QSAR Study of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors of Antimalarial Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
Model B3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Data
4.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulation (MDS)
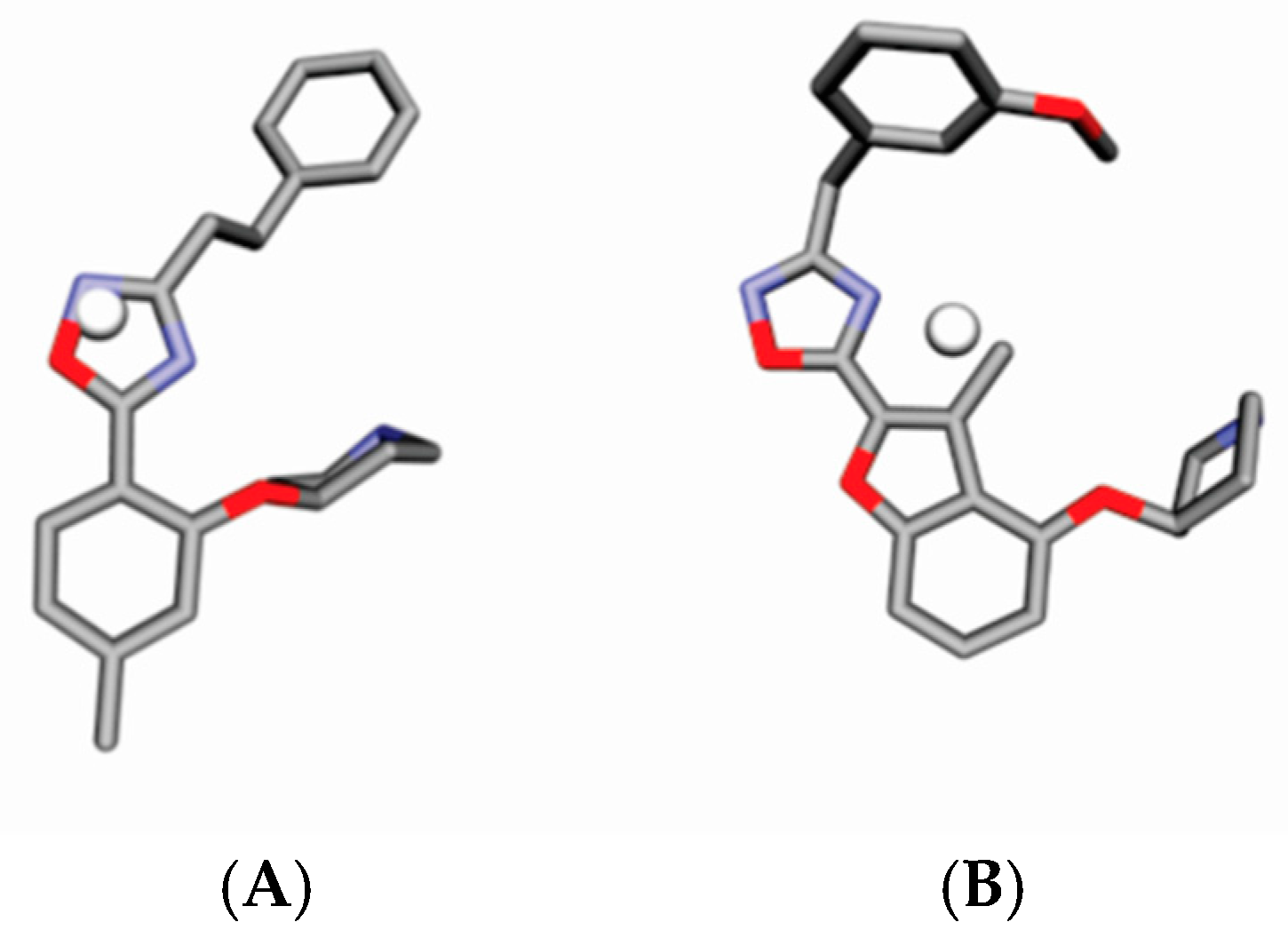
4.3. Alignment Definition
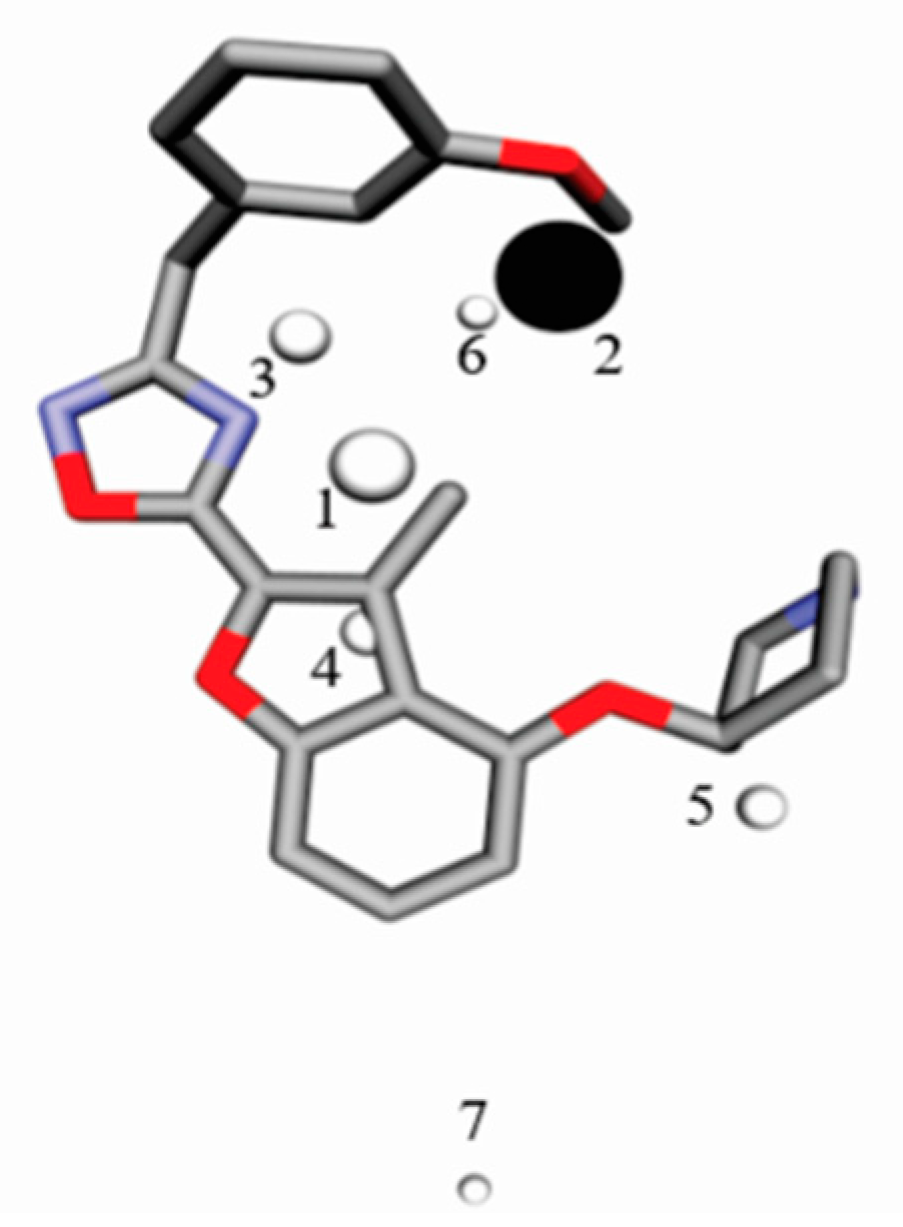
4.4. Interaction Pharmacophore Elements
- (1)
- Coefficient of determination (r2): is a measure of how well the regression line represents the data.
- (2)
- Adjusted cross-validated squared correlation coefficient (q2adj): allows the comparison between models with different number of variables.
- (3)
- Correlation coefficient of external validation set (R2pred): reflects the degree of correlation between the observed (YExp(test))and predicted (YPred(test)) activity data of the test set:where is average value for the dependent variable for the training set.
- (4)
- Modified r2 (r2m(test)) equation determining the proximity between the observed and predicted values with the zero axis intersection:
- (5)
- Y-randomization (R2r) consists of the random exchange of the independent variable values. Thus, the R2r value must be less than the correlation coefficient of the non-randomized models.
- (6)
- R2p penalizes the model R2 for the difference between the squared mean correlation coefficient (R2r) of randomized models and the square correlation coefficient (r2) of the non-randomized model:
4.5. Conformational Selection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Njoroge, M.; Njuguna, N.M.; Mutai, P.; Ongarora, D.S.B.; Smith, P.W.; Chibale, K. Recent Approaches to Chemical Discovery and Development against Malaria and the Neglected Tropical Diseases Human African Trypanosomiasis and Schistosomiasis. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11138–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Learn, G.H.; Rudicell, R.S. Origin of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature 2010, 467, 420–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krungkrai, S.R.; Krungkrai, J. Insights into the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway of human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum as chemotherapeutic target. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, R.G. Medical need, scientific opportunity and the drive for antimalarial drugs. Nature 2002, 415, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, E.W.; Bell, A.S.; Rackham, M.D.; Wright, A.H. N-yristoyltransferase as a potential drug target in malaria and leishmaniasis. Parasitology 2014, 141, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidock, D.A.; Nomura, T.; Talley, A.K.; Cooper, R.A.; Dzekunov, S.M.; Ferdig, M.T.; Ursos, L.M.B.; Sidhu, A.B.S.; Naude, B.; Deitsch, K.W. Mutations in the P-falciparum digestive vacuole transmembrane protein PfCRT and evidence for their role in chloroquine resistance. Mol. Cell. 2000, 6, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Nosten, F.; Yi, P.; Das, D.; Phyo, A.P.; Tarning, J.; Lwin, K.M.; Ariey, F.; Hanpithakpong, W.; Lee, S.J. Artemisinin Resistance in Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okombo, J.; Chibale, K. Antiplasmodial drug targets: A patent review (2000–2013). Expert.Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldston, A.M.; Sharma, A.I.; Paul, K.S.; Engman, D.M. Acylation in trypanosomatids: An essential process and potential drug target. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.H.; Heal, W.P.; Mann, D.J.; Tate, E.W. Protein myristoylation in health and disease. J. Chem. Biol. 2010, 3, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratne, R.S.; Sajid, M.; Ling, I.T.; Tripathi, R.; Pachebat, J.A.; Holder, A.A. Characterization of N-myristoyltransferase from Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadas, B.; ZUpec, M.E.; Freeman, S.K.; Brown, D.L.; Nagarajan, S.; Sikorski, J.A.; McWherter, C.A.; Getman, D.P.; Gordon, J.I. Design and Syntheses of Potent and Selective Dipeptide Inhibitors of Candida albicans Myristoyl-CoA: Protein N-Myristoyltransferase. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1837–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, L.A.; Zheng, G.; DeFrees, S.A.; Cassady, J.M.; Geahlen, R.L. S-(2-Oxopentadecyl)-CoA, a Nonhydrolyzable Analogue of Myristoyl-CoA, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Myristoyl-CoA: Protein N-Myristoyltransferase. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1665–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, V.; Brannigan, J.A.; Laporte, A.; Bell, A.S.; Robert, S.M.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Leatherbarrow, R.J.; Tate, E.W. Structure-guided optimization of quinoline inhibitors of Plasmodium N-myristoyltransferase. Med. Chem. Comm. 2016, 8, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leatherbarrow, R.; Tate, E.; Yu, Z.; Racklam, M. Novel Compounds and Their Use in Therapy. London Patent WO 2013/083991, 13 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hopfinger, A.J.; Wang, S.; Tokarski, J.S.; Jin, B.Q.; Albuquerque, M.G.; Madhav, P.J.; Duraiswami, C. Construction of 3D-QSAR models using the 4D-QSAR analysis formalism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10509–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.P.; Paul, S.; Mitra, I.; Roy, K. On Two Novel Parameters for Validation of Predictive QSAR Models. Molecules 2009, 14, 1660–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Chakraborty, P.; Mitra, I.; Ojha, P.K.; Kar, S.; Das, R.N. Some case studies on application of “rm2” metrics for judging quality of quantitative structure-activity relationship predictions: Emphasis on scaling of response data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.H.; Liu, J.Z.; Senese, C.; Hopfinger, A.J.; Tseng, Y. Characterization of a ligand-receptor binding event using receptor-dependent four-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3075–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.M.; Sing, B.; Bhardwaj, V.; Palkar, M.; Shaikh, M.S.; Rane, R.; Alwan, W.S.; Gadad, A.K.; Noolvi, M.N.; Karpoormath, R. Design, synthesis and evaluation of small molecule imidazo [2,1-b][1,3,4] thiadiazoles as inhibitors of transforming growth factor-beta type-I receptor kinase (ALK5). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinspiration Cheminformatics (Nova ulica, Slovensky Grob, Slovak Republic). Available online: http://www.molinspiration.com/ (accessed on 13 September 2018).
