Targeted and Non-Targeted HPLC Analysis of Coffee-Based Products as Effective Tools for Evaluating the Coffee Authenticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Coffee Adulteration
3. By-Products of Coffee Industry
4. Analysis of Antioxidants in Coffee Products Using HPLC
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Targeted Analysis
4.3. Non-Targeted Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Núñez, N.; Collado, X.; Martínez, C.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Authentication of the origin, variety and roasting degree of coffee samples by non-targeted HPLC-UV fingerprinting and chemometrics. Application to the detection and quantitation of adulterated coffee samples. Foods 2020, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Coffee Organization (ICO). Total Production by All Exporting Countries. Available online: http://www.ico.org/prices/po-production.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Diviš, P.; Pořízka, J.; Kříkala, J. The effect of coffee beans roasting on its chemical composition. Potravinarstvo 2019, 13, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Govaerts, R.; Bridson, D.M.; Stoffelen, P. An annotated taxonomic conspectus of the Genus Coffea (Rubiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 152, 465–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidel, A.; von Stetten, D.; Rodrigues, C.; Máguas, C.; Hildebrandt, P. Discrimination of Green Arabica and Robusta coffee beans by raman spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11187–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feria-Morales, A.M. Examining the case of green coffee to illustrate the limitations of grading systems/expert tasters in sensory evaluation for quality control. Food Qual. Prefer. 2002, 13, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vossen, H.; Bertrand, B.; Charrier, A. Next generation variety development for sustainable production of arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.): A review. Euphytica 2015, 204, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, P.; Khampa, N.; Horadee, S.; Chaiwarith, J.; Rattanapanone, N. Quality and bioactive compounds of blends of Arabica and Robusta spray-dried coffee. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Macrae, J.R. (Eds.) Coffee Volume 1: Chemistry, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, P.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R.; Toci, A.T. Relationship between the different aspects related to coffee quality and their volatile compounds. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobková, A.; Jakabová, S.; Belej, Ľ.; Jurčaga, L.; Čapla, J.; Bobko, M.; Demianová, A. Analysis of caffeine and chlorogenic acids content regarding the preparation method of coffee beverage. Int. J. Food Eng. 2021, 17, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Díez, I.; González-Sáiz, J.M.; Sáenz-González, C.; Pizarro, C. Coffee varietal differentiation based on near infrared spectroscopy. Talanta 2007, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Domínguez-López, I.; López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú Queralt, A. Current strategies to guarantee the authenticity of coffee. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega, F.V.; Ferranti, P. Life Cycle Assessment of Coffee Production in Time of Global Change. In Encyclopedia of Food Security and Sustainability; Ferranti, P., Berrym, E.M., Anderson, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Galluzzi, L.; de Paulis, T.; Farah, A. Three centuries on the science of coffee authenticity control. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture—USDA. Coffee: World Markets and Trade. 2021. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/psdonline/circulars/coffee.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- International Coffee Organization (ICO). Coffee Market Report. Available online: https://www.ico.org/news/August%202020%20Market%20Report-E-attachment.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Del Campo, G.; Berregi, I.; Caracena, R.; Zuriarrain, J. Quantitative determination of caffeine, formic acid, trigonelline and 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural in soluble coffees by 1H NMR spectrometry. Talanta 2010, 81, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, B.; Boulanger, R.; Dussert, S.; Ribeyre, F.; Berthiot, L.; Descroix, F.; Joët, T. Climatic factors directly impact the volatile organic compound fingerprint in green Arabica coffee bean as well as coffee beverage quality. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebska, M.; Stanek, N.; Barabosz, K.; Jaszkiewicz, A.; Kulesza, R.; Matejuk, R.; Andrzejewski, D.; Biłos, Ł.; Porada, A. Comparison of chemical compounds and their influence on the taste of coffee depending on green beans storage conditions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T. Analytical methods applied for the characterization and the determination of bioactive compounds in coffee. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihadi, A.R.; Maimulyanti, A. Chemical Compounds of Coffee Ground and Spent Coffee Ground for Pharmaceutical Products. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. J. 2020, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Sultan, M.T. Coffee and its consumption: Benefits and risks. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.E.; Ramalakshmi, K.; Mohan Rao, L.J. A perception on health benefits of coffee. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 464–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prediger, R.D.S. Effects of caffeine in Parkinson’s disease: From neuroprotection to the management of motor and non-motor symptoms. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, J.-A.; Hong, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Jo, T.-H.; Park, Y.-I.; Lee, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid on scopolamine-induced amnesia via anti-acetylcholinesterase and anti-oxidative activities in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-F.; Chang, W.-H.; Black, R.M.; Liu, J.-R.; Sompol, P.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, I.H. Crude caffeine reduces memory impairment and amyloid β1-42 levels in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendash, G.W.; Mori, T.; Cao, C.; Mamcarz, M.; Runfeldt, M.; Dickson, A.; Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Tan, J.; Citron, B.A.; Lin, X.; et al. Caffeine reverses cognitive impairment and decreases brain amyloid-β levels in aged alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 17, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendash, G.W.; Cao, C. Caffeine and coffee as therapeutics against Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S117–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokcen, B.B.; Sanlier, N. Coffee consumption and disease correlations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Koh, W.-P.; Wang, R.; Govindarajan, S.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, J.-M. Coffee consumption and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Fndings from the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, P.; Jimenez, V.M. Functional properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Lean, M.E.J.; Ashihara, H.; Crozier, A. Coffee: Biochemistry and potential impact on health. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1695–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchtaridi, M.; Lestari, D.; Ikram, N.K.K.; Gazzali, A.M.; Hariono, M.; Wahab, H.A. Decaffeination and Neuraminidase Inhibitory Activity of Arabica Green Coffee (Coffea arabica) Beans: Chlorogenic Acid as a Potential Bioactive Compound. Molecules 2021, 26, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułdak, R.J.; Hejmo, T.; Osowski, M.; Bułdak, Ł.; Kukla, M.; Polaniak, R.; Birkner, E. The impact of coffee and its selected bioactive compounds on the development and progression of colorectal cancer in vivo and in vitro. Molecules 2018, 23, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Donangelo, C.M. Phenolic compounds in coffee. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 18, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Stanisz, E.; De Peña, M.P. Relationship between antioxidant capacity, chlorogenic acids and elemental composition of green coffee. LWT 2016, 73, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Bao, Z.; Zou, J.; Dong, J. Coffee consumption and risk of cancers: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, S.; Ohishi, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Oishi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Isemura, M. Anti-cancer effects of green tea epigallocatchin-3-gallate and coffee chlorogenic acid. Molecules 2020, 25, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regazzoni, L.; Saligari, F.; Marinello, C.; Rossoni, G.; Aldini, G.; Carini, M.; Orioli, M. Coffee silver skin as a source of polyphenols: High resolution mass spectrometric profiling of components and antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Marquina, A.; Tarín, J.J.; Cano, A. The impact of coffee on health. Maturitas 2013, 75, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieber, K. The impact of coffee on health. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.Y.; Weinstein, S.J.; Albanes, D.; Taylor, P.R.; McGlynn, K.A.; Virtamo, J.; Sinha, R.; Freedman, N.D. The association of coffee intake with liver cancer incidence and chronic liver disease mortality in male smokers. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herawati, D.; Giriwono, P.E.; Dewi, F.N.A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Andarwulan, N. Three major compounds showing significant antioxidative, α-glucosidase inhibition, and antiglycation activities in Robusta coffee brew. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Fukutomi, R.; Shoji, Y.; Goto, S.; Isemura, M. The beneficial effects of principal polyphenols from green tea, coffee, wine, and curry on obesity. Molecules 2021, 26, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.F.; Pinheiro, C.A.; Osório, V.M.; Pereira, L.L. Chemical Constituents of Coffee. In Quality Determinants in Coffee Production; Food Engineering Series; Louzada Pereira, L., Rizzo Moreira, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 209–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, G.M.R.N.; Dresch, D.; Melchert, W.R. Use of non-volatile compounds for the classification of specialty and traditional Brazilian coffees using principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parliment, T.H.; Ho, C.-T.; Schieberle, P. (Eds.) Caffeinated Beverages: Health Benefits, Physiological Effects and Chemistry, 1st ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, S.; De Filippis, M.; Bucci, R.; Magrì, A.D.; Magrì, A.L.; Marini, F. Characterization of the effects of different roasting conditions on coffee samples of different geographical origins by HPLC-DAD, NIR and chemometrics. