Decision-Making of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain Based on Grey Entropy Weight and Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
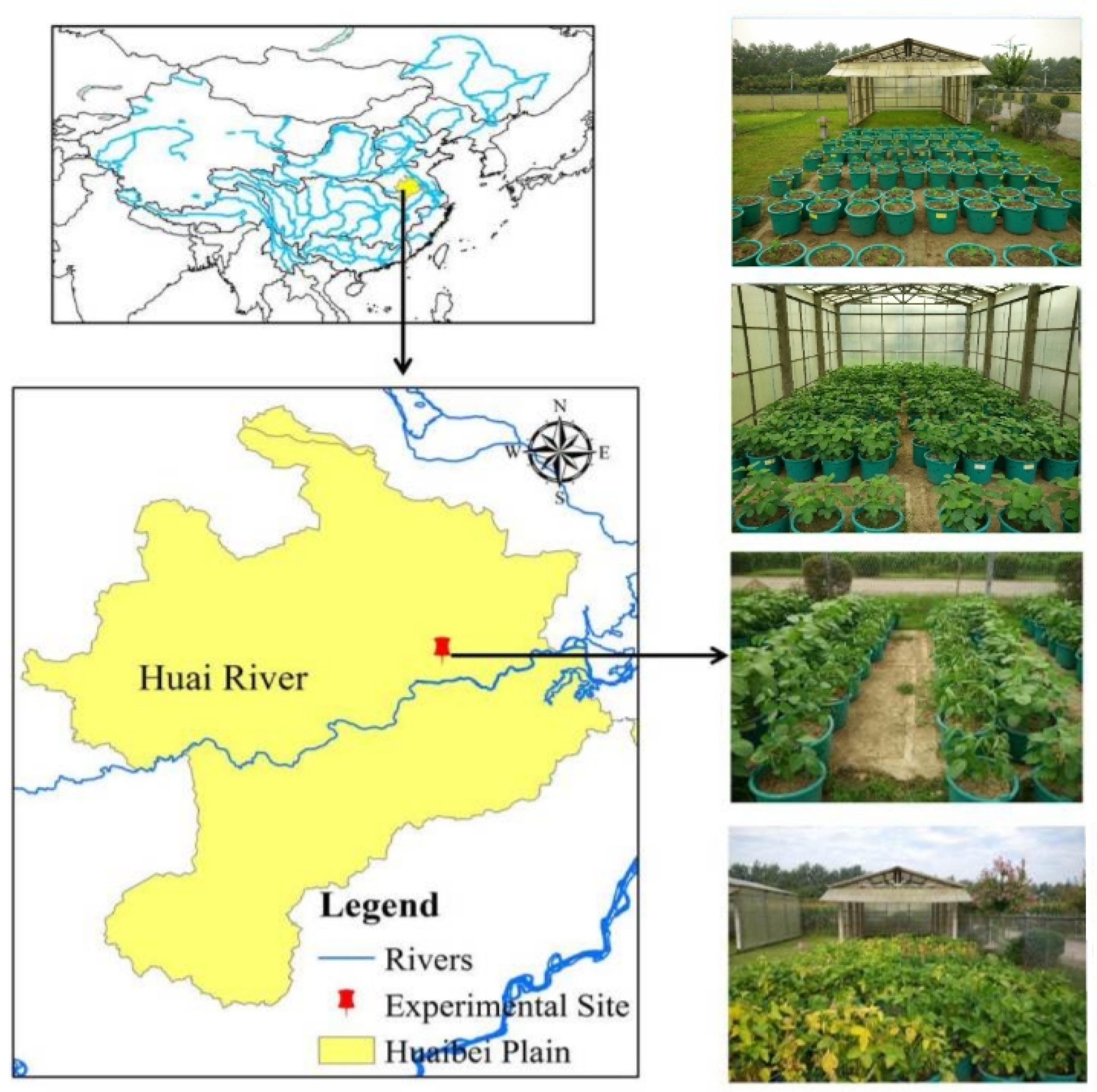
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Crop Management
2.3. Irrigation Scheme Design
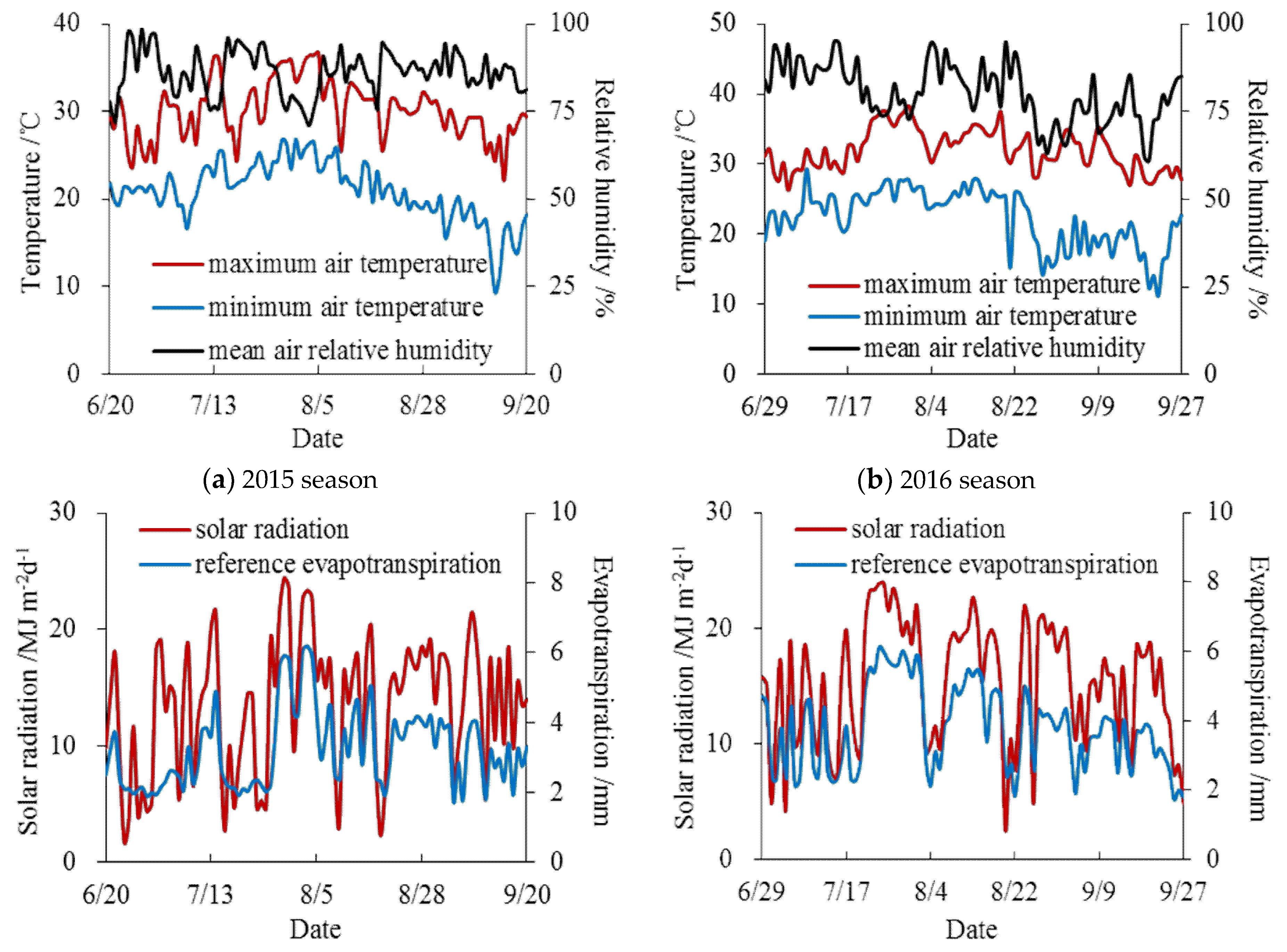
2.4. Measurements
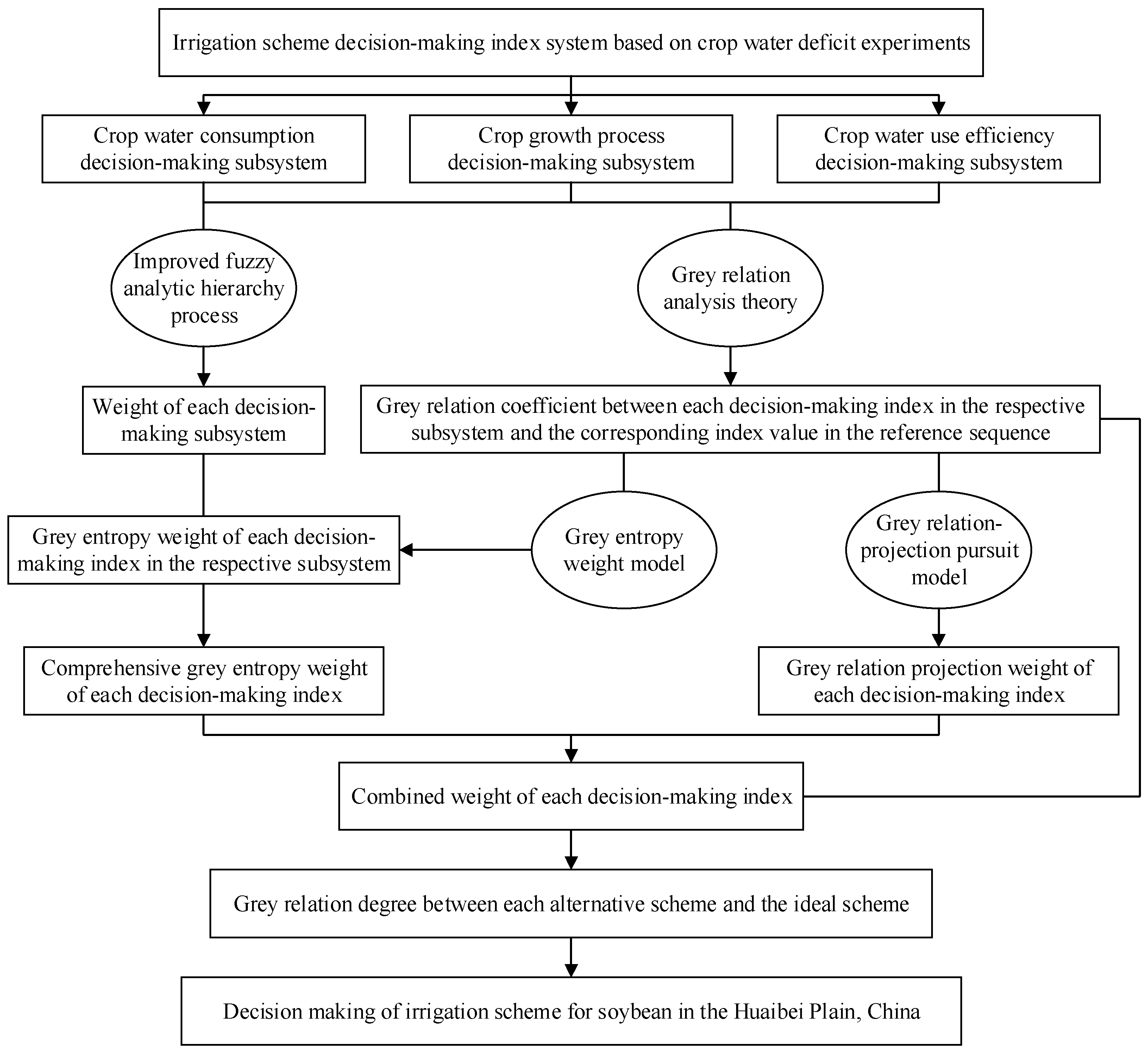
2.5. Irrigation Scheme Decision-Making Model
3. Results and Discussion
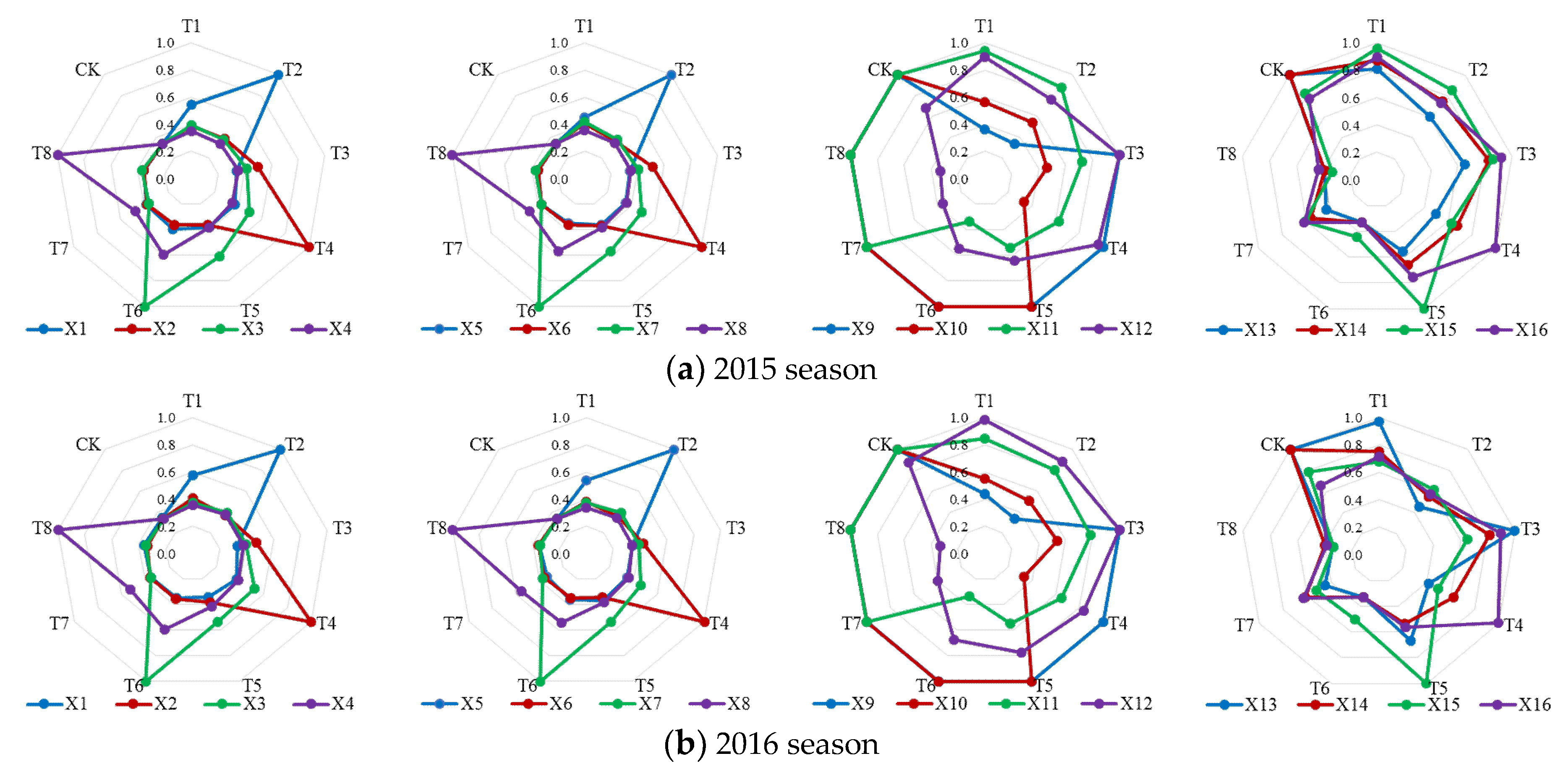
3.1. Irrigation Scheme Decision-Making Index Values
3.2. Grey Relation Coefficient of Each Decision-Making Index
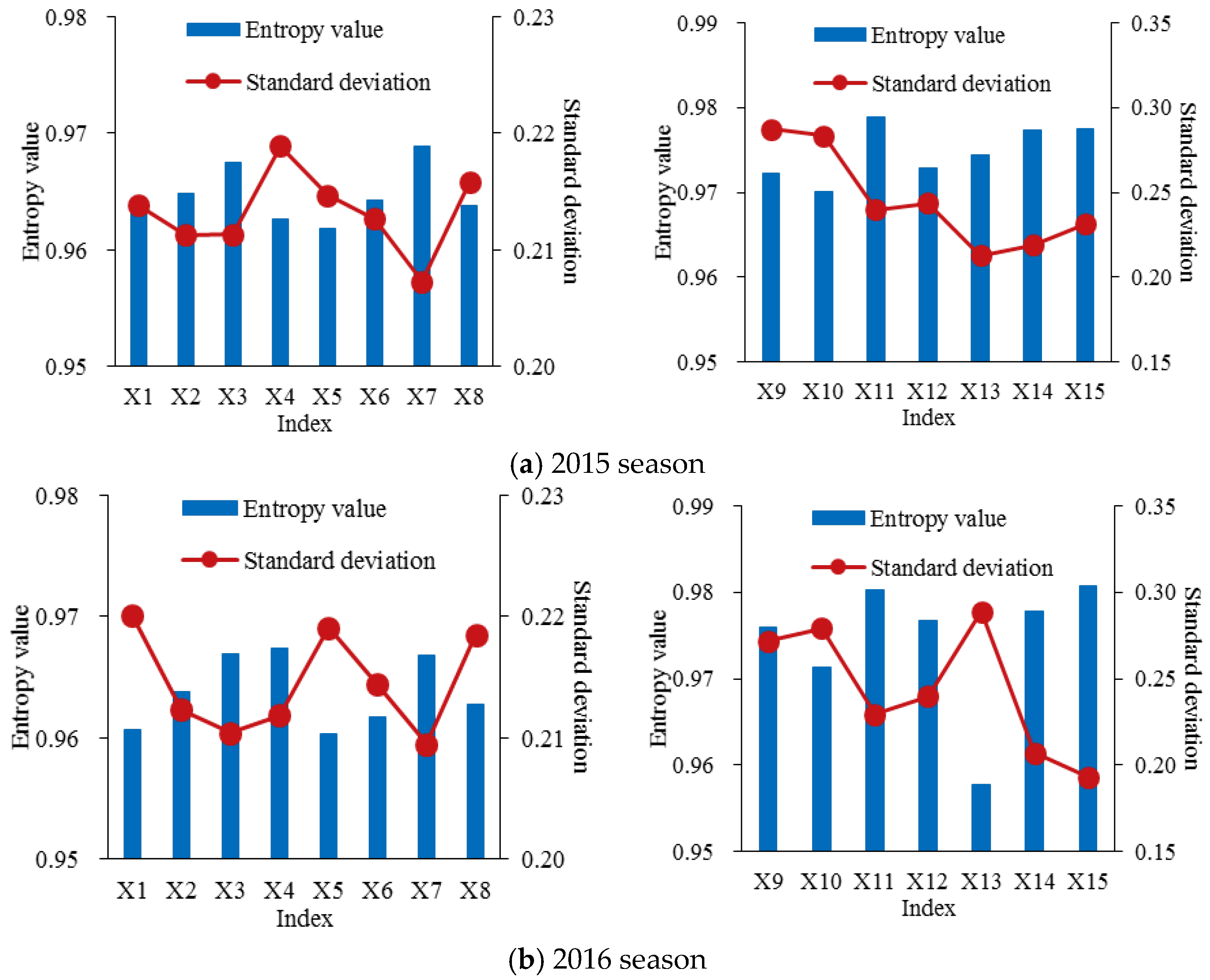
3.3. Grey Entropy Weight of Each Decision-Making Index
3.3.1. Weight of Each Decision-Making Subsystem
3.3.2. Weight of Each Decision-Making Index in the Respective Subsystem
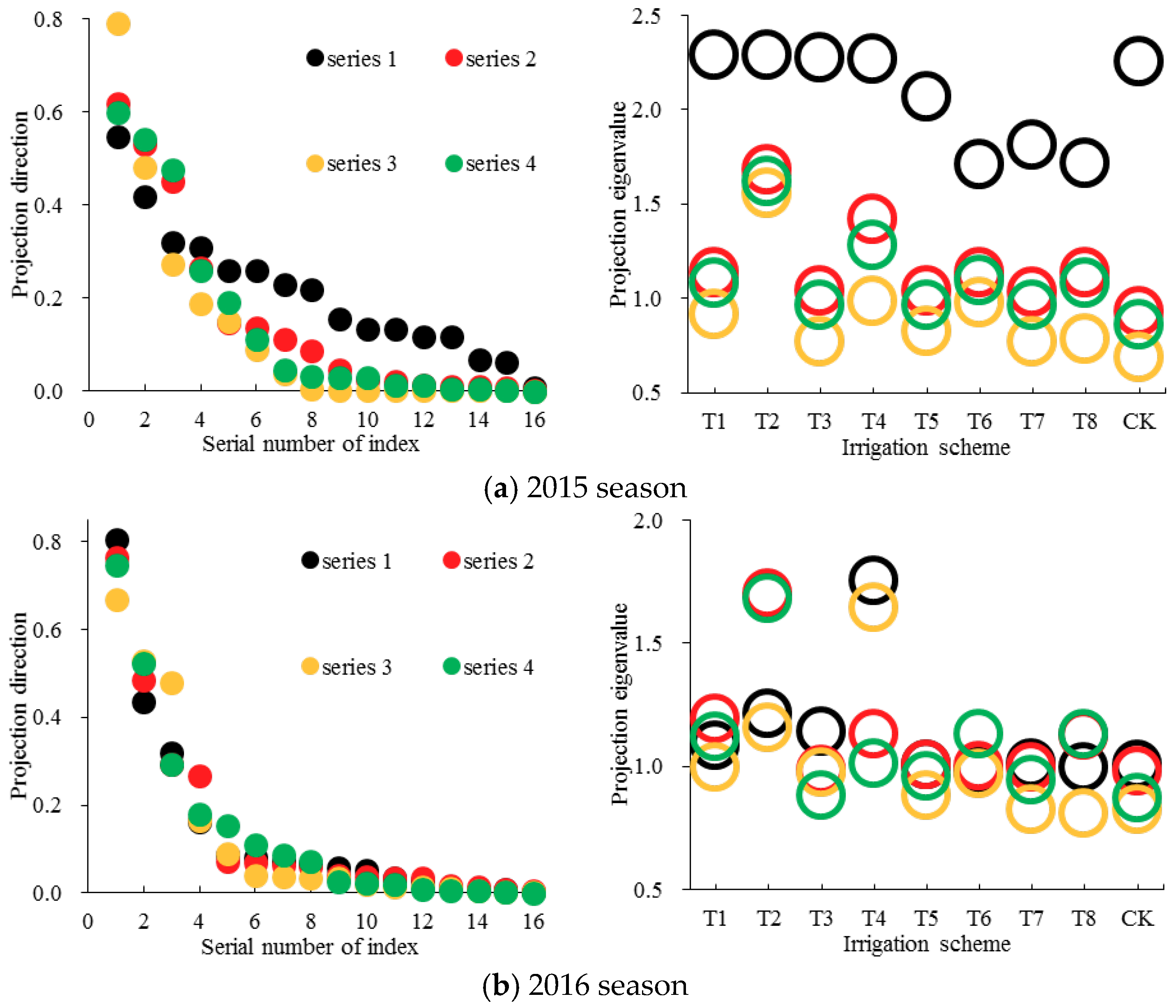
3.4. Grey Relation Projection Weight of Each Decision-Making Index
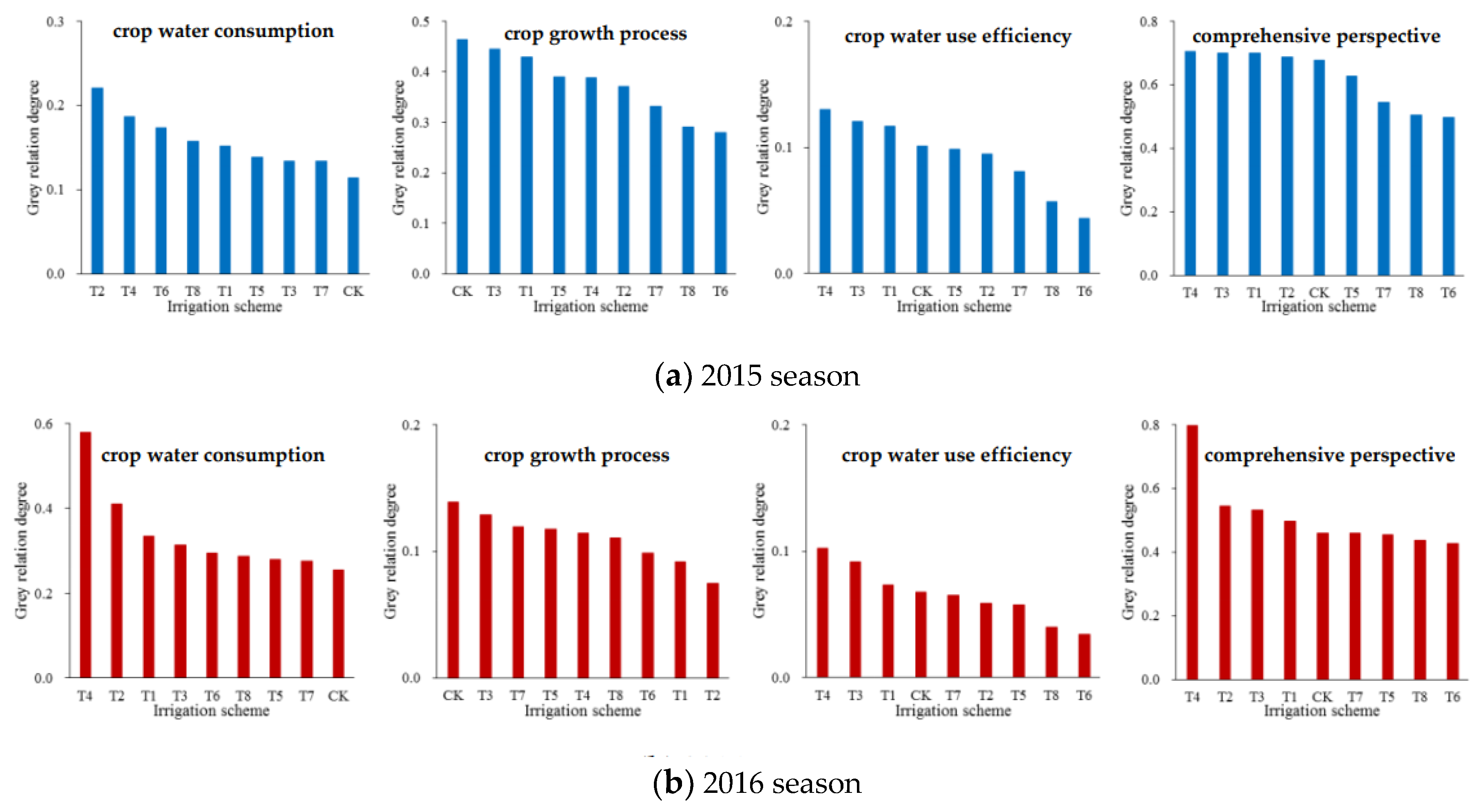
3.5. Decision-Making Results of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.B.; Jin, H.; Wang, G.H.; Herbert, S.J. Soybean yield physiology and development of high-yielding practices in Northeast China. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Paredes, P.; Liu, Y.; Chi, W.W.; Pereira, L.S. Modelling transpiration, soil evaporation and yield prediction of soybean in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, S.M.; Jin, J.L.; Ning, S.W.; Feng, P. Quantitative assessment of soybean drought loss sensitivity at different growth stages based on S-shaped damage curve. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Jin, J.L.; Jiang, S.M.; Ning, S.W.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.L. Simulated assessment of summer maize drought loss sensitivity in Huaibei Plain, China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, M.M.; Steinemann, A.C. Assessing vulnerability to natural hazards: Impact-based method and application to drought in Washington State. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2009, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. Drought modeling—A review. J. Hydrol. 2011, 403, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragues, R.; Medina, E.T.; Claveria, I.; Martinez-Cob, A.; Faci, J. Regulated deficit irrigation, soil salinization and soil sodification in a table grape vineyard drip-irrigated with moderately saline waters. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 134, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounzer, O.; Pedrero-Salcedo, F.; Nortes, P.A.; Bayona, J.M.; Nicolas-Nicolas, E.; Alarcon, J.J. Transient soil salinity under the combined effect of reclaimed water and regulated deficit drip irrigation of Mandarin trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Li, J.S.; Li, Y.F.; Yin, J.F. Effects of drip system uniformity on yield and quality of Chinese cabbage heads. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 110, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, D.J.; Van den Ende, B. Productivity of peach trees: Factors affecting dry weight distribution during tree growth. Ann. Bot. 1975, 39, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosadi, R.B.; Senge, M.; Ito, K.; Adomako, J.T. The effect of water stress in regulated deficit irrigation on soybean yield (Glycine max[L.] Merr.). Paddy Water Environ. 2007, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincik, M.; Candogan, B.N.; Demirtas, C.; Buyukcangaz, H.; Yazgan, S.; Goksoy, A.T. Deficit irrigation of soya bean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] in a sub-humid climate. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2008, 194, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Kirnak, H.; Copur, O. Deficit irrigations during soybean reproductive stages and CROPGRO-soybean simulations under semi-arid climatic conditions. Field Crops Res. 2007, 103, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondani, F.; Khani, K.; Honarmand, S.J.; Saeidi, M. Evaluating effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the radiation use efficiency and yield of soybean (Glycine max) under water deficit stress condition. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, F.; Garcia, C.; Pintos, F.; Otero, A. Effects of irrigation regime on the growth and yield of irrigated soybean in temperate humid climatic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, B.; Kresovic, B.; Tapanarova, A.; Zivotic, L.; Todorovic, M. Effect of irrigation regime on yield, harvest index and water productivity of soybean grown under different precipitation conditions in a temperate environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Kumar, S.N.; Ines, A.V.M. Responses of soybean to water stress and supplemental irrigation in upper Indo-Gangetic Plain. Field Crops Res. 2018, 219, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Willardson, L.S.; Deng, W.; Li, X.J.; Liu, C.J. Crop water deficit estimation and irrigation schedule in western Jilin Province. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmah, M.M.; Lescourret, F.; Yao, X.; Lavigne, C. Metaheuristics for agricultural land use optimization. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 975–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Patnaik, A.; Chauhan, R. Optimization of tribological properties of cement kiln dust-filled brake pad using grey relation analysis. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.W.; Ryu, S.G.; Oh, J.H. Optimum design of a large area, flexure based XY theta mask alignment stage for a 12-inch wafer using grey relation analysis. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 58, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.Y. Stochastic multicriteria decision-making approach based on SMAA-ELECTRE with extended gray numbers. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2019, 26, 2032–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Lim, M.; Wu, K.J.; Zhou, L.; Bui, D.T.D. A novel approach for enhancing green supply chain management using converged interval-valued triangular fuzzy numbers-grey relation analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Sahoo, S.; Dhar, A.; Pradhan, B. Effectiveness evaluation of objective and subjective weighting methods for aquifer vulnerability assessment in urban context. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Kawachi, T.; Singh, V.P. Entropy-based assessment and clustering of potential water resources availability. J. Hydrol. 2005, 309, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.G.; Chen, X.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, X.S.; Zhao, S.W. A fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model for flood risk based on the combination weight of game theory. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.P.; Ruan, B.Q.; Xie, J.C. Multi-objective and multilevel fuzzy optimization model and its application in water security evaluation. Resour. Sci. 2003, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Feng, P.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, L. Water resources carrying capacity evaluation and diagnosis based on set pair analysis and improved the entropy weight method. Entropy 2018, 20, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Fu, Q.; Liu, D.; Li, T.X.; Cheng, K.; Cui, S. Spatiotemporal analysis of the agricultural drought risk in Heilongjiang Province, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhou, R.J. Interval multi-attribute decision of watershed ecological compensation schemes based on projection pursuit cluster. Water 2018, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Tang, G.M. Study on optimization of irrigation regime and the Jensen model parameter for rain fed crop in Huaibei District of Anhui Province. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2007, 30, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Z.; Sun, J.M.; Wang, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, R.J. Breeding and application of soybean cultivar Zhonghuang 13 with wide adaptability, high yield and high protein content traits. Soybean Sci. 2019, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Liu, H.; Tian, L.; Dong, X.B.; Shen, S.H.; Qu, L.Q. Integrated and comparative proteomics of high-oil and high-protein soybean seeds. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desclaux, D.; Huynh, T.; Roumet, P. Identification of soybean plant characteristics that indicate the timing of drought stress. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Kang, S.Z.; Du, T.S.; Qiu, R.J.; Guo, P.; Chen, R.Q. Quantitative response of greenhouse tomato yield and quality to water deficit at different growth stages. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L. Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.X.; Yang, D.L. Methods for identifying and improving the consistency of fuzzy judgment matrix. Syst. Eng. 2003, 21, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.X.; Pan, Z.W.; Jin, J.L.; Li, C.H.; Ning, S.W. Forewarning model of regional water resources carrying capacity based on combination weights and entropy principles. Entropy 2017, 19, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Lu, H.W. An integrated model of water resources optimization allocation based on projection pursuit model - Grey wolf optimization method in a transboundary river basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, C.; Schneider, L. The impact of the prior density on a minimum relative entropy density: A case study with SPX option data. Entropy 2014, 16, 2642–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Ning, S.W.; Cui, Y.; Jin, J.L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wu, C.G. Quantitative assessment and diagnosis for regional agricultural drought resilience based on set pair analysis and connection entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Xie, L.G.; Li, X.J. Calculation of rice evapotranspiration under the condition of unsufficient irrigation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1995, 2, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroud, N.; Mündel, H.H.; Saindon, G.; Entz, T. Effect of level and timing of moisture stress on soybean plant development and yield components. Irrig. Sci. 1993, 13, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E. Analyzing fish condition factor index through skew-Gaussian information theory quantifiers. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2016, 15, 1650013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, S.M.; Feng, P.; Jin, J.L.; Yuan, H.W. Winter wheat evapotranspiration estimation under drought stress during several growth stages in Huaibei Plain, China. Water 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendig, S.R.; Rupe, J.C.; Scott, H.D. Effect of irrigation and soil water stress on densities of Macrophomina phaseolina in soil and roots of two soybean cultivars. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.R.; Winter, J.M.; Elliott, J.; Ruane, A.C.; Porter, C.; Hoogenboom, G. Integrating growth stage deficit irrigation into a process based crop model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 243, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, E.N.; Zhang, Z.X. Evaluation of high yield cultivation and regulated deficit irrigation system of soybean based on grey relation projection model. Water Sav. Irrig. 