Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Analogs of Didehydroepiandrosterone as Potential New Anticancer Agents
Abstract
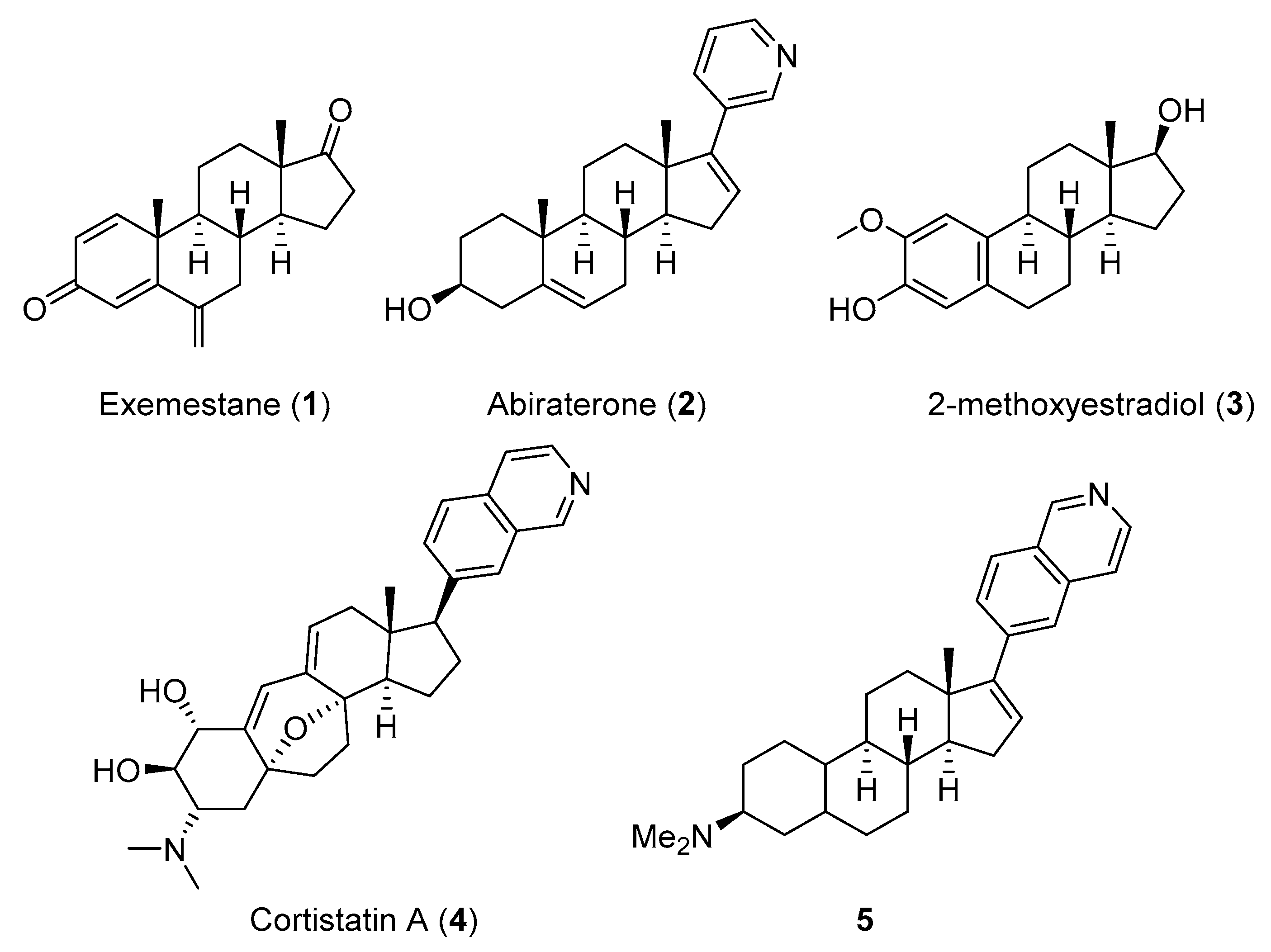
1. Introduction
2. Results
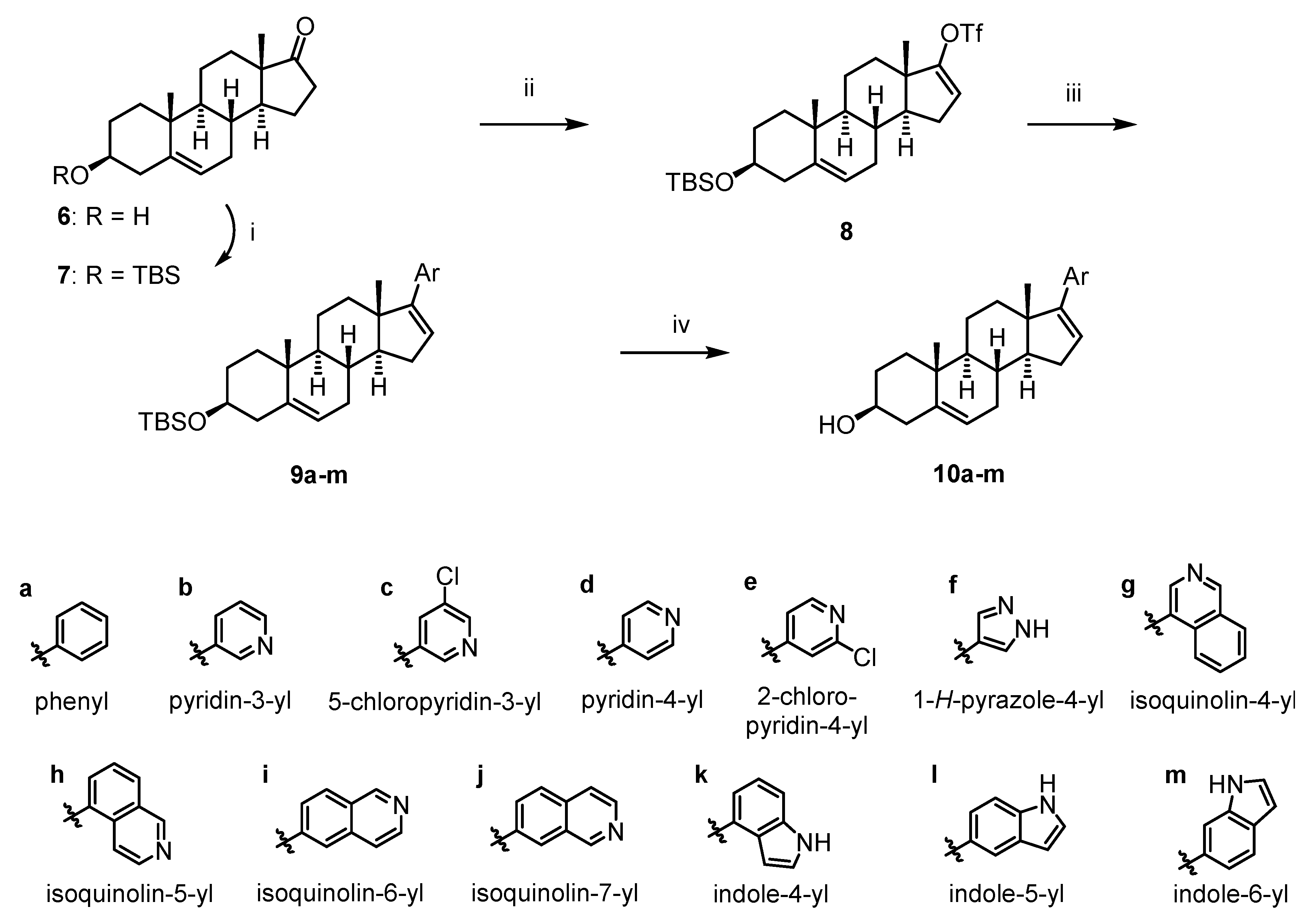
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Methods
3.1.2. A General Procedure for the Deprotection
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Cell Studies
3.2.2. Protein Kinase Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lossignol, D. A little help from steroids in oncology. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2016, 4, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombes, R.C.; Kilburn, L.S.; Snowdon, C.F.; Paridaens, R.; Coleman, R.E.; Jones, S.E.; Jassem, J.; Van de Velde, C.J.H.; Delozier, T.; Alvarez, I.; et al. Survival and safety of exemestane versus tamoxifen after 2–3 years’ tamoxifen treatment (Intergroup Exemestane Study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 369, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.A.; Barrie, S.E.; Jarman, M.; Rowlands, M.G. Novel Steroidal Inhibitors of Human Cytochrome P45017.alpha.-Hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase): Potential Agents for the Treatment of Prostatic Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B., Jr.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribluda, V.S.; Gubish, E.R.; Gubish, E.R.; LaVallee, T.M.; Treston, A.; Swartz, G.M.; Green, S.J. 2-Methoxyestradiol: An Endogenous Antiangiogenic and Antiproliferative Drug Candidate. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000, 19, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solum, E.J.; Cheng, J.-J.; Sylte, I.; Vik, A.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of new analogs of the anti-cancer agent 2-methoxyestradiol: Potent inhibitors of angiogenesis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32497–32504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Czakó, B.; Kürti, L.; Mammoto, A.; Ingber, D.E.; Corey, E.J. Discovery of Potent and Practical Antiangiogenic Agents Inspired by Cortistatin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9014–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatcher, J.M.; Wang, E.S.; Johannessen, L.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Sim, T.; Gray, N.S. Development of Highly Potent and Selective Steroidal Inhibitors and Degraders of CDK8. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Sanagawa, M.; Setiawan, A.; Kotoku, N.; Kobayashi, M. Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, Anti-angiogenic Steroidal Alkaloids, from the Marine Sponge Corticium simplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3148–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Sun, Y.-P.; Peng, X.-S.; Polet, D.; Chen, D.Y.K. Total Synthesis of (+)-Cortistatin A. Angew. Chem. Int. 2008, 120, 7420–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, Z.C.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Odell, A.T.; Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Lee, T.; Pelish, H.E.; Shair, M.D.; Dowell, R.D.; Old, W.M.; Taatjes, D.J. Identification of Mediator Kinase Substrates in Human Cells using Cortistatin A and Quantitative Phosphoproteomics. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelish, H.E.; Liau, B.B.; Nitulescu, I.I.; Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Poss, Z.C.; Da Silva, D.H.; Caruso, B.T.; Arefolov, A.; Fadeyi, O.; Christie, A.L.; et al. Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML. Nature 2015, 526, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flyer, A.N.; Si, C.; Myers, A.G. Synthesis of cortistatins A, J, K and L. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Aoki, S.; Tanabe, D.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Cortistatins E, F, G, and H, four novel steroidal alkaloids from marine sponge Corticium simplex. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 4074–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solum, E.J.; Cheng, J.-J.; Sørvik, I.B.; Paulsen, R.E.; Vik, A.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis and biological evaluations of new analogs of 2-methoxyestradiol: Inhibitors of tubulin and angiogenesis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al-Kazaale, N.; Tran, P.T.; Haidari, F.; Solum, E.J.; Liekens, S.; Vervaeke, P.; Sylte, I.; Cheng, J.-J.; Vik, A.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis, molecular modeling and biological evaluation of potent analogs of 2-methoxyestradiol. Steroids 2018, 136, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solum, E.; Hansen, T.V.; Aesoy, R.; Herfindal, L. New CDK8 inhibitors as potential anti-leukemic agents—Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canela, M.-D.; Pérez-Pérez, M.-J.; Noppen, S.; Sáez-Calvo, G.; Díaz, J.F.; Camarasa, M.-J.; Liekens, S.; Priego, E.