Importance of Chiral Recognition in Designing Metal-Free Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA
Abstract
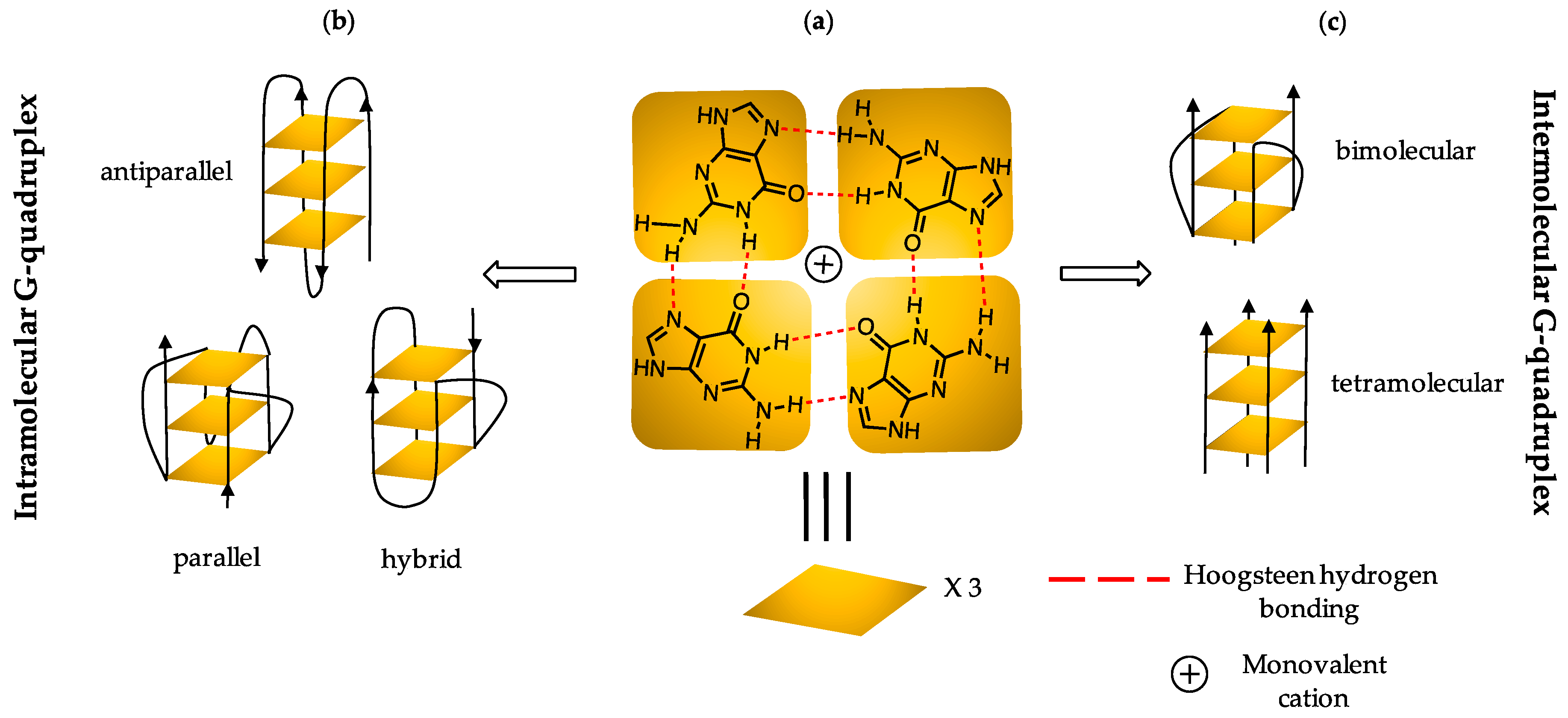
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
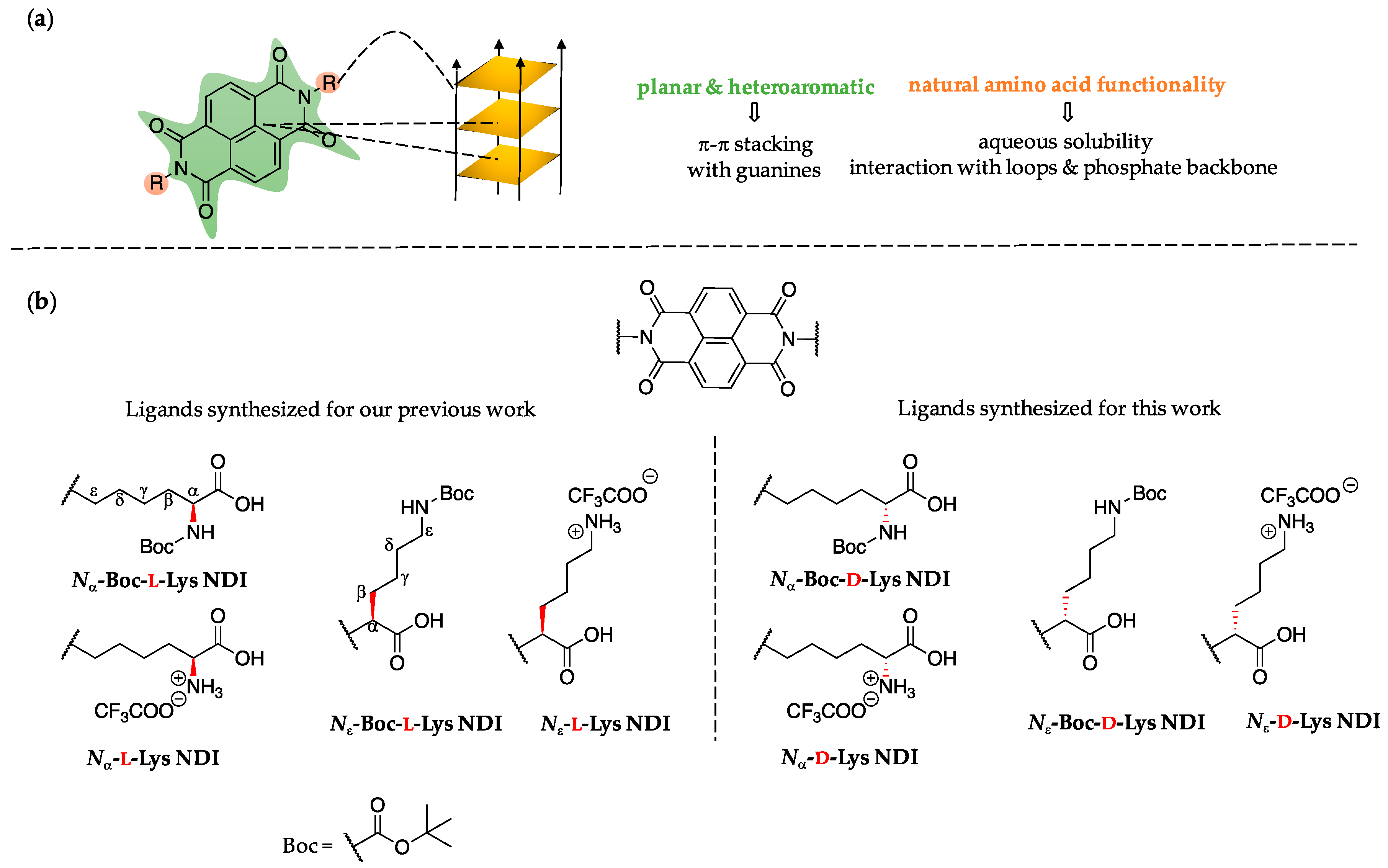
2.1. Ligand Design
2.2. G4 DNA Topology Analysis
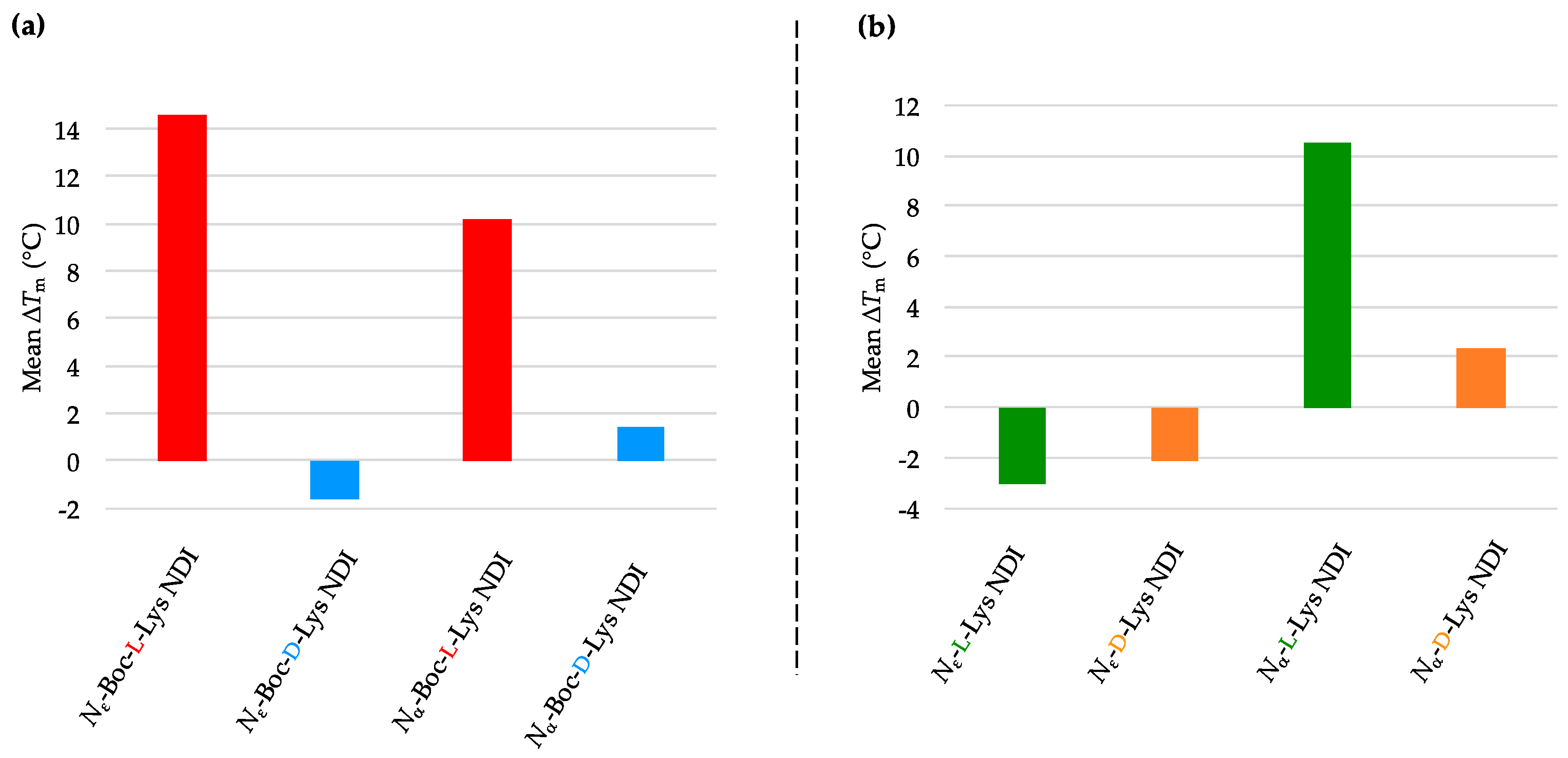
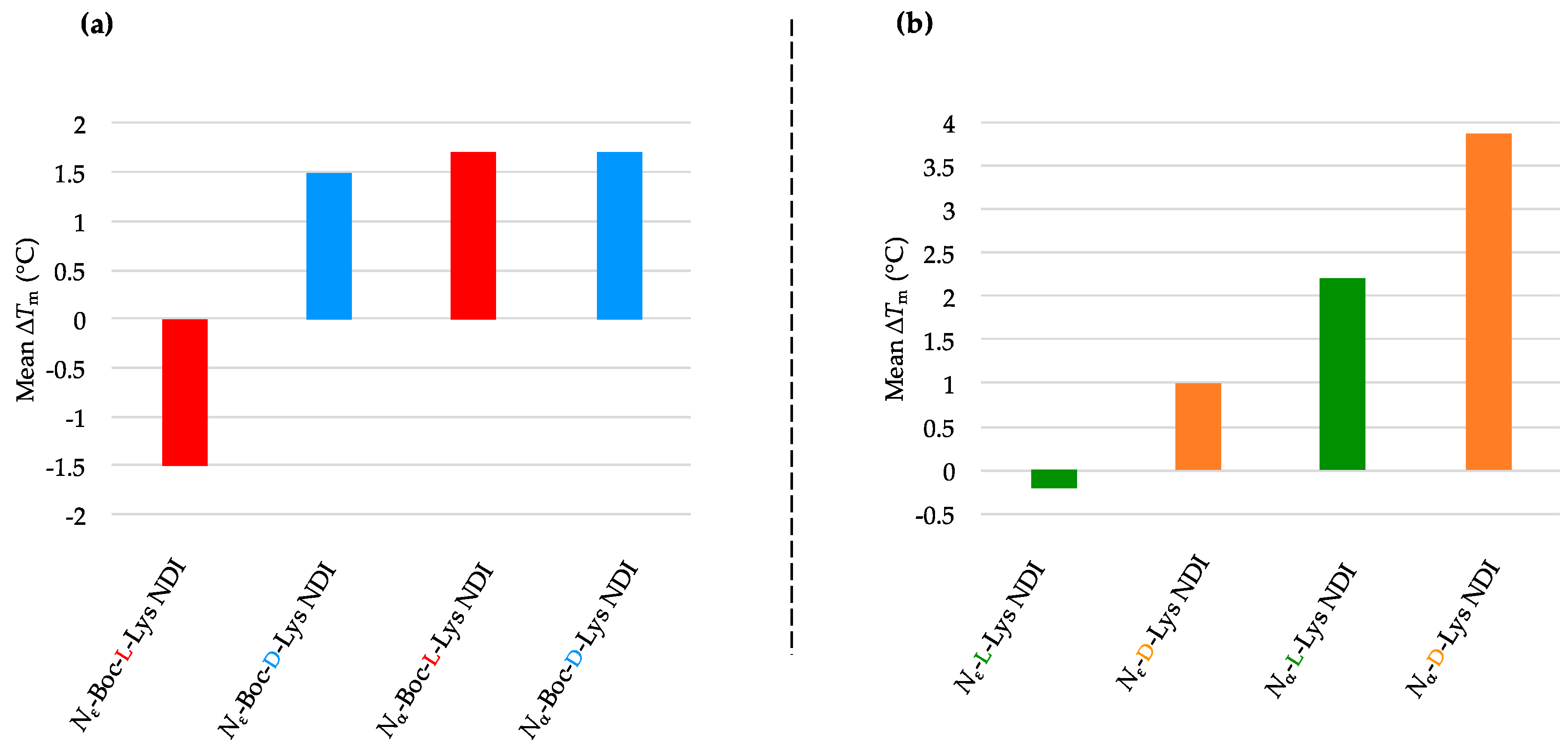
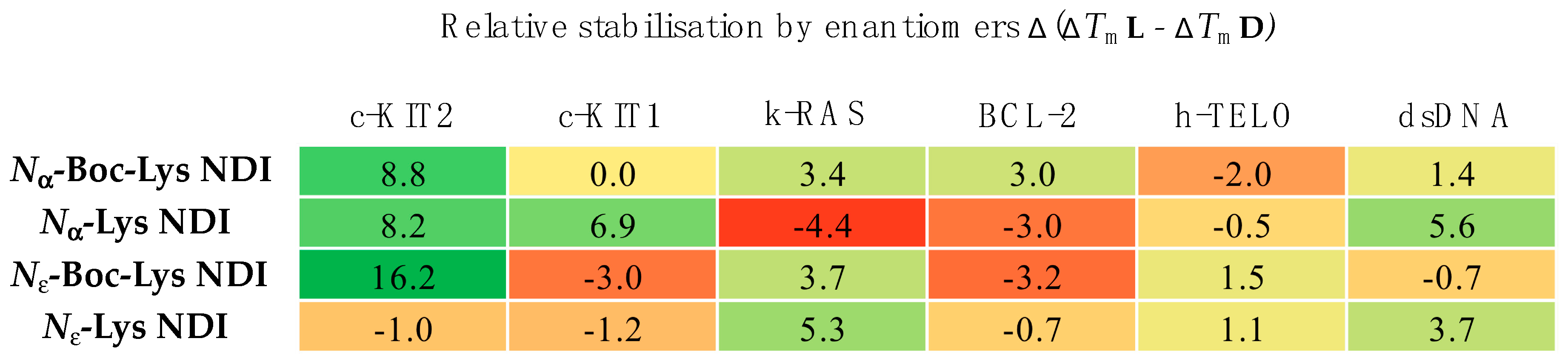
2.3. CD Thermal Melting Studies
2.3.1. c-KIT2
2.3.2. c-KIT1
2.3.3. k-RAS
2.3.4. BCL-2
2.3.5. h-TELO
2.3.6. dsDNA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Nα-Boc-d-Lys and Nε-Boc-d-Lys NDIs
3.2. Synthesis of Nα-d-Lys and Nε-d-Lys NDIs
3.3. Variable-Temperature CD Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koirala, D.; Dhakal, S.; Ashbridge, B.; Sannohe, Y.; Rodriguez, R.; Sugiyama, H.; Balasubramanian, S.; Mao, H. A single-molecule platform for investigation of interactions between G-quadruplexes and small-molecule ligands. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.-Q.; Ghanbarian, A.T.; Spiegel, J.; Martínez Cuesta, S.; Beraldi, D.; Di Antonio, M.; Marsico, G.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. DNA G-quadruplex structures mold the DNA methylome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bončina, M.; Podlipnik, Č.; Piantanida, I.; Eilmes, J.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P.; Vesnaver, G.; Lah, J. Thermodynamic fingerprints of ligand binding to human telomeric G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10376–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. G-quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8627–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochman, M.L.; Paeschke, K.; Zakian, V.A. DNA secondary structures: Stability and function of G-quadruplex structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smargiasso, N.; Rosu, F.; Hsia, W.; Colson, P.; Baker, E.S.; Bowers, M.T.; De Pauw, E.; Gabelica, V. G-Quadruplex DNA Assemblies: Loop Length, Cation Identity, and Multimer Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10208–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, S.; Reszka, A.P.; Huppert, J.; Zloh, M.; Parkinson, G.N.; Todd, A.K.; Ladame, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Neidle, S. Putative DNA Quadruplex Formation within the Human c-kit Oncogene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10584–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Promontorio, R.; Hampel, S.M.; Micco, M.; Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Structural Basis for Telomeric G-Quadruplex Targeting by Naphthalene Diimide Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Minarini, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Moraca, F.; Parrotta, L.; Alcaro, S.; Rigo, R.; Sissi, C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; et al. Macrocyclic naphthalene diimides as G-quadruplex binders. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3819–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, S.M.; Pepe, A.; Greulich-Bode, K.M.; Malhotra, S.V.; Reszka, A.P.; Veith, S.; Boukamp, P.; Neidle, S. Mechanism of the Antiproliferative Activity of Some Naphthalene Diimide G-Quadruplex Ligands. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Wickstrom, L.; Cieplak, P.; Lin, C.; Yang, D. Resolving the Ligand-Binding Specificity in c-MYC G-Quadruplex DNA: Absolute Binding Free Energy Calculations and SPR Experiment. J. Physic. Chem. B 2017, 121, 10484–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.; Shirude, P.S.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplex recognition by bis-indole carboxamides. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3055–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Paladhi, S.; Debnath, M.; Dash, J. Selective recognition of c-MYC G-quadruplex DNA using prolinamide derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głuszyńska, A.; Juskowiak, B.; Kuta-Siejkowska, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Haider, S. Carbazole Derivatives’ Binding to c-KIT G-Quadruplex DNA. Molecules 2018, 23, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Saha, P.; Das, T.; Bessi, I.; Schwalbe, H.; Dash, J. Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex Selective Fluoro-Isoquinolines Induce Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschin, M.; Cianni, L.; Pitorri, M.; Micheli, E.; Cacchione, S.; Frezza, C.; Serafini, M.; Hu, M.-H.; Su, H.; Huang, Z.; et al. Natural Aromatic Compounds as Scaffolds to Develop Selective G-Quadruplex Ligands: From Previously Reported Berberine Derivatives to New Palmatine Analogues. Molecules 2018, 23, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaut, A.; Jantos, K.; Wietor, J.-L.; Rodriguez, R.; Sanders, J.K.M.; Balasubramanian, S. Exploring the Differential Recognition of DNA G-Quadruplex Targets by Small Molecules Using Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Kumari, S.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Small-molecule-mediated G-quadruplex isolation from human cells. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Pantoş, G.D.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Controlled-folding of a small molecule modulates DNA G-quadruplex recognition. Chem. Commun. 2009, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejugam, M.; Sewitz, S.; Shirude, P.S.; Rodriguez, R.; Shahid, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Trisubstituted Isoalloxazines as a New Class of G-Quadruplex Binding Ligands: Small Molecule Regulation of c-kit Oncogene Expression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12926–12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantos, K.; Rodriguez, R.; Ladame, S.; Shirude, P.S.; Balasubramanian, S. Oxazole-Based Peptide Macrocycles: A New Class of G-Quadruplex Binding Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13662–13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.; Buurma, N.J.; Gade, L.H. A Water-Soluble Tetraazaperopyrene Dye as Strong G-Quadruplex DNA Binder. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6314–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.P.N.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Sanders, J.K.M. Tetramethylpyridiniumporphyrazines—A new class of G-quadruplex inducing and stabilising ligands. Chem. Commun. 2006, 4685–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Pantoş, G.D.; Gonçalves, D.P.N.; Sanders, J.K.M.; Balasubramanian, S. Ligand-Driven G-Quadruplex Conformational Switching by Using an Unusual Mode of Interaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5405–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.; Waller, Z.A.E.; Pantoş, G.D.; Balasubramanian, S. Synthesis and Binding Studies of Novel Diethynyl-Pyridine Amides with Genomic Promoter DNA G-Quadruplexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, S.