Pretreatment of Anthocyanin from the Fruit of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Acts as a Potent Inhibitor of TNF-α Effect by Inhibiting NF-κB-Regulated Genes in Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
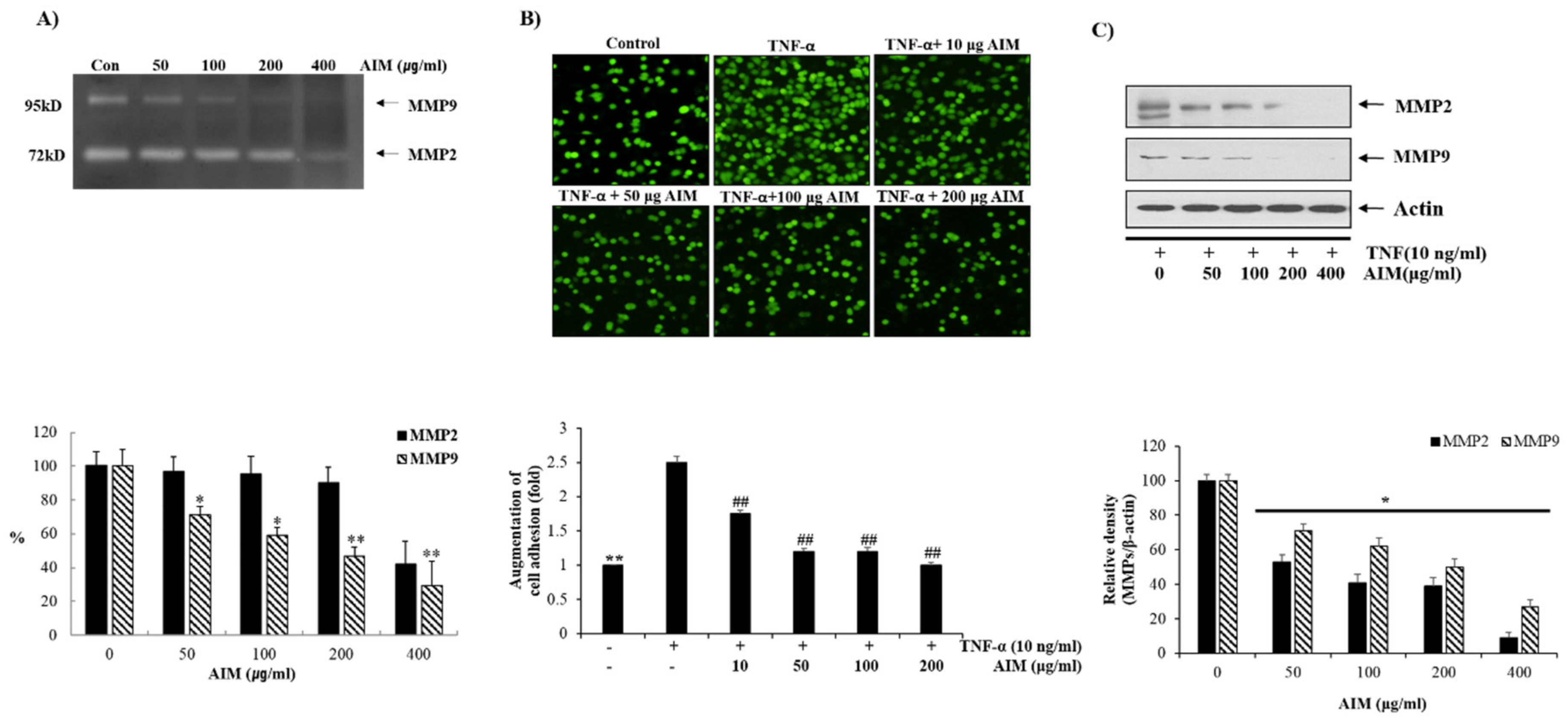
2.1. Anthocyanins Isolated from Meoru (AIM) Inhibited the Cell Proliferation, Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-Augmented Cell Adhesion of MCF–7 Cells
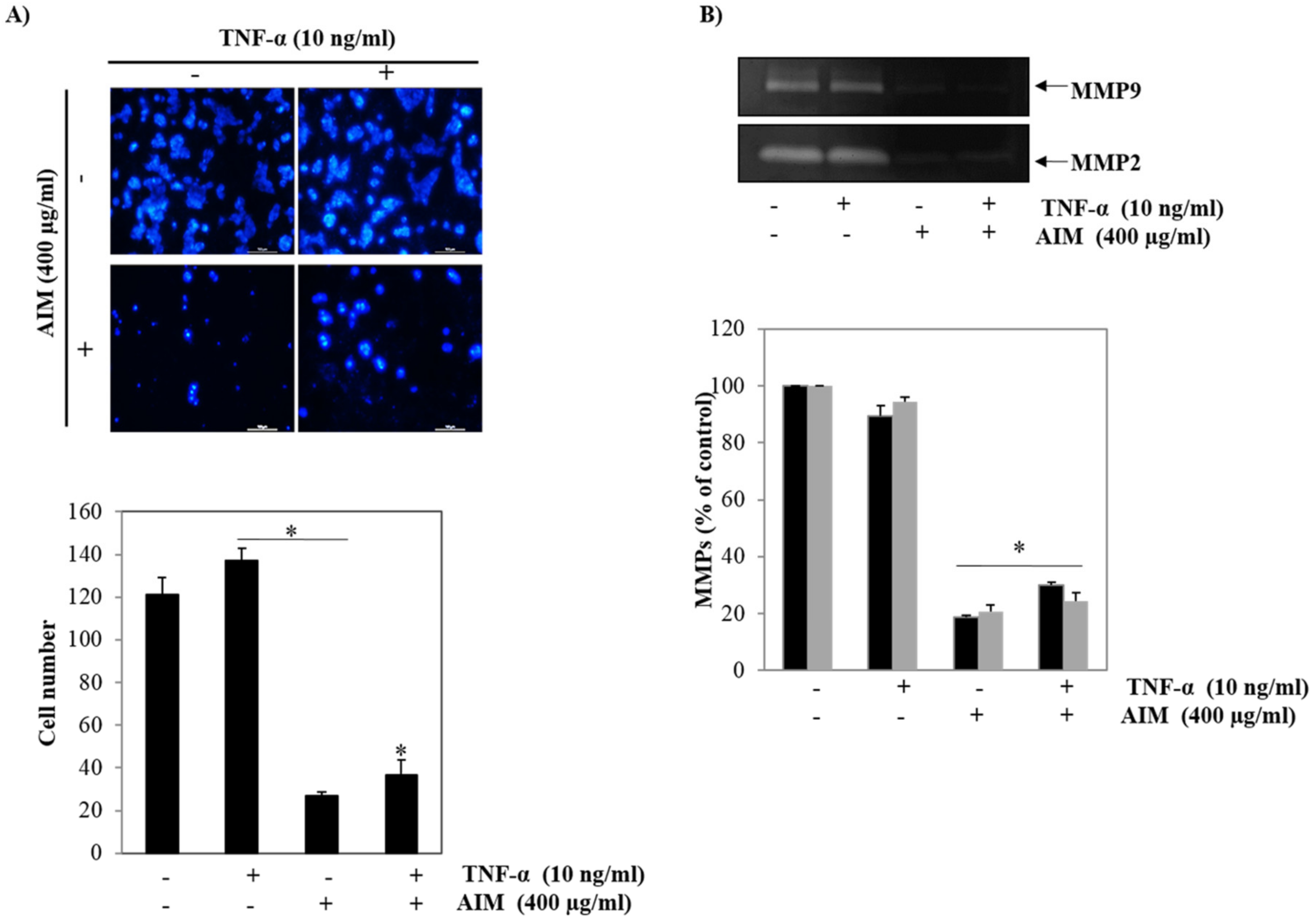
2.2. Pre-Treatment of AIM Inhibits TNF-α Induced Metastasis Activity
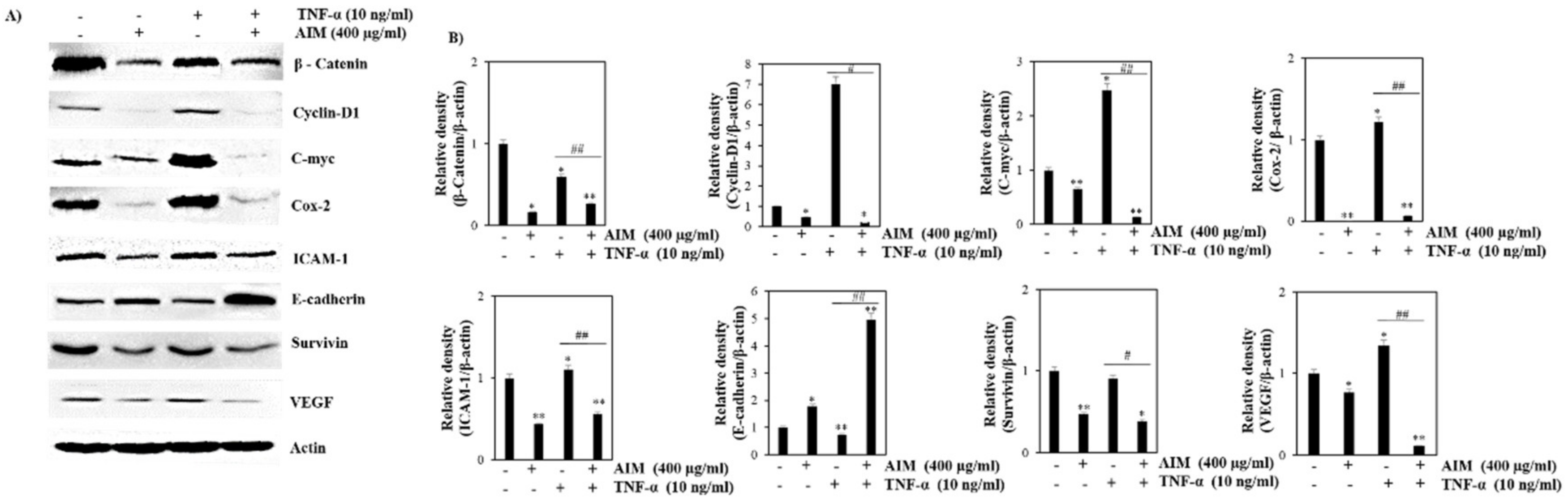
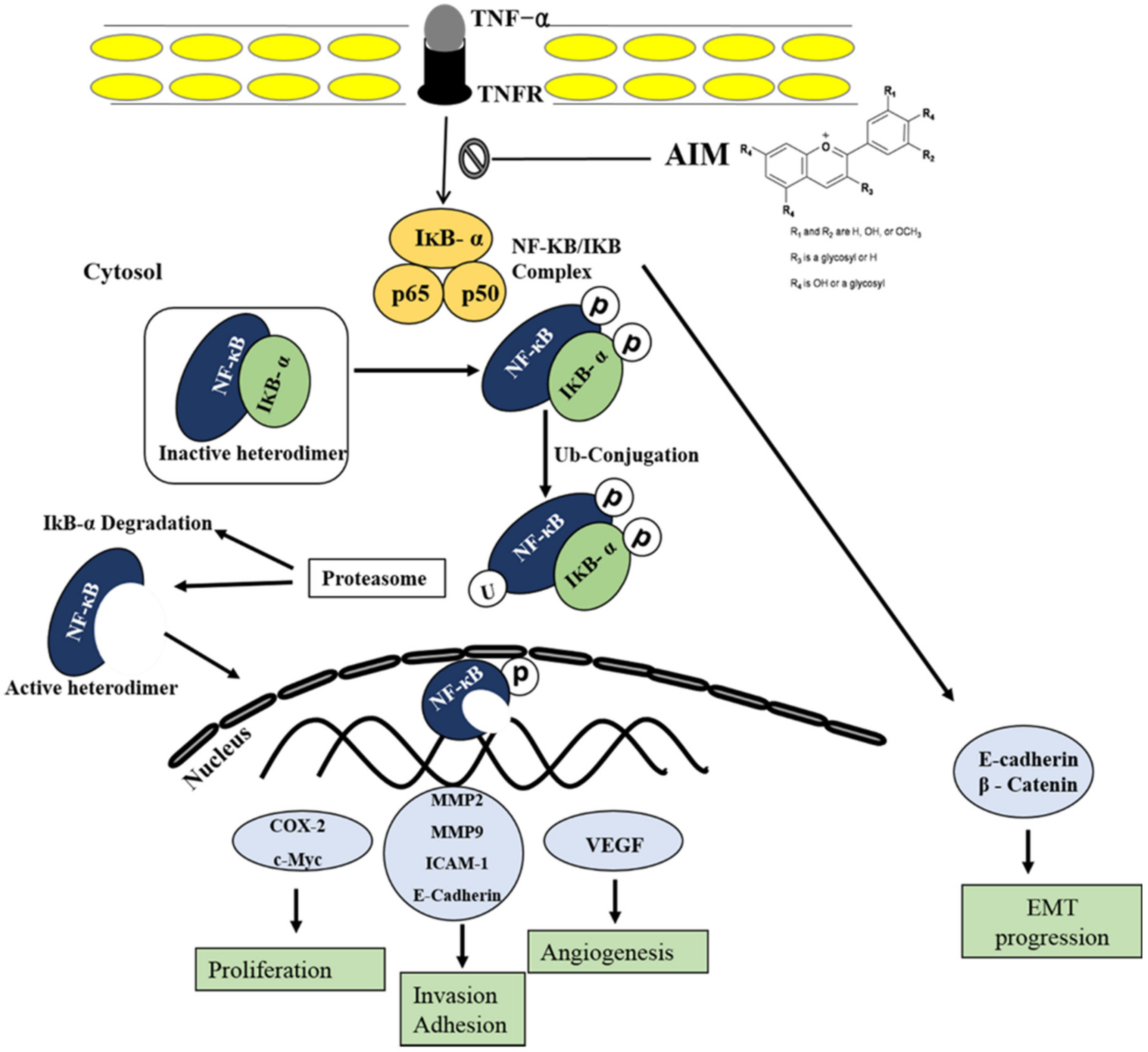
2.3. TNF-α Induced Effect Was Reversed with the Treatment of AIM Prior by Suppression of NF-κB Regulated Proteins Involved in Proliferation, Invasion, and Angiogenesis
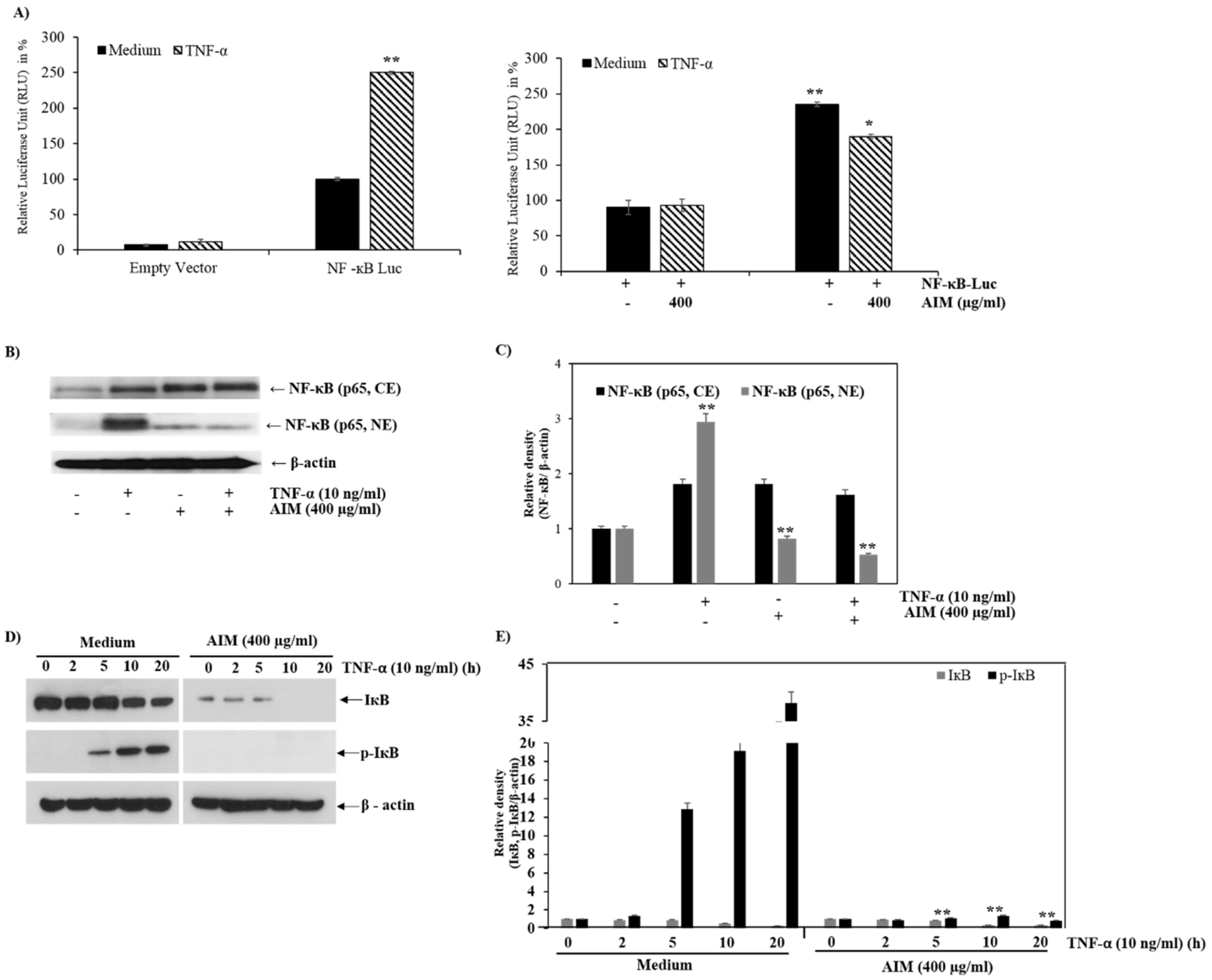
2.4. AIM Suppresses NF-κB Activity Partially Through Degradation of IκBα Phosphorylation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Chemicals
4.2. AIM Preparation
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assays
4.4. Adhesion Assay
4.5. Cell Invasion Assay
4.6. Gelatin Zymography
4.7. Transfection
4.8. Luciferase Assay
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comsa, S.; Cimpean, A.M.; Raica, M. The story of MCF-7 breast cancer cell line: 40 years of experience in research. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, M. Significance, detection and markers of disseminated breast cancer cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 1033–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G.; Lehembre, F. Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.N.; Afaq, F.; Sarfaraz, S.; Khan, N.; Kedlaya, R.; Setaluri, V.; Mukhtar, H. Delphinidin inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via modulation of Met receptor phosphorylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2008, 231, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favot, L.; Martin, S.; Keravis, T.