Purification, Characterization, and Application for Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides of Extracellular Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. H2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
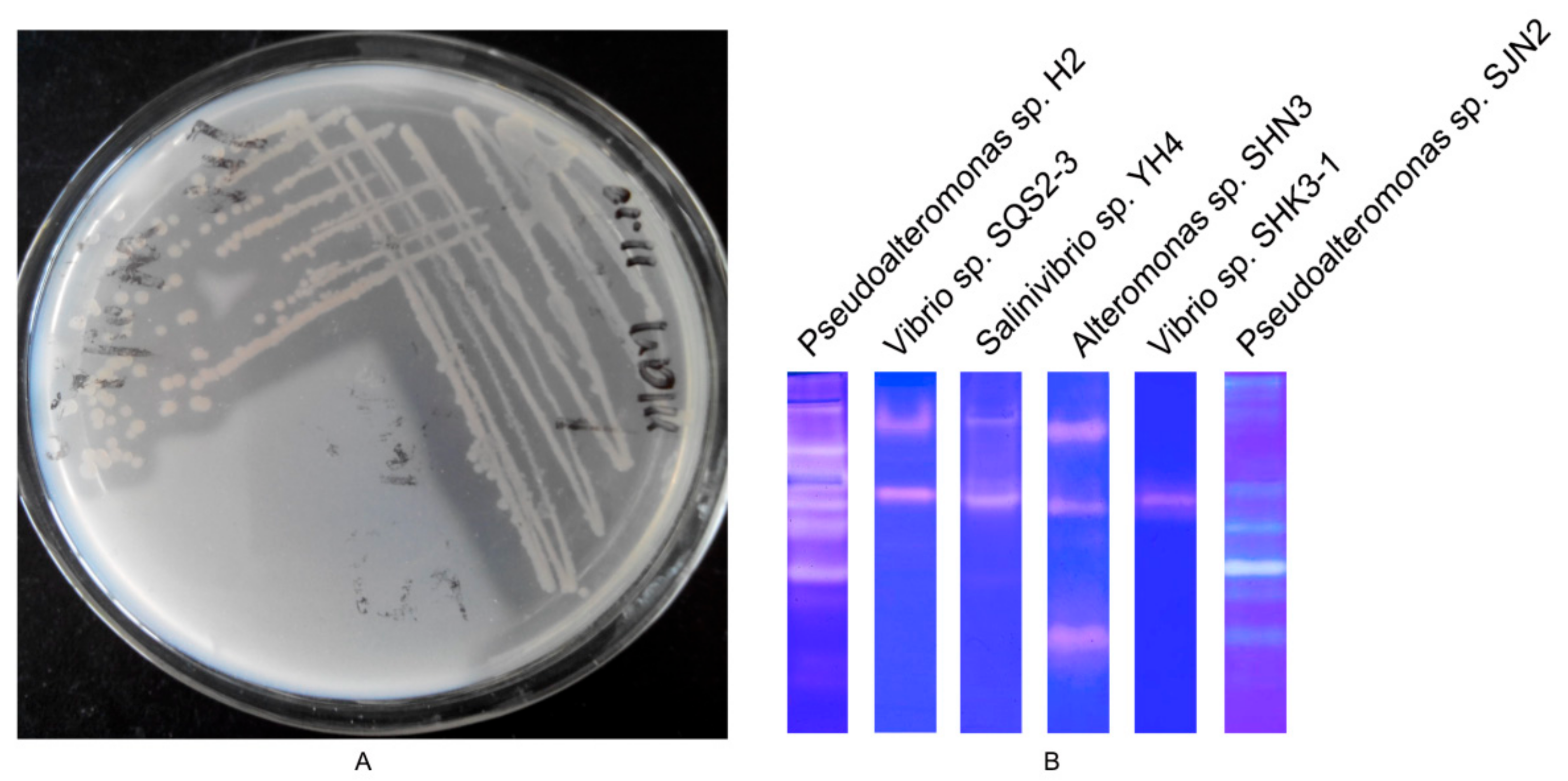
2.1. Screening of Strain with High Protease-Producing Ability
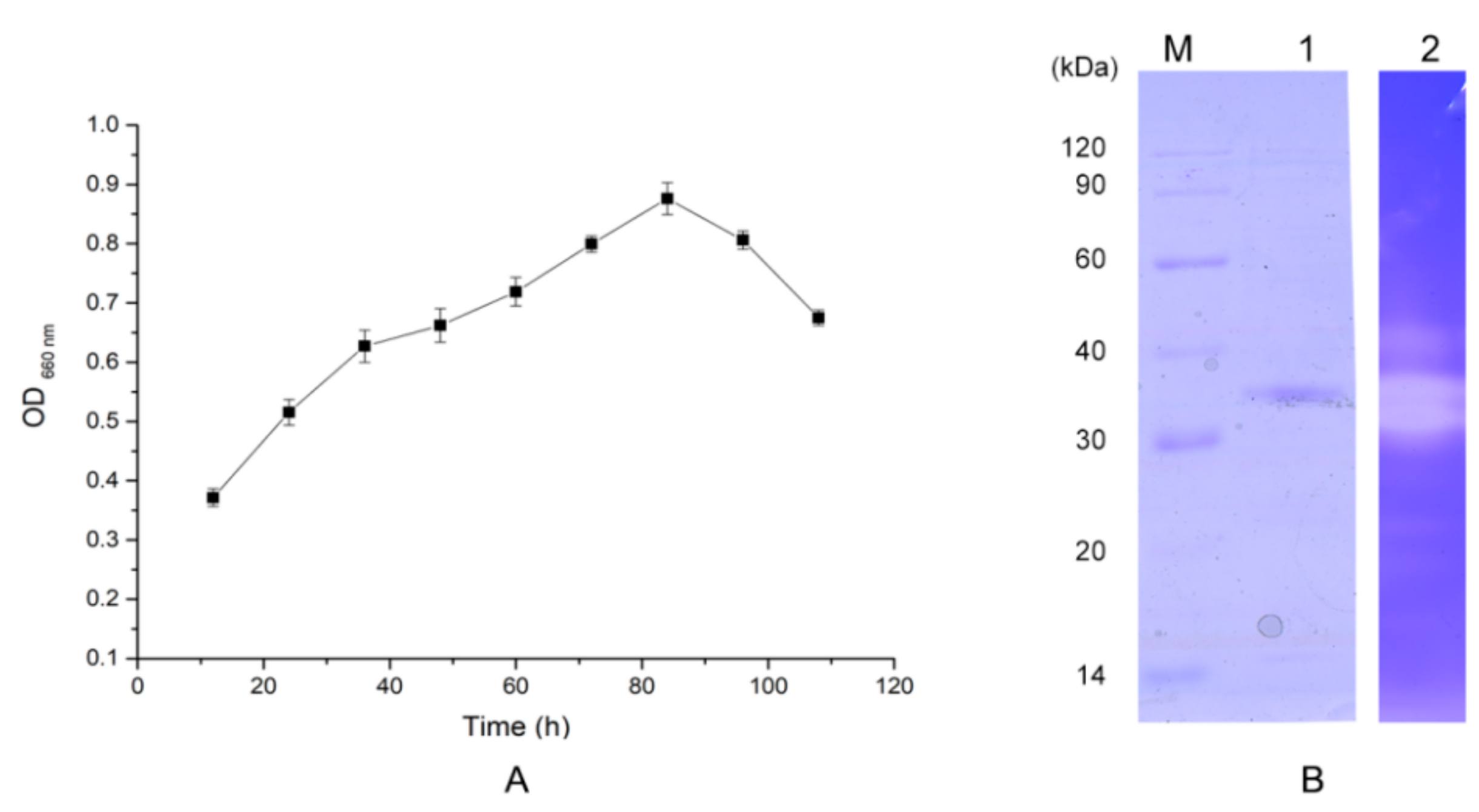
2.2. Protease Production and Purification
2.3. Characterization of EH2
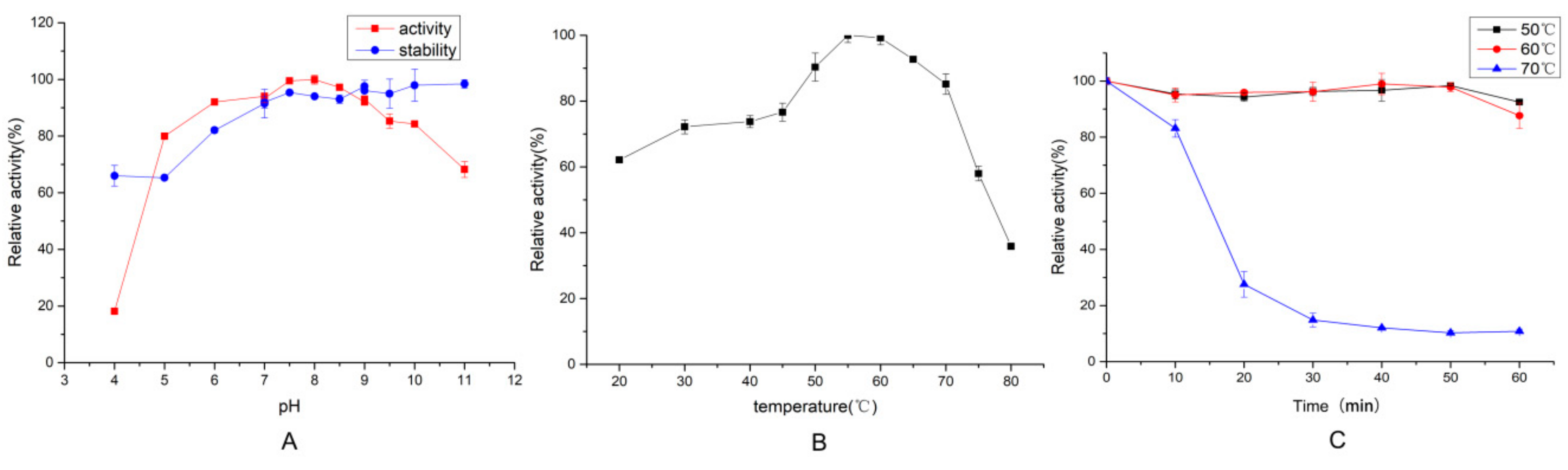
2.3.1. Effect of Temperature and pH on Protease Activity and Stability
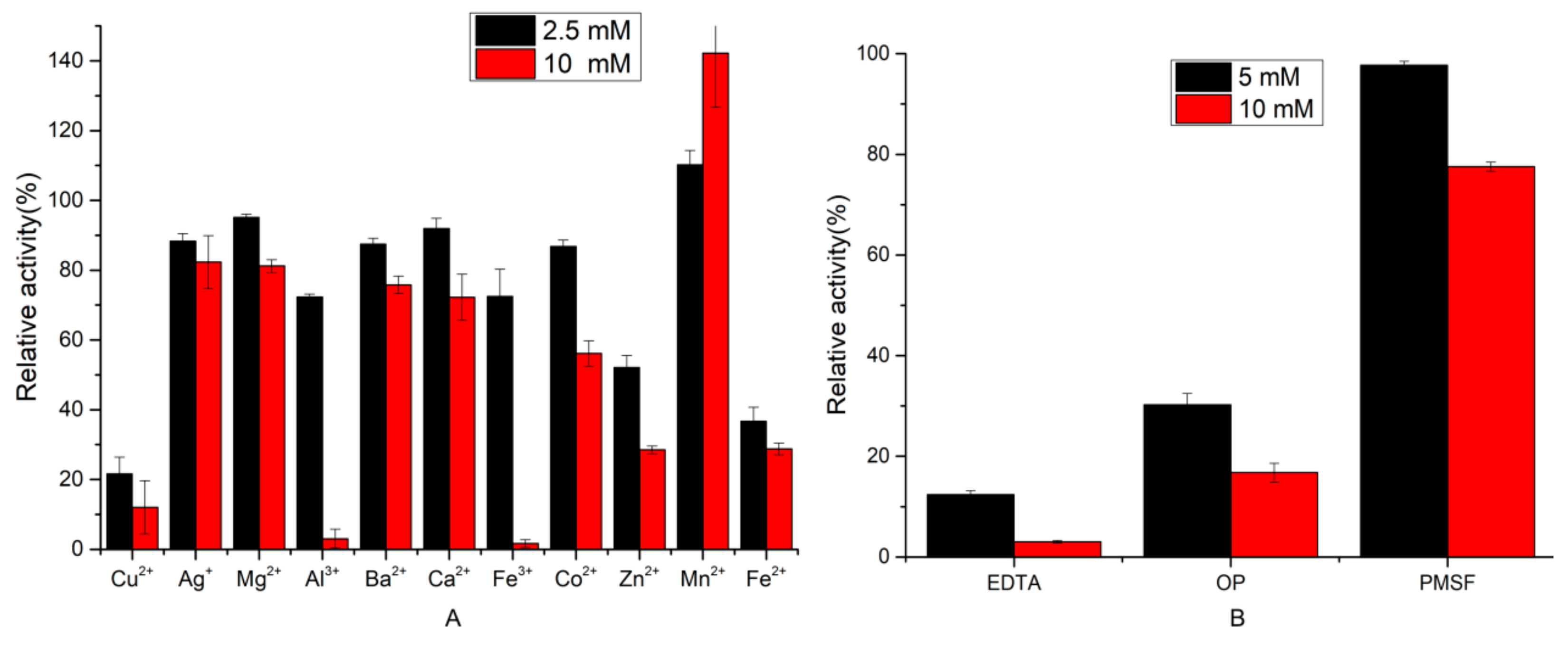
2.3.2. Effect of Inhibitors and Metal Ions on Protease Activity
2.3.3. Effect of Surfactants, Oxidizing Agents, and Organic Solvents on Protease Activity
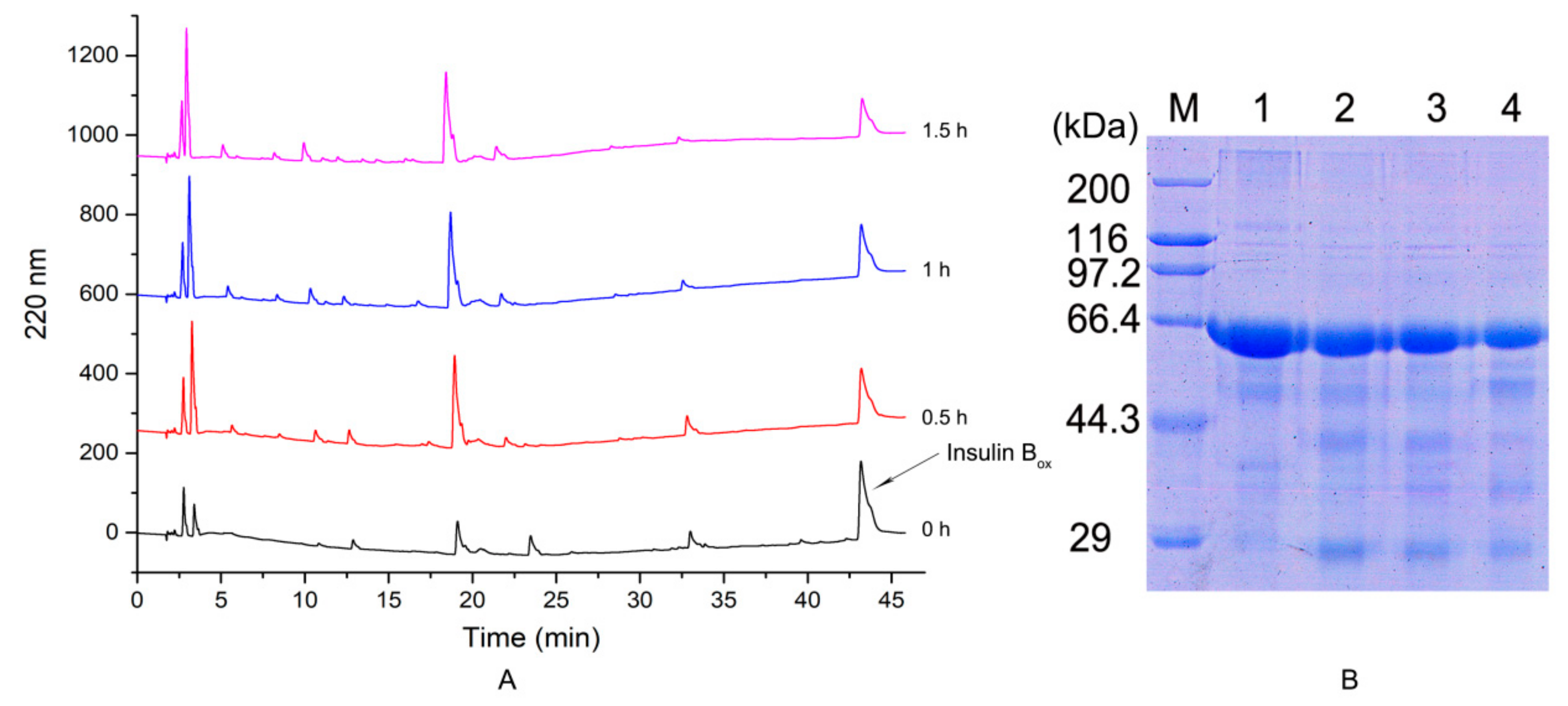
2.3.4. Hydrolysis of Bovine Serum Albumin and Insulin Box
2.4. Mass Spectrum Identification of the Protease
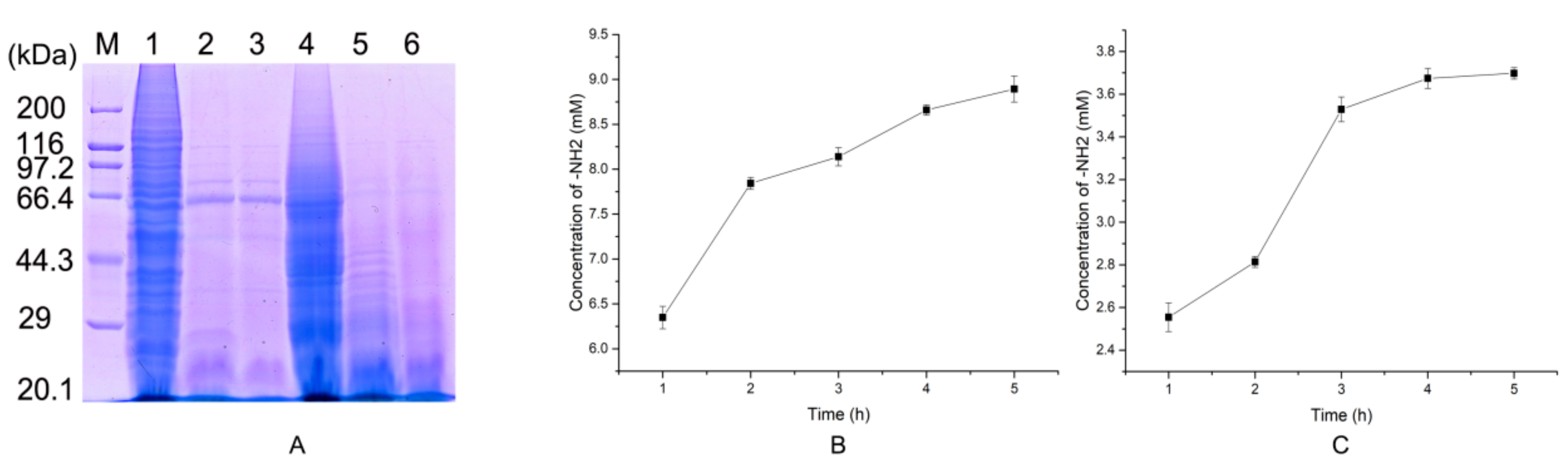
2.5. Preparation of Native Collagen Hydrolytic Peptides
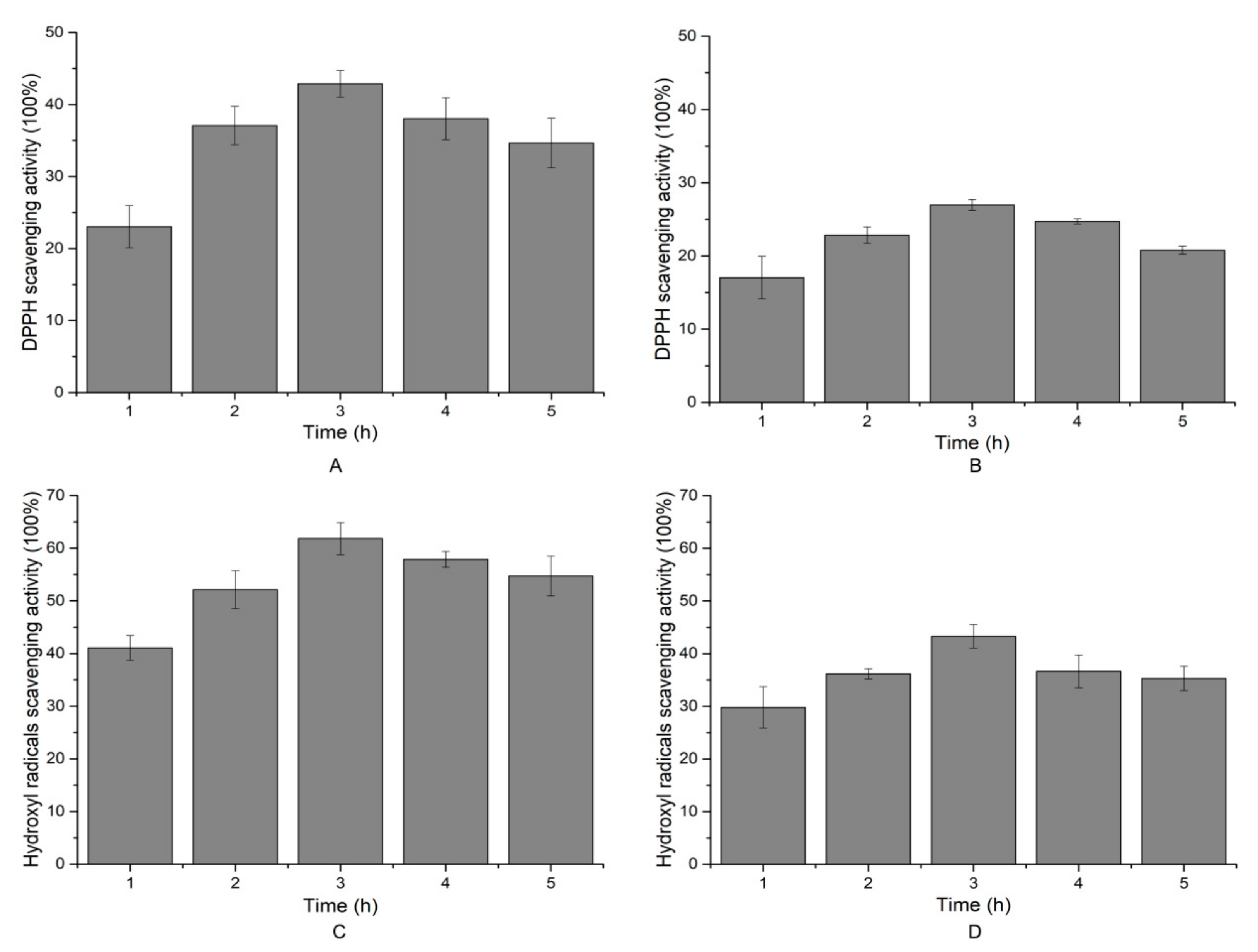
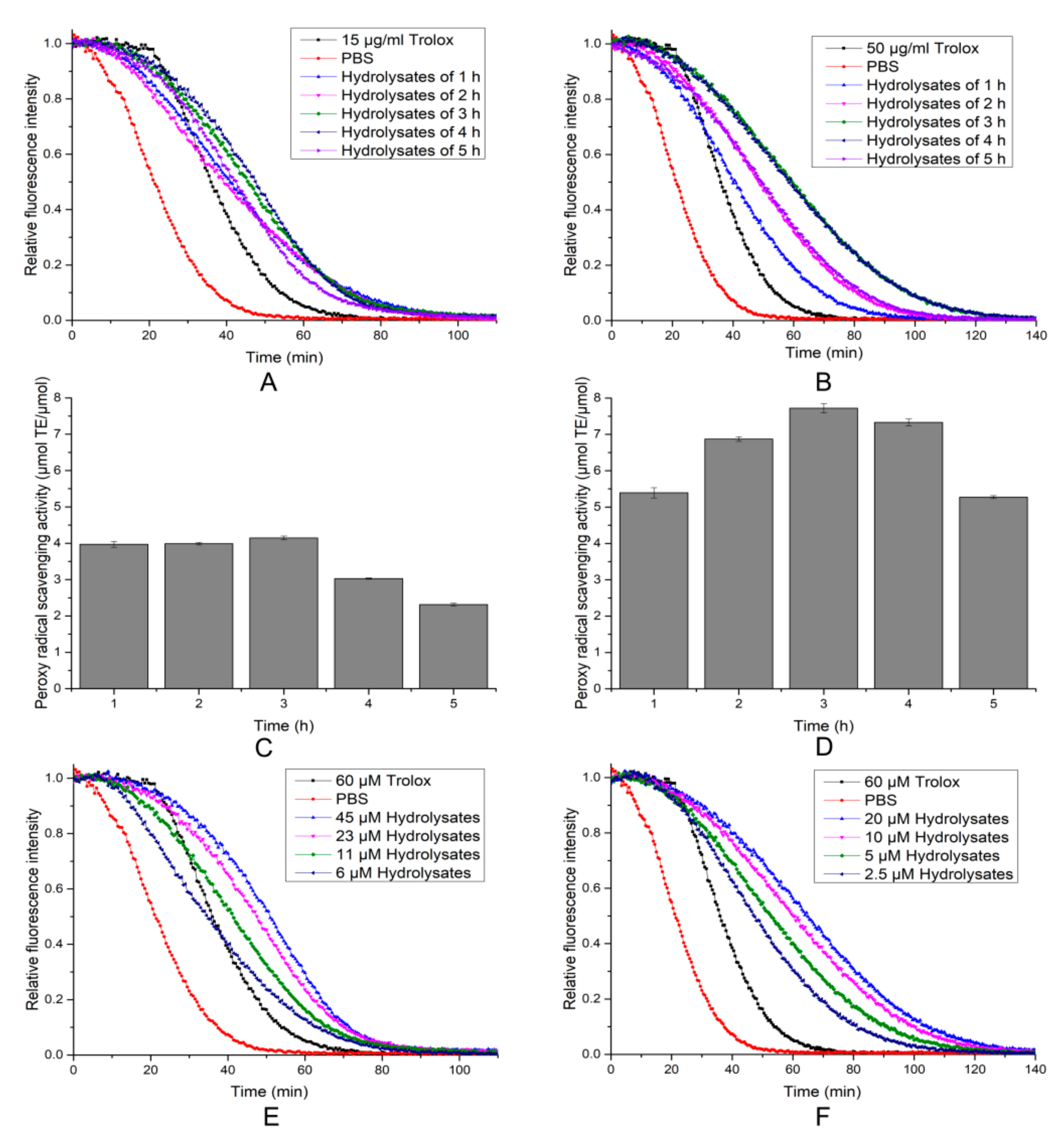
2.6. Antioxidant Activity of the Hydrolytic Peptides
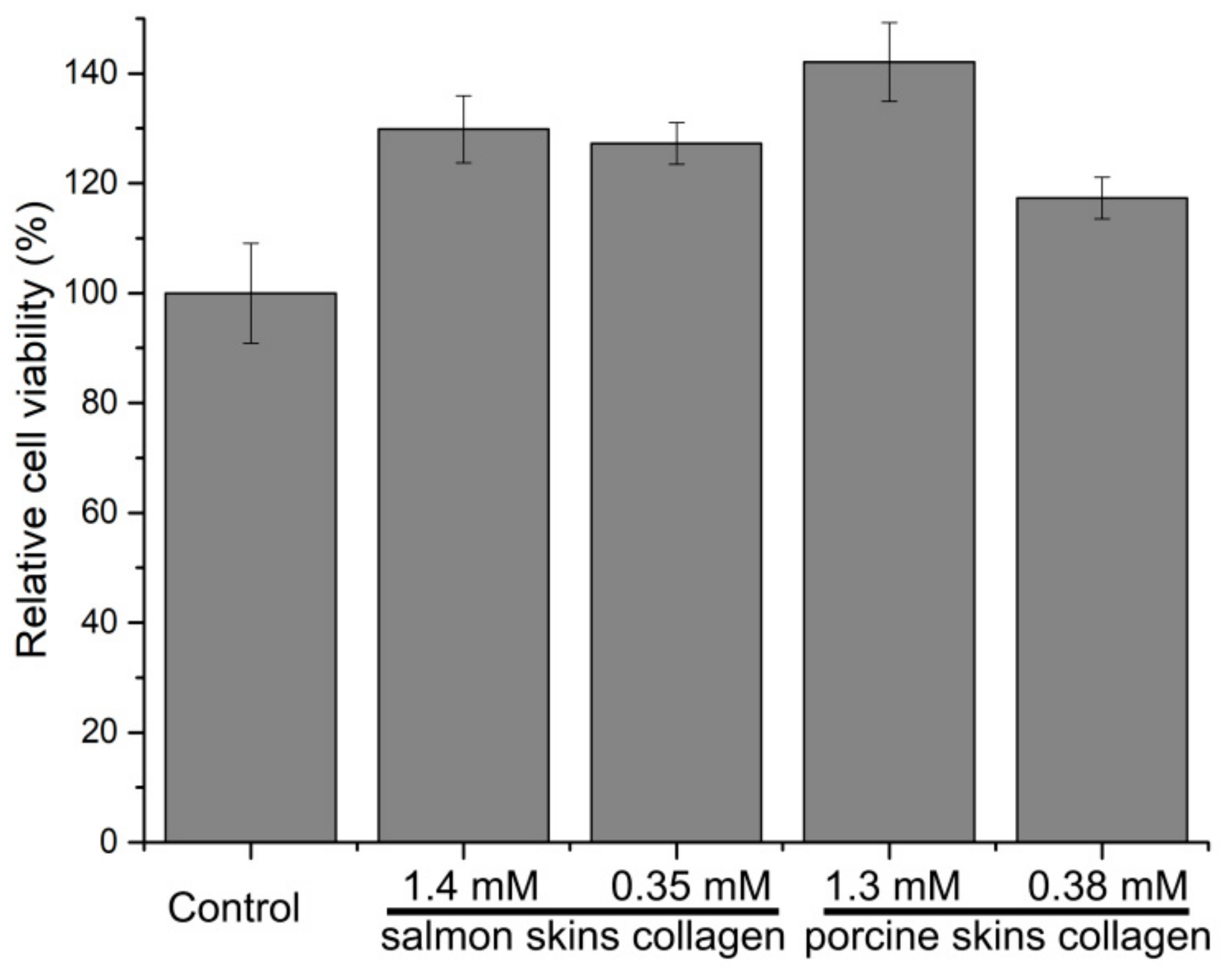
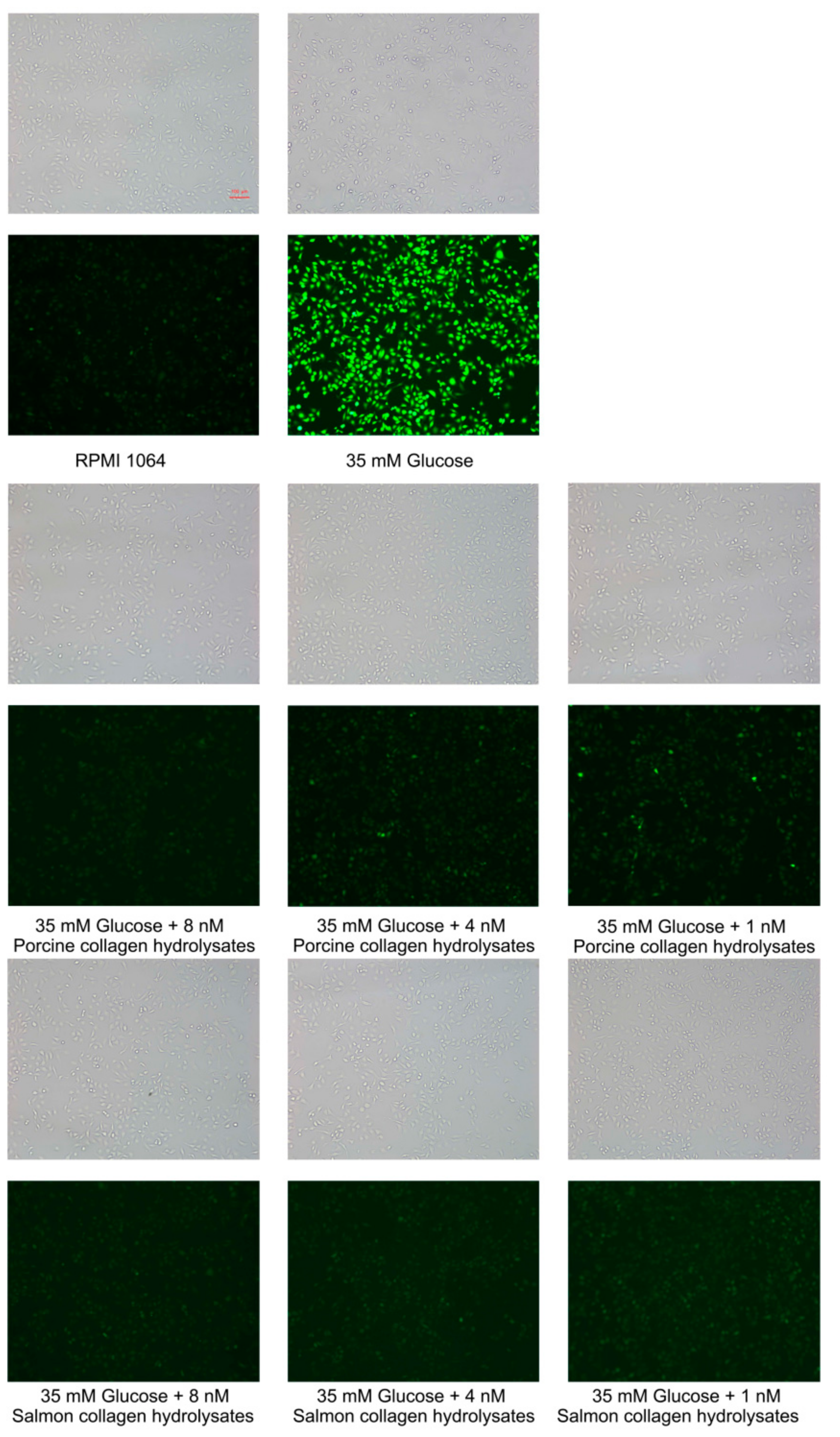
2.7. Cytotoxicity and Intracellular Antioxidant Activity of the Hydrolytic Peptides of the Hydrolytic Peptides on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bacterial Culture
3.3. Preparation of Proteases
3.4. Protease Assay
3.5. Protease Purification
3.6. Zymography and SDS-PAGE Analysis
3.7. Characterization of the Protease
