Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-κ Dielectric Sr2NiMO6 (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Type
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction
2.2. Unpolarized Raman Spectroscopy
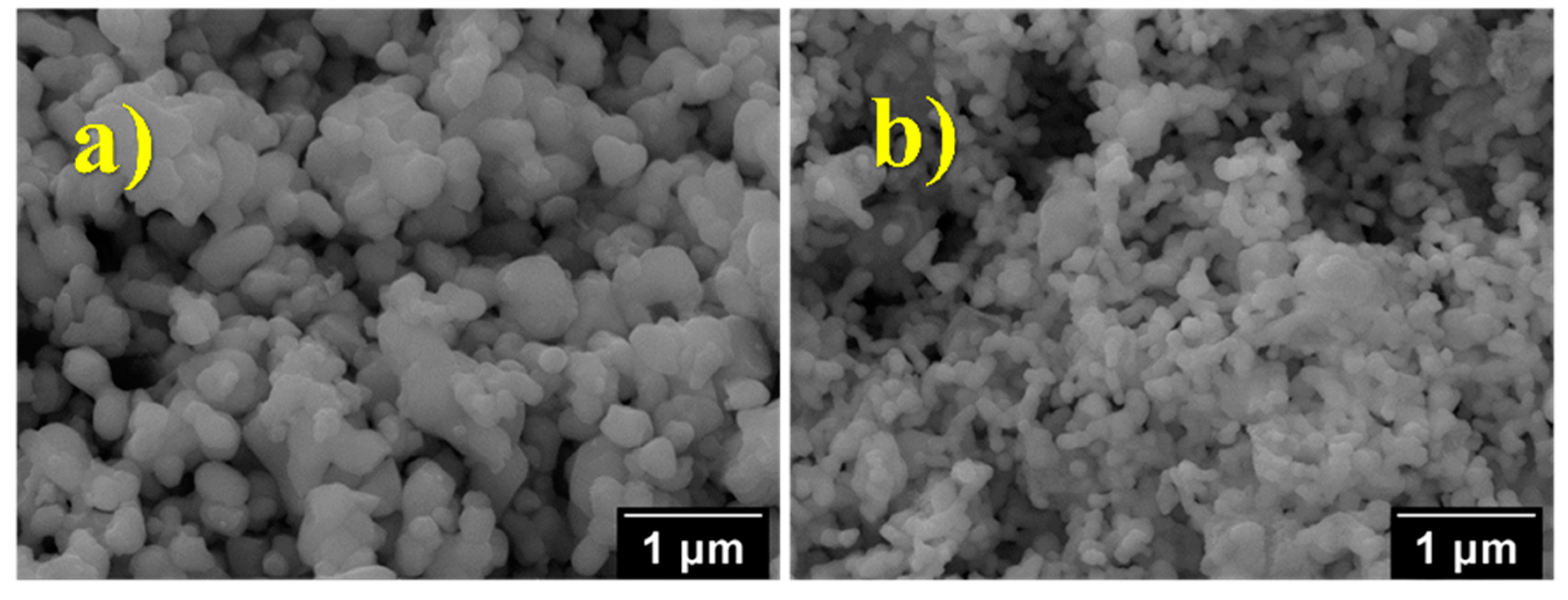
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
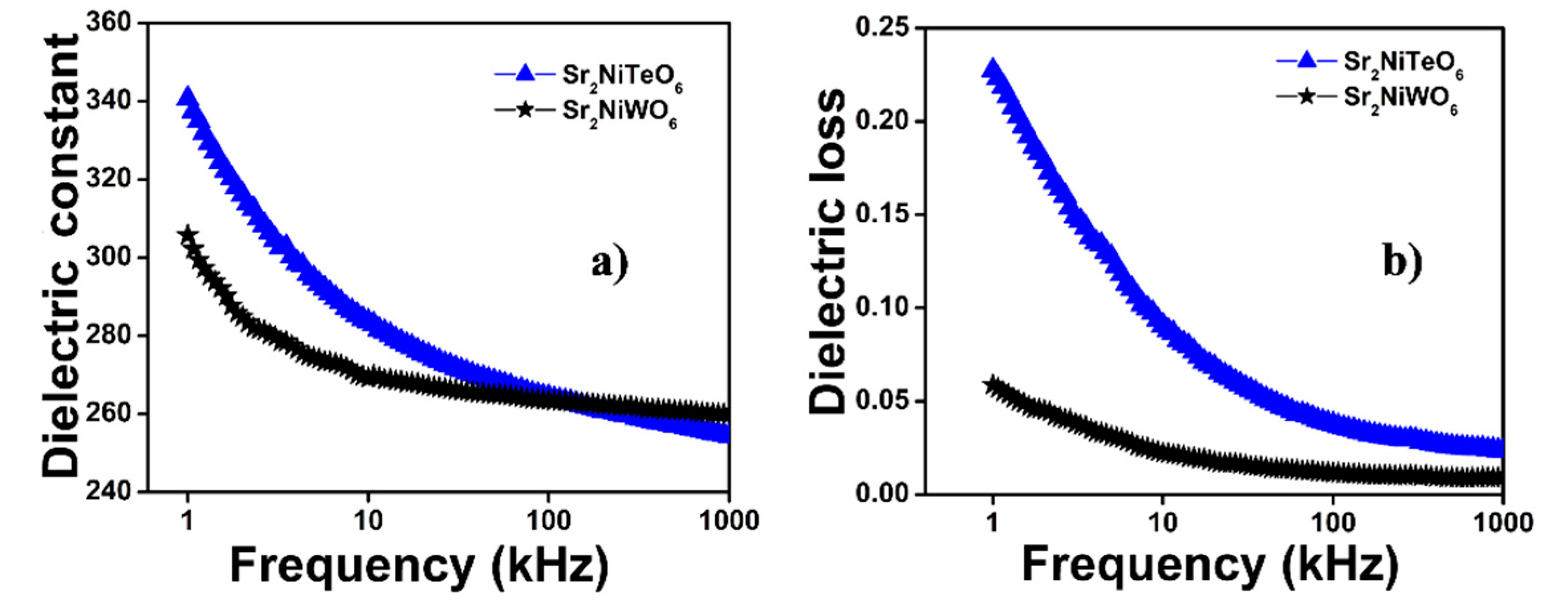
2.4. Dielectric Properties
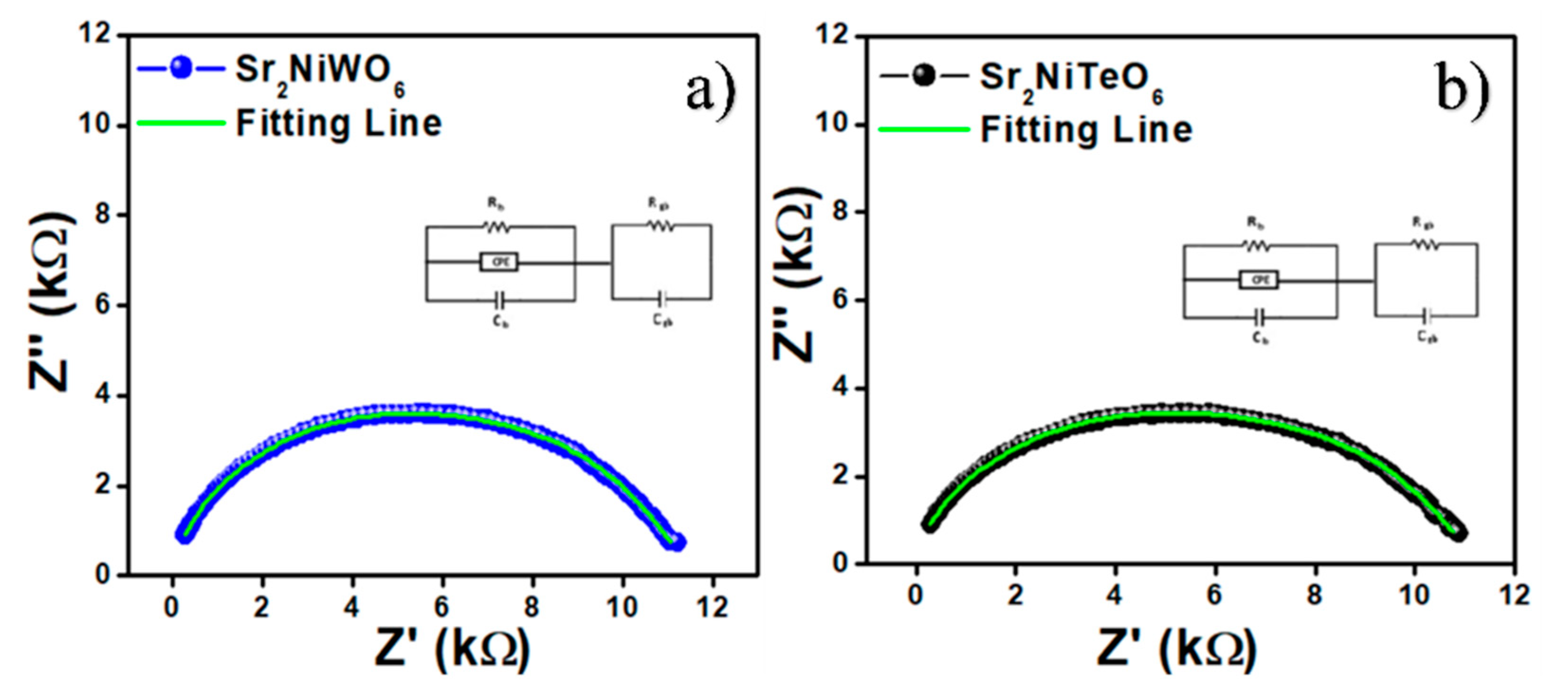
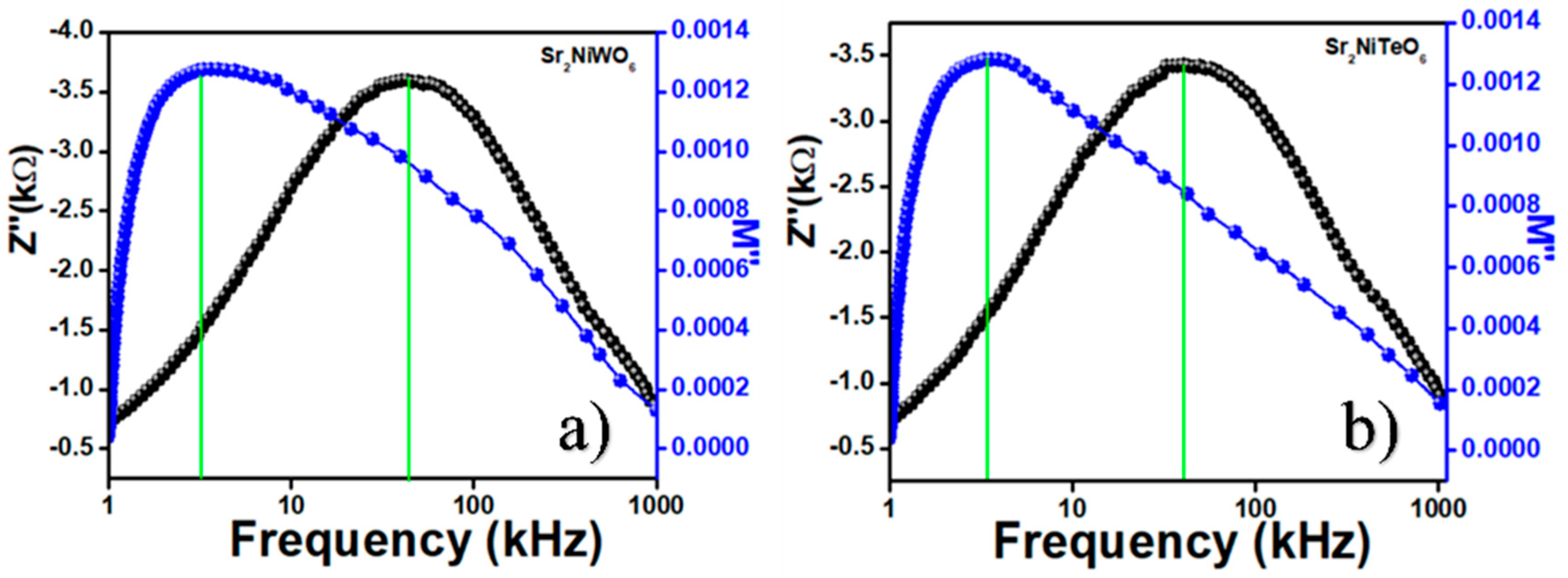
2.5. Impedance Spectroscopy
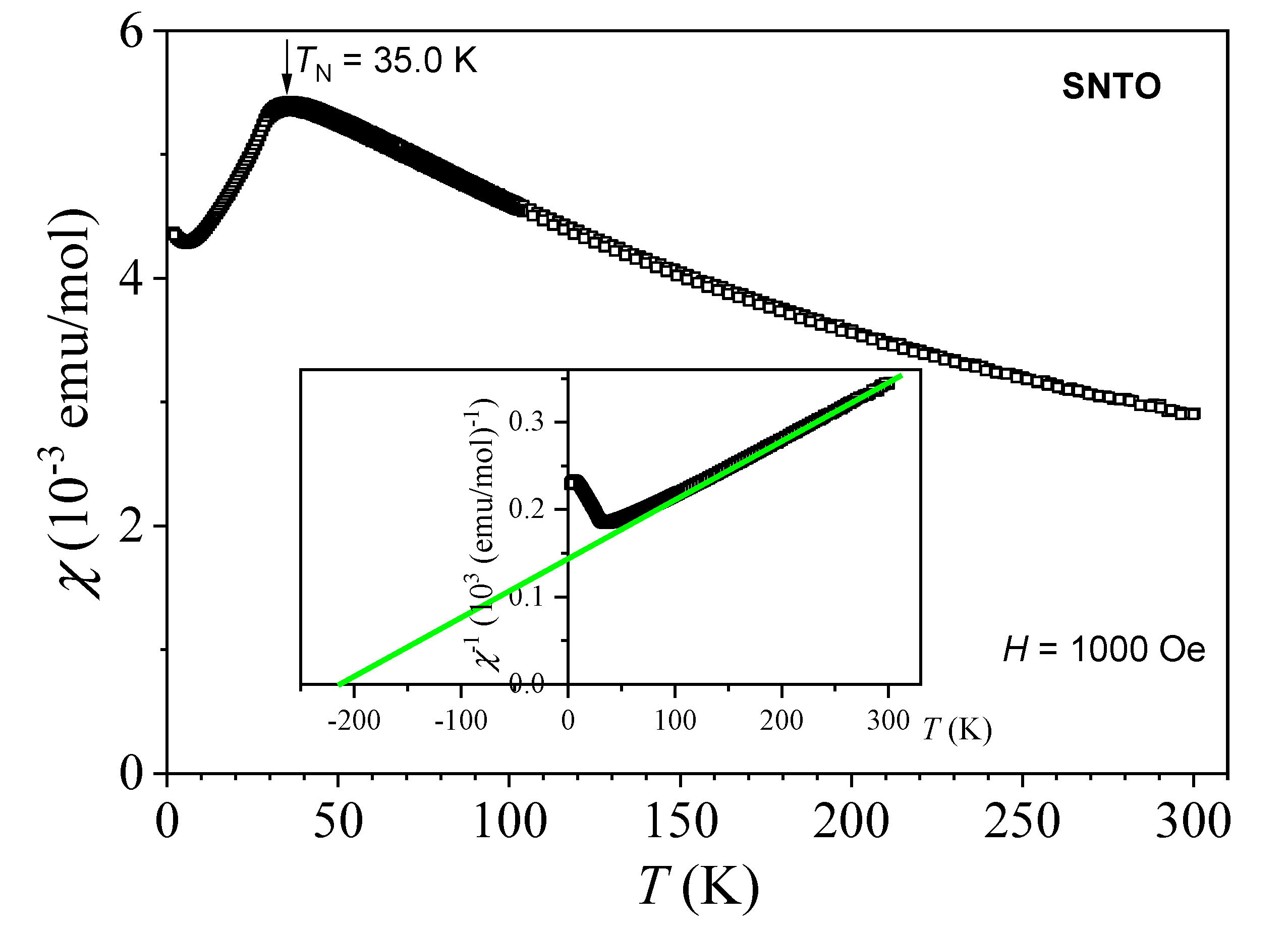
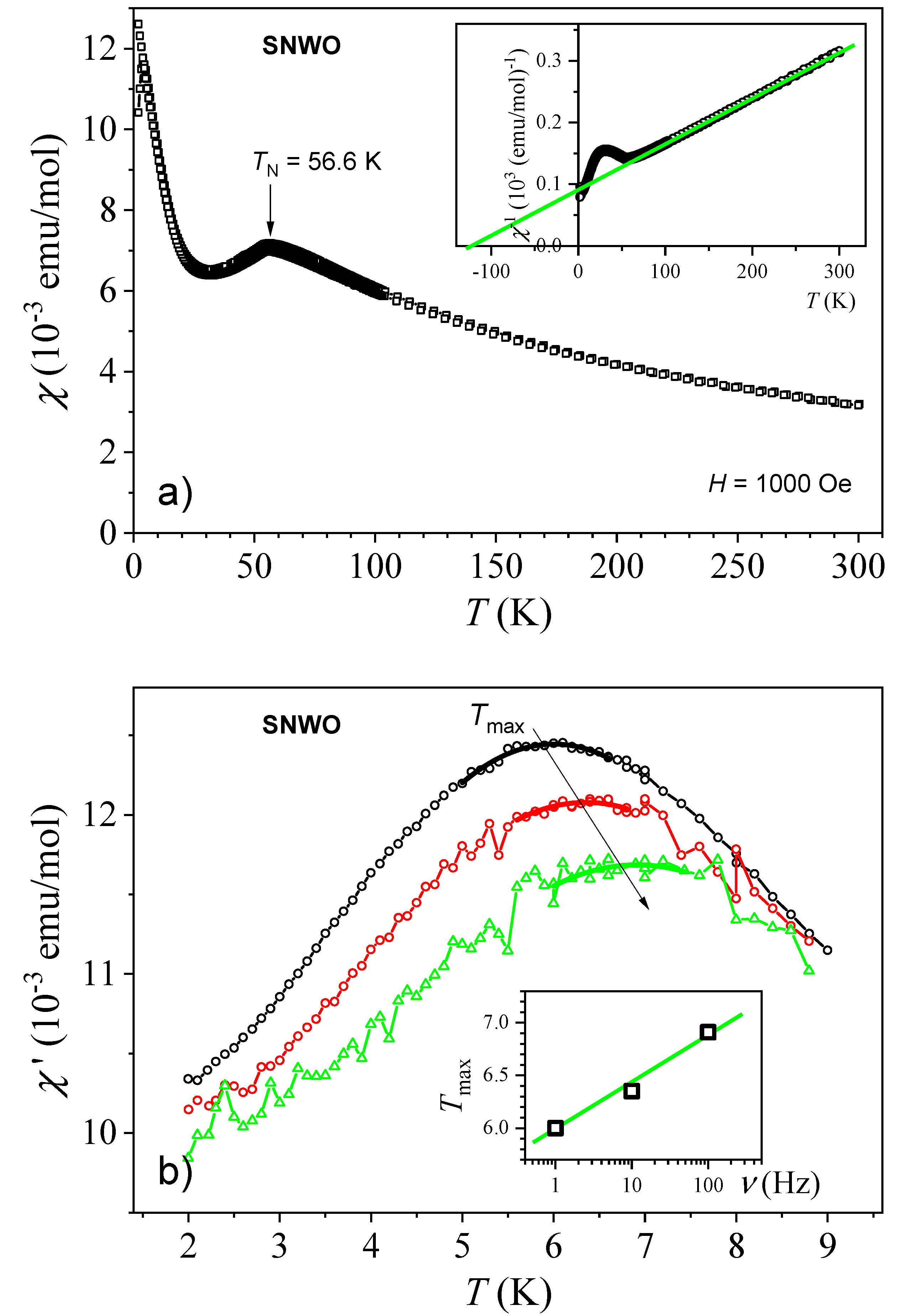
2.6. Magnetic Properties
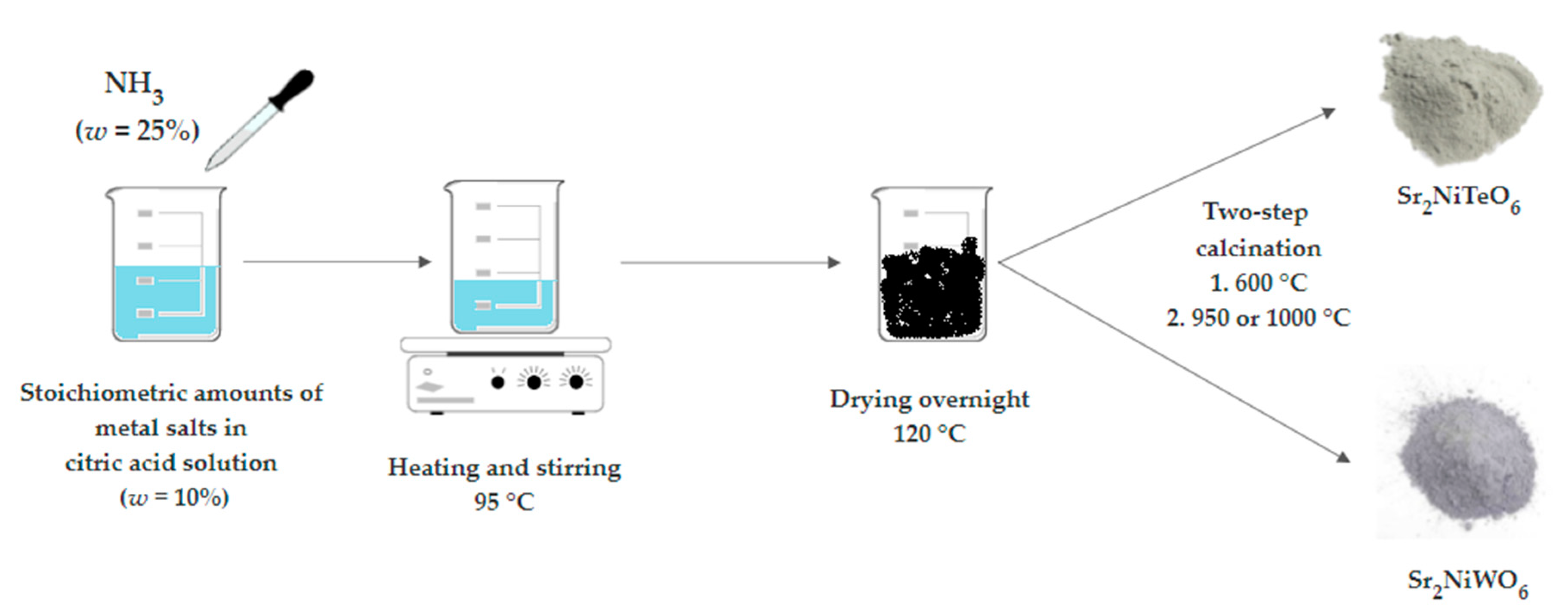
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ketsko, V.A.; Beresnev, E.N.; Kop’Eva, M.A.; Elesina, L.V.; Baranchikov, A.E.; Stognii, A.I.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Kuznetsov, N.T. Specifics of pyrohydrolytic and solid-phase syntheses of solid solutions in the (MgGa2O4)x (MgFe2O4)1 − x system. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 55, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnik, D.; Klygach, D.; Zhivulin, V.; Malkin, A.; Vakhitov, M.; Gudkova, S.; Galimov, D.M.; Zherebtsov, D.A.; Trofimov, E.; Knyazev, N.; et al. Electromagnetic properties of BaFe12O19:Ti at centimeter wavelengths. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 755, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Tashkandi, N.; Baykal, A.; Saraç, M.; Trukhanov, A.; Ercan, I.; Belenli, I.; Ozçelik, B. The effect of Nb substitution on magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 nanohexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Wilkinson, K.J. Aquatic Colloids and Nanoparticles: Current Knowledge and Future Trends. Environ. Chem. 2006, 3, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.; Noble, R.; Reich, M. Natural gold nanoparticles. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.X.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J. Size-dependent Curie temperature in nanoscale MnFe2O4 particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 3602–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, G.U.; Kannan, K.R.; Arunarkavalli, T.; Rao, C.N.R.; Joshi, S.K.; Mashelkar, R.A. Particle-size effects on the value of Tc of MnFe2O4: Evidence for finite-size scaling. Linus Pauling—Selected Sci. Pap. 1995, 49, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zaag, P.J.; Noordermeer, A.; Johnson, M.T.; Bongers, P.F. Comment on “Size-dependent Curie temperature in nanoscale MnFe2O4 particles”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zaag, P.J.; Brabers, V.A.M.; Johnson, M.T.; Noordermeer, A.; Bongers, P.F. Comment on “Particle-size effects on the value of TC of MnFe2O4: Evidence for finite-size scaling.”. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 12009–12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Devlin, E.; Kostikas, A. Size-dependent magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 fine particles synthesized by coprecipitation. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 9288–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Chinnasamy, C.N.; Greneche, J.M.; Chen, Y.; Yoon, S.D.; Hsu, K.; Vittoria, C.; Harris, V.G. Large tunability of Néel temperature by growth-rate-induced cation inversion in Mn-ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2009, 94, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.; Balaji, G.; Ghafari, M. Magnetic Properties of Nanostructured MnFe2O4 Synthesized by Precursor Technique. Phys. Status Solidi A 2002, 189, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Tian, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Rao, G. Antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic transition in Bi-doped LaFeO3 nanocrystalline ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 20472–20476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Han, Z.; Zheng, J.G.; Wang, X.L.; Geng, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.D. Spin canting and spin-flop transition in antiferromagnetic Cr2O3 nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 053913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Q.-U.-A.; Feng-Ping, W.; Rafique, M.Y.; Toufiq, A.M.; Iqbal, M.Z. Canted antiferromagnetic and optical properties of nanostructures of Mn2O3 prepared by hydrothermal synthesis. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 117311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouadi, H.; Ghodbane, O.; Hosni, F.; Touati, F. Mn3O4 Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Dielectric Properties. ISRN Spectrosc. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, E.V.; Malini, K.A.; Saravanan, S.; Kumar, D.S.; Yoshida, Y.; Anantharaman, M.R. Evidence for polaron conduction in nanostructured manganese ferrite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 185005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.; Joy, P.; Anantharaman, M.R. Effect of mechanical milling on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of coprecipitated ultrafine zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 269, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Hajra, S.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Structural, Bulk Permittivity, and Magnetic Properties of Lead-Free Electronic Material: Ba1Bi1Cu1Fe1Ni1Ti3O12. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 32, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.V.; Rao, G.N.; Chen, J.-W.; Babu, D. Abnormal high dielectric constant in SmFeO3 semiconductor ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 1670–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.E.-R.; Afify, A.S.; Parashar, S.K.S. Dielectric, tunability, leakage current, and ferroelectric properties of (K0.45Na0.55)0.95Li0.05NbO3 lead free piezoelectric. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babeer, A.M.; El-Sadek, M.S.A.; Mahmoud, A.E.-R.; Afify, A.S.; Tulliani, J.-M.; El-Sadek, M.S.A. Structural, humidity sensing and dielectric properties of Ca-modified Ba(Ti0.9Sn0.1)O3 lead free ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7622–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefflinger, B. ITRS: The International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors. In CHIPS 2020, New Vistas in Nanoelectronics, 2nd ed.; The Frontiers Collection; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Bao, Y.; Zha, J.-W.; Zhao, J.; Dang, Z.-M.; Hu, G.-H. Improved Dielectric Properties of Nanocomposites Based on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Functionalized Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6273–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, H. Dielectric Nanomaterials for Power Energy Storage: Surface Modification and Characterization. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shen, Z.; Qian, J.; Dan, Z.; Guo, M.; He, Y.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C.-W.; Chen, L.; Shen, Y. Synergy of Micro-/Mesoscopic Interfaces in Multilayered Polymer Nanocomposites Induces Ultrahigh Energy Density for Capacitive Energy Storage. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Cui, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Xiong, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q. High-Energy-Density Dielectric Polymer Nanocomposites with Trilayered Architecture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, B.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, P. High-κ Polymer Nanocomposites with 1D Filler for Dielectric and Energy Storage Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 100, 187–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.-M.; Zha, J.-W.; Zheng, M.-S. 1D/2D Carbon Nanomaterial-Polymer Dielectric Composites with High Permittivity for Power Energy Storage Applications. Small 2016, 12, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraati, A.S.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U. Silver Nanowire/MnO2 Nanowire Hybrid Polymer Nanocomposites: Materials with High Dielectric Permittivity and Low Dielectric Loss. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14328–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deotale, A.J.; Nandedkar, R. Correlation between Particle Size, Strain and Band Gap of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Yin, W.-J.; Yan, Y. Bandgap Engineering of Stable Lead-Free Oxide Double Perovskites for Photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.R. Crystal Structures and Crystal Chemistry. Solid State Chemistry and its Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Vasala, S.; Karppinen, M. A2B′B″O6 perovskites: A review. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2015, 43, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qin, C.; Wan, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, Y.; Qin, L.; Seo, H.J. Sol–gel preparation, band structure, and photochemical activities of double perovskite A2NiWO6 (A = Ca, Sr) nanorods. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresia, E.J.; Katz, L.; Ward, R. Cation Substitution in Perovskite-like Phases1,2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 4783–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brixner, L.H. Preparation and Structure Determination of Some New Cubic and Tetragonally-Distorted Perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 64, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Kawakubo, T.T. Phase Transition in Sr(NiW)0.5O3-Ba(NiW)0.5O3 System. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1962, 17, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Nakagawa, T. Magnetic Properties and Optical and Paramagnetic Spectra of Divalent Nickel in Sr2(NiW)O6. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 21, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhl, P. Die Kristallstruktur von Perowskiten A2IINiIIMVIO6II. Das Sr2NiWO6. