Extraction of Metal Ions with Metal–Organic Frameworks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Stability of MOFs in Aquatic Environment
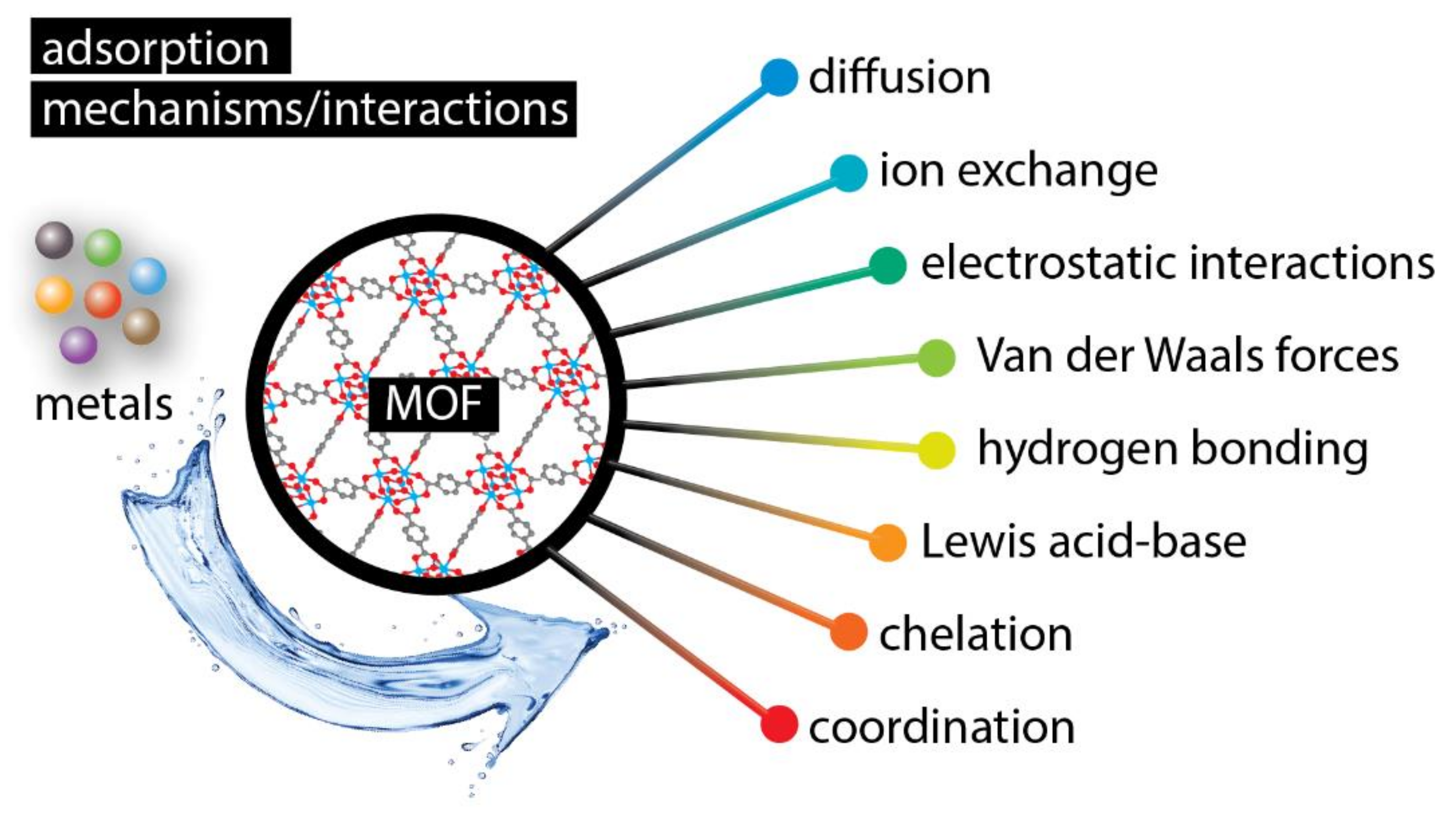
3. Mechanisms of Metal Ions Extraction with Metal–Organic Frameworks
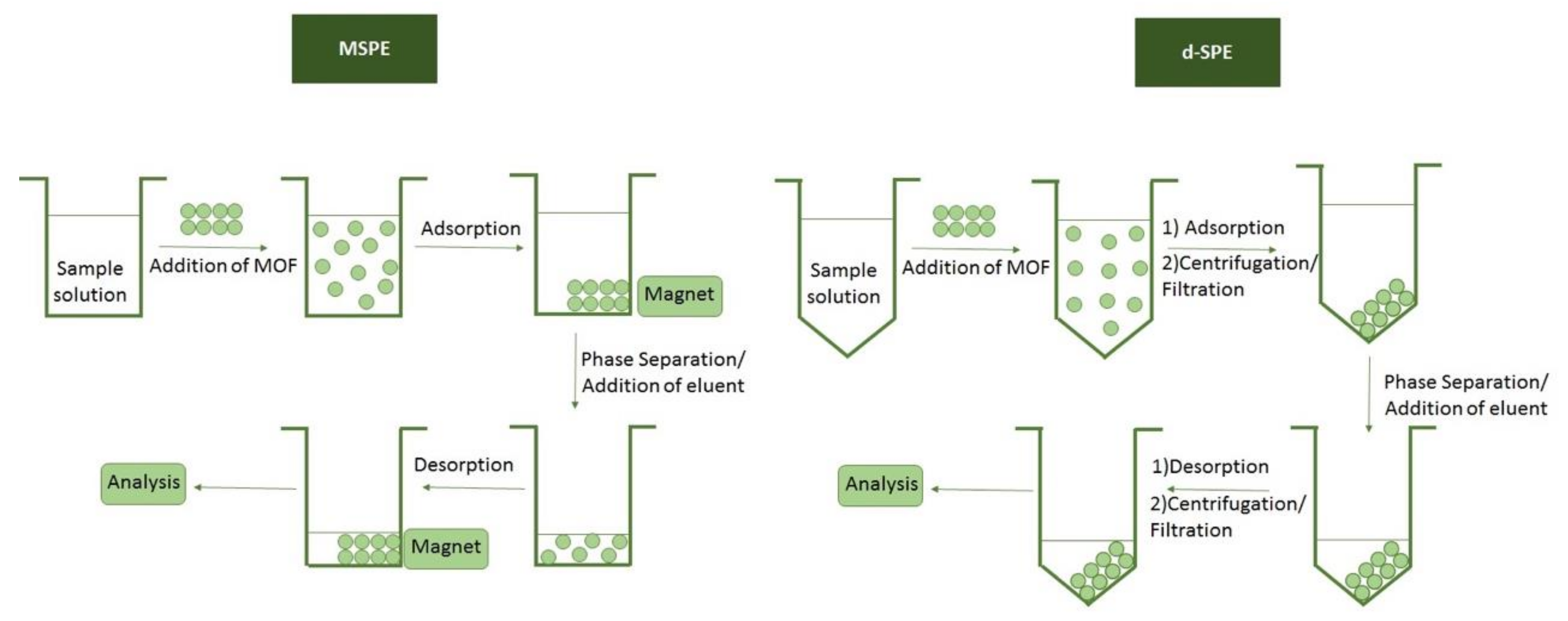
4. Sample Preparation Techniques for the Extraction of Metal Ions
5. Applications of Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Extraction of Metal Ions
5.1. Extraction of Palladium
5.2. Extraction of Lead
5.3. Extraction of Mercury
5.4. Extraction of Copper
5.5. Extraction of Cadmium
5.6. Extraction of Thorium
5.7. Extraction of Uranium
5.8. Extraction of Selenium
5.9. Multielement Extraction
5.10. Application of ZIFs for the Extraction of Metal Ions
5.11. Application of COFs for the Extraction of Metal Ions
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaghi, O.; Li, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of a Metal-Organic Framework containing large rectangular channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10401–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, O.K.; Eryazici, I.; Jeong, N.C.; Hauser, B.G.; Wilmer, C.E.; Sarjeant, A.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Nguyen, S.T.; Yazaydin, A.Ö.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-Organic Framework materials with ultrahigh surface areas: Is the sky the limit? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, U.; Schubert, M.; Teich, F.; Puetter, H.; Schierle-Arndta, K.; Pastréa, J. Metal-Organic Frameworks—Prospective industrial applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Pashow, K.; Della Rocca, J.; Xie, Z.; Tran, S.; Lin, W. Postsynthetic modifications of iron-carboxylate nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for imaging and drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14261–14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H.; Llabres i Xamena, F.X.L.I. Engineering Metal Organic Frameworks for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4606–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getman, R.; Bae, Y.; Wilmer, C.; Snurr, R. Review and analysis of molecular simulations of methane, hydrogen, and acetylene storage in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Aung, T.; Guo, N.; Weichselbaum, R.; Lin, W. Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks for Therapeutic, Imaging, and Sensing Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Asiri, A.; Garcia, H. 2D Metal–Organic Frameworks as multifunctional materials in heterogeneous catalysis and electro/photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Detoxification of Chemical Warfare Agents, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Raza, N.; Kim, K. Metal-Organic Frameworks as advanced sorbents for the extraction and determination of pollutants from environmental, biological, and food media. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, W.; Kukkar, D.; Saulat, H.; Raza, N.; Azam, M.; Mehmood, A.; Kim, K. Metal-Organic Frameworks as an emerging tool for sensing various targets in aqueous and biological media. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. Metal-organic frameworks for air purification of toxic chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5695–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Lei, Y.; Song, H. Evaluation of Fe3O4@SiO2–MOF-177 as an advantageous adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of phenols in environmental water samples. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7842–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Jia, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, P.; He, L.; Hou, X. A combined experimental/computational study on metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) as a SPE sorbent for the determination of sulphonamides in environmental water samples coupling with UPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 2016, 15, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Zhong, C.; Hu, B. Polydimethylsiloxane/metal-organic frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detector for the determination of estrogens