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Lugnier, C. Involvement of cyclin-dependent pathway in the inhibitory effect of delphinidin on angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.W.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lu, J.N.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, D.C.; Choi, E.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, Y.K.; et al. Characterization of a profile of the anthocyanins isolated from Vitis coignetiae Pulliat and their anti-invasive activity on HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-W.; Moon, S.-K.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ko, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Cho, G.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, C.-H. Novel and therapeutic effect of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma cells: Complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by dual mechanism. Faseb J. 2004, 18, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear transcription factor-κB as a target for cancer drug development. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Natural polyphenols for prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB Antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckman, C.A.; Mehew, J.W.; Boxer, L.M. NF-κB activates Bcl-2 expression in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.J.; Prickril, B.; Rasooly, A. Mechanisms of phytonutrient modulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inflammation related to cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Yun, J.W.; Lu, J.N.; Lee, S.J.; Tsoy, I.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, C.H.; et al. Anti-invasive activity of anthocyanins isolated from Vitis coignetiae in human hepatocarcinoma cells. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, B.N.; Chen, T.T.; Wan, Y.Y.; DeGregori, J.; Wang, J.Y. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis requires p73 and c-ABL activation downstream of RB degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 4438–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Lin, Y. Tumor necrosis factor and cancer, buddies or foes? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, Z. TNF-alpha promotes colon cancer cell migration and invasion by upregulating TROP-2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3820–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liabakk, N.B.; Talbot, I.; Smith, R.A.; Wilkinson, K.; Balkwill, F. Matrix metalloprotease 2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloprotease 9 (MMP-9) type IV collagenases in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Motokura, T.; Arnold, A. PRAD1/cyclin D1 proto-oncogene: Genomic organization, 5′ DNA sequence, and sequence of a tumor-specific rearrangement breakpoint. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1993, 7, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amawi, H.; Ashby, C.R.; Samuel, T.; Peraman, R.; Tiwari, A.K. Polyphenolic nutrients in cancer chemoprevention and metastasis: Role of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal (EMT) pathway. Nutrients 2017, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-kappaB: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin, D.; Blanchette, M.; Barrette, S.; Moghrabi, A.; Beliveau, R. Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and suppression of TNF-induced activation of NFkappaB by edible berry juice. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 937–948. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Takada, Y.; Sandur, S.K.; Shishodia, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates expression of cell proliferation and antiapoptotic and metastatic gene products through suppression of IkappaBalpha kinase and Akt activation. Mol. Pharm. 