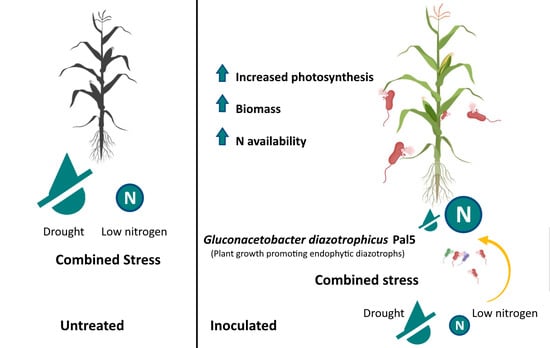
Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5 Enhances Plant Robustness Status under the Combination of Moderate Drought and Low Nitrogen Stress in Zea mays L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Inoculum Preparation
2.1.2. Pot Experiment Setup
2.2. Plant Analysis
2.3. DNA Isolation
2.4. G. diazotrophicus Pal5 Detection
2.5. Design of Novel nifH Primers and Validation
2.6. Quantification of nifH and G. diazotrophicus Pal5 16S rRNA Genes in Plant Tissues
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of G. diazotrophicus Inoculation on Maize Plant Growth
3.2. Plant Photosynthetic Efficiency
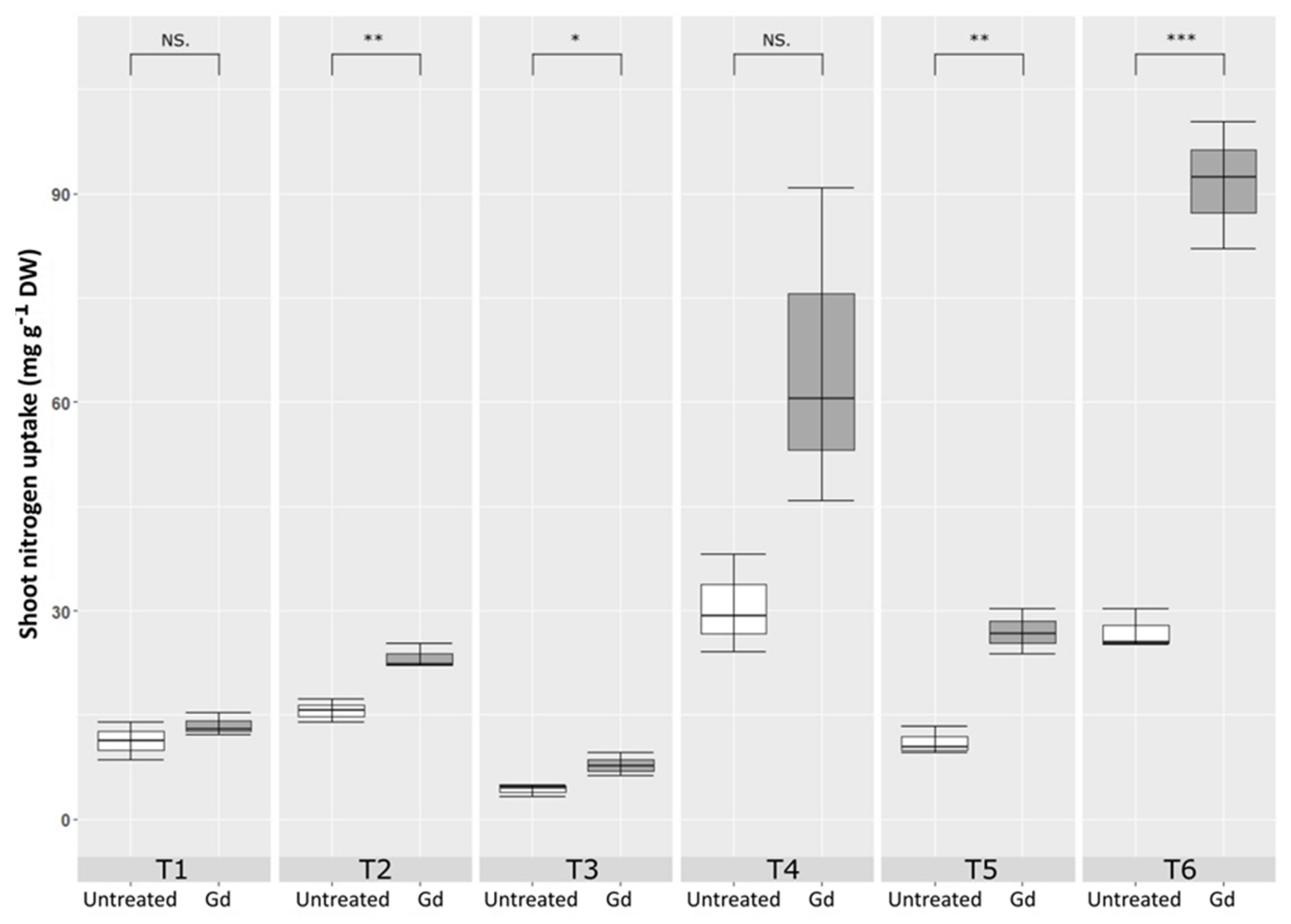
3.3. Nitrogen Contents in Plants and NUE
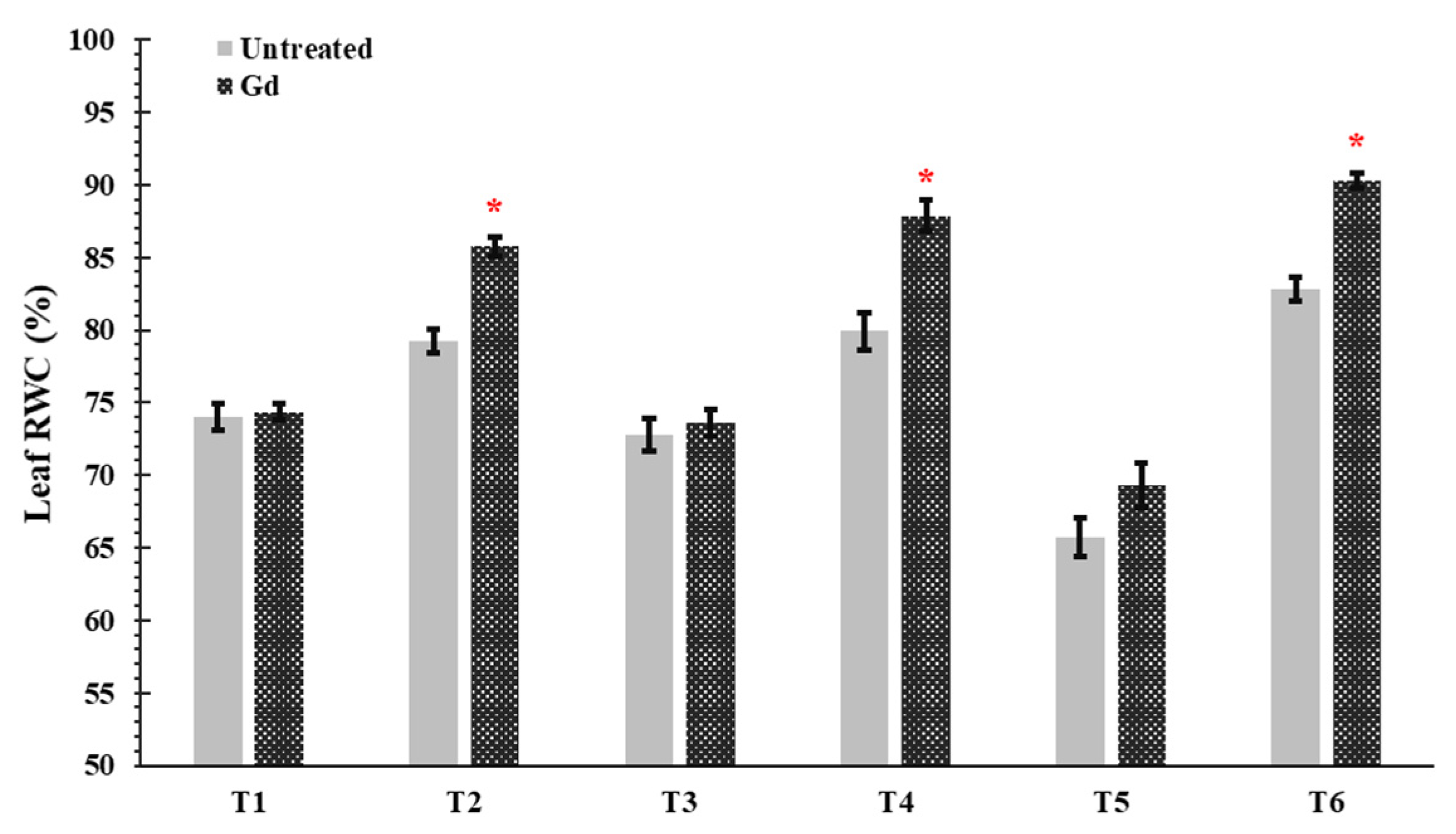
3.4. Plant Water Consumption, Water Use Efficiency, and Leaf Rolling Scores
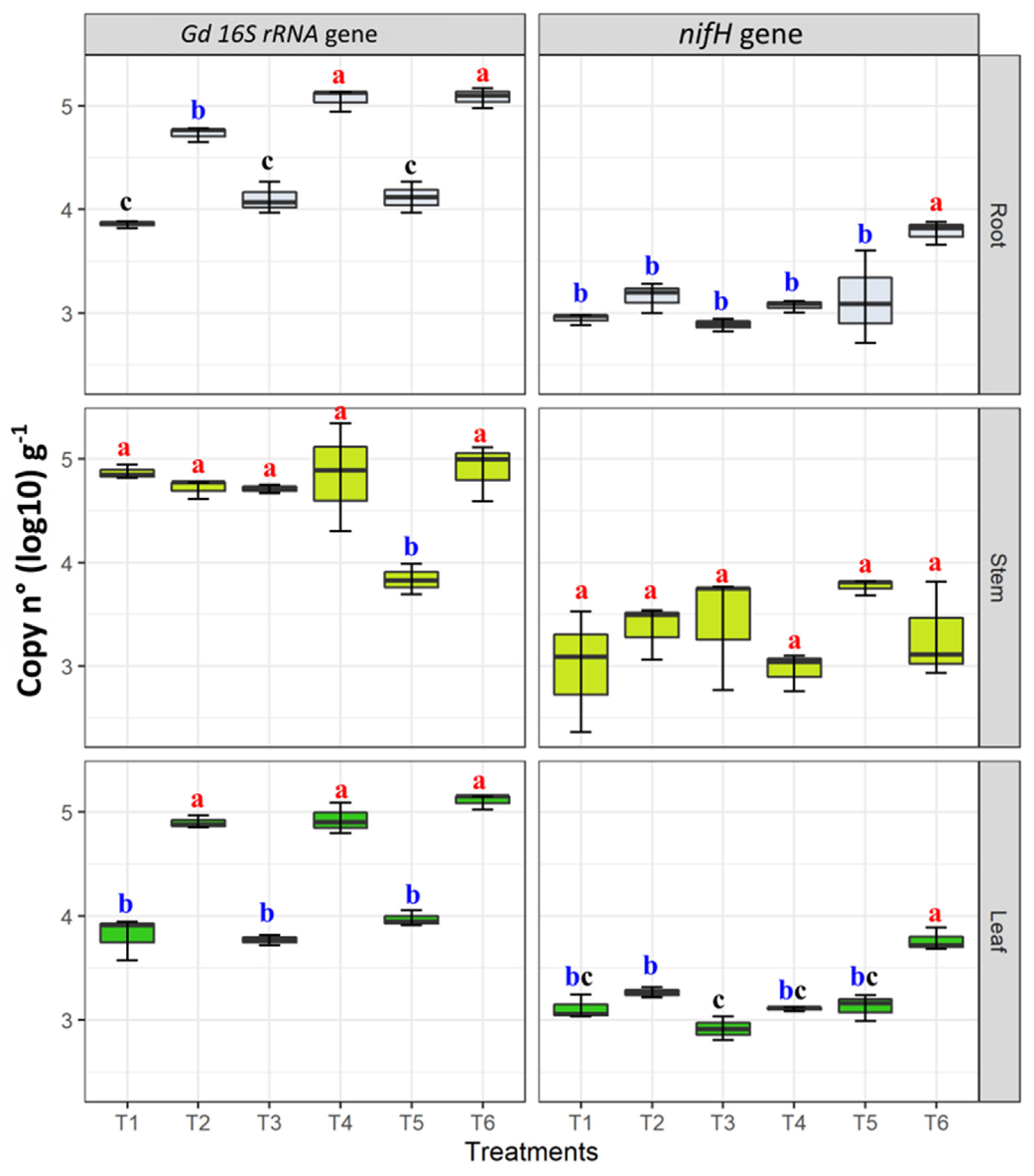
3.5. nifH and G. diazotrophicus 16S rRNA Genes Abundance in Plant Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, S.; Hao, X.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Su, X.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, R. Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P. Steep, cheap and deep: An ideotype to optimize water and N acquisition by maize root systems. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bänziger, M.; Edmeades, G.O.; Beck, D.L.; Bellon, M.R. Breeding for Drought and Nitrogen Stress Tolerance in Maize: From Theory to Practice; Cimmyt: Texcoco, Mexico, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.-A. Global synthesis of drought effects on maize and wheat production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmeades, G.O. Drought Tolerance in Maize: An Emerging Reality; International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-Biotech Applications (ISAAA): Metro Manila, Philippines, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, P.J.; Ingram, J.S.; Brklacich, M. Climate change and food security. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN General Assembly. Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Erisman, J.; Bleeker, A.; Galloway, J.; Sutton, M. Reduced nitrogen in ecology and the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Grizzetti, B.; Anglade, J.; Garnier, J. 50 year trends in nitrogen use efficiency of world cropping systems: The relationship between yield and nitrogen input to cropland. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Diet, Nutrition, and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases: Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 916. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The Impact of Disasters and Crises on Agriculture and Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnell, D.; Eddleston, M.; Phillips, M.R.; Konradsen, F. The global distribution of fatal pesticide self-poisoning: Systematic review. BMC Public Health 2007, 7, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretty, J.; Bharucha, Z.P. Sustainable intensification in agricultural systems. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1571–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulanda, A.; Barea, J.; Azcón, R. An indigenous drought-tolerant strain of Glomus intraradices associated with a native bacterium improves water transport and root development in Retama sphaerocarpa. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavamura, V.N.; Santos, S.N.; da Silva, J.L.; Parma, M.M.; Ávila, L.A.; Visconti, A.; Zucchi, T.D.; Taketani, R.G.; Andreote, F.D.; de Melo, I.S. Screening of Brazilian cacti rhizobacteria for plant growth promotion under drought. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliute, I.; Buzaite, O.; Baniulis, D.; Stanys, V. Bacterial endophytes in agricultural crops and their role in stress tolerance: A review. Zemdirb. Agric. 2015, 102, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda, M.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 183, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Germaine, K.; Franks, A.; Ryan, D.J.; Dowling, D.N. Bacterial endophytes: Recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Anandham, R.; Madhaiyan, M.; Venkateswaran, V.; Sa, T. Endophytic bacteria: Perspectives and applications in agricultural crop production. In Bacteria in Agrobiology: Crop Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 61–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Nisar, M.; Ali, H.; Hazrat, A.; Hayat, K.; Keerio, A.A.; Ihsan, M.; Laiq, M.; Ullah, S.; Fahad, S.; et al. Drought tolerance improvement in plants: An endophytic bacterial approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7385–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardoim, P.R.; Van Overbeek, L.S.; Berg, G.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Compant, S.; Campisano, A.; Döring, M.; Sessitsch, A. The hidden world within plants: Ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaby, J.C.; Buckley, D.H. A comprehensive evaluation of PCR primers to amplify the nifH gene of nitrogenase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangjaroen, C.; Rerkasem, B.; Teaumroong, N.; Noisangiam, R.; Lumyong, S. Promoting plant growth in a commercial rice cultivar by endophytic diazotrophic bacteria isolated from rice landraces. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Panwar, J.; Akhtar, M.S.; Jha, P.N. Endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria as biofertilizer. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 183–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, L.; Silva, R.; Almeida, I.; Vidal, M.; Baldani, J.I.; Meneses, C.H.S.G. Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus mitigates drought stress in Oryza sativa L. Plant Soil 2019, 451, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Burris, R.H.; Gunapala, N.; Kennedy, C. Comparison of benefit to sugarcane plant growth and 15N2 incorporation following inoculation of sterile plants with Acetobacter diazotrophicus wild-type and nif mutant strains. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, L.; Santa Brigida, A.B.; Mota Filho, J.P.; De Carvalho, T.G.; Rojas, C.A.; Vaneechoutte, D.; Van Bel, M.; Farrinelli, L.; Ferreira, P.C.; Vandepoele, K. Drought tolerance conferred to sugarcane by association with Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus: A transcriptomic view of hormone pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Sah, R.P. Genetic component in baby corn (Zea mays L.). Plant Arch. 2012, 12, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Singode, A.; Mukri, G.; Sah, R.P.; Tiwana, U.S.; Kumar, B. Evaluation of normal and specialty corn for fodder yield and quality traits. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2016, 37, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, M.; Said, S.; Abdelaal, A. Effect of food types of Galleria mellonella L. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on biological aspects and life table of Apanteles galleriae Wilkinson (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 16, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.; Ahmed, S.; Malaviya, D.; Saxena, P. Identification of consistence performing dual purpose maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes under semi-arid condition. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2016, 37, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Naveed, M.; Mitter, B.; Reichenauer, T.G.; Wieczorek, K.; Sessitsch, A. Increased drought stress resilience of maize through endophytic colonization by Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN and Enterobacter sp. FD17. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 97, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNickle, G.G.; Deyholos, M.K.; Cahill, J.F., Jr. Ecological implications of single and mixed nitrogen nutrition in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Ecol 2013, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. Microsc. Microanal. 2019, 25, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čatský, J. Determination of water deficit in disks cut out from leaf blades. Biol. Plant. 1960, 2, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, L.; Carter, P. Corn hybrid response to nitrogen fertilization in the Northern Corn Belt. J. Prod. Agric. 1988, 1, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Janz, B.; Engedal, T.; de Neergaard, A. Effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen rates on water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes Boa Sorte, P.M.; Simões-Araujo, J.L.; Varial de Melo, L.H.; de Souza Galisa, P.; Leal, L.; Baldani, J.I.; Divan Baldani, V.L. Development of a real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus in sugarcane grown under field conditions. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, T.; Suga, Y.; Yahiro, N.; Matsuguchi, T. Remarkable N2-fixing bacterial diversity detected in rice roots by molecular evolutionary analysis of nifH gene sequences. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efeoğlu, B.; Ekmekçi, Y.; Çiçek, N. Physiological responses of three maize cultivars to drought stress and recovery. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2009, 75, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Bi, Y.-M.; Rothstein, S.J. Understanding plant response to nitrogen limitation for the improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakabe, Y.; Osakabe, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tran, L.S. Response of plants to water stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, D.; Cocking, E. Establishing symbiotic nitrogen fixation in cereals and other non-legume crops: The greener nitrogen revolution. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belimov, A.A.; Zinovkina, N.Y.; Safronova, V.I.; Litvinsky, V.A.; Nosikov, V.V.; Zavalin, A.A.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Rhizobial ACC deaminase contributes to efficient symbiosis with pea (Pisum sativum L.) under single and combined cadmium and water deficit stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 167, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, M.; Andrade, L.; Vespoli, L.; Moreira, J.; Pimentel, V.; Soares, F.; Passamani, L.; Silveira, V.; de Souza Filho, G. Comparative proteomics reveals essential mechanisms for osmotolerance in Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Res. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Ramirez, L.E.; Jimenez-Salgado, T.; Abarca-Ocampo, I.R.; Caballero-Mellado, J. Acetobacter diazotrophicus, an indoleacetic acid producing bacterium isolated from sugarcane cultivars of México. Plant Soil 1993, 154, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, C.; Imperlini, E.; Calogero, R.; Senatore, B.; Pucci, P.; Defez, R. Indole-3-acetic acid regulates the central metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.J.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Hashem, A. Phytohormones and beneficial microbes: Essential components for plants to balance stress and fitness. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirinbayan, S.; Khosravi, H.; Malakouti, M.J. Alleviation of drought stress in maize (Zea mays) by inoculation with Azotobacter strains isolated from semi-arid regions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 133, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalan, M.; Albano, R.; de Pádua, V.; Rouws, L.; Rojas, C.; Hemerly, A.; Teixeira, K.; Schwab, S.; Araujo, J.; Oliveira, A.