3.7.1. Effect of Temperature and pH on Protease Activity and Stability
3.7.2. Effect of Inhibitors and Metal Ions on Protease Activity
3.7.3. Effect of Surfactants, Oxidizing Agents, and Organic Solvents on Protease Activity
3.8. Hydrolysis of Bovine Serum Albumin and Insulin Chain B by the Protease
3.9. Mass Spectrum Identification of the Protease
3.10. Preparation of Collagen Hydrolytic Peptides
3.11. DPPH Radical Scavenging, Hydroxyl Radicals Scavenging and ORAC Activity Assay
3.12. The Cytotoxicity of Collagen Hydrolytic Peptides by MTT Methods
3.13. Determination of ROS Level
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, R.; Wu, C.; He, H.; Li, H. In situ demonstration and characteristic analysis of the protease components from marine bacteria using substrate immersing zymography. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, R.M.; Prakash, M. Laundry detergent compatibility of the alkaline protease from Bacillus cereus. Microbiol. Res. 2004, 159, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Barbato, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M.; Selan, L. Anti-biofilm activity of the Antarctic marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Satyanarayana, T. Characteristics and applications of a recombinant alkaline serine protease from a novel bacterium Bacillus lehensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhao, H.L.; Dang, H.Y.; Luan, X.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; He, H.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Diversity of both the cultivable protease-producing bacteria and their extracellular proteases in the sediments of the South China sea. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.B.; Shu, Y.L.; Qin, Q.L.; Rong, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Shi, M.; He, H.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Genome Sequences of Type Strains of Seven Species of the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2746–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Sun, C. Purification and biochemical characterization of an alkaline protease from marine bacteria Pseudoalteromonas sp. 129-1. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Peng, M.; Li, J.; Tang, B.L.; Shao, X.; Zhao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Shi, M.; et al. Preparation and functional evaluation of collagen oligopeptide-rich hydrolysate from fish skin with the serine collagenolytic protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp SM9913. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, R.; Liu, D.; Liao, B.; Lei, M.; Wang, M.; Huan, R.; Zhou, M.; Ma, C.; He, H. Mechanistic Insight into the Binding and Swelling Functions of Prepeptidase C-Terminal (PPC) Domains from Various Bacterial Proteases. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S. Marine Fish Proteins and Peptides for Cosmeceuticals: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.T.; Law, Y.C.; Wong, F.C.; Kim, S.K. Enzyme-Assisted Discovery of Antioxidant Peptides from Edible Marine Invertebrates: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqash, S.Y.; Nazeer, R.A. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions for the production of antioxidant peptides from muscles of Nemipterus japonicus and Exocoetus volitans using response surface methodology. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Porro, C.; Mellado, E.; Bertoldo, C.; Antranikian, G.; Ventosa, A. Screening and characterization of the protease CP1 produced by the moderately halophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp strain CP76. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Hou, Y.H.; Xu, Z.; Miao, J.L.; Li, G.Y. Purification and properties of an extracellular cold-active protease from the psychrophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp NJ276. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 38, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.G.; Takagi, H. Microbial alkaline proteases: From a bioindustrial viewpoint. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 561–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.R.; Mahamad, S.; Salleh, A.B.; Basri, M. A new organic solvent tolerant protease from Bacillus pumilus 115b. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2007, 34, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.O.; Kato, J.; Nakashima, K.; Kuroda, A.; Ikeda, T.; Takiguchi, N.; Ohtake, H. Cloning and characterization of extracellular metal protease gene of the algicidal marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp strain A28. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2002, 66, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Moody, M.W.; Portier, R.J.