- Rocha, G.B.; Freire, R.O.; Simas, A.M.; Stewart, J.J.P. RM1: A reparameterization of AM1 for H, C, N, O, P, S, F, Cl, Br, and I. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Páll, S.; Abraham, M.J.; Kutzner, C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. Tackling Exascale Software Challenges in Molecular Dynamics Simulations with GROMACS. In International Conference on Exascale Applications and Software; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.A.; Ramalho, T.C.; da Cunha, E.F.F. QSAR Study of Androstenedione Analogs as Aromatase Inhibitors. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2009, 6, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, E.F.F.; Albuquerque, M.G.; Antunes, O.A.C.; de Alencastro, R.B. 4D-QSAR models of HOE/BAY-793 analogues as HIV-1 protease inhibitors. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2015, 24, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, G.B.; Ramalho, T.C.; da Cunha, E.F.F. Application of 4D-QSAR studies to a series of benzothiophene analogs. J. Mol. Mod. 2014, 20, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiralj, R.; Ferreira, M.M.C. Basic Validation Procedures for Regression Models in QSAR and QSPR Studies: Theory and Application. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Paul, S. Exploring 2D and 3D QSARs of 2,4-Diphenyl-1,3-oxazolines for Ovicidal Activity against Tetranychus urticae. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2009, 28, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasamy, R.; Rajak, H.; Jain, A.; Sivadasan, S.; Varghese, C.P.; Agrawal, R.K. Validation of QSAR Models—Strategies and Importance. Int. J. Drug Des. Discov. 