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1973, 401, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todate, Y. Exchange interactions in antiferromagnetic complex perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1999, 60, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, D.; Inaguma, Y.; Itoh, M. Structure and magnetic properties of Sr2NiAO6 (A = W, Te). Mater. Res. Bull. 2000, 35, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gateshki, M.; Igartua, J.M.; Hernandez-Bocanegra, E. X-ray powder diffraction results for the phase transitions in Sr2MWO6 (M = Ni, Zn, Co, Cu) double perovskite oxides. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 6199–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, C.; Ji, X.; Jiang, B. Structure and properties of the ordered double perovskites Sr2MWO6 (M=Co, Ni) by sol-gel route. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2747–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Fuh, H.R.; Wang, Y.K. Expansion research on half-metallic materials in double perovskites of Sr2BB′O6 (B = Co, Cu, and Ni; B′ = Mo, W, Tc, and Re; and BB′ = FeTc). Comp. Mater. Sci. 2014, 92, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Holcombe, A.; Gellesch, M.; Sturza, M.I.; Rodan, S.; Morrow, R.; Maljuk, A.; Woodward, P.; Morris, P.; Wolter, A.; et al. Flux growth and characterization of Sr2NiWO6single crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2015, 421, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, N.; Hashemifar, T.; Alaei, M.; Shahbazi, F.; Hashemifar, S.J.; Akbarzadeh, H. Ab initio investigation of magnetic ordering in the double perovskite Sr2NiWO6. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze-Rhonhof, E.; Reinen, D. Die Kristallstruktur von Perowskiten A2IINiIIMVIO6I. Das Sr2[NiTe]O6. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1970, 378, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, A. Schwingungsspektroskopische Untersuchungen an Hexaoxotelluraten vom Perowskittyp. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1972, 392, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, G.R.; Shannon, R.D.; Waring, R.K. Origin of the yellow color of complex nickel oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 1981, 39, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-San-Martin, L.; Chapman, J.P.; Cuello, G.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J.M.; Arriortua, M.I.; Rojo, T. Crystal Structure of the Ordered Double Perovskite, Sr2NiTeO6. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 2005, 631, 2127–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orayech, B.; Ortega-San-Martín, L.; Urcelay-Olabarria, I.; Lezama, L.; Rojo, T.; Arriortua, M.I.; Igartua, J.M. The effect of partial substitution of Ni by Mg on the structural, magnetic and spectroscopic properties of the double perovskite Sr2NiTeO6. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 14378–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic-structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroumova, E.; Aroyo, M.I.; Mato, J.M.; Kirov, A.; Capillas, C.; Ivantchev, S.; Wondratschek, H. Bilbao Crystallographic Server: Useful Databases and Tools for Phase-Transition Studies. Phase Transit. 2003, 76, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.N.; Guedes, I.; Ayala, A.P.; López, C.A.; Augsburger, M.S.; del Viola, M.C.; Pedregosa, J.C. Optical-active phonons in A3Fe2B″O9 (A=Ca, Sr; B″=Te, W) double perovskites. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 043512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijelic, J.; Stanković, A.; Medvidović-Kosanović, M.; Markovic, B.; Cop, P.; Sun, Y.; Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Vukmirovic, J.; Markovic, D.; et al. Rational Sol–Gel-Based Synthesis Design and Magnetic, Dielectric, and Optical Properties Study of Nanocrystalline Sr3Co2WO9 Triple Perovskite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 12794–12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.P.; Guedes, I.; Silva, E.N.; Augsburger, M.S.; Viola, M.D.C.; Pedregosa, J.C. Raman investigation of A2CoBO6 (A=Sr and Ca, B=Te and W) double perovskites. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 123511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoun, B.; Igartua, J.M.; Lazor, P. High temperature Raman spectroscopy studies of the phase transitions in Sr2NiWO6 and Sr2MgWO6 double perovskite oxides. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 971, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.R. Raman Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, A.K.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Ravindran, T.R.; Sivasubramanian, V. Raman spectroscopy of optical phonon confinement in nanostructured materials. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.; Fauchet, P. The effects of microcrystal size and shape on the one phonon Raman spectra of crystalline semiconductors. Solid State Commun. 1986, 58, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Purohit, V.; Panigrahi, R.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Investigation of structural, electrical and magnetic characterization of erbium substituted lead free electronic materials. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 096319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Akishige, Y. Electrical properties of multiferroic BiFeO3 ceramics synthesized by spark plasma sintering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 445403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Purohit, V.; Choudhary, R. Dielectric, conductivity and ferroelectric properties of lead-free electronic ceramic: 0.6Bi(Fe0.98Ga0.02)O3-0.4BaTiO3. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setter, N.; Waser, R. Electroceramic materials. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabbs, F.E.; Machin, D.J. Magnetism and Transition Metal Complexes; Dover Publications, Inc. Mineola: New York, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Jagodic, M.; Jagličić, Z.; Jelen, A.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Dolinšek, J. Surface-spin magnetism of antiferromagnetic NiO in nanoparticle and bulk morphology. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 215302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mydosh, J.A. Spin Glasses: An Experimental Introduction; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bijelić, J.; Stankovic, A.; Matasović, B.; Marković, B.; Bijelić, M.; Skoko, Ž.; Popović, J.; Stefanic, G.; Jagličić, Z.; Zellmer, S.; et al. Structural characterization and magnetic property determination of nanocrystalline Ba3Fe2WO9 and Sr3Fe2WO9 perovskites prepared by a modified aqueous sol–gel route. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, G.A.; Berry, J.F. Diamagnetic Corrections and Pascal’s Constants. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon Database of Ionic Radii. Available online: http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/ptable.php (accessed on 14 April 2020).
