The Suitability of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Pharmacokinetic Studies in Veterinary Medicine
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Materials
2.2. Stock Solutions and Working Solutions
2.3. Investigated Drugs and Study Designs Employed
2.3.1. Ketamine
2.3.2. Medetomidine
2.3.3. Lidocaine
2.4. Sample Collection
2.4.1. Plasma
2.4.2. DBS
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.5.1. Plasma Extraction
2.5.2. DBS Extraction
2.6. Drug Quantification
2.7. Statistical Analysis
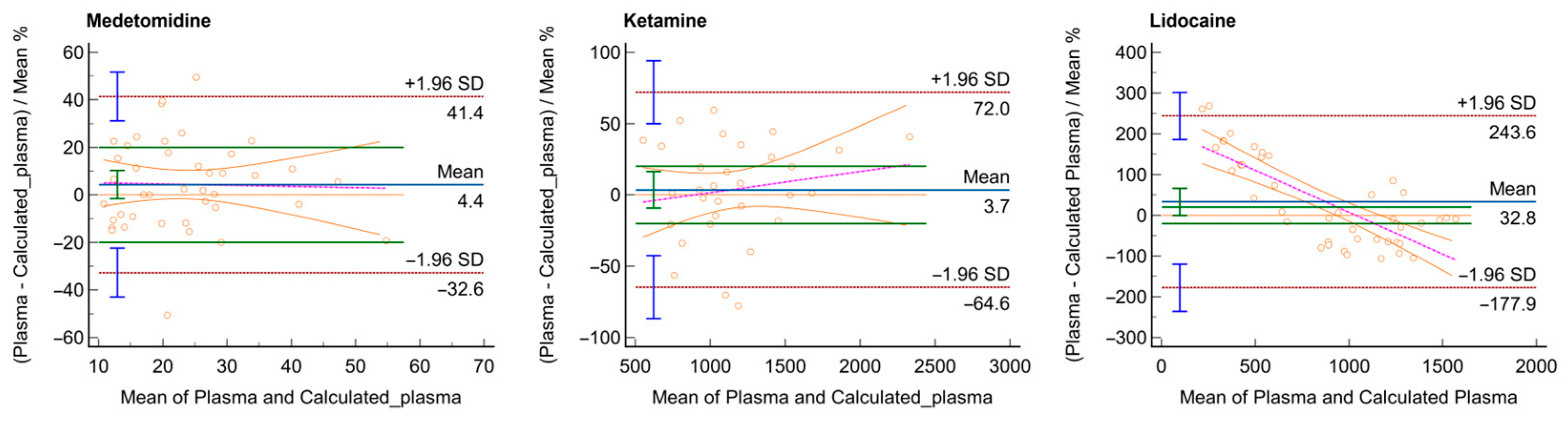
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baillargeon, K.R.; Mace, C.R. Microsampling Tools for Collecting, Processing, and Storing Blood at the Point-of-care. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, W.H.; Therrell, B.L., Jr. Overview of the History and Applications of Dried Blood Samples. In Dried Blood Spots; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-118-89083-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chace, D.H.; De Jesús, V.R.; Spitzer, A.R. Clinical Chemistry and Dried Blood Spots: Increasing Laboratory Utilization by Improved Understanding of Quantitative Challenges. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2791–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enderle, Y.; Foerster, K.; Burhenne, J. Clinical Feasibility of Dried Blood Spots: Analytics, Validation, and Applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, E.A.; Rast, G.; Cantow, C.; Schiwon, J.; Krause, F.; De Meyer, G.R.Y.; Guns, P.-J.; Guth, B.D.; Markert, M. Optimization of Bioanalysis of Dried Blood Samples. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2023, 123, 107296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canning, J.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Miedzybrodzka, Z.; Marioni, R.E.; Melbye, M.; Porteous, D.J.; Hurles, M.E.; Sattar, N.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Collins, R.; et al. Methods Applied to Neonatal Dried Blood Spot Samples for Secondary Research Purposes: A Scoping Review. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2024, 61, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.R.; Costa, R.A.; Gomes, L.H.F.; dos Santos Cunha, W.D.; Tyszler, L.S.; Freitas, S.; Llerena Junior, J.C.; de Vasconcelos, Z.F.M.; Nicholls, R.D.; da Guida, L.C. A Newborn Screening Pilot Study Using Methylation-Sensitive High Resolution Melting on Dried Blood Spots to Detect Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.; Ip, T.H.R.; Jenkins, B.; Yip, P.K.; Clarke, P.; Ponnusamy, V.; Michael-Titus, A.T.; Koulman, A.; Shah, D.K. Lipid Profiles from Dried Blood Spots Reveal Lipidomic Signatures of Newborns Undergoing Mild Therapeutic Hypothermia after Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, H.; Nakajima, D.; Konno, R.; Hijikata, A.; Higashiguchi, M.; Nihira, H.; Shimodera, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Nishitani-Isa, M.; Hiejima, E.; et al. A Non-Targeted Proteomics Newborn Screening Platform for Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2025, 45, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musteata, F.M. Pharmacokinetic Applications of Microdevices and Microsampling Techniques. Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, V.J.; Rudinsky, A.J.; Chew, D.J. Vitamin D Metabolism in Canine and Feline Medicine. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 250, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.S.R.; Taneja, I.; Rashid, M.; Sonkar, A.K.; Wahajuddin, M.; Singh, S.P. DBS-Platform for Biomonitoring and Toxicokinetics of Toxicants: Proof of Concept Using LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fipronil and Its Metabolites in Blood. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Espinosa, L.; Toledo-López, A.; Chávez-Pacheco, J.L.; Alemón-Medina, R.; Gómez-Garduño, J.; Lugo-Goytia, G.; García-Álvarez, R.; Juárez-Olguín, H.; Torres-Espíndola, L.M.; Pérez-Guillé, M.