Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Interfacial Adhesion and Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Unidirectional Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Bamboo Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mechanical Properties
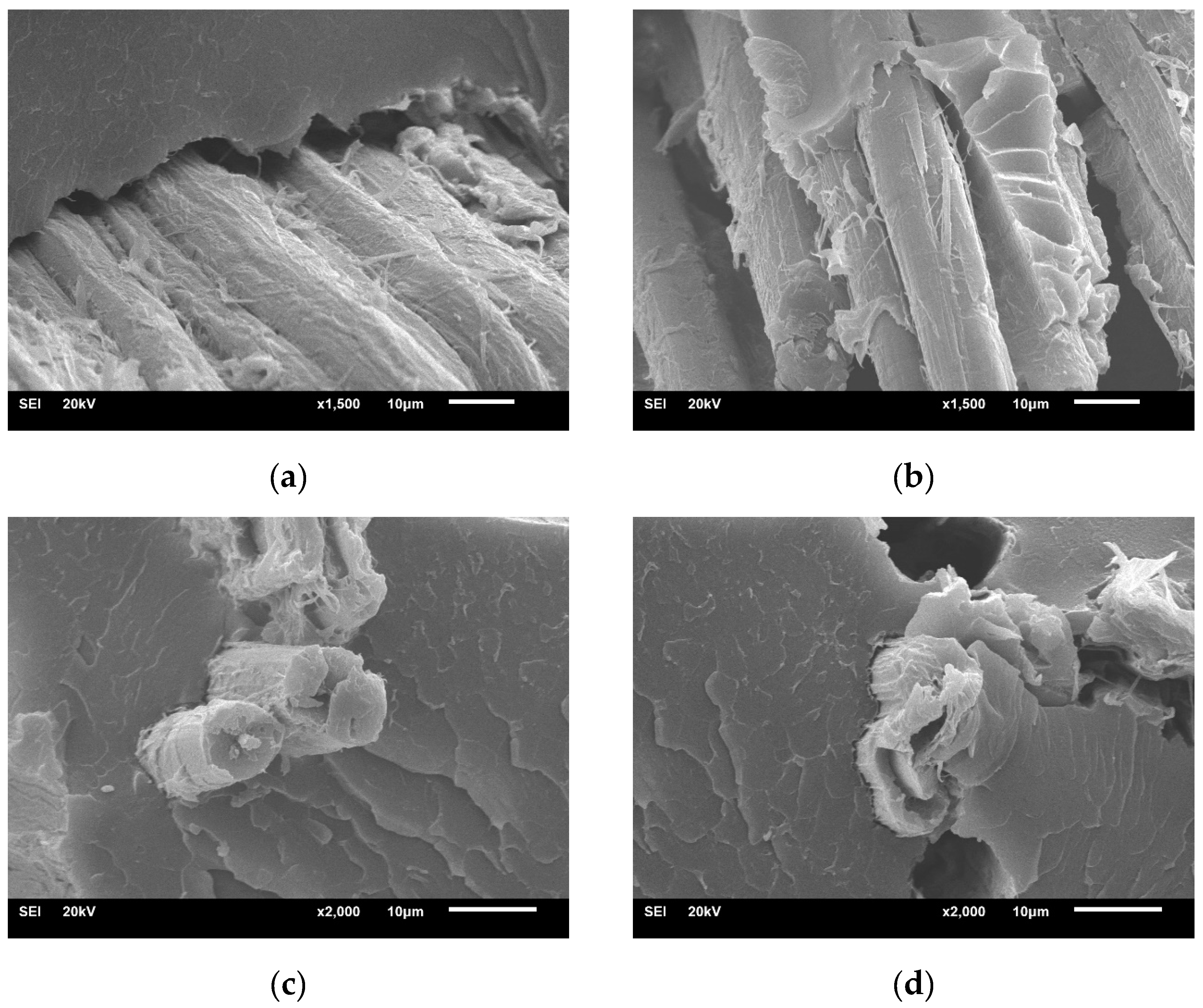