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds Sr2NiTeO6 and Sr2NiWO6 are available on demand from the authors. |
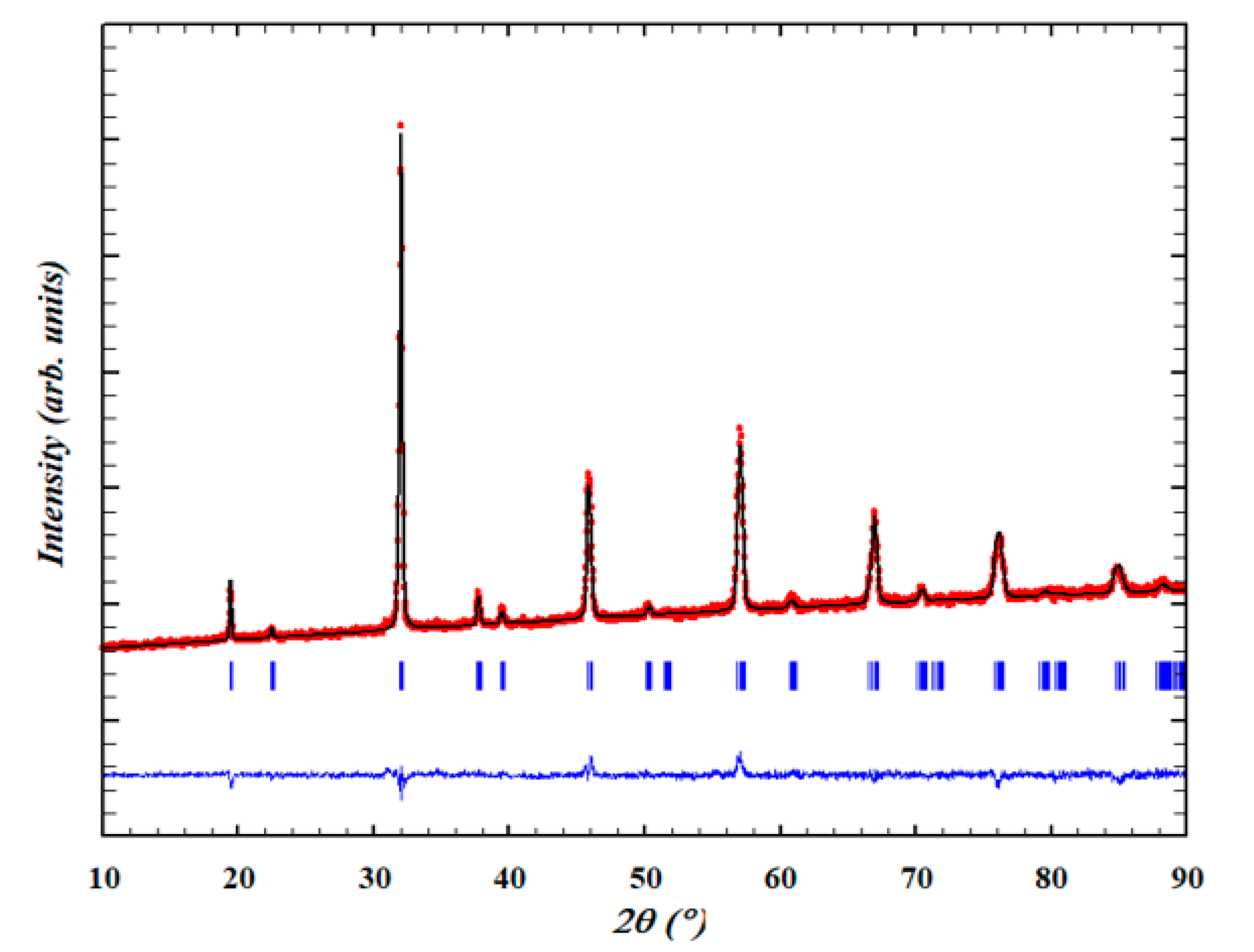
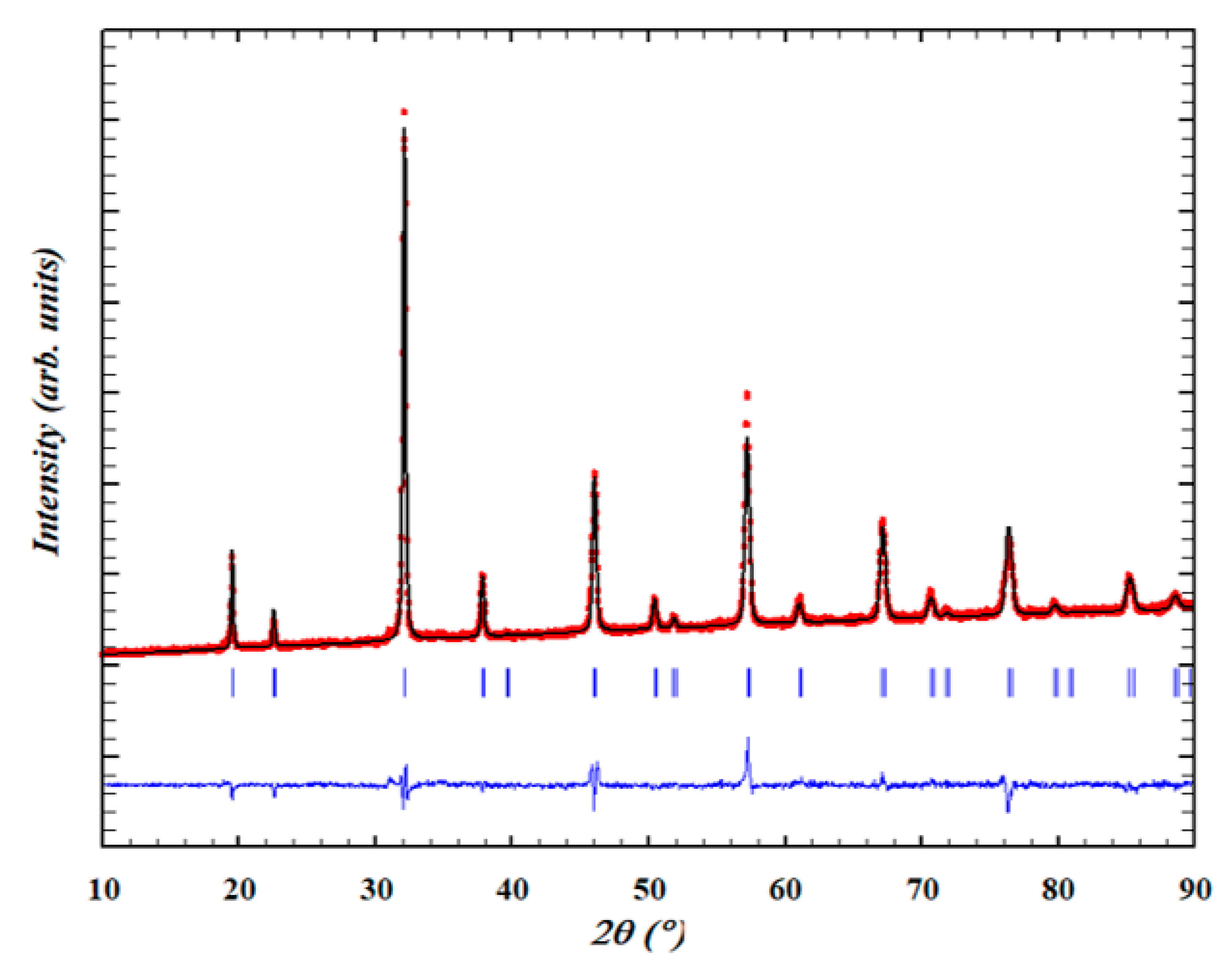
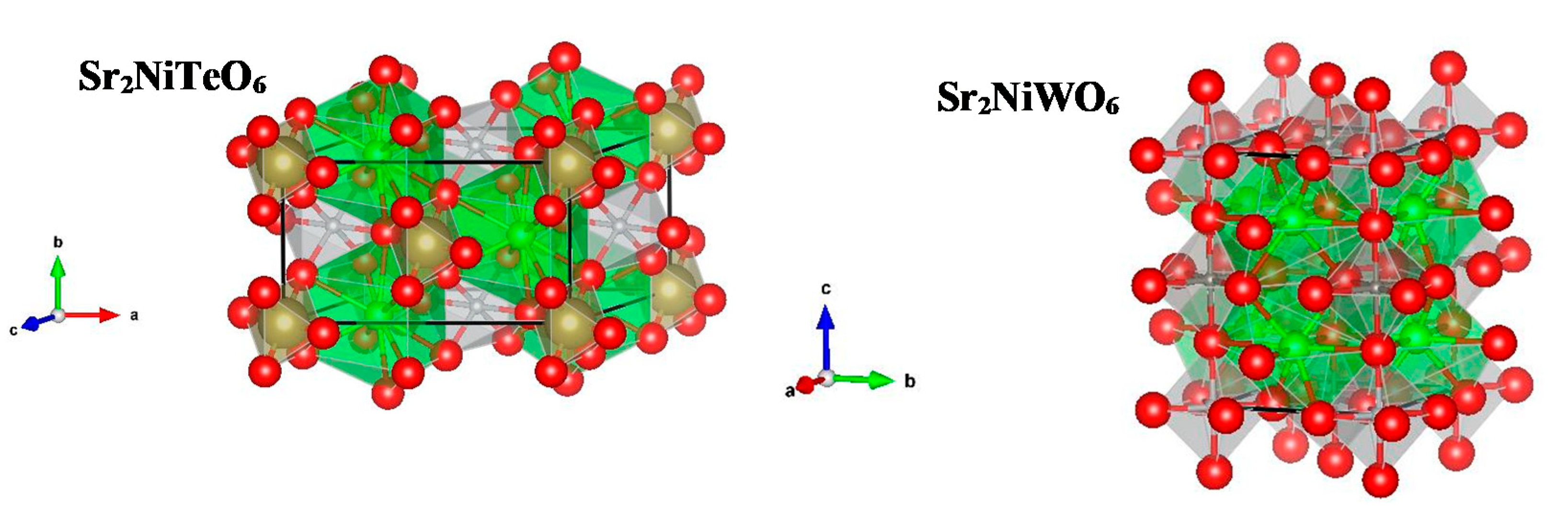
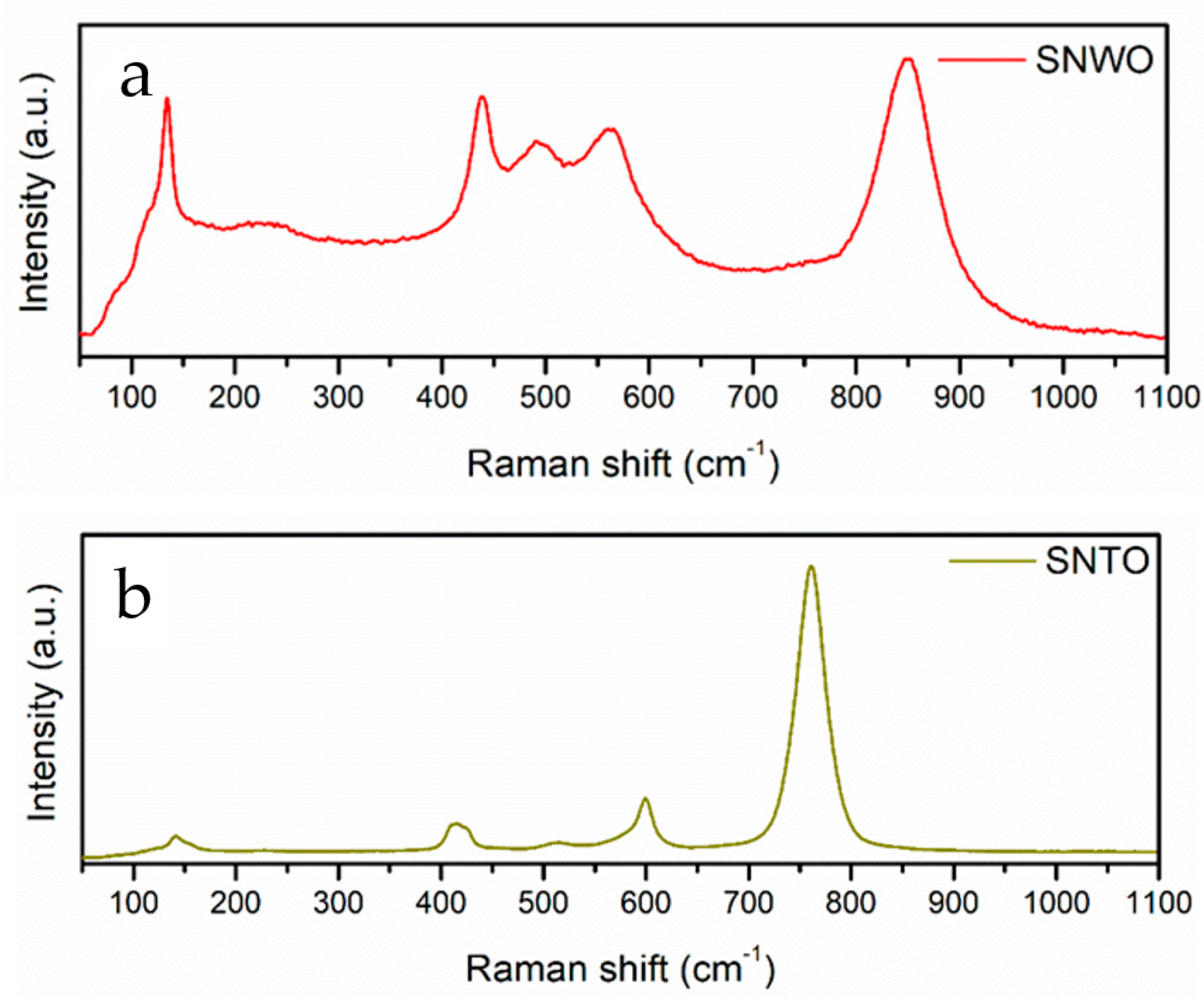
| Chemical Formula | Sr2NiTeO6 | Sr2NiWO6 |
|---|---|---|
| Space group | C12/m1 (12) | I4/m (87) |
| Molecular weight | 457.53 | 513.77 |
| Z | 2 | |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Tetragonal |
| Lattice parameters (Å) | a = 9.663(1) b = 5.6132(2) c = 5.5833(2) β = 125.32(1)° | a = 5.5644(2) c = 7.9025(4) |
| Cell volume (Å3) | 247.09(4) | 244.68(2) |
| Calculated density (g/cm3) | 6.15 | 6.97 |
| Data collection range | 10–90° | |
| No. of parameters refined | 24 | 18 |
| No. of bond lengths restrained | 11 | 0 |
| No. of bond angles restrained | 0 | 0 |
| Average apparent crystallite size (nm) | 77 | 49 |
| Average apparent microstrains (×10−4) | 17.462 | 11.828 |
| Phase composition (wt %) | 100 | |
| RB (%) | 5.84 | 6.1 |
| Conventional Rp, Rwp, Re (%) | 27.0, 16.5, 11.8 | 19.9, 14.4, 9.31 |
| χ2 | 1.961 | 2.398 |
| Atom | Wyckoff Position | x a | y a | z a | B (Å2) b | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | 4i | 0.751(1) | 0 | 0.235(2) | 0.9(1) | |
| Ni | 2d | 0 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.1(1) | |
