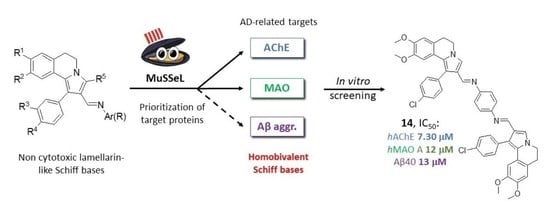
Homobivalent Lamellarin-Like Schiff Bases: In Vitro Evaluation of Their Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential
Abstract
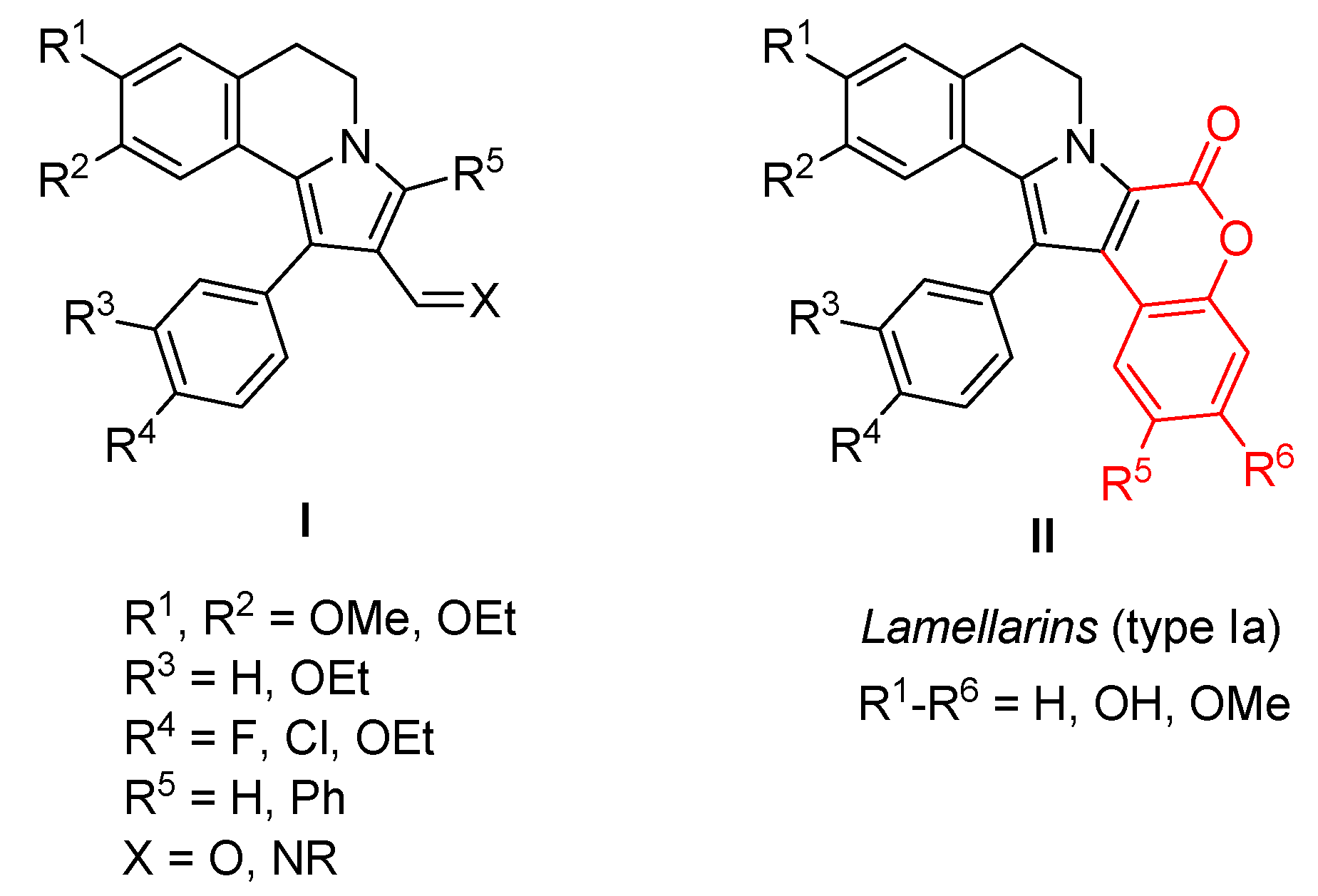
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
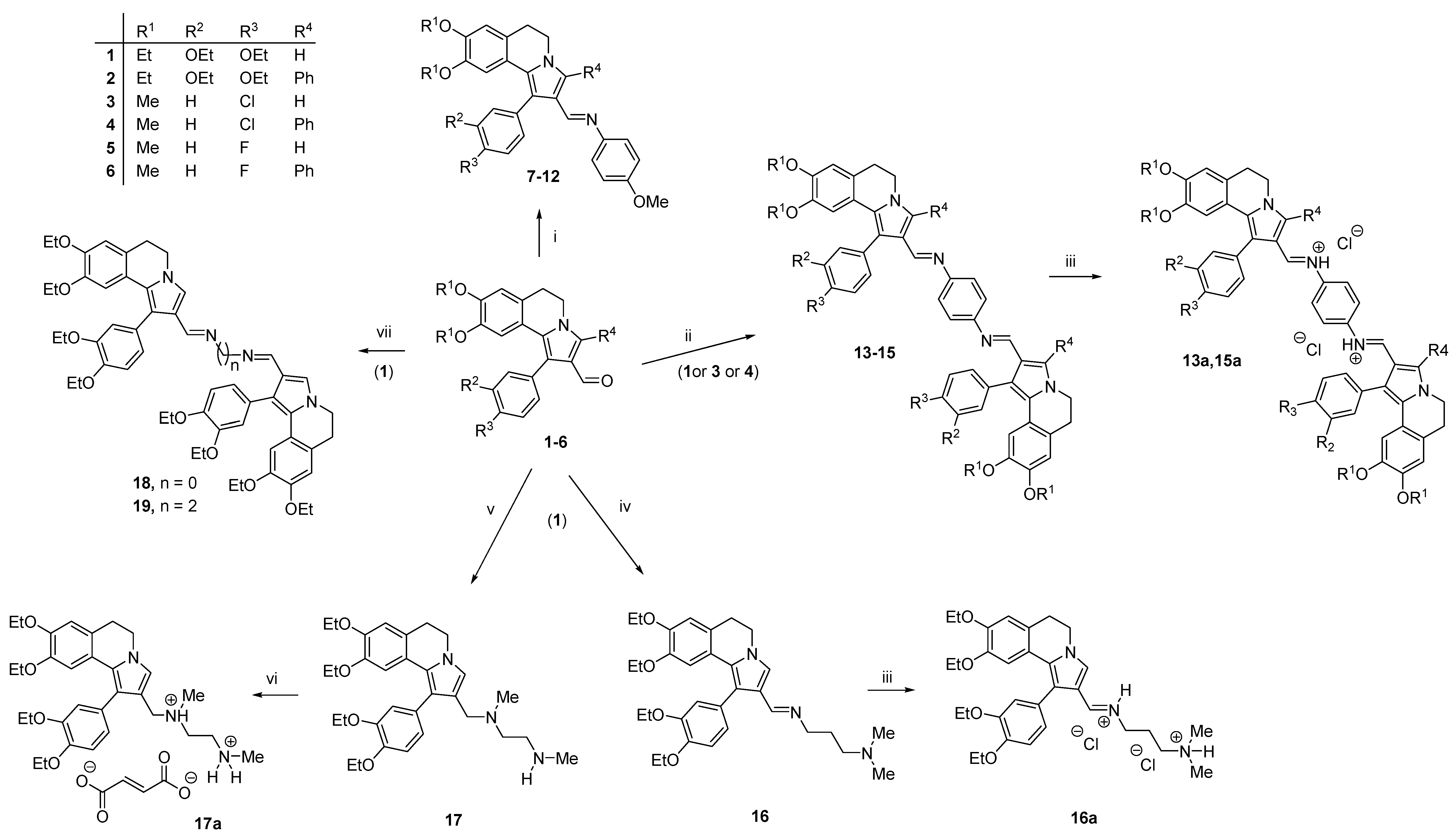
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.3. Target Protein Prediction by Similarity Search
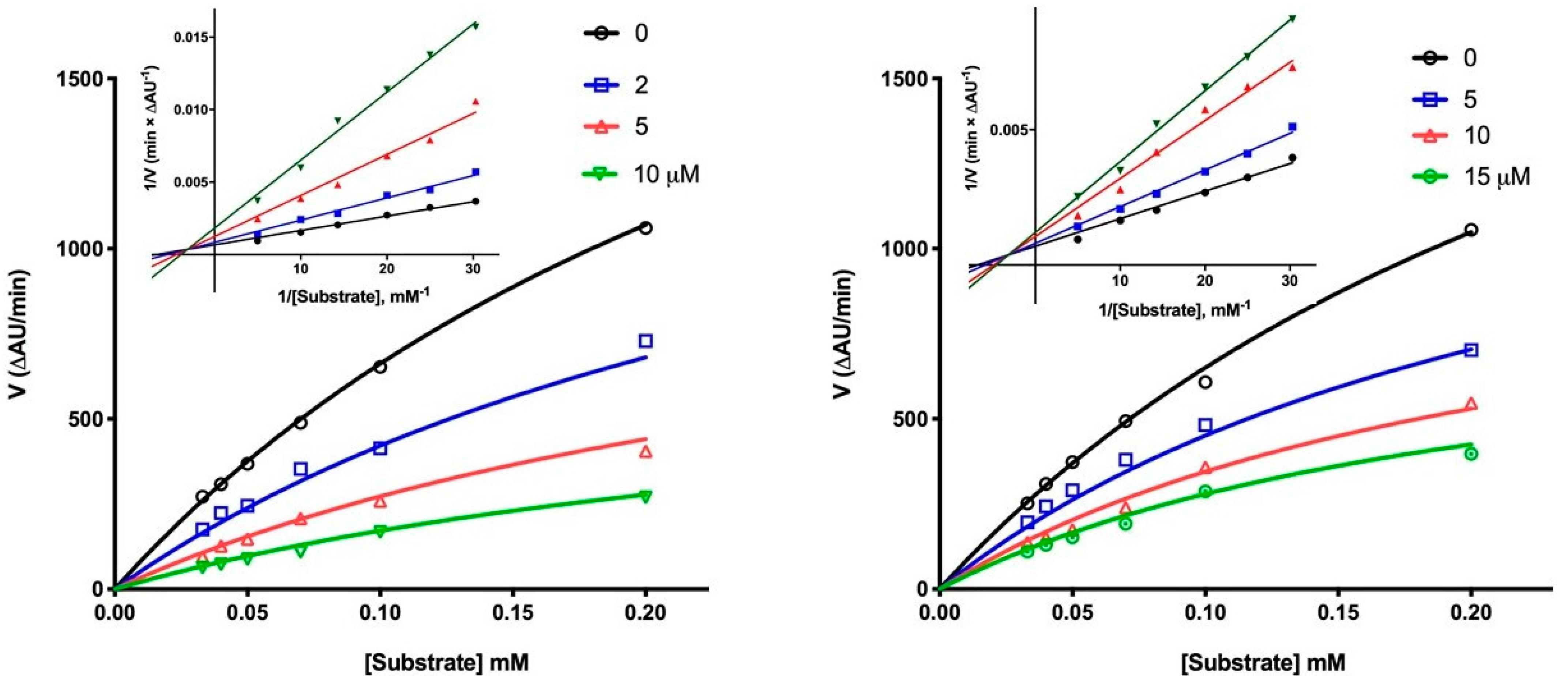
2.4. Inhibition of AD-Related Targets
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of Schiff Bases 7–15
3.1.2. Preparation of Quaternary Salts 13a, 15a and 16a
3.1.3. Synthesis of Compounds 18 and 19
3.2. Chemoinformatics and Computational Chemistry
3.3. Cell Viability Assays
3.3.1. Cell Lines
3.3.2. In Vitro Growth Inhibition Assay
3.4. Enzymatic Assays
3.4.1. Cholinesterases
3.4.2. Monoamine Oxidases
3.5. Inhibition Assay of β-Amyloid Aggregation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matveeva, M.D.; Purgatorio, R.; Voskressensky, L.G.; Altomare, C.D. Pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoquinoline scaffold in drug discovery: Advances in synthesis and medicinal chemistry. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2735–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, A.R.; García Grávalos, M.D.; Fernández Puentes, J.L. Polyaromatic alkaloids from marine invertebrates as cytotoxic compounds and inhibitors of multidrug resistance caused by P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, M.D.; Borisova, T.N.; Titov, A.A.; Anikina, L.V.; Dyachenko, S.V.; Astakhov, G.S.; Varlamov, A.V.; Voskressensky, L.G. Domino reactions of 1-aroyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinolines with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. Synthesis 2017, 49, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevskaya, A.A.; Matveeva, M.D.; Borisova, T.N.; Niso, M.; Colabufo, N.A.; Boccarelli, A.; Purgatorio, R.; de Candia, M.; Cellamare, S.; Voskressensky, L.G.; et al. A new class of 1-aryl-5,6-dihydropyrrolo[2,1-a]isoquinoline derivatives as reversers of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in tumor cells. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaruli, M.; Alberga, D.; Ciriaco, F.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Tondo, A.R.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. Accelerating drug discovery by early protein drug target prediction based on multi- fingerprint similarity search. Molecules 2019, 24, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberga, D.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Montaruli, M.; Leonetti, F.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. A new approach for drug target and bioactivity prediction: The Multi-fingerprint Similarity Search aLgorithm (MuSSeL). J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Doran, A.C.; Di, L.; West, M.A.; Osgood, S.M.; Mancuso, J.Y.; Shaffer, C.L.; Tremaine, L.; Liras, J. Prediction of human brain penetration of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein substrates using in vitro transporter studies and animal models. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Dubey, R. Target enzyme in Alzheimer’s disease: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Reconsideration of anticholinesterase therapeutic strategies against Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Catto, M.; Rullo, M.; Farina, R.; Denora, N.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. Investigating alkyl nitrates as nitric oxide releasing precursors of multitarget acetylcholinesterase-monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wei, Y.-B.; Zhang, C.; Ning, F.-X.; Qiao, W.; Huang, S.-L.; Ma, L.; Huang, Z.-S.; Gu, L.-Q. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of oxoisoaporphine and oxoaporphine derivatives as new dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase/butyrylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2523–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; De Palma, A.; Giangregorio, N.; Miniero, D.V.; Pesce, P.; Nicolotti, O.; Campagna, F.; Altomare, C.D.; Catto, M. Mannich base approach to 5-methoxyisatin 3-(4-isopropylphenyl)hydrazone: A water-soluble prodrug for a multitarget inhibition of cholinesterases, beta-amyloid fibrillization and oligomer-induced cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellamare, S.; Stefanachi, A.; Stolfa, D.A.; Basile, T.; Catto, M.; Campagna, F.; Sotelo, E.; Acquafredda, P.; Carotti, A. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of glycine-based molecular tongs as inhibitors of Abeta1-40 aggregation in vitro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 4810–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, M.; Pellarin, R.; Catto, M.; Carotti, A.; Caflisch, A. 9,10-Anthraquinone hinders beta-aggregation: How does a small molecule interfere with Abeta-peptide amyloid fibrillation? Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 792–800. [Google Scholar]
- Catto, M.; Arnesano, F.; Palazzo, G.; De Stradis, A.; Calò, V.; Losacco, M.; Purgatorio, R.; Campagna, F. Investigation on the influence of (Z)-3-(2-(3-chlorophenyl)hydrazono)-5,6-dihydroxyindolin-2-one (PT2) on β-amyloid(1–40) aggregation and toxicity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 560, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, K.I.; Herrmann, N.; Walker, S.E. Current place of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in the treatment of depression. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binde, C.D.; Tvete, I.F.; Gasemyr, J.; Natvig, B.; Klemp, M. A multiple treatment comparison meta-analysis of monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors for Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and iron chelators in depressive illness and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1719–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberga, D.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Mansouri, K.