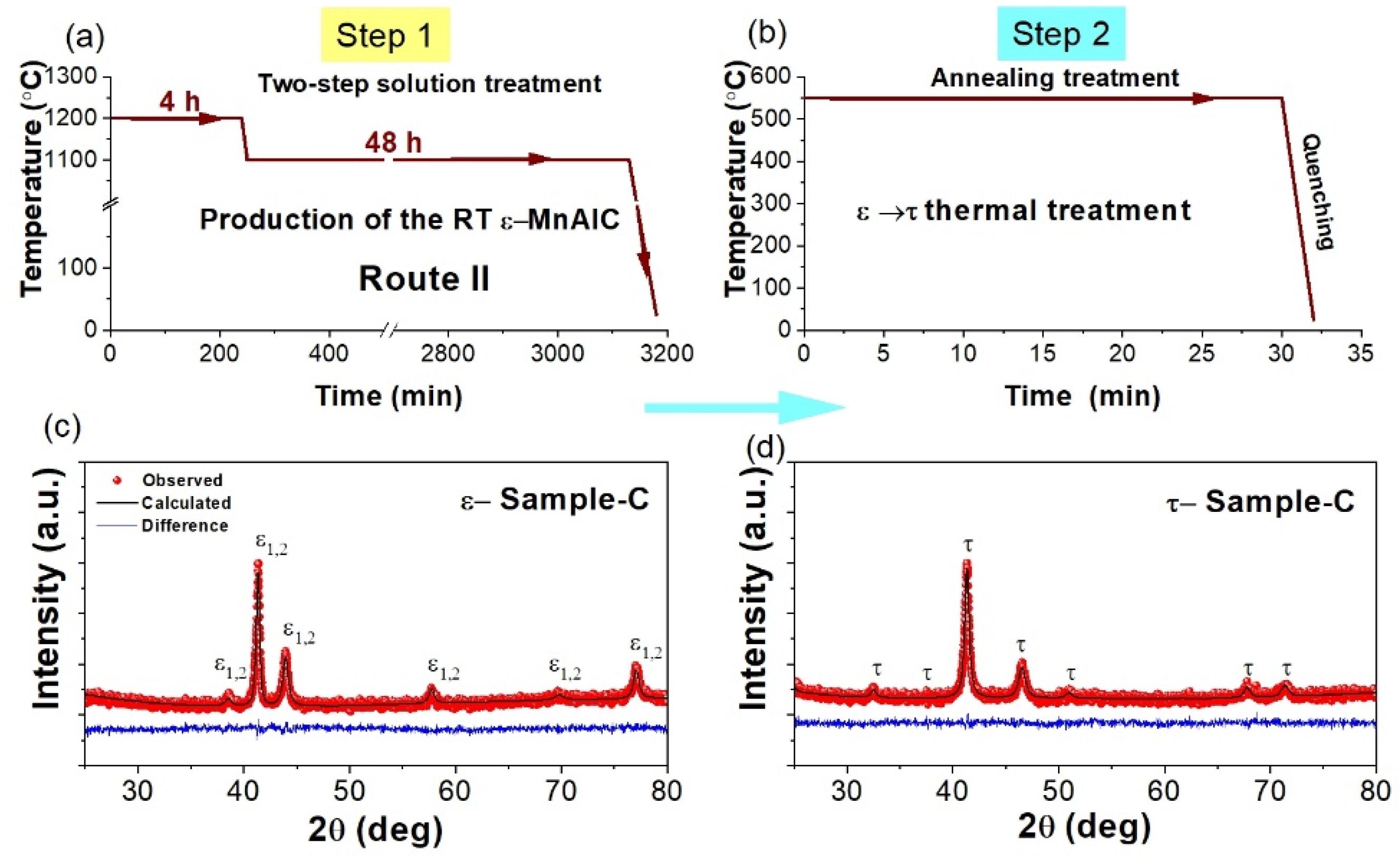
2.2. Preparation of the Quenched ε–MnAlC
2.3. Annealing Treatment to Obtain the τ-MnAlC
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
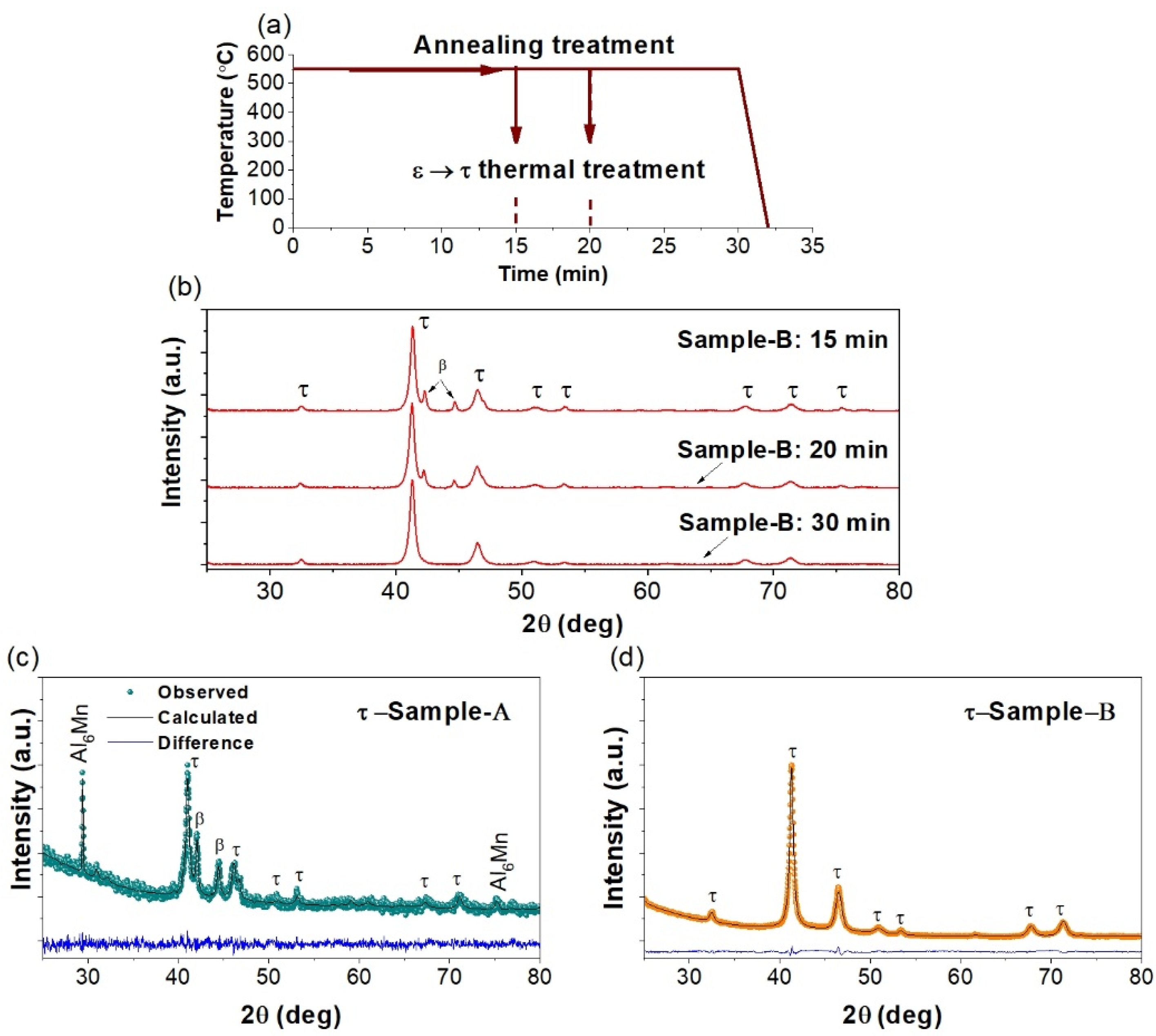
3.1. XRD Characterization
3.2. Magnetic Characterization
3.3. TEM Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Koch, A.J.J.; Hokkeling, P.; Steeg, M.G.; De Vos, K.J. New Material for permanent Magnets on a Base of Mn and Al. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, S75–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreizler, W.; Menth, A. Transformation kinetics of the ferromagnetic alloy Mn-Al-C. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1980, 16, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareti, L.; Bolzoni, F.; Leccabue, F.; Ermakov, A.E. Magnetic anisotripy of MnAl and MnAlC permanent magnet materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 59, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Baker, I.; Cui, J.B.; Yan, Z.C. Structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured Mn–Al–C magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohmoto, O.; Kageyama, N.; Kageyama, Y.; Haji, H.; Uchida, M.; Matsushima, Y. Magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Mn-Al-C powders. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 266, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, L.; Cui, E.; Deng, B.; Batalu, D.; Lu, W. Effect of cooling rates on the microstructure and magnetic properties of MnAl permanent magnetic alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, J.; Palmero, E.M.; Bollero, A. Efficient Nanostructuring of Isotropic Gas-Atomized MnAl Powder by Rapid Milling (30 s). Engineering 2020, 6, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.G.; Tan, B.H.; Ramanujan, R.V. Phase transitions and hard magnetic properties for rapidly solidified MnAl alloys doped with C, B, and rare earth elements. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, A.; Mazaleyrat, F.; LoBue, M.; Fazakas, E.; Varga, L.K. Hard magnetic properties of melt-spun Mn-Al-C alloys. EPJ Web Conf. 2013, 40, 06008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucis, M.J.; Prost, T.E.; Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Shield, J.E. Phase Transitions in Mechanically Milled Mn-Al-C Permanent Magnets. Metals 2014, 4, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Shyam, R.; Upadhyay, N.K.; Dhar, A. Development of Rare-Earth Free Mn-Al Permanent Magnet Employing Powder Metallurgy Route. IOP Conf. Ser. Mat. Scien. Eng. 2015, 73, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Mudgil, V.; Anand, K.; Srivastava, A.; Kotnala, R.; Dhar, A. Influence of processing on structure property correlations in τ–MnAl rare-earth free permanent magnet material. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 633, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Al–C alloy powders prepared by ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.C.; McDonald, I.J.; Lewis, L.H. Quantification of the strain-induced promotion of τ–MnAl via cryogenic milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 404, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Irie, S. Metamagnetic behavior in L10-MnAl synthesized by the post annealing of electrodeposited MnAl powder. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoydick, D.P.; Palmiere, E.J.; Soffa, W.A. On the formation of the metastable Llo phase in manganese-aluminum-base permanent magnet materials. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrman, M.; Pasko, A.; Perriere, L.; Etgens, V.; Isnard, O.; Mazaleyrat, F. Effect of Carbon Addition on Magnetic Order in Mn–Al–C Alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 2101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Kuo, P.C. Influence of carbon on the phase transformation kinetics and magnetic properties of MnAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1994, 22, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. New permanent magnets; manganese compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2014, 26, 064211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, T.; Bittner, F.; Müller, K.H.; Schultz, L.; Woodcock, T.G. Alloying with a few atomic percent of Ga makes MnAl thermodynamically stable. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsamrit, W.; Charoensuk, T.; Saetang, P.; Jantaratana, P.; Ruttanapun, C.; Sirisathitkul, C. Effects of Carbon Doping and Annealing Temperature on Magnetic MnAl Powders and MnAl Polymeric Composites. Appl. Scienc. 2021, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. Magnetic properties of Mn–Al system alloys produced by mechanical alloying. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8686–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Application of Mechanochemical Synthesis to Manufacturing of Permanent Magnets. JOM 2015, 67, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmero, E.M.; Casaleiz, D.; De Vicente, J.; Skårman, B.; Vidarsson, H.; Larsson, P.O.; Botello, A. Effect of particle size distribution on obtaining novel MnAlC-based permanent magnet composites and flexible filaments for 