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Pensa, E.; Albrecht, T.; Vilar, R. A Redox-Activated G-Quadruplex DNA Binder Based on a Platinum(IV)-Salphen Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petenzi, M.; Verga, D.; Largy, E.; Hamon, F.; Doria, F.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P.; Guédin, A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Mella, M.; Freccero, M. Cationic Pentaheteroaryls as Selective G-Quadruplex Ligands by Solvent-Free Microwave-Assisted Synthesis. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14487–14496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, F.; Largy, E.; Guédin-Beaurepaire, A.; Rouchon-Dagois, M.; Sidibe, A.; Monchaud, D.; Mergny, J.-L.; Riou, J.-F.; Nguyen, C.-H.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P. An Acyclic Oligoheteroaryle That Discriminates Strongly between Diverse G-Quadruplex Topologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8745–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, N.; Georgiades, S. Investigation of ‘Head-to-Tail’-Connected Oligoaryl N,O-Ligands as Recognition Motifs for Cancer-Relevant G-Quadruplexes. Molecules 2017, 22, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Silva, J.; Guédin, A.; Salgado, G.F.; Mergny, J.-L.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cabrita, E.J.; Cruz, C. Phenanthroline-bis-oxazole ligands for binding and stabilization of G-quadruplexes. BBA—Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drygin, D.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; O’Brien, S.; Schwaebe, M.; Lin, A.; Bliesath, J.; Ho, C.B.; Proffitt, C.; Trent, K.; Whitten, J.P.; et al. Anticancer Activity of CX-3543: A Direct Inhibitor of rRNA Biogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7653–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, S.M.; Sidibe, A.; Gunaratnam, M.; Riou, J.-F.; Neidle, S. Tetrasubstituted naphthalene diimide ligands with selectivity for telomeric G-quadruplexes and cancer cells. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6459–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpima, S.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Barletta, M.; Husby, J.; Pett, L.C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Hilton, S.T.; Neidle, S. The influence of positional isomerism on G-quadruplex binding and anti-proliferative activity of tetra-substituted naphthalene diimide compounds. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6162–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Răsădean, D.M.; Sheng, B.; Dash, J.; Pantoş, G.D. Amino-Acid-Derived Naphthalenediimides as Versatile G-Quadruplex Binders. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8491–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, C.; Zyner, K.