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. Prediction of acute oral systemic toxicity using a multifingerprint similarity approach. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 167, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feartherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; De Palma, A.; Farina, R.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. Discovery of potent dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors via homo- and heterodimerization of coumarin-based moieties. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purgatorio, R.; de Candia, M.; Catto, M.; Carrieri, A.; Pisani, L.; De Palma, A.; Toma, M.; Ivanova, O.A.; Voskressensky, L.G.; Altomare, C.D. Investigating 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroazepino[4,3-b]indole as scaffold of butyrylcholinesterase-selective inhibitors with additional neuroprotective activities for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cmpd | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | IC50 (μM) b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD | HCT116 | HeLa | A549 | K562 | |||||
| 1 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 21.3 ± 1.2 c | 11.8 ± 0.1 c | 44.5 ± 2.0 c | 19.7 ± 0.3 c | |
| 2 | Et | OEt | OEt | Ph | 365 ± 23 c | 183 ± 0.1 c | 229 ± 21 c | ||
| 3 | Me | H | Cl | H | 17.6 ±3.2 | 22.0 ± 4.0 | 33.0 ± 4.5 | 38.6 ± 3.2 | |
| 4 | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 163 ± 20 | 252 ± 11 | 109 ± 5 | 105 ± 11 | |
| 5 | Me | H | F | H | 17.8 ± 0.4 | 32.2 ± 0.3 | 33.8 ± 1.0 | 41.3 ± 2.0 | |
| 6 | Me | H | F | Ph | 91.1 ± 10.9 | 261 ± 13 | |||
| 7 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 132 ± 4 | 38.5 ± 6.6 | 34.9 ± 1.8 | 79.5 ± 6.8 | 171 ± 12 |
| 8 | Et | OEt | OEt | Ph | 412 ± 20 | 286 ± 5 | 304 ± 10 | ||
| 9 | Me | H | Cl | H | 76.4 ± 4.7 | 37.2 ± 2.4 | 35.2 ± 0.7 | 99.4 ± 1.1 | 105 ± 8 |
| 10 | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 211 ± 9 | ||||
| 11 | Me | H | F | H | 145 ± 1 | 114 ± 4 | 87.2 ± 1.1 | 153 ± 2.2 | |