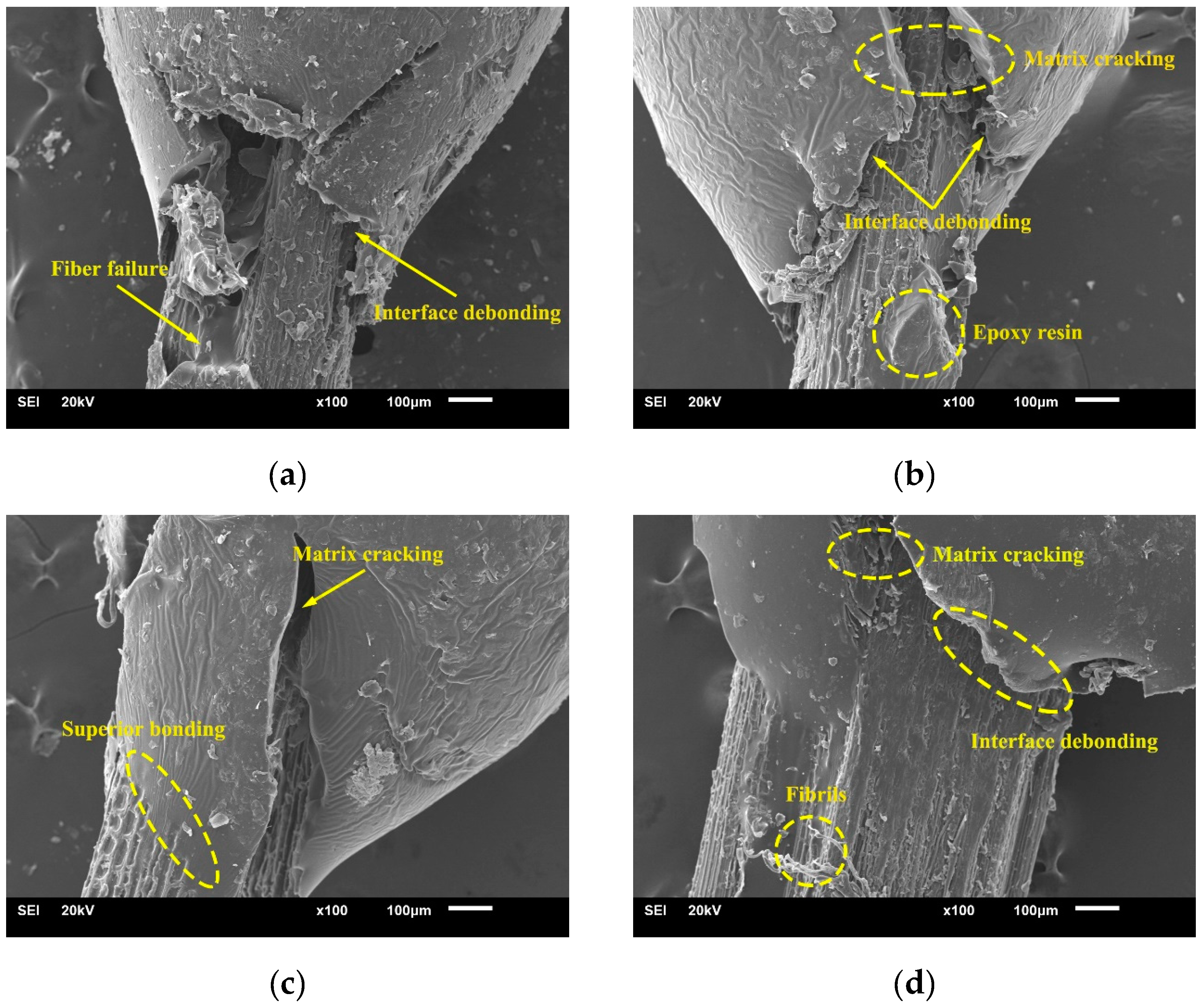
2.2. Fracture Morphology
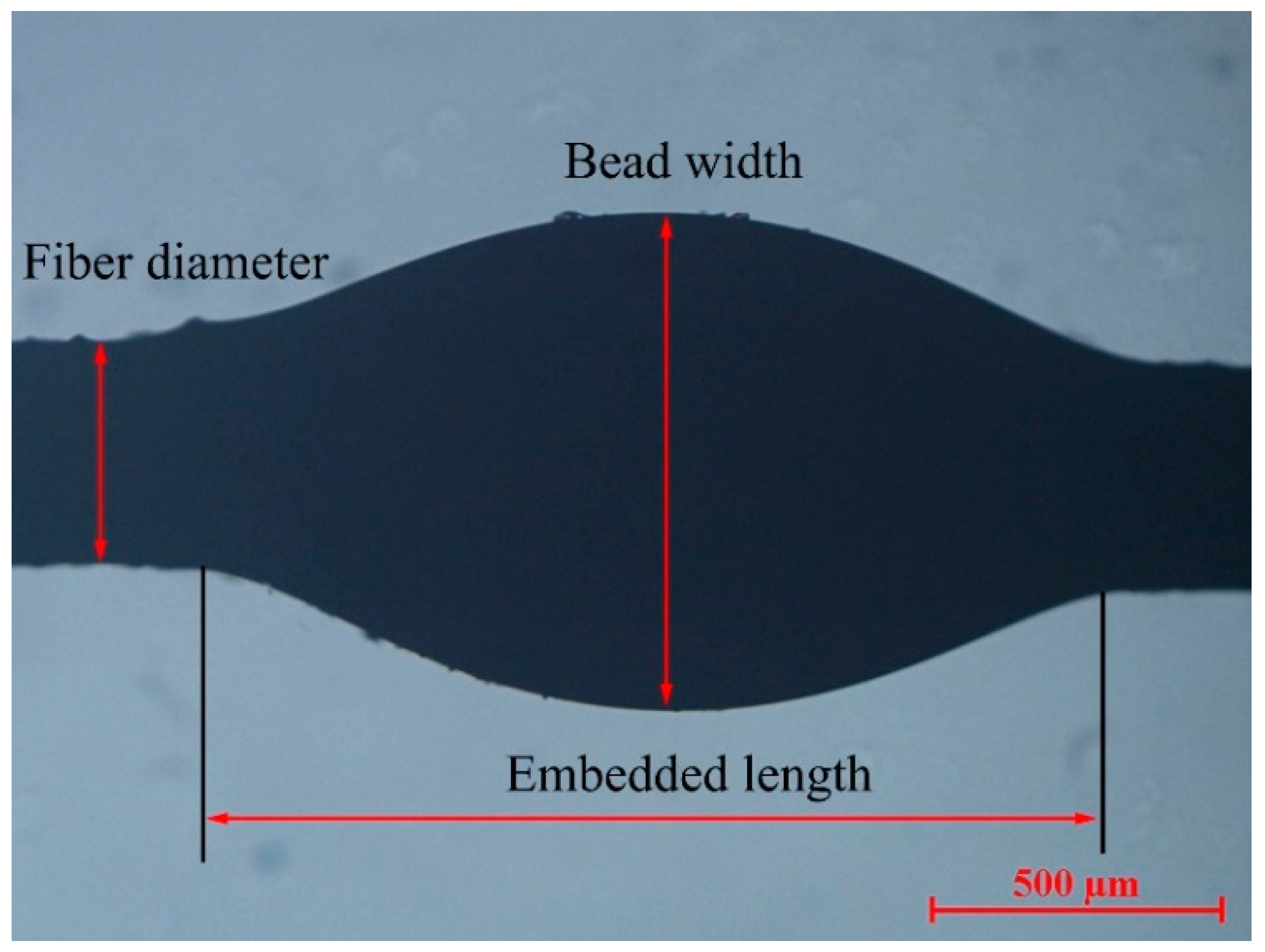
2.3. Interfacial Properties
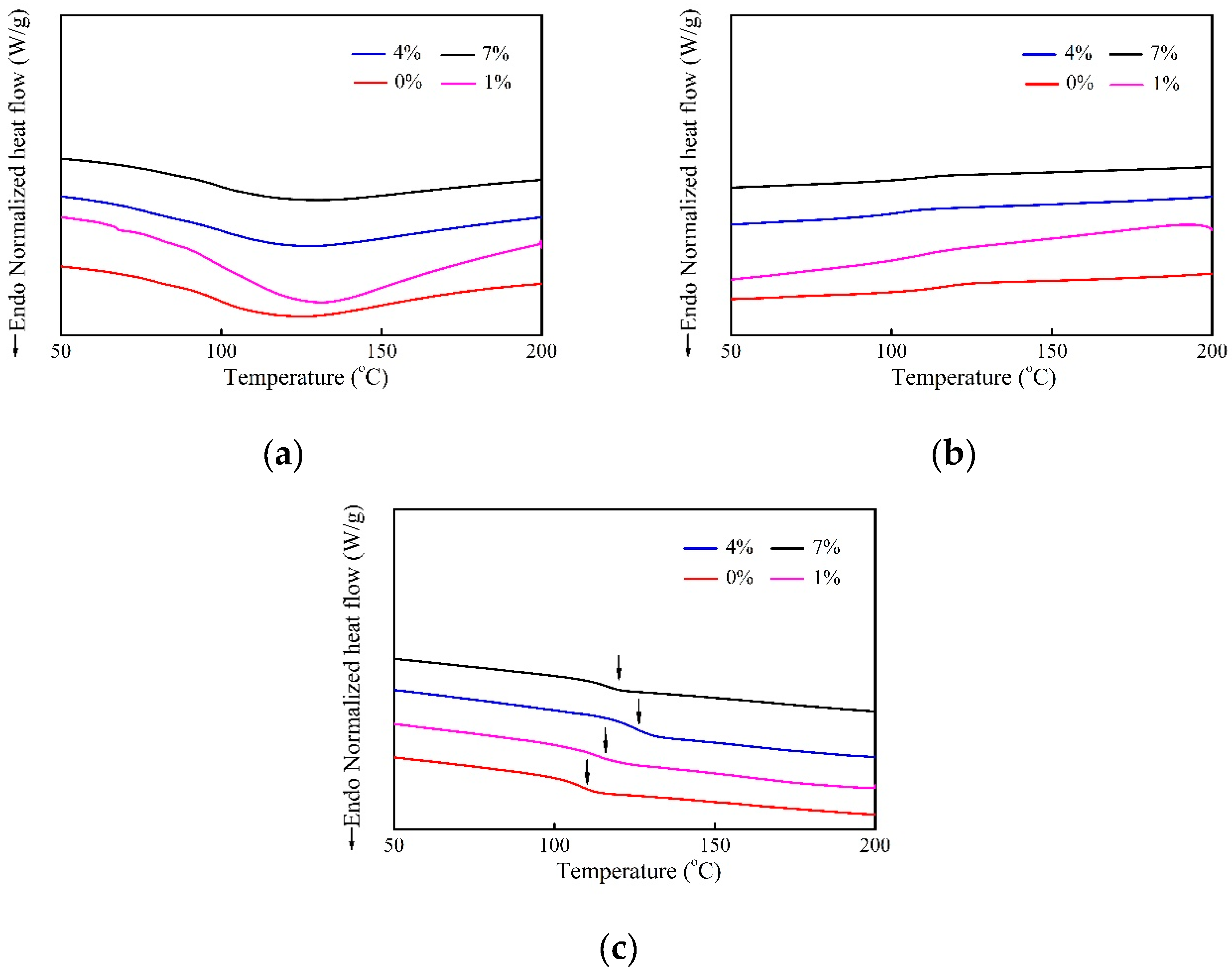
2.4. Glass Transition Temperature
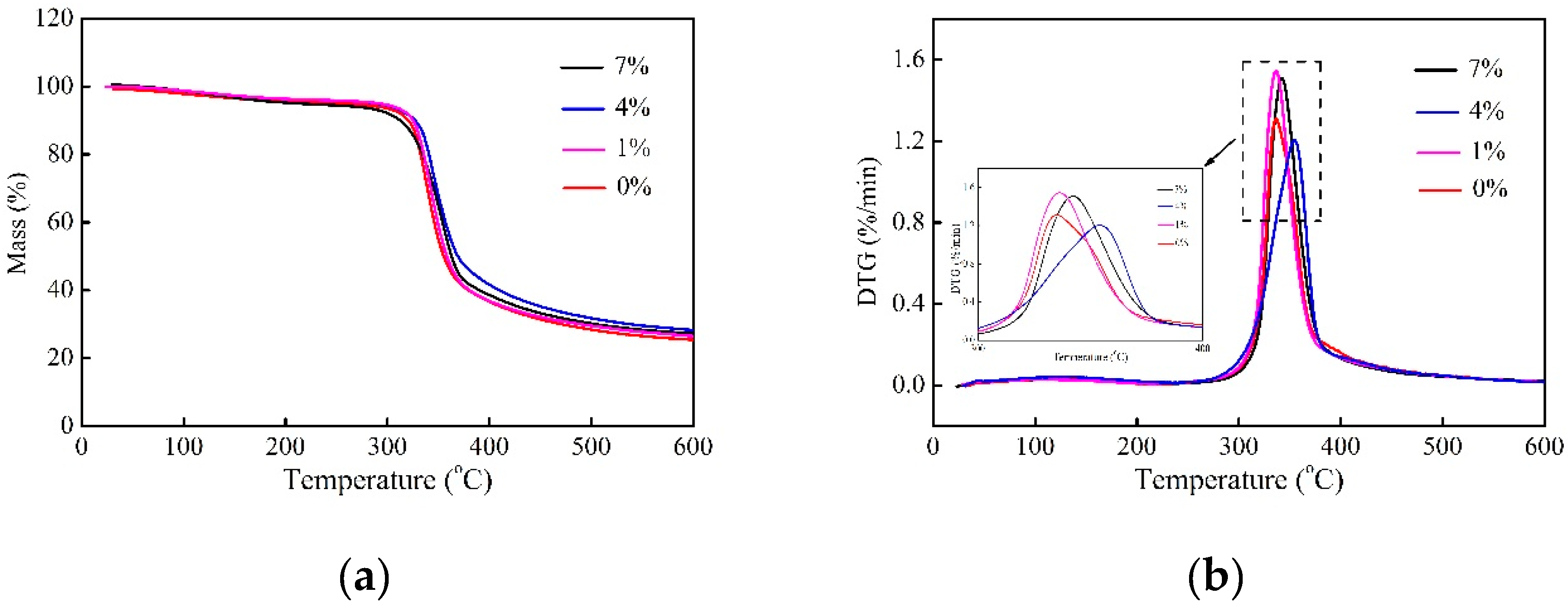