2017, 6, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, L.Y.; Li, H.; Li, T.X.; Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Study on the optimization of dry land irrigation schedule in the downstream Songhua River Basin based on the SWAT model. Water 2019, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Q.; Song, J.; Wu, Y. Discussion of soybean water demand regulation and sprinkling irrigation pattern. Water Sav. Irrig. 2003, 3, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, D.B.; Bruening, W.P. Water stress, photosynthesis, seed sucrose levels and seed growth in soybean. J. Agric. Sci. 2004, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, T.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Neumaier, N.; Farias, J.R.B.; Tobita, S.; Ito, O. Drought tolerance characteristics of Brazilian soybean cultivars—Evaluation and characterization of drought tolerance of various Brazilian soybean cultivars in the field. Plant Prod. Sci. 2004, 7, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Sand (%) | 3.45 |
| Silt (%) | 70.52 |
| Clay (%) | 26.03 |
| pH (in water solution) | 7.5 |
| Organic matter (%) | 0.85 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.36 |
| Field capacity at −0.03 MPa (cm3/cm3) | 0.38 |
| Wilting point at −1.5 MPa (cm3/cm3) | 0.12 |
| Cultivar Parameters | Value | Seed Characteristics | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole growth period (d) | 97 | Protein content (%) | 43.73 | |
| Plant height (cm) | 46.3 | Oil content (%) | 19.10 | |
| Number of nods on main stem | 13.8 | Vitamin E content (μg/g) | 181.9 ± 25.1 | |
| Number of branches per plant | 2.3 | Fatty acid (%) | 16: 0 | 11.5 ± 0.5 |
| Number of pods per plant | 40.0 | 18: 0 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | |
| Number of seeds per pod | 2.04 | 18: 1 | 25.5 ± 0.5 | |
| Weight of 100 seeds (g) | 24.0 | 18: 2 | 51.8 ± 0.8 | |
| Seed yield (t/ha) | 3.04 | 18: 3 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | |
| Description of Growth Stage | 2015 Season | 2016 Season |
|---|---|---|
| Germination stage, from sowing to seed germination | From June 20 to July 3, 14 days | From June 29 to July 14, 16 days |
| Seedling stage, from seed germination to plants with four fully expanded leaves | From July 4 to July 14, 11 days | From July 15 to July 27, 13 days |
| Branching stage, from plants with four fully expanded leaves to first flower appearance | From July 15 to August 3, 20 days | From July 28 to August 10, 14 days |
| Flowering-podding stage, from first flower appearance to the beginning of pod filling | From August 4 to August 20, 17 days | From August 11 to August 31, 21 days |
| Seed filling stage, from the beginning of pod filling to plant maturation | From August 21 to September 20, 31 days | From September 1 to September 27, 27 days |