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Robson, M.; Haider, S.M.; Morton, J.P.; Marsico, G.; Vo, T.; Laughlin-Toth, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; et al. Targeting Multiple Effector Pathways in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with a G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2500–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadai, M.; Doria, F.; Scalabrin, M.; Pirota, V.; Grande, V.; Bergamaschi, G.; Amendola, V.; Winnerdy, F.R.; Phan, A.T.; Richter, S.N.; et al. A Catalytic and Selective Scissoring Molecular Tool for Quadruplex Nucleic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14528–14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadai, M.; Doria, F.; Di Antonio, M.; Sattin, G.; Germani, L.; Percivalle, C.; Palumbo, M.; Richter, S.N.; Freccero, M. Naphthalene diimide scaffolds with dual reversible and covalent interaction properties towards G-quadruplex. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnmacht, S.A.; Marchetti, C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Besser, R.J.; Haider, S.M.; Di Vita, G.; Lowe, H.L.; Mellinas-Gomez, M.; Diocou, S.; Robson, M.; et al. A G-quadruplex-binding compound showing anti-tumour activity in an in vivo model for pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Fujii, S.; Sato, S.; Okauchi, T.; Takenaka, S. A Selective G-Quadruplex DNA-Stabilizing Ligand Based on a Cyclic Naphthalene Diimide Derivative. Molecules 2015, 20, 10963–10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, G.; Silvent, S.; Saka, S.; Lamberto, M.; Kosenkov, D. Thermodynamics of Binding of Di- and Tetrasubstituted Naphthalene Diimide Ligands to DNA G-Quadruplex. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3335–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Chiral Drugs: An Overview. IJBS 2006, 2, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Mc.Conathy, J.; Owens, M.J. Stereochemistry in Drug Action. Prim. Care Companion J. Clinic. Psychiatry 2003, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, S.; Ritson, D.J.; Garner, T.; Searle, M.; Moses, J.E. Tuneable DNA-based asymmetric catalysis using a G-quadruplex supramolecular assembly. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Metallo-supramolecular Complexes Enantioselectively Eradicate Cancer Stem Cells in Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16201–16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Fu, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Chiral metallo-supramolecular complexes selectively recognize human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5695–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, D.M.; Stratmann, L.M.; Clever, G.H. Structure-Property Relationships in Cu II -Binding Tetramolecular G-Quadruplex DNA. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, D.M.; Nowack, J.; Clever, G.H. Copper-Induced Topology Switching and Thrombin Inhibition with Telomeric DNA G-Quadruplexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11640–11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.-P.; Qin, J.-L.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.-L.; Meng, T.; Zhou, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, Z.-F. Chiral platinum (II)-4-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)- formamide oxo-aporphine (FOA) complexes promote tumor cells apoptosis by directly targeting G-quadruplex DNA in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, C.; Qu, X. G-Quadruplex binding enantiomers show chiral selective interactions with human telomere. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-X.; Zhu, L.-N.; Wu, B.; Huo, Y.