-G. Determination of Blood Dexmedetomidine in Dried Blood Spots by LC-MS/MS to Screen Therapeutic Levels in Paediatric Patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.; Shaner, R.L.; Feyereisen, M.C.; Wharton, R.E.; Kaplan, P.; Hamelin, E.I.; Johnson, R.C. Determination of Fentanyl Analog Exposure Using Dried Blood Spots with LC-MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretzel, L.; Thomas, A.; Geyer, H.; Pop, V.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M. Dried Blood Spots (DBS) in Doping Controls: A Complementary Matrix for Improved in- and out-of-Competition Sports Drug Testing Strategies. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7596–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiau, S.; Veenhof, H.; Koster, R.A.; Bergqvist, Y.; Boettcher, M.; Halmingh, O.; Keevil, B.G.; Koch, B.C.P.; Linden, R.; Pistos, C.; et al. Official International Association for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Guideline: Development and Validation of Dried Blood Spot-Based Methods for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, N.N.B.; Ho, P.C.-L. Dried Blood Spots—A Platform for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) and Drug/Disease Response Monitoring (DRM). Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2023, 48, 467–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.S.D.; Christianson, C.D.; Johnson, C.J.L.; Needham, S.R. Recent Advances in the Bioanalytical Applications of Dried Matrix Spotting for the Analysis of Drugs and Their Metabolites. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, A.; Rumbeiha, W.; Shlosberg, A.; Stuart, K.; Johnson, M.; Domenech, R.; Langner, H. Diagnostic Analysis of Veterinary Dried Blood Spots for Toxic Heavy Metals Exposure. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosypal, A.C.; Pick, L.D.; Hernandez, J.O.E.; Lindsay, D.S. Evaluation of a Novel Dried Blood Spot Collection Device (HemaSpotTM) to Test Blood Samples Collected from Dogs for Antibodies to Leishmania infantum. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickremsinhe, E.R.; Perkins, E.J. Using Dried Blood Spot Sampling to Improve Data Quality and Reduce Animal Use in Mouse Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2015, 54, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Saushkin, N.Y.; Samsonova, J.V.; Osipov, A.P.; Kondakov, C.E.; Efimova, M.A.; Chernov, A.N. A New Sampling Format for the Diagnostics of Bovine Infectious Diseases in Dried Blood Spots by ELISA. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 71, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.; Nunes, T.; Fonseca, C.; Vieira-Pinto, M.; Almeida, V.; Gortázar, C.; Correia-Neves, M. Spatial Analysis of Wildlife Tuberculosis Based on a Serologic Survey Using Dried Blood Spots, Portugal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaway, D.; Alexander, J.E.; Carvell-Miller, L.J.; Reynolds, R.M.; Winder, C.L.; Weber, R.J.M.; Lloyd, G.R.; Southam, A.D.; Dunn, W.B. Suitability of Dried Blood Spots for Accelerating Veterinary Biobank Collections and Identifying Metabolomics Biomarkers with Minimal Resources. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 887163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechmann, J.; Gehrig, O.; Luginbühl, M.; Fraefel, C.; Gaugler, S. Fully Automated Dried Blood Spot Sample Handling and Extraction for BoHV-1 Antibody Testing by ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 310, 114626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, E.L.; de Vries, A.; Esser, H.J.; Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Sprong, H. Detection of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Ear Tissue and Dried Blood Spots from Naturally Infected Wild Rodents. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonova, J.V.; Saushkin, N.Y.; Osipov, A.P. Dried Blood Spots Technology for Veterinary Applications and Biological Investigations: Technical Aspects, Retrospective Analysis, Ongoing Status and Future Perspectives. Vet. Res. Commun. 2022, 46, 655–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-e-Silva, J.; Jiménez-Ruiz, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Santos, E.