Abstract
With the development of economic globalization, the uncertainty of supply chains is also increasing, and alleviating the bullwhip effect has become an important issue. From previous discussions on alleviating the bullwhip effect, there was no research on alleviating it by enhancing supply chain agility through improving big data. Moreover, it has not been found that quality function deployment is used to analyze the interdependence between big data and supply chain agility, as well as between supply chain agility and the bullwhip effect. In particular, the interaction of bullwhip effect factors are not considered. In this study, the multicriteria decision-making integrated framework is proposed and the largest relay manufacturer in China is taken to identify key big data enablers to enhance supply chain agility and mitigate the bullwhip effect, thus providing an effective method for electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises to develop a supply chain that can quickly respond to changes and uncertainties. These big data enablers can enhance supply chain agility and reduce the bullwhip effect. This framework provides an effective method for electronic manufacturers to formulate supply chain agility indicators and big data enablers to mitigate the bullwhip effect and also provides a reference for other manufacturing enterprises in supply chain management.
1. Introduction
With the advent of globalization, integration, and the knowledge economy, competition among enterprises is increasingly intensified [1]. Enterprise competition can be regarded as the competition between supply chains [2]. When supply chains began to proliferate globally, their management, organization, and coordination became undoubtedly great challenges for enterprises [3]. Due to the lack of effective information flow and sharing mechanisms among many organizations in the supply chain development process, it is easy to produce a common phenomenon of supply chains—the bullwhip effect [4]. The bullwhip effect exists widely in supply chain management, especially in the electronics industry and other fast-growing industries [5]. For example, influenced by the bullwhip effect and the global economy, Cisco of the United States experienced over USD 2 billion of inventory product write-offs in 2001, and Cisco’s stock price fell by 6%, resulting in huge losses [6]. Similarly, Hewlett-Packard was affected by distortions in information demand, which resulted in the loss of millions of dollars of inventory and unnecessary increases in capacity costs [7]. Although the demand for many foods increased and market shelves emptied during the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for other products decreased, and many companies had to stop production. These processes clearly demonstrate the emergence and adverse effects of the bullwhip effect [8]. In this regard, the bullwhip effect will not only lead to low efficiency of the supply chain but will even affect the survival of enterprises [9]. Therefore, reducing the bullwhip effect plays an important role in improving the performance of supply chain management, helping enterprises solve problems in supply chain management, and ensuring effective supply chain operation [1,5].
Improving supply chain agility is an effective method for reducing the negative impact of the bullwhip effect [10,11,12,13]. Supply chain agility is a broad multidimensional concept with alertness, accessibility, resolution, rapidity, and flexibility [14,15], which enables the supply chain to rapidly adapt to market changes, reduce inventory, and quickly respond to customer demand [16]. Therefore, supply chain managers are under pressure to establish agility in the supply chain to cope with market instability and improvements in competitiveness [17,18].
In addition, big data has attracted extensive attention regarding effective organizational decision-making, especially in supply chain management [19,20,21]. Agility makes the supply chain more information and data-centric, deepening the understanding of order capacity. Big data has a positive and significant impact on supply chain agility, thus improving it [22,23,24]. Considering the increasing influence of big data decisions on supply chains, which can improve their responsiveness, rapidity, and adjustment to external changes, enterprises should attach importance to the contribution of big data in developing supply chain agility [23,24,25,26].
In recent years, Quality function deployment (QFD) has been successfully applied to solve the problems of various supply chains, such as food [27,28,29], sustainable [30,31,32], garment industry [33], shipping [34,35], and green supply chains [36,37]. However, there are few studies on the application of QFD in electronic equipment manufacturing supply chain. Deepu and Ravi, 2020 employed an integrated Analysis network procedure (ANP) and QFD approach to prioritize customer and design requirements in the electronic supply chain [38]. Hsu et al., 2021 obtained the order of elastic enhancement by developing two houses of quality in the elevator manufacturing supply chain to connect studies on interruption risk, elastic capability, and elastic enhancement characteristics [39].However, there is no research on the development of two houses of quality to connect bullwhip effect factors (BEFs), supply chain agility indicators (SCAIs), and Big data enablers (BDEs), and build the ability of China’s electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises’ supply chains to deal with the bullwhip effect by integrating the multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) method and QFD.
China is the largest developing country and one of the largest manufacturers of electronic equipment in the world. Owing to the rapid development of its electronics manufacturing industry, it is essential that it utilizes big data analytics (BDA) tools in its supply chain to ensure its competitiveness on a global scale. The use of BDA tools in the manufacturing supply chain may help in improving supply chain agility and reducing bullwhip effect to gain competitive advantage. In addition, owing to the limited resources of electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises, enterprises must invest capital and manpower in the most critical place. Therefore, the following issues were discussed in this study to address the aforementioned deficiencies:
- 1.
- What are the key BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs in the electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises’ supply chains?
- 2.
- How could QFD and MCDM be integrated to link the relationships among three groups of variables?
- 3.
- Can these findings help industry decision makers formulate strategies for implementing big data analytics?
To address the aforementioned research questions, this research has the following objectives:
- a.
- To determine the key BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs in the supply chain of electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises.
- b.
- To establish the relationship between the three groups of variables using the QFD method based on the integrated MCDM framework.
- c.
- To suggest some managerial implications for the use of the proposed BDA in the supply chain of electronic equipment manufacturing enterprises.
To achieve this goal, the key BDEs were selected using the MCDM-QFD method. QFD provides a structured approach that aims to integrate customer requirements with product and service design specifications by using charts and matrices [40]. Among the many available management methods, the most common is MCDM. MCDM can be considered a complex and dynamic process [41]. Scholars have integrated MCDM into QFD to improve the practicality of QFD and proposed valuable extensions [42,43,44,45].
The study’s remaining chapters are organized as follows: Section 2 determines initial BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs based on the literature review. Section 3 focuses on the integrated MCDM-QFD framework. Section 4 carries on the empirical research and the result analysis with the enterprise case. Finally, the contributions and future research directions of this study are presented in Section 5.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Bullwhip Effect
The bullwhip effect, also known as demand information amplification or the Forrester effect [46], is a phenomenon in which small changes in customer demand lead to significant fluctuations in orders received by upstream suppliers in the supply chain system [47]. The bullwhip effect reflects the existence of various forms of uncertainty in the supply chain system [48], which is also one of the most studied phenomena in supply chain management [49]. Wang and Disney, 2016 defined the bullwhip effect as the amplification of order fluctuations throughout the supply chain [50]. In manufacturing, this means amplifying changes in demand from nodes in the supply chain.
Braz et al., 2018 believed that the bullwhip effect could negatively impact the supply chain [49]. This is because the bullwhip effect leads to inefficiencies, such as uncertain production schedules and overstocking, resulting in high costs, low service levels for all members of the supply chain, excess upstream inventory levels, forecasting and scheduling difficulties, and poor supplier and customer relationships [50,51]. In fact, the lower the bullwhip effect, the higher the efficiency regarding managing the supply chain. Therefore, the bullwhip effect is considered one of the main criteria for evaluating supply chain performance [52].
Alleviating the bullwhip effect is one of the key issues in supply chain management [53]. One must first understand its causes to weaken or eliminate it. Many scholars have different views on the causes of the bullwhip effect. For example, Bolarin et al., 2011 analyzed the impact of price fluctuations on order variability in traditional multi-level supply chains [54]. Furthermore, Hussain and Saber, 2012 believe that demand forecasting, batch size, shortage game, lack of synchronization, information asymmetry, periodicity of demand changes, sales time, production delay, inventory strategy, and order processing are the main reasons for the bullwhip effect [55]. Dominguez et al., 2014 believe that demand prediction, order or delivery lead times, neglecting time delays, company processes, information asymmetry, demand changes, inventory strategies, and lack of coordination in the supply chain [56]. Hofmann, 2015 proposed the periodicity of demand prediction, batch ordering strategy, shortage game, and lack of learning and demand [57]. Khan and Ahmad, 2016 believe that the bullwhip effect is the result of many factors, including demand prediction, batch ordering strategies, economic fluctuations, the shortage game, delivery lead times, company processes, lack of synchronization, information asymmetry, factory capacity constraints, decision-making mechanisms, demand periodicity, the multiplier effect, lack of coordination in supply chains, and local optimization without global vision and inventory strategies [58]. Dai et al., 2017 identified demand forecasting, batch size, price or economic volatility, and inventory strategies [59]. Pastore et al., 2019 identified demand forecasting, batch ordering strategies, batch sizes, the shortage game, lack of learning or training, limited supply, factory capacity constraints, and inventory strategies [60]. Michna et al., 2020 argued that demand forecasting, price volatility, delivery lead times, and order processing lead to the bullwhip effect [61]. Finally, Dahlin, 2021 believes that there are two types of reasons: operational reasons and behavioral reasons. In this regard, operational reasons include updated demand forecasts, ordering strategies and batch processing, the influence of inventory strategies, the influence of delivery times, the shortage game, price fluctuations, and lack of transparency. Behavioral reasons include concerns about inventory shortage, lack of learning and training, neglect of time delays, the risk of coordinating work, and distrust [62].
Based on the above discussion and a comprehensive literature review [63], this study sorted out 27 BEFs. The explanations of the chosen BEFs are shown in Appendix A (Table A1). These factors contributing to the bullwhip phenomenon will be evaluated in Section 4.
2.2. Supply Chain Agility
Agility as a business concept originated in manufacturing, especially in flexible manufacturing systems [64]. Later, this concept was extended to a wider business context, and the concept of supply chain agility as an organizational characteristic was born [65]. Supply chain agility is an operational strategy focusing on the speed and flexibility of supply chain drive [66]. The basic principle of supply chain agility is that supply chain members must be able to quickly coordinate their collective capabilities in response to changes in supply and demand [67]. Supply chain agility is presented as a means of improving customer responsiveness and addressing market changes [17]. Meyer et al., 2017 pointed out that supply chain agility is an emerging dynamic capability that has been widely accepted as an important aspect of successful supply chain management [68]. Supply chain agility needs to be able to respond to changes in supply and demand, ensure that the company remains competitive and have a shorter life cycle, promote the company’s sustainable development, create new products and services, and foster social, environmental, and economic sustainability within the supply chain [69].
Therefore, many scholars have done the following research on supply chain agility indicators: Bargshady et al., 2016 believe that the main indicators affecting the agility of the supply chain are customer satisfaction, information technology, personnel, change and uncertainty, and advertising [70]. Sangari et al., 2016 summarized 12 evaluation criteria for achieving supply chain agility, recognized as agility requirements, to integrate the agility into supply chain strategies in the background: management ability, employee ability, cooperation within the organization, collaboration between supply chain partners, supply chain information flow and continuous monitoring of the business environment, supply chain monitoring, using supporting agile techniques, to create a culture of learning and change [71]. In evaluating supply chain agility, Wu et al., 2017 divided the evaluation criteria into five levels: collaboration, process integration, information integration, customer-based measures, and strategic alliance of supply chain ecological design [72]. Martinez-Sanchez and Lahoz-Leo, 2018 identified market sensitivity, virtualization, process integration, and network-based as key indicators to promote supply chain agility [73]. Irfan et al., 2019 believe that supply elasticity, process integration, and product complexity can improve supply chain agility [74]. Rasyidi and Kusumasstuti, 2020 evaluated supply chain agility from four levels: flexibility, responsiveness, effectiveness, and maturity [75]. Shukor et al., 2020 highlighted an interactive relationship between supply chain agility and organizational flexibility, and supply chain integration positively impacts enterprise supply chain agility and organizational flexibility [76]. Rehman et al., 2020 and Al-Zabidi et al., 2021 believe that the driving factors of supply chain agility include six levels: organizational management, strategic management, information management, strategic commitment, customer sensitivity, and interpersonal competence [77,78]. Jindal et al., 2021 believe that the key indicators of agility are mainly divided into seven levels: infrastructure, supplier and customer information, analysis function, human resources, management decision-making power, operational flexibility, and time change [79]. Aprilia et al., 2021 verified and provided examples whereby supplier innovation, information sharing, and strategic resources significantly impact supply chain agility [80].
Based on the above discussion and a comprehensive review of the literature [81,82,83,84,85,86], this study sorted out 42 SCAIs. The explanations of the chosen SCAIs are shown in Appendix A (Table A2). In addition, these SCAIs will be evaluated in Section 4.
2.3. Big Data
Big data analysis can be defined as the application of advanced analysis techniques to big data, including data mining, statistical analysis, and predictive analysis, which is a new business intelligence practice [87]. It combines two main concepts: big data, which refers to the processing of data with volume, and diversity and velocity characteristics [88]. By applying statistics, mathematics, econometrics, simulation, optimizing, and deploying advanced analytical tools, valuable knowledge can be obtained from a large amount of data to help companies make better decisions [89]. In addition, case verification shows that big data has multiple advantages in supply chain management, including reducing operating costs, improving supply chain flexibility, and improving customer satisfaction [90,91,92]. Therefore, more and more enterprises are also applying big data to supply chain management.
