Graphene-Derivatized Silica Composite as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Combined with GC–MS/MS for the Determination of Polycyclic Musks in Aqueous Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of rGO@silica
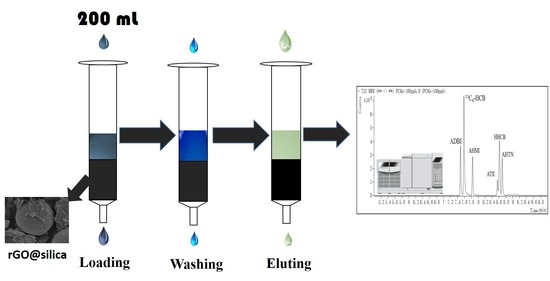
2.2. Optimization of SPE Procedures
2.2.1. Effect of the Elution Solvent
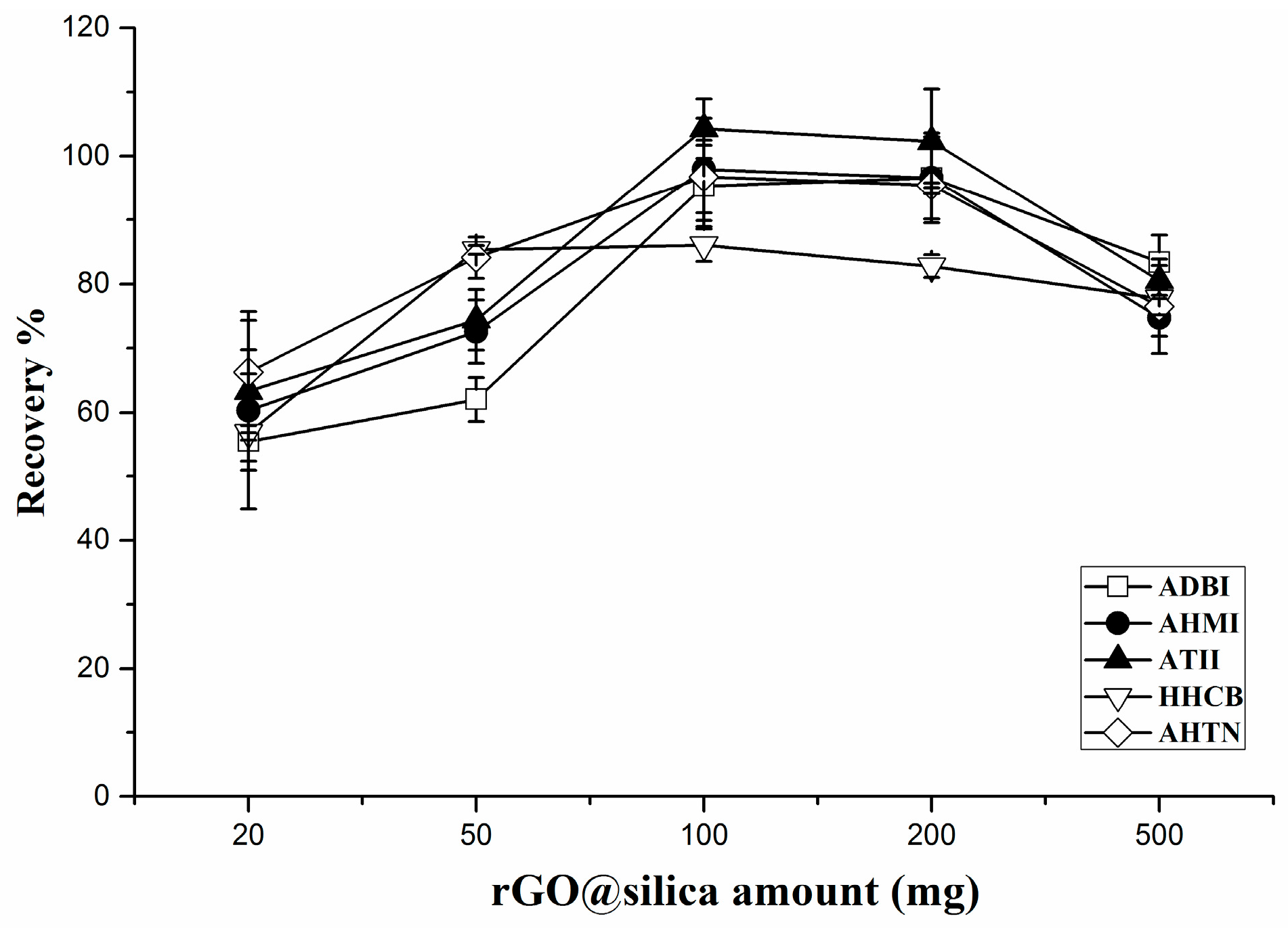
2.2.2. Effect of the Sorbent Amount
2.2.3. Effect of the Sample Volume and pH
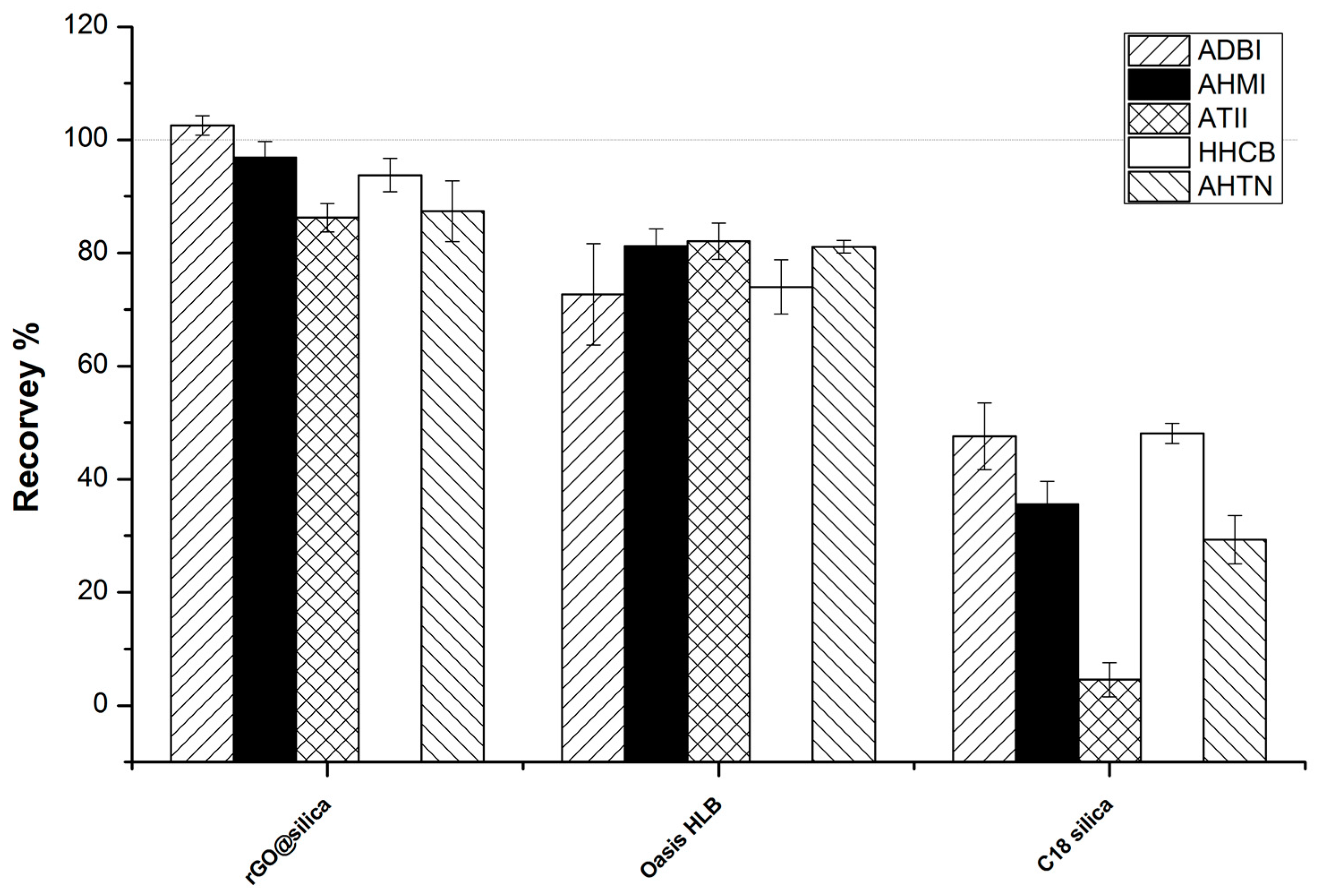
2.3. Comparison with Other Sorbents
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Application to Real Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of rGO@silica
3.3. Analytical Procedure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montes-Grajales, D.; Fennix-Agudelo, M.; Miranda-Castro, W. Occurrence of personal care products as emerging chemicals of concern in water resources: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.-J.; Pan, C.-G.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.-S.; Windfeld, R.; Salvito, D.; Selck, H.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of emerging organic chemicals in urban rivers: Guangzhou as a case study in china. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, C.A.; Helm, P.A.; Muir, D.; Puggioni, G.; Lohmann, R. Polycyclic musks in the air and water of the lower great lakes: Spatial distribution and volatilization from surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11575–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimkus, G.G. Polycyclic musk fragrances in the aquatic environment. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 111, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Kuch, B.; Metzger, J.W. Occurrence and fate of synthetic musk fragrances in a small german river. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, K.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Luan, T. Fully automatic exposed and in-syringe dynamic single-drop microextraction with online agitation for the determination of polycyclic musks in surface waters of the pearl river estuary and south china sea. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromme, H.; Otto, T.; Pilz, K. Polycyclic musk fragrances in different environmental compartments in Berlin (Germany). Water Res. 2001, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Składanowski, A.C.; Stepnowski, P.; Kleszczyński, K.; Dmochowska, B. Amp deaminase in vitro inhibition by xenobiotics: A potential molecular method for risk assessment of synthetic nitro- and polycyclic musks, imidazolium ionic liquids and n-glucopyranosyl ammonium salts. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Bao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, P. Ecotoxicological effects of polycyclic musks and cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, H.; Li, G.; An, T. Photo-induced oxidative damage to dissolved free amino acids by the photosensitizer polycyclic musk tonalide: Transformation kinetics and mechanisms. Water Res. 2017, 115, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, R.E.; Nishioka, M.; Standley, L.J.; Perovich, L.J.; Brody, J.G.; Rudel, R.A. Endocrine disruptors and asthma-associated chemicals in consumer products. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, P.H.; Muir, D.C.G. Identifying new persistent and bioaccumulative organics among chemicals in commerce. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, M.; Beltran, J. Determination of synthetic musk fragrances. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 96, 1213–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüssler, W.; Nitschke, L. Determination of trace amounts of Galaxolide® (HHCB) by HPLC. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 361, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklenyik, Z.; Bryant, X.A.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. SPE/SPME–GC/MS approach for measuring musk compounds in serum and breast milk. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 858, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Duan, H.; Wu, Y.; Berset, J.-D.; Shao, B. Simultaneous analysis of synthetic musks and triclosan in human breast milk by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Gopalan, A.-I.; Lee, K.-P. Enantioselective determination of polycyclic musks in river and wastewater by GC/MS/MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y. Rapid determination of trace sulfonamides in fish by graphene-based SPE coupled with UPLC/MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Consoli, L.; Zeffiro, A.; Profumo, A. Graphene-derivatized silica as an efficient solid-phase extraction sorbent for pre-concentration of fluoroquinolones from water followed by liquid-chromatography fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1379, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Zeng, L.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, G. Evaluation of graphene as an advantageous adsorbent for solid-phase extraction with chlorophenols as model analytes. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Liu, L.H.; Chen, Z.B.; Hong, L.M. Analysis of phthalate acid esters in environmental water by magnetic graphene solid phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1329, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Xia, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, M. Graphene as an efficient sorbent for the SPE of organochlorine pesticides in water samples coupled with GC–MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3586–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Han, Q.; Xia, J.; Xia, L.; Ding, M.; Tang, J. Graphene-based solid-phase extraction disk for fast separation and preconcentration of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Hong, H.; Liu, X.; Guan, W.; Meng, L.; Ye, Y.; Ma, Y. Graphene-dispersive solid-phase extraction of phthalate acid esters from environmental water. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Li, Z.; Zang, X.H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Solid-phase microextraction with a graphene-composite-coated fiber coupled with GC for the determination of some halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, T.; Zeng, L.; Jiang, G. Graphene and graphene oxide sheets supported on silica as versatile and high-performance adsorbents for solid-phase extraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5913–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Shi, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Graphene as solid-phase extraction adsorbent for CZE determination of sulfonamide residues in meat samples. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Mao, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Determination of chloramphenicol in aquatic products by graphene-based SPE coupled with HPLC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, F.; Ji, S.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. Graphene nanoplatelets as a highly efficient solid-phase extraction sorbent for determination of phthalate esters in aqueous solution. Talanta 2014, 120, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maidatsi, K.V.; Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Sakkas, V.A.; Stalikas, C.D. Octyl-modified magnetic graphene as a sorbent for the extraction and simultaneous determination of fragrance allergens, musks, and phthalates in aqueous samples by gas chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3758–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, R.; Ouyang, G. Preparation and evaluation of amino modified graphene solid-phase microextraction fiber and its application to the determination of synthetic musks in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.-B.; Zhu, G.-T.; Li, X.-S.; Yuan, B.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q. Facile fabrication of reduced graphene oxide-encapsulated silica: A sorbent for solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1299, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |



| Analyte | Linear Range (ng/L) | R | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADBI | 10–500 | 0.9992 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| AHMI | 10–500 | 0.9978 | 0.3 | 1.1 |
| ATII | 10–500 | 0.9958 | 0.8 | 2.1 |
| HHCB | 10–500 | 0.9976 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| AHTN | 10–500 | 0.9977 | 0.5 | 1.2 |
| Tap Water Sample | River Water Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | Spiked Levels (ng/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
| ADBI | 50 | 91.3 | 5.2 | 88.6 | 5.7 |
| 100 | 102.4 | 6.1 | 102.3 | 3.5 | |
| 200 | 97.8 | 4.5 | 82.9 | 3.9 | |
| AHMI | 50 | 89.4 | 1.9 | 87.1 | 2.6 |
| 100 | 99.2 | 2.3 | 97.1 | 3.8 | |
| 200 | 92.3 | 0.8 | 93.1 | 5.2 | |
| ATII | 50 | 99.1 | 2.1 | 96.9 | 5.8 |
| 100 | 98.8 | 2.4 | 101.1 | 3.3 | |
| 200 | 89.6 | 3.4 | 85.3 | 5.9 | |
| HHCB | 50 | 96.9 | 2.7 | 107.1 | 2.5 |
| 100 | 93.1 | 5.2 | 106.3 | 3.3 | |
| 200 | 86.6 | 1.7 | 103.9 | 3.1 | |
| AHTN | 50 | 93.3 | 5.9 | 99.7 | 5.7 |
| 100 | 95.6 | 2.9 | 96.4 | 4.3 | |
| 200 | 105.9 | 5.5 | 84.5 | 3.1 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ping, H.; Lu, A. Graphene-Derivatized Silica Composite as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Combined with GC–MS/MS for the Determination of Polycyclic Musks in Aqueous Samples. Molecules 2018, 23, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020318
Li C, Chen J, Chen Y, Wang J, Ping H, Lu A. Graphene-Derivatized Silica Composite as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Combined with GC–MS/MS for the Determination of Polycyclic Musks in Aqueous Samples. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Cheng, Jiayi Chen, Yan Chen, Jihua Wang, Hua Ping, and Anxiang Lu. 2018. "Graphene-Derivatized Silica Composite as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Combined with GC–MS/MS for the Determination of Polycyclic Musks in Aqueous Samples" Molecules 23, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020318
APA StyleLi, C., Chen, J., Chen, Y., Wang, J., Ping, H., & Lu, A. (2018). Graphene-Derivatized Silica Composite as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Combined with GC–MS/MS for the Determination of Polycyclic Musks in Aqueous Samples. Molecules, 23(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020318