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Lizana, V.; Martí-Marco, A.; Almeida, T.; Lopes, A.M.; Abrantes, J.; et al. Evaluation of Dried Blood Spots for Serological Surveys of Myxoma and Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses in Their Wild Reservoir. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 234, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhi, A.; Zaghini, A.; Levionnois, O.; Barbarossa, A. A Quick Approach for Medetomidine Enantiomer Determination in Dog Plasma by Chiral Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH M10 on Bioanalytical Method Validation—Scientific Guideline|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-scientific-guideline (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Martin, R.F. General Deming Regression for Estimating Systematic Bias and Its Confidence Interval in Method-Comparison Studies. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, A.; Joubert, A.; van der Merwe, M.; Norman, J.; Castel, S.; Denti, P.; Sliwa, K.; Maartens, G.; Sinxadi, P.; Wiesner, L. Validation of a Quantitative Multiplex LC-MS/MS Assay of Carvedilol, Enalaprilat, and Perindoprilat in Dried Blood Spots from Heart Failure Patients and Its Cross Validation with a Plasma Assay. J. Mass. Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab 2022, 27, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baietto, L.; Simiele, M.; D’Avolio, A. How Effective Is the Use of DBS and DPS as Tools to Encourage Widespread Therapeutic Drug Monitoring? Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daousani, C.; Karalis, V.; Loukas, Y.L.; Schulpis, K.H.; Alexiou, K.; Dotsikas, Y. Dried Blood Spots in Neonatal Studies: A Computational Analysis for the Role of the Hematocrit Effect. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Lee, J.A. Managing the Effect of Hematocrit on Dbs Analysis in A Regulated Environment. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.M.; Flores, S.R.; De Jesús, V.R. Influence of Hematocrit and Total-Spot Volume on Performance Characteristics of Dried Blood Spots for Newborn Screening. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2015, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermans, M.T.; de Kleijne, V.; Martens, F.; Heijboer, A.C. Hematocrit and Standardization in DBS Analysis: A Practical Approach for Hormones Mainly Present in the Plasma Fraction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 520, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-N.; Peng, Y.-F.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, G.-Y.; Weng, T.-I.; Kuo, C.-H. Development of the Dried Blood Spot Preparation Protocol for Comprehensive Evaluation of the Hematocrit Effect. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, N.G.L.; Rosing, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Procedures and Practices for the Validation of Bioanalytical Methods Using Dried Blood Spots: A Review. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2481–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.D. Dried Blood Spots for Global Health Diagnostics and Surveillance: Opportunities and Challenges. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malsagova, K.; Kopylov, A.; Stepanov, A.; Butkova, T.; Izotov, A.; Kaysheva, A. Dried Blood Spot in Laboratory: Directions and Prospects. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, R.; Allen, K.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Roche, P.; Greaves, R.F. Advantages and Challenges of Dried Blood Spot Analysis by Mass Spectrometry across the Total Testing Process. EJIFCC 2016, 27, 288–317. [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda, C.; Pham, R.; Fide, S.; Henne, K.; Xu, G.; Soto, M.; James, C.; Wong, P. Application of Automated Dried Blood Spot Sampling and LC–MS/MS for Pharmacokinetic Studies of AMG 517 in Rats. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainty, T.C.; Richmond, E.S.; Davies, I.; Blackwell, M.P. Dried Blood Spot Bioanalysis: An Evaluation of Techniques and Opportunities for Reduction and Refinement in Mouse and Juvenile Rat Toxicokinetic Studies. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarossa, A.; Bardhi, A.; Gazzotti, T.; Pagliuca, G. A Critical Point in Chiral Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Ketamine Metabolites. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routledge, P.A.; Barchowsky, A.; Bjornsson, T.D.; Kitchell, B.B.; Shand, D.G. Lidocaine Plasma Protein Binding. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 27, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Waters, N.J. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations for Drugs Binding to Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 2018, 36, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, K.R.; Harr, K.E.; Freeman, K.P.; Szladovits, B.; Walton, R.M.; Barnhart, K.F.; Blanco-Chavez, J. American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology ASVCP Reference Interval Guidelines: Determination of de Novo Reference Intervals in Veterinary Species and Other Related Topics. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sori, F.; Romagnoli, N.; Ferrara, D.; Zaghini, A.; Roncada, P. Plasma and Red Blood Cells Concentration Profiles of Ktamine after Single Intravenous Administration in an Anaesthetic Protocol in Horses. OJVM 2013, 3, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, N.; Al-Qudah, K.M.; Armorini, S.; Lambertini, C.; Zaghini, A.; Spadari, A.; Roncada, P. Pharmacokinetic Profile and Partitioning in Red Blood Cells of Romifidine after Single Intravenous Administration in the Horse. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ketamine | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Flow (mL/min) | % A | % B |
| 0.00 | 0.300 | 90 | 10 |
| 1.00 | 0.300 | 90 | 10 |
| 1.80 | 0.300 | 5 | 95 |
| 3.00 | 0.300 | 5 | 95 |
| 3.50 | 0.300 | 90 | 10 |
| 4.00 | 0.300 | 90 | 10 |
| Medetomidine | |||
| Time (min) | Flow (mL/min) | % A | % B |
| 0.00 | 0.350 | 40 | 60 |
| 1.00 | 0.350 | 5 | 95 |
| 2.70 | 0.350 | 5 | 95 |
| 3.00 | 0.350 | 40 | 60 |
| 3.50 | 0.350 | 40 | 60 |
| Lidocaine | |||
| Time (min) | Flow (mL/min) | % A | % B |
| 0.00 | 0.400 | 65 | 35 |
| 0.20 | 0.400 | 65 | 35 |
| 0.80 | 0.400 | 5 | 95 |
| 2.50 | 0.400 | 5 | 95 |
| 3.00 | 0.400 | 65 | 35 |
| 4.00 | 0.400 | 65 | 35 |
| Analyte | MRM Transition (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketamine | 238.1 > 124.9 | 20 | 26 |
| Ketamine-d4 | 242.0 > 129.0 | 20 | 26 |
| Medetomidine | 201.1> 94.9 | 28 | 18 |
| Medetomidine-d4 | 204.1 > 97.9 | 28 | 18 |
| Lidocaine | 235.1 > 85.9 | 30 | 17 |
| Lidocaine-d10 | 245.1 > 95.9 | 30 | 18 |
| Plasma | DBS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Ketamine (ng/mL) | Medetomidine (ng/mL) | Lidocaine (ng/mL) | Ketamine (ng/mL) | Medetomidine (ng/mL) | Lidocaine (ng/mL) |
| 1 (+QC) | 250 | 1 | 100 | 250 | 1 | 250 |
| 2 | 500 | 5 | 250 | 500 | 5 | 500 |
| 3 (+QC) | 1000 | 20 | 500 | 1000 | 20 | 1000 |
| 4 | 2500 | 50 | 1000 | 2500 | 50 | 2500 |
| 5 (+QC) | 5000 | 100 | 2500 | 5000 | 100 | 5000 |
| 6 | - | 200 | 5000 | - | 200 | 10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardhi, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Joubert, A.; Gehring, R.; Lambertini, C.; Romagnoli, N. The Suitability of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Pharmacokinetic Studies in Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050488
Bardhi A, Barbarossa A, Joubert A, Gehring R, Lambertini C, Romagnoli N. The Suitability of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Pharmacokinetic Studies in Veterinary Medicine. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050488
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardhi, Anisa, Andrea Barbarossa, Andrè Joubert, Ronette Gehring, Carlotta Lambertini, and Noemi Romagnoli. 2025. "The Suitability of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Pharmacokinetic Studies in Veterinary Medicine" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050488
APA StyleBardhi, A., Barbarossa, A., Joubert, A., Gehring, R., Lambertini, C., & Romagnoli, N. (2025). The Suitability of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Pharmacokinetic Studies in Veterinary Medicine. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050488






