Advances in Synthesis and Ignition Performance of Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Green Propellants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Liquid Propellant Capable of Self-Ignition
2.1. ILs Based on Borohydride-Rich Anions
2.2. ILs Based on Thiocyanate Anions
3. Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Liquid Propellant Requiring Promoters
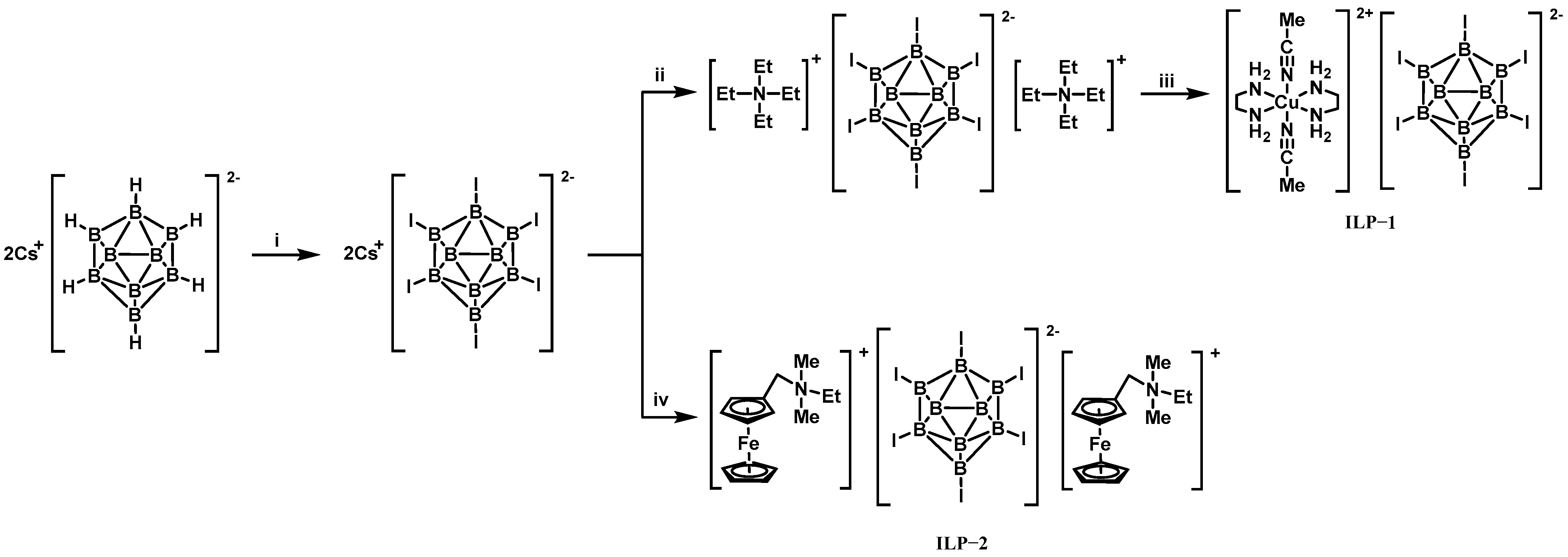
3.1. Promoters for ILs Based on Borohydride-Rich Anions and Hydrogen Peroxide
3.2. Promoters for ILs Based on Thiocyanate Anions and Hydrogen Peroxide
3.3. Promoters for ILs Based on Dicyanamide Anions and Hydrogen Peroxide
3.4. Promoters for ILs Based on Other Anions and Hydrogen Peroxide
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamal, F.; Yann, B.; Rachid, B.; Charles, K. Application of ionic liquids to space propulsion. Appl. Ion. Liq. Sci. Technol. 2011, 447, 466. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Song, D.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Sodium Azotetrazolate: A Novel Environmental-friendly Hydrogen-free Gas-Generating Pyrotechnics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T. Hypergolic ignition by head-on collision of N, N, N′, N′-tetramethylethylenediamine and white fuming nitric acid droplets. Combust. Flame 2016, 173, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Nie, F.; Yan, Q. Recent advances on the crystallization engineering of energetic materials. Energetic Mater. Front. 2020, 1, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Jeong, J.; Choi, J.; Churchill, D.G.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S. Additive-promoted hypergolic ignition of ionic liquid with hydrogen peroxide. Combust. Flame 2020, 214, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, Ł.J.; Boruc, Ł.; Kindracki, J. Pressure and temperature effect on hypergolic ignition delay of triglyme-based fuel with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2021, 287, 119370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Jiao, B.; Wang, B.; Cui, S.; Hao, Y. Review on Boronium-Anion-Based Hypergolic Ionic Liquids. Chin. J. Energetic Mater. 2022, 30, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Catoire, L.; Chaumeix, N.; Paillard, C. Chemical kinetic model for monomethylhydrazine/nitrogen tetroxide gas phase combustion and hypergolic ignition. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, I.; Hammerl, A.; Klapötke, T.M.; Nonnenberg, C.; Zewen, H. Processes during the hypergolic ignition between monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) in rocket engines. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. Int. J. Deal. Sci. Technol. Asp. Energetic Mater. 2005, 30, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenberg, C.; Frank, I.; Klapötke, T.M. Ultrafast cold reactions in the bipropellant monomethylhydrazine/nitrogen tetroxide: CPMD simulations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4586–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Stober, K.J.; Al Otaibi, R.; Alotaibi, M.; Almuqati, N.; Evans, B.J.; Gao, H.; Shreeve, J.N.; Cantwell, B.J. Ignition delay testing of various hypergolic ionic liquids and oxidizers. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016; p. 4782. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Shreeve, J.n.M. Energetic ionic liquids as explosives and propellant fuels: A new journey of ionic liquid chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10527–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauck, F.; Witte, J.; Negri, M.