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, I. Coffee Flavor Chemistry, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwarya, S.P.; Nisha, P. Unraveling the science of coffee foam—A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herawati, D.; Giriwono, P.E.; Dewi, F.N.A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Andarwulan, N. Critical roasting level determines bioactive content and antioxidant activity of Robusta coffee beans. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, C.; Ribeiro, M.; Cruz, A.C.S.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Bunzel, M.; Nunes, F.M. Nature of phenolic compounds in coffee melanoidins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7843–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniechwitz, D.; Reichardt, N.; Ralph, J.; Blaut, M.; Steinhart, H.; Bunzel, M. Isolation and characterisation of a coffee melanoidin fraction. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkovic, M.; Bornik, M.-A. Formation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (HMF) and 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furoic acid during roasting of coffee. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkovic, M.; Pichler, N. Analysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfual in coffee, dried fruits and urine. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarharum, W.B.; Williams, D.J.; Smyth, H.E. Complexity of coffee flavor: A compositional and sensory perspective. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, G.M.J. The Coffee Quality Program in Brazil. In Coffee Consumption and Industry Strategies in Brazil; de Almeida, L.F., Spers, E.E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Consumer Sci & Strat Market; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, H.D.; Boffo, E.F. Coffee beyond the cup: Analytical techniques used in chemical composition research—A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 749–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.I.; Santos, J.S.; Rodionova, O.Y.; Pomerantsev, A.; Chaves, E.S.; Rosso, N.D.; Granato, D. Chemometric authentication of Brazilian coffees based on chemical profiling. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho Martins, V.; de Oliveira Godoy, R.L.; Gouvêa, A.C.M.S.; de Araujo Santiago, M.C.P.; Borguini, R.G.; de Oliveira Braga, E.C.; Pacheco, S.; do Nascimento, L.D.S.D.M. Fraud investigation in commercial coffee by chromatography. Food Qual. Saf. 2018, 2, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Casal, S.; Alves, M.R.; Oliveira, M.B. Discrimination between Arabica and robusta coffee species on the basis of their tocopherol profiles. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, J.M.R.; Hoo Fung, L.A.; Grant, C.N. Geographic determination of the growing origins of Jamaican and international coffee using instrumental neutron activation analysis and other methods. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 309, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.M.; Batisa, B.L.; Varrique, R.M.; Coelho, V.A.; Campiglia, A.D.; Barbosa, F., Jr. The use of advanced chemometric techniques and trace element levels for controlling the authenticity of organic coffee. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, B.; Villarreal, D.; Laffargue, A.; Posada, H.; Lashermes, P.; Dussert, S. Comparison of the effectiveness of fatty acids, chlorogenic acids, and elements for the chemometric discrimination of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) varieties and growing origins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.A.; Smith, B.W. Chemical profiling to differentiate geographic growing origins of coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.F. Food Forensics: Stable Isotopes as a Guide to Authenticity and Origin, 1st ed.; Carter, J.F., Chesson, L.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Valencia, R.; Jurado, J.M.; Ceballos-Magña, S.G.; Alcázar, A.; Hernández-Díaz, J. Characterization of Mexican coffee according to mineral contents by means of multilayer perceptrons artificial neural networks. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2014, 34, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ramos, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S. Expresso beverages of pure origin coffee: Mineral characterization, contribution for mineral intake and geographical origin discrimination. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, B.; Redi-Abshiro, M.; Chandravanshi, B.S.; Combrinck, S.; McCrindle, R. Characterization of the Cultivation Region of Ethiopian Coffee by Elemental Analysis. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, J.L.; Watling, R.J. Provenance establishment of coffee using solution ICP-MS and ICP-AES. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.G.; Pablos, F.; Martín, M.J.; Leon-Camacho, M.; Valdenebro, M.S. HPLC analysis of tocopherols and triglycerides in coffee and their use as authentication parameters. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Pugajeva, I.; Czubinski, J.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Polewski, K. New insights regarding tocopherols in Arabica and Robusta species coffee beans: RP-UPLC-ESI/MSn and NP-HPLC/FLD study. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 36, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jham, G.N.; Winkler, J.K.; Berhow, M.A.; Vaughn, S.F. γ-Tocopherol as a Marker of Brazilian Coffee (Coffea arabica L.) Adulteration by Corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5995–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.D.A.