| Te | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.8(1) | |
| O1 | 8j | 0.0264(9) | 0.2443(9) | 0.266(1) | 1.7(2) | 1 |
| O2 | 4i | 0.2436(7) | 0 | 0.301(2) | 1.7(2) |
| Atom | Wyckoff Position | x a | y a | z a | B (Å2) b | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | 4d | 0 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 1.30(7) | |
| Ni | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.9(1) | |
| W | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/2 | 1.19(5) | |
| O1 | 8h | 0.269(3) | 0.200(3) | 0 | 2.35(4) | |
| O2 | 4e | 0 | 0 | 0.255(2) | 2.35(4) |
| Compound | Bond Type | Bond Length (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| Sr2NiTeO6 | Sr-O1 x2 | 2.707(7) |
| Sr-O1 x2 | 2.689(1) | |
| Sr-O1 x2 | 2.909(1) | |
| Sr-O1 x2 | 2.900(8) | |
| Sr-O2 x1 | 2.558(2) | |
| Sr-O2 x1 | 3.026(1) | |
| Sr-O2 x2 | 2.837(3) | |
| Ni-O1 x4 | 2.052(7) | |
| Ni-O2 x2 | 2.047(6) | |
| Te-O1 x4 | 1.929(6) | |
| Te-O2 x2 | 1.947(5) | |
| Sr2NiWO6 | Sr-O1 x4 | 2.606(1) |
| Sr-O1 x4 | 2.988(2) | |
| Sr-O2 x4 | 2.7825(1) | |
| Ni-O1 x4 | 1.873(2) | |
| Ni-O2 x2 | 2.0151(1) | |
| W-O1 x4 | 2.099(2) | |
| W-O2 x2 | 1.9361(1) |
| Composition | Rg (Ω) a | Cg (F) b | Rgb (Ω) c | Cgb (F) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr2NiWO6 | 1.054 × 104 | 1.270 × 10−10 | 1102 | 1.083 × 10−8 |
| Sr2NiTeO6 | 1.016 × 104 | 1.268 × 10−10 | 1179 | 1.057 × 10−8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bijelić, J.; Tatar, D.; Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Kim, S.J.; Jagličić, Z.; Djerdj, I. Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-κ Dielectric Sr2NiMO6 (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Type. Molecules 2020, 25, 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173996
Bijelić J, Tatar D, Hajra S, Sahu M, Kim SJ, Jagličić Z, Djerdj I. Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-κ Dielectric Sr2NiMO6 (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Type. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173996
Chicago/Turabian StyleBijelić, Jelena, Dalibor Tatar, Sugato Hajra, Manisha Sahu, Sang Jae Kim, Zvonko Jagličić, and Igor Djerdj. 2020. "Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-κ Dielectric Sr2NiMO6 (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Type" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173996
APA StyleBijelić, J., Tatar, D., Hajra, S., Sahu, M., Kim, S. J., Jagličić, Z., & Djerdj, I. (2020). Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-κ Dielectric Sr2NiMO6 (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Type. Molecules, 25(17), 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173996