| 12 | Me | H | F | Ph | >500 | 148 ± 14 | 450 ± 19 | >500 | |
| 13a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 390 ± 19 | 103 ± 8 | 205 ± 10 | 240 ± 18 | |
| 14 | Me | H | Cl | H | 269 ± 11 | 390 ± 16 | 310 ± 12 | >500 | |
| 15a | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 149 ± 3 | 102 ± 5 | 93.4 ± 2.6 | 120 ± 3.5 | 251 ± 17 |
| 16a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 72.8 ± 4.6 | 60.5 ± 0.7 | 63.1 ± 3.1 | 85.1 ± 0.2 | |
| 17a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 10.1± 0.1 | 18.6 ± 0.4 | 29.7 ± 0.9 | 35.9 ± 2.4 | 46.6 ± 1.5 |
| 18 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | >500 | 302 ± 23 | |||
| 19 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 65.1 ± 7.3 | 401 ± 8 | 84.0 ± 1.3 | 290 ± 12 | |
| Doxorubicin | 0.290 ± 0.021 | 0.142 ± 0.011 | 0.892 ± 0.013 | 0.380 ± 0.021 | 1.75 ± 0.06 | ||||
| Cmpd | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | IC50 (μM) or % Inhibition a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hAChE | hBChE | Aβ40 Self-Aggreg. | |||||
| 3 | Me | H | Cl | H | 32 ± 3% | n.i. | 66 ± 2.2 |
| 4 | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 7.90 ± 0.13 | n.i. | 35 ± 6% |
| 5 | Me | H | F | H | 33 ± 4% | n.i. | n.t. |
| 7 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 20.2 ± 3.1 | n.i. | 78 ± 5.1 |
| 9 | Me | H | Cl | H | 29.3 ± 2.3 | 13 ± 4% | 46 ± 5.0 |
| 10 | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 35 ± 7% | n.i. | 42 ± 5% |
| 11 | Me | H | F | H | 40 ± 2% | n.i. | 54 ± 2.2 |
| 13a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 13.1 ± 1.0 | 11 ± 3% | 42 ± 3.0 |
| 14 | Me | H | Cl | H | 7.30 ± 0.74 | 13 ± 1% | 13 ± 1.0 |
| 15a | Me | H | Cl | Ph | 25 ± 3% | n.i. | 50 ±6.3 |
| 16a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 32 ± 2% | n.i. | 48 ± 4% |
| 17a | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 16.4 ± 3.8 | n.i. | 31 ± 3% |
| 19 | Et | OEt | OEt | H | 37 ± 2% | n.i. | 48 ±3% |
| Galantamine | 0.721 ± 0.150 | 8.78 ± 0.36 | |||||