2006, 69, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.S.; Shishodia, S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Deguelin, an Akt inhibitor, suppresses IkappaBalpha kinase activation leading to suppression of NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression, potentiation of apoptosis, and inhibition of cellular invasion. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5612–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Ryu, C.H.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, D.C.; Kim, S.H.; Hah, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of invasion in human hepatoma cells by anthocyanins from meoru. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.N.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, M.J.; Yun, J.W.; Jung, J.H.; Yi, S.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.S.; et al. The inhibitory effect of anthocyanins on Akt on invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition is not associated with the anti-EGFR effect of the anthocyanins. Int J. Oncol 2014, 44, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, B.B.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Asim, M.; Malik, A.; Afaq, F.; Adhami, V.M.; Saleem, M.; Din, M.; Mukhtar, H. A dietary anthocyanidin delphinidin induces apoptosis of human prostate cancer PC3 cells in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8564–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, A.; Chen, D.; Haqqi, T.M. Delphinidin inhibits IL-1beta-induced activation of NF-kappaB by modulating the phosphorylation of IRAK-1(Ser376) in human articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxf.) 2013, 52, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.J.; Chen, G.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y.F. Activation of PI3K/Akt/IKK-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathway is required for the apoptosis-evasion in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: Its inhibition by quercetin. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Lapidus, R.G.; Hussain, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dan, H.C. Differential IKK/NF-κB activity is mediated by TSC2 through mTORC1 in PTEN-null prostate cancer and tuberous sclerosis complex tumor cells. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2015, 13, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tergaonkar, V.; Bottero, V.; Ikawa, M.; Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. IkappaB kinase-independent IkappaBalpha degradation pathway: Functional NF-kappaB activity and implications for cancer therapy. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 8070–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, S.; Mizuno, R.; Kosaka, T.; Saya, H.; Oya, M.; Okada, Y. Expression of TNF-alpha and CD44 is implicated in poor prognosis, cancer cell invasion, metastasis and resistance to the sunitinib treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Matsumine, A.; Sudo, A.; Uchida, A. TNF inhibitor suppresses bone metastasis in a breast cancer cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, G.S.; Park, O.J. Anthocyanins are novel AMPKalpha1 stimulators that suppress tumor growth by inhibiting mTOR phosphorylation. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Tsoy, I.; Park, J.M.; Chung, J.I.; Shin, S.C.; Chang, K.C. Anthocyanins from soybean seed coat inhibit the expression of TNF-α-induced genes associated with ischemia/reperfusion in endothelial cell by NF-κB-dependent pathway and reduce rat myocardial damages incurred by ischemia and reperfusion in vivo. Febs Lett. 2006, 580, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, G.S.; Kwon, D.J.; Ju, S.M.