2011, 3, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Cormanich, R.A.; Moreira, M.A.; Freitas, M.P.; Ramalho, T.C.; Anconi, C.P.A.; Rittner, R.; Contreras, R.H.; Tormena, C.F. 1hJFH coupling in 2-fluorophenol revisited: Is intramolecular hydrogen bond responsible for this long-range coupling? Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, M.S.; Ramalho, T.C.; Botrel, D.F.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; de Mello, W.C. Understanding the inactivation process of organophosphorus herbicides: A DFT study of glyphosate metallic complexes with Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Co3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, and Al3+. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2012, 112, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, A.A.; Prandi, I.G.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C. Organophosphorus degrading enzymes: Molecular basis and perspectives for enzymatic bioremediation of agrochemicals. Cienc. Agrotecnol. 2017, 41, 471–482. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of all compounds are available from the authors. |
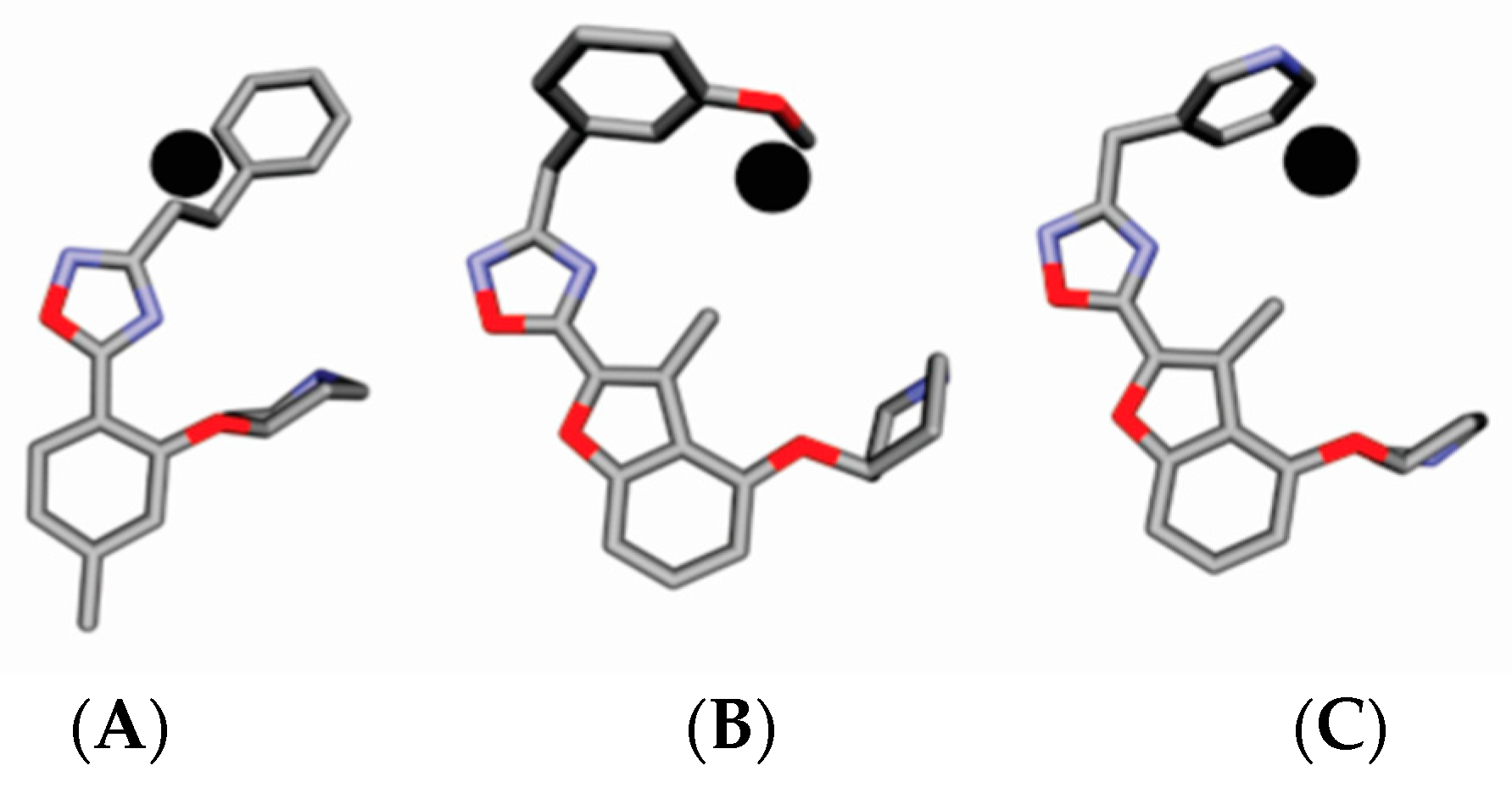
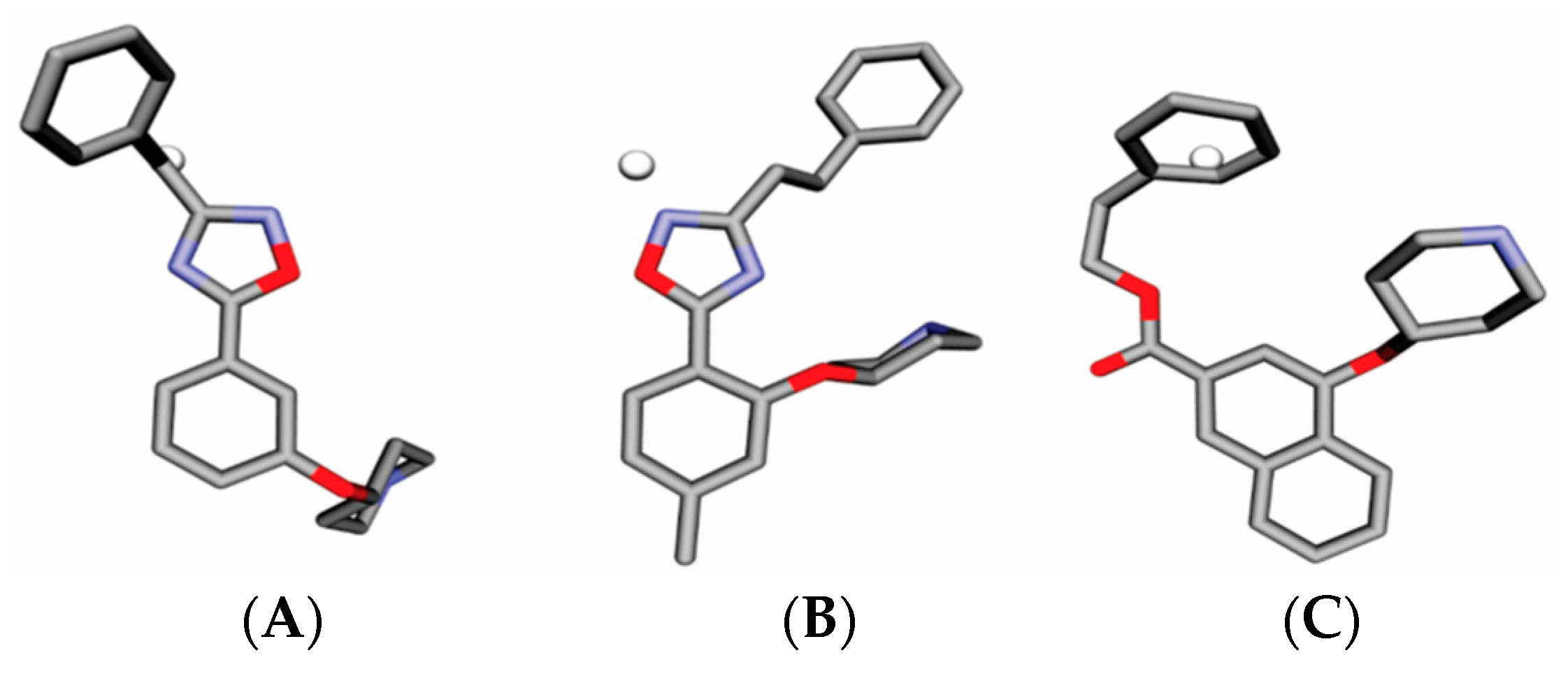
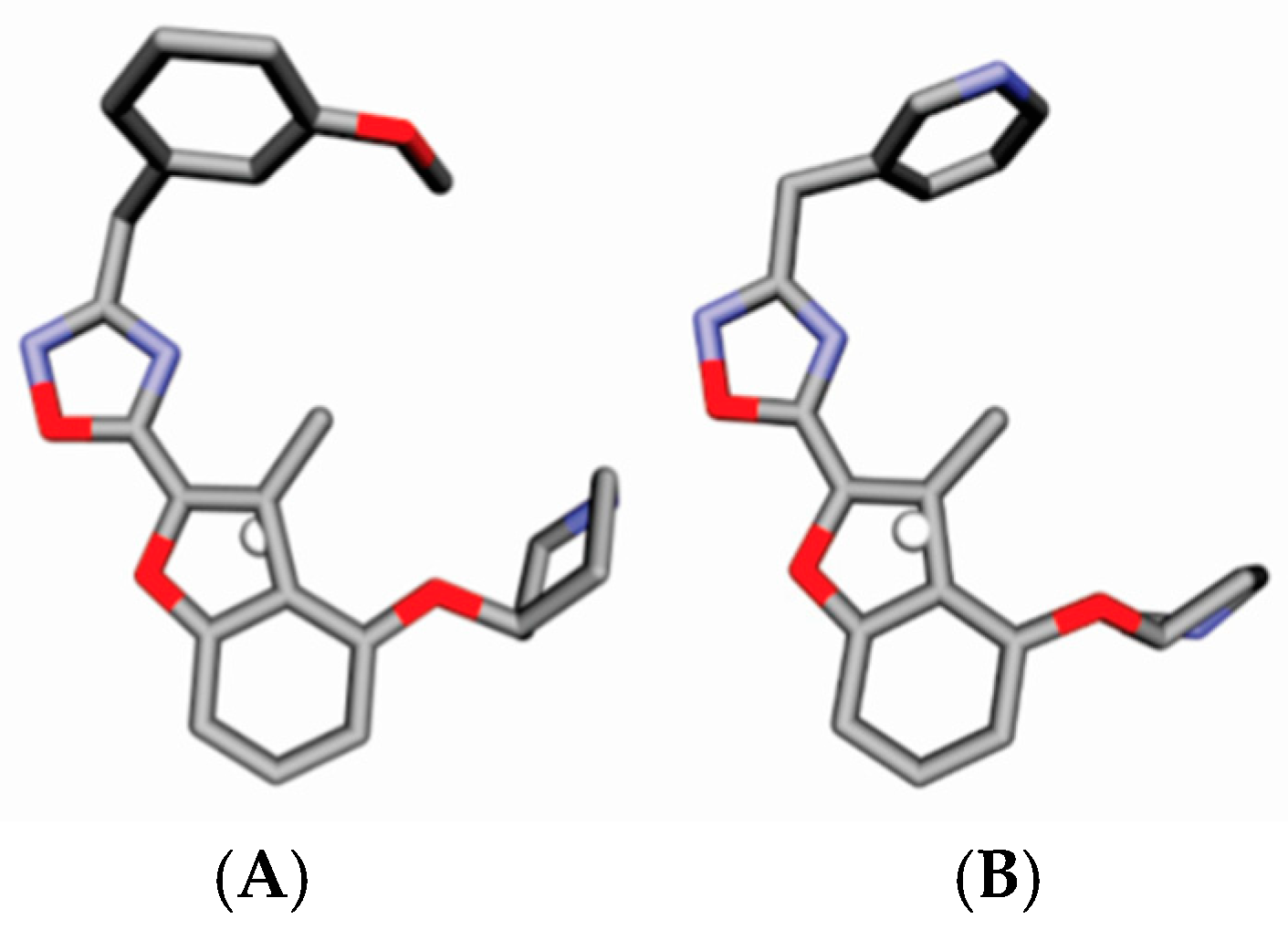
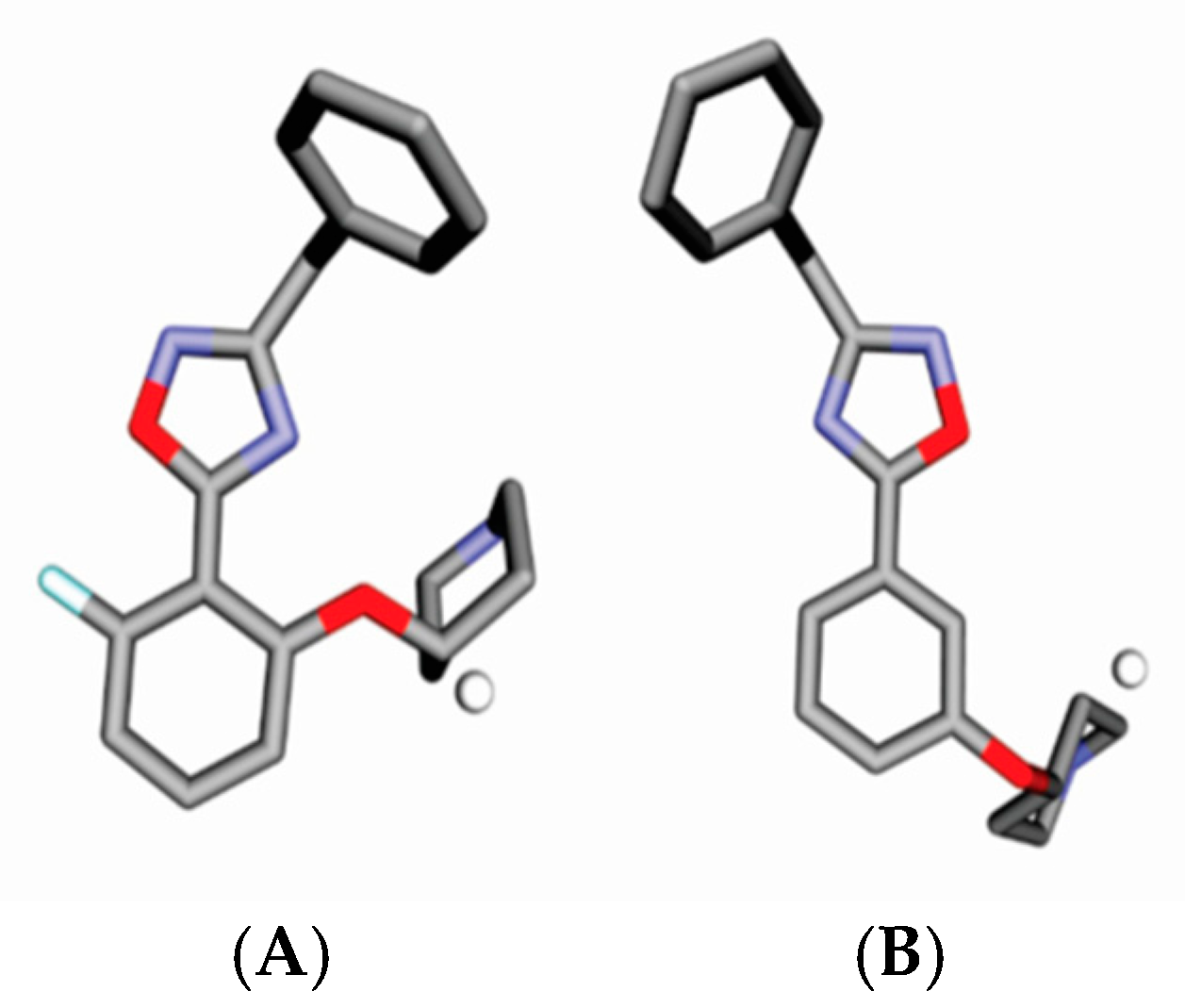


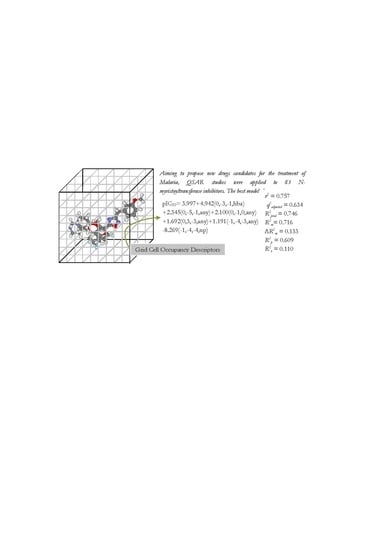
| Alignment | r2 | RMSEC | q2adj | RMSECV | R2Pred | RMSEP | r2m | R2r | R2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.746 | 0.481 | 0.607 | 0.549 | 0.532 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.312 | 0.82 |
| A2 | 0.744 | 0.478 | 0.608 | 0.548 | 0.548 | 0.663 | 0.692 | 0.343 | 0.799 |
| A3 | 0.761 | 0.469 | 0.609 | 0.546 | 0.508 | 0.702 | 0.735 | 0.182 | 0.994 |
| A4 | 0.708 | 0.508 | 0.576 | 0.579 | 0.588 | 0.595 | 0.645 | 0.287 | 0.825 |