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; Rodarte, M.P.; de Carvalho dos Anjos, V.; Bell, M.J.V. Origin geographical classification of green coffee beans (Coffea arabica L.) produced in different regions of the Minas Gerais state by FT-MIR and chemometric. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagliani, L.R.; Pellegrino, G.; Giugno, G.; Consonni, R. Quantifcation of Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora var. robusta in roasted and ground coffee blends. Talanta 2013, 106, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.C.E.; Benassi, M.D.T. Discrimination between Arabica and Robusta coffees using hydrosoluble compounds: Is the efficiency of the parameters dependent on the roast degree? Beverages 2015, 1, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlabachew, M.; Abebe, A.; Wubieneh, T.A.; Habtemariam, T.Y. Rapid and simultaneous determination of trigonelline, caffeine, and chlorogenic acid in green coffee bean extract. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5028–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, S.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Alves, M.R.; Ferreira, M.A. Discriminate analysis of roasted coffee varieties for trigonelline, nicotinic acid, and caffeine content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintello, C.; Forzato, C.; Gasparini, A.; Mammi, S.; Navarini, L.; Schievano, E. NMR quantification of 16-O-methylcafestol and kahweol in Coffea canephora var. robusta beans from different geographical origins. Food Control 2017, 75, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, Y.; Defernez, M.; Watson, A.D.; Beadman, N.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Le Gall, G.; Philo, M.; Garwood, H.; Williamson, D.; Davis, A.P.; et al. 16-O-methylcafestol is present in ground roast Arabica coffees: Implications for authenticity testing. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievano, E.; Finotello, C.; de Angelis, E.; Mammi, S.; Navarini, L. Rapid Authentication of Coffee Blends and Quantification of 16-OMethylcafestol in Roasted Coffee Beans by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12309–12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, E.D.; Barbieri, F.; Garcia, P.S.; Madeira, T.B.; Acquaro, V.R.; Scarminio, I.S.; da Camara, C.A.P.; Nixdorf, S.L. Detection of ground roasted coffee adulteration with roasted soybean and wheat. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, T.; do Lago, C.L. Detection of adulterations in processed coffee with cereals and coffee husks using capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3507–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, D.S.; Pauli, E.D.; de Abreu, J.E.M.; Massura, F.W.; Cristiano, V.; Santos, M.J.; Nixdorf, S.L. Detection of roasted and ground coffee Adulteration by HPLC and by amperometric and by post-column derivatization UV-Vis detection. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Ting, H.; Jin-Lan, Z. Novel identification strategy for ground coffee adulteration based on UPLC-HRMS oligosaccharide profiling. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, D.; Lopes, F.S.; dos Santos, V.B.; do Lago, C.L. Detection of coffee adulteration with soybean and corn by capillary electrophoresis-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klikarová, J.; Řeháková, B.; Česlová, L. Evaluation of regular and decaffeinated (un)roasted coffee beans using HPLC and multivariate statistical methods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suktham, T.; Soliven, A.; Jones, A.; Dennis, G.R.; Shalliker, R.A. Information rich chromatographic separations of natural samples: The analysis of antioxidants in coffee using post column derivatisation and the CUPRAC assay on narrow bore reaction flow HPLC columns. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.; Ciotoli, E.; Biancolillo, A.; Bucci, R.; Magrì, A.D.; Marini, F. Simultaneous quantification of caffeine and chlorogenic acid in coffee green beans and varietal classification of the samples by HPLC-DAD coupled with chemometrics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 28748–28759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, W.; Nemzer, B.; Stalmach, A.; Ali, S.; Combet, E. Polyphenolic and hydroxycinnamate contents of whole coffee fruits from China, India, and Mexico. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5298–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehari, B.; Chandravanshi, B.S.; Redi-Abshiro, M.; Combrinck, S.; McCrindle, R.; Atlabachew, M. Polyphenol contents of green coffee beans from different regions of Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Dwiecki, K.; Siger, A.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J.; Michalak, M.; Polewski, K. Contribution of phenolic acids isolated from green and roasted boiled-type coffee brews to total coffee antioxidant capacity. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Serra, F.; Reniero, F.; Héberger, K. Botanical and geographical characterization of green coffee (Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora): Chemometric evaluation of phenolic and methylxanthine contents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4224–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Syakfanaya, A.M.; Azminah, A.; Saputri, F.C.; Mun’im, A. Optimization of betaine-sorbitol natural deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity of chlorogenic acid and caffeine content from robusta green coffee beans. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, S.; Alves, M.R.; Mendes, E.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Ferreira, M.A. Discrimination between Arabica and Robusta coffee species on the basis of their amino acid enantiomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.J.; Pablos, F.; Gonzalez, A.G.; Valdenebro, M.S.; Leon-Camacho, M. Fatty acid profiles as discriminant parameters for coffee varieties differentiation. Talanta 2001, 54, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui Alves, M.; Casal, S.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Ferreira, M.A. Contribution of FA profile obtained by high-resolution GC/chemometric techniques to the authenticity of green and roasted coffee varieties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.; Santini, A.; Le Grottaglie, L.; Manzo, N.; Visconti, A.; Ritieni, A. Identification markers based on fatty acid composition to differentiate between roasted Arabica and Canephora (Robusta) coffee varieties in mixtures. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2014, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Knowledge Centre for Food Fraud and Quality. Available online: https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/food-fraud-quality/topic/food-fraud_en (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- De Lange, E. Draft Report on the Food Crisis, Fraud in the Food Chain and Control Thereof (2013/2091 (INI)); The European Parliament, Committee on the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety: Brussels, Belgium, 2013; Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/ENVI-PR-519759_EN.pdf?redirect (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Combes, M.C.; Joët, T.; Lashermes, P. Development of a rapid and efficient DNA-based method to detect and quantify adulterations in coffee (Arabica versus Robusta). Food Control 2018, 88, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Ruge, W.; Kuballa, T.; Ilse, M.; Winkelmann, O.; Diehl, B.; Thomas, F.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Rapid approach to identify the presence of Arabica and Robusta species in coffee using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, S.; Mendes, E.; Alves, M.R.; Alves, R.C.; Beatriz, M.; Oliveira, P.P.; Ferreira, M.A. Free and conjugated biogenic amines in green and roasted coffee beans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6188–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.J.; Pablos, F.; González, A.G. Discrimination between Arabica and Robusta green coffee varieties according to their chemical composition. Talanta 1998, 46, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Cogliati, C. NMR based geographical characterization of roasted coffee. Talanta 2012, 88, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquetti, I.; Link, J.V.; Lemes, A.L.G.; dos Santos Scholz, M.B.; Valderrama, P.; Bona, E. Partial least square with discriminant analysis and near infrared spectroscopy for evaluation of geographic and genotypic origin of Arabica coffee. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yener, S.; Romano, A.; Cappellin, L.; Granitto, P.M.; Aprea, E.; Navarini, L.; Märk, T.D.; Gasperi, F.; Biasioli, F. Tracing coffee origin by direct injection headspace analysis with PTR/SRI-MS. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncu, A.T.; Uncu, A.O. Plastid trnH-psbA intergenic spacer serves as a PCRbased marker to detect common grain adulterants of coffee (Coffea arabica L.). Food Control 2018, 91, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, T.C.B.; Rodrigues, D.R.; de Carvalho Polari Souto, U.T.; Lemos, S.G. A Simple voltammetric electronic tongue for the analysis of coffee adulterations. Food Chem. 2019, 273, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Farah, A.; Oliveira, T.C.; Lima, I.S.; Vitório, F.; Oliveira, E.M.M. Using real-time PCR as a tool for monitoring the authenticity of commercial coffees. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toci, A.T.; Farah, A.; Pezza, H.R.; Pezza, L. Coffee adulteration: More than two decades of research. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, B.; Apaydin, H.; Bilge, G.; Boyaci, I.H. Coffee arabica adulteration: Detection of wheat, corn and chickpea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, A.A.; Arrieta, P.L.; Mendoza, J.M. Analysis of coffee adulterated with roasted corn and roasted soybean using voltammetric electronic tongue. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toci, A.T.; de Moura Ribeiro, M.V.; de Toledo, P.R.A.B.; Boralle, N.; Pezza, H.R.; Pezza, L. Fingerprint and authenticity roasted coffees by 1H-NMR: The Brazilian coffee case. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, D.T.; Walker, M.J. Critical Review of Analytical and Bioanalytical Verification of the Authenticity of Coffee. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolessa, K.; Rademaker, M.; Baets, B.D.; Boeckx, P. Prediction of specialty coffee cup quality based on near infrared spectra of green coffee beans. Talanta 2016, 150, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, E.; Venturelo, A.; Giraudo, A.; Pellegrino, G.; Geobaldo, F. Simultaneous determination by NIR spectroscopy of the roasting degree and Arabic/Robusta ratio in roasted and ground coffee. Food Control 2016, 59, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermelinger, T.