A Novel Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing 1,8-Naphthyridine as a High Selectivity and Sensitivity Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
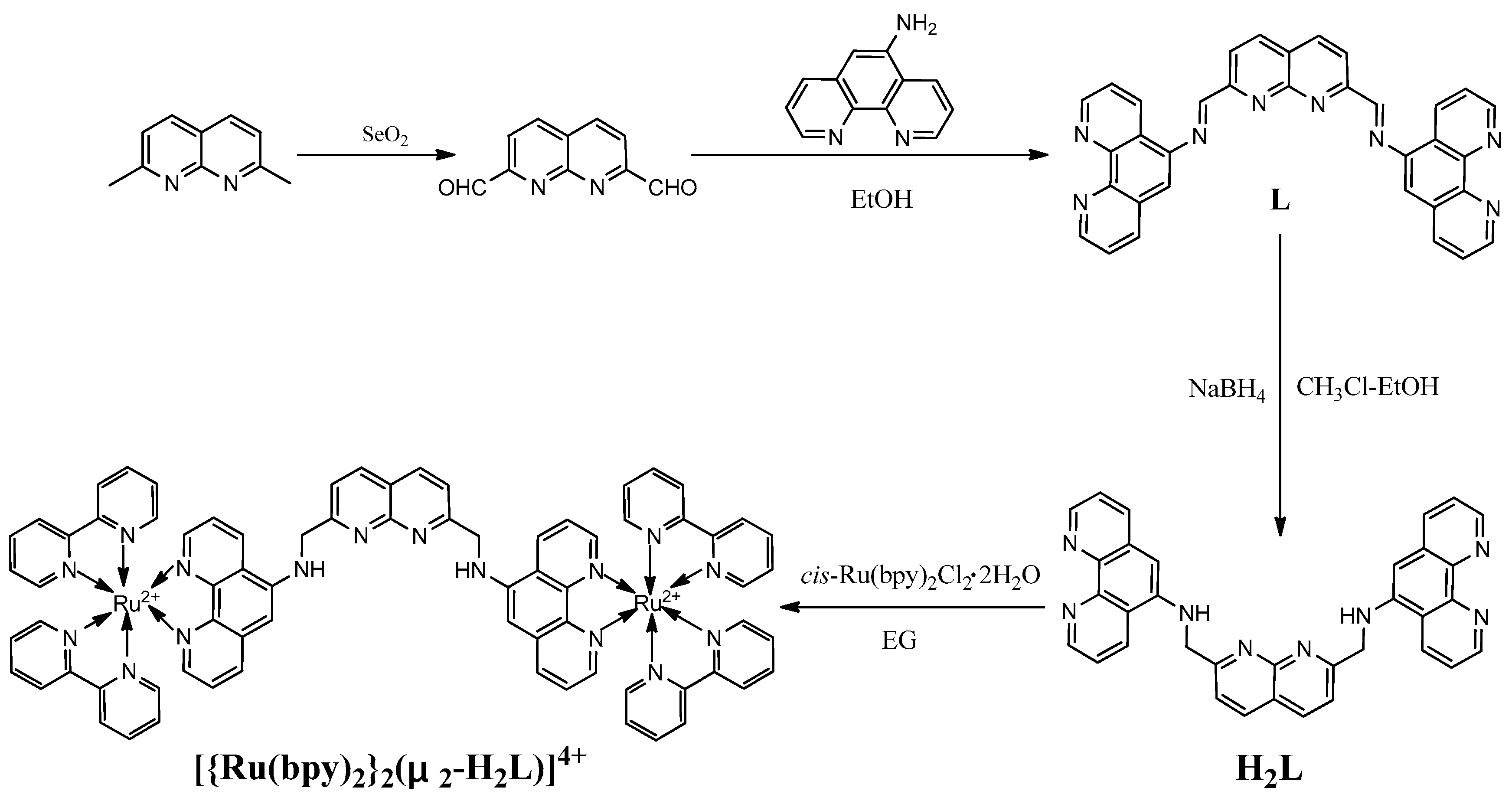
2.3. Synthesis of 1,8-Naphthyridine-2,7-Dicarbaldehyde
2.4. Synthesis of Compound L
2.5. Synthesis of H2L
2.6. Synthesis of [{Ru(bpy)2}2(μ2-H2L)](PF6)4
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
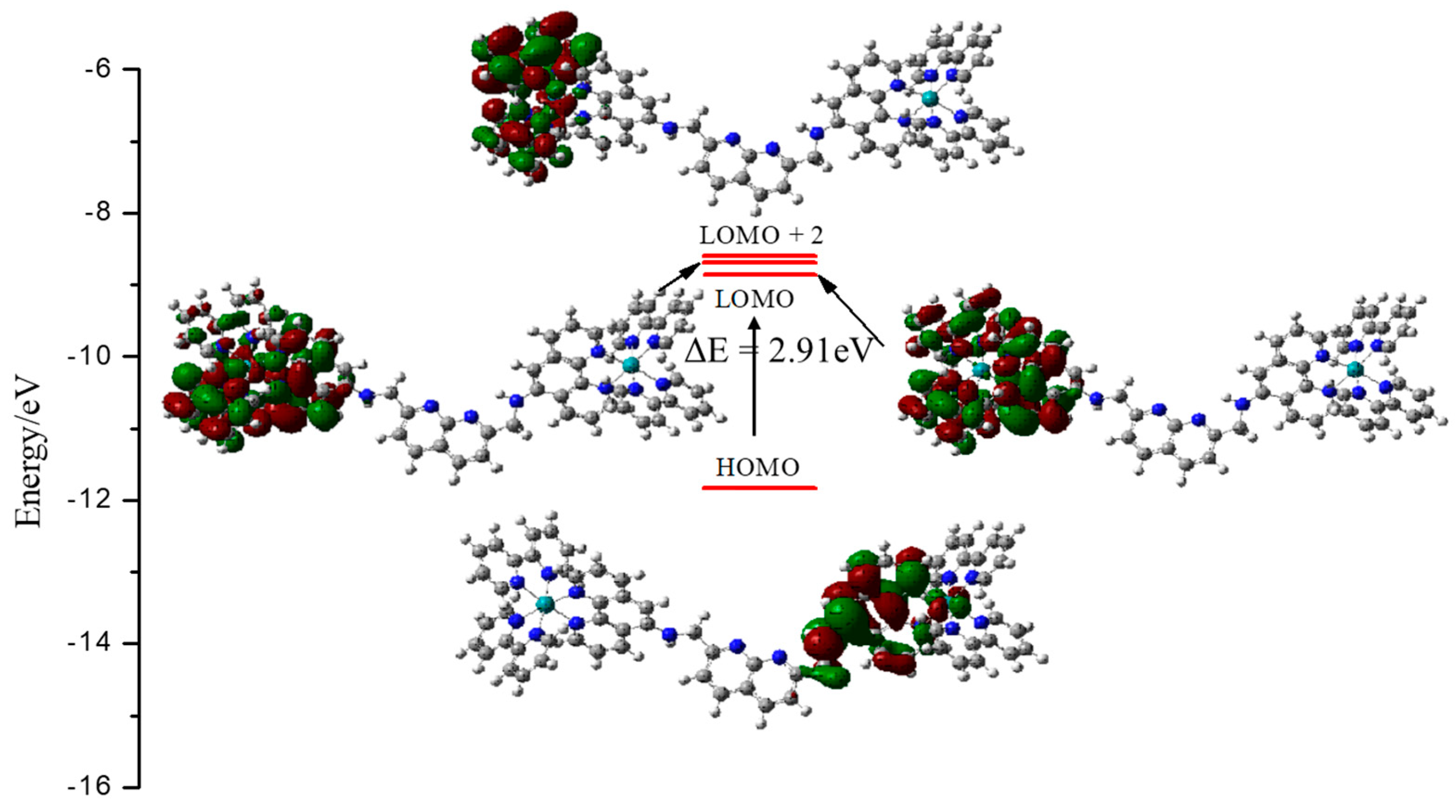
3.2. Computational Studies
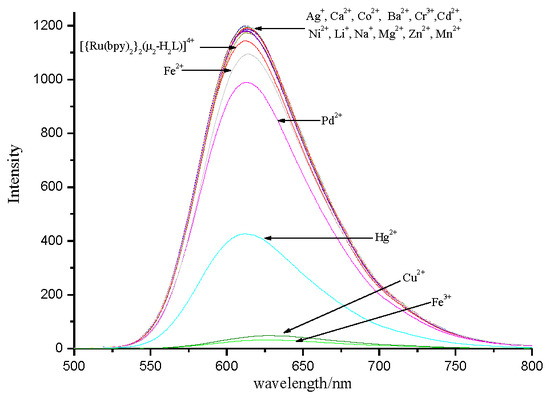
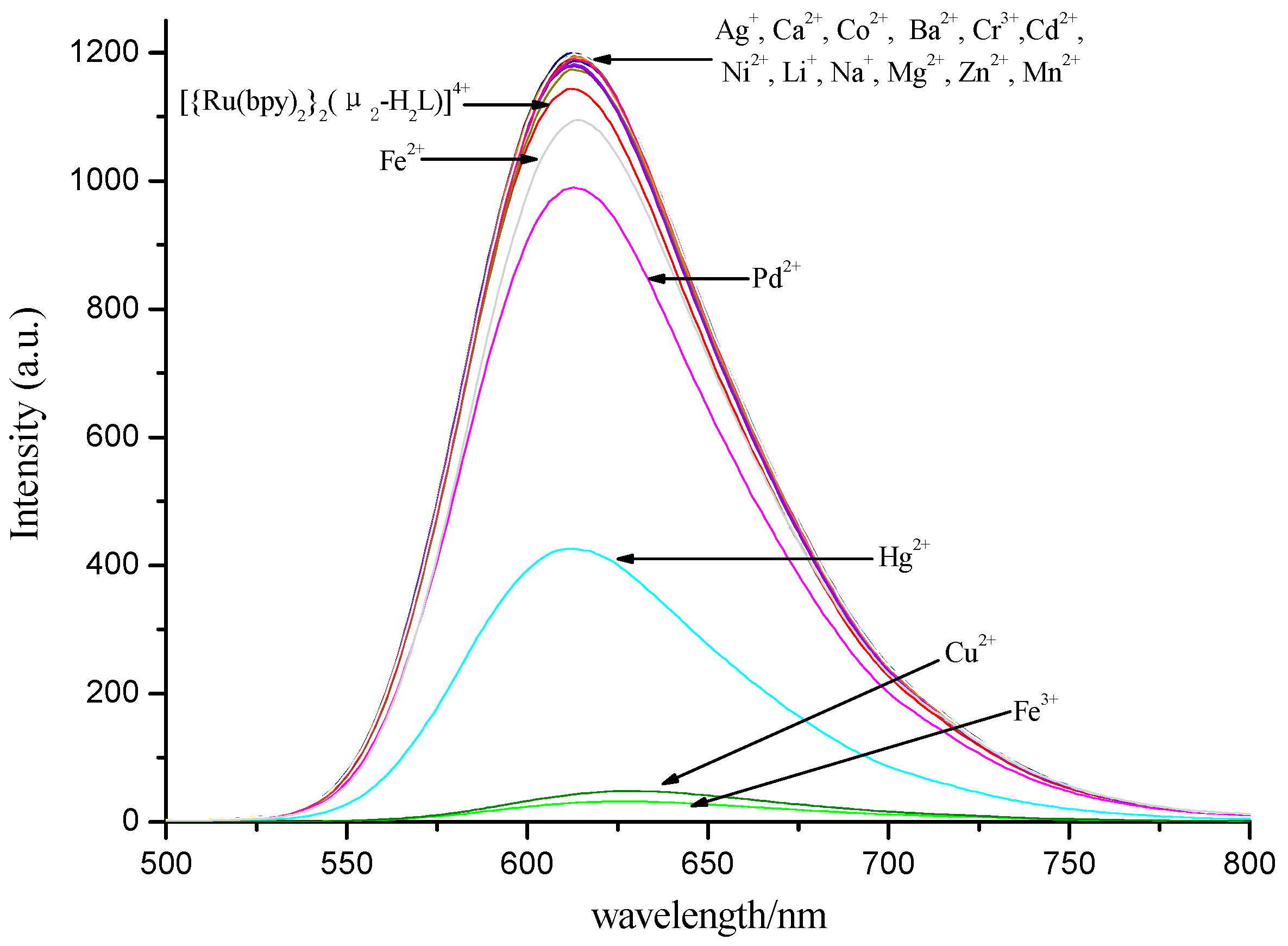
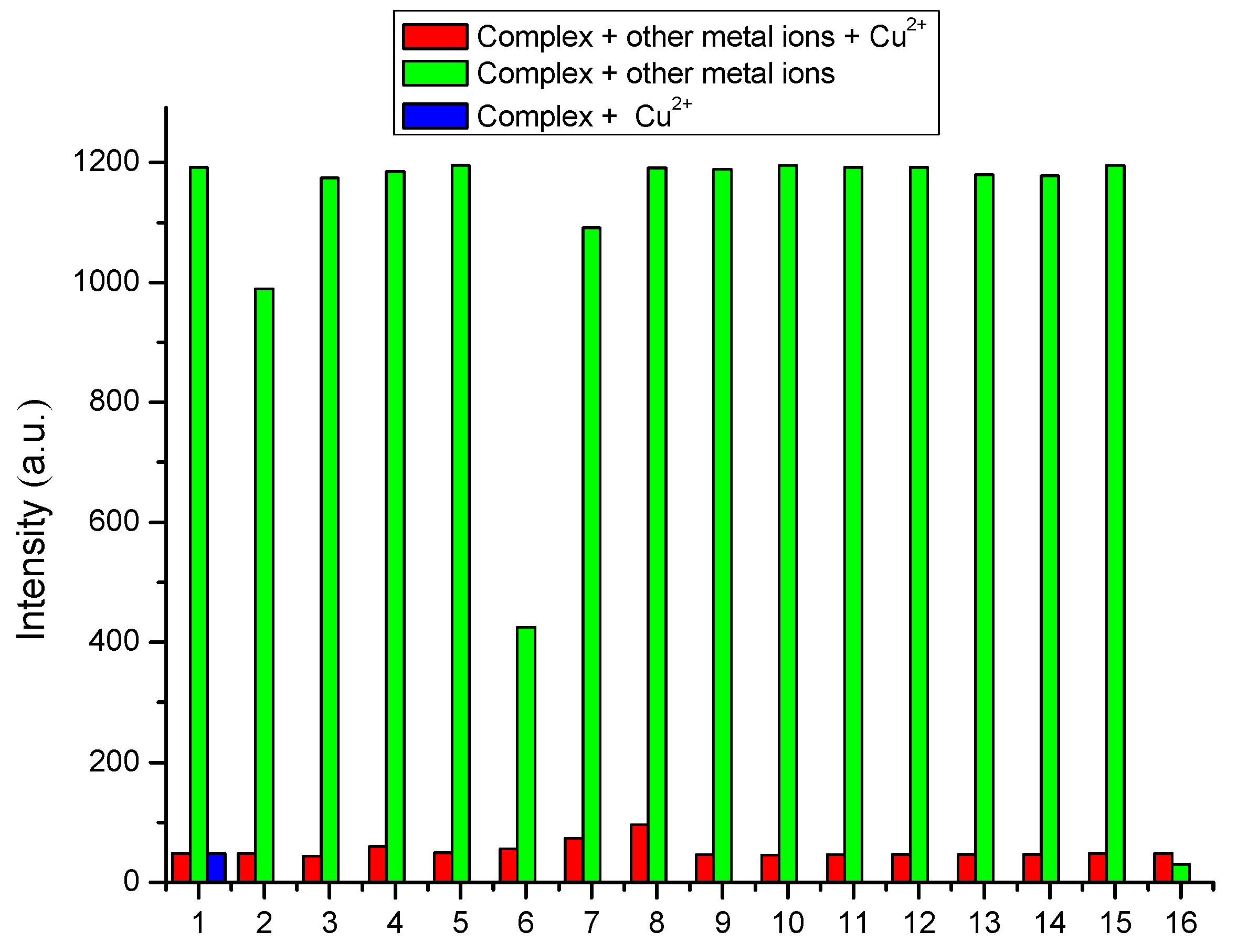
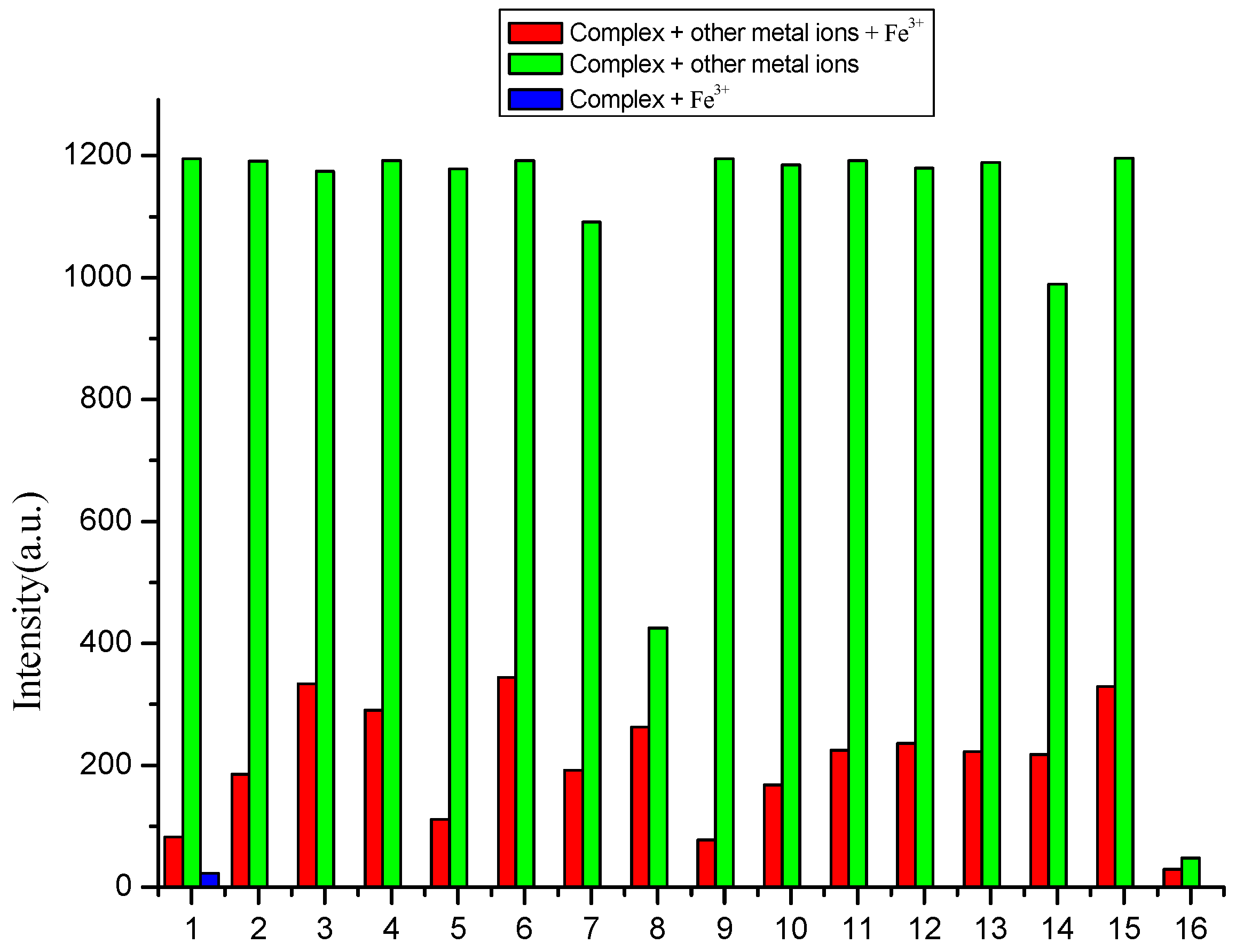
3.3. Selectivity of Complex to Metal Ions
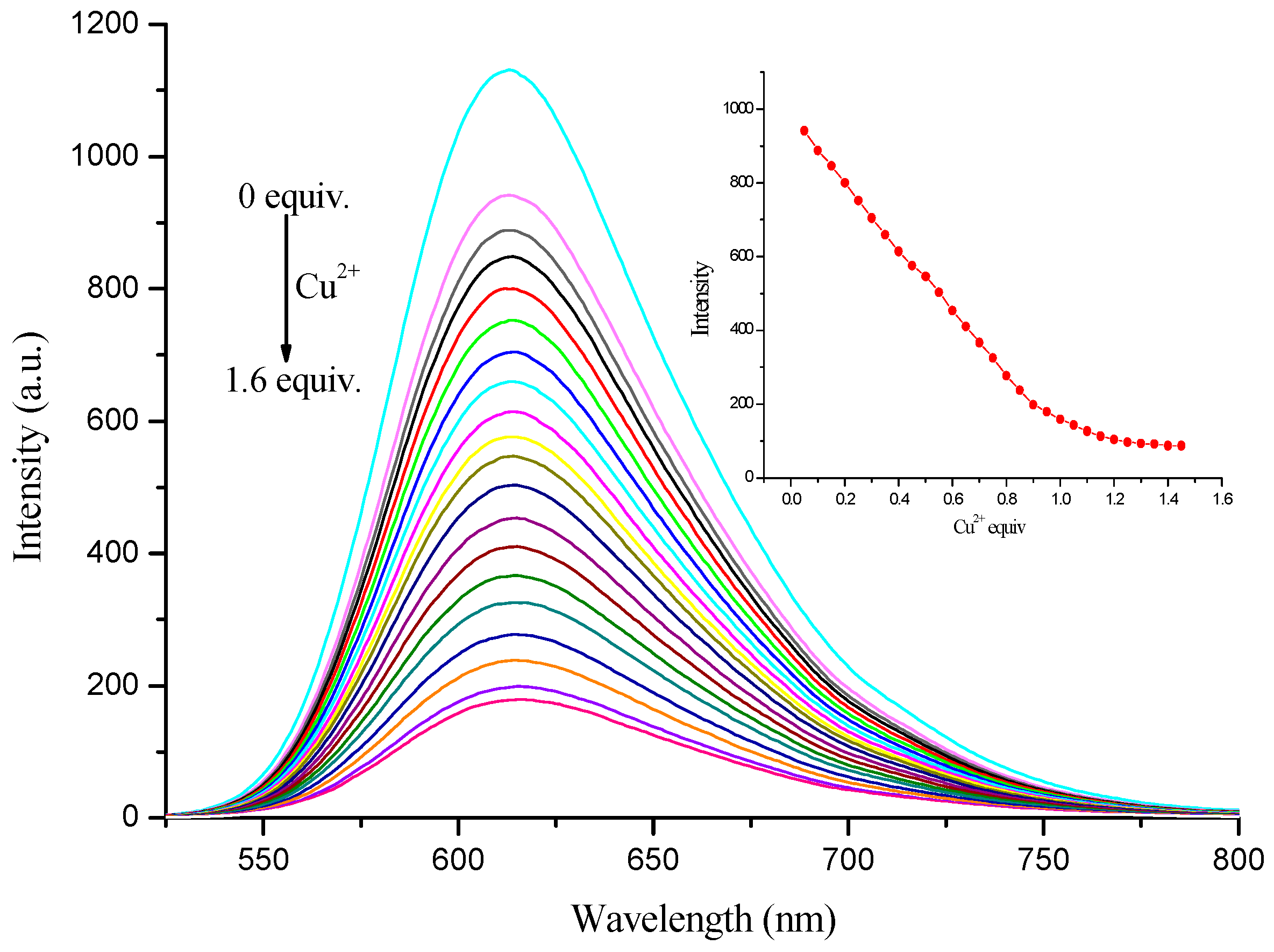
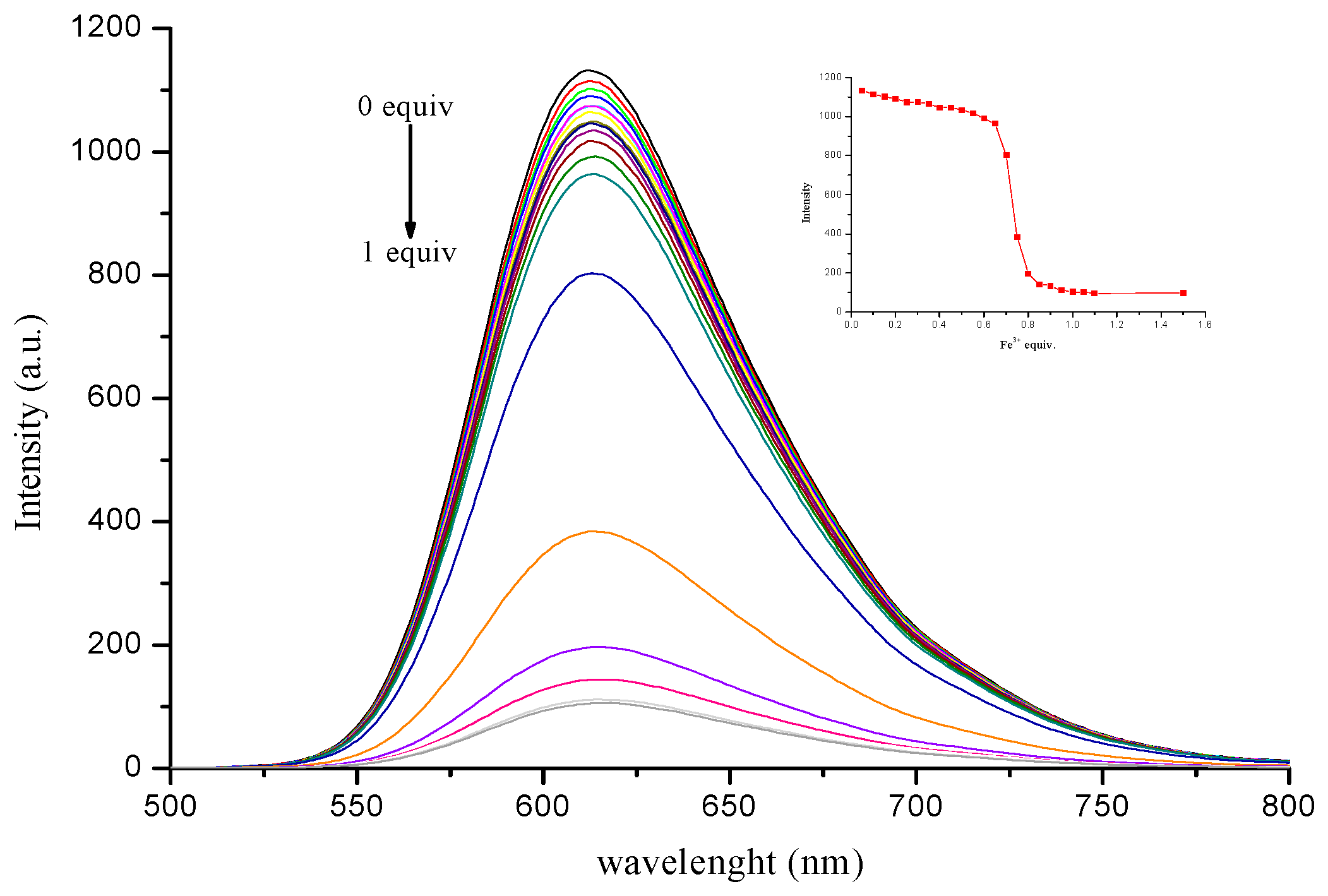
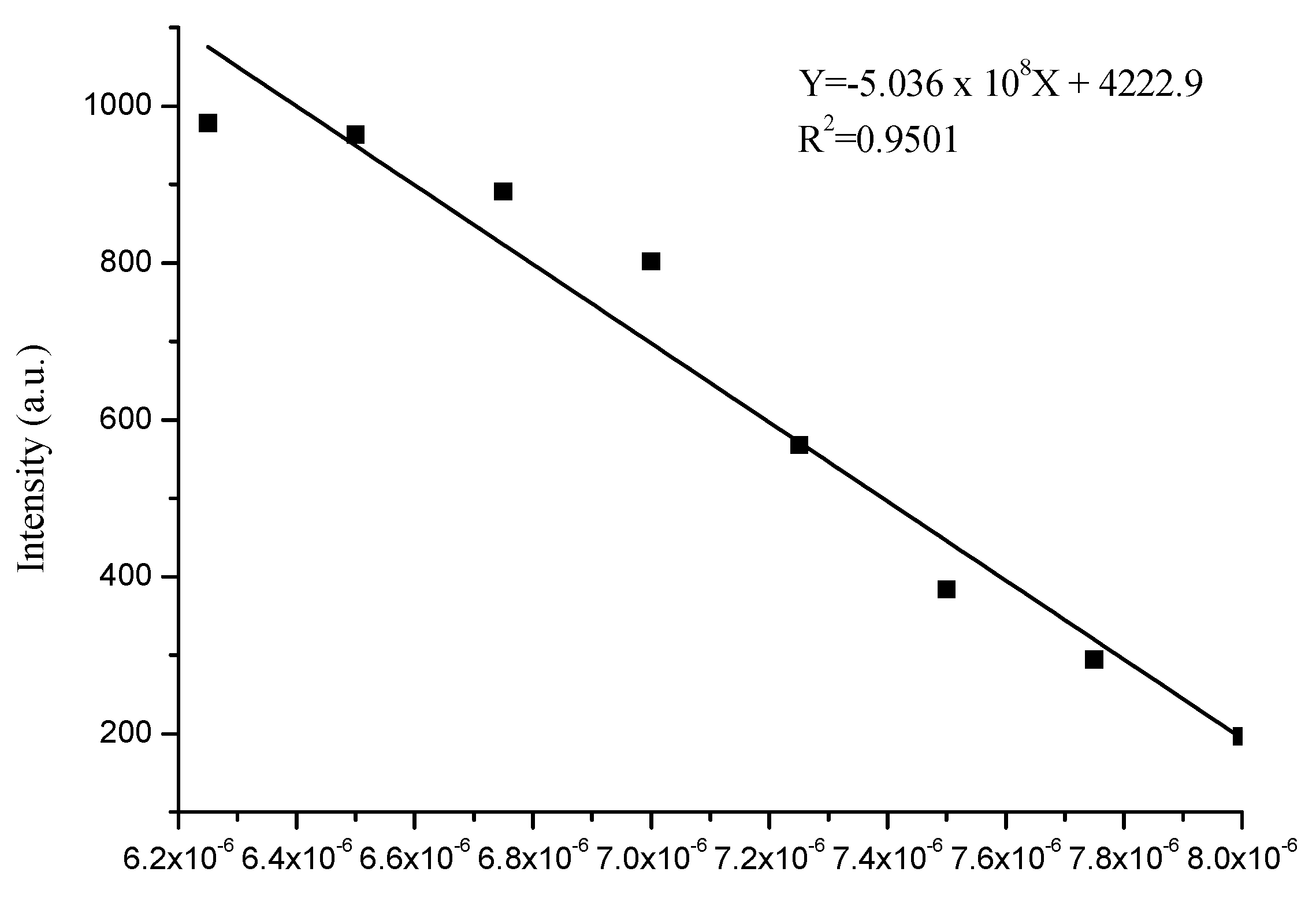
3.4. Sensitivity of Complex to Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions
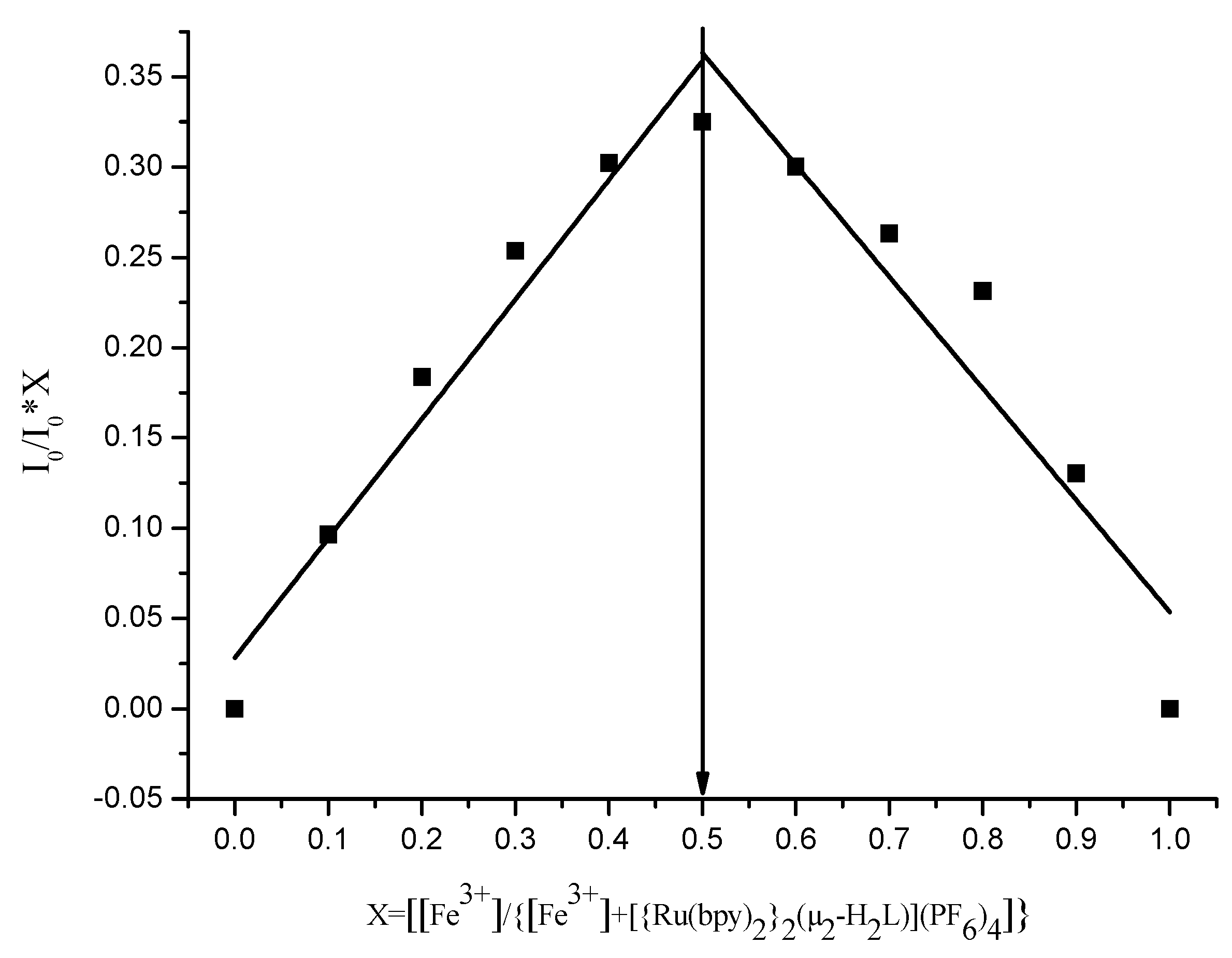
3.5. Mode of Binding with Cu2+ and Fe3+
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frausto da Silva, J.; Williams, R.J.P. The Biological Chemistry of the Elements; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Blake, D.A. Development and validation of a one-step immunoassay for determination of cadmium in human serum. Anal. Chem. 2011, 74, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Xia, S.; Bi, J.; Travis, P.; Wigstrom, T.P.; Valenzano, L.; Wang, J.; Tanasova, M.; Rudy, L.; Luck, R.L.; et al. Detecting Zn(II) ions in live cells with near-infrared fluorescent probes. Molecules 2019, 24, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Fang, M.; Wang, J.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Vegesna, G.; Zhang, S.; Marina Tanasova, M.; Luo, F.T.; et al. Near-infrared fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of Pb(II) ions in living cells. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2017, 468, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Theil, E.C. Ferritins: Dynamic management of biological iron and oxygen chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silvaand, J.J.R.F.; Williams, R.J.P. In the Biological Chemistry of the Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Gunlaugsson, T.; Huxley, A.J.M.; McCoy, C.P.; Rademacher, J.T.; Rice, T.E. Signaling recognition events with fluorescent sensors and switches. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1515–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mense, S.M.; Zhang, L. Heme: A versatile signaling molecule controlling the activities of diverse regulators ranging from transcription factors to MAP kinases. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domink, H.; Svetlana, L. Wilson disease: Not just a copper disorder. Analysis of a Wilson disease model demonstrates the link between copper and lipid metabolism. Mol. Biosyst. 2007, 3, 816–824. [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos, P.G.; Roy, A.; Yonone-Lioy, M.J.; Opiekun, R.E.; Lioy, P.J. Environmental copper: Its dynamics and human exposure issues. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2001, 4, 341–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, L.; Reddy, M.L.P.; Varma, R.L. Dansyl-styrylquinoline conjugate as divalent iron sensor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6626–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.P.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, J.P.; Chen, S.; Hu, Z.Q. Fluorescent probe for Fe(III) with high selectivity and its application in living cells. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 252, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitteland, M.; Lin, H. Quadruple-channel sensing: A molecular sensor with a single type of receptor site for selective and quantitative multi-ion analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ye, D.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Ni, L. Fluorescent and colorimetric detection of Fe(III) and Cu(II) by a difunctional rhodamine-based probe. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2017, 183, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayakumar, G.; Sreenath, K.; Gopidas, K.R. Phenothiazine attached Ru(bpy)32+ derivative as highly selective turn-ON luminescence chemodosimeter for Cu2+. Dalton Trans. 2009, 21, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.; Váradi, L.; Trinchi, A.; Suzie, M.; Reichman, S.M.; Bao, L.; Lan, M.; Wei, G.; Ivan, S.; Cole, I.S. The design and synthesis of fluorescent coumarin derivatives and their study for Cu2+ sensing with an application for aqueous Soil extracts. Molecules 2019, 24, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, T.; Ma, F.; Li, T.; Niu, Q. A novel fluorescent and colorimetric dual-channel sensor for the fast, reversible and simultaneous detection of Fe3+ and Cu2+ based on terthiophene derivative with high sensitivity and selectivity. J. Photoch. Photobiol. A 2019, 383, 111982–111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, K. Photophysics, photochemistry and solar energy conversion with tris(bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) and its analogs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1982, 46, 159–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Waraksa, C.C.; Lean, J.T.; Lewis, B.A.; Mallouk, T.E. Photocatalytic water oxidation in a buffered Tris(2,2′-bipyridyl) ruthenium complex-colloidal IrO2 system. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 5275–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, R.M.; Su, R.; Faddab, A.A.; Etmanb, H.A.; Tawfik, E.H.; El-Shafei, A. Effect of terthiophene spacer position in Ru(II) bipyridyl complexes on the photocurrent and photovoltage for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigments 2018, 156, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medved’ko, A.V.; Ivanov, V.K.; Kiskin, M.A.; Sadovnikov, A.A.; Apostolova, E.S.; Grinberg, V.A.; Emets, V.V.; Chizhov, A.O.; Nikitin, O.M.; Magdesieva, T.V.; et al. The design and synthesis of thiophene-based ruthenium(II) complexes as promising sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigments 2017, 140, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Sakai, K.; Ozawa, H. A new class of molecular-based photoelectrochemical cell for solar hydrogen production consisting of two mesoporous TiO2 Electrodes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Portillo, A.; Baldoví, H.G.; Carbonell, E.; Navalón, S.; Álvaro, M.; García, H.; Ferrer, B. Ruthenium(II) tris(2,2′-bipyridyl) complex incorporated in UiO-67 as photoredox catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 29190–29199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, H. Reduced graphene oxide-immobilized tris(bipyridine) ruthenium(II) complex for efficient visible-light-driven reductive dehalogenation reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12141–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Thummel, R.P. Mononuclear ruthenium polypyridine complexes that catalyze water oxidation. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6591–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabten, W.; Kärkaäs, M.D.; Åkermark, T.; Chen, H.; Liao, R.; Tinnis, F.; Sun, J.; Siegbahn, P.E.M.; Andersson, P.G.; Åkermark, B. Catalytic water oxidation by a molecular ruthenium complex: Unexpected generation of a single-site water oxidation catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 4611–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, K. pH-switchable Off-On-Off near-infrared luminescence based on a dinuclear ruthenium(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4775–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X. Selective visualization of the endogenous peroxynitrite in an inflamed mouse model by a mitochondria-targetable two-photon ratiometric fluorescent probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloonan, S.M.; Elmes, R.B.P.; Erby, M.L.; Bright, S.A.; Poynton, F.E.; Nolan, D.E.; Quinn, S.J.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Williams, D.C. Detailed biological profiling of a photoactivated and apoptosis inducing pdppz ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complex in cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4494–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Song, B.; Zhang, R.; Guo, W.; Yuan, J. Development of a novel lysosome-targeted ruthenium(II) complex for phosphorescence/time-Gated luminescence assay of biothiols. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4517–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, D.; Komatsu, H.; Son, A.; Nishimoto, S.; Tanabe, K. Water-soluble phosphorescent ruthenium complex with a fluorescent coumarin unit for ratiometric sensing of oxygen levels in living cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheet, S.K.; Sen, B.; Thounaojam, R.; Aguan, K.; Khatua, S. Ruthenium(II) complex-based luminescent bifunctional probe for Ag+ and phosphate ions: Ag+-assisted detection and imaging of rRNA. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilova, A.L.; Bosnich, B. Principles of mononucleating and binucleating Ligand Design. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 349–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, K.; Sando, S.; Saito, I. Recognition of a single guanine bulge by 2-acylamino-1,8-naphthyridine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoock, C.; Reichert, J.; Schmidtke, M. Fluorescent 1,7-dialkylamino-[1,8]-naphthyridines: Preparation and spectroscopic properties. Molecules 1999, 4, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakataniz, K.; Sando, S.; Kumasawa, H.; Kikuchi, J.; Saito, I. Recognition of guanine-guanine mismatches by the dimeric form of 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12650–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.; Walker, D.D.; Wells, J.; Fox, S. Elaboration of 1,8-naphthyridine-2,7-dicarboxaldehyde into novel 2,7-dimethylimine Derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2002, 829, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, M.A.; Cappo, V.M.; Alexander, C.J.; Good, M.L. Substituted 1,8-naphthyridine complexes of iron(II) and iron(III). Inorg. Chem. 1976, 11, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.J.; Deady, L.W.; Reiss, J.A.; Tzimos, V. The synthesis of macrocyclic polyether-diesters incorporating 1,10-phenanthrolino and 1,8-naphthyridino subunits. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1982, 19, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.P.; Salmon, D.J.; Meyer, T.J. Monomeric and dimeric pyrazole and pyrazolyl complexes of ruthenium. Inorg. Chem. 1978, 17, 3334–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, Q.A.; Xu, R.S.; McCarroll, M.E.; Wang, L.C.; Dyer, D.J. Design and investigation of a series of rhodamine-based fluorescent probes for optical measurements of pH. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3219–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.T.; Li, P.; Liao, C.; Luo, T.; Kou, X.; Xiao, D. A highly sensitive luminescent probe based on Ru(II)-bipyridine complex for Cu2+, l-histidine detection and cellular imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2018, 201, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, S.; Lu, W.; Gao, B.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Jiang, D.; Xu, H.J.; Ma, M.; Cao, F. A novel fluorescence turn off-on nano-sensor for detecting Cu2+ and Cysteine in living cells. J. Photoch. Photobiol. A 2018, 362, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, S.; Ravishankaran, R.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Karande, A.A.; Pombeiro, A.J. Differentially selective chemosensor with fluorescence off−on responses on Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions in aqueous media and applications in pyrophosphate sensing, live cell imaging, and cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 6655–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; He, C.; Ren, M.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y. Two dinuclear Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes with different photophysical and cation recognition properties. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 136, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y. 2-Amino-5-(p-dimethylamino) phenyl-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoleasa selective fluorescent chemosensor for Hg2+. Chem. J. Chin. U. 2008, 29, 2531–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, N.; Hao, C.; Han, Q.; Duan, Y.; Wu, J. A novel fluorescence on-off-on peptide-based chemosensor forsimultaneous detection of Cu2+, Ag+ and S2-. Sens. Actuator B 2019, 280, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qin, W.; Tang, X.; Dou, W.; Liu, W.; Teng, Q.; Yao, X. A selective, cell-permeable fluorescent probe for Al3+ in living cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
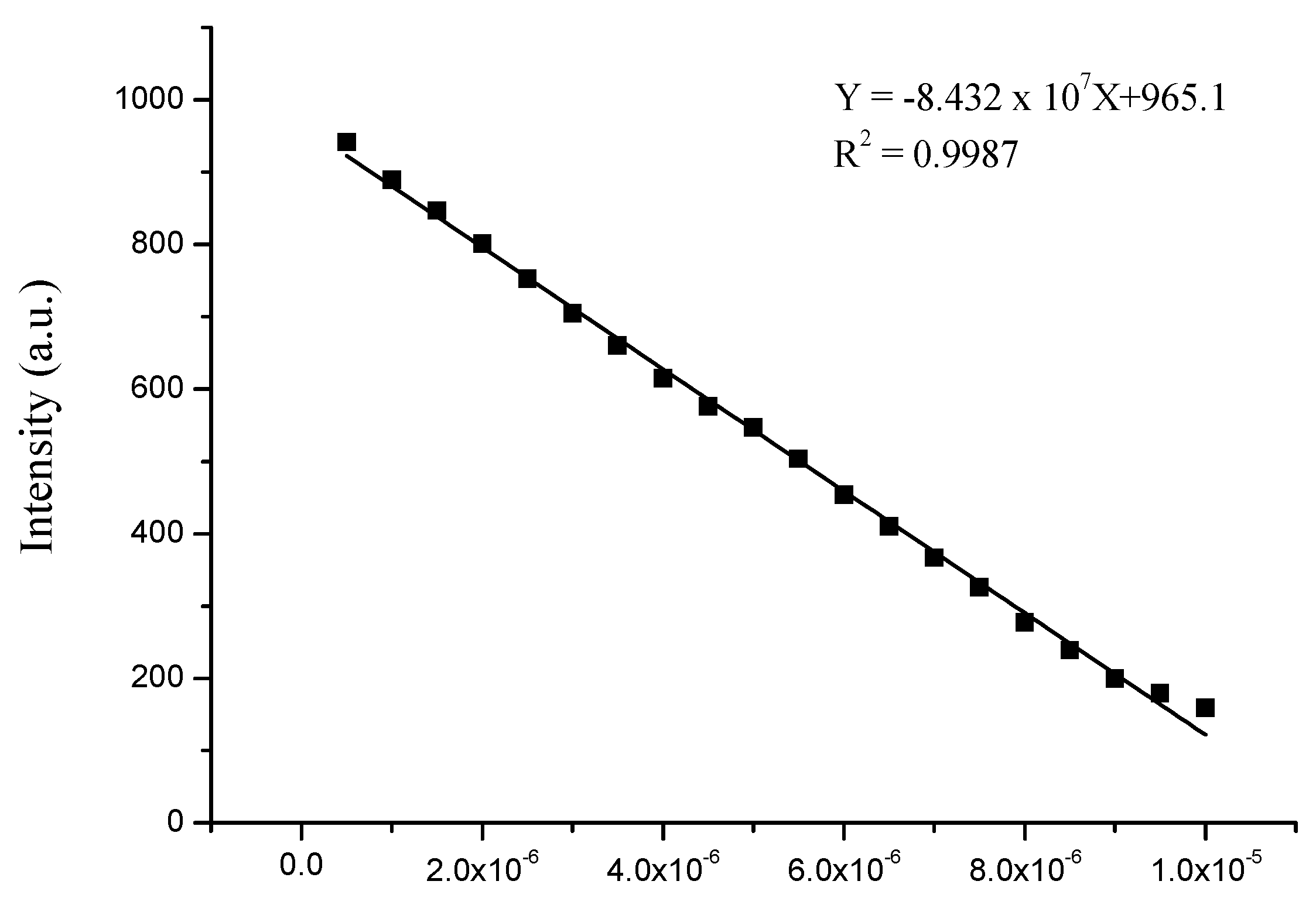
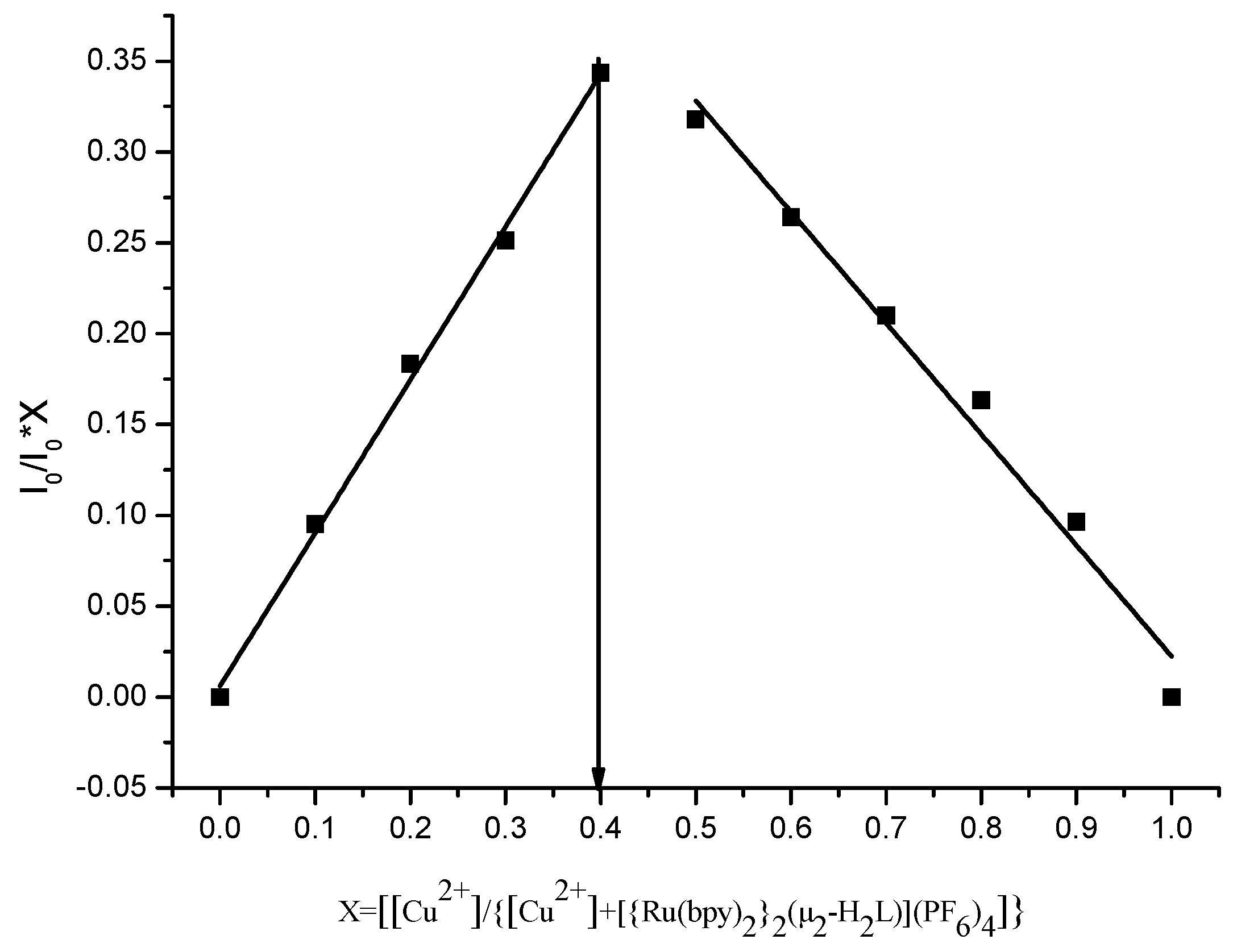
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Yu, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z.; Yao, L.; Cheng, F.; Liu, P. A Novel Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing 1,8-Naphthyridine as a High Selectivity and Sensitivity Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions. Molecules 2019, 24, 4032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224032
He C, Yu S, Ma S, Liu Z, Yao L, Cheng F, Liu P. A Novel Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing 1,8-Naphthyridine as a High Selectivity and Sensitivity Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions. Molecules. 2019; 24(22):4032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chixian, Shiwen Yu, Shuye Ma, Zining Liu, Lifeng Yao, Feixiang Cheng, and Pinhua Liu. 2019. "A Novel Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing 1,8-Naphthyridine as a High Selectivity and Sensitivity Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions" Molecules 24, no. 22: 4032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224032
APA StyleHe, C., Yu, S., Ma, S., Liu, Z., Yao, L., Cheng, F., & Liu, P. (2019). A Novel Ruthenium(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing 1,8-Naphthyridine as a High Selectivity and Sensitivity Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ Ions. Molecules, 24(22), 4032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224032