-F.; Duan, N.-N.; Kong, D.-M. Two cationic porphyrin isomers showing different multimeric G-quadruplex recognition specificity against monomeric G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8719–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.H.; Chan, C.W.; Lai, J.W.; Ooi, I.H.; Chong, K.V.; Maah, M.J.; Seng, H.L. Enantiomeric pair of copper(II) polypyridyl-alanine complexes: Effect of chirality on their interaction with biomolecules. J. Inorgan. Biochem. 2016, 160, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.; Costa, P.J.; Félix, V.; Williamson, M.P.; Thomas, J.A. Structural Studies on Dinuclear Ruthenium(II) Complexes That Bind Diastereoselectively to an Antiparallel Folded Human Telomere Sequence. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8674–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Chiral Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complexes: Stabilization of G-Quadruplex DNA, Inhibition of Telomerase Activity and Cellular Uptake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Mei, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, S. Synthesis and characterization of chiral ruthenium(II) complexes Λ/Δ-[Ru(bpy)2 (H2iip)](ClO4)2 as stabilizers of c—myc G-quadruplex DNA. J. Coord. Chem. 2015, 68, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Howson, S.E.; Zhao, C.; Ren, J.; Scott, P.; Wang, C.; Qu, X. Chiral metallohelices enantioselectively target hybrid human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5026–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Zhao, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Enantioselective targeting left-handed Z-G-quadruplex. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Song, H.; Scott, P.; Zhao, A.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Sugimoto, N.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Mirror-Image Dependence: Targeting Enantiomeric G-Quadruplex DNA Using Triplex Metallohelices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15723–15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diveshkumar, K.V.; Sakrikar, S.; Harikrishna, S.; Dhamodharan, V.; Pradeepkumar, P.I. Targeting Promoter G-Quadruplex DNAs by Indenopyrimidine-Based Ligands. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2754–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catz, S.D.; Johnson, J.L. BCL-2 in prostate cancer: A minireview. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chatterjee, S. G-Quadruplex surveillance in BCL-2 gene: A promising therapeutic intervention in cancer treatment. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1165–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, P.; Pantoş, G.D.; Otto, S.; Sanders, J.K.M. Efficient and Mild Microwave-Assisted Stepwise Functionalization of Naphthalenediimide with α-Amino Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7063–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.B.; Miles, H.T. Poly(inosinic acid) helixes: Essential chelation of alkali metal ions in the axial channel. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 6736–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkour, A.; Marquevielle, J.; Ivashchenko, S.; Yatsunyk, L.A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Salgado, G.F. High-resolution three-dimensional NMR structure of the KRAS proto-oncogene promoter reveals key features of a G-quadruplex involved in transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettler, J.M.; Lewis, E.A. Biophysical Studies of the Structure, Stability, and Ligand Binding Properties of G-Quadruplex DNA: Thoughts and Comparisons of the K-ras, c-MYC, and Bcl-2 Oncogene Promoter Sequence Quadruplexes. In Frontiers in Nucleic Acids; Sheardy, R.D., Winkle, S.A., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 1082, pp. 33–50. ISBN 978-0-8412-2623-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kuryavyi, V.; Phan, A.T.; Patel, D.J. Solution structures of all parallel-stranded monomeric and dimeric G-quadruplex scaffolds of the human c-kit2 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 6757–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Qi, C.; Meng, J.; Zhang, N.; Bing, T.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Shangguan, D. General Cell-Binding Activity of Intramolecular G-Quadruplexes with Parallel Structure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Noguchi, Y.; Sugiyama, H. The new models of the human telomere d[AGGG(TTAGGG)3] in K+ solution. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5584–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Dai, J.; Bialis, T.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type intramolecular G-quadruplex structure with mixed parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Carver, M.; Punchihewa, C.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Structure of the Hybrid-2 type intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex in K+ solution: insights into structure polymorphism of the human telomeric sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4927–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Punchihewa, C.; Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Structure of the intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex in potassium solution: a novel adenine triple formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Luu, K.N.; Patel, D.J. Structure of two intramolecular G-quadruplexes formed by natural human telomere sequences in K+ solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, K.N.; Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Lacroix, L.; Patel, D.J. Structure of the Human Telomere in K+ Solution: An Intramolecular (3 + 1) G-Quadruplex Scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9963–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.-N.; Xie, M.-X. Evidence of different G-quadruplex DNA binding with biogenic polyamines probed by electrospray ionization-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry, circular dichroism and atomic force microscopy. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J. Ruthenium (II) polypyridyl complexes stabilize the bcl-2 promoter quadruplex and induce apoptosis of Hela tumor cells. BioMetals 2013, 26, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.-X.; Chen, A.-C.; Yao, P.-F.; Zeng, D.-Y.; Lu, Y.-J.; Tan, J.-H.; Huang, Z.-S.; Ou, T.-M. Blocking the binding of WT1 to bcl-2 promoter by G-quadruplex ligand SYUIQ-FM05. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 5, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yan, J.; You, H. Folding/unfolding kinetics of G-quadruplexes upstream of the P1 promoter of the human BCL-2 oncogene. J. Biol. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Lin, C.; Mathad, R.I.; Carver, M.; Yang, D. The Major G-Quadruplex Formed in the Human BCL-2 Proximal Promoter Adopts a Parallel Structure with a 13-nt Loop in K+ Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onel, B.; Lin, C.; Yang, D. DNA G-quadruplex and its potential as anticancer drug target. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Hecht, S.M.; Hurley, L.H. The i-Motif in the bcl-2 P1 Promoter Forms an Unexpectedly Stable Structure with a Unique 8:5:7 Loop Folding Pattern. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17667–17676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Dexheimer, T.S.; Chen, D.; Carver, M.; Ambrus, A.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. An Intramolecular G-Quadruplex Structure with Mixed Parallel/Antiparallel G-Strands Formed in the Human BCL-2 Promoter Region in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, A.; Lötsch, D.; van Schoonhoven, S.; Roller, A.; Kowol, C.R.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K.; Barone, G. Another step toward DNA selective targeting: Ni II and Cu II complexes of a Schiff base ligand able to bind gene promoter G-quadruplexes. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7758–7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-T.D.; Varnai, P.; Bugaut, A.; Reszka, A.P.; Neidle, S.; Balasubramanian, S. A G-Rich Sequence within the c-kit Oncogene Promoter Forms a Parallel G-Quadruplex Having Asymmetric G-Tetrad Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13399–13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (NDI ligands) are available from the authors. |
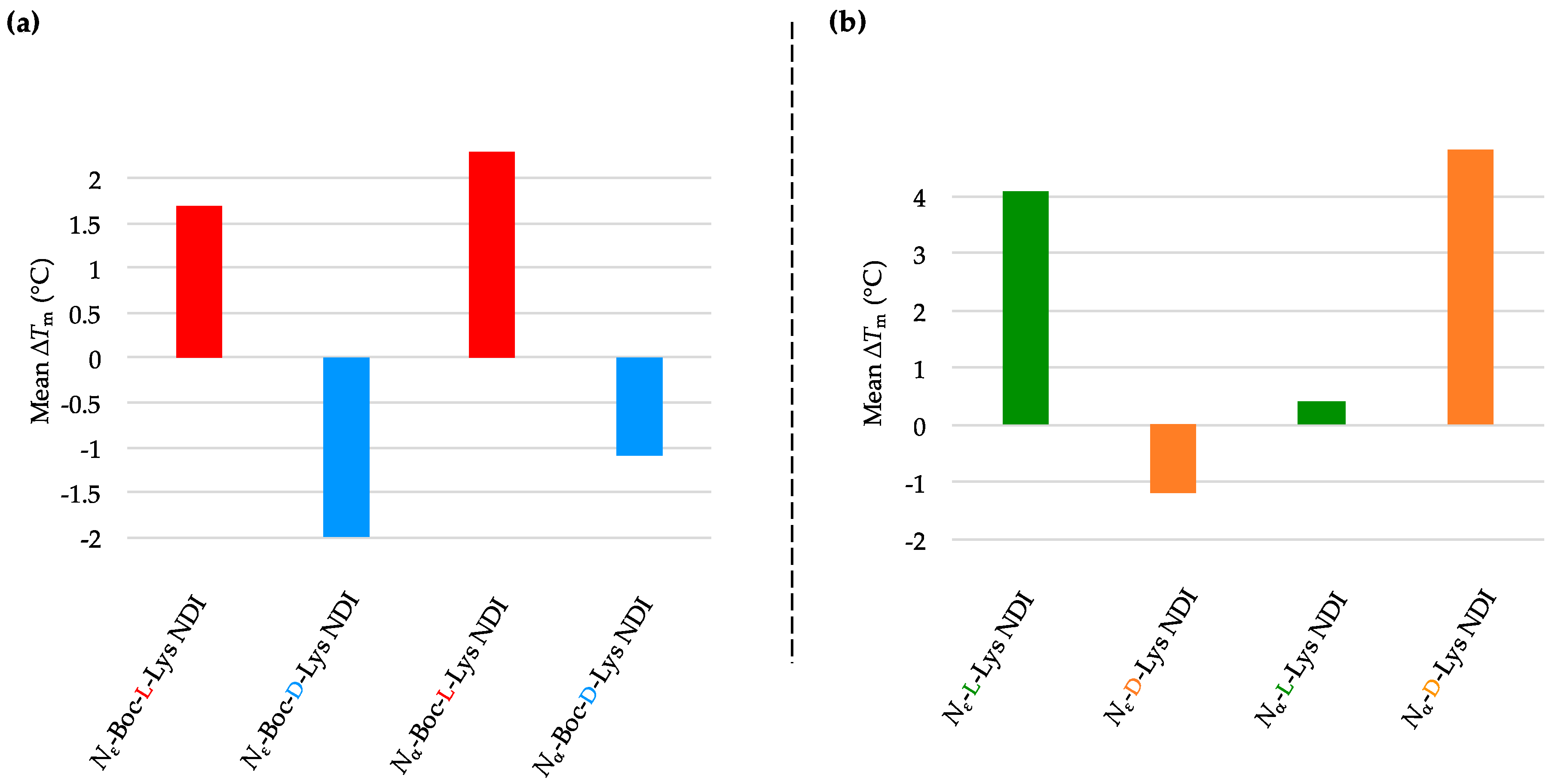
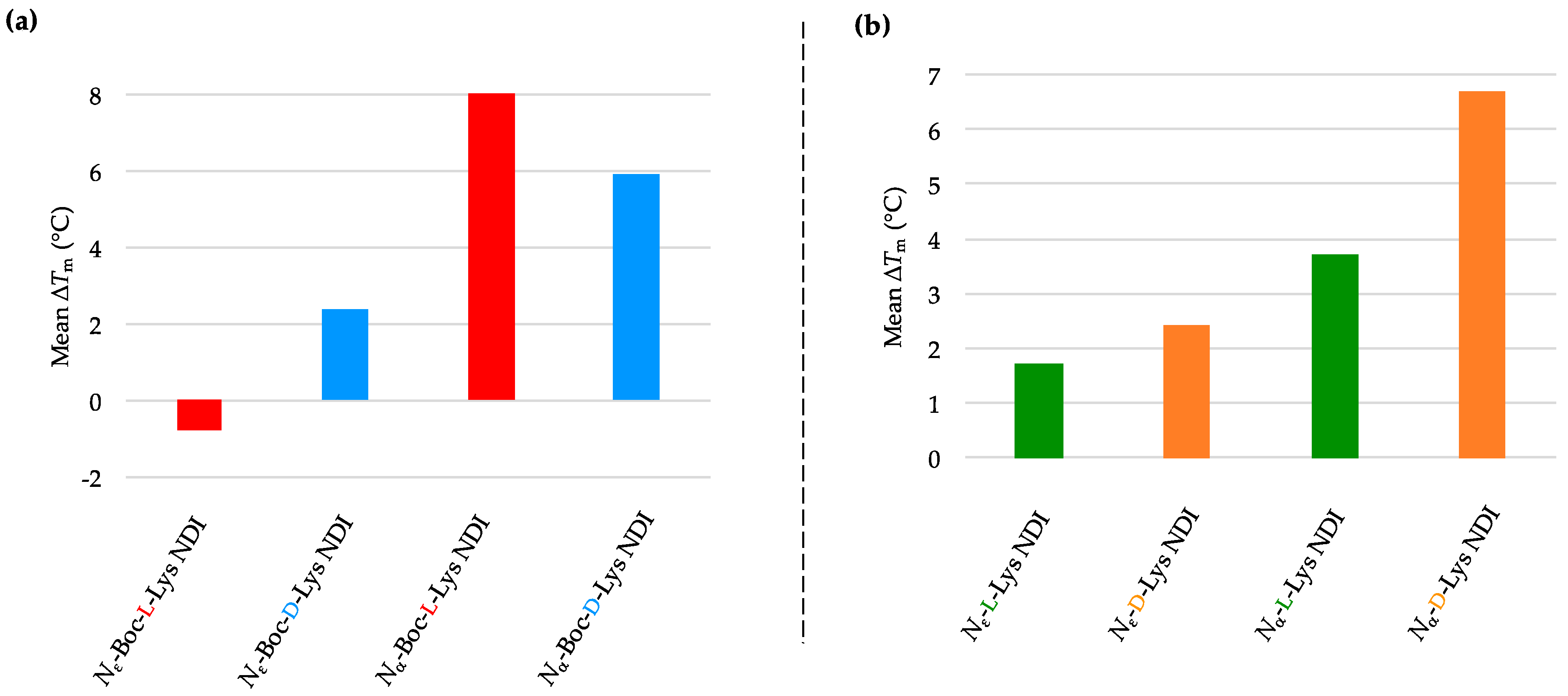
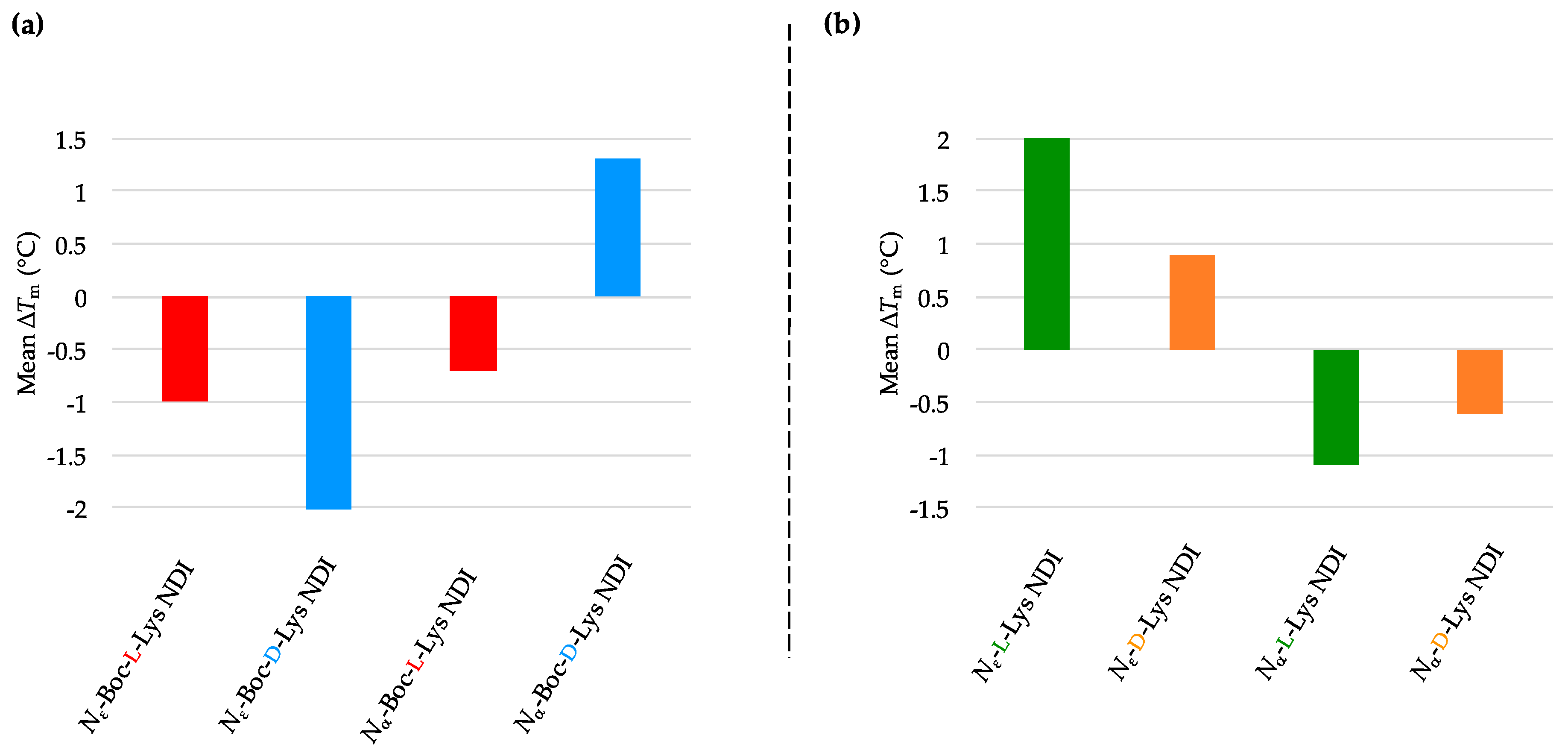
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| c-KIT2 only | 78.2 ± 2.7 a/78.9 ± 0.8 b | c-KIT2 only | 78.2 ± 2.7 a/78.9 ± 0.8 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 92.8 ± 5.9 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 75.1 ± 0.9 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 77.3 ± 0.4 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 76.8 ± 0.3 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 88.4 ± 8.4 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 88.7 ± 7.1 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 80.3 ± 0.1 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 81.2 ± 1.0 |
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| c-KIT1 only | 65.8 ± 0.4 a/65.4 ± 0.4 b | c-KIT1 only | 65.8 ± 0.4 a/65.4 ± 0.4 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 64.3 ± 0.4 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 65.6 ± 0.7 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 66.9 ± 0.2 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 66.4 ± 0.2 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 67.5 ± 1.0 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 68.0 ± 0.8 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 67.1 ± 0.2 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 69.3 ± 0.3 |
