Investigating the Impact of Surfactant-Based Warm-Mix Additives on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt
2.1.2. Rejuvenator
2.1.3. Warm-Mix Additive
2.1.4. Mixture Proportion Design
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Physical Performance Tests
2.2.2. Dynamic Shear Rheological Experiment
2.2.3. High-Temperature Rutting Experiment
2.2.4. Low-Temperature Fracture Resistance Experiment
2.2.5. Water Stability Test
3. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.1. Physical Index Results
3.2. Dynamic Shear Rheological Test Results
3.3. High-Temperature Rutting Test Results
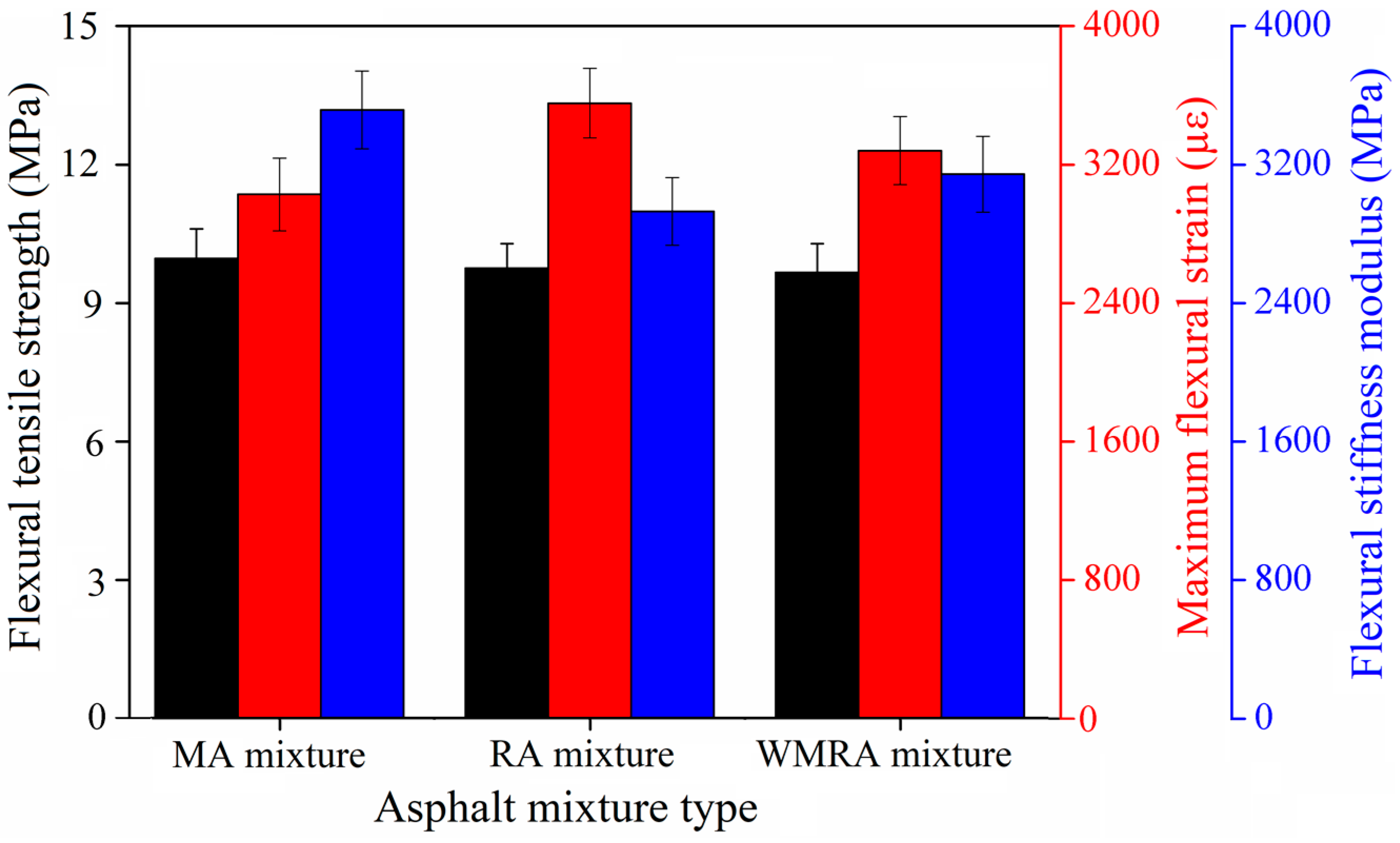
3.4. Low-Temperature Performance Test Results
3.5. Water Stability Test Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Compared to base asphalt, aged asphalt exhibits a decrease in penetration and ductility, as well as an increase in the softening point. With the addition of the base asphalt, rejuvenator, and warm-mix rejuvenator, the penetration decreases, the softening point decreases, and ductility increases. Both rejuvenation methods were found to restore the penetration and softening points of the aged asphalt to those of the base asphalt. However, the restorative effect on the ductility of asphalt was not satisfactory for either of the rejuvenation methods.
- (2)
- The addition of fresh asphalt, rejuvenator, and warm-mix rejuvenator to aged asphalt can effectively reduce its viscosity. The restorative effect on the workability performance of the asphalt varied; the warm-mix rejuvenator demonstrated the highest effect, followed by the rejuvenator and base asphalt. Both the warm-mix rejuvenator and rejuvenator decrease the resistance of asphalt to deformation under high-temperature conditions.