Many scholars have studied the application of big data in logistics and supply chain management. Cakici et al., 2011 use radio frequency identification (RFID) data to redesign optimal inventory strategies [93]. Tan et al., 2015 proposed big data infrastructure based on deductive graph theory to improve supply chain innovation capability [89]. Zhong et al., 2015 explained how big data information could be used for effective logistics planning, production planning, and scheduling [94]. Furthermore, Mishra and Singh, 2016 proposed a big data method to minimize waste in the food supply chain [95]. Beyond these studies, many areas of supply chain management can benefit from big data, including alleviating the bullwhip effect, multi-criteria decision-making [96], planning and scheduling [97], predictive maintenance based on sensor data, efficient logistics [98], forecasting and demand management [99], and sustainable supply chain management [100,101].
In addition, many scholars have also conducted relevant studies on the enablers of big data. Chen et al., 2015 believe that technology-driven, organization-driven, and environment-driven big data capabilities can be improved [102]. Queiroz and Telles, 2018 verified the promotion of big data analysis from the perspective of supply chain partnerships, personnel knowledge level, and innovation culture [103]. Mandal, 2018 classifies the professional knowledge capabilities of big data personnel into technical knowledge, technology management knowledge, business knowledge, and relational knowledge [24]. Further, Mandal, 2019 believes that big data management capabilities include planning, investment decision-making, coordination, and control [25]. Arunachalam et al., 2018 proposed that data generation ability, data integration and management function, advanced analytical ability, data visualization ability, and data-driven culture are key to positively influencing big data analysis [104]. Moktadir et al., 2019 reported that there are five obstacles that should be overcome for the use of BDA in manufacturing supply chains: lack of infrastructure, complexity of data integration, data privacy, lack of availability of BDA tools, and high investment costs [105]. Ali et al., 2020 proposed three building blocks of big data capability: management capability, technical capability, and personnel professional knowledge capability [106]. Hassen and Hassen, 2020 point out that human, financial, and technical resources can promote big data capabilities in the supply chain [107].
Based on the above discussion and a comprehensive literature review [108,109,110,111], this study has selected 21 BDEs. The explanations of the chosen BDEs are shown in Appendix A (Table A3). These BDEs are evaluated in Section 4.
2.4. Bullwhip Effect and Supply Chain Agility
Scholars believe that the agility of the supply chain can effectively weaken the bullwhip effect [10,11,12,13]. Studies on the bullwhip effect and supply chain agility are as follows:
According to Kim and Lee, 2010, reducing the bullwhip effect requires collaboration among members of the supply chain [112]. Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay, 2011 point out that information transparency and coordination are needed upstream and downstream of the supply chain to reduce the bullwhip effect [63]. Chen et al., 2011 believe that establishing trust among supply chain members is an important factor in reducing the bullwhip effect because it directly affects the availability and quality of the information in the supply chain [113]. Zhang et al., 2012 established system dynamics models of traditional and flexible supply chains by using the concept of systems engineering and verified that shortening the length of the supply chain, sharing information, cooperation, and shortening lead time can reduce the bullwhip effect [114]. Lin et al., 2014 argue that improving customer service capability can stabilize the bullwhip effect [115]. Lee et al., 2014 posit that using information technology to improve the visibility of the entire supply chain is also considered an effective means to mitigating the bullwhip effect, and the ability to respond to customers’ demands on time at multiple levels of the supply chain is another key factor in mitigating it [116]. Meanwhile, Seles et al., 2016 proposed that, like customer demand, environmental demand sometimes changes significantly and is transmitted along the supply chain to varying degrees. The timely development of environmental threats can prevent the generation of the green bullwhip effect from developing environmental management practices that can respond to market environment changes [117]. Dai et al., 2017 used case analysis to show that inventory strategy in supplier management is an effective way to reduce the bullwhip effect [59]. Sabbaghnia et al., 2018 treated order demand as the best controller to suppress inventory fluctuations at each node in the entire supply chain network, thereby controlling the bullwhip effect [118]. Ojha et al., 2019 used a simulation study to verify that using information sharing to coordinate orders in a supply chain can reduce the negative effects of the bullwhip effect [119]. Ran et al., 2020 reduce the bullwhip effect and improve performance by increasing the level at which digital technology is applied in the supply chain [120]. Saffari et al., 2021 determined that shortening product delivery times is an effective strategy to reduce the bullwhip effect in a closed-loop supply chain by explaining the structural model [121].
Based on the above, most past studies focused on the influence of individual indicators of supply chain agility on the bullwhip effect. However, there is still a limited volume of literature to sort out the complete list of indicators of supply chain agility to mitigate the bullwhip effect. Therefore, the general indicators of supply chain agility obtained through the literature review provide a more comprehensive discussion regarding weakening the bullwhip effect.
2.5. Supply Chain Agility and Big Data
In recent years, research on big data has become increasingly common in various fields [94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102]. Relevant research on supply chain agility and big data is as follows.
Giannakis et al., 2016 developed a multi-agent-based supply chain system architecture and showed how agent-based big data analysis and processing systems could improve supply chain agility [22]. Mandal, 2018 believes that the prominent contributing factors of supply chain agility are technology management knowledge, business knowledge, and relationship knowledge [24]. Dubey, 2018 established a theoretical framework in terms of the dynamic capabilities view and contingency theory. By checking the validity of the proposed path by partial least squares, it is concluded that big data analysis has a positive and significant impact on the agility of the supply chain 138 [122]. Through path analysis by the partial least square method, Mandal, 2019 concluded that planning, coordination, and control in big data management ability are key contributing factors to supply chain agility [25]. Srimarut and Mekhum, 2020 believe that big data capabilities have a significant positive impact on supply chain agility, improving supply chain quality [123].
Based on the above studies, it can be seen that in previous studies on the bullwhip effect, supply chain agility and big data were mostly pin-pall studies. At present, there is no discussion combining all three. Therefore, this paper builds a two-stage house of quality (HoQ) framework to fill this gap by integrating MCDM-QFD based on existing research, and linking BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs to find out key BDEs to strengthen supply chain agility and mitigate the bullwhip effect. Furthermore, this paper provides a point of reference for supply chain decisions of electronic equipment manufacturers.
3. Methodology
This section begins with a brief description of the proposed MCDM-QFD method, followed by a further introduction to the method used. The methods in this study include the fuzzy Delphi method (FDM), fuzzy interpretive structural modeling (FISM), the analysis network procedure (ANP), and grey relational analysis (GRA).
3.1. Introduction to the MCDM-QFD Method
QFD is a well-known customer-driven approach for capturing customer relationships and translating them into applicable professional attributes that enable designers to accurately develop products or services [124]. A key technology of QFD is HOQ [125]. As the basic structure of QFD, HoQ includes technical attributes, the importance weight of customer demand, and the technical attribute and relationship matrix between customer demand and technical attributes [126]. The first step in building an HoQ is to understand the customer’s requirements fully. Customer requirements vary in importance to different customers; therefore, weighting techniques should be used to measure customers’ requirements. Technical attributes are associated with customer requirements. The relational matrix represents how each customer requirement affects its related technical attributes, which helps determine the technical attributes of the utmost importance [127]. In this study, MCDM was integrated into QFD to obtain the most valuable factors.
There are two HoQs in this study’s QFD framework, elaborating the connection between BEFs and SCAIs as well as the connection between SCAIs and BDEs through an integrated framework to improve supply chain agility and weaken the bullwhip effect. The first HoQ links the BEFs to SCAIs. Therefore, BEFs are shown as “what” in this HoQ because electronic equipment manufacturers first need to identify the bullwhip effect. SCAIs are shown as “how” because they directly affect how the bullwhip effect is handled. The second HoQ then relates SCAIs derived from the first HoQ to BDEs. Thus, SCAIs are listed as “what” in the second HoQ, while BDEs are listed as “how” because they are practical measures that electronic equipment manufacturers can use to improve supply chain agility. In addition, as shown in Figure 1, the grey correlation degree of SCAIs calculated in the first HoQ serves as the starting point for constructing the second HoQ and can be directly used as the importance weight of the second HoQ. Follow the steps in the first HoQ when constructing the second HoQ. These steps in this study are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The symbols numbered from ① to ⑫ in the text correspond to the relevant steps in Figure 1 and Figure 2 for easy recognition.
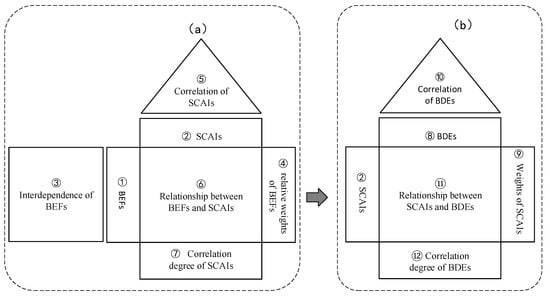
Figure 1.
Two-stage HoQs. (a) The first HoQ; (b) The second HoQ.
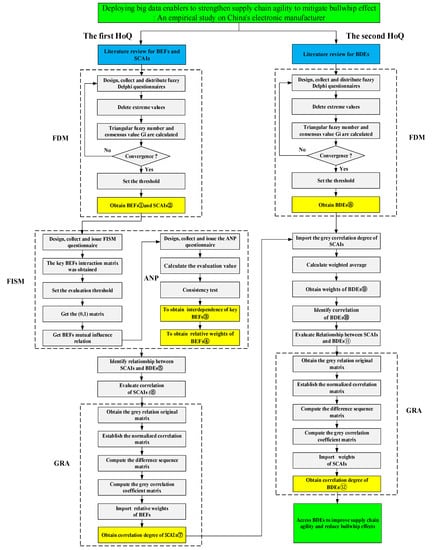
Figure 2.
Research flow chart.
3.2. HoQ1: Linking BEFs and SCAIs
Firstly, the initial BEFs were determined, then the potential causes and influence relationships were confirmed by inviting experts in the industry, and the first round of FDM questionnaires was designed. Secondly, the consensus value of the bullwhip effect was obtained using the FDM. According to the threshold value, the top BEFs will be listed as key BEFs ①, and these selected key BEFs will be further used to evaluate the interaction matrix ③ and obtain the key BEFs weight values ④. The operation of determining the key SCAIs is the same. The consensus value of SCAIs is calculated according to the FDM, and the top key SCAIs ② is listed. Then, the correlation matrix ⑤ of the key SCAIs and the correlation matrix ⑥ of the key BEFs and SCAIs are determined. Based on the interaction between the two, the grey correlation analysis method is used to get the grey correlation ranking ⑦ of the key SCAIs.
3.3. HoQ2: Linking SCAIs and BDEs
After determining the initial BDEs, FDM was used to screen out the key BDEs according to the reasonable threshold. Then, the grey correlation degree of each key SCAIs was weighted and averaged to obtain the key SCAIs weight value ⑨. Next, the key BDEs association matrix ⑩ and the key SCAIs and BDEs correlation matrix ⑪ were identified. Finally, the grey correlation ranking ⑫ of key BDEs was obtained by using GRA.
3.4. The Fuzzy Delphi Method (FDM)
Murray et al., 1985 proposed an optimized FDM, which combined the traditional Delphi method with fuzzy theory [128]. The expert’s judgment in the FDM is represented by fuzzy numbers. This study uses FDM to screen the key factors that are larger than the threshold because it can: (1) reduce survey data, (2) fully express the ideas of experts, (3) rationalize requirements, and (4) save more time and cost [129]. The specific steps of FDM are as follows:
Step A: The FDM questionnaire was developed based on the factors obtained from the literature analysis. The value range was indicated to target the level of importance of the evaluation targets. The minimum value of this value range represents the “most conservative cognitive value” by the experts. By contrast, the maximum value of the value range represents the “most optimistic cognitive value.”
Step B: The most conservative value and optimistic values given by all the experts were calculated. Fuzzy theory was adopted to calculate the minimum value ,geometric mean ,and maximum value in the conservative value, as well as the minimum value , geometric mean , and maximum value in the optimistic value.
Step C: In accordance with Step B, the conservative value of the triangular fuzzy number for every assessment item , and the triangular fuzzy number of the “most optimistic cognitive value” were obtained, .
Step D: The consensus level was calculated. refers to the “value importance level that has reached a consensus” as far as the experts’ opinions are concerned. The higher the is, the higher the consensus on a particular assessment criterion among the experts. can be calculated in the following three ways:
- (1)
- If the fuzzy triangular numbers show no overlap, then signifies that the opinion intervals of the experts possess a consensus section. If so, then the evaluation item i “value importance level that has reached a consensus”, , equals the average of and , which is expressed as
- (2)
- If two fuzzy triangular numbers overlap, then and , where .Then, the consensus importance degree of the evaluation item is equal to the fuzzy set obtained from the intersection operation of the fuzzy relation of the two trigonometric fuzzy functions. The quantized score with the maximum membership degree of the modified fuzzy set is then obtained using the following formula:
- (3)
- If the triangle fuzzy functions overlap, and , there is no consensus segment in the opinion interval value of each questionnaire object, and the two objects, given the extreme value, have greatly different opinions from other questionnaire objects, resulting in diverging opinions. Therefore, the evaluation items whose opinions do not converge are provided to the respondents for reference, and the steps from A to D are repeated for another round of questionnaires until all the evaluation items can converge and the value of consensus importance is calculated.
Step E: After setting the threshold, delete all factors that are smaller than the threshold.
3.5. Fuzzy Interpretative Structural Modeling (FISM)
Warfield, 1974 first proposed FISM [130], and ISM enables researchers and managers to gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between key issues [131]. Ragade, 1976 proposed the method of FISM by combining fuzzy theory with interpretive structural modeling [132]. As another extension of ISM, FISM solves the limitations of ISM through the interactive advantages of a 0–1 scale and transforms the unclear and unclear system cognitive model into a vivid and well-defined model [133]. The specific calculation steps are as follows:
Step A: Have each expert evaluate the value of the interaction between each key factor.
Step B: According to the concept of fuzzification, the minimum value and maximum value of each evaluation item are taken as the two endpoints of the fuzzy trigonometric function to calculate the geometric average value of the evaluation value:
where I refers to the number of questionnaire objects and refers to the evaluation project score.
Step C: Further obfuscation, find is equal to .
Step D: Set the evaluation threshold value and value for comparison, and transform the structural model into {0, 1} binary variable matrix, where “0” indicates that there is no mutual influence between the two variables, and “1” represents that there is a mutual influence between the two variables, to obtain the FISM matrix of the internal relationship of the reaction factors.
3.6. Analysis Network Procedure (ANP)
Professor Saaty, 1996 proposed ANP [134], which was developed based on analytic hierarchy process and is one of the most widely used methods in MCDM [135]. The network analysis procedure improves the interdependence of elements in the analytic hierarchy process, allowing complex mutual relations between decision levels and attributes, and reasonably assessing the mutual influence of factors to ensure the objectivity and accuracy of the evaluation [136].
In this study, ANP was used to evaluate the correlation and importance of factors. Table 1 is the evaluation scale of the ANP, and its evaluation scale is “1” to “9” points, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
ANP assessment scale.
The various steps involved in the ANP are described as follows:
Step A: According to the results of the questionnaire in the previous stage, the paired comparison matrix of factors is established, where is the evaluation value filled by experts for the comparison of factors and , as shown below:
Step B: Calculate the eigenvector weight values of each matrix using the following formula:
Step C: Due to numerous factors, the matrix is required to pass the consistency test. The consistency ratio was used to judge its consistency, and the value of must be <0.1. If it is greater than 0.1, the questionnaire must be filled out again to ensure the accuracy of the data. The formula for the consistency test is as follows:
where is a stochastic index, Table 2 below is the corresponding Stochastic index for factors.