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Design and first results of an injector test setup for green hypergolic propellants. In Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2019 Forum, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 August 2019; p. 4279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huo, H.; Li, H.; Nie, F.; Yin, H.; Chen, F.-X. Cyanotetrazolylborohydride (CTB) anion-based ionic liquids with low viscosity and high energy capacity as ultrafast-igniting hypergolic fuels. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8300–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, M. Long term storability of hydrogen peroxide. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005; p. 4551. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, X. Role of cation structures for energetic performance of hypergolic ionic liquids. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10055–10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Hawkins, T.; Ahmed, Y.; Rosander, M.; Hudgens, L.; Mills, J. Green bipropellants: Hydrogen-rich ionic liquids that are hypergolic with hydrogen peroxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5886–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Kulkarni, S.G.; Kulkarni, P.S. Theoretical performance evaluation of hypergolic ionic liquid fuels with storable oxidizers. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9889–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Jeong, J.; Kwon, S. Ignition of boron-based green hypergolic fuels with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2019, 255, 115729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fei, L.; Xia, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Q. Organic superbase-mediated synthesis of borohydride ionic liquids as novel composite hypergolic fuels. Energetic Mater. Front. 2023, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauck, F.; Balkenhohl, J.; Negri, M.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Green bipropellant development—A study on the hypergolicity of imidazole thiocyanate ionic liquids with hydrogen peroxide in an automated drop test setup. Combust. Flame 2021, 226, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, S.C.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. The impact of cation structures on hypergolicity of thiocyanate ionic liquids with hydrogen peroxide. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 16128–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, S.C.; Brüggemann, D.; Freudenmann, D.; Ricker, R.; Schlechtriem, S. Protic thiocyanate ionic liquids as fuels for hypergolic bipropellants with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2022, 328, 125290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stölzle, S.C.; Kruse, L.; Freudenmann, D. Trialkylsulfonium Thiocyanate Ionic Liquids: Investigation on Temperature-Dependent Ignition Behavior of Green Hypergolic Propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2024, 49, e202400151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, A.K.; Petrutik, N.; Wang, K.; Shlomovich, A.; Shamis, O.; Tov, D.S.; Sućeska, M.; Yan, Q.-L.; Dobrovetsky, R.; Gozin, M. Effects of closo-icosahedral periodoborane salts on hypergolic reactions of 70% H2O2 with energetic ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19989–19997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chinnam, A.K.; Petrutik, N.; Komarala, E.P.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Q.