-M. Novel Colchicine-Site Binders with a Cyclohexanedione Scaffold Identified through a Ligand-Based Virtual Screening Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3924–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs Iii, W.H.; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule–kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansbeke, K.V.; Solum, E.J.; Liekens, S.; Vik, A.; Hansen, T.V. Regioselective monoalkylation of 17β-estradiol for the synthesis of cytotoxic estrogens. Steroids 2017, 124, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 10a–10m are available from the authors. |
| Compound | CEM Cell Assay IC50 (µM) a | HeLa Cell Assay IC50 (µM) a | HMEC-1 Cell Assay IC50 (µM) a | CDK8 Per Cent of Control (POC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10a | >100 | >100 | >100 | n.d. b |
| 10b | 16 ± 3 | 90 ± 14 | 17 ± 4 | n.d. |
| 10c | 18 ± 4 | 97 ± 4 | 60 ± 4 | 95% |
| 10d | >100 | 2.1 ± 1.7 | 88 ± 8 | n.d. |
| 10e | 10 ± 1 | 18 ± 11 | 8.2 ± 1.9 | 100% |
| 10f | 24 ± 16 | 7.0 ± 2.5 | 11 ± 1 | n.d. |
| 10g | 14 ± 1 | 24 ± 6 | 15 ± 0 | n.d. |
| 10h | 16 ± 2 | 24 ± 8 | 13 ± 0 | 32% |
| 10i | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 9.2 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 100% |
| 10j | 5.8 ± 3.1 | 8.7 ± 0.0 | 5.4 ± 3.6 | 100% |
| 10k | 26 ± 17 | 91 ± 12 | 8.4 ± 4.3 | 100% |
| 10l | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 0.59 ± 0.07 | 100% |
| 10m | 50 ± 21 | 44 ± 2 | 14 ± 2 | n.d. |
| 2-ME (3) | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 0.41 ± 0.06 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | n.d. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
J. Solum, E.; Liekens, S.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Analogs of Didehydroepiandrosterone as Potential New Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133052
J. Solum E, Liekens S, Hansen TV. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Analogs of Didehydroepiandrosterone as Potential New Anticancer Agents. Molecules. 2020; 25(13):3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133052
Chicago/Turabian StyleJ. Solum, Eirik, Sandra Liekens, and Trond Vidar Hansen. 2020. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Analogs of Didehydroepiandrosterone as Potential New Anticancer Agents" Molecules 25, no. 13: 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133052
APA StyleJ. Solum, E., Liekens, S., & Hansen, T. V. (2020). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Analogs of Didehydroepiandrosterone as Potential New Anticancer Agents. Molecules, 25(13), 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133052