Table 2.
Stochastic index.
3.7. Grey Relational Analysis (GRA)
GRA was first proposed by Deng, 1982 based on grey correlation space theory [137]. It is used to solve the uncertainty problem in the case of discrete data and incomplete information [138]. Its advantages include ease of understanding and calculation, the use of relatively little data or factors with large variables, and to help solve problems with complex interrelationships among multiple factors [139]. In addition, GRA has the advantage of converting qualitative evaluation factors into quantitative analysis and provides a comprehensive evaluation in multi-attribute decision-making [140].
The calculation steps for grey correlation analysis are as follows:
Step A: Construct the original matrix. The GRA original matrix is obtained by standardizing the direct relation matrix.
Step B: The factor values are processed according to the performance. Transform original matrices with different definitions or units into comparable sequences. The calculation formula is as follows:
Step C: Calculate the difference between the normalized value and parameter value, and calculate the grey correlation distance formula as follows:
Step D: The formula for calculating the grey correlation coefficient is as follows:
is the distinguished coefficient, [0,1], which aims to control the size of the gray correlation coefficient for the convenience of judgment. However, it is generally recommended to set 0.5 [138], but decision-makers can choose different values for calculation according to their personal preferences.
Step E: The grey correlation degree of factors was calculated. The grey correlation coefficient is multiplied by the integration weight value, and the weighted average value is the grey correlation degree.
Step F: Compare and rank—According to the grey correlation degree of each factor, the influence importance degree is arranged according to height.
4. Empirical Study
The largest and the leading relay manufacturing and sales enterprises in China and the world were selected as the research object. The main business areas of the research case included the design and manufacture of various types of solid state and optical relays, which are widely used in automotive, home appliances, intelligent power supply, industrial control, and other fields. Presently, there are 2903 employees in the case companies and the production base covers an area of 49.42 acres. Electronic equipment manufacturing companies were selected because it has several electronic product manufacturers with different types of components suppliers, fluctuations in the order of each supplier and frequent distortion of demand information, which results in a bullwhip effect and inventory backlog. This is to ensure the identification of key large data analysis to promote measures to weaken the bullwhip effect. In this study, six experts with rich subject knowledge from different departments were selected for in-depth interviews. Thereafter, we made an overall judgment and designed questionnaires as shown in Appendix B (Table A4, Table A5, Table A6, Table A7, Table A8, Table A9, Table A10, Table A11, Table A12, Table A13, Table A14, Table A15, Table A16, Table A17, Table A18 and Table A19) based on their opinions. The obtained data and analysis results were transformed into two-stage HoQs to verify the proposed framework. The overview of the experts interviewed is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Survey of interviewees.
4.1. First HoQ Linking BEFs and SCAIs
4.1.1. Stage Ⅰ: Confirmation of Important BEFs and SCAIs, Using FDM
A fuzzy Delphi questionnaire was designed and distributed based on the initial 27 BEFs and 47 SCAIs.
Calculate the value using formulas (1) and (2). After discussions with experts, this study sets the threshold of BEFs as 5.26 and the threshold of SCAIs as 6.41. Other factors and indicators that are smaller than the threshold will be deleted. According to the value, the first 14 factors will be listed as the key BEFs, and the calculation results are shown in Table 4. Similarly, the first 14 factors will be listed as key SCAIs, as shown in Table 5.