in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1310, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Sun, Z.; Song, C.; Lu, S.; Chen, G.; You, J. Sensitive and background-free determination of thiols from wastewater samples by MOF-5 extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection using a novel fluorescence probe of carbazole-9-ethyl-2-maleimide. Talanta 2016, 161, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, M.; Hu, B.; Yao, M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.; Pang, J. Electrospun UiO-66/polyacrylonitrile nanofibers as efficient sorbent for pipette tip solid-phase extraction of phytohormones in vegetable samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1542, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Taima-Mancera, T.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Metal-Organic Frameworks in green analytical chemistry. Separations 2019, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, K.; Aqel, A.; Alothman, Z. Metal-Organic Frameworks in chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1348, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L. Chiral metal–organic framework used as stationary phases for capillary electrochromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 830, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, G.; Taima-Mancera, I.; Lago, A.; Ayala, J.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Mixed functionalization of organic ligands in UiO-66: A tool to design Metal–Organic Frameworks for tailored microextraction. Molecules 2019, 24, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; González-Hernández, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Afonso, A. Metal-Organic Frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Masoomi, M.; Yamini, Y.; Morsali, A. Application of mechanosynthesized azine-decorated Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Frameworks for highly efficient removal and extraction of some heavy-metal ions from aqueous samples: A comparative study. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 54, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, A.; Peters, A.; Vermeulen, N.; Wang, T.; Hupp, J.; Farha, O. Best Practices for the Synthesis, Activation, and Characterization of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2016, 29, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Are Metal-Organic Frameworks able to provide a new generation of solid-phase microextraction coatings?—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. EXS 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Anthemidis, A.; Kazantzi, V.; Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K. An automated flow injection system for metal determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry involving on-line fabric disk sorptive extraction technique. Talanta 2016, 156, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. A magnetic Metal-Organic Framework as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of copper(II), and its determination by electrothermal AAS. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanidou, V.; Sarakatsianos, I.; Manousi, N.; Georgantelis, D.; Goula, A.; Adamopoulos, K. Detection of mechanically deboned meat in cold cuts by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2018, 19, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Hu, B. Graphene oxide–TiO2 composite as a novel adsorbent for the preconcentration of heavy metals and rare earth elements in environmental samples followed by on-line inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry detection. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5996–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, I.; Soylak, M.; Elçi, L.; Doğan, M. Determination of trace metal ions by AAS in natural water samples after preconcentration of pyrocatechol violet complexes on an activated carbon column. Talanta 2000, 52, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B.; Malicka, E. Modification of carbon nanotubes for preconcentration, separation and determination of trace-metal ions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Zachariadis, G.; Deliyanni, E.; Samanidou, V. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks in food sample preparation. Molecules 2018, 23, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Yang, C.; Chang, N.; Yan, X. Metal–Organic Frameworks for analytical chemistry: From sample collection to chromatographic separation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Shen, W.; Deng, H.; Gao, Z. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks as stationary phases in chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Metal–Organic Frameworks as key materials for solid-phase microextraction devices—A Review. Separations 2019, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, N. Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks and covalent organic frameworks for sample preparation and chromatographic analysis. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 3059–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Sharma, V.K. Water-Stable Metal-Organic Frameworks for aqueous removal of heavy metals and radionuclides: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, S.; Fuentes-Fernandez, E.M.A.; Tan, K.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Chabal, Y.J.; Thonhauser, T. Understanding and controlling water stability of MOF-74. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2016, 4, 5176–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Defectous UiO-66 MOF Nanocomposites as Reactive Media of Superior Protection against Toxic Vapors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Hu, Y.; Florent, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Smart textiles of MOF/g-C3N4 nanospheres for the rapid detection/detoxification of chemical warfare agents. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Travlou, N.A.; Secor, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Oxidized g-C3N4 Nanospheres as Catalytically Photoactive Linkers in MOF/g-C3N4 Composite of Hierarchical Pore Structure. Small 2017, 13, 1601758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, C.J. Nanoparticle/Metal–Organic Framework Composites for Catalytic Applications: Current Status and Perspective. Molecules 2017, 2, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Jhung, S.H. Composites of metal-organic frameworks: Preparation and application in adsorption. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. Engineering the surface of a new class of adsorbents: Metal-organic framework/graphite oxide composites. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarra, A.; Frackowiak, E.; Beguin, F. The HSAB concept as a means to interpret the adsorption of metal ions onto activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 228, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Hupp, J.; Farha, O.K. Metal–Organic Frameworks for applications in remediation of oxyanion/cation-contaminated water. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 7245–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Pei, X.; Zhang, S.; Feng, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B. Water purification: Adsorption over Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.A.; Le, G.H.; Dao, C.D.; Dang, L.Q.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Dang, P.T.; Tran, H.T.K.; Duong, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; et al. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption using novel MIL-53(Fe) as a highly efficient adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Li, C.; Wu, C. Exploring a thiol-functionalized MOF for elimination of lead and cadmium from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, A.; Hosseinzadeh-Khanmiri, R.; Babazadeh, M.; Abolhasani, J.; Ghorbani-Kalhor, E. Determination of heavy metal ions in vegetable samples using a magnetic Metal–Organic Framework nanocomposite sorbent. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A 2015, 32, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, A.; Tehrani, A.; Shemirani, F.; Morsali, A. Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks as selective microporous materials for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 9193–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Qiu, L.G.; Yuan, Y.P.; Peng, F.M.; Jiang, X.; Xie, A.J.; Shen, Y.H.; Zhu, J.F. Thiol-Functionalization of Metal-Organic Framework by a facile coordination-based postsynthetic strategy and enhanced removal of Hg2+ from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audu, C.O.; Nguyen, H.G.T.; Chang, C.; Katz, M.J.; Mao, L.; Farha, O.K.; Hupp, J.T.; Nguyen, S.T. The dual capture of AsV and AsIII by UiO-66 and analogues. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6492–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Katz, M.J.; Wang, T.C.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Chapman, K.W.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. High efficiency adsorption and removal of selenate and selenite from water using Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.-R.; Yuan, D.-Q.; Sculley, J.; Li, J.-R.; Han, Z.-B.; Zhou, H.-C. Functional mesoporous metal-organic frameworks for the capture of heavy metal ions and size-selective catalysis. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 11637–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Asgharinezhad, A.; Pooladi, M.; Barzin, M.; Abbaszadeh, A.; Tadjarodi, A. A novel magnetic Metal-Organic Framework nanocomposite for extraction and preconcentration of heavy metal ions, and its optimization via experimental design methodology. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jian, M.P.; Liu, R.P.; Yao, J.F.; Zhang, X.W. Highly efficient removal of arsenic(III) from aqueous solution by zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with different morphology. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 481, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, E.; Mohaghegh, N. Removal of toxic metal ions from sungun acid rock drainage using mordenite zeolite, graphene nanosheets, and a Novel Metal–Organic Framework. Mine Water Environ. 2015, 35, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.P.; Liu, B.; Zhang, G.S.; Liu, R.P.; Zhang, X.W. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 465, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Eiroa, A.; Canle, M.; Leroy-Cancellieri, V.; Cerdà, V. Solid-Phase extraction of organic compounds: A critical review (Part I). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarian, M.; Ghanbarpour, A.; Behbahani, M.; Bagheri, S.; Bagheri, A. A Metal-Organic Framework sustained by a nanosized Ag12 cuboctahedral node for solid-phase extraction of ultra traces of lead(II) ions. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, J.; Chang, C.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, H. Solid-Phase extraction with the Metal-Organic Framework MIL-101(Cr) combined with direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry for the fast analysis of triazine herbicides. J. Sep. Sci 2014, 37, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzimichalakis, P.F.; Samanidou, V.F.; Verpoorte, R.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Development of a validated HPLC method for the determination of B-complex vitamins in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids after solid phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2004, 27, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousi, N.; Raber, G.; Papadoyannis, I. Recent advances in microextraction techniques of antipsychotics in biological fluids prior to liquid chromatography analysis. Separations 2017, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Aghamohammadhassan, M.; Chamsaz, M.; Akhlaghi, H.; Pedramrad, T. Dispersive solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakisikli, G.; Anthemidis, A.N. Magnetic materials as sorbents for metal/metalloid preconcentration and/or separation. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 789, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, F.; Cabello, C.P.; Frizzarin, R.M.; Estela, J.M.; Palomino, G.T.; Cerdà, V.; Turnes, G. Magnetic solid-phase extraction using Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltussen, E.; Sandra, P.; David, F.; Cramers, C. Stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), a novel extraction technique for aqueous samples: Theory and principles. J. Microcolumn Sep. 1999, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Zhong, C.; Hu, B. Sorptive extraction using polydimethylsiloxane/metal–organic framework coated stir bars coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1356, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Polydimethylsiloxane/metal-organic frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to gas chromatography-flame photometric detection for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental water samples. Talanta 2016, 156, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Kaykhaii, M.; Keikha, A.J.; Mirmoradzehi, E.; Sargazi, G. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of metal-organic framework based pipette-tip solid phase extraction of organic dyes from seawater and their determination with HPLC. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei Kahkha, M.; Daliran, S.; Oveisi, A.; Kaykhaii, M.; Sepehri, Z. The mesoporous porphyrinic zirconium Metal-Organic Framework for pipette-tip solid-phase extraction of mercury from fish samples followed by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Ye, G.; Ge, H.; Hu, X. Preparation of magnetic Metal-Organic Frameworks adsorbent modified with mercapto groups for the extraction and analysis of lead in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabi, M. Preconcentration of mercury(II) using a thiol-functionalized Metal-Organic Framework nanocomposite as a sorbent. Microchim. Acta 2013, 181, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Behnken, D.W. Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 1960, 2, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Behbahani, M.; Akbar Asgharinezhad, A.; Salarian, M.; Dehghani, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Amini, M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 2012, 99, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Ge, H.; Hu, X. Preparation of a functionalized magnetic Metal–Organic Framework sorbent for the extraction of lead prior to electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometer analysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8782–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalıoglu, S.; Yavuz, E.; Demir, S.; Patat, S. Zirconium-Based highly porous Metal-Organic Framework (MOF-545) as an efficient adsorbent for vortex assisted-solid-phase extraction of lead from cereal, beverage and water samples. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadjarodi, A.; Abbaszadeh, A. A magnetic nanocomposite prepared from chelator-modified magnetite (Fe3O4) and HKUST-1 (MOF-199) for separation and preconcentration of mercury(II). Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Song, Q.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, Q. Determination of Hg (II) in tea and mushroom samples based on Metal-Organic Frameworks as solid-phase extraction sorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.E.; Dadfarnia, S.; Emami, S.; Shabani, A.M.H. Sulfonated metal organic framework loaded on iron oxide nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction of cadmium from environmental water samples. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6337–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, Z.; Kaykhaii, M.; Khajeh, M.; Oveisi, A. Synthesis of UiO-66-OH zirconium Metal-Organic Framework and its application for selective extraction and trace determination of thorium in water samples by spectrophotometry. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 194, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J.; Chen, L.; Diwu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Ratiometric monitoring of thorium contamination in natural water using a dual-emission luminescent europium organic framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dai, X.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Gui, D.; et al. Highly sensitive and selective uranium detection in natural water systems using a luminescent mesoporous Metal–Organic Framework equipped with abundant lewis basic sites: A combined batch, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and first principles simulation investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol 2017, 51, 3911–3921. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantari, H.; Manoochehri, M. A nanocomposite consisting of MIL-101(Cr) and functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for extraction and determination of selenium(IV) and selenium(VI). Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.; Matbouie, Z.; Asgharinezhad, A.; Dehghani, A. Solid-Phase extraction of Cd(II) and Pb(II) using a magnetic metal-organic framework, and their determination by FAAS. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Kalhor, E. A metal-organic framework nanocomposite made from functionalized magnetite nanoparticles and HKUST-1 (MOF-199) for preconcentration of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II). Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Khanmiri, R.; Abolhasani, J.; Ghorbani-Kalhor, E.; Hassanpour, A. Solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions from agricultural samples with the aid of a novel functionalized magnetic metal–organic framework. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19884–19892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Yamini, Y.; Masoomi, M.; Morsali, A.; Mani-Varnosfaderani, A. Magnetic Metal-Organic Frameworks for the extraction of trace amounts of heavy metal ions prior to their determination by ICP-AES. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Wei, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Q. Postsynthetic modification of copper terephthalate metal-organic frameworks and their new application in preparation of samples containing heavy metal ions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 210, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Yang, Z.; Gui, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, X. Overcoming the crystallization and designability issues in the ultrastable zirconium phosphonate framework system. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, X.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, C.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Alekseev, E.V.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Distinctive two-step intercalation of Sr2+ into a coordination polymer with record high 90Sr uptake capabilities. Chem 2019, 5, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Diwu, J.; Chen, J.; Chai, Z.; et al. Efficient and selective uptake of TcO4 by a cationic Metal-Organic Framework material with open Ag+ sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework materials: Recent progress in synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16811–16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.-C.; Bennett, T.D.; Cheetham, A.K. Chemical structure, network topology, and porosity effects on the mechanical properties of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9938–9943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, J.; Xu, F.; Long, Ζ.; Hou, X. Ultrasensitive determination of inorganic arsenic by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry using Fe3O4@ZIF-8 nanoparticles for preconcentration. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Lee, H.K. Water stability of zeolite imidazolate framework 8 and application to porous membrane-protected micro-solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8490–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wang, W. Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Ding, X.; Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 18, 6010–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Du, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Recent advances in facile synthesis and applications of covalent organic framework materials as superior adsorbents in sample pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Hao, J.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. Fabrication of porous covalent organic frameworks as selective and advanced adsorbents for the on-line preconcentration of trace elements against the complex sample matrix. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Organic Linker of MOF | Metal of MOF | Modification | Matrix | Sample Preparation Technique | Detection Technique | Recovery (%) | LOD (ng mL−1) | Reusability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd(II) | Trimesic acid | Cu | Fe3O4@Py | Fish, sediment, soil, water, | MSPE | FAAS | 96.8–102.5 | 0.37 | - | [80] |