3D-printing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. Enhanced thermal stability of the τ-pase in MnAl-C alloys with Ni additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 871, 159554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Jia, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C. Microstructure and magnetic properties of (Mn54Al46)98C2 magnets fabricated by liquid-phase sintering with the Mn65Ga35 as an additive. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 534, 168037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, W.; Wachtel, E. Constitution and Magnetic Properties of Aluminum-Manganese Alloys with More Than 25 At.% Mn. Z. Fuer Met. 1960, 51, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Shtender, V.; Stopfel, H.; Hedlund, D.; Karlsson, D.; Pothala, R.; Skårman, B.; Olsson, F.; Vidarsson, H.; Andersson, G.; Svedlindh, P.; et al. Influence of nano-VC on the structural and magnetic properties of MnAlC-alloy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. The effect of Ti or Zr additions on the microstructure and magnetic properties of MnAl-C alloys. Results Phys. 2021, 29, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Freudenberger, J.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. Elimination of the non-recrystallised regions in the extruded MnAl-C-Ni magnet using pulverised melt-spun ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 163248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.; Feng, L.; Palmero, E.M.; Mix, T.; Rial, J.; Olsson, F.; Skårman, B.; Vidarsson, H.; Larsson, P.; Woodcock, T.; et al. Fabrication of bulk τ MnAl–C Magnets by hot pressing from ε-pase gas-atomized and milled poder. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 847, 156361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo Hernandez, J.S.; Maccari, F.; Marshall, L.G.; Tabares, J.A.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A. Exchange Coupling in MnAlC/α-Fe Nanocomposite Magnets. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 3941–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Sánchez, H.; Zamora Alfonson, L.E.; Trujillo Hernandez, J.S.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A. Evidence of exchange coupling in τ-MnAlC/FeCo system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 473, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.D.; Si, P.Z.; Lim, J.T.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.; Choi, C.J. Magnetic properties of Mn54Al46C2.44/Sm2Fe17N3 and Mn54Al46C2.44/Fe65Co35 composites. J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 2018, 73, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Sánchez, H.; Zamora Alfonso, L.E.; Trujillo Hernandez, J.S.; Salazar, D.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A. Improving the ferromagnetic exchange coupling in hard τ-Mn53.3Al45C1.7 and sof Mn50B50 magnetic alloys. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 843. [Google Scholar]