| Meteorological Element | Germination Stage | Seedling Stage | Branching Stage | Flowering-Podding Stage | Seed Filling Stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |
| Maximum air temperature (°C) | 27.8 | 29.8 | 30.9 | 33.8 | 32.2 | 34.2 | 31.5 | 32.8 | 28.9 | 30.6 |
| Minimum air temperature (°C) | 20.9 | 23.3 | 21.3 | 24.7 | 24.1 | 25.7 | 22.8 | 22.7 | 17.6 | 18.4 |
| Mean air temperature (°C) | 24.0 | 26.3 | 26.0 | 29.1 | 28.0 | 29.3 | 26.7 | 27.7 | 22.9 | 24.2 |
| Mean air relative humidity (%) | 88.4 | 87.8 | 82.2 | 81.3 | 85.9 | 84.2 | 86.4 | 79.3 | 86.7 | 74.8 |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 0.9 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Sunshine duration (h) | 0.5 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 6.4 | 3.6 | 7.4 | 5.3 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 6.6 |
| Solar radiation (MJ/(m2·d)) | 9.92 | 12.30 | 14.37 | 18.03 | 13.32 | 16.48 | 13.48 | 16.73 | 15.12 | 13.95 |
| Vapor pressure deficit (kPa) | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 0.80 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.37 | 0.76 |
| Reference evapotranspiration (mm/d) | 2.33 | 3.23 | 3.09 | 4.28 | 3.42 | 4.43 | 3.56 | 4.11 | 3.29 | 3.18 |
| Cropping Season | Irrigation Scheme | Seedling Stage | Branching Stage | Flowering-Podding Stage | Seed Filling Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 and 2016 | T1 | 55% | 75% | 75% | 75% |
| T2 | 35% | 75% | 75% | 75% | |
| T3 | 75% | 55% | 75% | 75% | |
| T4 | 75% | 35% | 75% | 75% | |
| T5 | 75% | 75% | 55% | 75% | |
| T6 | 75% | 75% | 35% | 75% | |
| T7 | 75% | 75% | 75% | 55% | |
| T8 | 75% | 75% | 75% | 35% | |
| CK | 75% | 75% | 75% | 75% |
| Decision-Making System | Decision-Making Index | Index Type |
|---|---|---|
| crop water consumption subsystem | X1 soybean evapotranspiration at the seedling stage (mm) | negative |
| X2 soybean evapotranspiration at the branching stage (mm) | negative | |
| X3 soybean evapotranspiration at the flowering-podding stage (mm) | negative | |
| X4 soybean evapotranspiration at the seed filling stage (mm) | negative | |
| X5 irrigation amount at the seedling stage (mm) | negative | |
| X6 irrigation amount at the branching stage (mm) | negative | |
| X7 irrigation amount at the flowering-podding stage (mm) | negative | |
| X8 irrigation amount at the seed filling stage (mm) | negative | |
| crop growth process subsystem | X9 soybean aboveground accumulated biomass at the seedling stage (t/ha) | positive |
| X10 soybean aboveground accumulated biomass at the branching stage (t/ha) | positive | |
| X11 soybean aboveground accumulated biomass at the flowering-podding stage (t/ha) | positive | |
| X12 soybean aboveground accumulated biomass at the seed filling stage (t/ha) | positive | |