| Malonic acid | Ag | - | Water | SPE | FAAS | >95 | 0.5 | Up to 5 times | [65] | |
| Pb(II) | Trimesic Acid | Cu | DHz, Fe3O4 | Water | MSPE | ETAAS | 97–102 | 0.0046 | At least 80 times | [81] |
| Trimesic Acid | Cu | Fe3O4@SH | Rice, pig liver, tea, water | MSPE | FAAS | >95 | 0.29–0.97 | - | [77] | |
| meso-tetra(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin | Zr | - | Cereal, beverage, water | d-SPE | FAAS | 90–107 | 1.78 | Up to 42 times | [82] | |
| Trimesic acid | Cu | Fe3O4@4-(5)-imidazole-dithiocarboxylic acid | Fish, canned tune | MSPE | CVAAS | 95–102 | 10 | At least 12 times | [83] | |
| Hg(II) | Trimesic acid | Cu | Thiol-modified silica | Fish, sediment, water | d-SPE | CV-AAS | 91–102 | 0.02 | - | [78] |
| 3′5,5′-azobenzenetetracarboxylic acid | Cu | - | Tea, mushrooms | d-SPE | AFS | Average 93.3 | >0.58 mg kg−1 | Up to 3 times | [84] | |
| Benzoic acid and meso-tetrakis(4-Carboxyphenyl)porphyrin | Zr | - | Fish | PT-SPE | CVAAS | 74.3–98.7 | 20 × 10−3 | At least 15 times | [76] | |
| Cu (II) | Aminoterephthalic acid | Zn | Fe3O4 | Water | MSPE | ETAAS | 98–102 | 0.073 | [29] | |
| Cd(II) | Terephthalic acid | Fe | Fe3O4@MAA, AMSA | Water | MSPE | FAAS | >96 | 0.04 | Up to 10 times | [85] |
| Th(IV) | 2 –hydroxyterephthalic acid | Zr | - | Water | d-SPE | Spectrophotometry | >90 | 0.35 | At least 25 times | [86] |
| [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid | Eu | - | Water | Probe | UV | N.A. | 24.2 | N.A. | [87] | |
| U(VI) | 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyltriimino)tris-benzoic acid | Te | - | Water | d-SPE | ICP-MS | 94.2–98.0 | 0.9 | At least 3 times | [88] |
| Se(IV), Se(VI) | Terephthalic acid | Cr | Fe3O4@dithiocarbamate | Water, agricultural samples | MSPE | ETAAS | >92 | 0.01 | Up to 12 times | [89] |
| Cd(II), Pb(II) | Trimesic acid | Cu | Fe3O4@Py | Fish, sediment water | MSPE | FAAS | 92.0–103.3 | 0.2–1.1 | - | [90] |
| Cd(II) Pb(II) Ni(II) | Trimesic acid | Cu | Fe3O4@TAR | Sea food, agricultural samples | MSPE | FAAS | 83–112 | 0.15–0.8 | - | [91] |
| Cd(II), Pb(II), Zn(II) Cr(III) | Trimesic acid | Cu | Fe3O4-benzoyl isothiocyanate | Vegetables | MSPE | FAAS | 80–114 | 0.12–0.7 | - | [54] |
| Terephthalic acid | Fe | Fe3O4-ethylenediamine | Agricultural samples | MSPE | FAAS | 87.3–110 | 0.15–0.8 | - | [92] | |
| Cd(II), Pb(II), Ni(II), Zn(II) | Trimesic Acid | Cu | Fe3O4@DHz | Fish, sediment, soil, water | MSPE | FAAS | 88–104 | 0.12–1.2 | - | [60] |
| Pb(II), Cu(II) | Trimesic acid | Dy | - | Water | d-SPE | FAAS | 95–105 | 0.26–0.40 | At least 5 times | [55] |
| Cd(II), Co(II), Cr(III), Cu(II), Pb(II) | 4-bpmb | Zn | - | Water | d-SPE | ICP-OES | 90–110 | 0.01–1 | - | [24] |
| Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II), Cr(III), Mn(II) | 4,4′-oxybisbenzoic acid | Cd | Fe3O4 | Water | MSPE | ICP-OES | >90 | 0.3–1 | - | [93] |
| Hg(II), Cr(VI) Pb(II) Cd(II) | Terephthalic acid | Cu | Dithioglycol | Tea | d-SPE | AFS, AAS | 95–99 | Not mentioned | Up to 3 times | [94] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manousi, N.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Rosenberg, E.; Zachariadis, G.A. Extraction of Metal Ions with Metal–Organic Frameworks. Molecules 2019, 24, 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244605
Manousi N, Giannakoudakis DA, Rosenberg E, Zachariadis GA. Extraction of Metal Ions with Metal–Organic Frameworks. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244605
Chicago/Turabian StyleManousi, Natalia, Dimitrios A. Giannakoudakis, Erwin Rosenberg, and George A. Zachariadis. 2019. "Extraction of Metal Ions with Metal–Organic Frameworks" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244605
APA StyleManousi, N., Giannakoudakis, D. A., Rosenberg, E., & Zachariadis, G. A. (2019). Extraction of Metal Ions with Metal–Organic Frameworks. Molecules, 24(24), 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244605