Table 4.
Important BEFs selected by FDM.

Table 5.
Important SCAIs selected by FDM.
By screening the FDM, the initial 27 BEFs are changed into 14, the initial 47 SCAIs are changed into 14, and the key BEFs and SCAIs are obtained. These key BEFs and SCAIs will be included in Parts ① and ② of the first HoQ, respectively, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3. As can be seen from Table 4, the three factors with the highest are “Information asymmetry,” “Batch ordering strategy,” and “Demand forecasting.” Table 5 shows that the three indicators with the highest values are “Improve data accuracy,” “Improve information transparency in the upstream and downstream of the supply chain,” and “Actively build a shared information platform with partners.”
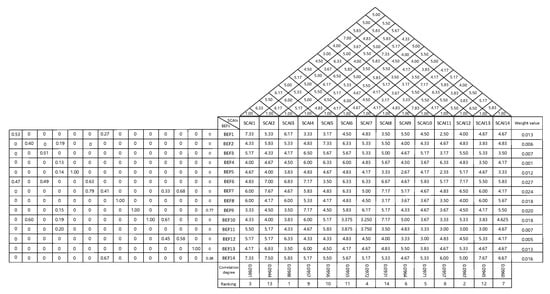
Figure 3.
The first HoQ between key BEFs and SCAIs.
4.1.2. Stage Ⅱ: Verification of the Interaction between Key BEFs
The interaction between related factors plays a key role in determining the dynamic behavior and operating performance of the system. The expert group was asked to evaluate the interaction matrix to understand the influence of BEFs on each other. Based on the results of the FDM screening, 14 key BEFs were further used to analyze the degree of interdependence. Evaluators were asked to consider whether BEFs influenced each other and were asked to evaluate them on a 0-1-2-3 scale.
After obtaining the expert evaluation of the key BEFs interaction matrix, Formulas (3) and (4) were used to calculate the evaluation value, and the evaluation threshold 2.1 was set to compare with the value of the key BEFs’ interaction matrix to convert the structural model into {0,1} binary variable matrix. The results revealed that there were mutual influences among BEF1 information asymmetry, BEF2 batch ordering strategy, BEF3 demand forecasting, BEF4 batch size, and BEF7 supply chain lack of coordination.
4.1.3. Stage III: Obtain the Key BEFs Interaction Coefficients and Weight Values, Using ANP
After the FISM of the second stage, it was known that there were mutual influences among BEF1 information asymmetry, BEF2 batch ordering strategy, BEF3 demand forecasting, BEF4 batch size, and BEF7 supply chain lack of coordination. The ANP questionnaire was designed and distributed on this basis, and experts were invited to score from “0” to “9” and assess the degree of interaction between key bullwhip factors.
According to Formulas (3)–(7), the corresponding evaluation values of each expert were calculated and integrated to obtain the interaction coefficient matrix of key BEFs and the weight value of key BEFs. The results are shown in Table 6. The BEFs’ interaction coefficient matrix will be included in Part ③ of the first HoQ, and the key BEFs weight values under the influence of the correlation matrix will be reflected in Part ④ of the first HoQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3.

Table 6.
Interaction coefficient matrix of key BEFs.
4.1.4. Stage Ⅳ: Identify the Association Matrix of Key SCAIs
Fourteen key SCAIs were selected as Part ② of the first HOQ, as shown in the figure. Next, experts will be invited to assess the internal correlations of key SCAIs to see whether they reinforce or conflict with each other. The correlation between key SCAIs was evaluated on a scale from “0” to “9”, with “1” indicating slight correlation, “3” indicating moderate correlation, and “9” indicating absolute correlation, and each intermediate value representing a weakening degree. The correlation matrix shown in Table 7 will be included in Part ⑤ of the first HOQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3.

Table 7.
Correlation matrix of key SCAIs.
4.1.5. Stage Ⅴ: Evaluate the Correlation Matrix between Key BEFs and SCAIs
Experts were invited to assess the relationship between key BEFs and SCAIs, and describe the interaction between the two using a scale from “0” to “9.” The evaluation results are the correlation matrix shown in Table 8, which will be included in Part ⑥ of the first HOQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3.

Table 8.
Correlation matrices of key BEFs and SCAIs.
4.1.6. Stage Ⅵ: Arrange the Priority of Key SCAIs
GRA can be used to obtain the correlation degree and ranking of key SCAIs that can reduce the bullwhip effect. The GRA is calculated as follows:
- A.
- Obtain the original evaluation matrix: multiply the matrices in Table 7 and Table 8 to obtain the original data matrix, then conduct the GRA, as shown in Table 9.
 Table 9. Important BEFs and SCAIs original evaluation matrix.
Table 9. Important BEFs and SCAIs original evaluation matrix. - B.
- Normalization of the original data matrix: Formula (10) is used to normalize the original evaluation matrix in Table 9 After normalization, the matrix will be between [0,1]. Table 10 shows the normalized matrix.
 Table 10. Normalized comprehensive evaluation matrix of key BEFs and SCAIs.
Table 10. Normalized comprehensive evaluation matrix of key BEFs and SCAIs. - C.
- Substitute the normalized comprehensive evaluation matrix in Table 10 into Equation (11) to obtain the difference sequence matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs, as shown in Table 11.
 Table 11. Difference sequence matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs.
Table 11. Difference sequence matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs. - D.
- Substitute Formula (12) into the difference sequence matrix in Table 11 to obtain the grey correlation coefficient matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs, as shown in Table 12.
 Table 12. Grey correlation coefficient matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs.
Table 12. Grey correlation coefficient matrix between key BEFs and SCAIs. - E.
- Multiply the moment of grey correlation degree in Table 12 by the weight value in Table 6, then calculate the grey correlation degree of each indicator using Formula (12), and sort the grey correlation degree, as shown in Table 13.
 Table 13. Grey correlation degree and ranking of key SCAIs.
Table 13. Grey correlation degree and ranking of key SCAIs.
As can be seen from Table 13, the top three key SCAIs that can be used to weaken the bullwhip effect are “SCAI3 Actively build a shared information platform with partners,” “SCAI12 Timely detecting threats in the environment,” and “SCAI1 Improve data accuracy.” In the grey correlation degree, the correlation between internal BEFs, the interaction between SCAIs, and the interaction between BEFs and SCAIs have been fully considered. Therefore, in the second HoQ, the grey correlation degree will be used as the weight basis for the key SCAIs. The calculation results shown in Table 13 will be included in part ⑦ of the first HoQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3.
In the first HoQ, the grey correlation degree and ranking of key SCAIs can be obtained using the FDM, FISM, ANP, and GRA. The first HoQ result in this framework is shown in Figure 3.
4.2. Second HoQ Linking SCAIs and BDEs
4.2.1. Stage I: Selection of Key BDEs Using FDM
In a globally competitive market with increasing uncertainties, manufacturers have recognized the need to create supply chains for manufacturing systems that respond quickly to uncertainties. From the perspective of the supply chain, this study mainly considers BDEs, SCAIs, and BDEs, and broadens the perspective of electronic equipment manufacturers’ supply chain management. Through example verification, the key findings are as follows:
In this study, the FDM and GRA are used to connect key SCAIs and BDEs. Through literature analysis and expert discussion, 21 initial enablers were selected. Based on this, the FDM questionnaire was designed and sent to experts, and the experts were asked to evaluate the minimum and maximum of each project in a range of 0–10. After collecting the questionnaires, extreme values exceeding two times the standard deviation were deleted. The results show that there is no extreme value in the range of two standard deviations. Formulas (1) and (2) were used to calculate the value.
According to the needs of the case company, the threshold value of this study was 6.55. The number of big data capability improvement strategies was screened from the original 21 to 10, and BDEs below the threshold were deleted. The filtering results, shown in Table 14, will be included in Part ⑧ of the second HoQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 4.

Table 14.
FDM results of key BDEs.
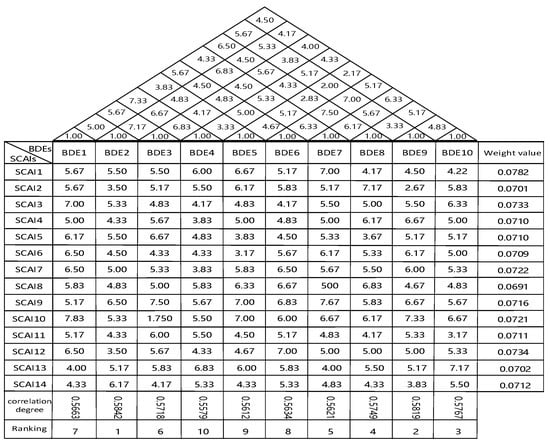
Figure 4.
The second HoQ between key SCAIs and BDEs.
4.2.2. Stage Ⅱ: Calculate the Weight Value of the Key SCAIs
In the first stage of the HoQ calculation, the grey correlation degree of 14 key SCAIs was obtained. Therefore, in the second stage of the HoQ, the grey correlation degree of each index was weighted and averaged to obtain the weight value of the key SCAIs in the second HoQ. The results are shown in Table 15 and will be included in Part ⑨ of the second HoQ, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 4.