| A5 | 0.736 | 0.511 | 0.589 | 0.566 | 0.477 | 0.698 | 0.766 | 0.245 | 0.895 |
| A6 | 0.739 | 0.477 | 0.582 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.637 | 0.67 | 0.286 | 0.83 |
| A7 | 0.722 | 0.503 | 0.584 | 0.571 | 0.555 | 0.656 | 0.683 | 0.291 | 0.831 |
| A8 | 0.746 | 0.445 | 0.605 | 0.551 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.606 | 0.216 | 0.891 |
| A9 | 0.734 | 0.491 | 0.578 | 0.566 | 0.547 | 0.684 | 0.693 | 0.25 | 0.861 |
| A10 | 0.723 | 0.519 | 0.583 | 0.572 | 0.503 | 0.676 | 0.74 | 0.311 | 0.816 |
| Alignment | r2 | RMSEC | q2adj | RMSECV | R2Pred | RMSEP | R2m | R2r | R2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0.728 | 0.504 | 0.617 | 0.544 | 0.728 | 0.532 | 0.688 | 0.301 | 0.476 |
| B2 | 0.728 | 0.515 | 0.607 | 0.553 | 0.763 | 0.496 | 0.749 | 0.289 | 0.482 |
| B3 | 0.757 | 0.472 | 0.634 | 0.527 | 0.746 | 0.515 | 0.716 | 0.11 | 0.609 |
| B4 | 0.704 | 0.549 | 0.585 | 0.573 | 0.782 | 0.476 | 0.765 | 0.253 | 0.473 |
| B5 | 0.725 | 0.5 | 0.601 | 0.55 | 0.706 | 0.553 | 0.692 | 0.198 | 0.526 |
| B6 | 0.692 | 0.559 | 0.576 | 0.581 | 0.771 | 0.489 | 0.755 | 0.272 | 0.448 |
| B7 | 0.69 | 0.556 | 0.581 | 0.577 | 0.751 | 0.509 | 0.735 | 0.289 | 0.437 |
| B8 | 0.73 | 0.514 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.489 | 0.75 | 0.209 | 0.527 |
| B9 | 0.723 | 0.528 | 0.605 | 0.555 | 0.786 | 0.472 | 0.773 | 0.229 | 0.508 |
| B10 | 0.744 | 0.501 | 0.619 | 0.542 | 0.779 | 0.48 | 0.744 | 0.289 | 0.502 |
| No. | Structure | pIC50 | No. | Structure | pIC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
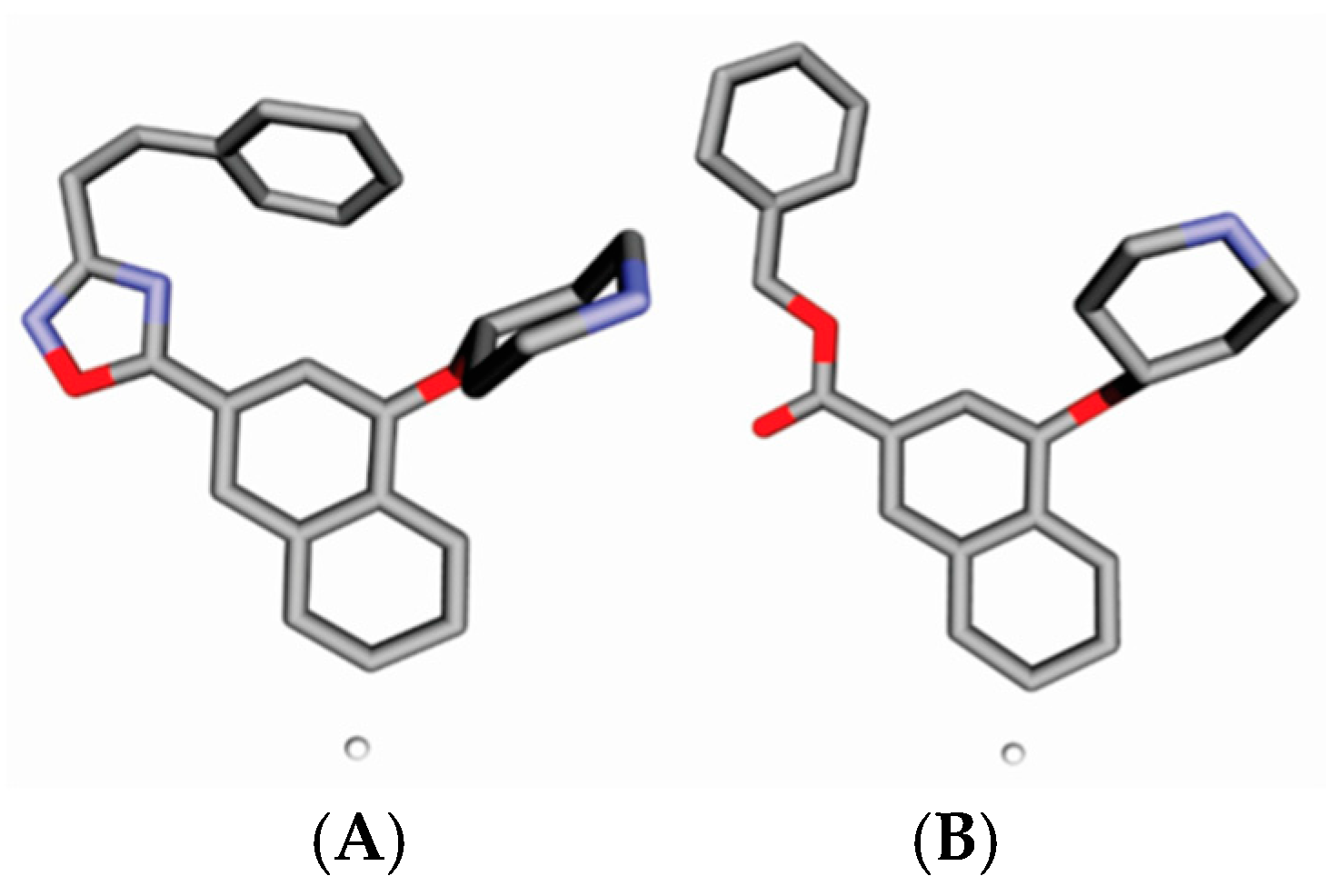
| A | 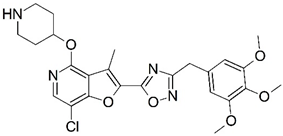 | 7.014 | B | 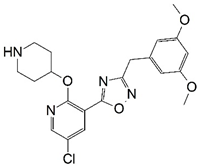 | 7.171 |