2.5. Thermal Stability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Alkali Treatment
3.3. Composite Preparation
3.4. Composite Characterization
3.4.1. Tensile Test
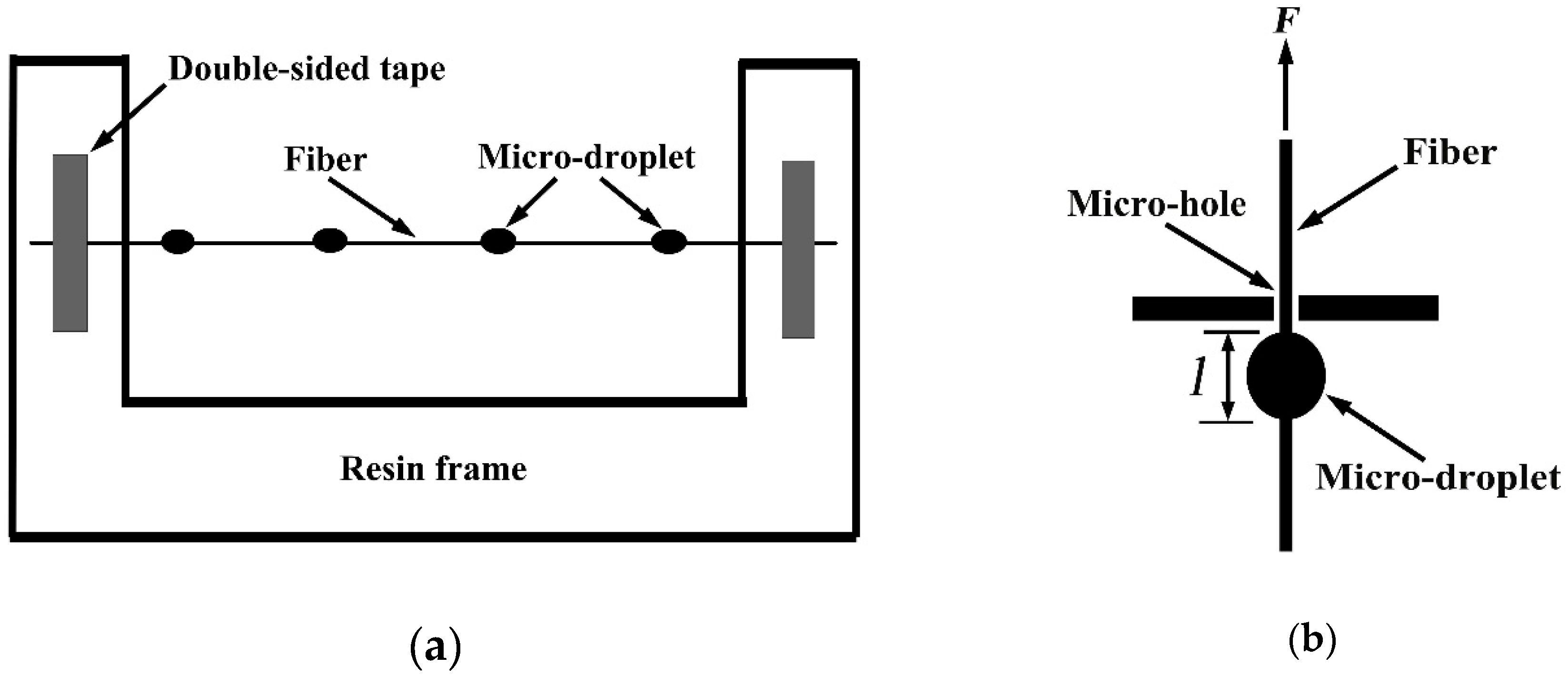
3.4.2. Micro-Bond Test
3.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
3.4.4. Differential Scanning Calorimeter Analysis
3.4.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The composite tensile strength is improved as the alkali concentration increases. However, when the concentration reaches 7%, the micro-fibril structure of the bamboo fibers is damaged, and contrarily the interfacial adhesion becomes weakened. Thus, the maximum value in composite strength is at 4% concentration. In this case, the interface compatibility also becomes optimal, as proved by the fracture morphology. Besides, the elongation at break increases as the concentration increases.
- (2)
- The IFSS of the fiber/matrix increases with increasing alkali concentrations, and reaches maximum value at a concentration of 4%. This alkali concentration strengthens the mechanical interlocking of the fiber surface with epoxy resin, enhancing the interface bonding. Thus, the interface failure is mainly caused by matrix damage.