Table 15.
Weight values of key SCAIs.
Stages III–V of the second HoQ are the same as stages IV–VI of the first HoQ: (1) The correlation matrix between BDEs, (2) the relationship matrix between SCAIs and BDEs, (3) the comprehensive relationship matrix between SCAIs and BDEs, and (4) the grey correlation degree and ranking of BDEs. (1) and (2) will be included in Parts ⑩ and ⑪ of the second HoQ, respectively, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 4.
Input the weight values of key SCAIs in Table 15 in the first HoQ into the second HoQ to calculate the grey correlation degree and rank of the BDEs. These will be included in the second HoQ, respectively, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 4. As can be seen from Table 16, the most important BDEs is “BDE2 Get financial support,” followed by “BDE9 Developing the Internet of Things.” Ranked third is “BDE10 Data visualization capability.” Ranked fourth and fifth are “BDE8 Developing cloud computing technology” and “BDE7 Develop IT infrastructure,” respectively. Table 16 and Figure 4 show the calculation results of the whole process.

Table 16.
Grey correlation degree and ranking of BDEs.
4.3. Discussion of Results
Regarding the results of the first HoQ linking BEFs and SCAIs, Table 4 shows that the first three BEFs are “BEF1 Information asymmetry,” “BEF2 Batch ordering strategy,” and “BEF3 Demand forecasting.” The ranking of key SCAIs shown in Table 13 reveals that “SCAI3 Actively build a shared information platform with partners,” “SCAI12 Timely detecting of threats in the environment,” and “SCAI1 Improve data accuracy” are the top issues on which the case enterprise’s senior management should pay attention.
As Figure 3 shows, prioritizing key SCAIs would significantly mitigate the bullwhip effect. The results show that SCAI3 ranks first in “Actively build a shared information platform with partners.” In the case of opaque information, it is easy to increase the variability of orders in the supply chain. Information sharing can actively make advance plans for orders and inventory changes. Therefore, SCAI3′s “Actively build a shared information platform with partners” is one of the most effective strategies to weaken the bullwhip effect. The second on the list is “SCAI12 Timely detecting of threats in the environment.” More and more companies face a wide range of environmental threats associated with their supply chains; for example, in 2001, Dutch customs officers blocked the import of nearly 1.3 million SONY PlayStation game consoles into Europe because the cadmium content in those cables exceeded new Dutch environmental regulations. As a result, SONY had to bear substantial costs regarding replacing parts, storing goods, and repackaging the final product. Therefore, the need to detect threats in the environment in a timely manner can reduce the bullwhip effect. In third place was “SCAI1 Improve data accuracy.” The nature of globalized businesses requires supply chain information integration to make responsive management decisions, such as forecasting and inventory replenishment, to fully meet the rapidly changing needs of international production and marketing activities. In view of this, the integration of information data has a certain inhibitory effect on the bullwhip effect. In addition, other key SCAIs screened by this study can also be used as a reference for case companies to reduce the bullwhip effect.
In the second HoQ linking SCAIs and BDEs, this study uses SCAIs as an intermediary of the other two variables. As can be seen from Table 16, the top five enablers for improving big data are “BDE2 Get financial support,” “BDE9 Developing the Internet of Things,” “BDE10 Data visualization capability,” “BDE8 Developing cloud computing technology,” and “BDE7 Develop IT infrastructure.”
BDE2 requires the case firm to invest in ensuring that it has specially designed hardware and software tools for data aggregation and processing across many supply chains. Meanwhile, in the supply chain, BDE9’s developing the Internet of Things helps to promote more accurate and timely information sharing in production, quality assurance, and distribution. BDE10 reduces the time lag between data collection, storage, analysis, and reporting processes, enhancing decision makers’ analytical capabilities. At the same time, BDE8 can really benefit firm’s supply chain management. Therefore, the above BDE10 and BDE8 strategies provide corresponding support from identifying supply chain bottlenecks to promoting supply chain recovery. Finally, a well-developed IT infrastructure (hardware, software, and expertise) lays a technical foundation for data analysis, equipped with which the firm can initiate the big data business enterprise smoothly. As supply chain agility is a multidimensional concept with multiple characteristics, it is difficult to improve supply chain agility through a single variable. Case companies should focus on integrating these five metrics to enhance supply chain agility. While improving supply chain agility, it can also reduce the bullwhip effect. At the same time, other key BDEs can also be used by case companies for decision-making to improve supply chain agility and mitigate the bullwhip effect.
5. Managerial Implications
The novelty of this study is established in the utilization of an integrated MCDM-QFD framework to provide a tool for withstanding fluctuations in supply chain demand. This will help decision-makers and managers in electronic equipment manufacturing industries understand the implications of adopting big data to improve agility and reduce bullwhip effects in the supply chain, and identify the most critical big data improvement measures. Further, this will encourage them to develop tactical and strategic plans for the adoption of big data. In addition, the research may help decision-makers in making management decisions. The management significance of this study is summarized as follows:
This study will enable the consolidation of the foundation of information technology and the formulation of management policies: it is crucial to develop advanced methods and technologies to support the application of big data analysis in supply chain management. In addition, the Internet of Things (IoT) is changing the traditional enterprise-to-customer interaction in an unprecedented manner, while cloud computing technology can effectively analyze and manage big data with parallel computing capabilities, thus improving the efficiency of big data acquisition and processing. To apply IoT and cloud computing technologies in every supply chain activity to build reliable supply chains, managers should develop big data analytics management policies in their manufacturing supply chains.
This study highlighted the expansion of investment and addition of advanced equipment for big data analytics: To maintain business in a competitive global market, it is critical to include advanced equipment for big data analytics to the manufacturing of enterprise supply chain. Because massive data sets are vast and complex, capital availability is a decisive factor in digital transformation. Therefore, managers should focus on securing funding for the development of big data analytics tools, and ensuring that they possess specially designed hardware and software tools for the aggregation and processing of data across numerous supply chains.
Develop strategic planning for the big data management of manufacturing supply chains: Plato principle emphasizes key management. Owing to the limited resources of enterprises, enterprises can invest the most important resources in strategic planning. On a global scale, the value of digital transformation has attracted widespread recognition by businesses and the society. Therefore, manufacturing enterprises need to integrate digital transformation thinking into strategic planning, and make strategic deployment of digital transformation resources from a top-level design perspective.
6. Conclusions
In a globally competitive market with increasing uncertainties, manufacturers have recognized the need to create supply chains for manufacturing systems that respond quickly to uncertainties. From the perspective of the supply chain, this study mainly considers BDEs, SCAIs, and BDEs, and broadens the perspective of electronic equipment manufacturers’ supply chain management. Through example verification, the key findings are as follows:
- The top three BEFs are “Information asymmetry,” “Batch ordering strategy,” and “Demand forecasting.”
- The top three SCAIs are “Actively build a shared information platform with partners,” “Timely detecting of threats in the environment,” and “Improve data accuracy.”
- The top five BDEs are “Get financial support,” “Developing the Internet of Things,” “Data visualization capability,” “Developing cloud computing technology,” and “Develop IT infrastructure.”
The main contributions of this study are described as follows:
Firstly, a QFD method based on the integrated FDM-FISM-ANP-GRA framework was proposed. By identifying key BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs, the constructed MCDM-QFD provides decision support for improving electronic equipment manufacturing
Secondly, BEFs, SCAIs, and BDEs are integrated into the QFD framework. By considering the mutual influence of BEFs, the relationship between BDEs and SCAIs, SCAIs, and BDEs is explored. It provides a feasible solution for electronic equipment manufacturing to apply BDEs to enhance supply chain agility and weaken the bullwhip effect.
Finally, electronic equipment manufacturers can effectively adjust their manufacturing system strategy, operations, and management through the proposed framework, and clearly understand where to improve their BDEs to enhance supply chain agility, thereby reducing the bullwhip effect.
This study provides two suggestions for future research. First, manufacturing systems in different industries can use the framework to reduce the bullwhip effect. However, the different characteristics of the industries being studied must be considered to determine the extent to which they require supply chain agility, which can then be imported into the proposed framework. Finally, a user-friendly decision support system can be developed for the framework to enable manufacturers and manufacturing systems to effectively establish big data and improve the level of automation of related activities to help monitor, plan, and optimize supply chains in real-time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-H.H. and X.-H.Y.; methodology, C.-H.H. and A.-Y.C.; software, X.-H.Y. and T.-Y.Z.; validation, C.-H.H., X.-H.Y. and A.-Y.C.; formal analysis, C.-H.H. and Q.-W.Z.; investigation, X.-H.Y. and Q.-W.Z.; resources, C.-H.H. and A.-Y.C.; data curation, X.-H.Y. and T.-Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-H.Y. and Q.-W.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.-H.H. and X.-H.Y.; visualization, C.-H.H. and Q.-W.Z.; supervision, C.-H.H. and A.-Y.C.; project administration, C.-H.H. and A.-Y.C.; funding acquisition, C.-H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Grant No. 2019J01790) and the Education and Scientific Research Foundation of Fujian Province Finance Department of China (Grant No. GY-Z21001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very much indebted to the Editor-in-Chief and anonymous referees who greatly helped to improve this paper with their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| (BEFs) | Bullwhip effect factors |
| (SCAIs) | Supply chain agility indicators |
| (BDEs) | Big data enablers |
| (BDA) | Big data analytics |
| (QFD) | Quality function deployment |
| (MCDM) | Multicriteria decision-making |
| (HoQ) | House of quality |
| (FDM) | Fuzzy Delphi method |
| (FISM) | Fuzzy interpretative structural modeling |
| (ANP) | Analysis network procedure |
| (GRA) | Grey relational analysis |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Important BEFs.
Table A1.
Important BEFs.
| NO. | Factors | A Brief Explanation of Each Factor | Relevant Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 1 | Information asymmetry | Information asymmetry occurring in the upstream of the supply chain | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]. |
| BEF 2 | Batch ordering strategy | Refers to the phenomenon involved in the placement of orders to upstream echelons in batches | Hussain and Saber (2012) [55]. |
| BEF 3 | Demand forecasting | Adjustment of the supply chain order and demand changes using a demand forecasting model | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]. |
| BEF 4 | Batch size | This refers to the quantity of a product, which is identical in quality, construction, and method of manufacture, produced at one time | Lee, Padmanabhan and Whang (1997) [47]. |
| BEF 5 | The multiplier effect | Generally refers to a case of direct multiplication of orders with a knock-on effect between product manufacturers and their capital equipment suppliers | Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |
| BEF 6 | Price fluctuation | Price changes caused by price discounts, coupons, and other special promotions in the market | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]. |
| BEF 7 | Lack of coordination in supply chain | Inadequate communication between suppliers and supply chain partners | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]. |
| BEF 8 | The company process | Includes the “variability of machine reliability and output” and “variability in process capability and subsequent product quality” | Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |
| BEF 9 | A shortage of game | This refers to the approach of Buyer in managing supply shortages in the event of a shortage event | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]. |
| BEF 10 | Factory capacity constraints | Capacity limits on merchandise in the warehouse of a dealer | Pastore, Alfieri and Zotteri (2019) [60]. |
| BEF 11 | Inventory policy | Inventory policies specify decision rules with respect to the point in time when a replenishment of the inventory should be initiated, as well as to the replenishment quantity that should be ordered from the supplying node in the supply network. | Dahlin and Safstrom (2021) [62]; Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |
| BEF 12 | Lead time | Refers to the order to delivery time | Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |
| BEF 13 | Local optimization without Global vision | This focuses only on the optimization of its own echelon without considering its impact on other echelons | Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |
| BEF 14 | Lack of synchronization | This includes the lack of synchronization in the delivery, receipt, ordering, transportation, and other aspects of supply chain members | Bhattacharya and Bandyopadhyay (2011) [63]. |