| X13 soybean aboveground biomass at harvest time (t/ha) | positive | |
| X14 soybean seed yield (t/ha) | positive | |
| X15 soybean 1000 seed weight (g) | positive | |
| crop water use efficiency subsystem | X16 soybean water use efficiency during the whole growth period (kg/m3) | positive |
| Cropping Season | Irrigation Scheme | Crop Water Consumption Decision-Making Subsystem | Crop Growth Process Decision-Making Subsystem | Crop Water Use Efficiency Decision-Making Subsystem | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | ||
| 2015 | T1 | 0.58 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.94 |
| T2 | 1.00 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.81 | |
| T3 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.96 | |
| T4 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 1.00 | |
| T5 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.84 | |
| T6 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.00 | |
| T7 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.44 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.69 | |
| T8 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.36 | |
| CK | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.85 | |
| 2016 | T1 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.80 |
| T2 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.87 | 0.94 | 0.41 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 0.63 | |
| T3 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.94 | |
| T4 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.30 | 0.70 | 0.49 | 1.00 | |
| T5 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0.61 | |
| T6 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.00 | |
| T7 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.60 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 0.55 | 0.71 | |
| T8 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.21 | |
| CK | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.74 | |
| Decision-Making System | Decision-Making Index | Improved Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process Method | Grey Entropy Weight Method | Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit Model | Combined Weight | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subsystem Weight | CIC | Index Weight | CIC | Comprehensive Index Weight | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||||||
| crop water consumption subsystem | X1 | 0.334 | 0.000 | 0.127 | 0.131 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.174 | 0.191 | 0.116 | 0.186 |
| X2 | 0.124 | 0.125 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.094 | 0.644 | 0.084 | 0.335 | |||||
| X3 | 0.120 | 0.119 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.018 | 0.030 | |||||
| X4 | 0.130 | 0.120 | 0.043 | 0.040 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.038 | 0.004 | |||||