- (3)
- The mobility of the epoxy molecular chains is restricted after the alkali treatment, leading to higher Tg. It is concluded that the alkali treatment could improve decomposition temperature and increase the residual mass, exhibiting improved thermal stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Bhat, I.U.H.; Jawaid, M.; Zaidon, A.; Hermawan, D.; Hadi, Y.S. Bamboo fibre reinforced biocomposites: A review. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, J.X.; Keer, L.M.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.Q. The effect of elementary fibre variability on bamboo fibre strength. Mater. Des. 2015, 75, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, J.X. Modified Weibull distribution for analyzing the tensile strength of bamboo fibers. Polymers 2014, 6, 3005–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, F. Effect of the statistical nature of fiber strength on the predictability of tensile properties of polymer composites reinforced with bamboo fibers: Comparison of Linear- and Power-law Weibull models. Polymers 2016, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.V.R.; Rao, K.M. Mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polyester composites: Jowar, sisal and bamboo. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4658–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.G.; Song, J.W.; Anderson, D.P.; Chang, P.R.; Hua, Y. Bamboo fiber and its reinforced composites: Structure and properties. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1449–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Sato, N.; Tölle, F.; Mulhaupt, R.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Fracture toughness and failure mechanism of graphene based epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 97, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, F.X.; Liang, W.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Duan, Z.W.; Yang, B. Thermal and mechanical properties of bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Rout, S.K. Influence of fibre-surface treatment on structural, thermal and mechanical properties of jute fibre and its composite. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.N.; Tashiro, K.; Xu, D.G.; Liu, J.; Bin, Y.Z. Crystallization behavior of poly(lactic acid)/microfibrillated cellulose composite. Polymer 2013, 54, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Paakkonen, E.; Jetsu, P.; Heinemann, S. Wood based PLA and PP composites: Effect of fibre type and matrix polymer on fibre morphology, dispersion and composite properties. Compos. Part A 2014, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, M.Q.; Zhou, S.J.; Ran, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Effect of fiber volume fraction on the thermal and mechanical behavior of polylactide-based composites incorporating bamboo fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslinda, A.B.; Majid, M.S.A.; Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Afendi, M.; Gibson, A.G. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hybrid interwoven cellulosic-cellulosic fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 167, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Okubo, K.; Fujii, T.; Takemura, K. Influence of fiber extraction and surface modification on mechanical properties of green composites with bamboo fiber. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wang, F.; Keer, L.M. Influence of surface modification on the microstructure and thermo-mechanical properties of bamboo fibers. Materials 2015, 8, 6597–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, S.J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.P. Changes in the morphological-mechanical properties and thermal stability of bamboo fibers during the processing of alkaline treatment. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E1421–E1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, S.J.; Yang, M.Q.; Chen, Z.Q.; Ran, S.Y. Thermo-mechanical performance of polylactide composites reinforced with alkali-treated bamboo fibers. Polymers 2018, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalo, A.C.; Wani, E.; Zukarnain, N.A.; Karunasena, W.; Lau, K.T. Effects of alkali treatment and elevated temperature on the mechanical properties of bamboo fibre-polyester composites. Compos. Part B 2015, 80, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.S.; Baek, Y.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Kwon, D.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; DeVries, K.L.; Park, J.M. Interfacial and wetting properties between glass fiber and epoxy resins with different pot lifes. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 544, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Duan, Y.G.; Zhang, J.J. A controllable interface performance through varying ZnO nanowires dimensions on the carbon fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Yu, Z.X.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, H.K.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y. Quantitative characterization of the interface between bamboo fiber and polypropylene with pull-out test and nanomechanical imaging. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Interfacial bonding of flax fibre/Poly(-lactide) bio-composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. Part B 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanegara, L.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. The effect of crystallization of PLA on the thermal and mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Puglia, D.; Dominici, F.; Santulli, C.; Boimau, K.; Valente, T.; Torrel, L. Biodegradable polycaprolactone-based composites reinforced with ramie and borassus fibres. Compos. Struct. 2017, 167, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.J.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, Z.G.; Hui, D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.W. Effect of surface modification of bamboo cellulose fibers on mechanical properties of cellulose/epoxy composites. Compos. Part B 2013, 51, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duigou, A.L.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Exploring durability of interfaces in flax fibre/epoxy micro-composites. Compos. Part A 2013, 48, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhandarov, S.; Mader, E. Characterization of fiber/matrix interface strength: Applicability of different tests, approaches and parameters. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Q.; Wang, F.; Zhou, S.J.; Lu, Z.S.; Ran, S.Y.; Li, L.; Shao, J.X. Thermal and mechanical performance of unidirectional composites from bamboo fibers with varying volume fractions. Polym. Compos. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.S.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Effect of fiber surface-treatments on the properties of laminated biocomposites from poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and kenaf fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Pickering, K.L.; Foreman, N.J. Influence of alkali treatment on the interfacial and physico-mechanical properties of industrial hemp fibre reinforced polylactic acid composites. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.Y.; Lau, K.T.; Tao, X.M.; Hui, D. A potential material for tissue engineering: Silkworm silk/PLA biocomposite. Compos. Part B 2008, 39, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Cao, Y.; Fukumoto, I. Press forming of short natural fiber-reinforced biodegradable resin: Effects of fiber volume and length on flexural properties. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, J.X.; Li, X. Statistics on the fracture strength of bamboo fibers. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, L.; Keer, L.M. Micromechanical modelling of the progressive failure in unidirectional composites reinforced with bamboo fibres. Mech. Mater. 2016, 94, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010; ASTM D638-10.
