ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
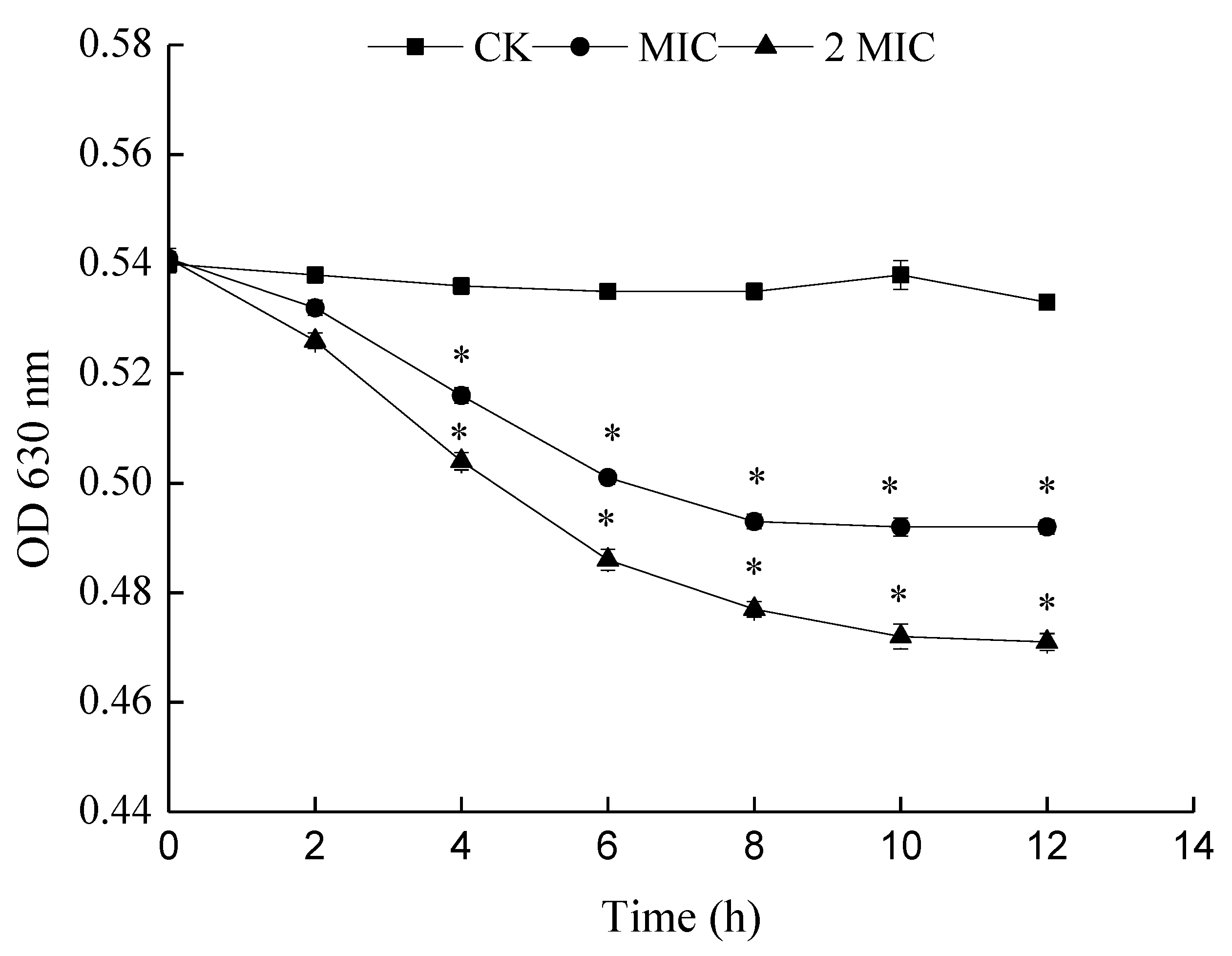
2.2. Growth Curve
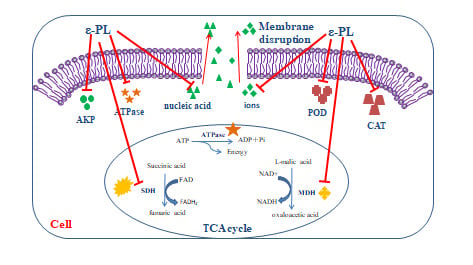
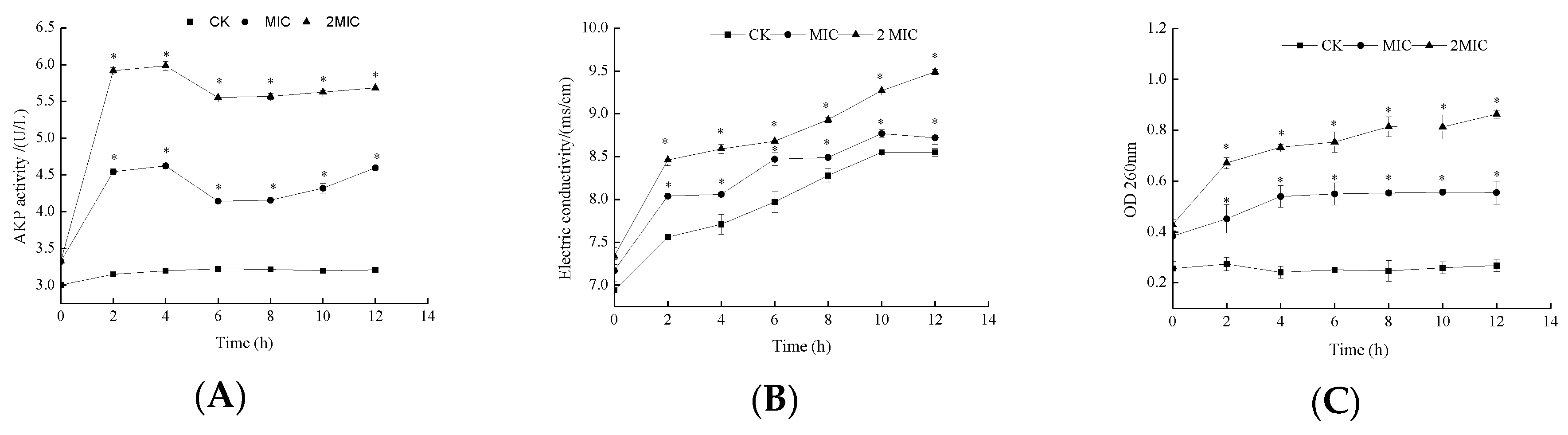
2.3. Characterizations of the Cell Membrane
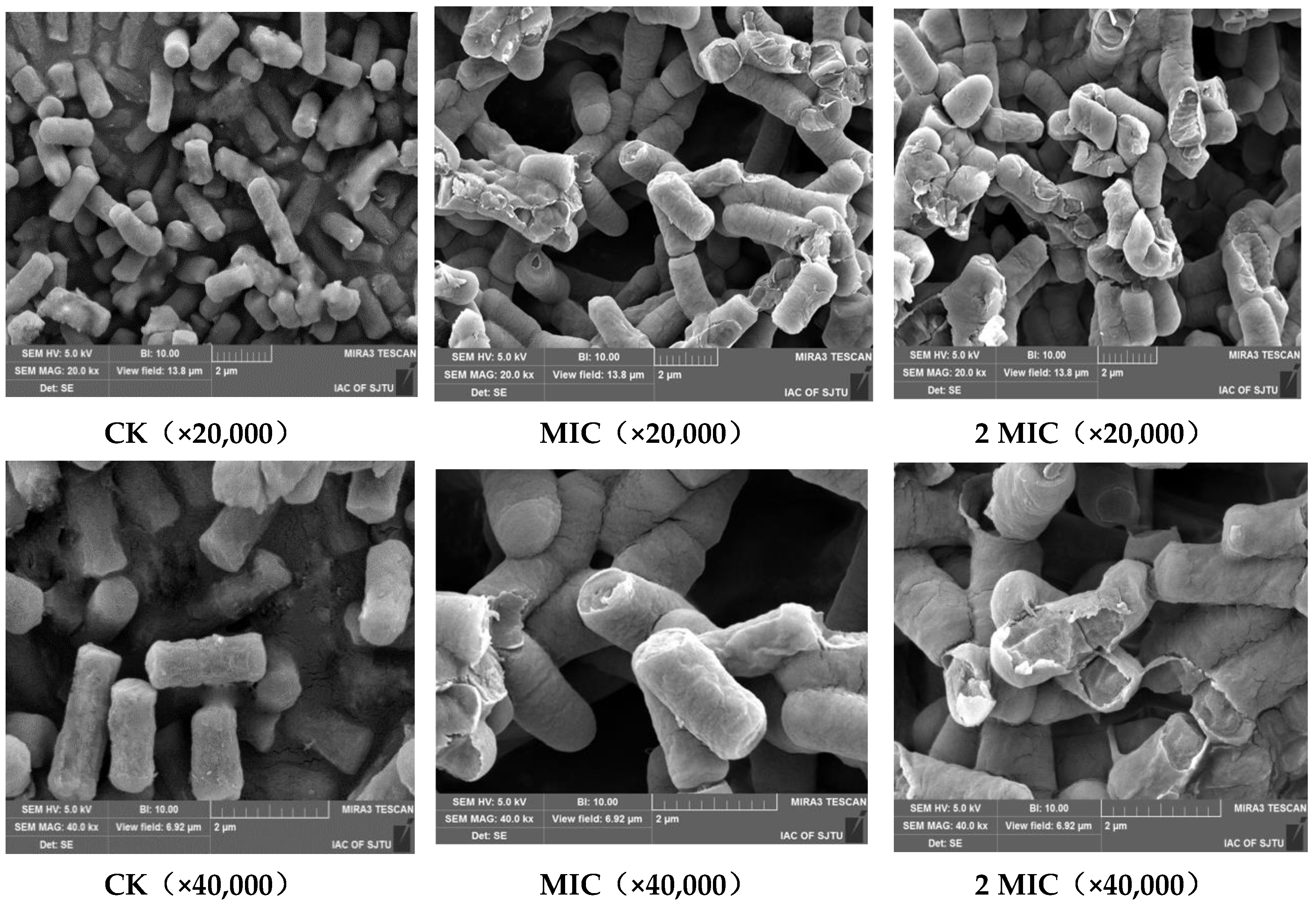
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
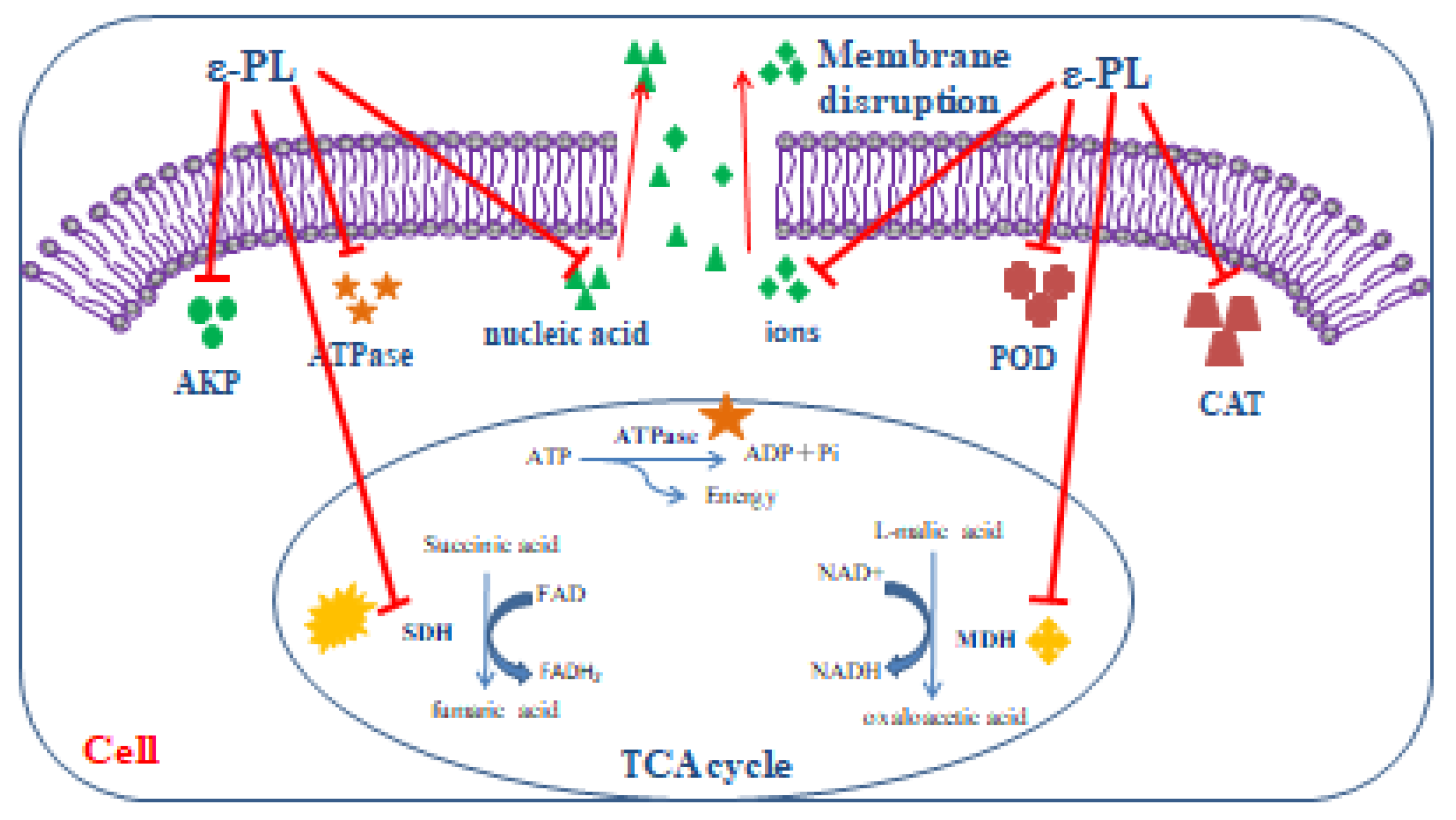
2.5. Effect of ε-PL on Respiratory Metabolism
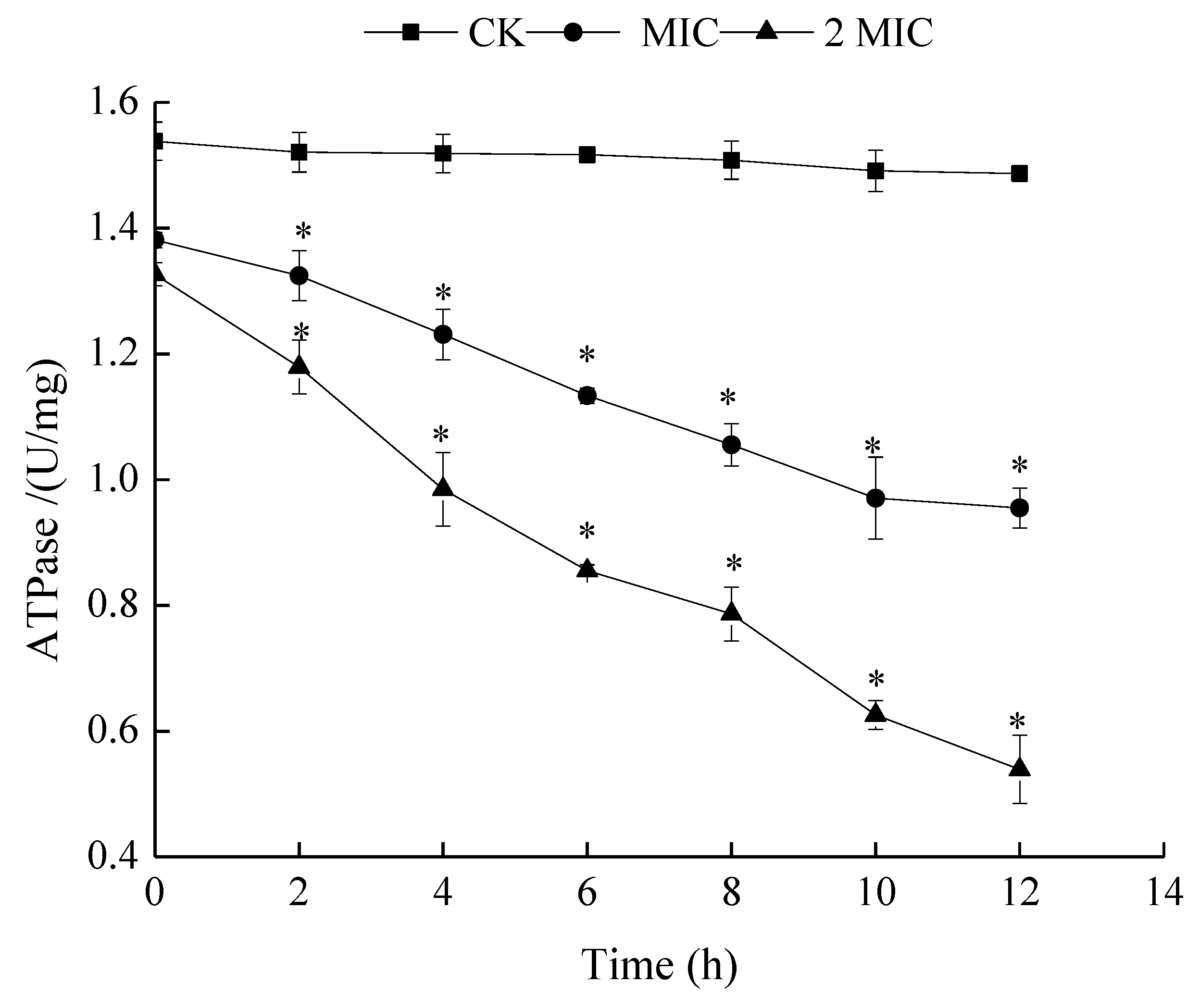
2.5.1. Measurement of ATPase Activities
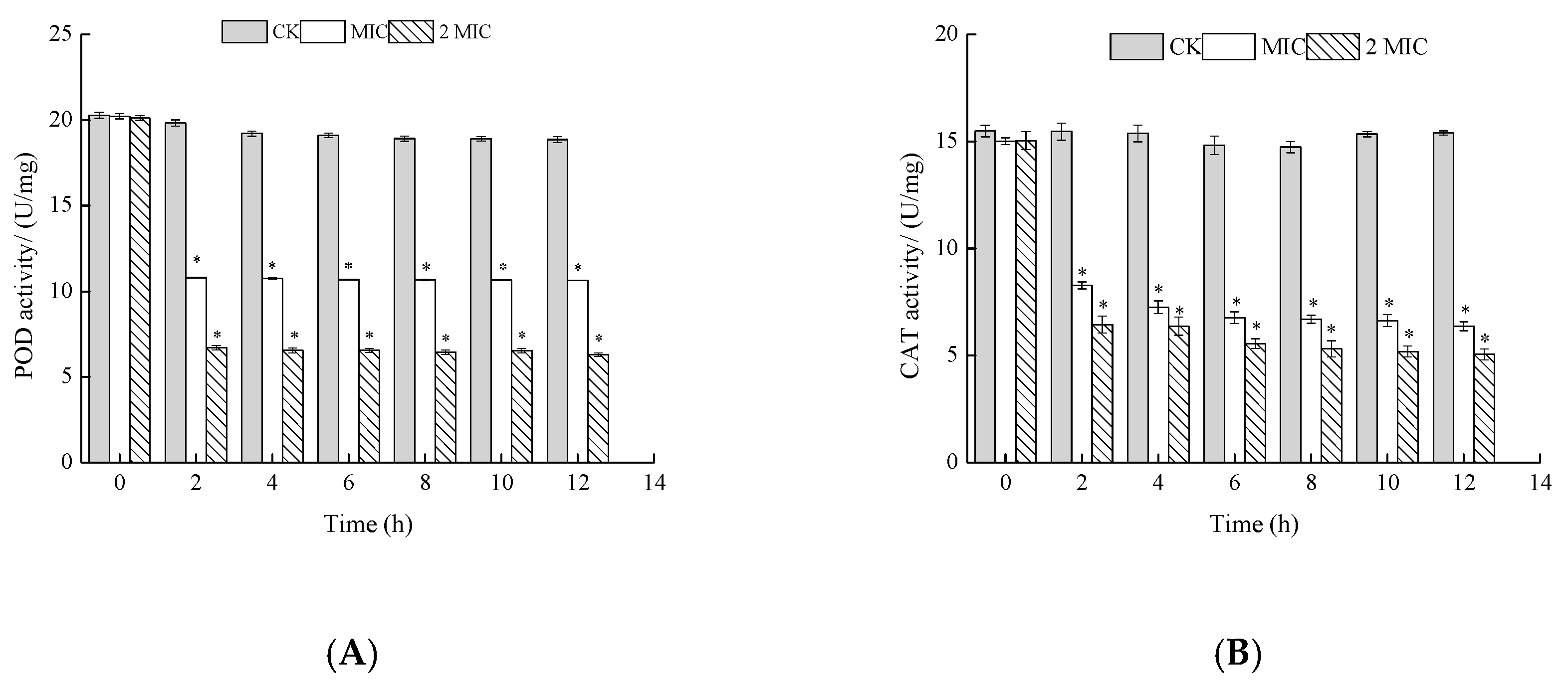
2.5.2. Measurement of Peroxidase (POD) and Catalase (CAT) Activities
2.5.3. Measurement of Succinodehydrogenase (SDH) and Malicdehydrogenase (MDH) Activities
2.5.4. Effect of ε-PL on Cellular Metabolism (Viability)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Culture
3.2. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
3.3. Bacterial Growth Curve
3.4. Effects of ε-PL on the Cell Wall and Membrane Permeability of S. putrefaciens
3.4.1. Alkaline Phosphate (AKP) Activity
3.4.2. Electrical Conductivity (EC) Measurement
3.4.3. Determination of Nucleic Acid Leakage (OD260nm)
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observations
3.6. Effect of ε-PL on Respiratory Metabolism
3.6.1. Measurement of Adenosine Triphosphatase (ATPase)
3.6.2. Measurement of Peroxidase (POD) and Catalase (CAT) Activities
