A Comprehensive Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Database to Accelerate Genetic Improvements in Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Retrieving and Processing pre-miRNA Sequences
2.2. Microsatellite Search and Localization and Primer Design
2.3. In Silico Characterization, Transferability, and Polymorphism of Primer Sets
2.4. Creation of PmiRNASM (Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker) Database
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Frequency, Density and Distribution of Simple Sequence Repeats
3.2. Occurrence and Relative Counts of Repeat Units
3.3. Effect of Nucleotide Composition on Simple Sequence Repeat Frequency, Density and Variation within pre-microRNAs
3.4. Location of Simple Sequence Repeat Loci in pre-microRNA Sequences
3.5. Pre-microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Development and In Silico Characterization, Transferability, and Polymorphism Test
3.6. PmiRNASSR (Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker) Database
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karaoglu, H.; Lee, C.; Meyer, W. Survey of Simple Sequence Repeats in Completed Fungal Genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-S.; Booth, J.G.; Gauch, H.G.; Sun, Q.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, K. Simple sequence repeats in Neurospora crassa: Distribution, polymorphism and evolutionary inference. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Gáspári, Z.; Jurka, J. Microsatellites in Different Eukaryotic Genomes: Survey and Analysis. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, M.V.; Ranjekar, P.K.; Gupta, V.S. Differential Distribution of Simple Sequence Repeats in Eukaryotic Genome Sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesacker, A.; Kishore, V.K.; Gao, W.; Tang, S.; Kolkman, J.M.; Gingle, A.; Matvienko, M.; Kozik, A.; Michelmore, R.M.; Lai, Z.; et al. SSRs and INDELs mined from the sunflower EST database: Abundance, polymorphisms, and cross-taxa utility. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Korol, A.B.; Fahima, T.; Nevo, E. Microsatellites within Genes: Structure, Function, and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, F.; da Maia, L.; de Oliveira, A. In silico comparative analysis of SSR markers in plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondon, J.W.; Garner, H.R. Molecular origins of rapid and continuous morphological evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18058–18063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, Y.; King, D.G. Simple sequence repeats as advantageous mutators in evolution. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, Y.; King, D.; Soller, M. Simple sequence repeats as a source of quantitative genetic variation. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifonov, E.N. Tuning function of tandemly repeating sequences: A molecular device for fast adaptation. In Evolutionary Theory and Processes: Modern Horizons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Schlotterer, C. The evolution of molecular markers [mdash] just a matter of fashion? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.F.; Consoli, L.; Bombonatto, E.A.D.S.; Bonato, A.L.V.; Maciel, J.L.N. Development of Genomic SSR Markers and Molecular Characterization of Magnaporthe oryzae Isolates from Wheat in Brazil. Biochem. Genet. 2014, 52, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. Analysis of genetic diversity among Chinese wild Vitis species revealed with SSR and SRAP markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würschum, T.; Langer, S.M.; Longin, C.F.H.; Korzun, V.; Akhunov, E.; Ebmeyer, E.; Schachschneider, R.; Schacht, J.; Kazman, E.; Reif, J.C. Population structure, genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in elite winter wheat assessed with SNP and SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaing, A.; Moe, K.; Hong, W.; Park, C.; Yeon, K.; Park, H.; Kim, D.; Choi, B.; Jung, J.; Chae, S.; et al. Phylogenetic relationships of chrysanthemums in Korea based on novel SSR markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 5335–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, G.; Simko, I. Development of genomic SSR markers for fingerprinting lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivars and mapping genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akfirat, F.S.; Uncuoglu, A.A. Genetic Diversity of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Revealed by SSR Markers. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 51, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayesh, E.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Bilkish, N.; Sun, X.; Leng, X.; Fang, J. Development of highly polymorphic EST-SSR markers and segregation in F1 hybrid population of Vitis vinifera L. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 3871–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, N.-C.; Jansen, J.; Nagappan, J.; Ishak, Z.; Chin, C.-W.; Tan, S.-G.; Cheah, S.-C.; Singh, R. Identification of QTLs Associated with Callogenesis and Embryogenesis in Oil Palm Using Genetic Linkage Maps Improved with SSR Markers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-G.; Chao, S.; Friesen, T.L.; Faris, J.; Zhong, S.; Xu, S.S. Identification of novel tan spot resistance QTLs using an SSR-based linkage map of tetraploid wheat. Mol. Breed. 2009, 25, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Bagchi, M.; Nath, U.K.; Biswas, D.; Natarajan, S.; Jesse, D.M.I.; Park, J.-I.; Nou, I.-S. Transcriptome wide SSR discovery cross-taxa transferability and development of marker database for studying genetic diversity population structure of Lilium species. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.K.; Nath, U.K.; Howlader, J.; Bagchi, M.; Natarajan, S.; Kayum, A.; Kim, H.-T.; Park, J.-I.; Kang, J.-G.; Nou, I.-S. Exploration and Exploitation of Novel SSR Markers for Candidate Transcription Factor Genes in Lilium Species. Genes 2018, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.C.; Grover, A.; Kahl, G. Mining microsatellites in eukaryotic genomes. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sheng, O.; Mayer, C.; Yi, G.; Deng, G. Genome-Wide Novel Genic Microsatellite Marker Resource Development and Validation for Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Analysis of Banana. Genes 2020, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Darbar, J.N.; Borrell, J.S.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Nuraga, G.W.; Demissew, S.; Wilkin, P.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. The landscape of microsatellites in the enset (Ensete ventricosum) genome and web-based marker resource development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sheng, O.; Mayer, C.; Yi, G. Genome-Wide Computational Analysis of Musa Microsatellites: Classification, Cross-Taxon Transferability, Functional Annotation, Association with Transposons & miRNAs, and Genetic Marker Potential. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, T.P.; Xie, F.; Freistaedter, A.; Burklew, C.E.; Zhang, B. Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their target genes in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Planta 2010, 232, 1289–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, V.; Ramchiary, N.; Paul, P.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.; Hur, Y.; Lim, Y.P. Identification of potential microRNAs and their targets in Brassica rapa L. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Ling, Y.; Su, Z. PMRD: Plant microRNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D806–D813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, N.; Soniya, E.V. Identification of an miRNA candidate reflects the possible significance of transcribed microsatellites in the hairpin precursors of black pepper. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2012, 12, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Hu, H.; Sun, Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of miRNA-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in rice. Rice 2013, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Wang, K.; Hu, T.; Shan, G.; Sun, J.; Guo, A.-Y. Genome-wide identification of SNPs in microRNA genes and the SNP effects on microRNA target binding and biogenesis. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mondal, T.K. Computational Identification of Conserved microRNAs and Their Targets in Tea (Camellia sinensis). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 01, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cannon, C.H.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. Conservation and divergence of plant microRNA genes. Plant J. 2006, 46, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Quan, C.; Cui, Y.; Bian, S. Computational identification of conserved microRNAs and their targets from expression sequence tags of blueberry (Vaccinium corybosum). Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e29462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Pan, X.P.; Cox, S.B.; Cobb, G.; Anderson, T.A. Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur-Arie, R.; Cohen, C.J.; Eitan, Y.; Shelef, L.; Hallerman, E.M.; Kashi, Y. Simple Sequence Repeats in Escherichia coli: Abundance, Distribution, Composition, and Polymorphism. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tan, Z.; Zeng, G.; Peng, J. Comprehensive Analysis of Simple Sequence Repeats in Pre-miRNAs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, F.M.; Huo, N.; Gu, Y.Q.; Luo, M.-C.; Ma, Y.; Hane, D.; Lazo, G.R.; Dvorak, J.; Anderson, O.D. BatchPrimer3: A high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrakumar, P.; Biswal, A.K.; Balachandran, S.M.; Srinivasarao, K.; Sundaram, R.M. Simple sequence repeats in organellar genomes of rice: Frequency and distribution in genic and intergenic regions. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Mondal, T.K. Genome-wide development of novel miRNA-based microsatellite markers of rice (Oryza sativa) for genotyping applications. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Singh, A.; Verma, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Mahima; Singh, S.; Mishra, V.; Sarkar, A.K. Role of miRNAs in root development of model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 22, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Smita, S.; Mishra, D.C.; Kumar, S.; Singh, B.K.; Rai, A. Abiotic stress responsive miRNA-target network and related markers (SNP, SSR) in Brassica juncea. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Genome-wide development of microRNA-based SSR markers in Medicago truncatula with their transferability analysis and utilization in related legume species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.G.; Singh, N.; Parashuram, S.; Bohra, A.; Mundewadikar, D.M.; Sangnure, V.R.; Babu, K.D.; Sharma, J. Genome wide identification, characterization and validation of novel miRNA-based SSR markers in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzana, G.; Musaza, J.; Wu, F.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Akoy, B.I.R.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide development and application of miRNA-SSR markers in Melilotus genus. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2021, 27, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Mehta, G.; Shefali; Muthusamy, S.K.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, G.P. Development and validation of heat-responsive candidate gene and miRNA gene based SSR markers to analysis genetic diversity in wheat for heat tolerance breeding. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, T.; Pandey, R.; Rustgi, S.; Mir, R.R. Development and use of miRNA-derived SSR markers for the study of genetic diversity, population structure, and characterization of genotypes for breeding heat tolerant wheat varieties. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0231063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
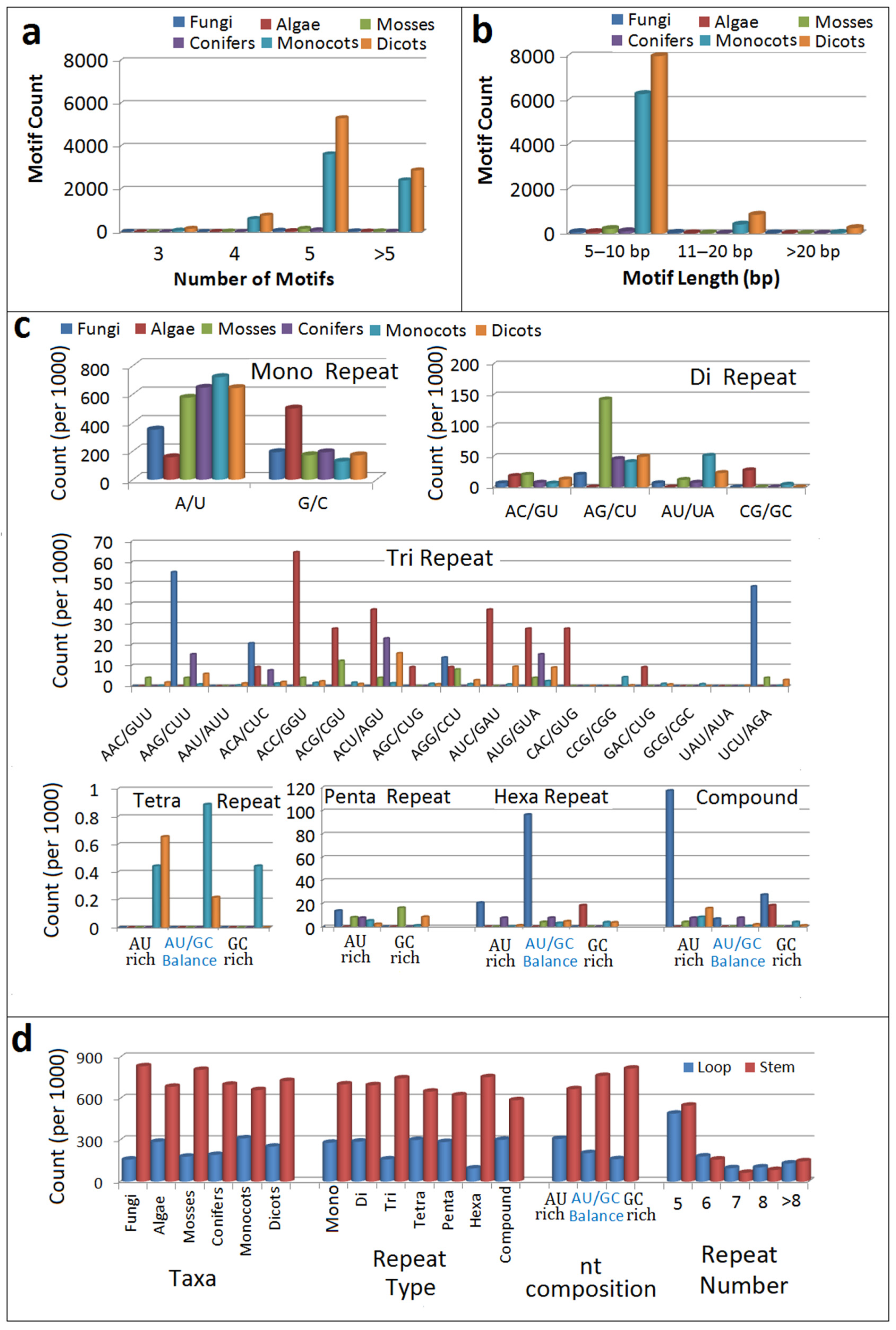
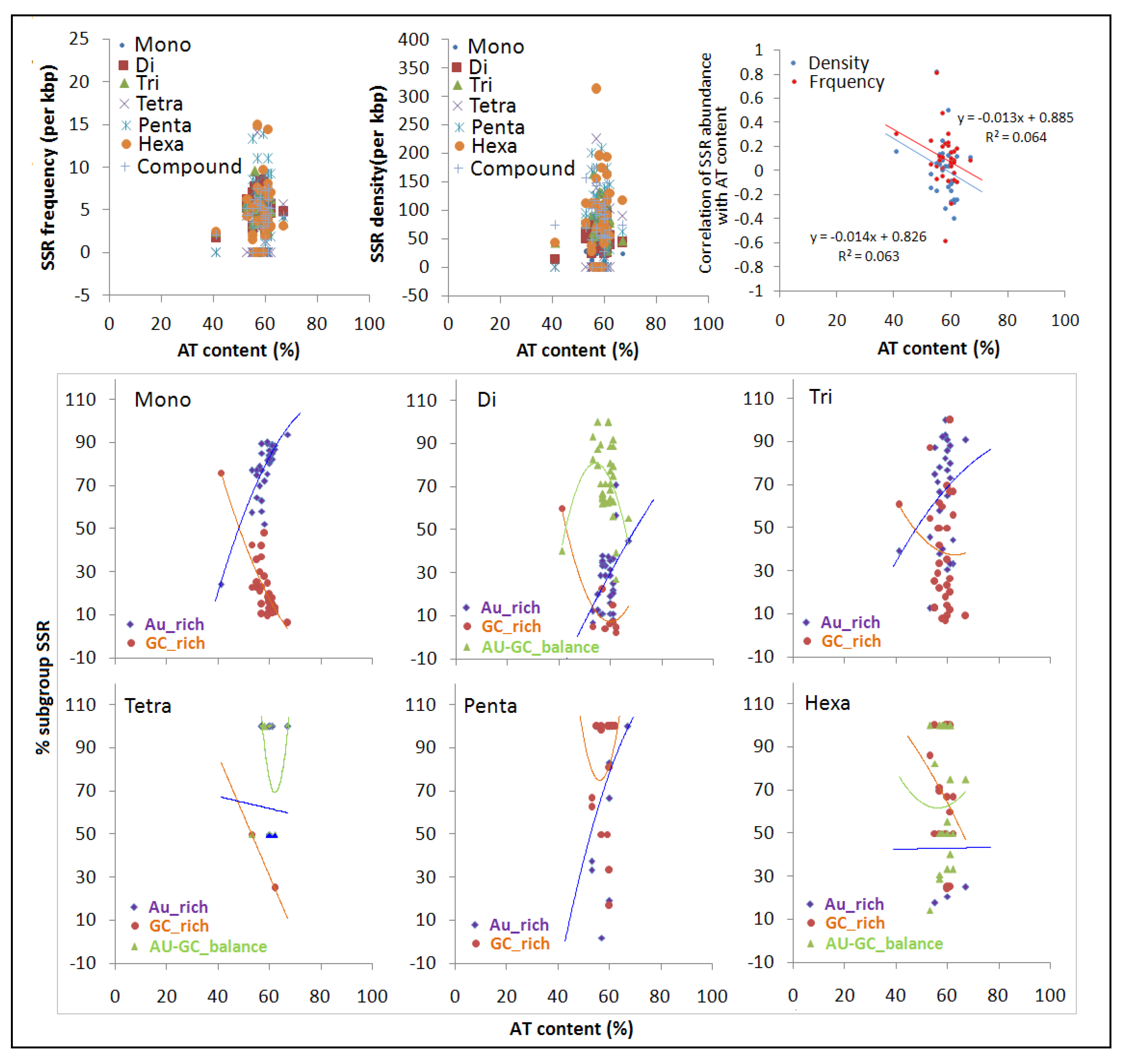



| Item | Fungi | Algae | Mosses | Conifers | Monocots | Dicots | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of species | 23 | 6 | 3 | 10 | 56 | 194 | 292 |
| No. of analyzed PMS | 45 | 109 | 425 | 248 | 6838 | 9227 | 16892 |
| Range length of PMS | 106–865 | 65–932 | 67–533 | 58–650 | 45–910 | 41–1021 | 41–1021 |