- Gamez, J.D.; Martínez Sánchez, H.; Valenzuela, J.L.; Marín, L.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Snoeck, E.; Zamora, L.E.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A.; Tabares, J.A. Magnetic τ-MnAlC thin film fabrication by high-vacuum thermal evaporation. Mater. Lett. 2021, 129657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Hsu, J.H.; Vinod, V.T.P.; Černík, M.; Kamat, V. Coercivity enhancement in Mn-Al-Cu flakes produced by surfactant-assisted milling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 192407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.Z.; Song, Z.G.; Yang, Y.B.; Liu, S.Q.; Du, H.L.; Han, J.Z.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.S.; Yang, C.Y.; Franz, A.; et al. τ-MnAl with high coercivity and saturation magnetization. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 127113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Baker, I. Nanostructured Mn–Al permanent magnets produced by mechanical milling. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08E902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliaev, I.; Besnus, M.J.; Meyer, A.J.P. Antiferromagnetisme de la phase ε hexagonale desórdonnee du systema Mn-Al. Sol. Stat. Comm. 1973, 13, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Villacorta, F.; Marion, J.L.; Oldham, J.; Daniil, M.; Willard, M.; Lewis, L. Magnetism-Structure Correlations during the ε→τ Transformation in Rapidly-Solidified MnAl Nanostructured Alloys. Metals 2014, 4, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Villacorta, F.; Marion, J.L.; Sepehrifar, T.; Daniil, M.; Willard, M.A.; Lewis, L.H. Exchange anisotropy in the nanostructured MnAl system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 112408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estey, C.M.; Cockcroft, S.L.; Maijer, D.M.; Hermesmann, C. Constitutive behaviour of A356 during the quenching operation. Mat. Scien. Engin. A 2004, 383, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, L.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. Microstuctural defects in hot deformed and as-transformed τ-MnAl-C. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 852, 156998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Kovacs, A.; Oezelt, H.; Fischbacher, J.; Zhao, P.; Woodcock, T.G.; Schrefl, T. Insights into MnAl-C nano-twin defects by micromagnetic characterization. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisany, D.; Kovács, A.; Hegde, O.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E.; Raabe, D.; Hickel, T.; Gault, B. Influence of crystalline defects on magnetic nanodomains in a rare-earth-free magnetocrystalline anisotropy alloy. Phys. Rev. Mat. 2021, 5, 064403. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zuo, S.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H. L10 rare-earth-free permanent magnets: The effects of twinning versus dislocations in Mn-Al magnets. Phys. Rev. Mat. 2020, 4, 094402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Skokov, K.; Maccari, F.; Gutfleisch, O.; Wu, H.; et al. Roadmap towards optimal magnetic properties in rare-earth-free L10-MnAl permanent magnets. Res. Sq. 2022; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madugundo, R.; Koylu-Alkan, O.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Bulk Mn-Al-C permanent magnets prepared by various techniques. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamm, S.; Hesse, J. A simple plot indicating interactions between single-domain particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1979, 27, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, H.; Haanstra, H.B. Evidence by Lorentz Microscopy for Magnetically Active Stacking Faults in MnAl Alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 2853–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Congiu, F.; Concas, G.; Cannas, C.; Mameli, V.; Yaacoub, N.; Hassa, R.S.; Fiorani, D.; Slimani, S.; Peddis, D. The Boundary Between Volume and Surface-Driven Magnetic Properties in Spinel Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Toro, J.A.; Vasilakak, M.; Lee, S.S.; Andersson, M.S.; Normile, P.S.; Yaacoub, N.; Murray, P.; Sánchez, E.H.; Muñiz, P.; Peddis, D.; et al. Remanence Plots as a Probe of Spin Disorder in Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8258–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
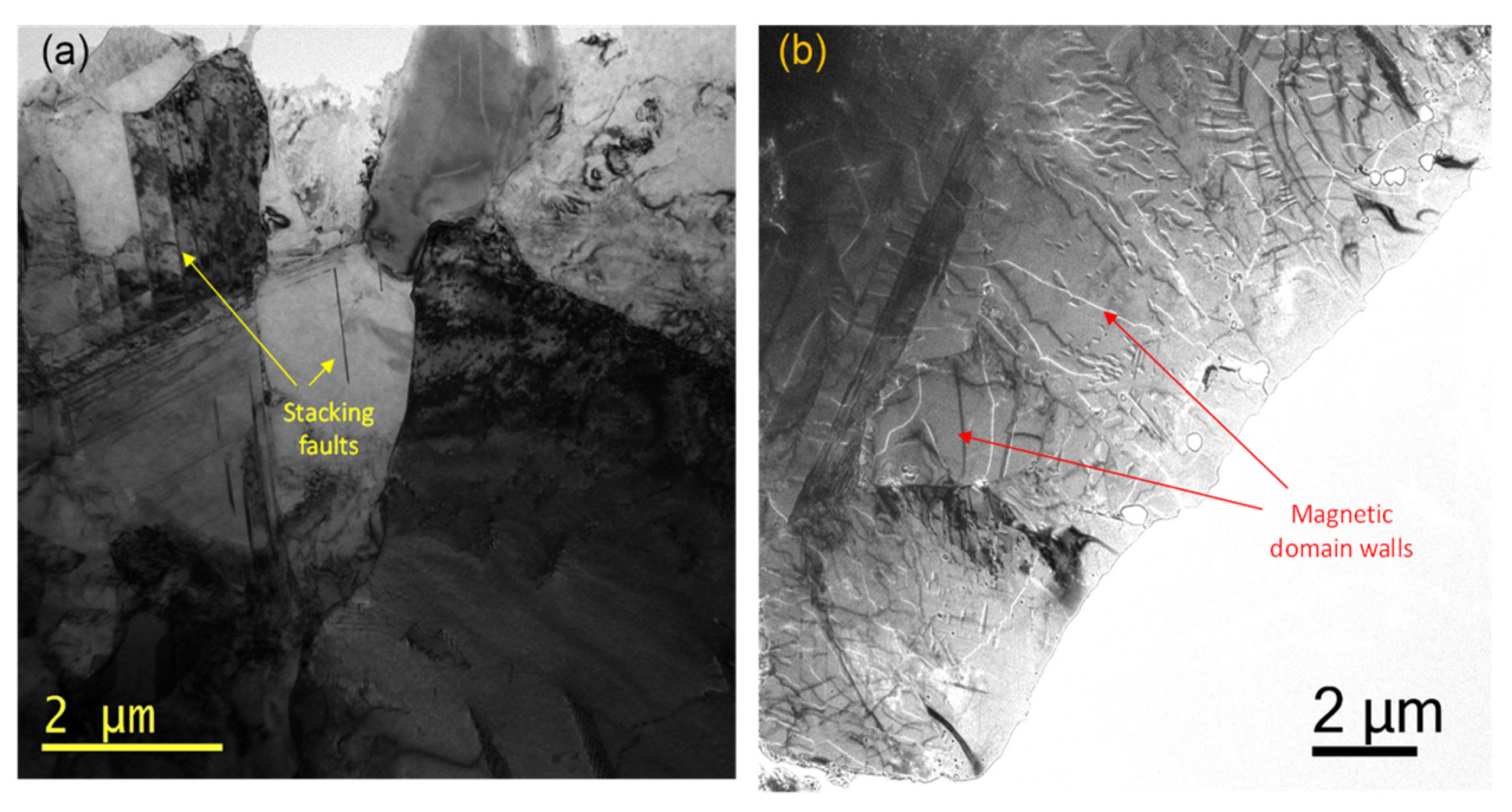



| Sample | Phases | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Weigth Fraction (wt.%) | Estimated Density (g/cm3) | χ2 | R (F2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε-Sample-A | ε1 | a = 2.705 c = 4.405 | 5 | 5.12 | 0.9264 | 0.1165 |
| ε2 | a = 2.700 c = 4.383 | 81 | 5.00 | |||
| τ-MnAlC | a = 3.914 c = 3.604 | 10 | 5.11 | |||
| Al6Mn | a = 7.798 b = 6.473 c = 8.801 | 4 | 3.24 | |||