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical properties of black drum and sheepshead seabream skin collagen. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8088–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Shahidi, F. Functionalities and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates from the muscle of ornate threadfin bream treated with pepsin from skipjack tuna. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinola, T.A.; Fagbemi, T.N.; Enujiugha, V.N.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E. Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera seed protein isolate and enzymatic hydrolysates. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.X.; Zhou, H.M.; Qian, H.F. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Q.; Sun, S.; Canning, C. Production and functional characterisation of antioxidative hydrolysates from corn protein via enzymatic hydrolysis and ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.S.; Jiang, Y.M.; Cui, C.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Optimization of antioxidant peptide production from grass carp sarcoplasmic protein using response surface methodology. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malomo, S.A.; He, R.; Aluko, R.E. Structural and functional properties of hemp seed protein products. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1512–C1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.K.; Koide, M.; Rao, T.P.; Okubo, T.; Ogasawara, Y.; Juneja, L.R. ORAC and DPPH assay comparison to assess antioxidant capacity of tea infusions: Relationship between total polyphenol and individual catechin content. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 61, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and in vitro antioxidative effects of giant squid muscle peptides on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, P.; Zeng, X.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. Resveratrol attenuates endothelial oxidative injury by inducing autophagy via the activation of transcription factor EB. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2019, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.E.; Jo, H.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, J.R.; Park, S.Y. Delphinidin prevents high glucose-induced cell proliferation and collagen synthesis by inhibition of NOX-1 and mitochondrial superoxide in mesangial cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 130, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hui, L.; Hong, Y.; Jingjing, Z.; Yuan, H.; Qi, C.; Nong, Z. HGF suppresses high glucose-mediated oxidative stress in mesangial cells by activation of PKG and inhibition of PKA. Free Radic. Bio Med. 2010, 49, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H. Antioxidant and anti-freezing peptides from salmon collagen hydrolysate prepared by bacterial extracellular protease. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Gao, P.J. Taste improvement of refrigerated meat treated with cold-adapted Protease. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, C.; Wu, R.; Huang, J.; Liao, B.; Lei, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, H. Comprehensive analysis of the phylogeny and extracellular proteases in genus Vibrio strain. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y.; He, H. Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Purification Stage | Total Protein | Total Enzyme Activity | Specific Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mg) | (U) | (U/mg) | |
| Crude enzyme | 350 | 3678 | 10.5 |
| Ammonium sulfate precipitation | 50.2 | 2326 | 46.3 |
| Anion exchange | 5.4 | 1597 | 295.7 |
| Size exclusion | 2.1 | 998 | 475.2 |
| Detergents | Residual Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| none | 100 |
| SDS (0.5%) | 69.57 ± 1.55 |
| Triton X-100 (1%) | 91.86 ± 4.84 |
| Tween 80 (1%) | 104.94 ± 1.84 |
| H2O2 (1%) | 72.87 ± 1.55 |
| Acetone (25% (v/v)) | 93.22 ± 5.72 |
| dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (25% (v/v)) | 128.08 ± 2.73 |
| ethanol (25% (v/v)) | 110.21 ± 3.35 |
| isopropanol (25% (v/v)) | 60.92 ± 2.46 |
| methanol (25% (v/v)) | 115.49 ± 0.70 |
| isoamyl alcohol (25% (v/v)) | 78.96 ± 2.73 |
| Peptide Mass | Peptide Sequence | Sequence Header | Similarity (%) | Mr (calc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1491 | 386GSNDWLVGQEIFK399 | metal protease [Pseudoalteromonas sp. A28] | 100 | 35 kDa |
| 1711 | 439AFYNLATTPGWDTQK453 | metal protease [Pseudoalteromonas sp. A28] | 100 | |
| 2093 | 386GSNDWLVGQEIFKGNGALR405 | metal protease [Pseudoalteromonas sp. A28] | 100 | |
| 2240 | 366SGGLNEAFSDMAGEAAEFYMK386 | metal protease [Pseudoalteromonas sp. A28] | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, R.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; Yan, X.; He, H.; Chen, L. Purification, Characterization, and Application for Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides of Extracellular Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. H2. Molecules 2019, 24, 3373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183373
Liu D, Huang J, Wu C, Liu C, Huang R, Wang W, Yin T, Yan X, He H, Chen L. Purification, Characterization, and Application for Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides of Extracellular Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. H2. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183373
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dan, Jiafeng Huang, Cuiling Wu, Congling Liu, Ran Huang, Weng Wang, Tingting Yin, Xiaotao Yan, Hailun He, and Leilei Chen. 2019. "Purification, Characterization, and Application for Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides of Extracellular Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. H2" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183373
APA StyleLiu, D., Huang, J., Wu, C., Liu, C., Huang, R., Wang, W., Yin, T., Yan, X., He, H., & Chen, L. (2019). Purification, Characterization, and Application for Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides of Extracellular Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. H2. Molecules, 24(18), 3373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183373