| X5 | 0.129 | 0.131 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.033 | 0.025 | |||||
| X6 | 0.126 | 0.128 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.001 | 0.102 | 0.002 | 0.135 | |||||
| X7 | 0.116 | 0.118 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.035 | 0.004 | |||||
| X8 | 0.126 | 0.128 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.017 | 0.037 | |||||
| crop growth process subsystem | X9 | 0.283 | 0.151 | 0.141 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.043 | 0.040 | 0.047 | 0.027 | 0.061 | 0.067 | |
| X10 | 0.157 | 0.154 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.033 | 0.001 | |||||
| X11 | 0.130 | 0.125 | 0.037 | 0.035 | 0.068 | 0.004 | 0.067 | 0.025 | |||||
| X12 | 0.149 | 0.139 | 0.042 | 0.039 | 0.299 | 0.001 | 0.151 | 0.011 | |||||
| X13 | 0.145 | 0.185 | 0.041 | 0.052 | 0.068 | 0.001 | 0.071 | 0.004 | |||||
| X14 | 0.133 | 0.134 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.052 | 0.003 | 0.060 | 0.021 | |||||
| X15 | 0.135 | 0.122 | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.102 | 0.001 | 0.084 | 0.013 | |||||
| crop water use efficiency subsystem | X16 | 0.383 | 1.000 | 1.000 | \ | \ | 0.383 | 0.383 | 0.024 | 0.007 | 0.130 | 0.102 | |
| Cropping Season | Optimized Projection Index Function Q(y) = SzDz | Projection Direction of Each Decision-Making Index (Projection Vector y) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sz | Dz | Q | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | |
| 2015 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.16 |
| 2016 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jin, J.; Feng, P.; Ning, S. Decision-Making of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain Based on Grey Entropy Weight and Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit. Entropy 2019, 21, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090877
Cui Y, Jiang S, Jin J, Feng P, Ning S. Decision-Making of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain Based on Grey Entropy Weight and Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit. Entropy. 2019; 21(9):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090877
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yi, Shangming Jiang, Juliang Jin, Ping Feng, and Shaowei Ning. 2019. "Decision-Making of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain Based on Grey Entropy Weight and Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit" Entropy 21, no. 9: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090877
APA StyleCui, Y., Jiang, S., Jin, J., Feng, P., & Ning, S. (2019). Decision-Making of Irrigation Scheme for Soybeans in the Huaibei Plain Based on Grey Entropy Weight and Grey Relation–Projection Pursuit. Entropy, 21(9), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21090877