| C | 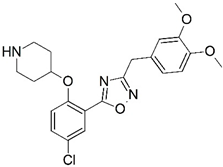 | 7.622 | D | 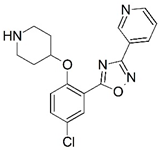 | 8.161 |
| E |  | 7.894 |
| Molecule | miLogP | MW | nON | nOHNH | n | nviolations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3.13 | 514.97 | 10 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| B | 2.74 | 430.89 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| C | 3.13 | 415.88 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
| D | 2.41 | 356.81 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| E | 3.52 | 415.88 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
| No. | Structure | pIC50 | No. | Structure | pIC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | 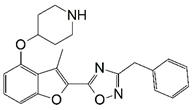 | 6.155 | 2 | 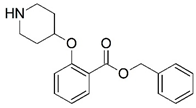 | 4.000 |
| 3 * | 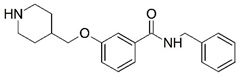 | 4.000 | 4 | 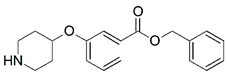 | 4.000 |
| 5 * | 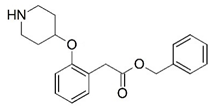 | 4.000 | 6 * |  | 4.000 |
| 7 | 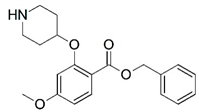 | 4.000 | 8 | 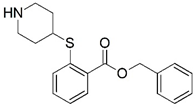 | 4.000 |
| 9 |  | 4.000 | 10 | 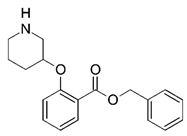 | 4.000 |
| 11 | 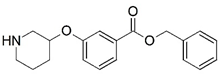 | 4.000 | 12 * | 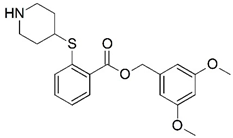 | 5.721 |
| 13 |  | 4.785 | 14 |  | 5.113 |
| 15 | 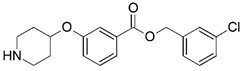 | 4.000 | 16 * | 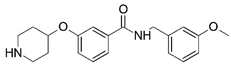 | 4.000 |
| 17 | 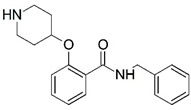 | 4.000 | 18 | 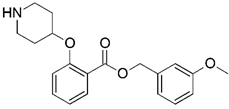 | 4.745 |
| 19 | 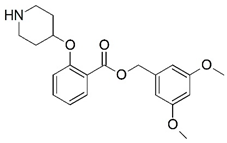 | 5.215 | 20 * |  | 4.366 |
| 21 | 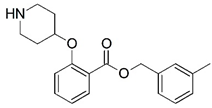 | 4.000 | 22 |  | 4.000 |
| 23 |  | 4.000 | 24 | 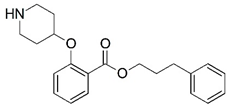 | 4.000 |