-L.; Dobrovetsky, R.; Gozin, M. Iodocuprate-containing ionic liquids as promoters for green propulsion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22819–22829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis and hypergolic properties of flammable ionic liquids based on the cyano (1 H-1, 2, 3-triazole-1-yl) dihydroborate anion. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6198–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, T.; Jin, Y.; Huang, S.; Petrutik, N.; Shem-Tov, D.; Yan, Q.-L.; Gozin, M.; Zhang, Q. “Tandem-action” ferrocenyl iodocuprates promoting low temperature hypergolic ignitions of “green” EIL–H2O2 bipropellants. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 14661–14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Kim, K.-S.; Kwon, S.; Churchill, D.G. Sodium iodide: A trigger for hypergolic ignition of non-toxic fuels with hydrogen peroxide. In Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2020 Forum, Virtually, 24–28 August 2020; p. 3824. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Gwak, J.; Kim, K.-S.; Churchill, D.G.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S. Rapid ignition of “green” bipropellants enlisting hypergolic copper (II) promoter-in-fuel. Fuel 2021, 297, 120734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Lee, K.; Yoon, H.; Kwon, S. Green bipropellant: Performance evaluation of hypergolic ionic liquid-biofuel with hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 2024, 376, 132688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Bhosale, V.K.; Im, H.; Kwon, S. Performance improvement of triglyme-based fuels using an ionic liquid with hydrogen peroxide. Combust. Flame 2024, 270, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, X.; Song, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q. Hunting for energetic complexes as hypergolic promoters for green propellants using hydrogen peroxide as oxidizer. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 17033–17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q. Energetic complexes as promoters for the green hypergolic bipropellant of EIL-H2O2 combinations. FirePhysChem 2022, 2, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stützer, R.G.; Balkenhohl, J.; Lauck, F.; Oschwald, M.; Schlechtriem, S. Hypergolic reaction between green ionic liquid EMIM SCN and hydrogen peroxide in lab-scale drop test chamber. Int. J. Energetic Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2022, 21, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, M.; Lauck, F. Hot Firing Tests of a Novel Green Hypergolic Propellant in a Thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2022, 38, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Tan, Z.; Chen, P.; Tan, Y.; Hong, L. Study on the Hypergolic Characteristics of Imidazole Thiocyanate Ionic Liquids and Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Xi’an JiaoTong Univ. 2022, 56, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.; Kang, H.; Park, Y.; Lee, J. Effects of oxidizing additives on the physical properties and ignition performance of hydrogen peroxide-based hypergolic propellants. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 200, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Hawkins, T.W.; Ahmed, Y.; Rosander, M. Catalytic Hypergolic Bipropellants. US 8,758,531 B1, 24 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, V.; Hürttlen, J.; Schaller, U.; Imiolek, A.; Kelzenberg, S. Green liquid oxidizers basing on solutions of ADN and AN in hydrogen peroxide for hypergolic propellants with high performance. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences (EUCASS), Milan, Italy, 3–6 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, K. Designing difunctional promoters for hypergolic ignitions of green bipropellants combining ionic liquids with H2O2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 17433–17439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q. Auto-ignition of ionic liquid fuels with hydrogen peroxide triggered by copper-containing liquid promoter. Energetic Mater. Front. 2024, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauck, F.; Negri, M.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Study on hypergolic ignition of ionic liquid solutions. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, Madrid, Spain, 1–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]

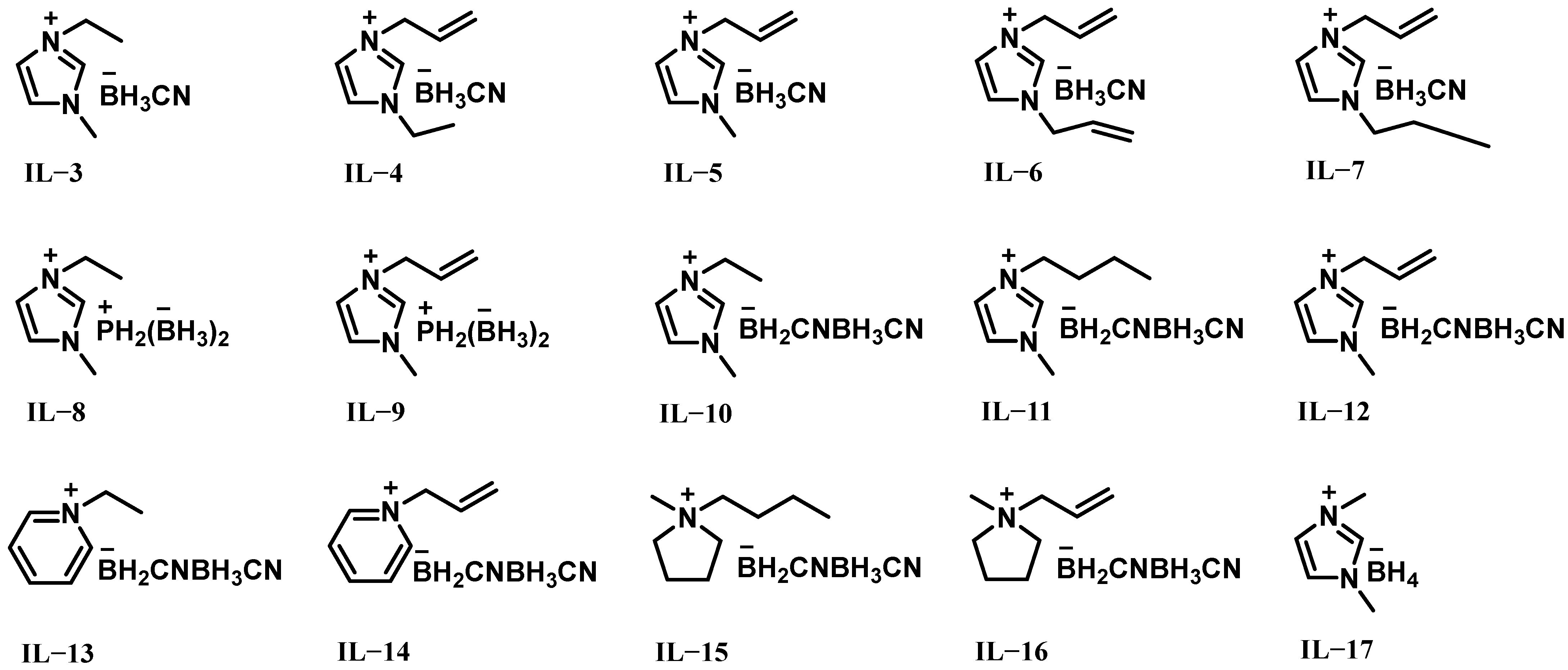
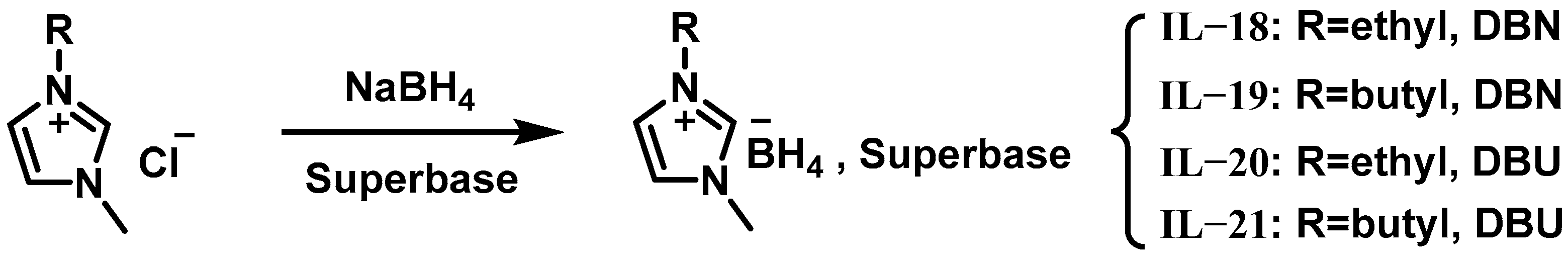
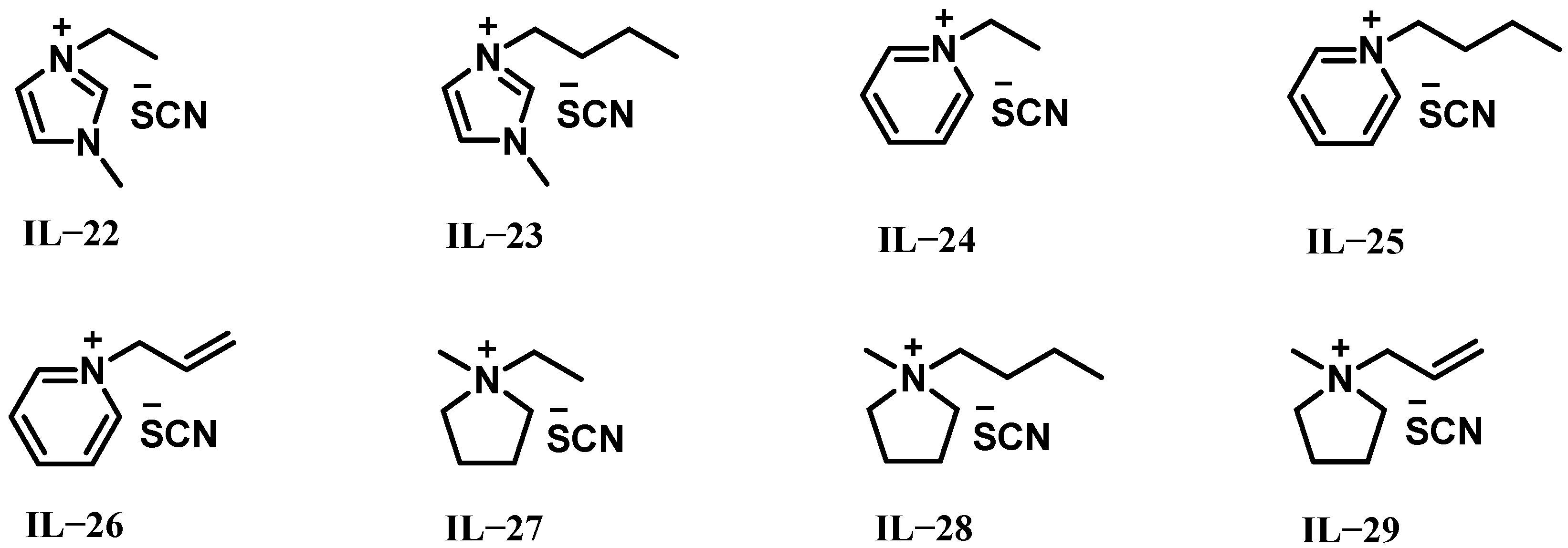



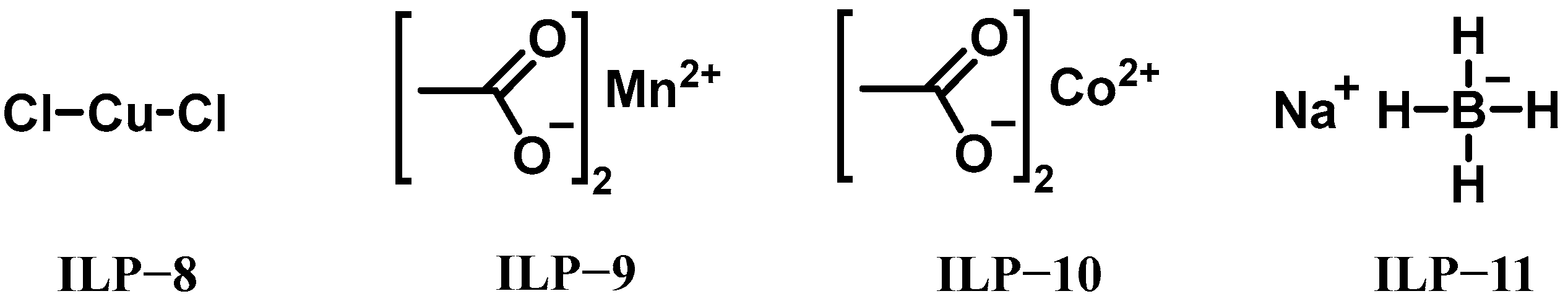



| Hypergolic Fuels | O/F a | Vc b (m s−1) | Isp c (s) | Ivac d (s) | ρ e (g cm−3) | ρIsp f (s g cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-3 | 3.5 | 1670 | 244.1 | 273.3 | 1.310 | 319.8 |
| IL-4 | 3.5 | 1663 | 243.1 | 272.1 | 1.299 | 315.9 |
| IL-5 | 3.5 | 1673 | 244.5 | 273.7 | 1.303 | 318.6 |
| IL-6 | 3.5 | 1668 | 243.9 | 272.9 | 1.301 | 317.4 |
| IL-7 | 3.5 | 1669 | 244.0 | 272.9 | 1.294 | 315.8 |
| IL-8 | 2.5 | 1664 | 243.2 | 271.9 | 1.234 | 300.2 |
| IL-9 | 2.5 | 1666 | 243.5 | 272.2 | 1.240 | 301.9 |
| IL-10 | 3.5 | 1646 | 240.6 | 269.6 | 1.288 | 309.9 |
| IL-11 | 3.5 | 1648 | 240.9 | 269.7 | 1.297 | 312.5 |
| IL-12 | 3.5 | 1650 | 241.1 | 270.2 | 1.292 | 311.4 |
| IL-13 | 3.5 | 1646 | 240.6 | 269.4 | 1.291 | 310.7 |
| IL-14 | 3.5 | 1642 | 240.0 | 268.8 | 1.294 | 310.7 |
| IL-15 | 4.0 | 1659 | 242.4 | 271.5 | 1.286 | 311.8 |
| IL-16 | 4.0 | 1661 | 242.7 | 272.0 | 1.292 | 313.7 |
| UDMH | 3.5 | 1694 | 247.7 | 276.9 | 1.224 | 303.3 |
| IL | ρ a (g cm−3) | η b (mPa s) | Td c (°C) | Tm d (°C) | ΔHf e (kJ mol−1) | Isp f (s) | O/F g | IDT h (ms) | State i | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | >3000 | liquid | 98% H2O2, 90% H2O2 |
| IL-2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | <30 | liquid | 98% H2O2, 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | 0.98 | 19 | 247 | −71 | 136 | 253 | 3.5 | >1000 | liquid | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-4 | 0.95 | 17 | 265 | <−50 | 225 | 253 | 3.5 | >1000 | liquid | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-17 | 0.92 | - | 130 | 50 | 132 | 258 | 3.5 | 18.5 | soild | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-18 | 1.02 | 58 | - | - | - | - | - | 28.3 | liquid | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-19 | 1.03 | 34 | - | - | - | - | - | 86.8 | liquid | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-20 | 1.01 | 110 | - | - | - | - | - | 344 | liquid | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-21 | 1.00 | 81 | - | - | - | - | - | 127 | liquid | 90% H2O2 |
| IL | ρ a (g cm−3) | η b (mPa s) | Td c (°C) | Tm d (°C) | ΔHf e (kJ mol−1) | Isp f (s) | O/F g | IDT h (ms) | State i | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-22 | 1.11 | 23 | - | −6 | 53 | 317 | 3.8 | 31.7 | liquid | 96.1% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | 1.07 | 36 | - | −29 | −5 | 319 | 4.2 | 45 | liquid | 96.1% H2O2 |