3.6.3. Measurement of Succinodehydrogenase (SDH) and Malicdehydrogenase (MDH) Activities
3.7. Effect of ε-PL on Cellular Metabolism (Viability)
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morten, H.; Tina, M.; Vad, B.S.; Marcel, S.; Otzen, D.E.; Meyer, R.L. The antimicrobial mechanism of action of epsilon-poly-l-lysine. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7758–7770. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, S.; Takahashi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakazawa, M.; Kuda, T.; Koiso, H.; Kimura, B. Development of a controlling method for Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. in fresh market beef by using polylysine and modified atmosphere packaging. Food Control 2014, 37, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, I.-L.; Shen, M.-H.; Van, Y.-T. Microbial synthesis of poly(ε-lysine) and its various applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zong, W. Effect of poly-ε-lysine incorporated into alginate-based edible coatings on microbial and physicochemical properties of fresh-cut kiwifruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 134, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.C.; Singh, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Mishra, A. Review on production and medical applications of ε-polylysine. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Han, Q.; Feng, J.-L.; Tian, W.-L.; Mo, H.-Z. Antibacterial characteristics and mechanisms of ɛ-poly-lysine against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2014, 43, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pei, H.; Han, Z.; Feng, G.; Li, D. The antimicrobial effects and synergistic antibacterial mechanism of the combination of ε-Polylysine and nisin against Bacillus subtilis. Food Control 2015, 47, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingqing, G.; Linglin, F.; Yanbo, W.; Junda, L. Identification and Characterization of Extracellular Cyclic Dipeptides As Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules from Shewanella baltica, the Specific Spoilage Organism of Pseudosciaena crocea during 4 °C Storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11645–11652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, A.; Feng, L.; Gao, H. Quorum sensing signals affect spoilage of refrigerated large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) by Shewanella baltica. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 217, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelegueda, L.I.; Zalazar, A.L.; Gliemmo, M.F.; Campos, C.A. Inhibitory effect and cell damage on bacterial flora of