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the sugarcane nitrogen-fixing endophyte Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaby, J.C.; Buckley, D.H. A comprehensive aligned nifH gene database: A multipurpose tool for studies of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Database 2014, 2014, bau001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defez, R.; Andreozzi, A.; Dickinson, M.; Charlton, A.; Tadini, L.; Pesaresi, P.; Bianco, C. Improved drought stress response in alfalfa plants nodulated by an IAA over-producing Rhizobium strain. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, V.; Ali, S.Z.; Grover, M.; Reddy, G.; Venkateswarlu, B. Effect of plant growth promoting Pseudomonas spp. on compatible solutes, antioxidant status and plant growth of maize under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 62, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, L.; Becker, S.; Cruz, V.M.V.; Byrne, P.F.; Dierig, D.A. Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doussan, C.; Pierret, A.; Garrigues, E.; Pagès, L. Water uptake by plant roots: II—modelling of water transfer in the soil root-system with explicit account of flow within the root system—comparison with experiments. Plant Soil 2006, 283, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C. Temporal and spatial profiling of root growth revealed novel response of maize roots under various nitrogen supplies in the field. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agurla, S.; Gahir, S.; Munemasa, S.; Murata, Y.; Raghavendra, A.S. Mechanism of stomatal closure in plants exposed to drought and cold stress. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1081, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mi, G.; Gao, Q. Reducing basal nitrogen rate to improve maize seedling growth, water and nitrogen use efficiencies under drought stress by optimizing root morphology and distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N. Abscisic acid and abiotic stress signaling. Plant. Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova, M.; Dobrev, P.; Motyka, V.; Gaudinova, A.; Malbeck, J.; Pospisilova, J.; Haisel, D.; Storchova, H.; Dobra, J.; Mok, M.C.; et al. Cytokinin function in drought stress response and subsequent recovery. In Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture 2006 and Beyond; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Baek, W.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.C. Function of ABA in stomatal defense against biotic and drought stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15251–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, D.J. Sugars: Their origin in photosynthesis and subsequent biological interconversions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 915s–921s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, L.J.; Canvin, D.T. The rate of photorespiration during photosynthesis and the relationship of the substrate of light respiration to the products of photosynthesis in sunflower leaves. Plant Physiol. 