Table A2.
Important SCAIs.
Table A2.
Important SCAIs.
| NO. | Indicators | A Brief Explanation of Each Indicator | Relevant Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCAI 1 | Improve data accuracy | This determines the accuracy of the data source or data source logic | Chan, Ngai and Moon(2017) [84]. |
| SCAI 2 | Improve information transparency in the upstream and downstream of the supply chain | Indicates adequate information sharing between an enterprise and a supplier | Yang (2014) [85]. |
| SCAI 3 | Actively build a shared information platform with partners | For establishing a shared information system between the company and suppliers, and sharing information between different business units | Rasi, Abbasi, Hatami (2019) [82]; Jermsittiparsert and Srisawat (2019) [83]. |
| SCAI 4 | Improve market sensitivity | Companies must be aware of any in-demand changes relating to consumer tastes and preferences | Jermsittiparsert and Srisawat (2019) [83]. |
| SCAI 5 | Jointly manage inventory with suppliers | Integrate and synchronize information to eliminate excess inventory and improve inventory | Pandeyand Garg (2009) [86]. |
| SCAI 6 | Improve logistics capability | Improve logistics planning and management ability | Pandeyand Garg (2009) [86]. |
| SCAI 7 | Supplier innovation | This is a process that creates opportunities for organizations to capture new markets and eliminate stagnation and downturns that threaten existing businesses | Rasi, Abbasi and Hatami (2019) [82]. |
| SCAI 8 | Strategic flexibility | Superior knowledge and ability to adjust objectives and improve the ability of a company to respond to the market environment | Chan, Ngai and Moon (2019) [84] |
| SCAI 9 | Using information technology | This includes a variety of tools for supply chain software solutions to meet the requirements of all stages of the supply chain | Pandey and Garg (2009) [86]. |
| SCAI 10 | Automation | This involves the replacement of manual operations with computerized methods, or the implementation of decisions with minimal human intervention | Pandey and Garg (2009) [86]. |
| SCAI 11 | Improve service quality | The result of providing products or services that meet customer requirements | Pandey and Garg (2009) [86]. |
| SCAI 12 | Timely detection of threats in the environment | The rapid response of an organization to various forces with which it must interact | Rasi, Abbasiand Hatami (2019) [82]. |
| SCAI 13 | Integrate supply chain partners | This refers to a shared mental framework between customers and suppliers regarding inter-enterprise dependency and principles of collaboration | Haq, Hameed and Raheem (2020) [81]. |
| SCAI 14 | Plan and form long-term cooperative partners with suppliers | Becoming a partner in operational cooperation | Yang (2014) [85]. |

Table A3.
Key BDEs.
Table A3.
Key BDEs.
| NO. | Enablers | A Brief Explanation of Each Enabler | Relevant Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDE1 | Data integration and management capability | The ability of an organization to collect, integrate, transform, and store data from heterogeneous data sources using tools and technologies | Lamba and Singh (2018) [110]. |
| BDE2 | Get financial support | A large amount of capital needs to be invested in various processes related to big data, such as data collection, storage, and processing | Lamba and Singh (2018) [110]. |
| BDE3 | Big data storage maintenance | This is one of the essential aspects, which involve hardware devices and storage systems or mechanisms | Zhong et al. (2016) [109]. |
| BDE4 | Advanced analytical skills | Defined as the ability of an organization to analyze supply chain data using tools and technologies in bulk, real-time, near-term, or as supply chain data flows and extracts meaningful decision insights | Arunachalam, Kumar and Kawalek (2018) [104]. |
| BDE5 | Data-driven culture | As an intangible resource, this enabler represents the beliefs, attitudes, and opinions of the people on data segmentation decisions Ensuring data privacy at different stages of the collection, storage, and processing of big data | Arunachalam, Kumar and Kawalek(2018) [104]. |
| BDE6 | Value data security and privacy | Ensuring data privacy at different stages of the collection, storage, and processing of big data | Lamba and Singh (2018) [110]. |
| BDE7 | Develop IT infrastructure | This refers to the physical resources available for implementing IT innovations | Lai, Sunand Ren (2018) [111]. |
| BDE8 | Developing cloud computing technology | Consideration of leveraging cloud computing infrastructure for data integration, storage, and analytics as a complementary resource | Arunachalam, Kumar and Kawalek(2018) [104]. |
| BDE9 | Developing the Internet of Things | Development enables the formation of interconnected networks by common physical objects that can be individually addressed | Raman et al. (2018) [108]. |
| BDE10 | Data visualization capability | This refers to the ability of an organization to leverage tools and technologies to present information visuals and visually deliver data-driven insights to decision makers in a timely manner | Arunachalam, Kumar and Kawalek(2018) [104]. |
Appendix B
Questionnaire has been included in the Appendix B.
See Table A4, Table A5, Table A6, Table A7, Table A8, Table A9, Table A10, Table A11, Table A12, Table A13, Table A14, Table A15, Table A16, Table A17, Table A18 and Table A19 (Note: As there are too many factors in the questionnaire, sample questionnaires are shown below.)
The questionnaire included in the first QFD:

Table A4.
Fuzzy Delphi questionnaire (taking bullwhip effect as an example, the questionnaire of the supply chain agility index was similar, and the importance was indicated using values from 0 to 9).
Table A4.
Fuzzy Delphi questionnaire (taking bullwhip effect as an example, the questionnaire of the supply chain agility index was similar, and the importance was indicated using values from 0 to 9).
| NO. | The Most Conservative Value | The Most Optimistic Value |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 1 | ||
| BEF 2 | ||
| BEF 2 | ||
| ... |

Table A5.
Bullwhip effect factors fuzzy interpretative structural assessment questionnaire: (paired matrix of bullwhip effect factors related influence relationship, with 0 to 3 indicating the degree of mutual influence).
Table A5.
Bullwhip effect factors fuzzy interpretative structural assessment questionnaire: (paired matrix of bullwhip effect factors related influence relationship, with 0 to 3 indicating the degree of mutual influence).
| BEF 1 | BEF 2 | BEF 3 | ... | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 1 | ||||
| BEF 2 | ||||
| BEF 3 | ||||
| ... |
Analysis network procedure Questionnaire (importance scale from 0 to 9).

Table A6.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 1 and BEF 6
Table A6.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 1 and BEF 6
| BEF 1 | BEF 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 1 | ||
| BEF 6 |

Table A7.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 2 and BEF 10
Table A7.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 2 and BEF 10
| BEF 2 | BEF 10 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 2 | ||
| BEF 10 |

Table A8.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 3 and BEF 6
Table A8.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 3 and BEF 6
| BEF 3 | BEF 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 3 | ||
| BEF 6 |

Table A9.
To evaluate the interaction between BEF 4 and BEF 2, BEF 5, BEF 9, BEF 10, and BEF 11
Table A9.
To evaluate the interaction between BEF 4 and BEF 2, BEF 5, BEF 9, BEF 10, and BEF 11
| BEF 4 | BEF 2 | BEF 5 | BEF 9 | BEF 10 | BEF 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 4 | ||||||
| BEF 2 | ||||||
| BEF 5 | ||||||
| BEF 9 | ||||||
| BEF 10 | ||||||
| BEF 11 |

Table A10.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 6 and BEF 7
Table A10.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 6 and BEF 7
| BEF 6 | BEF 7 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 6 | ||
| BEF 7 |

Table A11.
To evaluate the degree of interaction between BEF 7, BEF 1, and BEF 4)
Table A11.
To evaluate the degree of interaction between BEF 7, BEF 1, and BEF 4)
| BEF 7 | BEF 1 | BEF 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 7 | |||
| BEF 1 | |||
| BEF 4 |

Table A12.
To evaluate the degree of interaction between BEF 11, BEF 6, and BEF 9)
Table A12.
To evaluate the degree of interaction between BEF 11, BEF 6, and BEF 9)
| BEF 11 | BEF 6 | BEF 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 11 | |||
| BEF 6 | |||
| BEF 9 |

Table A13.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 12 and BEF 7
Table A13.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 12 and BEF 7
| BEF 12 | BEF 7 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 12 | ||
| BEF 7 |

Table A14.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 3 and BEF 9
Table A14.
Assessment of the interaction between BEF 3 and BEF 9
| BEF 3 | BEF 9 | |
|---|---|---|
| BEF 3 | ||
| BEF 9 |

Table A15.
Supply chain agility indicators correlation matrix (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
Table A15.
Supply chain agility indicators correlation matrix (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
| SCAI 1 | SCAI 2 | SCAI 3 | ... | SCAI 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCAI 1 | |||||
| SCAI 2 | |||||
| SCAI 3 | |||||
| ... | |||||
| SCAI 14 |

Table A16.
Correlation matrix between supply chain agility indicators and bullwhip effect factors (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
Table A16.
Correlation matrix between supply chain agility indicators and bullwhip effect factors (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
| SCAI 1 | SCAI 2 | SCAI 3 | ... | SCAI 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEF 1 | |||||
| BEF 2 | |||||
| BEF 3 | |||||
| ... | |||||
| BEF 14 |
Questionnaire included in the second QFD:

Table A17.
Fuzzy Delphi questionnaire (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
Table A17.
Fuzzy Delphi questionnaire (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
| NO. | The Most Conservative Value | The Most Optimistic Value |
|---|---|---|
| BDE 1 | ||
| BDE 2 | ||
| BDE 3 | ||
| ... |