| IL-24 | 1.13 | 28 | 247 | - | −149 | 313 | 4.3 | 26.8 | liquid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-25 | 1.09 | 87 | 258 | - | −126 | 317 | 4.5 | 33.9 | liquid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-26 | 1.14 | 38 | 197 | - | 93 | 317 | 4.2 | 29.5 | liquid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-27 | 1.07 | - | 264 | 55 | −162 | 320 | 4.5 | 43.1 | solid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-28 | 1.05 | 549 | 261 | - | −477 | 318 | 4.9 | 61.9 | liquid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-29 | 1.07 | 81 | 232 | - | −140 | 319 | 4.6 | 48.9 | liquid | 97.4% H2O2 |
| IL-30 | 1.36 | - | 219 | 106 | 127 | 309 | 3.0 | 7.3 | solid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-31 | 1.27 | - | 229 | 45 | 58 | 312 | 3.4 | 23.0 | solid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-32 | 1.14 | 77 | 237 | 2 | 49 | 314 | 3.6 | 42.8 | liquid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-33 | 1.09 | 170 | 250 | −18 | 11 | 318 | 4.0 | 46.1 | liquid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-34 | 1.28 | - | 252 | 84 | −14 | 310 | 3.4 | 16.5 | solid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-35 | 1.24 | - | 259 | 87 | −73 | 312 | 3.7 | 20.2 | solid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-36 | 1.08 | 126 | 270 | −74 | −2 | 318 | 4.0 | 28.4 | liquid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-37 | 1.26 | - | 116 | 66 | −176 | 307 | 3.0 | 55.1 (21 °C); 65.1 (1 °C); 83.6 (−25 °C) | solid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-38 | 1.13 | 26 | 119 | 0 | −170 | 311 | 4.1 | 30.8 (21 °C); 32.8 (1 °C); 51.8 (−25 °C) | liquid | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-39 | 1.09 | 34 | 123 | −13 | −269 | 314 | 4.5 | 61.8 (21 °C); 69.2 (1 °C); 79.2 (−25 °C) | liquid | 97% H2O2 |
| Fuels | IL-3 (wt.%) | IL-40 (wt.%) | Furfuryl Alcohol (wt.%) | NaBH3CN (wt.%) | ILP-17 (wt.%) | IDT (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF-1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >1000 |
| HF-2 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 95.5 |
| HF-3 | 93 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 93.6 |
| HF-4 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | <9 | 75.5 |
| HF-5 | 47.5 | 0 | 47.5 | 0 | 5 | 80.3 |
| HF-6 | 46.5 | 0 | 46.5 | 0 | 7 | 64.5 |
| HF-7 | 45.5 | 0 | 45.5 | 0 | 9 | 56.0 |
| HF-8 | 44.5 | 0 | 44.5 | 0 | <11 | 44.5 |
| HF-9 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 392.5 |
| HF-10 | 0 | 97 | 0 | 0 | <3 | 25.3 |
| HF-11 | 0 | 54 | 46 | 0 | 10 | 44.0 |
| HF-12 | 0 | 76 | 19 | 0 | 5 | 82.3 |
| HF-13 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | NO |
| HF-14 | 0 | 0 | 85 | 10 | 5 | 48.8 |
| HF-15 | 0 | 0 | 83 | 10 | 7 | 34.0 |
| HF-16 | 0 | 0 | 81 | 10 | 9 | 30.0 |
| HF-17 | 0 | 0 | 79 | 10 | <11 | 29.0 |
| IL | Promoter | wILP a (wt%) | ρ b (g cm−3) | η c (mPa s) | Td d (°C) | Tm e (°C) | ΔHf f (kJ mol−1) | Isp g (s) | IDT h (ms) | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-3 | ILP-1 | 8 | 3.13 | - | - | - | - | 237 | 69 | 70% H2O2 |
| 24 | 95% H2O2 | |||||||||
| IL-3 | ILP-2 | 8 | 2.73 | - | - | - | - | 237 | 45 | 70% H2O2 |
| 17 | 95% H2O2 | |||||||||
| IL-3 | NO | - | 0.98 | 19 | 247 | - | - | 269 | >1000 | 95% H2O2 |
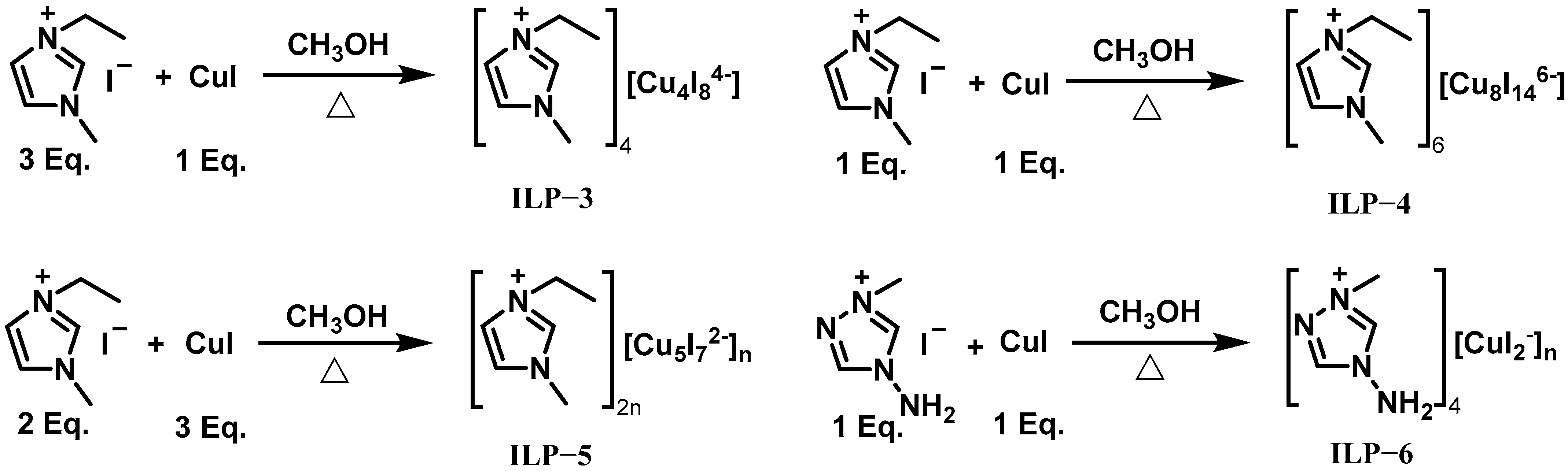
| IL-3 | ILP-3 | 10 | 1.02 | 42 | 220 | - | - | 265 | 37 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-4 | 10 | 1.02 | 48 | 221 | - | - | 261 | 36 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-5 | 10 | 1.03 | 50 | 219 | - | - | 264 | 24 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-6 | 10 | 1.02 | 55 | 214 | - | - | 262 | 38 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | NO | - | 0.93 | 5 | 263 | 267 | 393 | 95% H2O2 | ||