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| k-RAS only | 58.3 ± 0.6 a/55.8 ± 0.1 b | k-RAS only | 58.3 ± 0.6 a/55.8 ± 0.1 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 60.0 ± 0.5 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 62.4 ± 0.4 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 53.8 ± 0.1 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 54.6 ± 0.1 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 60.6 ± 0.3 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 58.7 ± 1.1 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 54.7 ± 0.1 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 60.6 ± 0.1 |
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| BCL-2 only | 66.0 ± 0.4 a/66.1 ± 0.4 b | BCL-2 only | 66.0 ± 0.4 a/66.1 ± 0.4 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 65.2 ± 0.5 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 67.7 ± 0.4 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 68.5 ± 0.4 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 68.5 ± 0.3 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 74.9 ± 0.8 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 69.7 ± 1.0 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 72.0 ± 0.3 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 72.8 ± 0.3 |
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| h-TELO only | 62.5 ± 0.3 a/65.8 ± 0.1 b | h-TELO only | 62.5 ± 0.3 a/65.8 ± 0.1 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 61.5 ± 0.6 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 64.5 ± 0.4 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 63.2 ± 0.1 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 66.7 ± 0.2 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 61.8 ± 0.4 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 61.4 ± 1.0 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 67.1 ± 0.1 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 65.2 ± 0.1 |
| (a) | (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) | Sequence/Assembly | Tm (°C) |
| dsDNA only | 55.1 ± 0.8 a/55.6 ± 0.3 b | dsDNA only | 55.1 ± 0.8 a/55.6 ± 0.3 b |
| Nε-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 52.6 ± 0.8 | Nε-L-Lys NDI | 56.9 ± 1.5 |
| Nε-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 53.8 ± 0.2 | Nε-D-Lys NDI | 53.7 ± 0.3 |
| Nα-Boc-L-Lys NDI | 57.0 ± 1.2 | Nα-L-Lys NDI | 55.8 ± 0.7 |
| Nα-Boc-D-Lys NDI | 56.1 ± 0.6 | Nα-D-Lys NDI | 50.7 ± 0.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Răsădean, D.M.; Harrison, S.W.O.; Owens, I.R.; Miramont, A.; Bromley, F.M.; Pantoș, G.D. Importance of Chiral Recognition in Designing Metal-Free Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA. Molecules 2019, 24, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081473
Răsădean DM, Harrison SWO, Owens IR, Miramont A, Bromley FM, Pantoș GD. Importance of Chiral Recognition in Designing Metal-Free Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081473
Chicago/Turabian StyleRăsădean, Dora M., Samuel W. O. Harrison, Isobel R. Owens, Aucéanne Miramont, Frances M. Bromley, and G. Dan Pantoș. 2019. "Importance of Chiral Recognition in Designing Metal-Free Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081473
APA StyleRăsădean, D. M., Harrison, S. W. O., Owens, I. R., Miramont, A., Bromley, F. M., & Pantoș, G. D. (2019). Importance of Chiral Recognition in Designing Metal-Free Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA. Molecules, 24(8), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081473