1971, 48, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri-Moghaddam, M.R.; Le Roy, K.; Xiang, L.; Rolland, F.; Van den Ende, W. Sugar signaling and antioxidant network connections in plant cells. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2022–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Treatments | Description |
|---|---|
| T1 | Soil moisture regime 35% of WHC with 100% nitrogen application |
| T2 | Soil moisture regime 50% of WHC with 100% nitrogen application |
| T3 | No nitrogen application with 100% WHC |
| T4 | 50% nitrogen application of recommended dose with 100% WHC |
| T5 | Soil moisture regime 35% of WHC with 50% of nitrogen application |
| T6 | Soil moisture regime 50% of WHC with 50% of nitrogen application |
| Treatments | PWC (mL) | WUE (mg/mL) | Leaf Rolling Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unt. | Gd | AOV | Unt. | Gd | AOV | Unt. | Gd | AOV | |
| T1 | 719.7 | 747.1 | * | 0.35 | 0.39 | ns | 4.8 | 4.5 | ns |
| T2 | 824.9 | 838.0 | * | 0.41 | 0.72 | ** | 2.1 | 1.6 | ** |
| T3 | 1069.4 | 1100.6 | ns | 0.16 | 0.37 | * | 1.3 | 1.2 | ns |
| T4 | 1120.2 | 1141.4 | * | 0.33 | 0.83 | *** | 1 | 1 | ns |
| T5 | 738.4 | 745.0 | ns | 0.41 | 0.49 | ns | 4.1 | 3.5 | * |
| T6 | 809.0 | 840.5 | ** | 0.69 | 1.99 | *** | 2.2 | 1.5 | ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tufail, M.A.; Touceda-González, M.; Pertot, I.; Ehlers, R.-U. Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5 Enhances Plant Robustness Status under the Combination of Moderate Drought and Low Nitrogen Stress in Zea mays L. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040870
Tufail MA, Touceda-González M, Pertot I, Ehlers R-U. Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5 Enhances Plant Robustness Status under the Combination of Moderate Drought and Low Nitrogen Stress in Zea mays L. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040870
Chicago/Turabian StyleTufail, Muhammad Aammar, María Touceda-González, Ilaria Pertot, and Ralf-Udo Ehlers. 2021. "Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5 Enhances Plant Robustness Status under the Combination of Moderate Drought and Low Nitrogen Stress in Zea mays L." Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040870
APA StyleTufail, M. A., Touceda-González, M., Pertot, I., & Ehlers, R.-U. (2021). Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5 Enhances Plant Robustness Status under the Combination of Moderate Drought and Low Nitrogen Stress in Zea mays L. Microorganisms, 9(4), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040870