| IL-40 | ILP-3 | 10 | 1.00 | 80 | 161 | - | - | 263 | 30 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-4 | 10 | 1.01 | 87 | 162 | - | - | 259 | 23 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-5 | 10 | 1.01 | 82 | 160 | - | - | 262 | 14 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-6 | 10 | 1.01 | 89 | 158 | - | - | 260 | 28 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-41 | NO | - | 1.11 | 35 | 203 | <−70 | 359 | - | NO | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-41 | ILP-7 | 15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ignition | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-42 | NO | - | 1.13 | 52 | 193 | <−70 | 472 | - | NO | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-42 | ILP-7 | 15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ignition | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-43 | NO | - | 1.12 | 28 | 241 | <−70 | 242 | - | NO | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-43 | ILP-7 | 15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ignition | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-8 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 139 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-9 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 395 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-10 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 887 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-11 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 73 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-12 | 5 | 1.30 | 24 | 242 | - | - | 240 | 87 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-13 | 10 | 1.03 | 28 | 205 | - | - | 239 | 38 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-14 | 10 | 1.03 | 35 | 210 | - | - | 240 | 31 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-5 | ILP-13 | 10 | 1.00 | 39 | 195 | - | - | 242 | 89 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-5 | ILP-14 | 10 | 1.01 | 47 | 197 | - | - | 242 | 56 | 95% H2O2 |
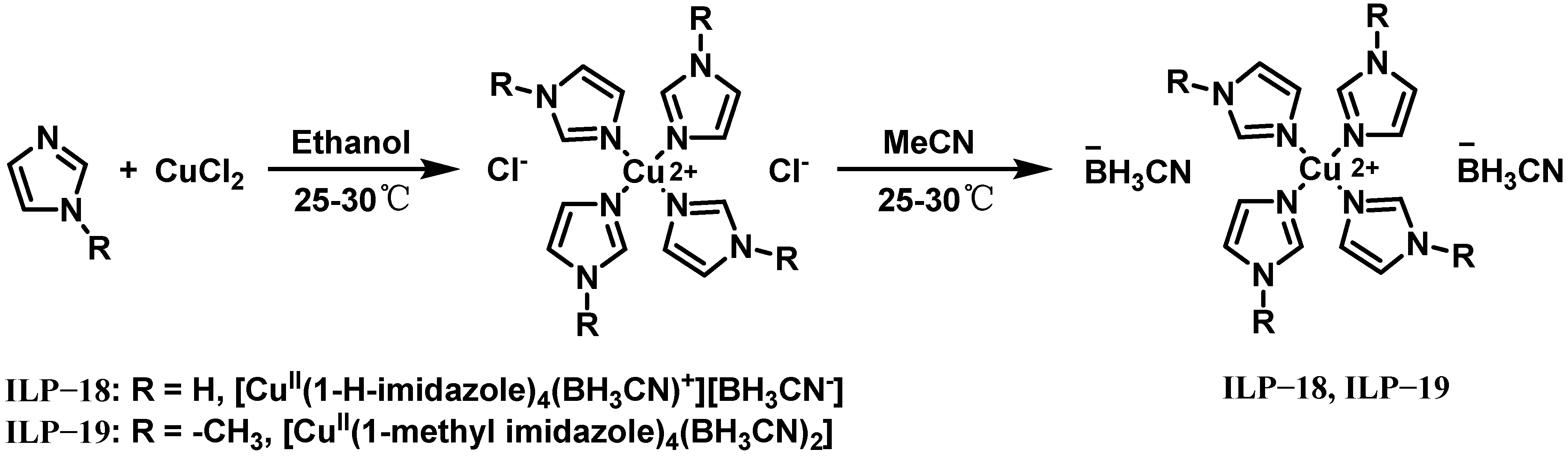
| IL-3 | ILP-18 | 13 | 0.98 | 26 | 156 | - | - | 240 | 9.5 | 95% H2O2 |
| TG | ILP-18 | 13 | 1.05 | 10 | 162 | - | - | 270 | 9.0 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-3/TG | ILP-18 | 13 | 1.02 | 21 | 160 | - | - | 248 | 7.8 | 95% H2O2 |
| ILethCu01 (IL-3/ethanol) | ILP-18 | 9 | 0.90 | 4 | - | - | - | 317 | 7.5 | 95% H2O2 |
| triglyme | ILP-18 | 13 | 1.02 | 5 | 156 | −45 | - | - | 18.7 | 95% H2O2 |
| TriGIL (IL-3/triglyme) | ILP-18 | 13 | 1.02 | 26 | 233 | <−80 | - | - | 8.0 | 95% H2O2 |
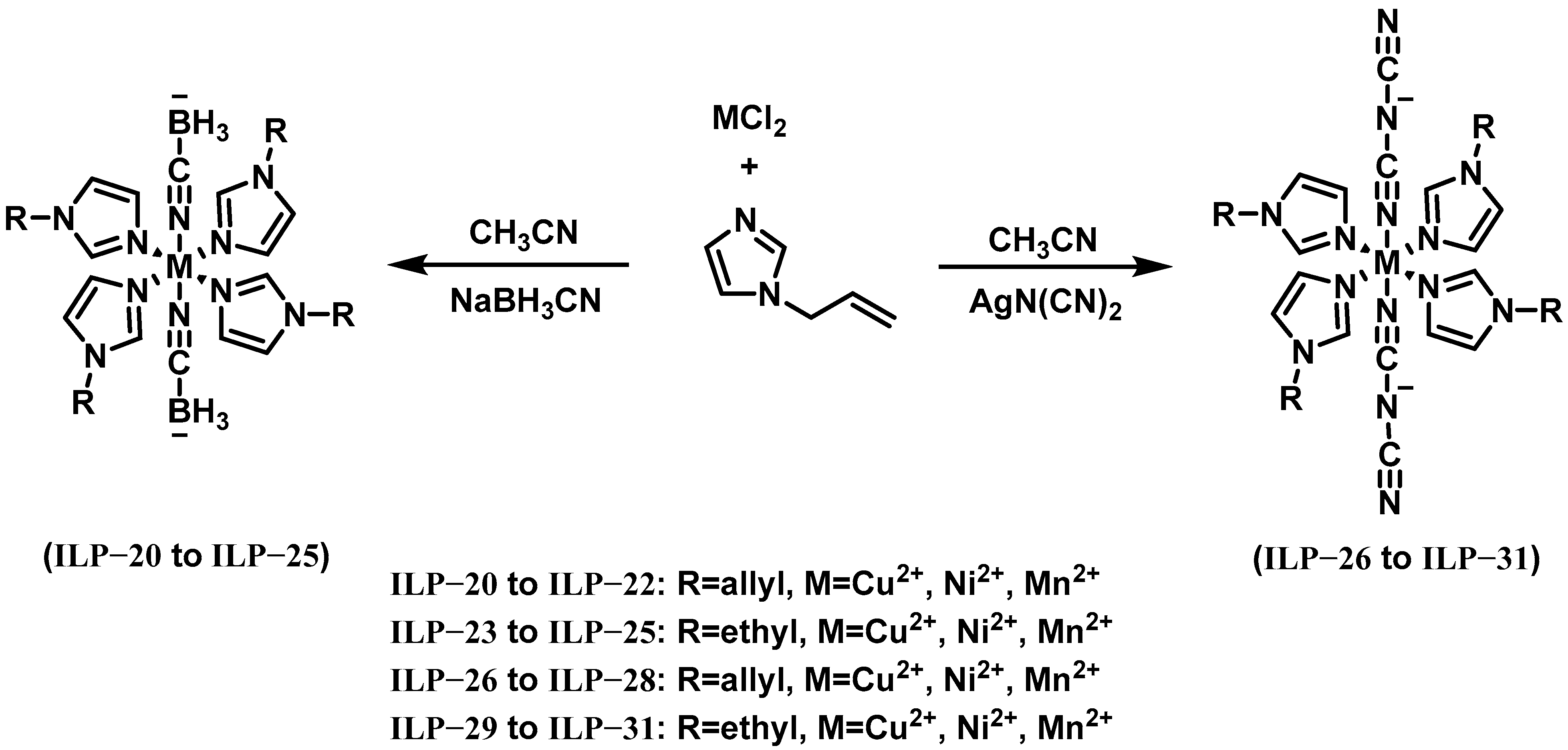
| IL-3 | ILP-20 | 10 | - | - | >240 | - | - | 278 | 37 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-22 | 10 | - | - | >240 | - | - | 277 | 62 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-26 | 10 | - | - | >240 | - | - | 277 | 31 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-28 | 10 | - | - | >240 | - | - | 277 | 70 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-23 | 10 | 0.94 | - | 250 | - | 261 | 287 | 104 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-25 | 10 | 0.95 | - | 257 | - | 229 | 287 | 105 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-29 | 10 | 0.96 | - | 256 | - | 243 | 287 | 94 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-3 | ILP-31 | 10 | 0.96 | - | 249 | - | 232 | 286 | 95 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL | Promoter | wILP a (wt%) | ρ b (g cm−3) | η c (mPa s) | Td d (°C) | Tm e (°C) | ΔHf f (kJ mol−1) | Isp g (s) | IDT h (ms) | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-22 | ILP-32 | 5 | 1.15 | 30 | 273 | - | - | - | 13.9 | 96.1% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | NO | - | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 23.0 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-35 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 22.9 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-35 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 319 | 21.5 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-35 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 316 | 19.3 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-35 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 302 | 15.0 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-36 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 21.6 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-36 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 21.9 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-36 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 319 | 23.0 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-22 | ILP-36 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 313 | 27.8 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | NO | - | - | - | - | - | - | 322 | 35.1 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-35 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 322 | 33.1 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-35 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 321 | 32.2 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-35 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 318 | 30.1 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-35 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 303 | 23.7 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-36 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 34.6 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-36 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 322 | 32.7 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-36 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 320 | 31.6 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-23 | ILP-36 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 314 | 36.7 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL | Promoter | wILP a (wt%) | ρ b (g cm−3) | η c (mPa s) | Td d (°C) | Tm e (°C) | ΔHf f (kJ mol−1) | Isp g (s) | IDT h (ms) | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
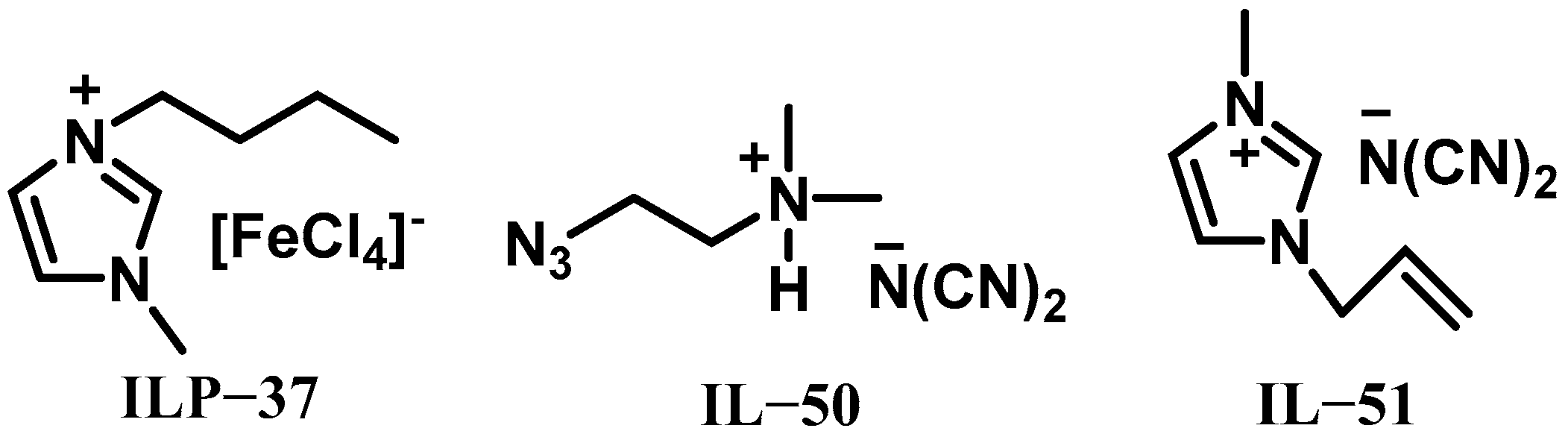
| IL-50 | ILP-37 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 110 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-50 | ILP-37 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 130 | 98% H2O2 |
| IL-51 | ILP | 15 | - | - | - | −5 | - | - | 9 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-51 | ILP | 15 | - | - | - | −11 | - | - | 11 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-51 | ILP | 15 | - | - | - | −25 | - | - | 22 | 80% H2O2 |
| IL-51 | ILP | 15 | - | - | - | −38 | - | - | 66 | 70% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | NO | - | 1.12 | 69 | 205 | - | - | 235 | >1000 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-13 | 10 | 1.14 | 78 | 182 | - | - | 235 | 54 | 95% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-14 | 10 | 1.15 | 84 | 188 | - | - | 235 | 42 | 95% H2O2 |