fish caused by chitosan, nisin and sodium lactate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Guo, Q.Y.; Wei, S.; Li, B.G.; Zhang, G.W. Inhibitory effects of chitosan combined with nisin on Shewanella spp. isolated from Pseudosciaena crocea. Food Control 2017, 79, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Hong, Y.L.; Cai, J.H.; Wei, Q.Q.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y.T.; Liu, Z.F.; Liu, L. Antimicrobial effect and mechanism of cinnamon oil and gamma radiation on Shewanella putrefaciens. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3353–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Lan, W.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Xie, J. Antibacterial mechanism of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract when applied to Shewanella putrefaciens and Saprophytic staphylococcus. Aquac. Fish. 2018, 3, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinai Chittezham, T.; Sadykov, M.R.; Chaudhari, S.S.; Joselyn, J.; Endres, J.L.; Widhelm, T.J.; Jong-Sam, A.; Jawa, R.S.; Zimmerman, M.C.; Bayles, K.W. A central role for carbon-overflow pathways in the modulation of bacterial cell death. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004205. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, A.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q. Synergistic effect of the combined bio-fungicides ε-poly-l-lysine and chitooligosaccharide in controlling grey mould (Botrytis cinerea) in tomatoes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 276, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Gu, Y.; Li, C.; Vittayapadung, S.; Cui, H. Antibacterial mechanism of ε-Poly-lysine against Listeria monocytogenes and its application on cheese. Food Control 2018, 91, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, W.; Dou, Z.M.; Chen, R.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, H. Antimicrobial effect of black pepper petroleum ether extract for the morphology of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.G.; Liu, T.; Hu, Q.P.; Cao, X.M. Chemical Composition, Antibacterial Properties and Mechanism of Action of Essential Oil from Clove Buds against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2016, 21, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Qi, D.; Xu, M.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of monolauroyl-galactosylglycerol against Bacillus cereus. Food Control 2018, 85, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Quek, S.Y. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2016, 59, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, S.; Xu, J.; Ye, H. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus membrane. Food Control 2015, 47, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.H.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, J.I.; Yim, M.J.; Jeon, J.M.; Kim, H.W.; Son, K.T.; Je, J.Y. The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9795–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filomena, N.; Florinda, F.; Laura, D.M.; Raffaele, C.; Vincenzo, D.F. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Q.; Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Tian, P. Multipath effects of berberine on peach Brown rot fungus Monilinia fructicola. Crop Prot. 2019, 116, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, K.; Song, Z.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; Yuan, L.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Guo, Z.; Chen, G. Antioxidative response of Phanerochaete chrysosporium against silver nanoparticle-induced toxicity and its potential mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Xia, H.; Su, X.; Peng, L.; Pan, S. Use of active extracts of poplar buds against Penicillium italicum and possible modes of action. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Mendoza, J.; Cajal-Medrano, R.; Maske, H. INT (2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-Nitrophenyl)-5-(Phenyl) Tetrazolium Chloride) Is Toxic to Prokaryote Cells Precluding Its Use with Whole Cells as a Proxy for In Vivo Respiration. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.-q.; Pan, X.-h.; Lu, Y.-h.; Cao, P. Antibacterial effects of cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) bark essential oil on Porphyromonas gingivalis. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-h.; Zhou, T.-t.; Wei, C.-h.; Lan, W.-q.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.-j.; Wu, V.C.H. Antibacterial effect and mechanism of anthocyanin rich Chinese wild blueberry extract on various foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2018, 94, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LAN, W.; ZHANG, N.; LIU, S.; CHEN, M.; XIE, J. ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage. Molecules 2019, 24, 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203727
LAN W, ZHANG N, LIU S, CHEN M, XIE J. ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203727
Chicago/Turabian StyleLAN, Weiqing, Nannan ZHANG, Shucheng LIU, Mengling CHEN, and Jing XIE. 2019. "ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203727
APA StyleLAN, W., ZHANG, N., LIU, S., CHEN, M., & XIE, J. (2019). ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage. Molecules, 24(20), 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203727