| Average length of PMS | 370 | 241 | 158 | 150 | 142 | 141 | 200 |
| Total length of PMS | 16,659 | 26,258 | 67,258 | 37,139 | 973,200 | 1,300,562 | 2,421,076 |
| Average GC content | 48.39 | 57.58 | 47.77 | 46.23 | 44.45 | 44.37 | 48 |
| No. of non-SSR PMS | 7 | 60 | 265 | 154 | 3373 | 4382 | 8241 |
| No. of SSR-containing PMS | 38 | 49 | 160 | 94 | 3465 | 4845 | 8651 |
| % of SSR-containing PMS | 84 | 45 | 38 | 38 | 51 | 53 | 51 |
| Total no. of SSRs | 145 | 108 | 245 | 130 | 6754 | 9149 | 16531 |
| Density of SSRs per bp of PMS | 115 | 243 | 275 | 286 | 144 | 142 | 146 |
| Range of SSR occurrence in PMS | 1–13 | 1–12 | 1–5 | 1–4 | 1–10 | 1–29 | 1–29 |
| Average no. of SSRs per PMS | 3.2 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 |
| Class I SSRs | 25 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 73 | 286 | 401 |
| Class II SSRs | 120 | 101 | 240 | 125 | 6681 | 8863 | 16,130 |
| GC-rich SSRs | 37 | 78 | 52 | 28 | 1071 | 1786 | 3052 |
| AU-rich SSRs | 89 | 28 | 152 | 94 | 5330 | 6724 | 12417 |
| GC–AU balanced SSRs | 19 | 2 | 41 | 8 | 353 | 639 | 1062 |
| Plant Groups | No. of PMS | Repeat Type | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono | Di | Tri | Tetra | Penta | Hexa | Compound | |||
| Fungi | 45 | 79(1.76) | 5(0.11) | 20(0.45) | 0(0.00) | 2(0.04) | 17(0.38) | 22(0.49) | 145(3.22) |
| Algae | 109 | 71(0.65) | 5(0.05) | 28(0.26) | 0(0.00) | 0(0.00) | 2(0.02) | 2(0.02) | 108(0.99) |
| Mosses | 425 | 183(0.43) | 43(0.10) | 11(0.03) | 0(0.00) | 6(0.01) | 1(0.00) | 1(0.00) | 245(0.56) |
| Conifers | 248 | 109(0.44) | 8(0.03) | 8(0.03) | 0(0.00) | 1(0.00) | 2(0.01) | 2(0.01) | 130(0.52) |
| Monocots | 6838 | 5725(0.84) | 698(0.10) | 138(0.02) | 12(0.00) | 44(0.01) | 49(0.01) | 88(0.01) | 6754(0.99) |
| Dicots | 9227 | 7454(0.81) | 791(0.07) | 533(0.06) | 8(0.00) | 101(0.01) | 88(0.01) | 174(0.02) | 9149(0.99) |
| Total | 16,892 | 13,621(0.81) | 1550(0.09) | 738(0.04) | 20(0.00) | 154(0.01) | 159(0.01) | 289(0.02) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, M.K.; Biswas, D.; Bagchi, M.; Yi, G.; Deng, G. A Comprehensive Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Database to Accelerate Genetic Improvements in Crops. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112298
Biswas MK, Biswas D, Bagchi M, Yi G, Deng G. A Comprehensive Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Database to Accelerate Genetic Improvements in Crops. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112298
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Manosh Kumar, Dhiman Biswas, Mita Bagchi, Ganjun Yi, and Guiming Deng. 2021. "A Comprehensive Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Database to Accelerate Genetic Improvements in Crops" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112298
APA StyleBiswas, M. K., Biswas, D., Bagchi, M., Yi, G., & Deng, G. (2021). A Comprehensive Plant microRNA Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Database to Accelerate Genetic Improvements in Crops. Agronomy, 11(11), 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112298