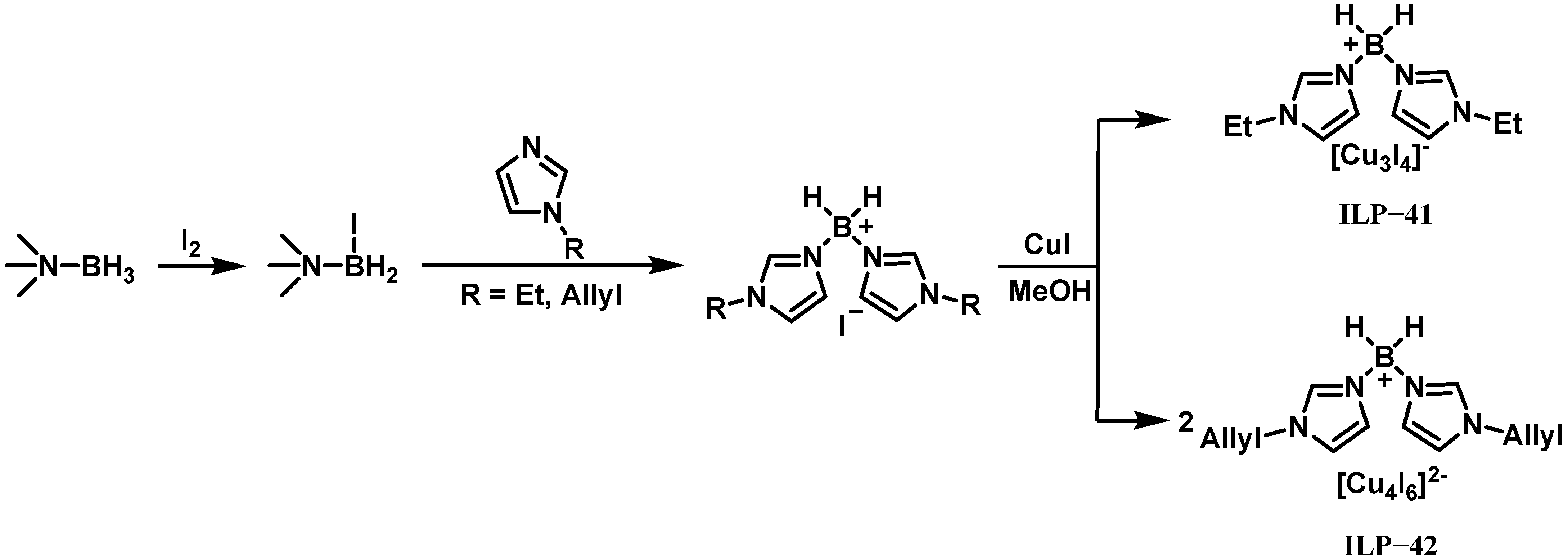
| IL-40 | ILP-41 | 5 | 1.14 | 17 | 257 | <−70 | - | 272 | 75 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-42 | 3 | 1.13 | 19 | 256 | <−70 | - | 275 | 112 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-42 | 5 | 1.14 | 17 | 254 | <−70 | - | 274 | 74 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-42 | 10 | 1.15 | 24 | 252 | <−70 | - | 272 | 59 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-42 | 15 | 1.20 | 31 | 248 | <−70 | - | 270 | 47 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-40 | ILP-42 | 20 | 1.25 | 40 | 244 | <−70 | - | 268 | 34 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-53 | ILP-41 | 5 | 1.09 | 27 | 273 | <−70 | - | 264 | 161 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-53 | ILP-42 | 5 | 1.09 | 27 | 272 | <−70 | - | 266 | 113 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-43 | 12 | 1.13 | 35 | 238 | - | - | 297 | 16 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-44 | 12 | 1.15 | 37 | 240 | - | - | 297 | 36 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-45 | 12 | 1.15 | 35 | 236 | - | - | 298 | 29 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-46 | 12 | 1.13 | 34 | 238 | - | - | 296 | 20 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-52 | ILP-47 | 12 | 1.11 | 40 | 239 | - | - | 299 | 59 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-51 | ILP-43 | 12 | 1.13 | 42 | 239 | - | - | 296 | 26 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-53 | ILP-43 | 12 | 1.10 | 52 | 243 | - | - | 295 | 36 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-54 | ILP-43 | 12 | 1.17 | 40 | 212 | - | - | 298 | 27 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL-55 | ILP-43 | 12 | 1.16 | 43 | 214 | - | - | 298 | 17 | 90% H2O2 |
| IL | Promoter | wILP a (wt%) | ρ b (g cm−3) | η c (mPa s) | Td d (°C) | Tm e (°C) | ΔHf f (kJ mol−1) | Isp g (s) | IDT h (ms) | Oxidizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-56 | ILP-37 | 14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 170 | 98% H2O2 |
| IL-57 | ILP-37 | 22 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 50 | 98% H2O2 |
| IL-58 | ILP-37 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 960 | 98% H2O2 |
| IL-59 | ILP-48/49 | 10/8.7 | 1.05 | 97 | - | - | - | 326 | 28 | 97% H2O2 |
| IL-59 | ILP-48/49 | 19.4/7.8 | 1.02 | 37 | - | - | - | 326 | 28 | 97% H2O2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Q. Advances in Synthesis and Ignition Performance of Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Green Propellants. Molecules 2025, 30, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081789
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Yin D, Zhang Q. Advances in Synthesis and Ignition Performance of Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Green Propellants. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081789
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongting, Xing Zhang, Dangyue Yin, and Qinghua Zhang. 2025. "Advances in Synthesis and Ignition Performance of Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Green Propellants" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081789
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, X., Yin, D., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Advances in Synthesis and Ignition Performance of Ionic Liquid–Hydrogen Peroxide Green Propellants. Molecules, 30(8), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081789