- (3)
- The performance indicators of the recycled asphalt mixture met the specifications. The warm-mix rejuvenator and rejuvenator reduced the high-temperature stability of the mixture while enhancing its low-temperature and water stability. This is primarily owing to the softening effect of the rejuvenators on the asphalt, which leads to a decrease in its deformation resistance. Additionally, the rejuvenators improved the stress relaxation capability of asphalt under low-temperature conditions.
- (4)
- Warm-mix rejuvenation technology, which achieves energy conservation and emission reduction by lowering the temperature, is a green and environmentally friendly pavement construction technique developed in response to the current global challenges of energy depletion and severe atmospheric pollution. In the future, the focus of research should be on the development of more high-performance and cost-effective warm-mix additives.
- (5)
- Future research should concentrate on the impacts of diverse climate conditions on the performance of warm-mix recycled asphalt mixtures. It is crucial to optimize the mix design for enhanced environmental adaptability and explore eco-friendlier additive preparation methods to further boost the sustainable development potential of warm-mix recycling technology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gkyrtis, K.; Pomoni, M. An overview of the recyclability of alternative materials for building surface courses at pavement structures. Buildings 2024, 14, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, K. Review on performance of asphalt and asphalt mixture with waste cooking oil. Materials 2023, 16, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghian, G.; Falchetto, A.; You, Z.; Chen, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Westerhoff, J.; Moon, K.H.; Wistuba, M.P. Warm mix asphalt technology: An up to date review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A. A review of the warm mix asphalt (WMA) technologies: Effects on thermo-mechanical and rheological properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Behnood, A.; Nowruzi, A.; Haghshenas, H. Performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures containing warm mix asphalt (WMA) additives and reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Riccardi, C.; Jafari, B.; Falchetto, A.C.; Wistuba, M.P. Investigation on the effect of high amount of Re-recycled RAP with Warm mix asphalt (WMA) technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, P.; Abe, A.; Loise, V.; Porto, M.; Calandra, P.; Angelico, R.; Rossi, C.O. The role of additives in warm mix asphalt technology: An insight into their mechanisms of improving an emerging technology. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Duan, H.; Shi, C. Improvement of thermal and optical responses of short-term aged thermochromic asphalt binder by warm-mix asphalt technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xi, Z.; Cai, J.; Ding, G.; Xie, H. Performance evaluation of warm mix asphalt additive modified epoxy asphalt rubbers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Xiao, F. A comprehensive review on the utilization of reclaimed asphalt material with warm mix asphalt technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Z.; Ahmed, A.; Yombah, M.; Cui, C.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P.; Sheng, Y. Repurposing waste oils into cleaner aged asphalt pavement materials: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Peng, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, N. Performance evaluation of aged asphalt rejuvenated with various bio-oils based on rheological property index. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan Mirhosseini, A.; Tahami, A.; Hoff, I.; Dessouky, S.; Kavussi, A.; Fuentes, L.; Walubita, L.F. Performance characterization of warm-mix asphalt containing high reclaimed-asphalt pavement with bio-oil rejuvenator. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, N. Multi-performance evaluation of recycled warm-mix asphalt mixtures with high reclaimed asphalt pavement contents. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremotekhases, F.; Sadek, H.; Hassan, M.; Berryman, C. Impact of warm-mix asphalt technologies and high reclaimed asphalt pavement content on the performance of alternative asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Y.; Chen, F.; Han, F. Performance evaluation of new warm mix asphalt and water stability of its mixture based on laboratory tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Shen, A.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhai, C.; Yang, X. Effect of dry–wet and freeze–thaw repeated cycles on water resistance of steel slag asphalt mixture. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Performance evaluation of warm-mix recycled asphalt binders after long-term aging. J. Test. Eval. 2019, 47, 2889–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraj, F.; Khatib, J.; Castro, A.; Elkordi, A. Effect of Chemical Warm Mix Additive on the Properties and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Buildings 2022, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Huang, W.; Wu, K.; Yang, G.; Bao, X. Study on performance of recycled asphalt mixture based on blending state analysis of virgin and aged asphalt. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2165658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Bian, X.; Jiang, X.; Hao, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J. Study on rheological properties of warm mix large proportion recycled asphalt. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Rheological and physico-chemical properties of warm-mix recycled asphalt mastic containing high percentage of RAP binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Valters, A. Comparison of two low-temperature cracking tests for use in performance-based asphalt mixture design. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Gan, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, C. Study on betel nut fiber enhancing water stability of asphalt mixture based on response surface method. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Type | Penetration at 25 °C/0.1 mm | Softening Point/°C | Ductility at 15 °C/cm | Viscosity at 135 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH70# | 67.9 | 54.6 | >150 | 0.356 |
| DH70#PAV | 19.9 | 77.4 | 7 | 2.940 |
| Viscosity at 135 °C/Pa·s | Mass Loss After RTFOT/% | Viscosity Ratio After RTFOT | Flash Point/°C | Relative Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0072 | 2.74 | 0.77 | 260 | 0.931 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, H.; Yang, D.; Peng, S.; Gao, W. Investigating the Impact of Surfactant-Based Warm-Mix Additives on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2025, 18, 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081732
Xiang H, Yang D, Peng S, Gao W. Investigating the Impact of Surfactant-Based Warm-Mix Additives on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081732
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Hao, Desheng Yang, Shunxian Peng, and Wei Gao. 2025. "Investigating the Impact of Surfactant-Based Warm-Mix Additives on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures" Materials 18, no. 8: 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081732
APA StyleXiang, H., Yang, D., Peng, S., & Gao, W. (2025). Investigating the Impact of Surfactant-Based Warm-Mix Additives on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Materials, 18(8), 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081732