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. Curcumin ameliorates TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression and subsequent THP-1 adhesiveness via the induction of heme oxygenase-1 in the HaCaT cells. Bmb Rep. 2013, 46, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paramanantham, A.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, E.J.; Nagappan, A.; Yun, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, W.S. Pretreatment of Anthocyanin from the Fruit of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Acts as a Potent Inhibitor of TNF-α Effect by Inhibiting NF-κB-Regulated Genes in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102396
Paramanantham A, Kim MJ, Jung EJ, Nagappan A, Yun JW, Kim HJ, Shin SC, Kim GS, Lee WS. Pretreatment of Anthocyanin from the Fruit of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Acts as a Potent Inhibitor of TNF-α Effect by Inhibiting NF-κB-Regulated Genes in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102396
Chicago/Turabian StyleParamanantham, Anjugam, Min Jeong Kim, Eun Joo Jung, Arulkumar Nagappan, Jeong Won Yun, Hye Jung Kim, Sung Chul Shin, Gon Sup Kim, and Won Sup Lee. 2020. "Pretreatment of Anthocyanin from the Fruit of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Acts as a Potent Inhibitor of TNF-α Effect by Inhibiting NF-κB-Regulated Genes in Human Breast Cancer Cells" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102396
APA StyleParamanantham, A., Kim, M. J., Jung, E. J., Nagappan, A., Yun, J. W., Kim, H. J., Shin, S. C., Kim, G. S., & Lee, W. S. (2020). Pretreatment of Anthocyanin from the Fruit of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Acts as a Potent Inhibitor of TNF-α Effect by Inhibiting NF-κB-Regulated Genes in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules, 25(10), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102396