| ε-Sample-B | ε1 | a = 2.704 c = 4.376 | 69 | 5.16 | 1.4330 | 0.0170 |
| ε2 | a = 2.706 c = 4.381 | 31 | 4.98 | |||
| ε-Sample-C | ε1 | a = 2.697 c = 4.370 | 11 | 5.19 | 0.7139 | 0.0542 |
| ε2 | a = 2.670 c = 4.379 | 89 | 5.01 | |||
| τ-Sample-A | τ-MnAlC | a = 3.935 c = 3.590 | 60 | 5.08 | 0.0863 | 0.6470 |
| β-Mn | a = 6.440 | 33 | 6.83 | |||
| Al6Mn | a = 7.524 b = 6.459 c = 8.914 | 7 | 3.32 | |||
| τ-Sample-B | τ-MnAlC | a = 3.919 c = 3.596 | 100 | 4.93 | 3.4690 | 0.0420 |
| τ-Sample-C | τ-MnAlC | a = 3.919 c = 3.595 | 100 | 5.11 | 0.7497 | 0.0798 |
| ε-Phase | τ-Phase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1.8T (Am2/kg) | µ0Hc (T) | Mr (Am2/kg) | M1.8T (Am2/kg) | µ0Hc (T) | Mr (Am2/kg) | (BH)max (kJ/m3) | |
| Sample-A | 1.03 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 32.81 | 0.068 | 9.57 | ------ |
| Sample-B | 1.71 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 76.04 | 0.20 | 37.62 | 5.79 |
| Sample-C | 2.14 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 98.6 | 0.20 | 42.12 | 6.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Sánchez, H.; Gámez, J.D.; Valenzuela, J.L.; Colorado, H.D.; Marín, L.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Snoeck, E.; Gatel, C.; Zamora, L.E.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A.; et al. Optimized Route for the Fabrication of MnAlC Permanent Magnets by Arc Melting. Molecules 2022, 27, 8347. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238347
Martínez-Sánchez H, Gámez JD, Valenzuela JL, Colorado HD, Marín L, Rodríguez LA, Snoeck E, Gatel C, Zamora LE, Pérez Alcázar GA, et al. Optimized Route for the Fabrication of MnAlC Permanent Magnets by Arc Melting. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8347. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238347
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Sánchez, Hugo, Juan David Gámez, José Luis Valenzuela, Hernan Dario Colorado, Lorena Marín, Luis Alfredo Rodríguez, Etienne Snoeck, Christophe Gatel, Ligia Edith Zamora, Germán Antonio Pérez Alcázar, and et al. 2022. "Optimized Route for the Fabrication of MnAlC Permanent Magnets by Arc Melting" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8347. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238347
APA StyleMartínez-Sánchez, H., Gámez, J. D., Valenzuela, J. L., Colorado, H. D., Marín, L., Rodríguez, L. A., Snoeck, E., Gatel, C., Zamora, L. E., Pérez Alcázar, G. A., & Tabares, J. A. (2022). Optimized Route for the Fabrication of MnAlC Permanent Magnets by Arc Melting. Molecules, 27(23), 8347. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238347