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Klopprogge, B.; Yeretzian, C. Quantification of the Robusta fraction in a coffee blend via Raman spectroscopy: Proof of principle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9074–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, C.; Souard, F.; Delporte, C.; Deconinck, E.; Stoffelen, P.; Stévigny, C.; Kauffmann, J.-M.; De Braekeleer, K. Identification of coffee leaves using FT-NIR spectroscopy and SIMCA. Talanta 2018, 177, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellossi, C.; Taylor, E.J.; Lee, D.; Graziosi, G.; Donni, P. DNA Extraction and Analysis from Processed Coffee Beans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8432–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lim, L.-T.; Fu, Y. Review of analytical methods to detect adulteration in coffee. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.L.; Fang, M. HPLC-based chemometric analysis for coffee adulteration. Foods 2020, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.R.; Santos, J.R.; Almeida, P.J.; Rodrigues, J.A. Screening of Antioxidant Compounds in Green Coffee by Low Pressure Chromatography with Amperometric Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, S.P.; Irifune, T.; Fukusaki, E. GC/MS based metabolite profiling of Indonesian specialty coffee from different species and geographical origin. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinova, L.; Sirotiale, M.; Bartosova, A.; Soldan, M. Utilization of Waste from Coffee Production; Research Papers Faculty of Material Science and Technology Slovak University of Technology in Trnava; Slovak University of Technology: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2017; Volume 25, pp. 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi-Parizad, P.; De Nisi, P.; Scaglia, B.; Scarafoni, A.; Pilu, S.; Adani, F. Recovery of phenolic compounds from agro-industrial by-products: Evaluating antiradical activities and immunomodulatory properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, I.; Soyler, B.; Sezer, P.; Oztop, M.H.; Alpas, H. Improving the Recovery of Phenolic Compounds from Spent Coffee Grounds (SCG) by Environmentally Friendly Extraction Techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadi, A.; Angeloni, G.; Guerrini, L.; Corti, F.; Parenti, A.; Innocenti, M.; Bellumori, M.; Masella, P. Hydrodistillation of Coffee By-products to Recover of Bioactive Compounds: The Spent Coffee Ground and Coffee Silvers Skin Case-study. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 87, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Nzekoue, F.K.; Khamitova, G.; Angeloni, S.; Sempere, A.N.; Tao, J.; Maggi, F.; Xiao, J.; Sagratini, G.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G. Spent coffee grounds: A potential commercial source of phytosterols. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panusa, A.; Zuoro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Marrosa, G.; Petrucci, R. Recovery of natural antioxidant from spent coffee ground. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4162–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, V.; Padmanabhan, A.; Anu Appaiah, K.A. Utilization of coffee pulp waste for rapid recovery of pectin and polyphenols for sustainable material recycle. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, J.S.; Mertz, C.; Morel, G.; Lacour, S.; Belleville, M.-P.; Durand, N.; Dornier, M. Alcoholic fermentation as a potential tool for coffee pulp detoxification and reuse: Analysis of phenolic composition and caffeine content by HPLC-DADMS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzekoue, F.K.; Angeloni, S.; Navarini, L.; Angeloni, C.; Freschi, M.; Hrelia, S.; Vitali, L.A.; Sagratini, G.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G. Coffee silverskin extracts: Quantification of 30 bioactive compounds by a new HPLC-MS/MS method and evaluation of their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souard, F.; Delporte, C.; Stofelen, P.; Thévenot, E.A.; Noret, N.; Dauvergne, B.; Kaufmann, J.-M.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Stévigny, C. Metabolomics fingerprint of coffee species determined by untargeted-profling study using LC-HRMS. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čurlej, J.; Bobková, A.; Zajác, P.; Čapla, J.; Hleba, L. Sights to Authentication and Adulteration of the Coffee in Global Aspect. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 10, e4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheserek, J.J.; Ngugi, K.; Muthomi, J.W.; Omondi, C.O.; Ezekiel, K.N. Green bean biochemical attributes of Arabusta coffee hybrids from Kenya using HPLC and soxhlet extraction methods. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2021, 15, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, J.; dos Santos, L.S.; de Souza, R.G.G.; Lima, L.G.B.; Mattos, D.S.; Viana, B.P.P.B.; da Fonseca Bastos, A.C.S.; Muzzi, L.; Conte-Júnior, C.A.; Gimba, E.R.P.; et al. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effects in prostate cancer cells of green and roasted coffee extracts obtained by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE). Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianová, A.; Bobková, A.; Jurčaga, L.; Bobko, M.; Belej, Ľ.; Árvay, J. Determination of Geographical Origin of Green and Roasted Coffee Based on Selected Chemical Parameters. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 10, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelino, D.; Tassotti, M.; Brighenti, F.; Del Rio, D.; Mena, P. Niacin, alkaloids and (poly)phenolic compounds in the most widespread Italian capsule-brewed coffees. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, M.A.; Tappi, S.; Angeloni, S.; Cortese, M.; Caprioli, G.; Vittori, S.; Romani, S. Acrylamide formation and antioxidant activity in coffee during roasting—A systematic study. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, M.; Młodecki, Ł.; Dżugan, M. Caffeine Content and Antioxidant Activity of Various Brews of Specialty Grade Coffee. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2021, 20, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez Ortiz, A.L.; Berti, F.; Solano Sánchez, W.; Navarini, L.; Colomban, S.; Crisafulli, P.; Forzato, C. Distribution of p-coumaroylquinic acids in commercial Coffea spp. of different geographical origin and in other wild coffee species. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheiner, L.; Schmidt, A.; Mayer, H.K. A novel basis for monitoring the coffee roasting process: Isomerization reactions of 3-caffeoylquinic and 4-caffeoylquinic acids. LWT 2021, 152, 112343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, W.C.S.; Petry, F.C.; De Barros, W.M.; de Melo Moura, W.; da Conceição, E.C.; Bragagnolo, N. Effect of solid–liquid extraction on the bioactive content and reducing capacity of the green coffee fruit. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezicha, J.; Błazejewicz, D.; Brzezinska, J.; Grembecka, M. Green coffee VS dietary supplements: A comparative analysis of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 155, 112377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budryn, G.; Nebesny, E.; Podsędek, A.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Materska, M.; Jankowski, S.; Janda, B. Effect of different extraction methods on the recovery of chlorogenic acids, caffeine and Maillard reaction products in coffee beans. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.A.; Sanchez, L.; Caemmerer, B.; Kroh, L.W.; De Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Extraction of coffee antioxidants: Impact of brewing time and method. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.; Loftfeld, E.; Wedekind, R.; Freedman, N.; Kambanis, C.; Scalbert, A.; Sinha, R. A metabolomic study of the variability of the chemical composition of commonly consumed coffee brews. Metabolites 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preedy, V.R. (Ed.) Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Authenticity Assessment and Fraud Quantitation of Coffee Adulterated with Chicory, Barley, and Flours by Untargeted HPLC-UV-FLD Fingerprinting and Chemometrics. Foods 2021, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, K.; Setoyama, D.; Shimizu, H.; Seta, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, D.; Wariishi, H.; Nagai, C.; Nakahara, K. Identification of 3-methylbutanoyl glycosides in green Coffea arabica beans as causative determinants for the quality of coffee flavors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3742–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittipod, S.; Schwartz, E.; Paravisini, L.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of flavor modulating compounds that positively impact coffee quality. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lao, F.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Liao, X.; Chen, A.; Yang, S. Use of liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and metabolomic approach to discriminate coffee brewed by different methods. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.; Martínez, C.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. High-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection fingerprints as chemical descriptors to authenticate the origin, variety and roasting degree of coffee by multivariate chemometric methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, N.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Non-targeted HPLC-FLD fingerprinting for the detection and quantitation of adulterated coffee samples by chemometrics. Food Control 2021, 124, 107912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.; Pons, J.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Non-targeted high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and fluorescence detection fingerprinting for the classification, authentication, and fraud quantitation of instant coffee and chicory by multivariate chemometric methods. LWT 2021, 147, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viapiana, A.; Maggi, F.; Kaszuba, M.; Konieczynski, P.; Wesolowski, M. Quality assessment of Coffea arabica commercial samples. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 3154–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.; Scarminio, I.S. Chemometric discrimination of genetically modified Coffea arabica cultivars using spectroscopic and chromatographic fingerprints. Talanta 2013, 107, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizellini, F.C.; Marcheafave, G.G.; Rakocevic, M.; Bruns, R.E.; Scarminio, I.S.; Soares, P.K. PARAFAC HPLC-DAD metabolomic fingerprint investigation of reference and crossed coffees. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwareth, A.; Zayed, A.; Farag, M.A. Chemometrics-based aroma profiling for revealing origin, roasting indices, and brewing method in coffee seeds and its commercial blends in the Middle East. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcheafave, G.G.; Pauli, E.D.; Tormena, C.D.; Ortiz, M.C.V.; de Almeida, A.G.; Rakocevic, M.; Bruns, R.E.; Scarminio, I.S. Factorial design fingerprint discrimination of Coffea arabica beans under elevated carbon dioxide and limited water conditions. Talanta 2020, 209, 120591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