Sample Availability: Not available. |


| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | p (α = 0.05) | SD | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | p (α = 0.05) | SD | Elongation at Break (%) | p (α = 0.05) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 134.32 ± 19.77 | - | - | 0.82 ± 0.13 | - | - | 4.46 ± 0.10 | - | - |
| 1% | 158.20 ± 11.63 | 0.048 | Yes | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 0.268 | No | 5.17 ± 0.19 | 0.027 | Yes |
| 4% | 195.09 ± 17.91 | 0.007 | Yes | 0.72 ± 0.02 | 0.031 | Yes | 5.50 ± 0.32 | 0.002 | Yes |
| 7% | 173.17 ± 19.38 | 0.031 | Yes | 0.66 ± 0.04 | 0.012 | Yes | 6.32 ± 0.33 | 0.002 | Yes |
| Samples | IFSS (MPa) | p (α = 0.05) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 3.28 ± 0.34 | - | - |
| 1% | 4.29 ± 0.56 | 0.009 | Yes |
| 4% | 6.57 ± 0.69 | 0.0001 | Yes |
| 7% | 5.04 ± 0.32 | 0.00002 | Yes |
| Samples | Tg (°C) | p (α = 0.05) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 109.37 ± 0.87 | - | - |
| 1% | 112.62 ± 1.24 | 0.021 | Yes |
| 4% | 123.54 ± 2.22 | 0.0005 | Yes |
| 7% | 116.76 ± 0.81 | 0.0004 | Yes |
| Samples | Peak Temperature (°C) | p (α = 0.05) | SD | Loss Weight at 600 °C (%) | p (α = 0.05) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 342.4 ± 1.50 | - | - | 73.42 ± 1.28 | - | - |
| 1% | 346.4 ± 1.27 | 0.023 | Yes | 72.28 ± 0.33 | 0.015 | Yes |
| 4% | 352.5 ± 1.08 | 0.0002 | Yes | 70.65 ± 1.26 | 0.012 | Yes |
| 7% | 346.9 ± 1.54 | 0.011 | Yes | 71.22 ± 1.06 | 0.015 | Yes |
| Epoxide Equivalent Weight (g/mol) | Viscosity (mPa·s at 70 °C) | Solubility | Glass Transition Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180–195 | 600–1000 | Insoluble in water | ≥150 | 21 | 480 | 3.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Lu, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Z.; Ran, S. Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Interfacial Adhesion and Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Unidirectional Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Bamboo Fibers. Molecules 2019, 24, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152682
Wang F, Lu M, Zhou S, Lu Z, Ran S. Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Interfacial Adhesion and Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Unidirectional Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Bamboo Fibers. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152682
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fang, Min Lu, Shujue Zhou, Zhisong Lu, and Siyan Ran. 2019. "Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Interfacial Adhesion and Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Unidirectional Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Bamboo Fibers" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152682
APA StyleWang, F., Lu, M., Zhou, S., Lu, Z., & Ran, S. (2019). Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Interfacial Adhesion and Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Unidirectional Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Bamboo Fibers. Molecules, 24(15), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152682