| Quercetin | 0.82 ± 0.07 | ||||||
| Cmpd | IC50 (μM) or % Inhibition a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| hMAO A | hMAO B | SH-SY5Y | |
| 9 | 39 ± 2% | 29 ± 5% | 22.1 ± 0.8 |
| 11 | 18.1 ± 1.2 | 22 ± 4% | 56.1 ± 2.4 |
| 13a | 12.3 ± 1.1 | 31 ± 3% | 101 ± 6 |
| 14 | 12.1 ± 2.3 | 19 ± 5% | 29.3 ± 0.1 |
| 17a | 38 ± 5% | 14.3 ± 1.4 | 17.9 ± 0.1 |
| Pargyline | 10.9 ± 0.6 | 2.69 ± 0.48 | |
| Camptothecin | 0.272 ± 0.010 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nevskaya, A.A.; Anikina, L.V.; Purgatorio, R.; Catto, M.; Nicolotti, O.; de Candia, M.; Pisani, L.; Borisova, T.N.; Miftyakhova, A.R.; Varlamov, A.V.; et al. Homobivalent Lamellarin-Like Schiff Bases: In Vitro Evaluation of Their Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential. Molecules 2021, 26, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020359
Nevskaya AA, Anikina LV, Purgatorio R, Catto M, Nicolotti O, de Candia M, Pisani L, Borisova TN, Miftyakhova AR, Varlamov AV, et al. Homobivalent Lamellarin-Like Schiff Bases: In Vitro Evaluation of Their Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020359
Chicago/Turabian StyleNevskaya, Alisa A., Lada V. Anikina, Rosa Purgatorio, Marco Catto, Orazio Nicolotti, Modesto de Candia, Leonardo Pisani, Tatiana N. Borisova, Almira R. Miftyakhova, Aleksey V. Varlamov, and et al. 2021. "Homobivalent Lamellarin-Like Schiff Bases: In Vitro Evaluation of Their Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential" Molecules 26, no. 2: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020359
APA StyleNevskaya, A. A., Anikina, L. V., Purgatorio, R., Catto, M., Nicolotti, O., de Candia, M., Pisani, L., Borisova, T. N., Miftyakhova, A. R., Varlamov, A. V., Nevskaya, E. Y., Borisov, R. S., Voskressensky, L. G., & Altomare, C. D. (2021). Homobivalent Lamellarin-Like Schiff Bases: In Vitro Evaluation of Their Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential. Molecules, 26(2), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020359