| 25 | 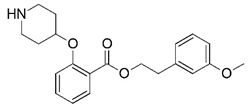 | 4.000 | 26 |  | 5.699 |
| 27 | 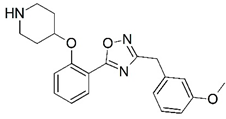 | 6.400 | 28 |  | 6.102 |
| 29 |  | 5.780 | 30 * | 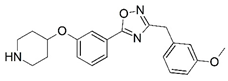 | 6.398 |
| 31 |  | 5.796 | 32 | 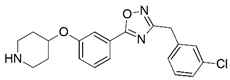 | 5.420 |
| 33 * |  | 5.292 | 34 |  | 6.456 |
| 35 | 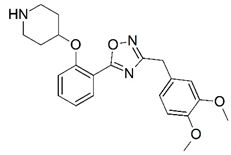 | 6.678 | 36 |  | 6.468 |
| 37 |  | 5.131 | 38 | 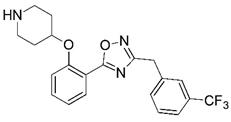 | 5.585 |
| 39 * |  | 4.730 | 40 * |  | 5.585 |
| 41 | 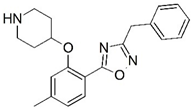 | 5.886 | 42 |  | 5.284 |
| 43 | 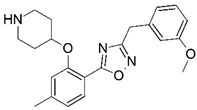 | 6.000 | 44 | 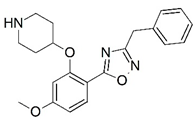 | 5.602 |
| 45 | 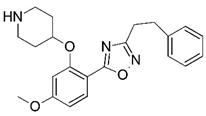 | 4.876 | 46 | 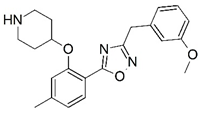 | 6.319 |
| 47 |  | 6.215 | 48 |  | 6.051 |
| 49 | 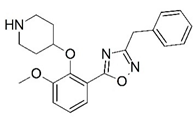 | 4.445 | 50 * | 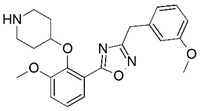 | 4.958 |
| 51 |  | 4.086 | 52 |  | 4.217 |
| 53 |  | 6.398 | 54 | 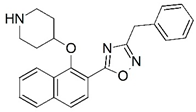 | 5.569 |
| 55 | 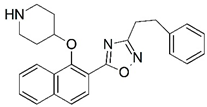 | 4.663 | 56 * | 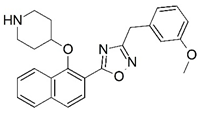 | 6.229 |
| 57 * | 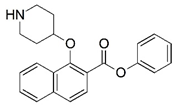 | 4.182 | 58 |  | 5.056 |
| 59 | 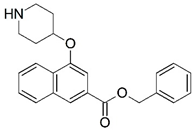 | 5.009 | 60 |  | 5.149 |
| 61 * | 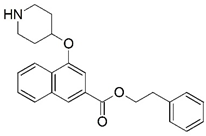 | 5.886 | 62 |  | 5.886 |
| 63 | 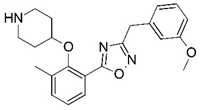 | 4.801 | 64 | 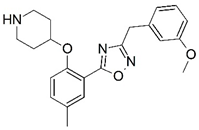 | 5.201 |
| 65 * | 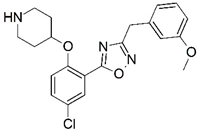 | 6.959 | 66 * | 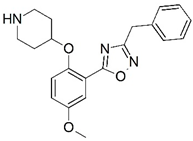 | 5.538 |
| 67 | 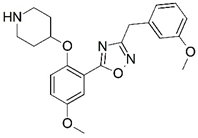 | 6.482 | 68 | 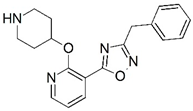 | 5.921 |