Table A18.
Association matrix of big data drivers (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
Table A18.
Association matrix of big data drivers (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
| BDE 1 | BDE 2 | BDE 3 | ... | BDE 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDE 1 | |||||
| BDE 2 | |||||
| BDE 3 | |||||
| ... | |||||
| BDE 10 |

Table A19.
Correlation matrix between supply chain agility indicators and big data enablers (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
Table A19.
Correlation matrix between supply chain agility indicators and big data enablers (importance on a scale of 0 to 9).
| BDE 1 | BDE 2 | BDE 3 | ... | BDE 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCAI 1 | |||||
| SCAI 2 | |||||
| SCAI 3 | |||||
| ... | |||||
| SCAI 14 |
References
- Zhang, F.; Gong, Z. Supply Chain Inventory Collaborative Management and Information Sharing Mechanism Based on Cloud Computing and 5G Internet of Things. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6670718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannisio, R.R. Factors Affecting Logistics and Supply Chain Management; Galgotias University: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Faludi, T. Measurement and reduction of the bullwhip effect. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Modern Research in Management, Economics and Accounting, Oxford, UK, 18–20 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, M.; Makvandi, P.; Saen, R.F.; Mohammad, D. What are causes of cash flow bullwhip effect in centralized and decentralized supply chains? Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 44, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C. Research on bullwhip effect management in supply chain based on system dynamics. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Application in Transportation Engineering, Ningbo, China, 5–6 June 2021; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.L.; Padmanabhan, V.; Whang, S. Comments on “Information distortion in a supply chain: The bullwhip effect”. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plebner, M.; Buhren, C.; Frank, B. Market research with the aid of a smartphone application–a case study. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, H. COVID-19 Pandemisinin sağlık tedarik zincirine kamçı etkisi. Kesit Akademi Dergisi 2020, 6, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackelprang, A.W.; Malhotra, M.K. The impact of bullwhip on supply chains: Performance pathways, control mechanisms, and managerial levers. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 36, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, A.; Lowry, P.B.; Ogden, J.A. Testing the Potential of RFID to Increase Supply-Chain Agility and to Mitigate the Bullwhip. In Innovations in Logistics and Supply Chain Management Technologies for Dynamic Economies; IGI Global: Derry Township, PA, USA; Commonwealth of Pennsylvania: Harrisburg, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 4, pp. 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Cho, H.; Kim, Y.S. Assessing business impacts of agility criterion and order allocation strategy in multi-criteria supplier selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H.; Jie, F. Impact of Internal Integration, Supply Chain Partnership, Supply Chain Agility, and Supply Chain Resilience on Sustainable Advantage. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkanlisoy, O. The covid-19 outbreaks effects and new inclinations in terms of logistics and supply chain activities: A conceptual framework. J. Manag. Mark. Logist. 2021, 8, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M.; Holcomb, M.C.; Stank, T.P. A multidisciplinary approach to supply chain agility: Conceptualization and scale development. J. Bus. Logist. 2013, 34, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.; Gligor, N.; Holcomb, M.; Bozkurt, S. Distinguishing between the concepts of supply chain agility and resilience: A multidisciplinary literature review. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2019, 30, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhsin, M.; Suryanto, T. The effect of supply agility mediation through the relationship between trust and commitment on supply chain performance. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2021, 9, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M.; Holcomb, M.C.; Feizabadi, J. An exploration of the strategic antecedents of firm supply chain agility: The role of a firm’s orientations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 179, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamout, M.D. Supply chain data analytics and supply chain agility: A fuzzy sets (fsQCA) approach. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2020, 28, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhtaroglu, F.C.P.; Demir, S.; Obali, M.; Girgin, C. Business model canvas perspective on big data applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, 6–9 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ngai, E.W.; Papadopoulos, T. Big data analytics in logistics and supply chain management: Certain investigations for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 176, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, S.; Gautam, P.; Jaggi, C.K. Role of Big Data Analytics in supply chain management: Current trends and future perspectives. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 1875–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, M.; Louis, M. A multi-agent based system with big data processing for enhanced supply chain agility. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2016, 29, 706–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J. Big data analytics capability in supply chain agility: The moderating effect of organizational flexibility. Manag. Decis. 2018, 57, 2092–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. An examination of the importance of big data analytics in supply chain agility development: A dynamic capability perspective. Manag. Res. Rev. 2018, 41, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. The influence of big data analytics management capabilities on supply chain preparedness, alertness and agility: An empirical investigation. Inf. Technol. People 2019, 32, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Pappas, I.O.; Krogstie, J.; Giannakos, M. Big data analytics capabilities: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Inf. Syst. e-Bus. Manag. 2018, 16, 547–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Fakhrzad, M.B.; Paghaleh, M.J. Food supply chain leanness using a developed QFD model. J. Food Eng. 2011, 102, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.N.; Boddu, V. Analysis of enablers for the implementation of leagile supply chain management using an integrated fuzzy QFD approach. J. Intell. Manuf. 2017, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayag, Z.; Samanlioglu, F.; Buyukozkan, G. A fuzzy QFD approach to determine supply chain management strategies in the dairy industry. J. Intell. Manuf. 2013, 24, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukozkan, G.; Cifci, G. An integrated QFD framework with multiple formatted and incomplete preferences: A sustainable supply chain application. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 3931–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wu, Z.; Xiang, W.; Goh, M.; Xu, Z.; Song, W.; Ming, X.; Wu, X. A novel Kano-QFD-DEMATEL approach to optimise the risk resilience solution for sustainable supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 1714–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Chang, A.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Lin, W.D.; Liu, W.L. Deploying Resilience Enablers to Mitigate Risks in Sustainable Fashion Supply Chains. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Quaddus, M.A. A multiple objective optimization based QFD approach for efficient resilient strategies to mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities: The case of garment industry of Bangladesh. Omega 2015, 57, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Bai, X. A quality function deployment approach to improve maritime supply chain resilience. Transp. Res. Part. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 92, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L. Designing a sustainable maritime supply chain: A hybrid QFD–ANP approach. Transp. Res. Part. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 78, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Huang, Z.X.; Serhat, Y.K.; Hasan, H. Analysis of the innovation strategies for green supply chain management in the energy industry using the QFD-based hybrid interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy decision approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110844. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, W.H.W.; Azlan, U.A.A. QFD Approach in Determining the Best Practices for Green Supply Chain Management in Composite Technology Manufacturing Industries. Malays. J. Compos. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 1, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepu, T.S.; Ravi, V. An integrated ANP–QFD approach for prioritization of customer and design requirements for digitalization in an electronic supply chain. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 1213–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Yu, R.Y.; Chang, A.Y.; Chung, W.H.; Liu, W.L. Resilience-Enhancing Solution to Mitigate Risk for Sustainable Supply Chain–An Empirical Study of Elevator Manufacturing. Processes 2021, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.; Rabbanimehr, M. Prioritising enablers of EFQM based on manager performance: An integration of 360 evaluation and house of quality (HoQ). Int. J. Procure. Manag. 2013, 6, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckstein, L.; Opricovic, S. Multiobjective optimization in river basin development. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T. Product design and selection using fuzzy QFD and fuzzy MCDM approaches. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, M.; Karsak, E.E. A QFD-based fuzzy MCDM approach for supplier selection. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 5864–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Zolfani, S.H.; Zavadskas, E.K. New integration of MCDM methods and QFD in the selection of green suppliers. J.Bus. Econ. Manag. 2016, 17, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Zolfani, S.H. Integrated QFD-MCDM framework for green supplier selection. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3728–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial dynamics: A major breakthrough for decision makers. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1958, 36, 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.L.; Padmanabhan, V.; Whang, S.J. Information distortion in a supply chain: The bullwhip effect. Manag. Sci. 1997, 43, 546–558. [Google Scholar]
- Derbel, M.; Chabchoub, H.; Hachicha, W.; Masmoudi, F. Measuring the impact of (s, S) ordering policy on the bullwhip effect by means of simulation optimization. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Advanced Logistics and Transport, Sousse, Tunisia, 29–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Braz, A.C.; Mello, A.M.; Gomes, L.A.V.; Nascimento, P.T. The bullwhip effect in closed-loop supply chains: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Disney, S.M. The bullwhip effect: Progress, trends and directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 250, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, S.; Lopez-Campos, M.; Dominguez, R.; Ashayeri, J.; Miranda, P.A. A simulation model of a coordinated decentralized supply chain. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2015, 22, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Saen, R.F. How to measure bullwhip effect by network data envelopment analysis? Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Ionescu, C.M.; Aghezzaf, E.H.; De Keyser, R. Decentralized and centralized model predictive control to reduce the bullwhip effect in supply chain management. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 73, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolarin, F.C.; Frutos, A.G.; Lise, A. Assessing the impact of prices fluctuation on demand distortion whitin a multi-echelon supply chain. Traffic Transp. 2011, 23, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Saber, H. Exploring the bullwhip effect using simulation and Taguchi experimental design. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2012, 15, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Framinan, J.M.; Cannella, S. Serial vs. divergent supply chain networks: A comparative analysis of the bullwhip effect. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 2194–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E. Big data and supply chain decisions: The impact of volume, variety and velocity properties on the bullwhip effect. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 5108–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Ahmad, S. Ranking operational causes of bullwhip effect in supply chain using AHP: Perception of managers in FMCG sector. Metamorphosis 2016, 15, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Peng, S.; Li, S. Mitigation of bullwhip effect in supply chain inventory management model. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, E.; Alfieri, A.; Zotteri, G. An empirical investigation on the antecedents of the bullwhip effect: Evidence from the spare parts industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 209, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michna, Z.; Disney, S.M.; Nielsen, P. The impact of stochastic lead times on the bullwhip effect under correlated demand and moving average forecasts. Omega 2020, 93, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, K.; Safstrom, O. Causes of the Bullwhip Effect: A Study of the Bullwhip Effect in the Volvo Group Service Market Logistics’ Supply Chain; Linköping University: Linköping, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Bandyopadhyay, S. A review of the causes of bullwhip effect in a supply chain. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 54, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R.N.; Dove, R. 21st Century Manufacturing Enterprise Strategy: An Industry-Led View; Diane Publishing: Collingdale, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher, M. The agile supply chain: Competing in volatile markets. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2000, 29, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, M.; Velmurugan, V.; Subashree, C. TADS: An assessment methodology for agile supply chains. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2015, 13, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M.; Holcomb, M.C. The role of logistics alliance orientation on forming the alliance structure: A conceptual framework. J. Transp. Manag. 2014, 17, 438–453. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.; Newsome, D.; Fuller, T.; Newsome, K.; Ghezzi, P.M. Agility: What It Is, How to Measure It, and How to Use It. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2021, 14, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, S.; Soosay, C.; Sandhu, S. Does agility foster sustainability: Development of a framework from a supply chain perspective. In Proceedings of the 12th ANZAM Operations, Supply Chain and Services Management Symposium, Auckland, New Zealand, 3–4 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bargshady, G.; Chegeni, A.; Kamranvand, S.; Zahraee, S.M. A Relational Study of Supply Chain Agility and Firms’ Performance in the Services Providers. Int. Rev. Manag. Mark. 2016, 2016, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sangari, M.S.; Razmi, J.; Gunasekaran, A. Critical factors for achieving supply chain agility: Towards a comprehensive taxonomy. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2016, 23, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Tseng, M.L.; Chiu, A.S.; Lim, M.K. Achieving competitive advantage through supply chain agility under uncertainty: A novel multi-criteria decision-making structure. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 190, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Lahoz-Leo, F. Supply chain agility: A mediator for absorptive capacity. Balt. J. Manag. 2018, 13, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Wang, M.; Akhtar, N. Enabling supply chain agility through process integration and supply flexibility: Evidence from the fashion industry. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2020, 32, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasyidi, R.A.; Kusumastuti, R.D. Supply chain agility assessment of an Indonesian humanitarian organization. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 10, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukor, A.A.A.; Newaz, M.S.; Rahman, M.K.; Taha, A.Z. Supply chain integration and its impact on supply chain agility and organizational flexibility in manufacturing firms. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2020, 16, 1721–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Al-Zabidi, A.; AlKahtani, M.; Umer, U.; Usmani, Y.S. Assessment of supply chain agility to foster sustainability: Fuzzy-DSS for a Saudi manufacturing organization. Processes 2020, 8, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zabidi, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Alkahtani, M. An approach to assess sustainable supply chain agility for a manufacturing organization. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Sangwan, K.S.; Gupta, G. Modelling supply chain agility antecedents using fuzzy dematel. Procedia CIRP 2021, 98, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprilia, A.; Laili, F.; Setyowati, P.B.; Waringga, K.F. The effect of supplier innovation on supply chain agility: Evidence from coffee shops in Malang area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 733, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Hameed, I.; Raheem, A. An empirical analysis of behavioral flexibility, relationship integration and strategic flexibility in supply chain agility: Insights from smes sector of pakistan. South Asian J. Manag. 2020, 14, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasi, R.E.; Abbasi, R.; Hatami, D. The effect of supply chain agility based on supplier innovation and environmental uncertainty. Int. J. Supply Oper. Manag. 2019, 6, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jermsittiparsert, K.; Srisawat, S. The Role of Supply Chain Visibility in Enhancing Supply Chain Agility. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Chang. 2019, 5, 485–501. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.T.; Ngai, E.W.; Moon, K.K. The effects of strategic and manufacturing flexibilities and supply chain agility on firm performance in the fashion industry. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 259, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Supply chain agility: Securing performance for Chinese manufacturers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 150, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Garg, S. Analysis of interaction among the enablers of agility in supply chain. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2009, 6, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russom, P. Big data analytics. TDWI Best Pract. Rep. Fourth Quart. 2011, 19, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ngai, E.W. Distribution network design with big data: Model and analysis. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.H.; Zhan, Y.; Ji, G.; Ye, F.; Chang, C. Harvesting big data to enhance supply chain innovation capabilities: An analytic infrastructure based on deduction graph. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 165, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffi, Y. Preparing for disruptions through early detection. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2015, 57, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, U.; Subramanian, N.; Parrott, G. Role of social media in retail network operations and marketing to enhance customer satisfaction. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakici, O.E.; Groenevelt, H.; Seidmann, A. Using RFID for the management of pharmaceutical inventory—system optimization and shrinkage control. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 51, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Huang, G.Q.; Lan, S.; Dai, Q.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T. A big data approach for logistics trajectory discovery from RFID-enabled production data. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 165, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Singh, A. Use of twitter data for waste minimisation in beef supply chain. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Khodaverdi, R.; Jafarian, A. A fuzzy multi criteria approach for measuring sustainability performance of a supplier based on triple bottom line approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.T.; Prakash, A.; Mishra, N. Priority-based scheduling in flexible system using AIS with FLC approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 4880–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Soleimani, H.; Kannan, D. Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain: A comprehensive review to explore the future. Eur. J. Operat. Res. 2015, 240, 603–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenherr, T.; Speier-Pero, C. Data science, predictive analytics, and big data in supply chain management: Current state and future potential. J. Bus. Logist. 2015, 36, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Kadziński, M.; Sivakumar, R. Application of a novel PROMETHEE-based method for construction of a group compromise ranking to prioritization of green suppliers in food supply chain. Omega 2017, 71, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, D. Role of multiple stakeholders and the critical success factor theory for the sustainable supplier selection process. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 195, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q.; Preston, D.S.; Swink, M. How the use of big data analytics affects value creation in supply chain management. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2015, 32, 4–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Telles, R. Big data analytics in supply chain and logistics: An empirical approach. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, D.; Kumar, N.; Kawalek, J.P. Understanding big data analytics capabilities in supply chain management: Unravelling the issues, challenges and implications for practice. Transp. Res. Part. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 114, 416–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moktadir, M.A.; Ali, S.M.; Paul, S.K.; Shukla, N. Barriers to big data analytics in manufacturing supply chains: A case study from Bangladesh. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 128, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Poulova, P.; Yasmin, F.; Danish, M.; Akhtar, W.; Usama Javed, H.M. How Big Data Analytics Boosts Organizational Performance: The Mediating Role of the Sustainable Product Development. J. Open Innov. Technol. Market. Complex. 2020, 6, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Hassen, A.; Chen, B. Big Data Analytics for Agriculture Input Supply Chain in Ethiopia: Supply Chain Management Professionals Perspective; Linnaeus University: Växjö, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, S.; Patwa, N.; Niranjan, I.; Ranjan, U.; Moorthy, K.; Mehta, A. Impact of big data on supply chain management. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2018, 21, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Newman, S.T.; Huang, G.Q.; Lan, S. Big Data for supply chain management in the service and manufacturing sectors: Challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 572–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, K.; Singh, S.P. Modeling big data enablers for operations and supply chain management. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 629–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Sun, H.; Ren, J. Understanding the determinants of big data analytics (BDA) adoption in logistics and supply chain management: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 676–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, R.P. Systems collaboration and strategic collaboration: Their impacts on supply chain responsiveness and market performance. Decis. Sci. 2010, 41, 955–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.V.; Yen, D.C.; Rajkumar, T.M.; Tomochko, N.A. The antecedent factors on trust and commitment in supply chain relationships. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2011, 33, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Research on demand-driven leagile supply chain operation model: A simulation based on anylogic in system engineering. Syst. Eng. Procedia 2012, 3, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.J.; Jiang, Z.B.; Liu, R.; Wang, L. The bullwhip effect in hybrid supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 2062–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Klassen, R.D.; Furlan, A.; Vinelli, A. The green bullwhip effect: Transferring environmental requirements along a supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 156, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seles, B.M.R.P.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Dangelico, R.M. The green bullwhip effect, the diffusion of green supply chain practices, and institutional pressures: Evidence from the automotive sector. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbaghnia, A.; Razmi, J.; Babazadeh, R.; Moshiri, B. Reducing the Bullwhip effect in a supply chain network by application of optimal control theory. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 2018, 52, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, D.; Sahin, F.; Shockley, J.; Sridharan, S.V. Is there a performance tradeoff in managing order fulfillment and the bullwhip effect in supply chains? The role of information sharing and information type. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 208, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, S. Coordination Mechanism of Supply Chain considering the Bullwhip Effect under Digital Technologies. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3217927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari Darberazi, A.; Malekinejad, P.; Ziaeian, M. Design a conceptual model of bullwhip effect reduction strategies in closed loop supply chains (Case study: Automotive oil production industries). J. Strateg. Manag. Stud. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, R.; Altay, N.; Gunasekaran, A.; Blome, C.; Papadopoulos, T.; Childe, S.J. Supply chain agility, adaptability and alignment: Empirical evidence from the Indian auto components industry. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimarut, T.; Mekhum, W. From Supply Chain Connectivity (SCC) to Supply Chain Agility (SCA), Adaptability and Alignment: Mediating Role of Big Data Analytics Capability. Int. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Haber, N.; Fargnoli, M.; Sakao, T. Integrating QFD for product-service systems with the Kano model and fuzzy AHP. Total. Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2020, 31, 929–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Pekkarinen, S. QFD-based modular logistics service design. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2011, 26, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Song, W.Y. Technical attribute prioritisation in QFD based on cloud model and grey relational analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 5751–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, H.; Chang, J.; Al-barakati, A. Green-duilding-material supplier selection with a rough-set-enhanced quality function deployment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T.J.; Pipino, L.L.; van Gigch, J.P. A pilot study of fuzzy set modification of Delphi. Hum. Syst. Manag. 1985, 5, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejab, M.M.; Azmi, N.F.M.; Chuprat, S. Fuzzy Delphi Method for evaluating HyTEE model. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Warfield, J.W. Developing interconnected matrices in structural modeling. IEEE Transcr. Syst. Men Cybern. 1974, 4, 51–81. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, J.P.; Vrat, P. Scenario building: A critical study of energy conservation in the Indian cement industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 1992, 41, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragade, R.K. Fuzzy interpretive structural modeling. Cybern. Syst. 1976, 6, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, J.P.; Vrat, P. Policy and Strategy Formulation: An Application of Flexible Systems Methodology; GIFT Pub: New Delhi, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T. Decision Making with Dependence and Feedback: The Analytic Network Process: The Organization and Prioritization of Complexity, 1st ed.; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.P.O.; Shieh, H.M.; Leu, J.D.; Tzeng, G.H. A novel hybrid MCDM model combined with DEMATEL and ANP with applications. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 5, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Valmohammadi, C. Using the analytic network process in business strategy selection: A Case Study. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 5205–5213. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J. Control problems of grey system. Syst. Control. Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.L. Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.; Yang, T.; Huang, G.W. The use of grey relational analysis in solving multiple attribute decision-making problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2008, 55, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.T. Analysis model of the sustainability development of manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprises in Taiwan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).