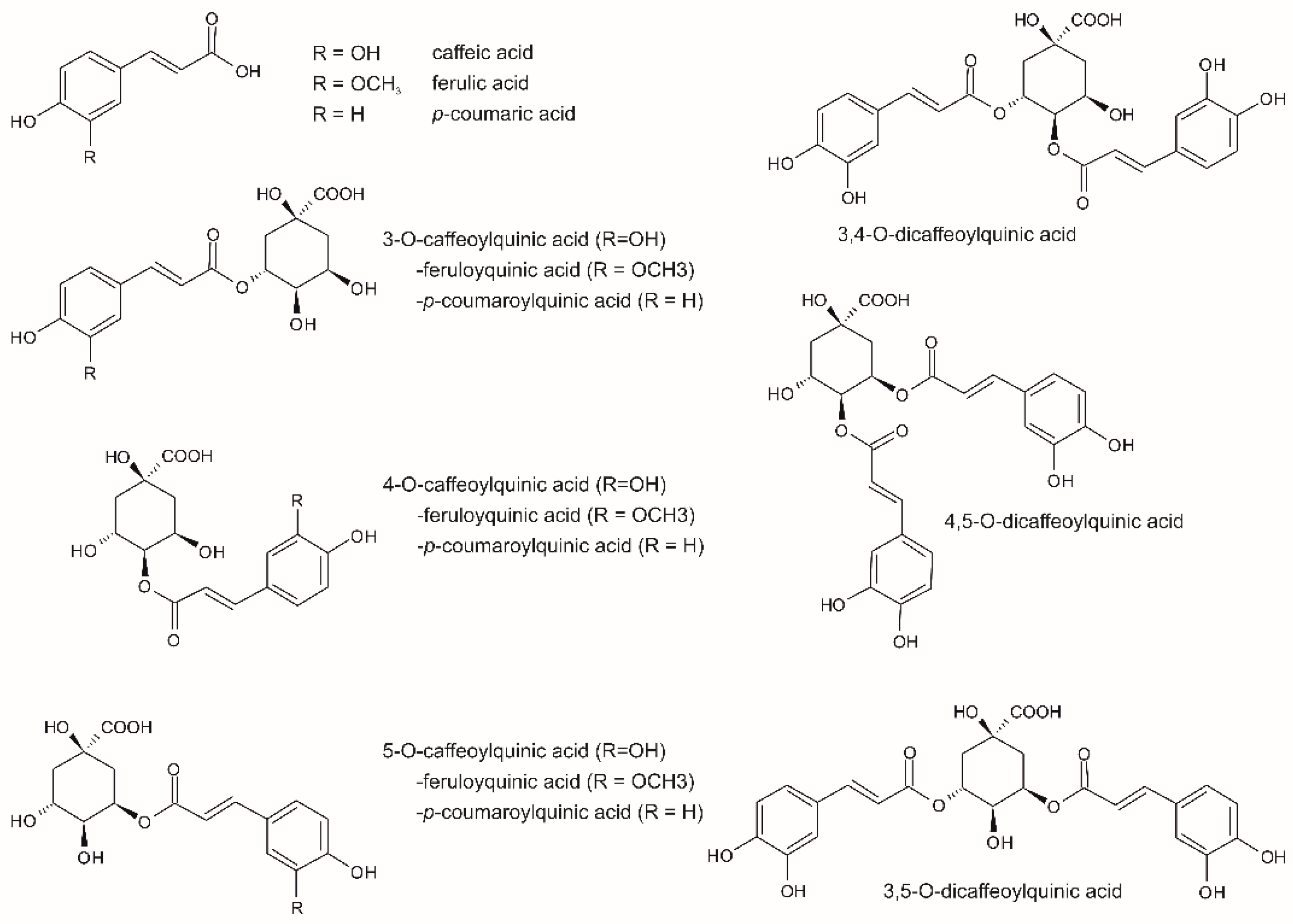
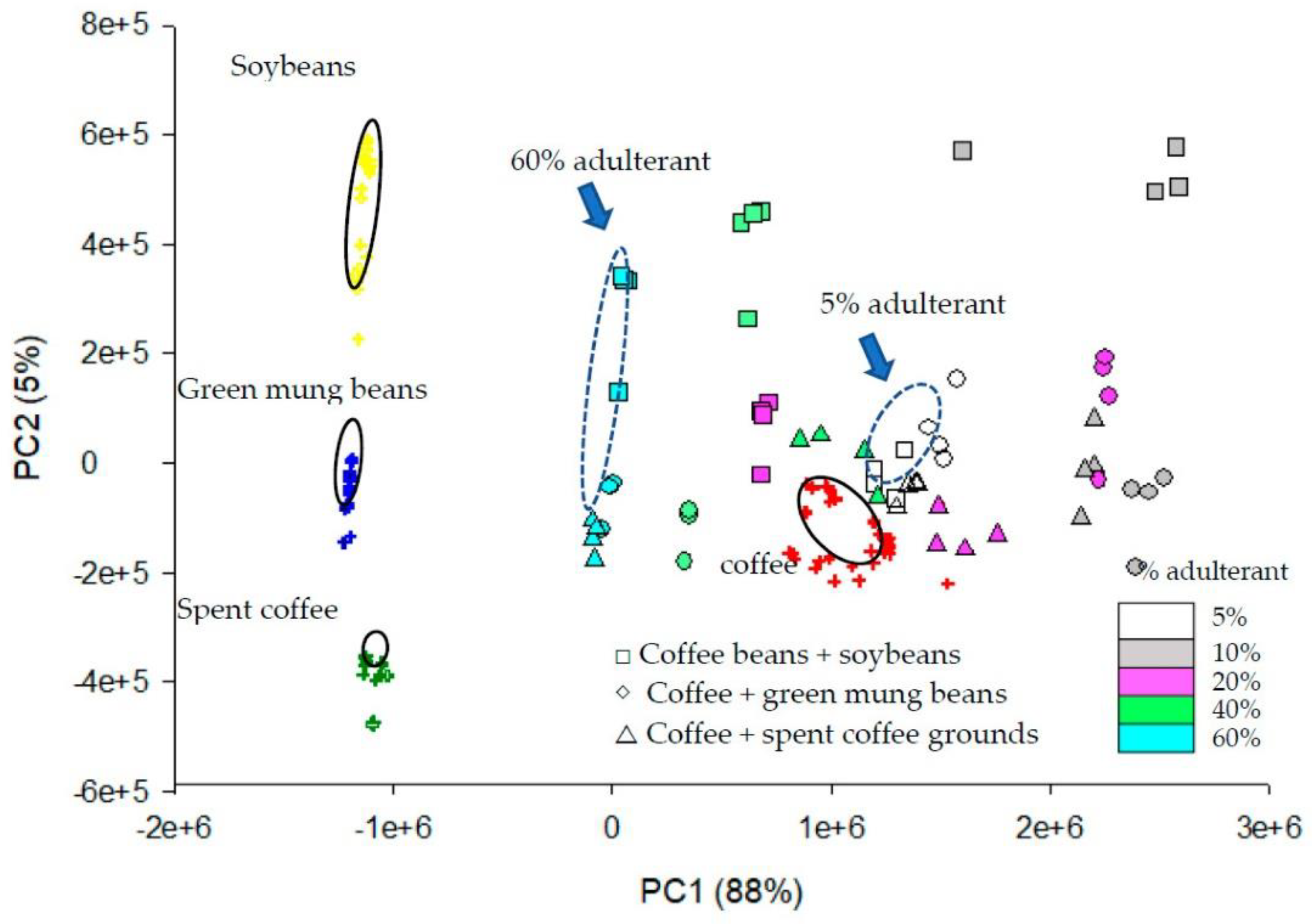


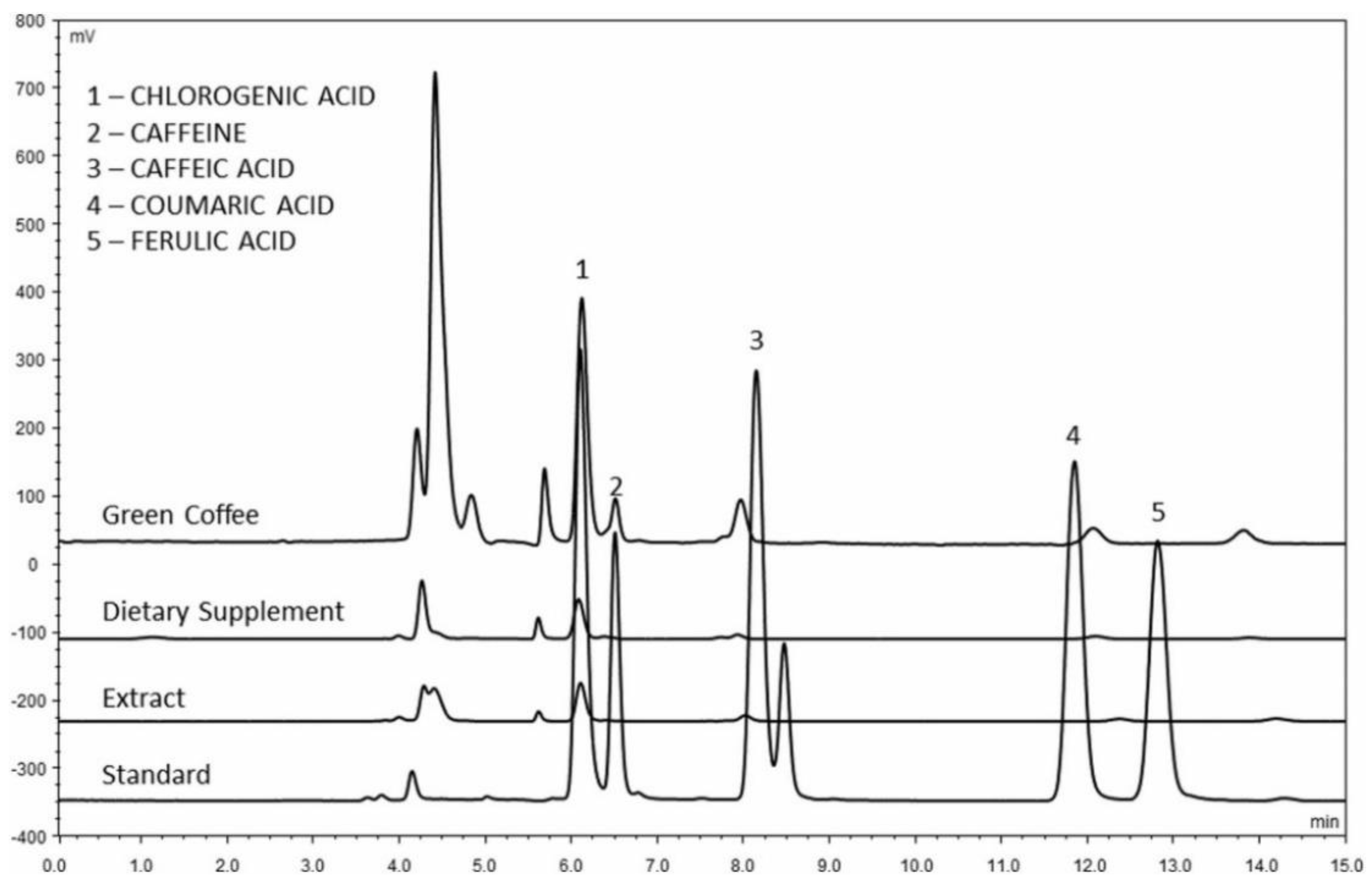
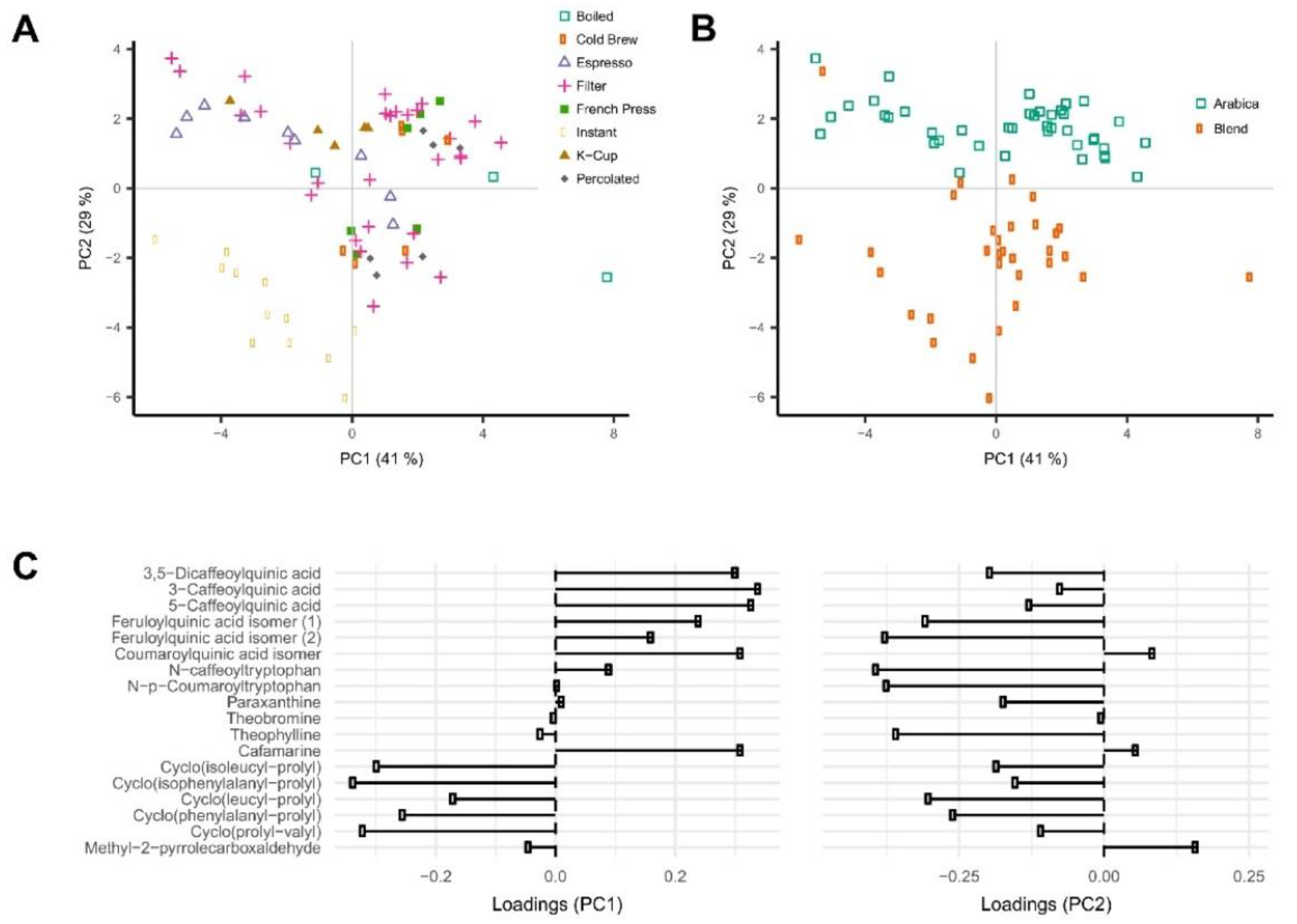
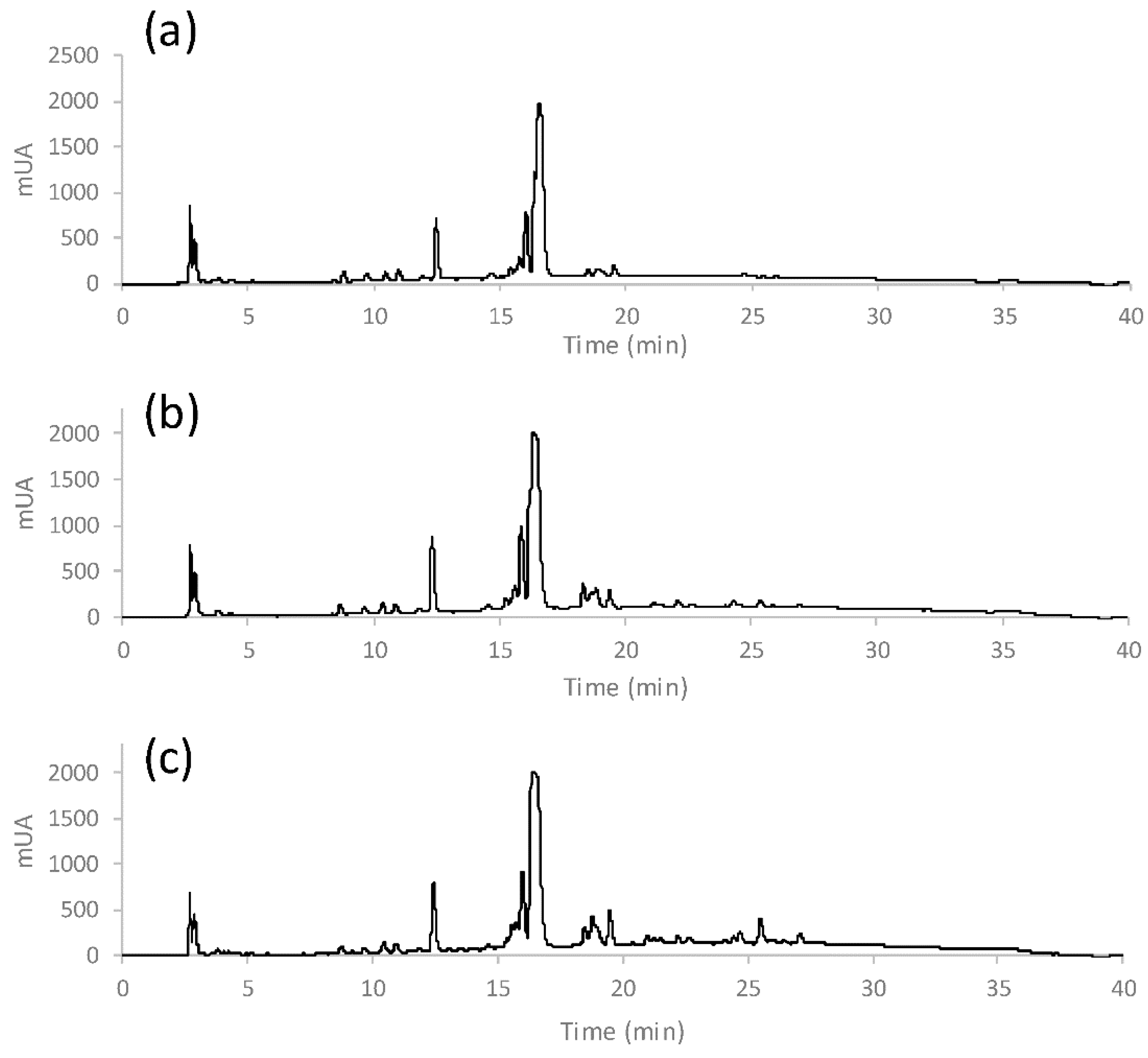
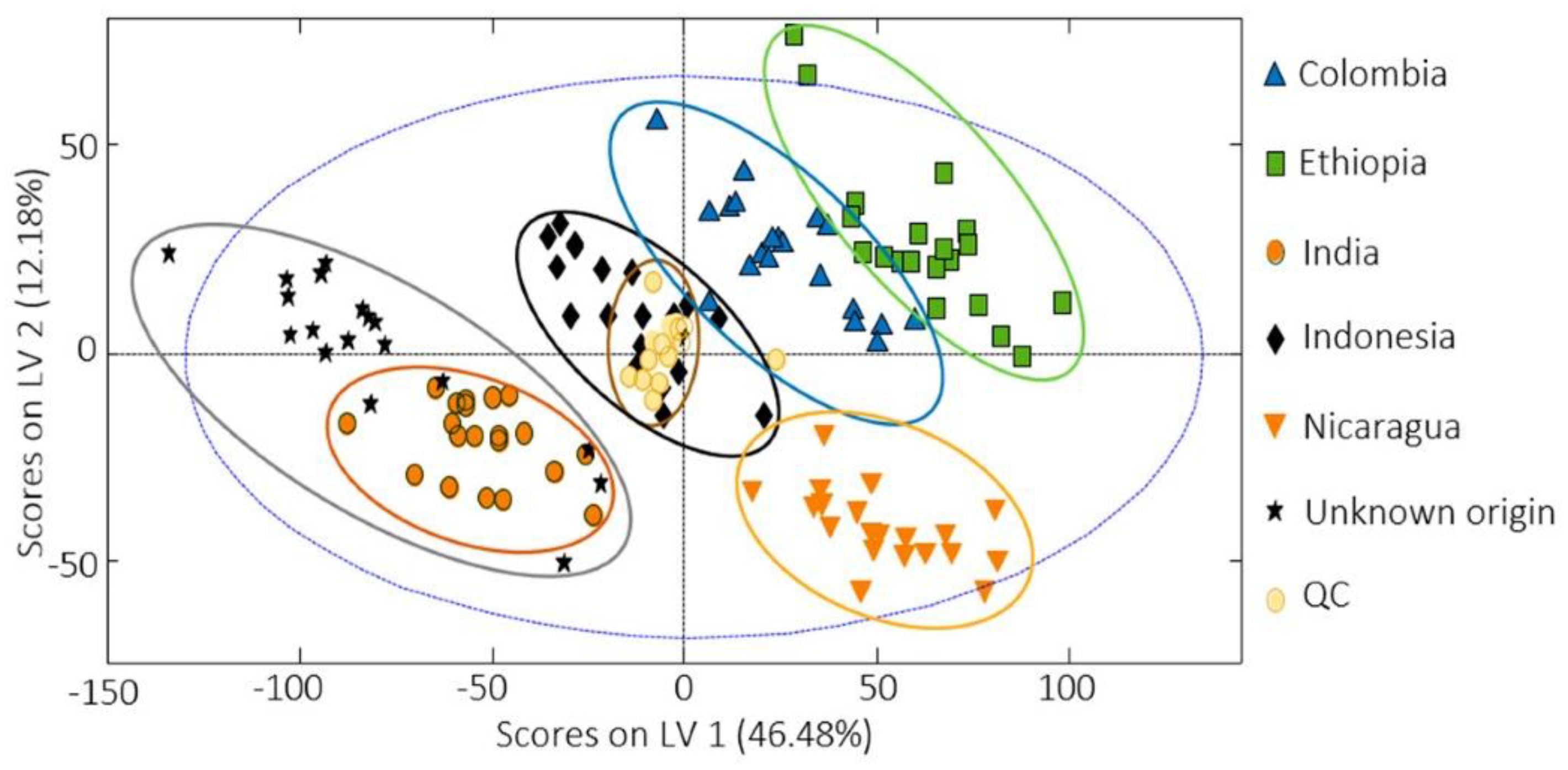
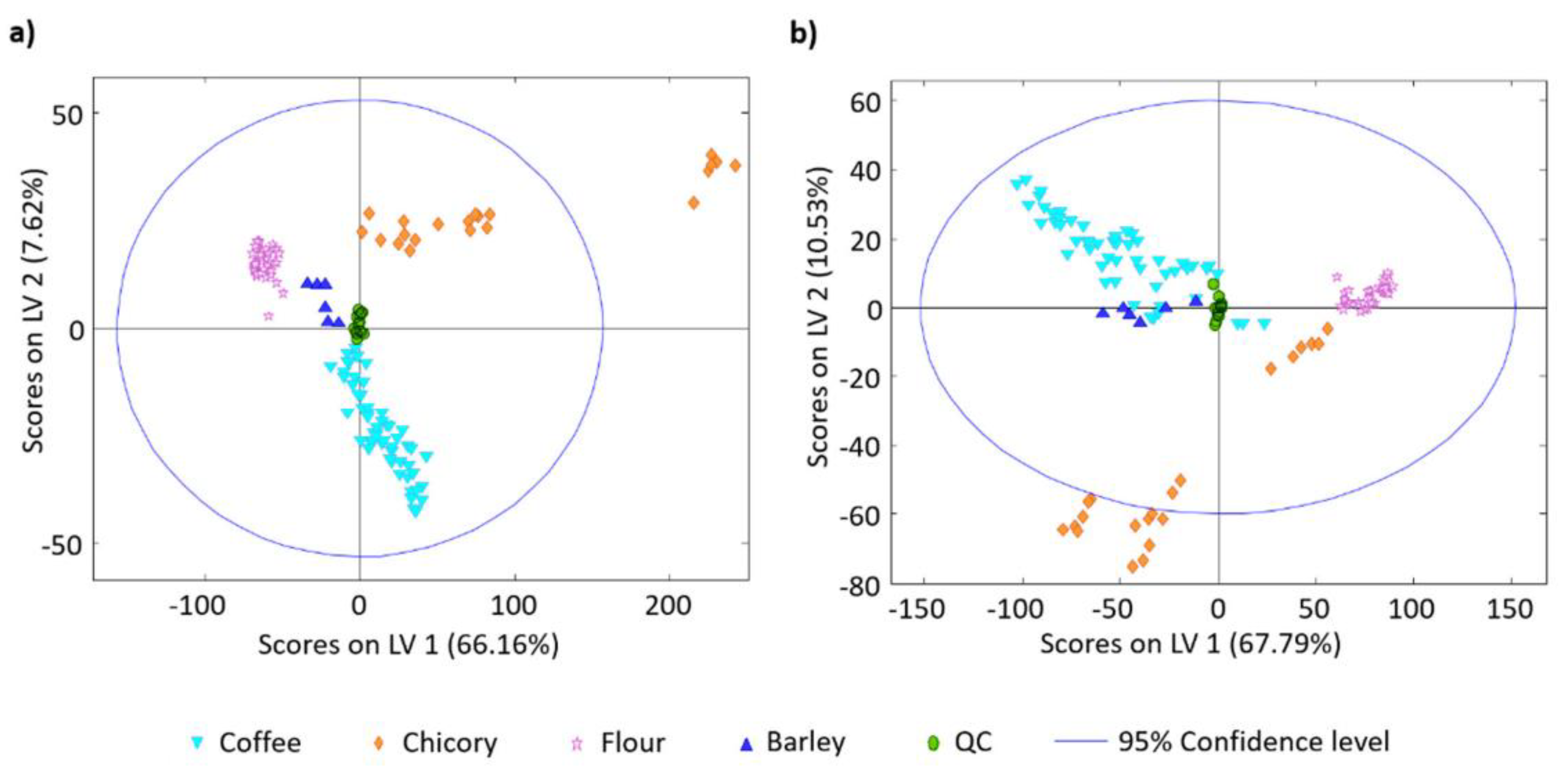
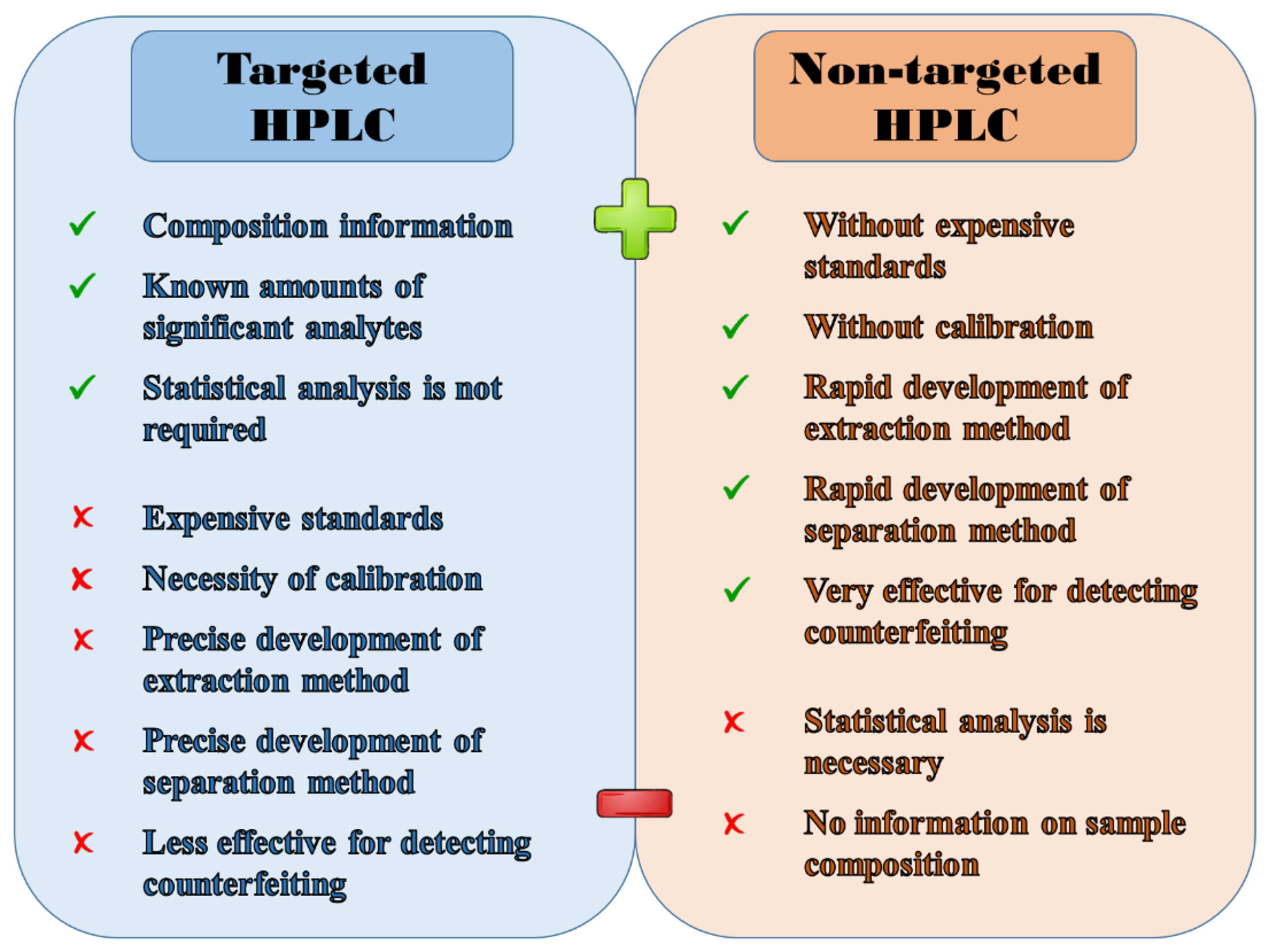
| Kind of Sample | Sample Pre-Treatment | Impact of Cultivation, Brewing, Roasting, Decaffeination, Botanical and/or Geographical Origin | Detection | Statistical Data Treatment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabica roasted coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | Br | UV/VIS | PCA and ANOVA | [11] |
| Coffee beans from West Java | s–l (hot water) | D | UV/VIS | - | [34] |
| Green, roasted, and spent coffee and coffee silverskin | s–l (organic solvents) | R and D | UV/VIS and MS | PCA | [40] |
| Specialty and traditional coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | - | UV/VIS | PCA | [47] |
| Conventional and organic Brazilian coffee samples | s–l (hot water) | C; B; and G | UV/VIS | DA, PLS-DA, DD-SIMCA, SVM, and k-NN | [60] |
| Roasted and green coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | R; D; B; and G | UV/VIS | PCA, FA, and ANOVA | [88] |
| Green coffee beans | s–l (organic solvents) | - | AMP | - | [124] |
| Kenyan green coffee beans and their hybrids | NS | B | NS | PCA | [137] |
| Arabica roasted and green coffee beans | UAE and MAE | R | UV/VIS | - | [138] |
| American, African, and Asian green coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | R and G | UV/VIS | ANOVA | [139] |
| Italian capsules of (de) caffeinated coffee | s–l (hot water) | D | MS/MS | PCA | [140] |
| Arabica and Robusta coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | R and B | MS/MS | ANOVA | [141] |
| Specialty and commercial coffee beans | s–l (hot water) | Br; B; and G | UV/VIS | - | [142] |
| Commercially available coffee beans and wild species | s–l (hot water) | R; B; and G | UV/VIS | - | [143] |
| Arabica and Robusta coffee beans | s–l (organic solvents) | R and B | UV/VIS | - | [144] |
| Green coffee beans and food supplements | UAE | - | Corona | - | [146] |
| Roasted coffee beans | depends on the brewing | Br; R; D; B; and G | MS | PCA | [149] |
| Kind of Sample (Number) | Sample Pre-Treatment | Impact of Brewing, Roasting, Decaffeination, Botanical and/or Geographical Origin | Adulteration Studies, Cupping Score Investigation | Detection | Statistical Data Treatment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially available Arabica, Robusta, and their mixtures (306) | Nespresso machine or moka | R; B; and G | Adulteration | UV/VIS | PCA, PLS, and PLS-DA | [1] |
| Arabica and Robusta beans (6) | s–l (hot water) | R and B | - | UV/VIS (+IR fingerprint) | ASCA, PLS-DA, SIMCA | [49] |
| Vietnamese Arabica, Robusta coffee beans, their mixtures and samples of chicory, barley, and flour (123) | s–l (water-MeOH mixture) | B and G | Adulteration | UV/VIS and FLD | PLS and PLS-DA | [151] |
| Arabica beans (40) | s–l (hot water-MeOH mixture) | - | Cupping score | MS | OPLS | [152] |
| Arabica and Robusta beans (18) | drip-coffee maker and clean-up (SPE) | G | Cupping score | MS | OPLS | [153] |
| Arabica beans (3) | s–l (hot/cold water) | Br and G | - | MS | ANOVA, PCA, HCA, and OPLS-DA | [154] |
| Commercially available Arabica, Robusta, and their mixtures (186) | Nespresso machine or moka | R; B; and G | Adulteration | FLD | PCA and PLS-DA | [155] |
| Commercially available Arabica, Robusta, and their mixtures (8) | Nespresso machine or moka | R; B; and G | Adulteration | FLD | PLS and PLS-DA | [156] |
| Regular and decaffeinated coffee beans and instant and ground chicory samples (88) | moka or s–l (hot water) | D | Adulteration | UV/VIS and FLD | PCA and PLS-DA | [157] |
| Arabica coffee beans (24) | NS | G | - | NS | PCA | [158] |
| Green beans of different cultivars of Arabica (4) | UAE (organic solvents) | B | - | UV/VIS (+IR fingerprint) | PCA | [159] |
| Green beans of different cultivars of Arabica (2) | UAE (organic solvents) | B | - | UV/VIS | PARAFAC | [160] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klikarová, J.; Česlová, L. Targeted and Non-Targeted HPLC Analysis of Coffee-Based Products as Effective Tools for Evaluating the Coffee Authenticity. Molecules 2022, 27, 7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217419
Klikarová J, Česlová L. Targeted and Non-Targeted HPLC Analysis of Coffee-Based Products as Effective Tools for Evaluating the Coffee Authenticity. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217419
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlikarová, Jitka, and Lenka Česlová. 2022. "Targeted and Non-Targeted HPLC Analysis of Coffee-Based Products as Effective Tools for Evaluating the Coffee Authenticity" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217419
APA StyleKlikarová, J., & Česlová, L. (2022). Targeted and Non-Targeted HPLC Analysis of Coffee-Based Products as Effective Tools for Evaluating the Coffee Authenticity. Molecules, 27(21), 7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217419