| 69* | 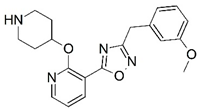 | 6.769 | 70 |  | 5.569 |
| 71 |  | 6.824 | 72 |  | 6.051 |
| 73 |  | 7.222 | 74 |  | 6.000 |
| 75 |  | 6.620 | 76 * |  | 6.638 |
| 77 | 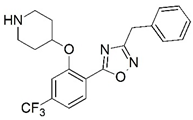 | 5.495 | 78 | 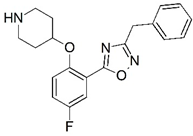 | 5.959 |
| 79 | 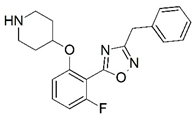 | 6.181 | 80 * | 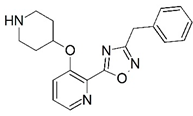 | 5.187 |
| 81 | 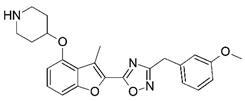 | 7.301 | 82 | 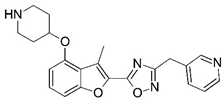 | 6.921 |
| 83 |  | 6.201 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Garcia, L.; De Mecenas Filho, M.A.; Musilek, K.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C.; Da Cunha, E.F.F. QSAR Study of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors of Antimalarial Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092348
Santos-Garcia L, De Mecenas Filho MA, Musilek K, Kuca K, Ramalho TC, Da Cunha EFF. QSAR Study of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors of Antimalarial Agents. Molecules. 2018; 23(9):2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092348
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Garcia, Letícia, Marco Antônio De Mecenas Filho, Kamil Musilek, Kamil Kuca, Teodorico Castro Ramalho, and Elaine Fontes Ferreira Da Cunha. 2018. "QSAR Study of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors of Antimalarial Agents" Molecules 23, no. 9: 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092348
APA StyleSantos-Garcia, L., De Mecenas Filho, M. A., Musilek, K., Kuca, K., Ramalho, T. C., & Da Cunha, E. F. F. (2018). QSAR Study of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors of Antimalarial Agents. Molecules, 23(9), 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092348